Application of Rayleigh Wave Elliptic Polarization in Shield Tunnel Stratum Disturbance Exploration
-
摘要:
为解决传统物探方法在城市盾构隧道工程中难以对地层扰动达到较好探测和监测目的,提出了主动源瑞利面波椭圆极化方法. 采用二维有限元数值模拟对实际盾构隧道施工背景下的地层情况进行全波场正演模拟,并对其波场传播、速度频散和椭圆极化频散等特征进行分析;结合工程实例,进一步将椭圆极化方法和传统速度频散方法进行对比研究. 研究结果表明:主动源瑞利面波椭圆极化方法在探测地下介质结构分布及监测地下空洞等异常结构的变化方面具有和传统速度频散方法同样的探测效果,但由于其不需要长大检波器排列,对周围环境震动等噪声抗干扰能力相对较强,因此更适合城市等场地受限和具有一定震动和噪声干扰的环境,从而具有更广阔的应用前景.
Abstract:In order to solve the problem that traditional geophysical methods are difficult to achieve better detection and monitoring of stratum disturbance in urban shield tunnel engineering, the application of active source Rayleigh surface wave elliptical polarization method is proposed. Firstly, the 2D finite element numerical simulation is used to simulate the full-wave field forward modeling of the stratum under the actual shield tunnel construction background, and the characteristics of wave field propagation, velocity dispersion and elliptical polarization dispersion are analyzed. Then, the elliptical polarization method and the traditional velocity dispersion method are further analyzed and compared on the basis of a combination of examples. The results indicate that the active source Rayleigh surface wave elliptic polarization method has the same detection effect as the traditional velocity dispersion method in detecting the distribution of underground medium structure and monitoring the changes of underground cavity and other abnormal structures. However, because it does not need the arrangement of long and long geophones, it has relatively strong anti-interference ability to the vibration and other noise of the surrounding environment. Therefore, it is more suitable for the environment with limited sites such as cities and certain vibration and noise interference, so it has a broader application prospect.
-
表 1 数值模型介质参数
Table 1. Medium parameters of numerical model
编号 弹性
模量/
MPa密度/
(kg•m−3)纵波
波速/
(m•s−1)横波
波速/
(m•s−1)面波
波速/
(m•s−1)泊松比 1 280 1800 630 234 221 0.42 2 11 1500 524 160 151 0.45 表 2 数值模拟结果特征分析
Table 2. Characteristic analysis of numerical simulation results
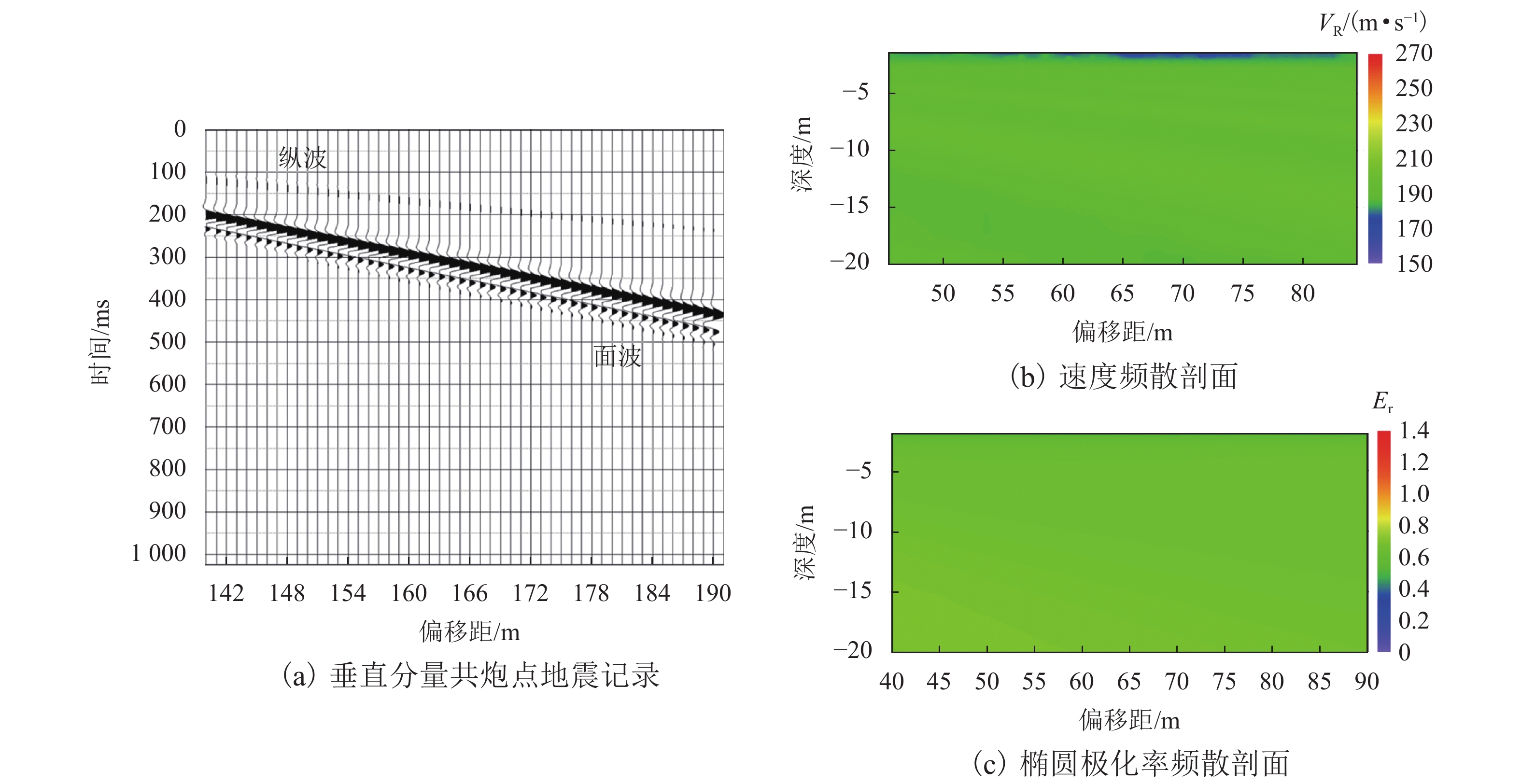
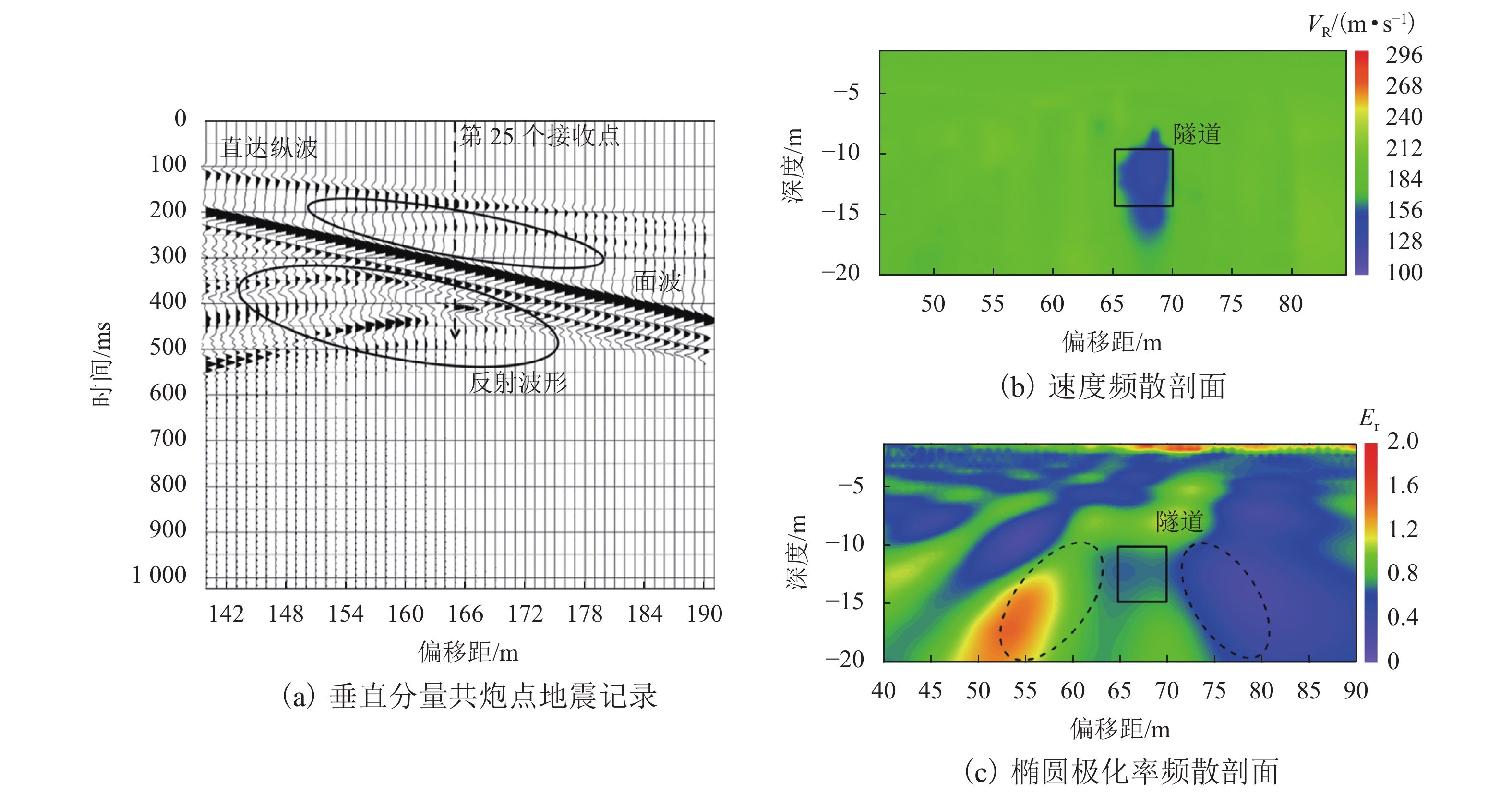
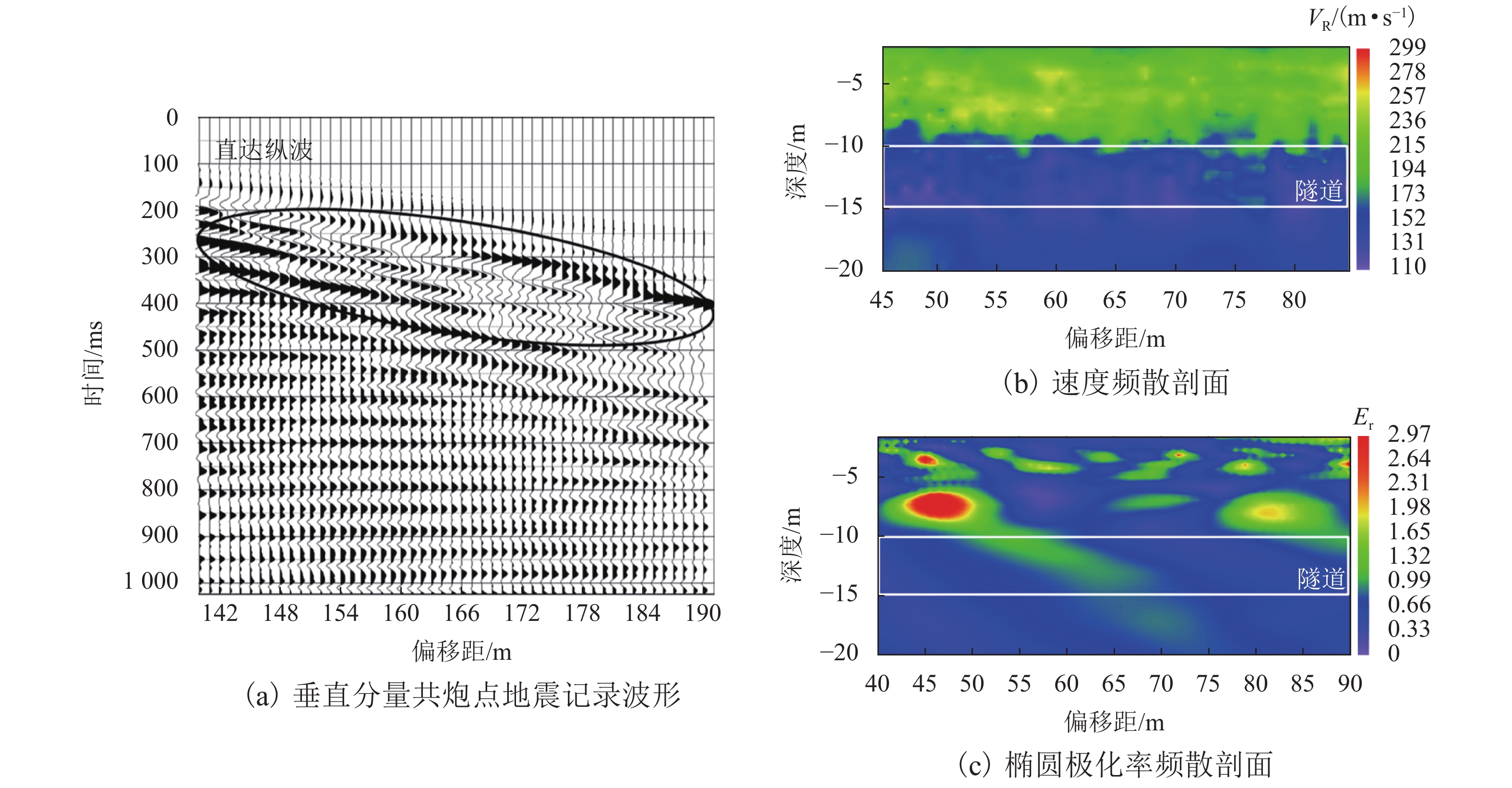
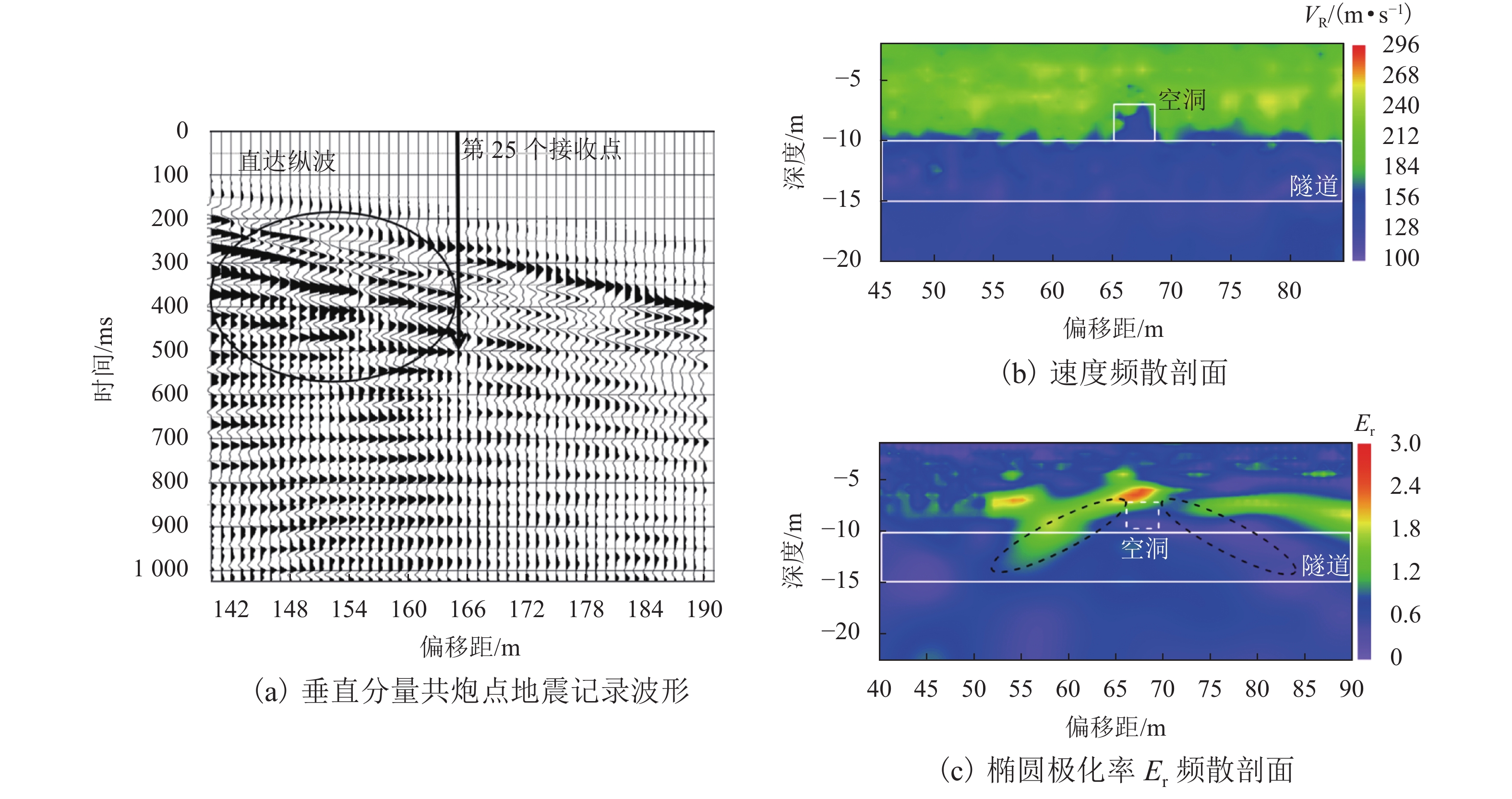
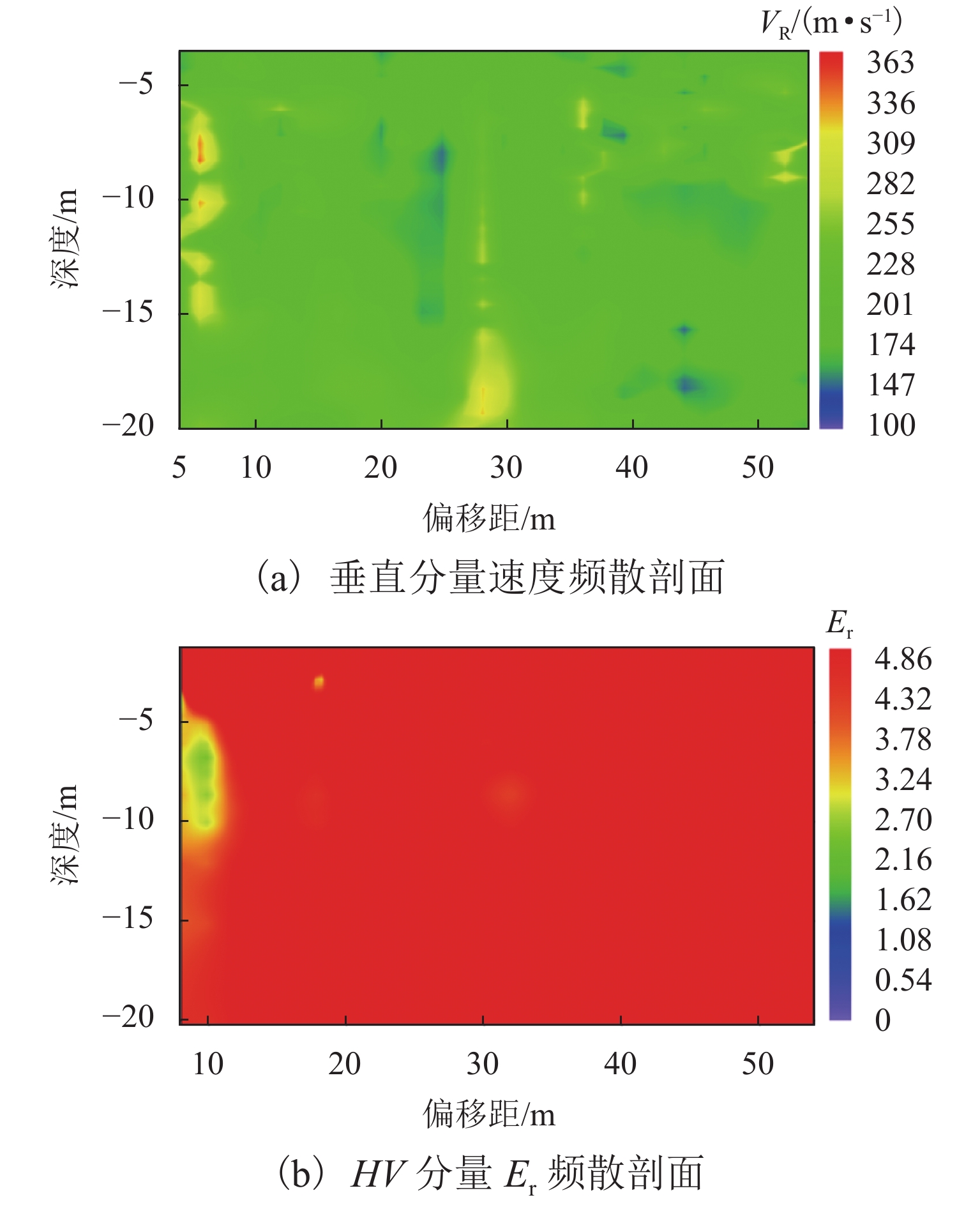
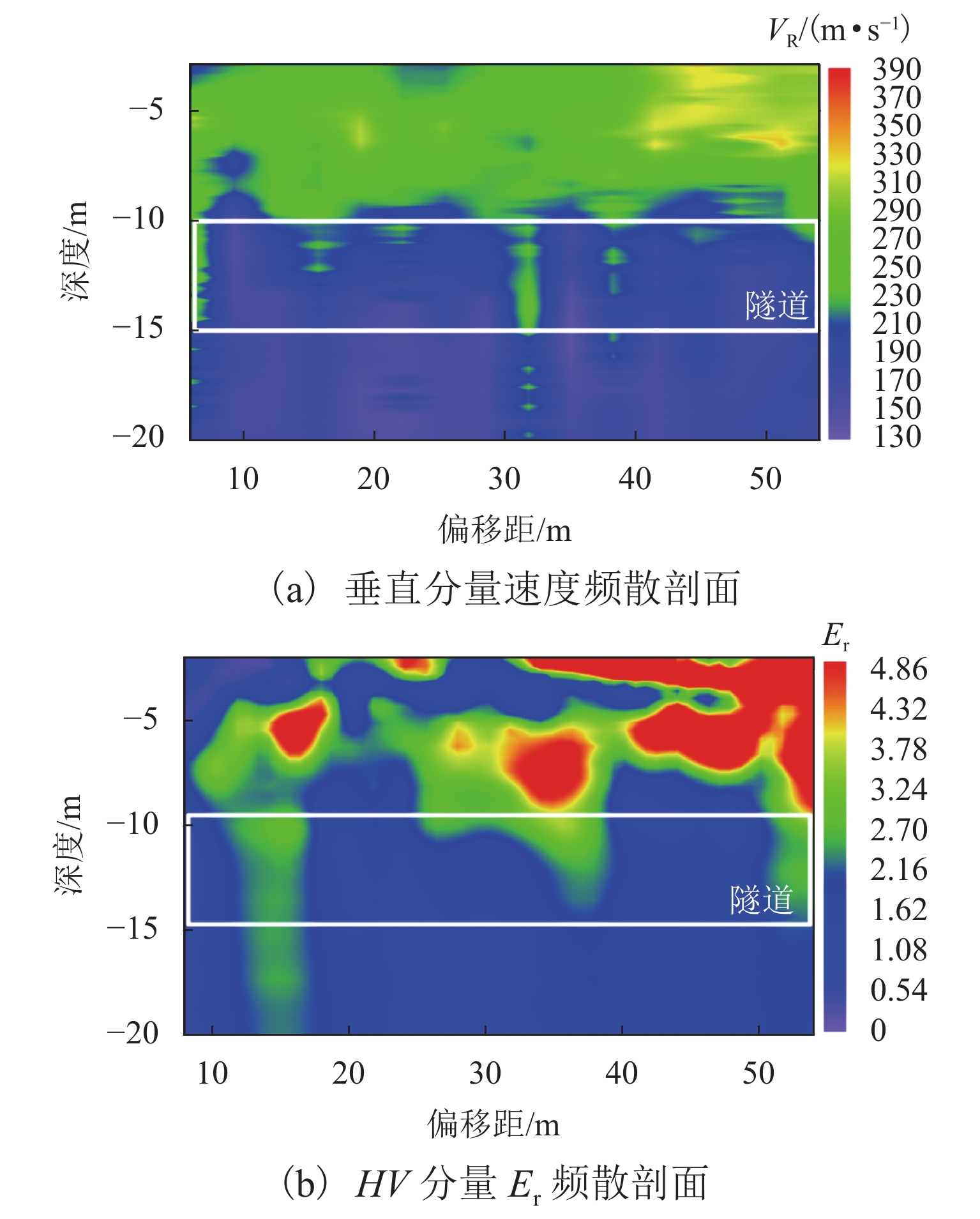
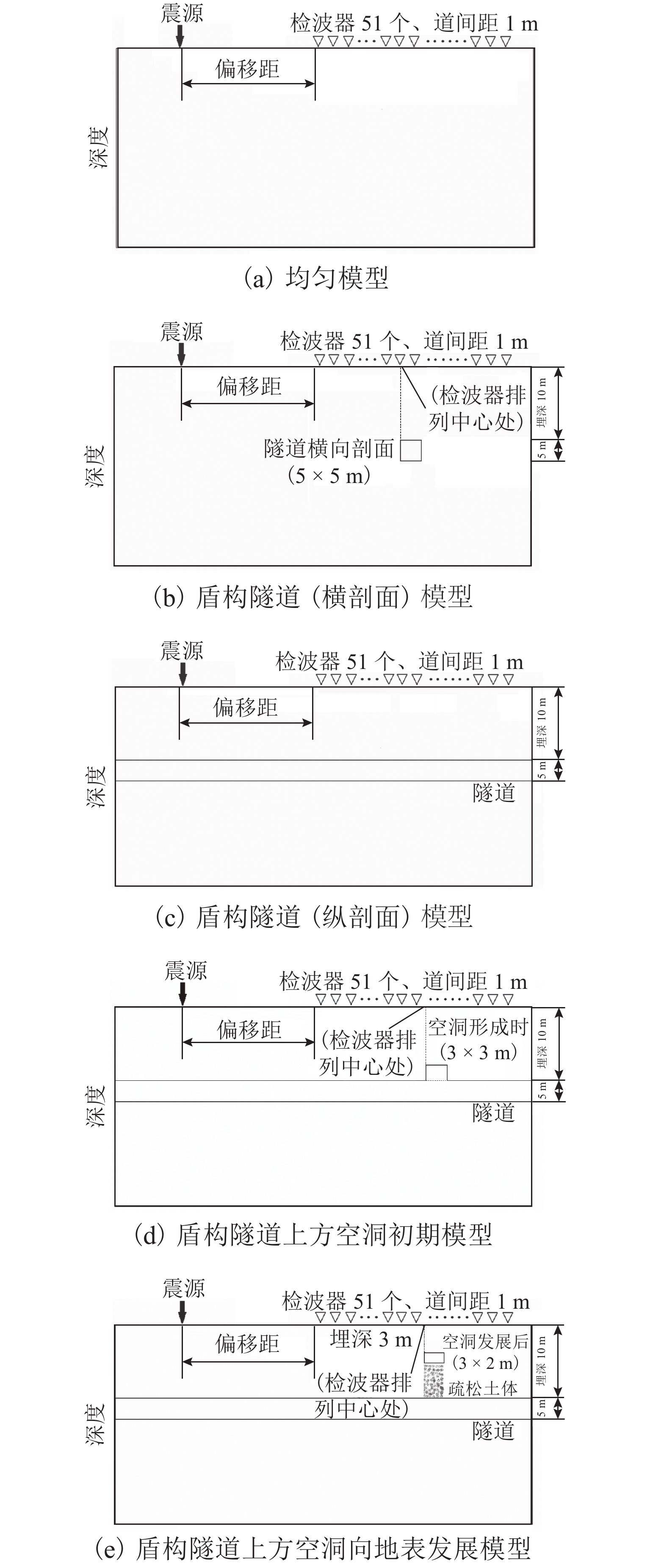
模型 波场传播特征 速度频散特征 椭圆极化特征 a 直达纵波和面波同相轴均为直线,且随着偏移距增大,纵波衰减较快,面波衰减较慢 Vr 基本为200~220 m/s,与均匀介质模型Vr 理论值 221 m/s 基本吻合 椭圆极化率值 Er 趋于均一,整体 Er 值分布在 0.8 附近 b 直达纵波和面波之间以及面波下方都出现了弯曲弧形同相轴(实线圈处),且弧形同相轴顶点位于第25 个接收点附近 黑色实线区内(偏移距65 m、深度10 m 附近)介质 Vr 为130~160 m/s,呈相对低速特征,其周围介质整体速度相对较为均匀,约190~220 m/s,为相对高速特征,该高速值与设置的围岩 Vr 值221 m/s 相符合 隧道断面(黑色实线区)周围出现分别向两侧斜下方倾斜的 Er 异常,其左侧(左虚线圈)为向左下方微倾斜的散射状Er(1.0~1.4)区域,右侧(右虚线圈)为向右下方微倾斜的散射状低 Er(0.1~0.5)区域,黑色实线区 Er 为 0.6~0.8,介于两侧 Er 之间 c 直达纵波 DP 下方,每隔一定 x-t 间隔出现一组振幅较强的同相轴波形(实线圈范围内) 以10 m 处白色实线为界有明显的速度差异,隧道(白色实线区域)及以下呈明显低速特征,其 Vr 约为110~160 m/s,隧道上层介质速度为200~235 m/s,与模型设置围岩 Vr 221 m/s 接近 深度10 m 即隧道界面附近,椭圆极化特征大致呈上下两层分布,其中上层椭圆极化率值高低较不均匀,呈区块状分布,其中较高(1.3~2.5)或较低(0.1~0.7)的 Er 值区块,整体上,上层 Er 大于下层 d 空洞位置即第25个检波器偏移距65 m附近,体波下方及面波分布区中叠加有弯曲的弧形同相轴(实线圈处)波形 空洞区域及隧道(上下两个白色实线框)下方介质均为低速特征,面波波速 Vr 为120~170 m/s,上方介质Vr 较高为195~235 m/s,与设置的围岩面波速度 221 m/s 较吻合 偏移距 65 m 处即空洞(白色实线小框)下方 Er 值分别向两侧斜下方呈放射状高低相间排列的分布规律,其中左侧为 Er 高值区(左虚线圈所示, 1.0~2.0),右侧为 Er 低值区(右虚线所示,0.3~0.9),空洞异常在两侧放射状高低 Er 之间的顶部位置;且 Er 分布规律整体上呈上下两层分布,上侧 Er 明显高于下侧 e 空洞位置即第25 个检波器偏移距65 m 附近,体波下方及面波分布区中叠加有弧形同相轴(实线圈处) 空洞运动轨迹范围(白色实线区域和白色虚线区域)内堆积土体介质的低速特征,其速度约为 120~170 m/s,周围介质速度仍为原来设定的190~230 m/s 左侧 Er 高值区(左虚线圈所示)为1.6~2.5,右侧 Er 低值区(右虚线圈所示)0.3~1.2,空洞异常仍在两侧高低 Er 之间的顶部位置,且 Er 分布规律整体上呈上下两层分布,上侧 Er 值明显高于下侧 -
[1] 张成平,张顶立,王梦恕,等. 城市隧道施工诱发的地面塌陷灾变机制及其控制[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(增刊1): 303-309.ZHANG Chengping, ZHANG Dingli, WANG Mengshu, et al. Catastrophe mechanism and control technology of ground collapse induced by urban tunneling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(S1): 303-309. [2] 侯艳娟,张顶立,李鹏飞. 北京地铁施工安全事故分析及防治对策[J]. 北京交通大学学报,2009,33(3): 52-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0291.2009.03.011HOU Yanjuan, ZHANG Dingli, LI Pengfei. Analysis and control measures of safety accidents in Beijing subway construction[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2009, 33(3): 52-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0291.2009.03.011 [3] 郭汉章. 武汉地铁七号线盾构隧道施工对地面沉降及建筑物变形影响分析[D]. 武汉: 武汉工程大学, 2017. [4] 周松,荣建,陈立生,等. 单管双线大直径地铁盾构隧道施工与监测[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2013,9(2): 365-372.ZHOU Song, RONG Jian, CHEN Lisheng, et al. Construction and monitoring of single underground railway tunnel with dual carriageway using large-diameter shield[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2013, 9(2): 365-372. [5] 王红庭. 盾构隧道注浆病害探地雷达检测实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019. [6] 刘宏岳,黄佳坤,孙智勇,等. 微动探测方法在城市地铁盾构施工“孤石”探测中的应用: 以福州地铁1号线为例[J]. 隧道建设,2016,36(12): 1500-1506. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.1672-741X.2016.12.014LIU Hongyue, HUANG Jiakun, SUN Zhiyong, et al. Application of microtremor method to boulders detection in urban metro shield construction: case study of Fuzhou metro line No. 1[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2016, 36(12): 1500-1506. doi: 10.3973/j.issn.1672-741X.2016.12.014 [7] SHEN L Y, CHEN X W, ZHANG X, et al. Seismic characterization for underground construction projects using microtremor survey method: a case study in Shenzhen Subway Line 10[C]//SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2017. Houston: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2017: 5453-5457. [8] SHEN L Y, CHEN X W, ZHENG Y, et al. Seismic characterization for underground construction projects using microtremor survey method: a case study in Chengdu Line 18[C]//SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018. Anaheim: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2018: 1-5. [9] 张新. 基于随机源模型的新型微动探测技术在上软下硬地层盾构隧道中的应用研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2020,57(5): 43-50.ZHANG Xin. Research on application of random source model based new microtremor survey technology to shield tunnelling in upper soft and lower hard strata[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2020, 57(5): 43-50. [10] 张立,刘争平,熊自英. 利用地脉动H/V谱比反演地层Vs结构剖面[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2009,6(增1): 4-5.ZHANG Li, LIU Zhengping, XIONG Ziying. S-wave velocity profiling by inversion of microtremor H/V spectra[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2009, 6(S1): 4-5. [11] BOORE D M, NAFI TOKSÖZ M. Rayleigh wave particle motion and crustal structure[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1969, 59(1): 331-346. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0590010331 [12] TANER M, SHERIFF R. Application of amplitude, frequency, and other attributes to stratigraphic and hydrocarbon determination: section 2, application of seismic reflection configuration to stratigraphic interpretation[J]. Railway Technical Reasearch Institute, Quarterly Reports, 1989, 30(1): 20-24. [13] TOKIMATSU K, MIYADERA Y. Characteristics of Rayleigh waves in microtremors and their relation to underground structures[J]. Journal of Structural and Construction Engineering (Transactions of AIJ), 1992, 439: 81-87. doi: 10.3130/aijsx.439.0_81 [14] 蒋通,崔哲,李文艺. 层状介质中的瑞雷面波理论及其在场地脉动观测中的应用[J]. 上海力学,1999,20(3): 252-258.JIANG Tong, CUI Zhe, LI Wenyi. Theory of Rayleigh wave in multi-layered media and its application in microseism observation[J]. Shanghai Journal of Mechanical, 1999, 20(3): 252-258. [15] ARAI H. S-wave velocity profiling by joint inversion of microtremor dispersion curve and horizontal-to-vertical (H/V) spectrum[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2005, 95(5): 1766-1778. doi: 10.1785/0120040243 [16] 张立. 层状介质中瑞利面波波场特征分析和反演方法研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2009. [17] 于文福. 点源横向非均匀介质瑞利面波波场数值模拟研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. [18] 陈伟,徐义贤,张煜. 瑞雷面波在弹性楔状体中的传播特性研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2009,6(2): 143-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2009.02.003CHEN Wei, XU Yixian, ZHANG Yu. Study of transmission characteristics of Rayleigh waves on an elastic wedge[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2009, 6(2): 143-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2009.02.003 [19] 苏传行,刘争平,谭屹,等. 二维起伏地形瑞利面波速度频散特性数值模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(2): 810-816. doi: 10.6038/pg2019BB0384SU Chuanhang, LIU Zhengping, TAN Yi, et al. Study to the dispersion characteristics of Rayleigh waves trvalling along topographies with numerical modeling[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(2): 810-816. doi: 10.6038/pg2019BB0384 [20] 张碧星,鲁来玉,鲍光淑. 瑞利波勘探中“之”字形频散曲线研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2002,45(2): 263-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2002.02.013ZHANG Bixing, LU Laiyu, BAO Guangshu. A study on zigzag dispersion curves in Rayleigh wave exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2002, 45(2): 263-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2002.02.013 [21] 张凯,刘争平,熊自英,等. 声电效应在瑞利面波频散特性物理模拟中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,2015,30(6): 2955-2962. doi: 10.6038/pg20150665ZHANG Kai, LIU Zhengping, XIONG Ziying, et al. Application of seismoelectric effect to the experiment measurememt of Rayleigh surface waves[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(6): 2955-2962. doi: 10.6038/pg20150665 [22] 张立,刘争平. 水平层状介质中基阶瑞利面波椭圆极化特征数值分析与研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2013,56(5): 1686-1695. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130526ZHANG Li, LIU Zhengping. A study of the elliptic polarization characteristics of fundamental mode Rayleigh wave based on numerical simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(5): 1686-1695. doi: 10.6038/cjg20130526 [23] 刘争平,张立,阎胜. 局部非均质体的瑞利面波动力学响应数值模拟研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报,2009,6(增刊1): 1-3.LIU Zhengping, ZHANG Li, YAN Sheng. The dynamic feature analysis of Rayleigh surface wave on a local inhomogeneity using the numerical method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2009, 6(S1): 1-3. [24] 郭明珠,谢礼立,凌贤长. 弹性介质面波地脉动单点谱比法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2004,26(4): 450-453. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.04.004GUO Mingzhu, XIE Lili, LING Xianzhang. Research on spectral ratio of horizontal to vertical component for elastic model and surface microtremors[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004, 26(4): 450-453. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.04.004 [25] 白永学,漆泰岳,吴占瑞. 砂卵石地层盾构施工引发的滞后地面塌陷机理[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程,2013,35(1): 12-19.BAI Yongxue, QI Taiyue, WU Zhanrui. Lagged surface collapse mechanism of shield construction in sandy pebble stratum[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering, 2013, 35(1): 12-19. [26] 罗松,张浩然. 成都富水砂卵石地层盾构施工滞后沉降防控措施探讨[J]. 隧道建设,2010,30(3): 317-319,335.LUO Song, ZHANG Haoran. Discussion on prevention and control of delayed settlement induced by shield tunneling in water-rich sandy cobble stratum in Chengdu[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2010, 30(3): 317-319,335. [27] 李哲生. 瞬态多道瑞利波勘探技术在岩土工程勘察中的应用[J]. 工程勘察,1996,24(3): 33-34.LI Zhesheng. Application of transient multichannel Rayleigh wave exploration technique in geotechnical engineering investigation[J]. Geotichnical Investigation and Surveying, 1996, 24(3): 33-34. [28] FÄH D, KIND F, GIARDINI D. Inversion of local S-wave velocity structures from average H/V ratios, and their use for the estimation of site-effects[J]. Journal of Seismology, 2003, 7(4): 449-467. doi: 10.1023/B:JOSE.0000005712.86058.42 [29] 邓瑞. 横向非均匀介质多模态瑞利面波波场数值模拟研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020. [30] 李梦. 水平层状介质中多模式瑞利面波波场有限元数值模拟研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020. -




 下载:
下载: