Low-Scale Morphological Feature Recalibration Method for Breast Ultrasound Classification
-
摘要:
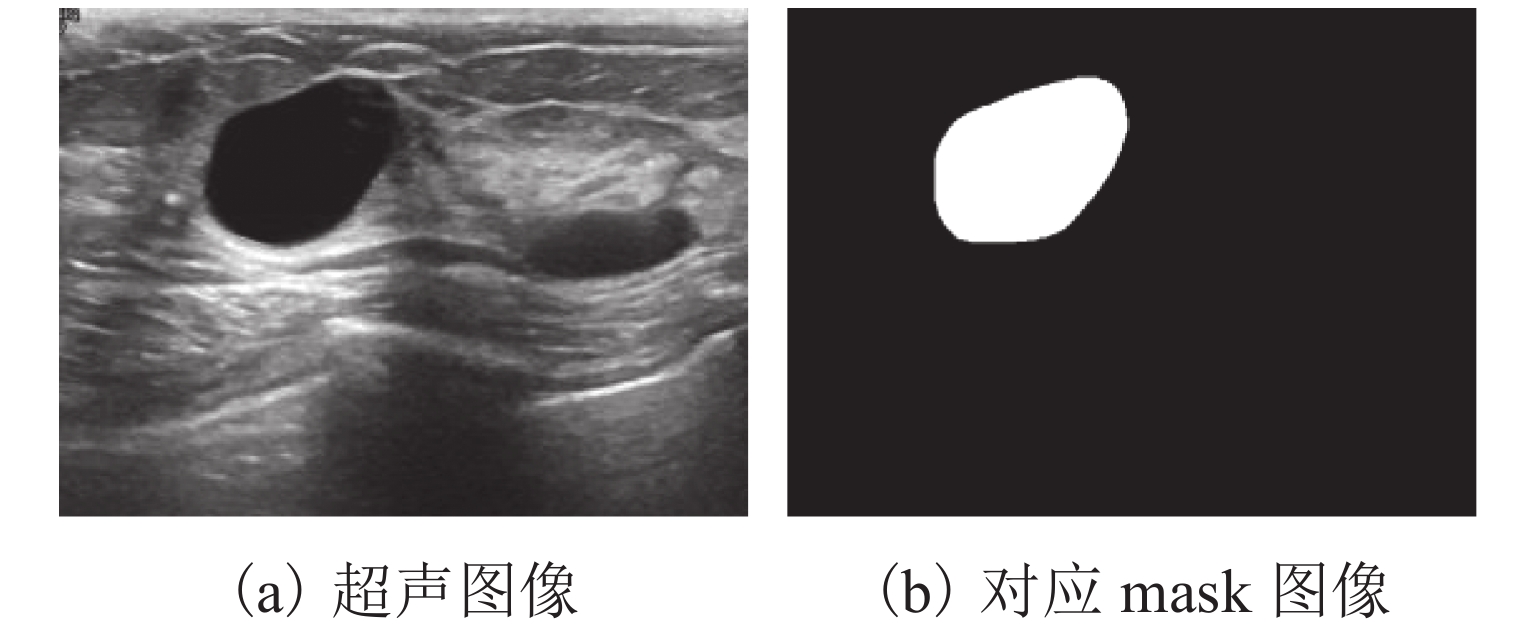
针对乳腺超声图像具有类内差异大、类间差异小以及结节形状复杂多变等问题,提出一种形状特征重校准的乳腺超声图像算法,实现乳腺超声的自动化诊断. 首先,构建端到端的网络模型,采用渐进训练方式,充分学习图像中更具辨别力的区域,获取更细粒度的特征信息;其次,提出分区打乱机制,降低网络中打乱图像时破坏结节区域所产生的噪声;然后,将模型底层提取的特征与通过掩膜图像获得的形状特征进行重校准,提出低尺度重校准损失函数;最后,构建一个包含1550张乳腺超声图像数据集LSRD (low-scale recalibration database),验证所提方法的有效性. 实验结果表明:本文模型在LSRD上准确率94.3%、敏感性91.2%、特异性93.6%、ROC (receiver operator characteristic curve)与坐标围成的面积(area under curve,AUC)为0.941,均优于对比模型;在BUSI (breast ultrasound image)数据集上,相较于对比模型,其分类精度提升3.3%.
Abstract:Breast ultrasound images have large intra-class differences, small inter-class differences, and complex and variable nodule shapes. In order to address these issues, a breast ultrasound image algorithm with morphological feature recalibration was designed to realize automatic diagnosis of breast ultrasound. First, an end-to-end network model was built, which adopted progressive training to fully learn the more discriminative regions in the image and obtain more fine-grained feature information. Secondly, a partition shuffle mechanism was proposed to reduce the noise caused by the disruption of the nodule region when the image was shuffled. Then, the features extracted from the bottom layer of the model were recalibrated with the morphological features obtained through the mask image, and a low-scale recalibration loss function was proposed. Finally, in order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, a low-scale recalibration database (LSRD) containing 1 550 breast ultrasound images was constructed. The experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed model on LSRD is 94.3%; the sensitivity is 91.2%; the specificity is 93.6%, and the area (AUC) under the receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC) is 0.941, all of which are superior to other comparison models. On the breast ultrasound image (BUSI) dataset, compared with the other models, the classification accuracy of the proposed model is improved by 3.3%.
-
表 1 不同主干网络分类精度对比
Table 1. Comparison of classification accuracy for different backbone networks
% 网络模型 训练集 测试集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 ResNet18 83.5 82.0 82.3 81.7 ResNet34 85.6 84.9 84.8 82.3 ResNet50 90.8 87.6 81.2 76.3 VGG-16 80.9 79.8 80.6 79.6 VGG-19 82.5 81.6 80.0 79.5 表 2 分块尺度对比实验
Table 2. Comparison experiments of partition scales
% 块尺度
大小/块训练集 训练集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 16 83.1 82.9 82.8 82.3 8 84.2 83.9 83.2 82.5 4 89.6 89.3 88.3 87.7 2 86.1 85.7 85.3 85.1 表 3 图像打乱对比实验
Table 3. Comparison experiments of shuffled images
% 打乱方法 训练集 测试集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 未打乱 85.6 84.9 84.8 82.3 随机打乱 88.2 87.9 87.2 86.5 分区打乱 89.6 89.3 88.3 87.7 表 4 重校准损失函数对分类精度的影响
Table 4. Influence of recalibration loss function on classification accuracy
% 损失函数 训练集 测试集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 Log-Cosh 91.7 91.6 90.3 90.8 MAE 88.3 88.5 86.1 86.7 SMAE 89.3 89.1 90.6 90.2 MSE 93.8 92.5 91.3 91.7 表 5 重校准损失函数和分类损失函数的权重对分类精度的影响
Table 5. Influence of weights of recalibration loss function and classification loss function on classification accuracy
% 损失函数权重 训练集 测试集 Ls Lcla 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 1.00 1.00 93.8 92.5 91.3 91.7 0.25 0.75 90.3 89.7 89.3 88.3 0.50 0.50 91.5 90.8 90.6 90.2 0.75 0.25 92.3 91.2 90.8 90.5 表 6 不同融合方法对分类精度的影响
Table 6. Influence of different fusion methods on classification accuracy
% 融合方法 训练集 测试集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 Max 93.4 92.9 92.7 92.2 Sum 92.6 92.0 92.3 91.7 Conv 94.9 94.5 94.3 93.6 表 7 不同打乱方法和重校准损失函数下的消融实验
Table 7. Ablation experiments with different shuffle methods and recalibration loss functions
% 打乱方法 损失函数 训练集 测试集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 未打乱 Log-Cosh 86.2 85.3 84.8 83.3 MAE 85.2 84.9 83.7 83.1 SMAE 85.6 84.7 84.2 83.9 MSE 86.8 86.2 85.9 85.7 随机打乱 Log-Cosh 87.2 86.9 87.2 86.3 MAE 86.2 86.9 86.2 86.3 SMAE 86.7 86.3 85.8 85.6 MSE 87.9 87.3 87.1 86.5 分区打乱 Log-Cosh 91.7 91.6 90.3 90.8 MAE 88.3 88.5 86.1 86.7 SMAE 89.3 89.1 90.6 90.2 MSE 93.8 92.5 91.3 91.7 表 8 BUSI数据集实验结果
Table 8. Experimental results of BUSI dataset
% 融合方法 训练集 测试集 精度 F1 分数 精度 F1 分数 Max 93.4 92.9 92.7 92.2 Sum 92.6 92.0 92.3 91.7 Conv 94.9 94.5 94.3 93.6 表 9 本文模型与主流方法性能比较
Table 9. Performance comparison between proposed method and popular methods
-
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] HOOLEY R J, SCOUTT L M, PHILPOTTS L E. Breast ultrasonography: state of the art[J]. Radiology, 2013, 268(3): 642-659. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13121606 [3] 龚勋,杨菲,杜章锦,等. 甲状腺、乳腺超声影像自动分析技术综述[J]. 软件学报,2020,31(7): 2245-2282.GONG Xun, YANG Fei, DU Zhangjin, et al. Survey of automatic ultrasonographic analysis for thyroid and breast[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 31(7): 2245-2282. [4] LO C M, CHANG Y C, YANG Y W, et al. Quantitative breast mass classification based on the integration of B-mode features and strain features in elastography[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2015, 64: 91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.06.013 [5] FLORES W G, DE ALBUQUERQUE PEREIRA W C, INFANTOSI A F C. Improving classification performance of breast lesions on ultrasonography[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(4): 1125-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.06.006 [6] 任丽,刘洋洋,童莹,等. 乳腺肿瘤超声图像的多特征提取及分类研究[J]. 中国医疗器械杂志,2020,44(4): 294-301.REN Li, LIU Yangyang, TONG Ying, et al. Multi-feature extraction and classification of breast tumor in ultrasound image[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Instrumentation, 2020, 44(4): 294-301. [7] SPANHOL F A, OLIVEIRA L S, PETITJEAN C, et al. Breast cancer histopathological image classification using convolutional neural networks[C]//2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Vancouver: IEEE, 2016: 2560-2567. [8] WEI B Z, HAN Z Y, HE X Y, et al. Deep learning model based breast cancer histopathological image classification[C]//2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analysis (ICCCBDA). Chengdu: IEEE, 2017: 348-353. [9] XIE J, SONG X S, ZHANG W, et al. A novel approach with dual-sampling convolutional neural network for ultrasound image classification of breast tumors[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2020, 65(24): 245001.1-245001.15. [10] CAO Z T, DUAN L X, YANG G W, et al. An experimental study on breast lesion detection and classification from ultrasound images using deep learning architectures[J]. BMC Medical Imaging, 2019, 19(1): 51.1-51.9. [11] 孔小函,檀韬,包凌云,等. 基于卷积神经网络和多信息融合的三维乳腺超声分类方法[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2018,37(4): 414-422.KONG Xiaohan, TAN Tao, BAO Lingyun, et al. Classification of breast mass in 3D ultrasound images with annotations based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 37(4): 414-422. [12] 迟剑宁,于晓升,张艺菲. 融合深度网络和浅层纹理特征的甲状腺结节癌变超声图像诊断[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2018,23(10): 1582-1593.CHI Jianning, YU Xiaosheng, ZHANG Yifei. Thyroid nodule malignantrisk detection in ultrasound image by fusing deep and texture features[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(10): 1582-1593. [13] 杜章锦,龚勋,罗俊,等. 乳腺超声图像中易混淆困难样本的分类方法[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2020,25(7): 1490-1500.DU Zhangjin, GONG Xun, LUO Jun, et al. Classification method for samples that are easy to be confused in breast ultrasound images[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(7): 1490-1500. [14] DU R Y, CHANG D L, BHUNIA A K, et al. Fine-grained visual classification via progressive multi-granularity training of jigsaw patches[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2020: 153-168. [15] 杨丽娜. 乳腺癌超声图像报告中的BI-RADS与术后病理结果之间的相关性[J]. 世界复合医学,2018,4(6): 51-53.YANG Li’na. Correlation between BI-RADS and postoperative pathological findings in breast cancer ultrasound image reports[J]. World Journal of Complex Medicine, 2018, 4(6): 51-53. [16] LAMPLE G, OTT M, CONNEAU A, et al. Phrase-based & neural unsupervised machine translation[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Brussels: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018: 5039-5049. [17] CHEN Y, BAI Y L, ZHANG W, et al. Destruction and construction learning for fine-grained image recognition[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach: IEEE, 2019: 5152-5161. [18] AL-DHABYANI W, GOMAA M, KHALED H, et al. Dataset of breast ultrasound images[J]. Data in Brief, 2020, 28: 104863.1-104863.5. [19] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2014-09-14)[2021-09-02]. https://ar5iv.labs.arxiv.org/html/1409.1556. [20] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [21] WEI M W, DU Y Z, WU X M, et al. A benign and malignant breast tumor classification method via efficiently combining texture and morphological features on ultrasound images[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2020, 2020: 5894010.1-5894010.12. [22] ABED MOHAMMED M, AL-KHATEEB B, RASHID A N, et al. Neural network and multi-fractal dimension features for breast cancer classification from ultrasound images[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2018, 70: 871-882. [23] SHIN S Y, LEE S, YUN I D, et al. Joint weakly and semi-supervised deep learning for localization and classification of masses in breast ultrasound images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(3): 762-774. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2872031 -





 下载:
下载: