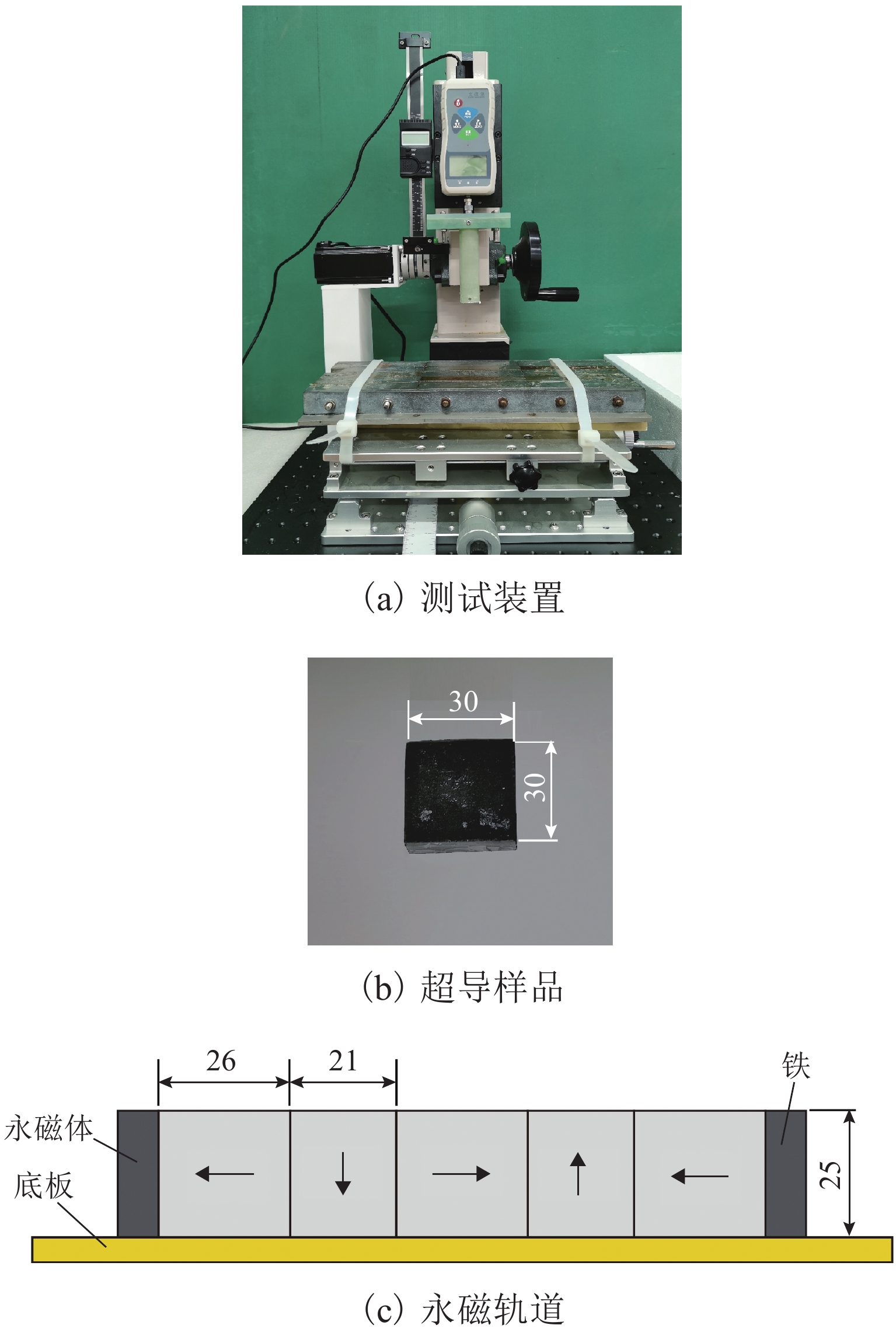
Quasi-Static Force Relaxation Characteristics of High Temperature Superconducting Magnetic Levitation
-
摘要:
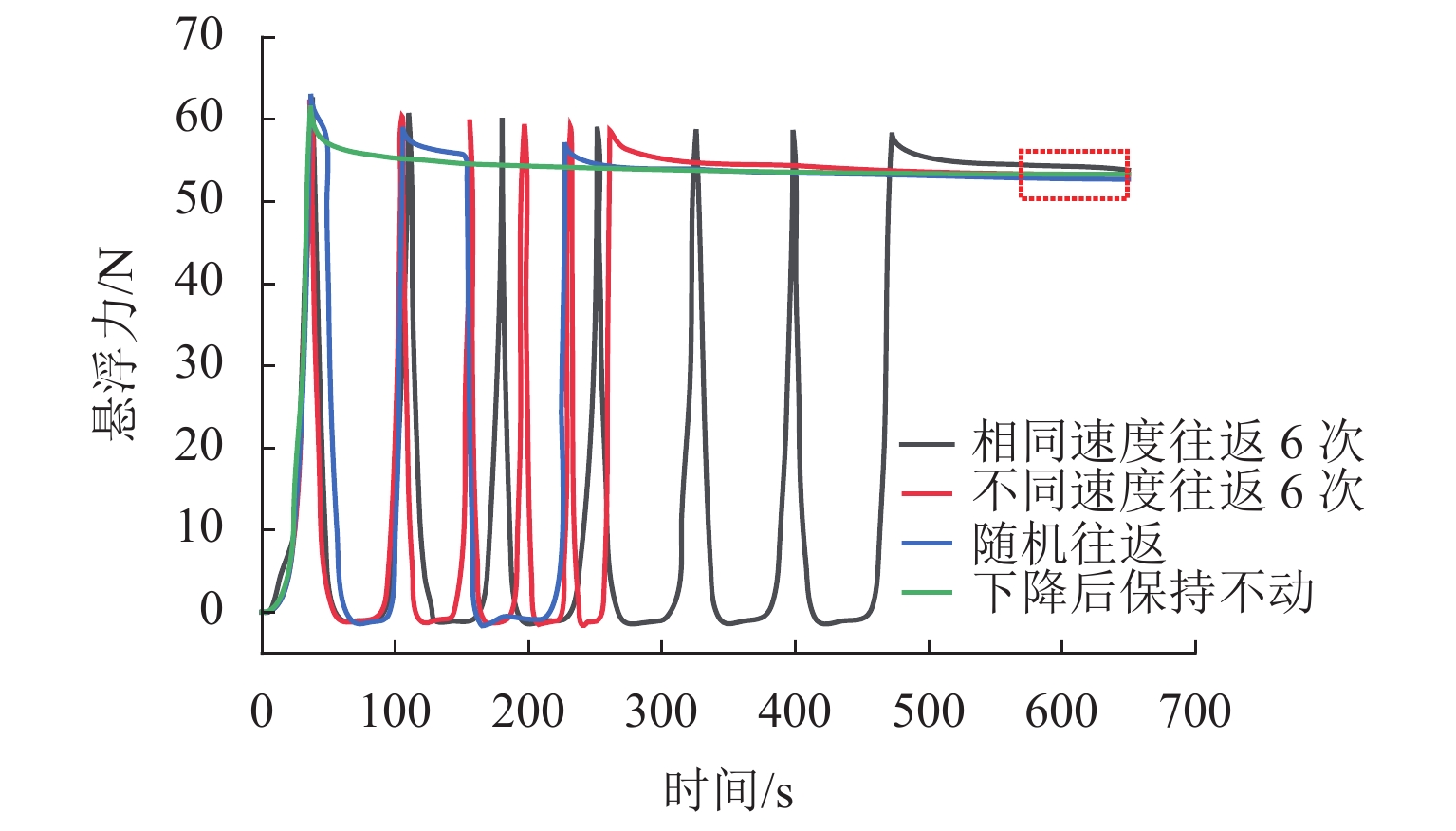
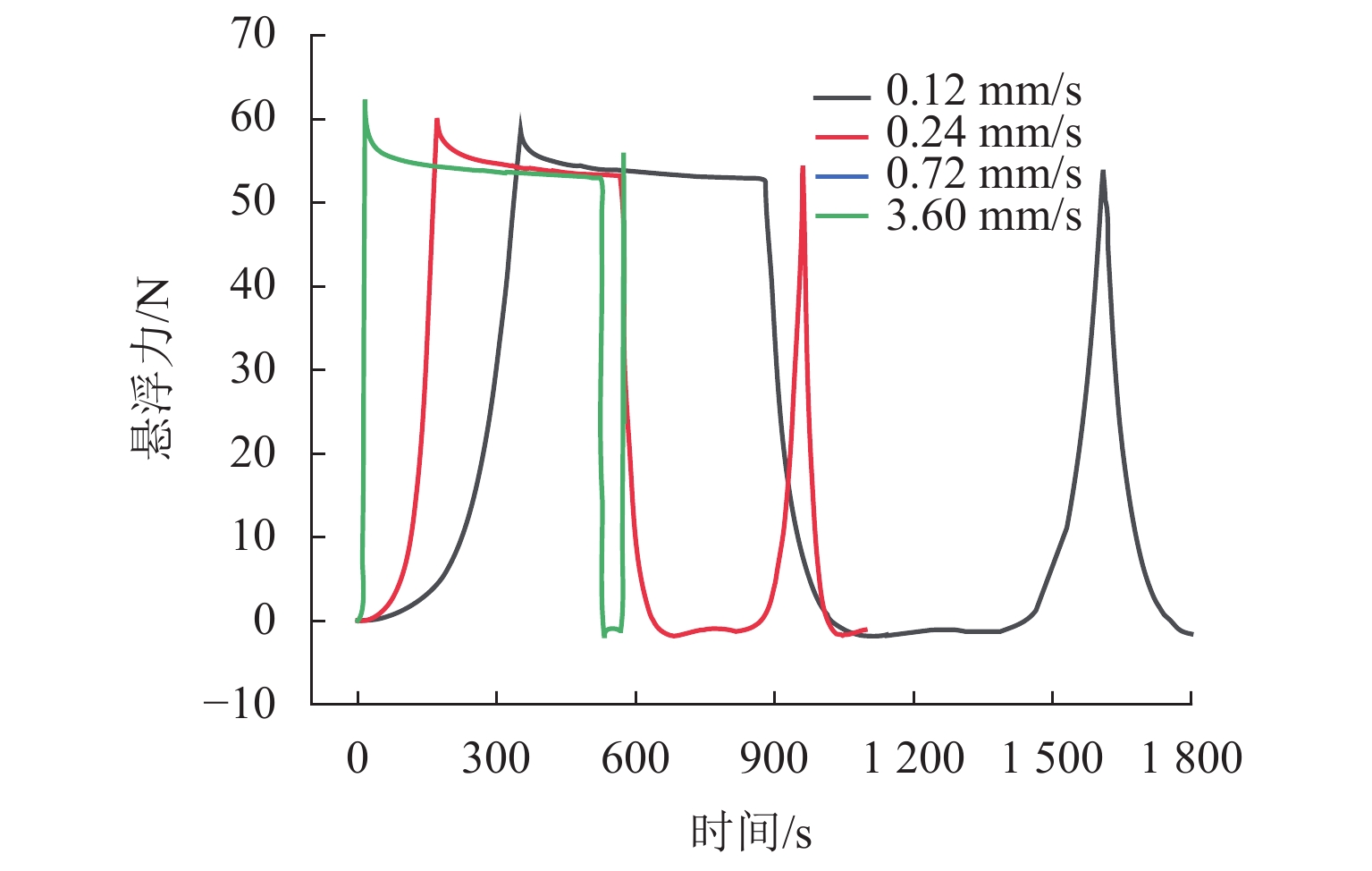
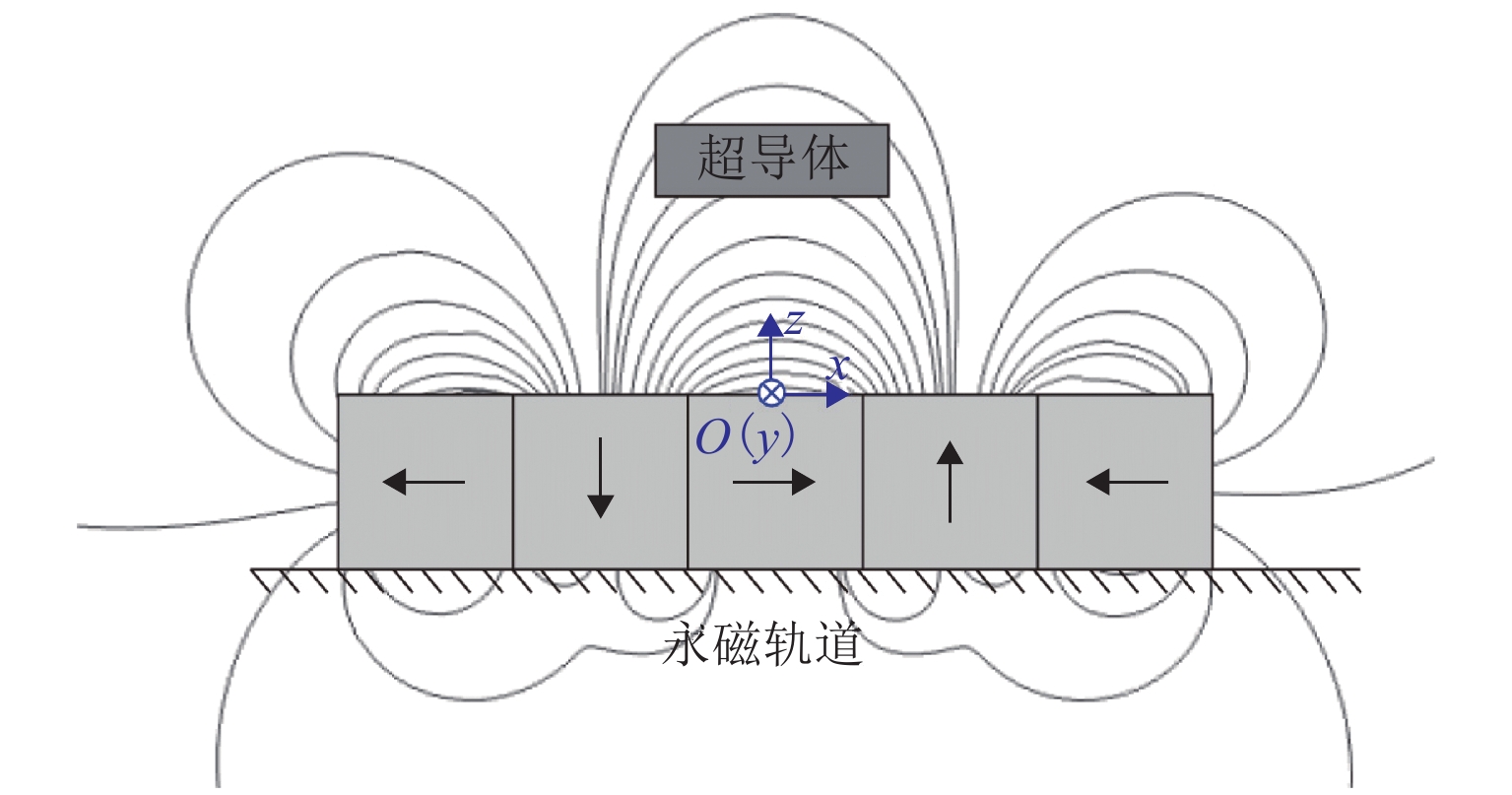
为了研究顶部籽晶熔融织构法制备的钇钡铜氧超导块材在Halbach永磁轨道上的准静态悬浮力弛豫特性,定义了弛豫完整过程,划分为激励过程(含起始状态、中间过程、终止状态)、弛豫过程和稳态结果;在激励过程起始和终止状态相同时,通过搭建的悬浮力测试装置,研究了复杂中间过程对稳态结果的影响;基于磁化和Anderson-Kim模型建立了弛豫分析模型,对力弛豫规律进行分析和总结. 研究结果表明:4种不同中间过程位移形式的稳态结果趋于一致,但位移过程中的最大悬浮力受到往返次数以及速度的影响,其中最大悬浮力点分布在随时间对数衰减的曲线周围;弛豫过程前终止状态的悬浮力与移动速度正相关,经过弛豫过程后的稳态结果趋于一致,而弛豫过程后以不同移动速度重复往返一次,移动速度对最大悬浮力的影响明显减弱(最大悬浮力差值由3.7 N降低为2.0 N);超导体在激励过程和弛豫过程中皆存在弛豫现象,而移动速度以及往返次数对最大悬浮力的影响结果是激励过程力弛豫的表现.
Abstract:To investigate the quasi-static force-relaxation characteristics of a YBCO bulk levitated above a Halbach permanent-magnetic guideway, using the top-seed-melt-texture-growth method, the complete relaxation process is defined and divided into the excitation process (involved initial state, dynamics process, and termination state), relaxation process, and steady state. With the same initial and termination states, the effect of different displacements of the dynamics process on the steady state is experimentally investigated using a specialized apparatus. Then, on the basis of magnetization and the Anderson-Kim model, a relaxation model is established and several laws are formulated. The results indicate that the steady states of the four displacements tend to be the same. However, the maximum levitation force (MLF) is affected by the round-trip times and displacement velocity. The MLF points are distributed around a curve that decays logarithmically with time. Prior to the relaxation process, the levitation force of the terminating state is positively correlated with the velocity; the steady state results after the relaxation process tend to be consistent. Furthermore, after the relaxation process, the influence of the velocity on the MLF is greatly reduced (the MLF difference decreases from 3.7 N to 2.0 N). Relaxation phenomena are in both the excitation and relaxation processes of superconductors, and the effect of the velocity and round-trip times on the MLF is manifested in the relaxation during the excitation process.
-
表 1 不同时刻悬浮力的比较
Table 1. The comparison of levitation force at different time
N v/(m·s−1) F2 F3 F4 0.12 58.6 52.8 53.9 0.24 60.1 53.1 54.4 0.72 61.8 53.0 54.6 3.60 62.3 52.9 55.9 -
[1] WANG J S, WANG S Y. High temperature superconducting magnetic levitation[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2017: 132-133. [2] WANG J S, WANG S Y, ZENG Y W, et al. The first man-loading high temperature superconducting Maglev test vehicle in the world[J]. Physica C:Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2002, 378/379/380/381: 809-814. [3] DENG Z G, ZHANG W H, ZHENG J, et al. A high-temperature superconducting maglev ring test line developed in Chengdu, China[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(6): 3602408.1-3602408.8. [4] DENG Z G, ZHANG W H, ZHENG J, et al. A high-temperature superconducting maglev-evacuated tube transport (HTS maglev-ETT) test system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2017, 27(6): 3602008.1-3602008.8. [5] SCHULTZ L, DE HAAS O, VERGES P, et al. Superconductively levitated transport system-the SupraTrans project[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2005, 15(2): 2301-2305. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.849636 [6] MATTOS L S, RODRIGUEZ E, COSTA F, et al. MagLev-cobra operational tests[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(3): 3600704.1-3600704.4. [7] D’OVIDIO G, CRISI F, LANZARA G. A “V” shaped superconducting levitation module for lift and guidance of a magnetic transportation system[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2008, 468(14): 1036-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.physc.2008.05.154 [8] DENG Z, WANG J, ZHENG J, et al. High-efficiency and low-cost permanent magnet guideway consideration for high-Tc superconducting Maglev vehicle practical application[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2008, 21(11): 115018.1-115018.9. doi: 10.1088/0953-2048/21/11/115018 [9] HULL J R. Superconducting bearings[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2000, 13(2): 1-15. doi: 10.1088/0953-2048/13/2/201 [10] KIM Y B, HEMPSTEAD C F, STRNAD A R. Critical persistent currents in hard superconductors[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1962, 9(7): 306-309. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.9.306 [11] SIAMAKI M, STOREY J G, BADCOCK R A. Towards a non-destructive method of mapping the E-J relation using force decay measurements on superconducting bulks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2021, 31(5): 9000405.1-9000405.5. [12] MOON F C, CHANG P Z, HOJAJI H, et al. Levitation forces, relaxation and magnetic stiffness of melt-quenched YBa2Cu3O x[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1990, 29(7): 1257-1258. [13] RIISE A B, JOHANSEN T H, BRATSBERG H, et al. Logarithmic relaxation in the levitation force in a magnet-high Tc superconductor system[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1992, 60(18): 2294-2296. doi: 10.1063/1.107034 [14] QIN Y J, LU Y Y, WANG S Y, et al. Levitation force relaxation of HTS bulk above NdFeB guideways at different approaching speeds[J]. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 2009, 22(5): 511-516. doi: 10.1007/s10948-009-0449-x [15] STARIKOVSKII A S, OSIPOV M A, RUDNEV I A. Levitation properties of pre-magnetized HTS tape stacks[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1686(1): 012058.1-012058.6. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1686/1/012058 [16] SOTELO G G, DIAS D H N, DE ANDRADE R, et al. Tests on a superconductor linear magnetic bearing of a full-scale MagLev vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2011, 21(3): 1464-1468. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2010.2086034 [17] YUAN Y H, LI J P, DENG Z G, et al. Dynamic performance of HTS maglev and comparisons with another two types of high-speed railway vehicles[J]. Cryogenics, 2021, 117: 103321.1-103321.8. doi: 10.1016/j.cryogenics.2021.103321 [18] POSTREKHIN E, MA K B, YE H, et al. Dynamics and relaxation of magnetic stress between magnet and superconductor in a levitation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2001, 11(1): 1984-1987. doi: 10.1109/77.920242 [19] 马光同. 高温超导磁悬浮三维理论模型及其数值计算研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2009. [20] 黄欢. 高温超导磁悬浮磁-力特性实验与仿真研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. [21] 王璐琳. 永磁外场中高温超导体悬浮力弛豫的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2008. [22] DENG Z G, ZHENG J, ZHANG J, et al. Studies on the levitation height decay of the high temperature superconducting maglev vehicle[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2007, 463/464/465: 1293-1296. [23] MA G T, LIN Q X, WANG J S, et al. Method to reduce levitation force decay of the bulk HTSC above the NdFeB guideway due to lateral movement[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2008, 21(6): 065020.1-065020.5. doi: 10.1088/0953-2048/21/6/065020 [24] HUANG C G, XU B, ZHOU Y H. Strategies to improve the dynamic levitation performance of superconducting maglevs against force decay and disturbance[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 127(19): 193907.1-193907.13. doi: 10.1063/5.0003502 [25] JING H, WANG J, WANG S, et al. A two-pole Halbach permanent magnet guideway for high temperature superconducting Maglev vehicle[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2007, 463/464/465: 426-430. [26] JING H, WANG S Y, JIANG M, et al. Influence of the vertical movement of bulk on the levitation force at different temperatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2012, 22(6): 6800505.1-6800505.5. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2012.2218103 [27] ANDERSON P W. Theory of flux creep in hard superconductors[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1962, 9(7): 309-311. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.9.309 [28] ANDERSON P W, KIM Y B. Hard superconductivity: theory of the motion of abrikosov flux lines[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1964, 36(1): 39-43. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.36.39 -




 下载:
下载: