Fast Calibration Method of Odometer Parameters Based on Speed Information of Strapdown Inertial Navigation System
-
摘要:
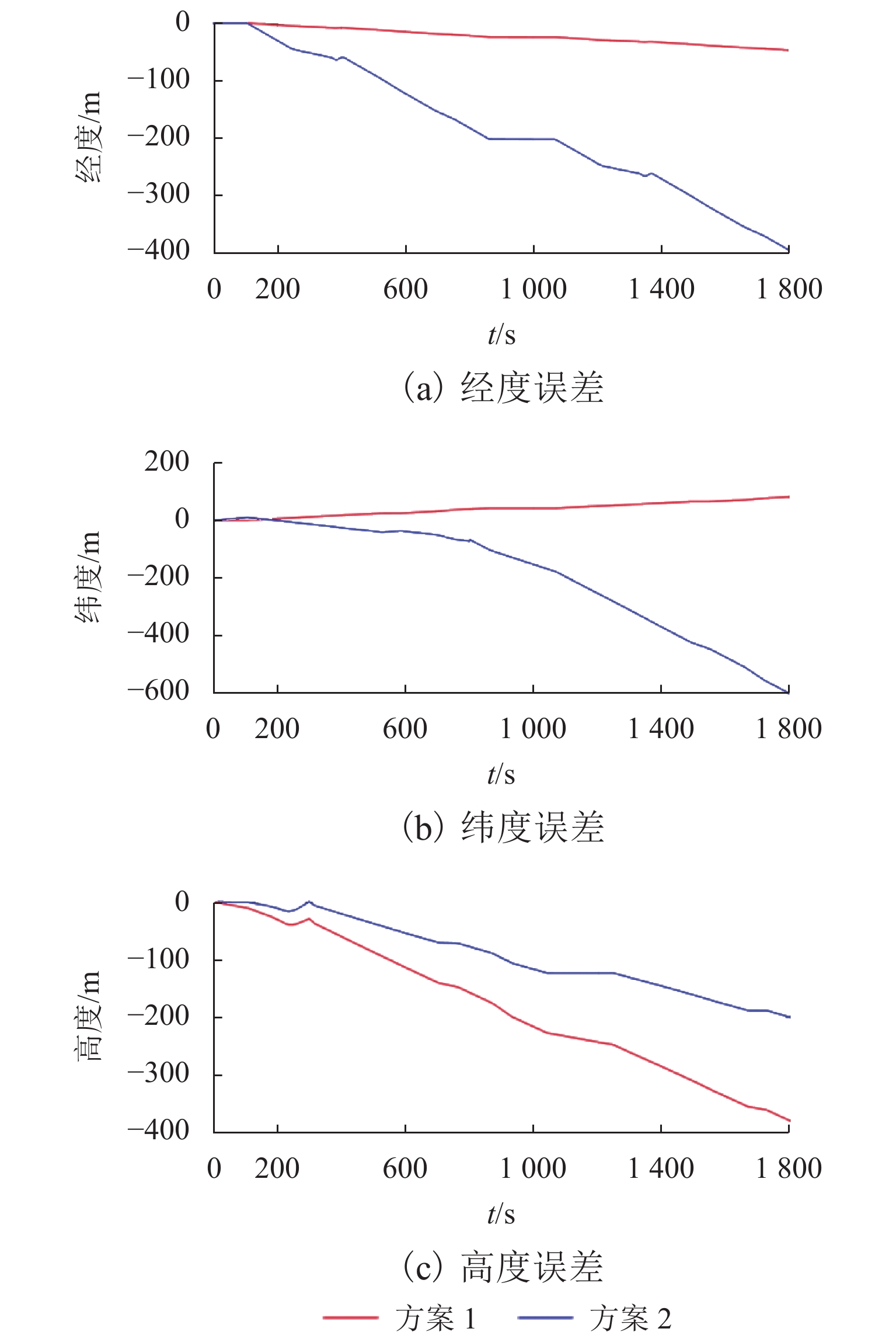
针对里程计标度因数误差和安装误差对捷联惯导/里程计组合导航精度的显著影响,提出一种基于短时捷联惯导系统(strapdown inertial navigation system,SINS)速度信息的里程计参数标定方法. 通过建立航位推算误差模型,构建惯性测量单元(inertial measurement unit,IMU)坐标系内惯导系统输出速度与里程计输出之间的关系式,得到里程计参数的计算公式;利用最小二乘法对里程计标度因数和安装误差进行标定. 该方法只利用了捷联惯导信息,在1 min内就可实现里程计参数的初次标定,不需要相关参数误差值为小量的假设,并可以忽略杆臂效应对标定效果的影响. 试验结果表明:当车辆行驶30 min后,利用该方法标定后的水平航位推算精度比传统标定方法定位精度高92.3%.
Abstract:To solve the problem that the scale factor error and installation error of odometers have a great influence on the accuracy of strapdown inertial navigation/odometer integrated navigation, a fast calibration method based on short-term SINS (strapdown inertial navigation system) information is proposed for odometer parameters. By establishing a dead-reckoning error model, the relationship between the output speed of the inertial navigation system and the output of the odometer in the inertial measurement unit (IMU) coordinate system is constructed, and the formula of calculating the odometer parameters is obtained. The least squares method is utilized to calibrate the odometer scale factor and installation error. This method only uses strap-down inertial navigation information to achieve the initial calibration of the odometer parameters within 1 min. It does not require the assumption that the error value of the relevant parameters is small, and ignores the influence of the lever arm effect on the calibration effect. The test results show that, when the vehicle has been running for 30 min, the accuracy of the horizontal dead-reckoning method calibrated by this method is 92.3% higher than that of the traditional calibration method.
-
Key words:
- odometer /
- scale factor /
- installation error /
- SINS /
- least squares method
-
表 1 $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}} } $为小量时不同方案标定结果
Table 1. Calibration results of different schemes with small quantity of $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}} } $
方案 $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{θ}} } $/(°) $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}} } $/(°) $ {\hat K_{{\text{OD}}}} $/(m·脉冲−1) 1 0.008444 0.499448 0.013037 2 0.178213 −12.608224 0.019387 表 2 $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}}} $不为小量时不同方案标定结果
Table 2. Calibration results of different schemes with no small quantity of $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}} } $
方案 $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{θ}} } $/(°) $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}} } $/(°) $ {\hat K_{{\text{OD}}}} $/(m·脉冲−1) 1 0.008444 90.499448 0.013037 2 0.182691 79.700219 0.017921 表 3 $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}}} $不为小量时不同方案标定结果 (原s系绕z轴再逆时针旋转90°)
Table 3. Calibration results of different schemes with no small quantity of $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}} } $ (original s system rotating 90° counterclockwise around z axis)
方案 $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{θ}} } $/(°) $ {\hat \alpha _{\text{ψ}}} $/(°) $ {\hat K_{{\text{OD}}}} $/(m·脉冲−1) 1 0.008464 180.499446 0.013033 2 0.202691 163.700219 0.015921 -
[1] SKOP I, HANDEL P. In-car positioning and navigation technologies: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(1): 4-21. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2008.2011712 [2] MOURIKIS A I, TRAWNY N, ROUMELIOTIS S I, et al. Vision-aided inertial navigation for spacecraft entry, descent, and landing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2009, 25(2): 264-280. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2009.2012342 [3] FU Q W, LIU Y, LIU Z B, et al. High-accuracy SINS/LDV integration for long-distance land navigation[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2018, 23(6): 2952-2962. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2018.2875151 [4] WANG M S, WU W Q, HE X F, et al. Consistent ST-EKF for long distance land vehicle navigation based on SINS/OD integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(11): 10525-10534. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2939679 [5] GAO J X, LI K, CHEN Y P. Study on integration of FOG single-axis rotational INS and odometer for land vehicle[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(2): 752-763. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2772308 [6] 高军强,汤霞清,张环,等. 基于因子图的车载INS/GNSS/OD组合导航算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2018,40(11): 2547-2553.GAO Junqiang, TANG Xiaqing, ZHANG Huan, et al. Vehicle INS/GNSS/OD integrated navigation algorithm based on factor graph[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(11): 2547-2553. [7] CHANG L B, HE H Y, QIN F J. In-motion initial alignment for odometer aided strapdown inertial navigation system based on attitude estimation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(3): 766-773. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2633428 [8] CHANG L, NIU X J, LIU T Y. GNSS/IMU/ODO/ LiDAR-SLAM integrated navigation system using IMU/ODO pre-integration[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(17): 4702.1-4702.18. doi: 10.3390/s20174702 [9] 黄湘远,汤霞清,武萌. 基于降维CKF和平滑的SINS/OD动基座对准[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2016,38(9): 2135-2141.HUANG Xiangyuan, TANG Xiaqing, WU Meng. Research on moving base initial alignment of SINS/OD with reduced dimension CKF and smoother[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(9): 2135-2141. [10] 赵洪松,缪玲娟,沈军. 捷联惯导/里程计高精度组合导航算法[J]. 兵工学报,2014,35(4): 433-440.ZHAO Hongsong, MIAO Lingjuan, SHEN Jun. High accuracy algorithm for SINS/odometer integrated navigation system[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(4): 433-440. [11] 李艳,杨波,薛亮,等. 基于车辆运动约束的里程计误差在线标定方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2016,24(4): 485-489.LI Yan, YANG Bo, XUE Liang, et al. Online calibration method for odometer's errors based on vehicle motion constraints[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2016, 24(4): 485-489. [12] 刘永红,刘明雍,谢波. 航位推算组合导航系统在线标定技术[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2015,23(4): 434-437.LIU Yonghong, LIU Mingyong, XIE Bo. Online calibration technique for integrated vehicular navigation system[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(4): 434-437. [13] 刘鹏飞,师鹏宇,智奇楠,等. 车载自主导航系统里程计误差在线标定方法[J]. 数字通信世界,2019(12): 8-10.LIU Pengfei, SHI Pengyu, ZHI Qinan, et al. On-line Calibration Method of Odometer Error for Vehicle Autonomous Navigation System[J]. Digital Communication World, 2019(12): 8-10. [14] 肖烜,王清哲,程远,等. 捷联惯导系统/里程计高精度紧组合导航算法[J]. 兵工学报,2012,33(4): 395-400.XIAO Xuan, WANG Qingzhe, CHENG Yuan, et al. High accuracy navigation algorithm for tightly coupled INS/odometer[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2012, 33(4): 395-400. [15] 宋金龙,石志勇,王律化,等. 基于运动学非完整约束的里程计参数在线辨识[J]. 中国惯性技术学报,2018,26(3): 352-358.SONG Jinlong, SHI Zhiyong, WANG Lvhua, et al. Online identification of odometer parameters based on kinematics incomplete constraints[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(3): 352-358. [16] LI L L, SUN H X, YANG S, et al. Online calibration and compensation of total odometer error in an integrated system[J]. Measurement, 2018, 123: 69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.044 [17] KLIMKOVICH B V. Self-calibration of a digital odometer integrated with a three-component SINS for a land vehicle[C]//2017 24th Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems (ICINS) Saint Petersburg: IEEE, 2017: 1-4. [18] 付强文. 车载定位定向系统关键技术研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: