Multiple-Mode Transient Inflow Impact with Entrapped Air Pocket in Deep Storage Tunnel Systems
-
摘要:
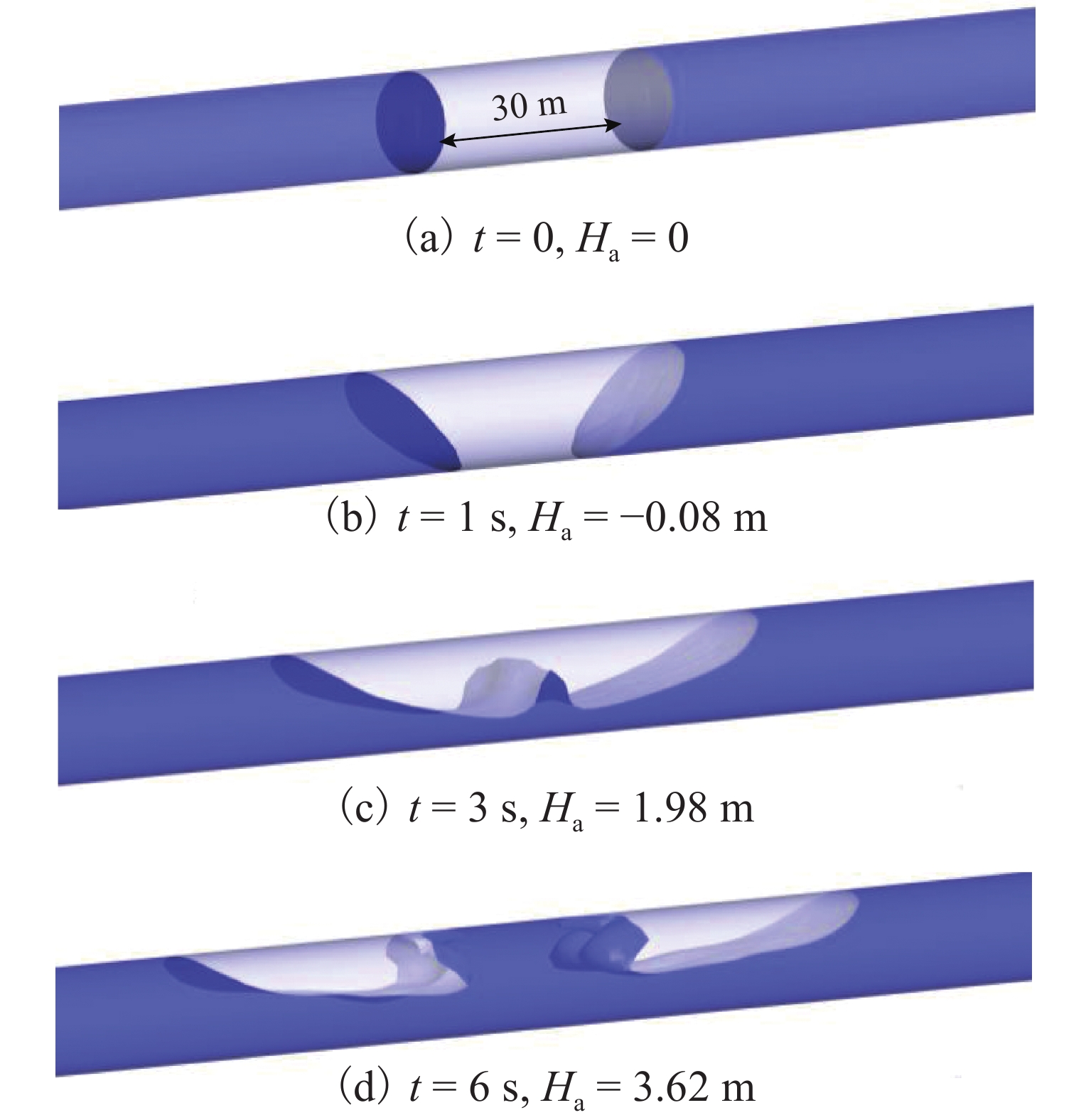
深隧系统作为一种有效的城市内涝防治措施,在多竖井入流时存在气团滞留,可能引发压力振荡等问题,从而威胁系统的运行安全. 依托苏州河段深隧工程,建立双竖井单隧洞深隧系统模型,采用计算流体力学方法进行数值计算,并通过模型充水试验进行验证,分析多工况入流冲击所导致的气团滞留对压力波动的影响,并总结其规律. 结果表明:在设计入流工况下,3.5%的气团滞留可导致最大压力达到35.36 m,相当于控制水位竖井静压的1.77倍;当竖井总入流量恒定时,流量分配对压力的影响较小,而对称入流时极值压力最大,比单侧入流分别偏高3%和6%;在对称入流情况下,随着总入流量的增加,气团的最大压力会先增加后趋于稳定,在总入流量为116 m3/s时,相较于29 m3/s时增大约30%.
Abstract:As an effective waterlogging control measure, deep storage tunnel systems have air pocket retention during the inflows of multiple shafts, causing issues like pressure surges and threatening the safety of system operation. According to the deep storage tunnel project of Suzhou section, a dual-shaft and single-tunnel system model is constructed. Numerical simulations are carried out with computational fluid dynamics methods and verified by water filling experiments, while the pressure surges of entrapped air pocket under different inflow conditions are analyzed and the variation law is summarized. The results show that under the design inflow condition, the maximum pressure of 3.5% entrapped air pocket can reach 35.36 m, which is 1.77 times of the static pressure of the shaft at the control water level. When the total inflow of shafts is constant, the flow distribution has little effect on the pressure. With symmetrical inflow, the extreme pressure is the largest, which is 3% and 6% larger than the unilateral inflow respectively. In case of symmetrical inflow, with the increase of total inflow, the maximum pressure of air pocket first increases and then stabilizes, and compared with that of 29 m3/s total inflow, it increases by about 30%, corresponding to the total inflow of 116 m3/s.
-
Key words:
- transient /
- numerical simulation /
- deep storage tunnel system /
- entrapped air pocket
-
-
[1] 张建云,王银堂,胡庆芳,等. 海绵城市建设有关问题讨论[J]. 水科学进展,2016,27(6): 793-799.ZHANG Jianyun, WANG Yintang, HU Qingfang, et al. Discussion and views on some issues of the sponage city construction in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2016, 27(6): 793-799. [2] 杨乾,杨庆华,陈峰,等. 气爆过程中折板型竖井水力特性试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(5): 1026-1036.YANG Qian, YANG Qinghua, CHEN Feng, et al. Experimental study on hydraulic characteristics in baffle-drop shaft during gas explosion[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(5): 1026-1036. [3] VASCONCELOS J G, WRIGHT S J. Experimental investigation of surges in a stormwater storage tunnel[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 131(10): 853-861. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:10(853) [4] WRIGHT S J, VASCONCELOS J G, CREECH C T, et al. Flow regime transition mechanisms in rapidly filling stormwater storage tunnels[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 8(5): 605-616. [5] 张健,郑源,刘德有,等. 参数对输水管道水流冲击气团压力的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2004,32(6): 655-660. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1980.2004.06.014ZHANG Jian, ZHENG Yuan, LIU Deyou, et al. Influences of relevant parameters on pressure of current rush to air mass in pipeline system[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2004, 32(6): 655-660. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1980.2004.06.014 [6] 郑源,张健,索丽生,等. 输水管道水流对截留气团的冲击[J]. 水利学报,2005,36(11): 1365-1370.ZHENG Yuan, ZHANG Jian, SUO Lisheng, et al. Impact pressure of pipeline water flow on detained air mass[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 36(11): 1365-1370. [7] 郑源,索丽生,张健,等. 输水管道系统气体特性与水流冲击截留气团研究[J]. 水科学进展,2005,16(6): 858-863.ZHENG Yuan, SUO Lisheng, ZHANG Jian, et al. Research on gas properties and current rush to interception air-mass in delivery pipeline system[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2005, 16(6): 858-863. [8] 刘德有,索丽生. 变特性长管道内水流冲击气团的刚性数学模型[J]. 水动力学研究与进展(A辑),2005,20(1): 44-49.LIU Deyou, SUO Lisheng. Rigid model of transient analysis for multiple-characteristic long pipelines with trapped air mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2005, 20(1): 44-49. [9] 王福军,王玲. 大型管道输水系统充水过程瞬变流研究进展[J]. 水力发电学报,2017,36(11): 1-12.WANG Fujun, WANG Ling. Advances in water filling transients in large pipeline transfer systems[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2017, 36(11): 1-12. [10] 刘德有,周领,索丽生,等. 水流冲击管道内滞留气团现象的VOF模型仿真分析[J]. 计算力学学报,2009,26(3): 390-394.LIU Deyou, ZHOU Ling, SUO Lisheng, et al. Simulation and analysis of the rapid filling in pipeline containing trapped air mass with VOF models[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2009, 26(3): 390-394. [11] ZHOU L, LIU D Y, OU C Q. Simulation of flow transients in a water filling pipe containing entrapped air pocket with VOF model[J]. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 2011, 5(1): 127-140. doi: 10.1080/19942060.2011.11015357 [12] ZHOU L, WANG H, KARNEY B, et al. Dynamic behavior of entrapped air pocket in a water filling pipeline[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 144(8): 04018045.1-04018045.14. [13] 卢坤铭,周领,刘静. 水流冲击多段滞留气团的三维数值模拟[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2021,39(3): 264-269.LU Kunming, ZHOU Ling, LIU Jing. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of transient pipe flow with multiple entrapped air pockets[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2021, 39(3): 264-269. [14] 王福军. 流体机械旋转湍流计算模型研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(2): 1-14.WANG Fujun. Research progress of computational model for rotating turbulent flow in fluid machinery[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(2): 1-14. [15] WANG. Y R, YU X D, HAN X X, et al. Influences of eccentricity ratio on the internal flow and cavitation characteristics of progressing cavity pump[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,2021,235(22):6111-6121. [16] HOU Q Z, TIJSSELING A S, LAANEARU J, et al. Experimental investigation on rapid filling of a large-scale pipeline[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 140(11): 04014053.1-04014053.14. -





 下载:
下载: