Review of Dynamic Behaviors and Constitutive Model of Soil Under Long-Term Cyclic Loading
-
摘要:
随着交通基础设施的快速发展,长期循环荷载下土体的动力性能与相应的本构模型体系愈发受到关注,其能为该类荷载下地基或者岩土构筑物的动力稳定性和服役性能评估提供理论基础与技术支撑. 最近20年来,国内外相关学者已开展了大量的室内试验探索长期循环荷载下土的动力特性与影响因素,建立相应的理论模型描述土体的长期循环变形特征,并努力将其应用于工程实践. 目前,对长期循环荷载下土体动力学性能与主要影响因素的研究基本明确,但在如何减少本构模型参数,增强本构模型在变幅值、变频率等复杂实际工况时的适用性等研究尚需进一步加强. 本文通过对该方向研究发展的总结,明确了未来的发展方向,并提出了当前研究局限的可能解决思路,有利于进一步推进相关研究成果应用于工程实践的进程.
Abstract:With the rapid development of transport infrastructure, the dynamic properties of soil under long-term cyclic loading and the corresponding constitutive model system are receiving increased attention, which can provide a theoretical basis and technical support for the assessment of the dynamic stability and service performance of foundations or geotechnical structures under such loading. In the past 20 years, Chinese and foreign scholars have carried out a large number of indoor experiments to explore the dynamic behaviors and influencing factors of soil under long-term cyclic loading, established corresponding theoretical models to describe the characteristics of long-term cyclic deformation of soil, and applied them to engineering practice. At present, the research on dynamic performance and the main influencing factors of soil under long-term cyclic loading is sufficient. However, how to reduce the parameters of these constitutive models and enhance their applicability in complex working conditions with variable amplitudes and frequencies needs to be further studied. Through the summary of research development, this paper clarified the development direction of this topic and proposed some possible solutions to the current research limitations, which was beneficial for applying research findings in engineering practice.
-
Key words:
- long-term cyclic loading /
- loading modes /
- accumulative strain /
- dynamic modulus /
- constitutive model
-
表 1 影响因素分类与表征指标
Table 1. Classification and characterization of influence factors
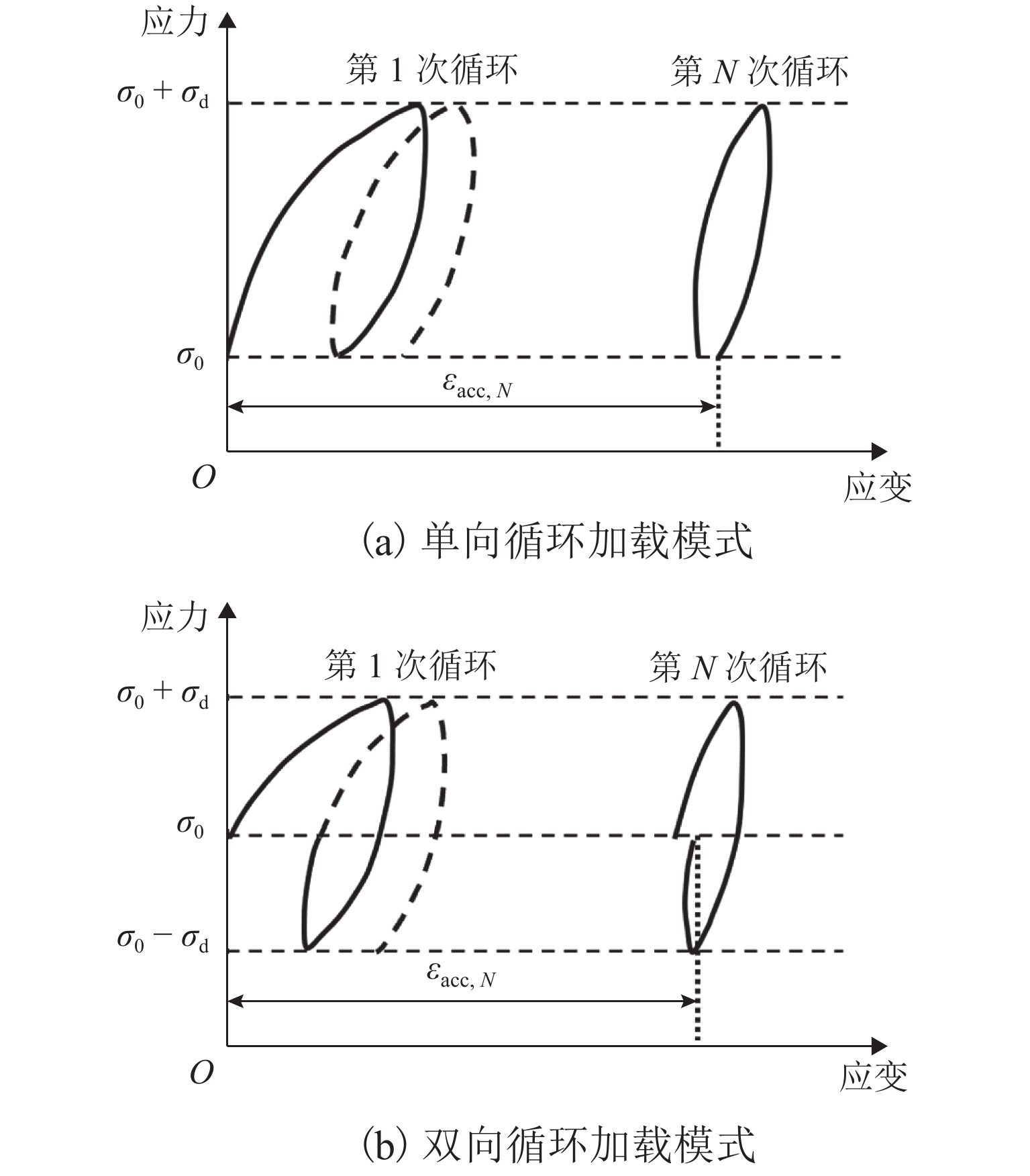
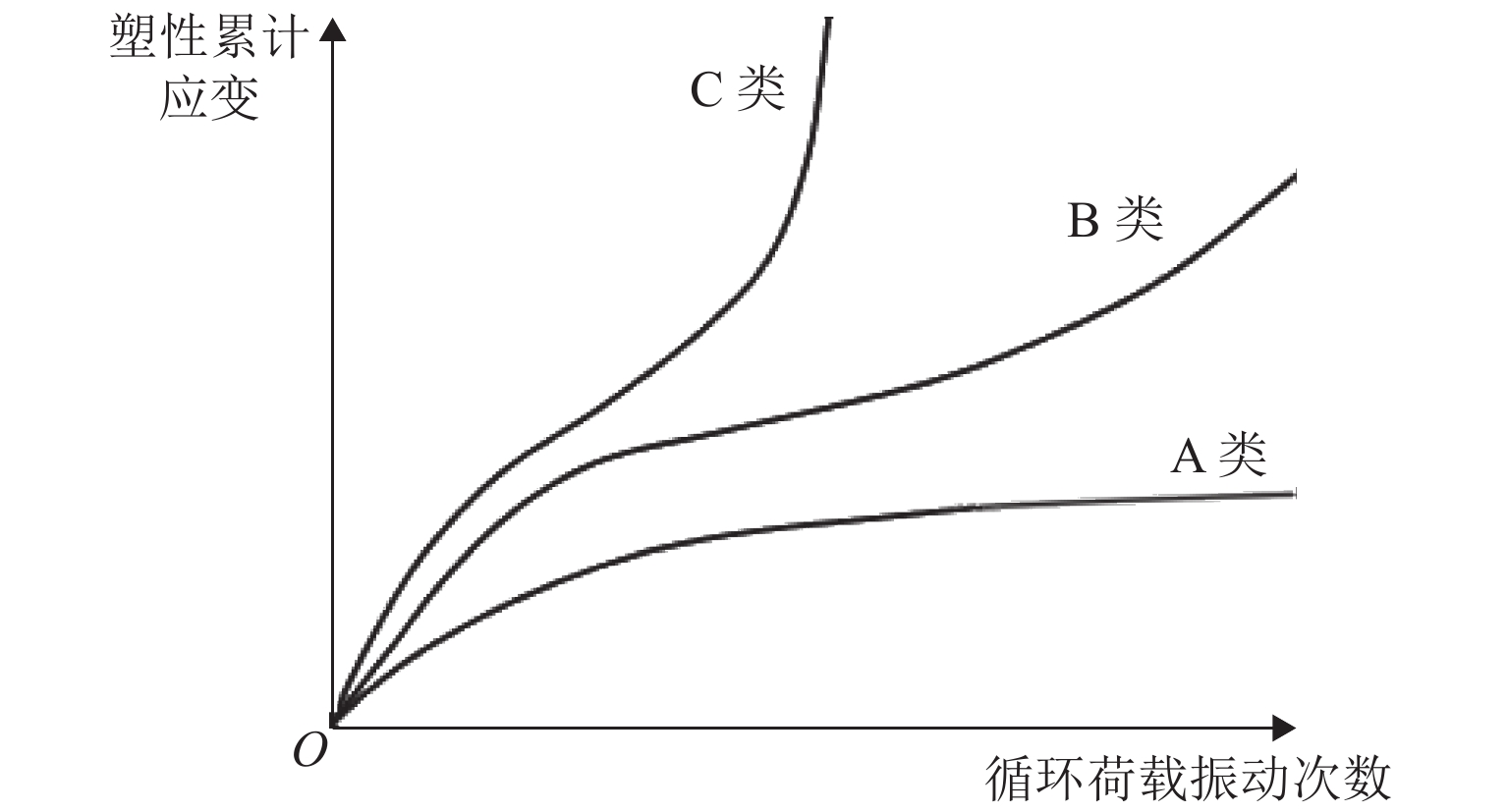
类别 考察指标 初始应力状态 主应力空间 围压${\sigma _3}$、轴向应力${\sigma _1}$、固结应力比$k = {{{\sigma _1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\sigma _1}} {{\sigma _3}}}} \right. } {{\sigma _3}}}$ $p {\text{-}} q$空间 初始平均主应力${p_0}$、初始剪应力${q_0}$、初始应力比${\eta _0} = {{{q_0}} / {{p_0}}}$ 循环应力特征 加载频率、循环应力波形、循环应力幅值、循环应力的偏振、主应力轴旋转等 土的物理特征 土的类型与级配特征,土的颗粒骨架的组构形式,初始孔隙比(相对密实度、压实度),含水量(饱和度),温度(冻结与否) -
[1] 谢定义. 土动力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011. [2] FUJIKAWA K, MIURA N, BEPPU I. Field investigation on the settlement of low embankment due to traffic load and its prediction[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1996, 36(4): 147-153. doi: 10.3208/sandf.36.4_147 [3] SAMANG L, MIURA N, SAKAI A. Long-term measurements of traffic load induced settlement of pavement surface in saga airport highway, Japan[J]. Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 2010, 12(4): 275-285. doi: 10.5614/jts.2005.12.4.5 [4] WICHTMANN T. Explicit accumulation model for non-cohesive soils under cyclic loading[D]. [S.l.]: Thesis, Ruhr-University Bochum, 2005. [5] 凌建明,王伟,邬洪波. 行车荷载作用下湿软路基残余变形的研究[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2002,30(11): 1315-1320. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2002.11.007LING Jianming, WANG Wei, WU Hongbo. On residual deformation of saturated clay subgrade under vehicle load[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2002, 30(11): 1315-1320. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2002.11.007 [6] 曹国安,邸旺亮,蒋永莉,等. 牙林线多年冻土地区路基下沉机理及整治研究[J]. 路基工程,1996(5): 40-42. [7] 朱占元. 青藏铁路列车行驶多年冻土场地路基振动反应与振陷预测[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009. [8] 牛富俊,林战举,鲁嘉濠,等. 青藏铁路路桥过渡段沉降变形影响因素分析[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(增2): 372-377.NIU Fujun, LIN Zhanju, LU Jiahao, et al. Study of the influencing factors of roadbed settlement in embankment-bridge transition section along Qinghai—Tibet Railway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(S2): 372-377. [9] 陈亮,沈军辉,沈中超,等. 川汶公路K95+300~K95+490段堰塞湖相沉积地层路基变形机制研究[J]. 中外公路,2017,37(5): 22-25.CHEN Liang, SHEN Junhui, SHEN Zhongchao, et al. The control of subgrade settlement in the sedimentary stratigraphy of barrier lake from K95+300 to K95+490 of Chuanwen highway[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2017, 37(5): 22-25. [10] 金辰. 基于路面开裂状况的薄沥青路面半刚性基层模量评估[J]. 公路工程,2022,47(2): 97-102.JIN Chen. Modulus evaluation of semi-rigid base of thin asphalt pavement based on pavement cracking[J]. Highway Engineering, 2022, 47(2): 97-102. [11] 李振存. 在役高速公路路基性能评价及快速检测技术[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2014. [12] CHEN W B, FENG W Q, YIN J H, et al. Characterization of permanent axial strain of granular materials subjected to cyclic loading based on shakedown theory[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 198(20): 751-761. [13] GU F, ZHANG Y Q, LUO X, et al. Characterization and prediction of permanent deformation properties of unbound granular materials for pavement ME Design[J]. Construction and Building Materials., 2017, 155: 584-592. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.116 [14] 王康宇,庄妍,耿雪玉. 铁路路基粗粒土填料临界动应力试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(6): 1865-1873.WANG Kangyu, ZHUANG Yan, GENG Xueyu. Experimental study on critical dynamic stress of coarse-grained soil in railway subgrade[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(6): 1865-1873. [15] SILVER M L, SEED H B. Deformation characteristics of sands under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1971, 97(8): 1081-1098. doi: 10.1061/JSFEAQ.0001648 [16] TARHOUNI M A A, HAWLADER B. Monotonic and cyclic behaviour of sand in direct simple shear test conditions considering low stresses[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2021, 150(11): 106931.1-106931.13. [17] 高广运,聂春晓,顾晓强. 砂土震陷室内试验研究综述[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2016,36(6): 1-7.GAO Guangyun, NIE Chunxiao, GU Xiaoqiang. A review of recent research in laboratory test of seismic compression of sands[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2016, 36(6): 1-7. [18] 鲁丽雪. Bouc-Wen土体动力本构模型及其阈值应变研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2013. [19] SORALUMP S, PRASOMSRI J. Cyclic pore water pressure generation and stiffness degradation in compacted clays[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2016, 142(1): 1-13. [20] XU L, WONG K K, FABBRI A, et al. Loading-unloading shear behavior of rammed earth upon varying clay content and relative humidity conditions[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2018, 58(4): 1001-1015. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2018.05.005 [21] 刘启旺,杨正权,刘小生,等. 超深厚覆盖层中深埋细粒土地震残余变形特性振动三轴试验研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2015,37(1): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2015.01.0021LIU Qiwang, YANG Zhengquan, LIU Xiaosheng, et al. Dynamic triaxial tests on seismic residual deformation characteristics of the fine-grained soil in super-deep overburden layer[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2015, 37(1): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2015.01.0021 [22] 李扬波,张家生,朱志辉,等. 循环荷载作用下铁路路基级配碎石填料累积变形研究[J]. 工程科学与技术,2018,50(5): 130-137.LI Yangbo, ZHANG Jiasheng, ZHU Zhihui, et al. Accumulated deformation of gravel filler of subgrade under cyclic loading[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2018, 50(5): 130-137. [23] 陈方敏,丁智,李绍朗,等. 地铁荷载作用下水泥土应变监测模型试验研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2018,55(2): 127-133. doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2018.02.018CHEN Fangmin, DING Zhi, LI Shaolang, et al. Model test of strain development in cement soil under subway loading[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2018, 55(2): 127-133. doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2018.02.018 [24] 陈靖宇. 公路路基填料长期动力特性试验研究与累积应变模型[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [25] HELM J, LAUE J, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. Untersuchungen an der RUB zur verformungsentwicklung von Böden unter zyklischen belastungen beiträge zum workshop: boden unter fast zyklischer belastung: erfahrungen und forschungsergebnisse[R]. Bochum: Institute of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Ruhr-University, 2000. [26] GOTSCHOL A. Veränderlich elastisches und plastisches verhalten nichtbindiger böden und schotter unter zyklisch-dynamischer beanspruchung[D]. Kassel: University Kassel, 2000. [27] LEI H Y, SONG Y J, QI Z Y, et al. Accumulative plastic strain behaviors and microscopic structural characters of artificially freeze-thaw soft clay under dynamic cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2019, 168: 102895. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102895 [28] MEI H H, SATVATI S, LENG W M. Experimental study on permanent deformation characteristics of coarse-grained soil under repeated dynamic loading[J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2021, 29(1): 94-107. doi: 10.1007/s40534-021-00233-2 [29] 庄心善,赵汉文,陶高梁,等. 循环荷载下弱膨胀土累积变形与动强度特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(10): 3192-3200. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.2180ZHUANG Xinshan, ZHAO Hanwen, TAO Gaoliang, et al. Accumulated deformation and dynamic strength properties of weak expansive soil under cyclic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 3192-3200. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2019.2180 [30] SAWICKI A, MIERCZYŃSKI J, ŚWIDZIŃSKI W. Strains in sand due to cyclic loading in triaxial conditions[J]. Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics, 2009, 56(1/2): 85-98. [31] WANG J H, LING X Z, LI Q L, et al. Accumulated permanent strain and critical dynamic stress of frozen silty clay under cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 153: 130-143. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.05.007 [32] WICHTMANN T, NIEMUNIS A, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. Strain accumulation in sand due to cyclic loading: drained triaxial tests[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2005, 25(12): 967-979. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2005.02.022 [33] YANG J Q, CUI Z D. Influences of train speed on permanent deformation of saturated soft soil under partial drainage conditions[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2020, 133: 106120.1-106120.12. [34] OZEL M R, MOHAJERANI A. Permanent deformation behaviour of two Victorian subgrade soils under repeated loading[J]. Journal and News of the Australian Geomechanics Society, 2002, 37(3): 41-50. [35] HUANG J, CHEN J, LU Y, et al. Deformation behaviors and dynamic backbone curve model of saturated soft clay under bidirectional cyclic loading[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 20(4): 1-12. [36] BENOOT J, HAEGEMAN W, FRANÇOIS S, et al. Experimental study of strain accumulation of silica sand in a cyclic triaxial test[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd European Young Geotechnical Engineers Conference. Barcelona: [s.n.], 2014: 3-6. [37] CHEN C, XUA G F, ZHOU Z M, et al. Undrained dynamic behaviour of peaty organic soil under long-term cyclic loading, part Ⅱ: constitutive model and simulation[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2020, 129: 1-10. [38] XIONG Y L, LIU G B, ZHENG R Y, et al. Study on dynamic undrained mechanical behavior of saturated soft clay considering temperature effect[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2018, 115: 673-684. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.09.026 [39] 聂如松,李亚峰,冷伍明,等. 列车间歇荷载作用下路基细粒土填料的塑性变形行为及临界动应力研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(4): 828-841. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0778NIE Rusong, LI Yafeng, LENG Wuming, et al. Plastic deformation and critical dynamic stress of fine-grained soils under intermittent loading of trains[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(4): 828-841. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0778 [40] 丁智,郑勇,魏新江,等. 不同加载频率及循环应力水平对人工冻融软土动力特性影响试验研究[J]. 铁道学报,2020,42(3): 122-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.03.015DING Zhi, ZHENG Yong, WEI Xinjiang, et al. Experimental study on the effect of different loading frequency and cyclic stress level for dynamic behaviour of artificial frozen-thawed soft soil[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(3): 122-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.03.015 [41] ZHANG X, ZHAO C F, ZHAI W M. Importance of load frequency in applying cyclic loads to investigate ballast deformation under high-speed train loads[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2019, 120: 28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.01.023 [42] 贾鹏飞,孔令伟. 高周循环荷载作用过程中土体塑性包络的弹塑性累积模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(12): 2542-2549. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.1422JIA Pengfei, KONG Lingwei. Elastoplastic accumulation model for predicting soil plastic envelope due to high-cyclic loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(12): 2542-2549. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.1422 [43] WICHTMANN T, NIEMUNIS A, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. Flow rule in a high-cycle accumulation model backed by cyclic test data of 22 sands[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2014, 9: 695-709. doi: 10.1007/s11440-014-0302-7 [44] WICHTMANN T, NIEMUNIS A, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. Experimental evidence of a unique flow rule of non-cohesive soils under high-cyclic loading[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2006, 1(1): 59-73. doi: 10.1007/s11440-006-0006-8 [45] WICHTMANN T. Soil behavior under low- and high-cycle loading—Element tests vs. constitutive models[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 2021, 27: 1-18. [46] PANG Y X, GU C, WANG J, et al. Strain evolution of saturated clays under cyclic loadings in three-dimensional stress condition[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 278: 1-16. [47] FAKHARIAN K, AHMAD A. Effect of anisotropic consolidation and rubber content on dynamic parameters of granulated rubber-sand mixtures[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2021, 141: 1-14. [48] ZHOU W, CHEN Y, MA G, et al. A modified dynamic shear modulus model for rockfill materials under a wide range of shear strain amplitudes[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2017, 92: 229-238. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.10.027 [49] GU C, WANG J, CAI Y Q, et al. Influence of cyclic loading history on small strain shear modulus of saturated clays[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2014, 66: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2014.06.027 [50] HU X Q, ZHANG Y, GUO L, et al. Cyclic behavior of saturated soft clay under stress path with bidirectional shear stresses[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2018, 104: 319-328. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.10.016 [51] CHEN G X, ZHOU Z L, PAN H, et al. The influence of undrained cyclic loading patterns and consolidation states on the deformation features of saturated fine sand over a wide strain range[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 204: 77-93. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.02.008 [52] 梁珂,何杨,陈国兴. 南沙珊瑚砂的动剪切模量和阻尼比特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(1): 23-31,38.LIANG Ke, HE Yang, CHEN Guoxing. Experimental study of dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio characteristics of coral sand from Nansha Islands[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 23-31,38. [53] 陈国兴,杨文保,岳文泽,等. 金塘海峡海洋土动剪切模量与阻尼比特性研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2020,40(1): 1-8. doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2020.01.001CHEN Guoxing, YANG Wenbao, YUE Wenze, et al. Experimental studies on the dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio characteristics of marine soils in the Jintang strait[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2020, 40(1): 1-8. doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2020.01.001 [54] 刘方成,尚守平,王海东. 循环荷载下黏土应变积累积强化模型研究[J]. 岩土力学,2008(9): 2457-2462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.09.027LIU Fangcheng, SHANG Shouping, WANG Haidong. Study of strain accumulation strengthened model for clay under cyclic loadings[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008(9): 2457-2462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.09.027 [55] 黄博,施明雄,陈云敏,等. 循环振动对饱和粉土初始动剪模量的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(5): 764-771. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.05.020HUANG Bo, SHI Mingxiong, CHEN Yunmin, et al. Effects of seismic vibration on small strain shear modulus of saturated silt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(5): 764-771. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.05.020 [56] LBIBB S, MANZARI M T. Stress-strain behavior of Ottawa sand in cyclic direct simple shear and modeling of cyclic strength using artificial neural networks[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2022, 164: 1-17. [57] STAMATOPOULOS K, PETRIDIS P, ALLKJA P S, et al. Improvement of dynamic soil properties induced by preloading verified by a field test and embankment failure[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 163: 101-112. [58] 尚守平,刘方成,杜运兴,等. 应变累积对黏土动剪模量和阻尼比影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(5): 683-688. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.05.001SHANG Shouping, LIU Fangcheng, DU Yunxing, et al. Experimental study on effect of shear strain accumulation on dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of clay soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(5): 683-688. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.05.001 [59] 张炜,李亚,周松望,等. 南海北部区域黏土循环动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(7): 2413-2423. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2242ZHANG Wei, LI Ya, ZHOU Songwang, et al. Experimental research on cyclic behaviors of clay in the northern region of South China Sea[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(7): 2413-2423. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.2242 [60] YE Y, CAI D, YAO J, et al. Review on dynamic modulus of coarse-grained soil filling for high-speed railway subgrade[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 27(6): 1-6. [61] SOLTANI-JIGHEH H, SOROUSH A. Cyclic behavior of mixed clayey soils[J]. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 2010, 8(2): 99-106. [62] ZHOU Y G, CHEN Y M. Influence of seismic cyclic loading history on small strain shear modulus of saturated sands[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2005, 25(5): 341-353. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2005.03.001 [63] LIN B, ZHANG F, FENG D C, et al. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of thawed saturated clay under long-term cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 145: 93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.10.003 [64] VUCETIC M. Cyclic threshold shear strains in soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 120(12): 2208-2228. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:12(2208) [65] 柏立懂. 荷载历史对砂土最大剪切模量影响的共振柱试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(11): 2366-2374.BAI Lidong. Effects of loading history on maximum shear modulus of sand by resonant column tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(11): 2366-2374. [66] WICHTMANN T, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. Influence of a cyclic and dynamic loading history on dynamic properties of dry sand, part Ⅰ: cyclic and dynamic torsional prestraining[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2004, 24(2): 127-147. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2003.10.004 [67] WICHTMANN T, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. Influence of a cyclic and dynamic loading history on dynamic properties of dry sand, part Ⅱ: cyclic axial preloading[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2004, 24(11): 789-803. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.05.002 [68] KARG C, HAEGEMAN W. Elasto-plastic long-term behavior of granular soils: experimental investigation[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2009, 29(1): 155-172. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2008.01.001 [69] 黄茂松,李帅. 长期往复荷载作用下近海饱和软黏土强度和刚度的弱化特性[J]. 岩土工程学报,2010,32(10): 1491-1498.HUANG Maosong, LI Shuai. Degradation of stiffness and strength of offshore saturated soft clay under long-term cyclic loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2010, 32(10): 1491-1498. [70] LING X Z, LI Q L, WANG L N, et al. Stiffness and damping radio evolution of frozen clays under long-term low-level repeated cyclic loading: experimental evidence and evolution model[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2013, 86: 45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2012.11.002 [71] NIE R S, SUN B L, LENG W M, et al. Resilient modulus of coarse-grained subgrade soil for heavy-haul railway: an experimental study[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2021, 150(4): 1-10. [72] MUHAMMAD N, SIDDIQUA S. Moisture-dependent resilient modulus of chemically treated subgrade soil[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 285: 1-13. [73] LIU X L, ZHANG X M, WANG H, et al. Laboratory testing and analysis of dynamic and static resilient modulus of subgrade soil under various influencing factors[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 195: 178-186. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.061 [74] SU Y, CUI Y J, DUPLA J C, et al. Effect of water content on resilient modulus and damping ratio of fine/coarse soil mixtures with varying coarse grain contents[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 26: 1-11. [75] BOZBEY I, KUBILAY KELESOGLU M, DEMIR D, et al. Effects of soil pulverization level on resilient modulus and freeze and thaw resistance of a lime stabilized clay[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 151: 323-334. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.03.023 [76] HAN Z, VANAPALLI S K. Relationship between resilient modulus and suction for compacted subgrade soils[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 211: 85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.06.020 [77] REN J P, VANAPALLI S K. Empirical model for predicting the resilient modulus of frozen unbound road materials using a hyperbolic function[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2018, 17: 66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2018.09.011 [78] FAN C, ZHANG W, LAI Y, et al. Mechanical behaviors of frozen clay under dynamic cyclic loadings with freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2021, 181: 1-10. [79] LACKENBY J, INDRARATNA B, MCDOWELL G, et al. Effect of confining pressure on ballast degradation and deformation under cyclic triaxial loading[J]. Geotechnique, 2007, 57: 527-536. doi: 10.1680/geot.2007.57.6.527 [80] ATTIA M, ABDELRAHMAN M. Sensitivity of untreated reclaimed asphalt pavement to moisture, density, and freeze thaw[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2010, 22(12): 1260-1269. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000135 [81] CORONADO O, CAICEDO B, TAIBI S, et al. Effect of water content on the resilient behavior of non standard unbound granular materials[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2016, 7: 29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2016.04.004 [82] NG C W W, ZHOU C, YUAN Q, et al. Resilient modulus of unsaturated subgrade soil: experimental and theoretical investigations[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2013, 50: 223-232. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2012-0052 [83] ALNEDAWI A, ULLAH S, AZAM A, et al. Integrated and holistic knowledge map of resilient modulus studies for pavement materials: a scientometric analysis and bibliometric review of research frontiers and prospects[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2021, 33: 1-22. [84] 郭林,蔡袁强,王军,等. 长期循环荷载作用下温州结构性软黏土的应变特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(12): 2249-2254.GUO Lin, CAI Yuanqiang, WANG Jun, et al. Long-term cyclic strain behavior of Wenzhou structural soft clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(12): 2249-2254. [85] SUIKER A S J, SELIG E T, FRENKEL R. Static and cyclic triaxial testing of ballast and subballast[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2005, 131(6): 771-782. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:6(771) [86] ZHOU C. Cyclic behaviour of an unsaturated silt at various suctions and temperatures[J]. Geotechnique, 2014, 64: 709-720. doi: 10.1680/geot.14.P.015 [87] SINGHA A, AL FARUQUE M A, BALACHANDAR R. Vortices and large-scale structures in a rough open-channel flow subjected to bed suction and injection[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 138(5): 491-501. [88] YANG C, CUI Y J, PEREIRA J M, et al. A constitutive model for unsaturated cemented soils under cyclic loading[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2008, 35(6): 853-859. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2008.08.005 [89] GAO Z, ZHAO J. Constitutive modeling of artificially cemented sand by considering fabric anisotropy[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2012, 41: 57-69. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2011.10.007 [90] GAO Z, ZHAO J, LI X S, et al. A critical state sand plasticity model accounting for fabric evolution[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 2014, 38(4): 370-390. [91] SINGH A K, SAHOO J P. Rutting prediction models for flexible pavement structures: a review of historical and recent developments[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2021, 8(3): 315-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2021.04.003 [92] 龙尧,张家生,丁建源,等. 粗粒土路基循环荷载试验及累积变形模型研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2017,36(16): 128-133. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.16.020LONG Yao, ZHANG Jiasheng, DING Jianyuan, et al. The cyclic load experiments and an accumulated deformation model for coarse-grained soil filling[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(16): 128-133. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.16.020 [93] GUO L, WANG J, CAI Y Q, et al. Undrained deformation behavior of saturated soft clay under long-term cyclic loading[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 50(7): 28-37. [94] FRANÇOIS S, KARG C, HAEGEMAN W, et al. A numerical model for foundation settlements due to deformation accumulation in granular soils under repeated small amplitude dynamic loading[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2010, 34(3): 273-296. [95] LI D, SELIG E T. Cumulative plastic deformation for fine-grained subgrade soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1996, 122(12): 1006-1013. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1996)122:12(1006) [96] ULLDITZ P. Mathematical model for pavement performance under moving wheel load[C]//Transportation Research Record. 1384, Transportation Research Board. Washington, D. C.: [s.n.], 1993: 94-99. [97] PUPPALA A J, SARIDE S, CHOMTID S. Experimental and modeling studies of permanent strains of subgrade soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(10): 1379-1389. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000163 [98] CHAI J C, MIURA N. Traffic-load-induced permanent deformation of road on soft subsoil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(11): 907-916. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:11(907) [99] 黄茂松,姚兆明. 循环荷载下饱和软黏土的累积变形显式模型[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(3): 325-331.HUANG Maosong, YAO Zhaoming. Explicit model for cumulative strain of saturated clay subjected to cyclic loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(3): 325-331. [100] GIDEL G. A new approach for investigating the permanent deformation behaviour of unbound granular material using the repeated load triaxial apparatus[J]. Bulletin des Laboratoires des Ponts et Chaussees, 2001, 233: 5-21. [101] NIEMUNIS A, WICHTMANN T, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS T. A high-cycle accumulation model for sand[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2005, 32(4): 245-263. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2005.03.002 [102] LI Q L, LING X Z, SHENG D C. Elasto-plastic behaviour of frozen soil subjected to long-term low-level repeated loading, part Ⅱ: constitutive modelling[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2016, 122: 58-70. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.11.009 [103] PASTEN C, SHIN H, CARLOS SANTAMARINA J. Long-term foundation response to repetitive loading[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 140(4): 1-11. [104] QIAN J, LI S, GU X, et al. A unified model for estimating the permanent deformation of sand under a large number of cyclic loads[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 181: 293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.03.051 [105] WU Z X, YIN Z Y, DANO C, et al. Cyclic volumetric strain accumulation for sand under drained simple shear condition[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2020, 101: 1-10. [106] SUN Q D, INDRARATNA B, NIMBALKAR S. Deformation and degradation mechanisms of railway ballast under high frequency cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2015, 142(1): 04015056.1-04015056.12. [107] MIAO Y, ZHANG H, HE H J, et al. In-situ properties of Poisson’s ratio based on KiK-net seismic observations[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 296: 1-14. [108] LIU Z, HE Z H, ZHANG W Z, et al. Laboratory test and prediction model of dynamic resilient modulus of carbonaceous mudstone coarse-grained soil[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 18: 1-15. [109] XIA P X, SHAO L T, DENG W. Stress-state dependency of the strain ratio of quasi-elastic granular soils under cyclic loading[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 2022, 34(3): 1-14. [110] 汤大明,曾纪全,胡应德,等. 关于泊松比的试验和取值讨论[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2001(增1): 1772-1775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2001.z1.035TANG Daming, ZENG Jiquan, HU Yingde, et al. Discussion on testing and interpretation for poisson’s ratio[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2001(S1): 1772-1775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2001.z1.035 [111] GAO H M, BU C Y, WANG Z H, et al. Dynamic characteristics of expanded polystyrene composite soil under traffic loadings considering initial consolidation state[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2017, 102: 86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.08.012 -




 下载:
下载: