Influence of Speed on Levitation Force of Medium−Low-Speed Maglev Train
-
摘要:
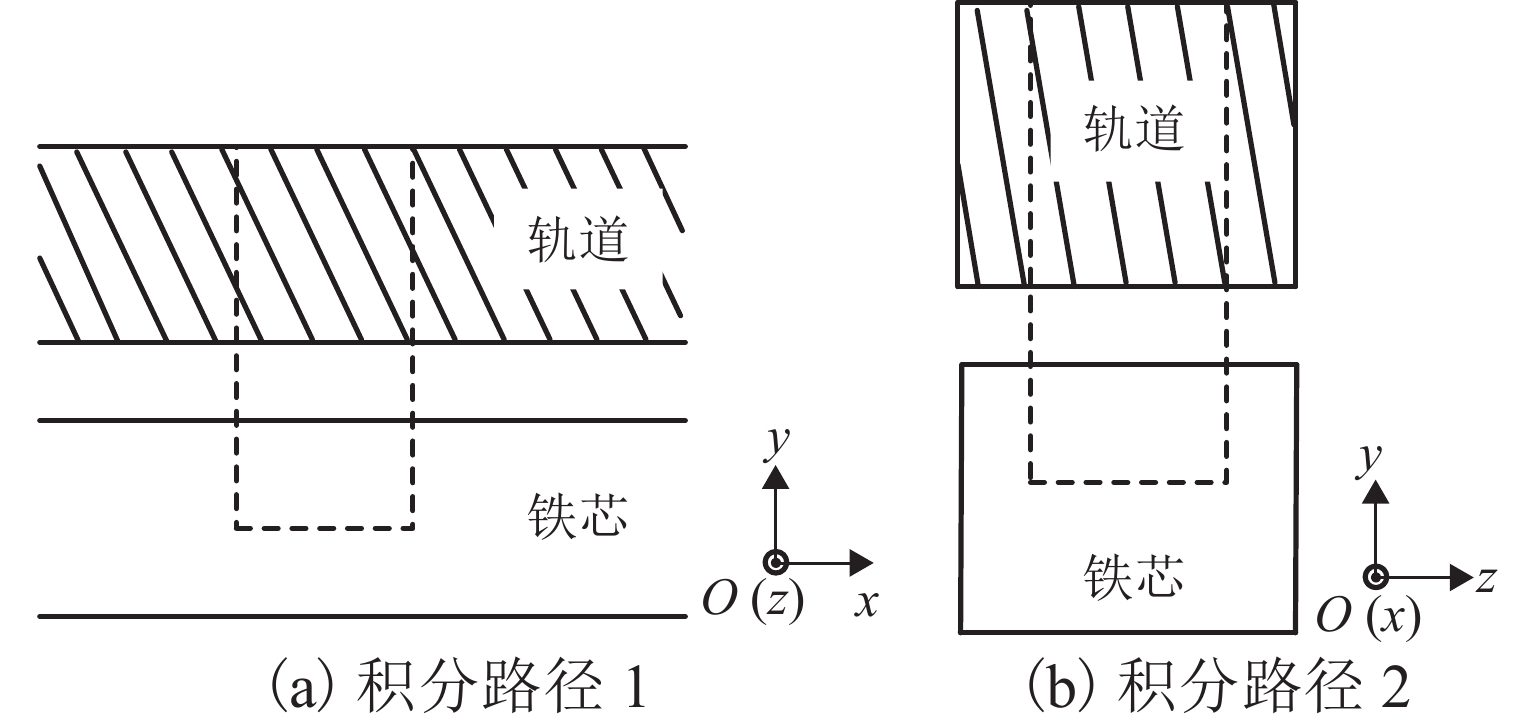
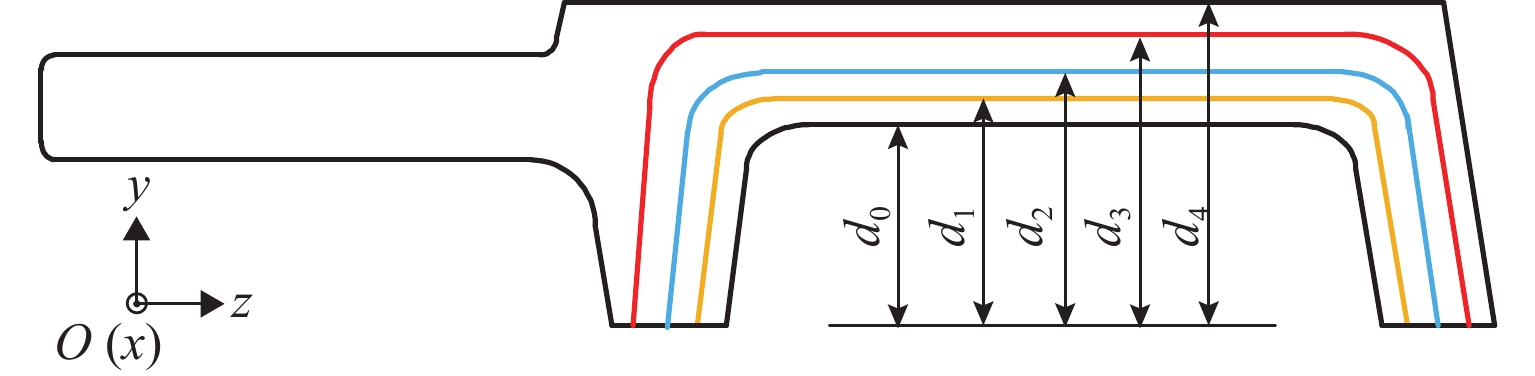
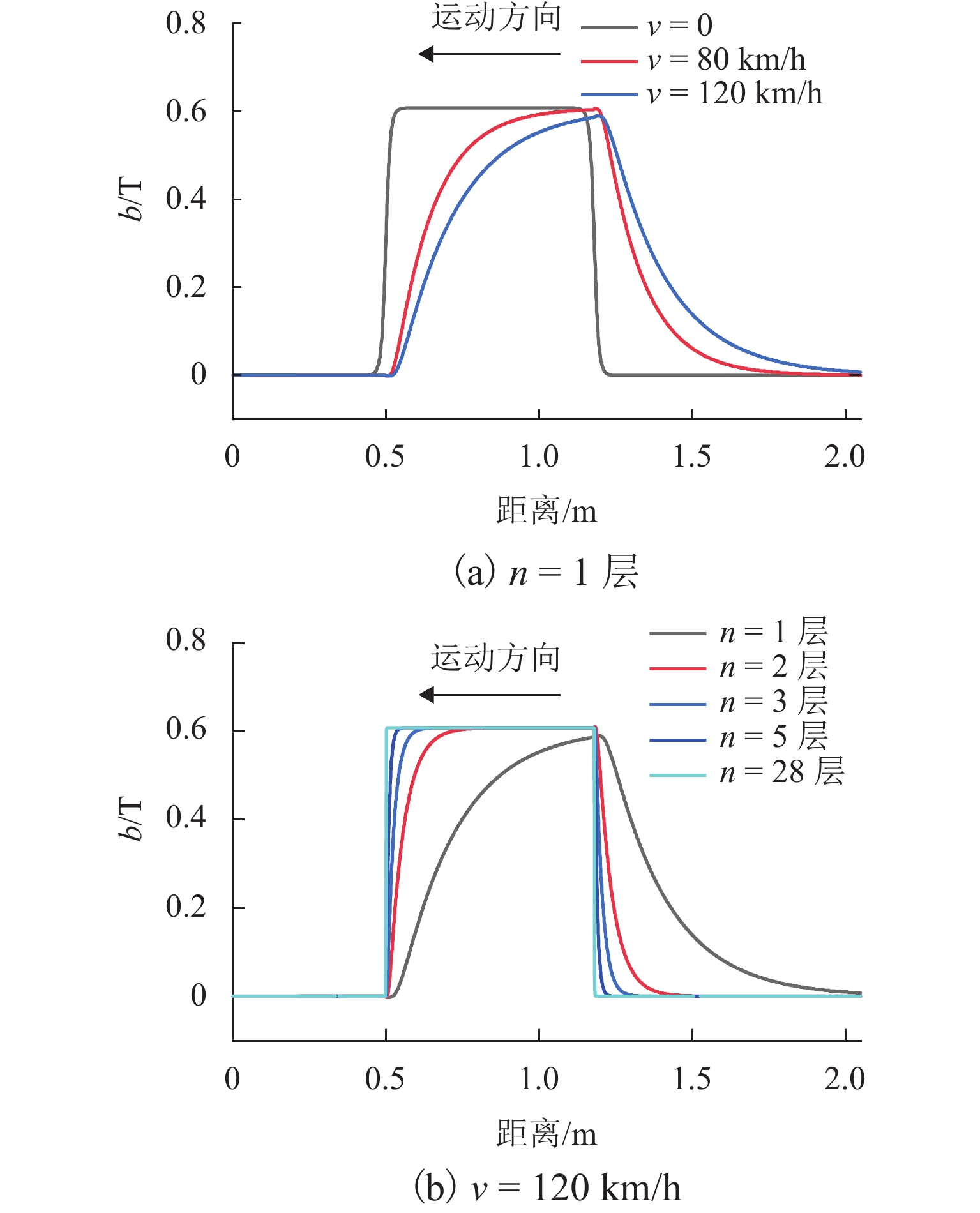
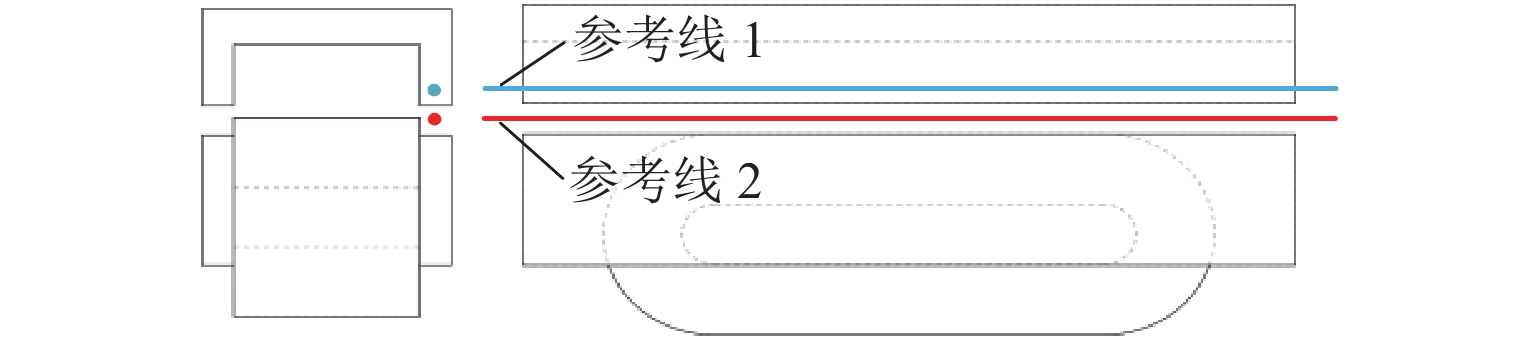
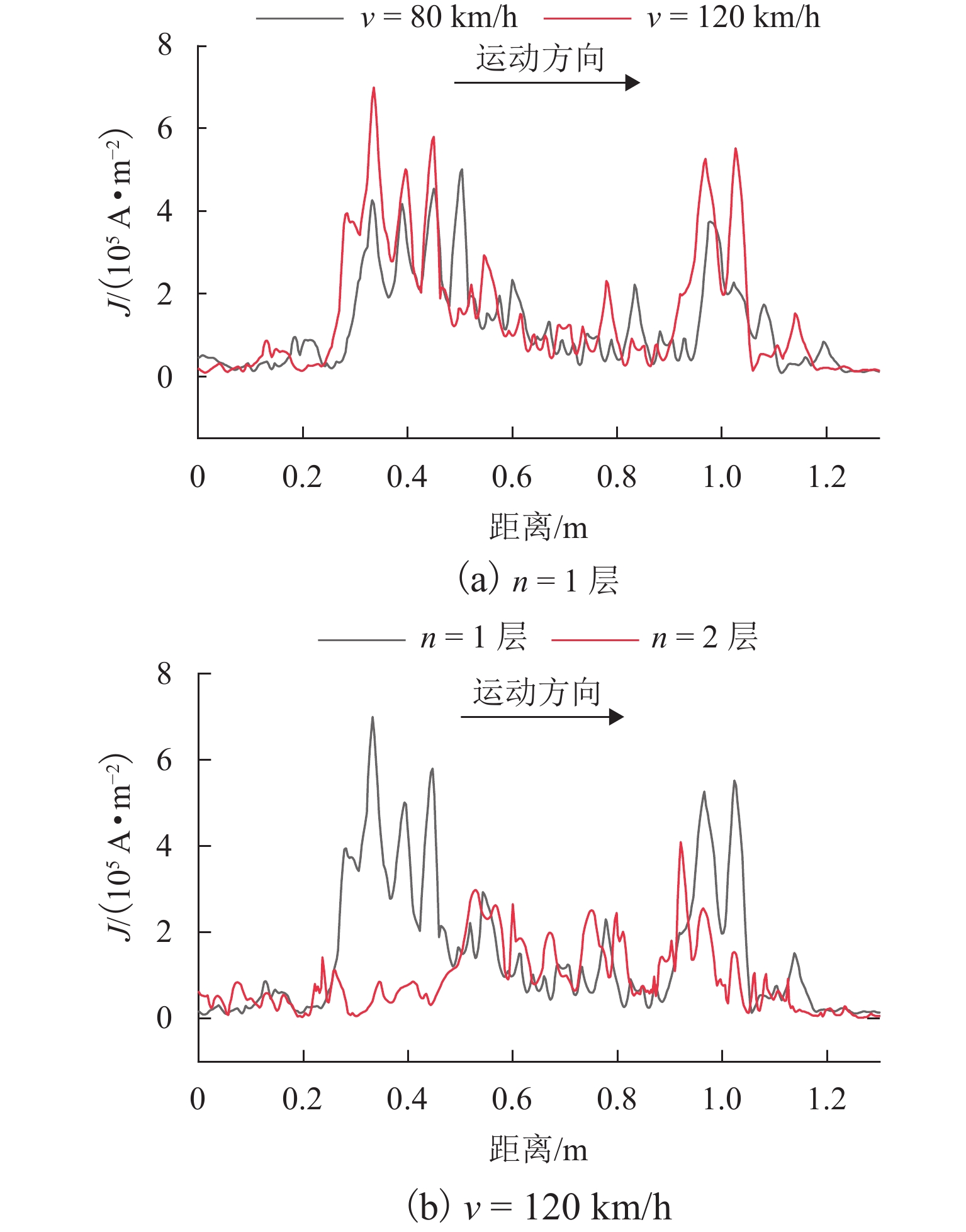
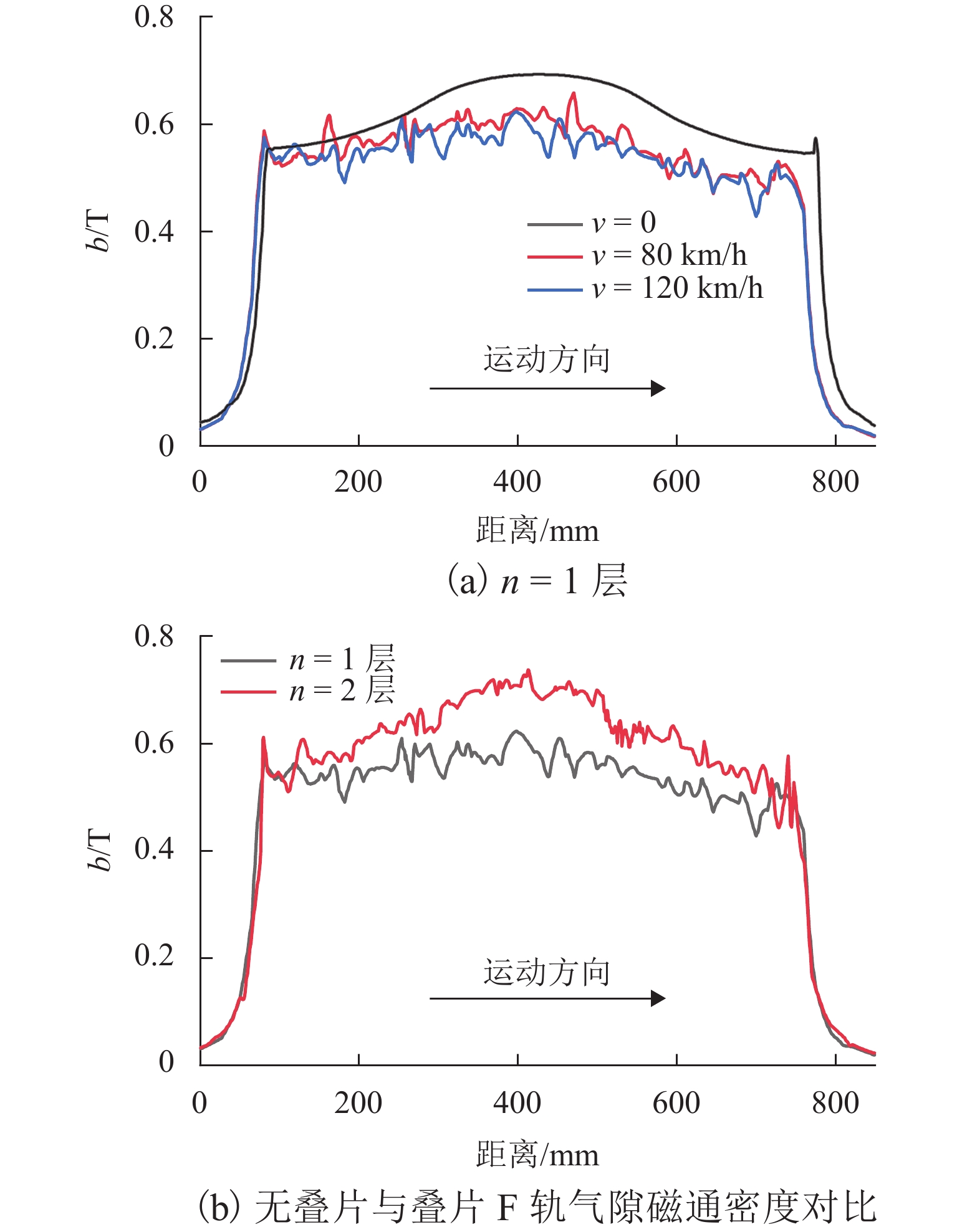
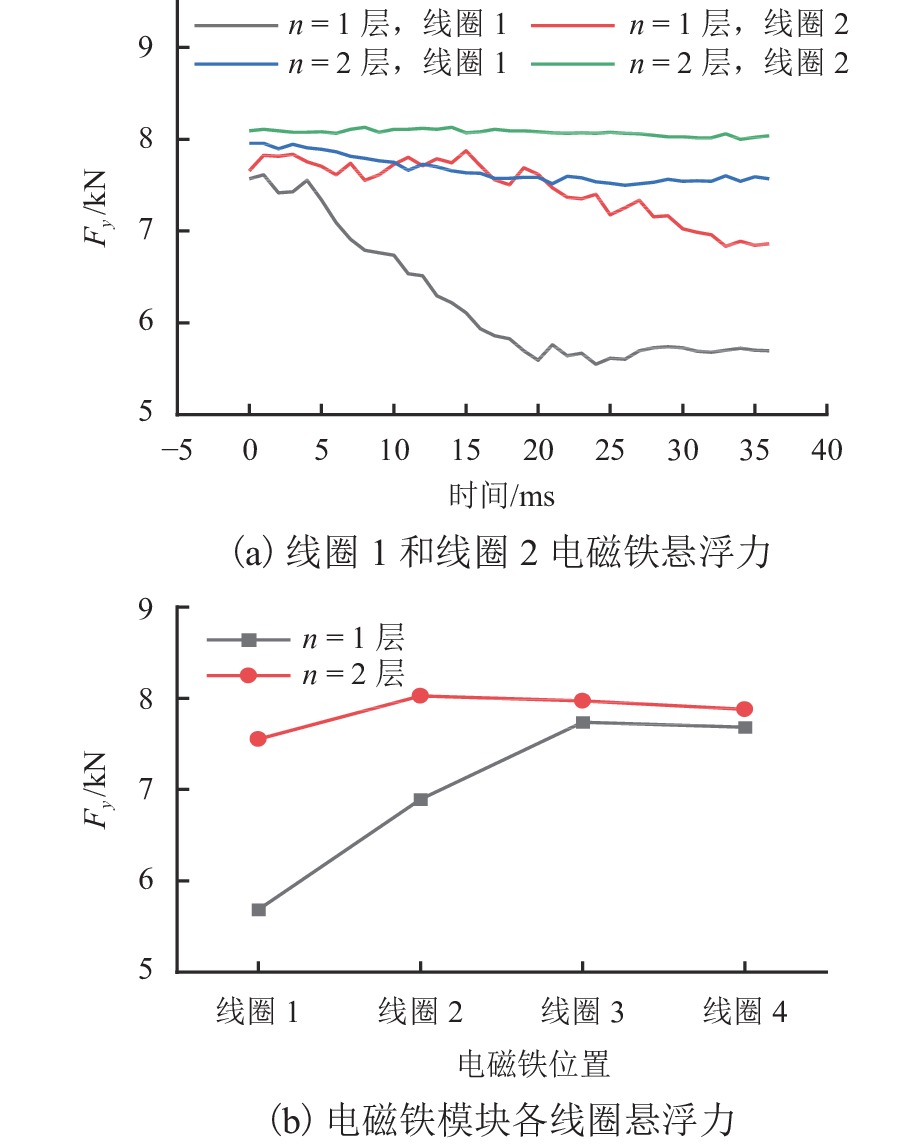
电磁铁为中低速磁浮列车提供悬浮力,其与轨道发生相对运动时,在轨道上产生涡流,同时,轨道涡流产生的外加磁场抵消了部分电磁铁产生的原磁场,进而使得电磁铁提供的悬浮力下降. 为此,首先分析轨道涡流的形成规律,以及列车不同速度时涡流对气隙磁场的影响,进一步研究了列车速度对悬浮力的影响;其次,采用叠片F轨的方法来抑制涡流效应,结合叠片F轨提升悬浮力的机理,分析F轨不同叠片层数结构下轨道涡流对悬浮力的影响;最后,以长沙磁浮快线电磁铁结构为例,使用有限元软件进行仿真分析. 结果表明:使用叠片F轨后可以降低轨道中的涡流,随着叠片数量的增加,气隙磁场逐渐逼近静态条件下的气隙磁场;悬浮电磁铁模块的端部线圈以120 km/h的速度运动时,得到轨道为无叠片F轨时悬浮力为5.7 kN,轨道为两层叠片F轨时悬浮力为7.5 kN,相比较无叠片F轨悬浮力增长30%.
Abstract:Electromagnet provides suspension force for medium−low-speed maglev train. When the electromagnet moves relatively to a rail, eddy current is generated on the rail. The external magnetic field generated by the track eddy current offsets part of the original magnetic field generated by the electromagnet, causing the decrease of the suspension force provided by the electromagnet. Firstly, the formation of rail eddy current and its effects on air gap magnetic field are analyzed at different vehicle speeds. The influence of train speeds on the suspension force is further studied. Secondly, the laminated F-rail is used to suppress eddy current effect. Combined with the mechanism of the laminated F-rail lifting suspension force, the influence of rail eddy current on the suspension force is analyzed with the F-rails of different laminated layers. Finally, the electromagnet structure of Changsha Maglev Fast Line is simulated by using finite element software. The results show that the laminated F-rail can reduce the rail eddy current, and the air gap magnetic field gradually approaches the one under static conditions. When the coil at the end of the electromagnet model moves at the speed of 120 km/h, the suspension force is 5.7 kN without the non-laminated F-rail and 7.5 kN with the laminated F-rail of two layers, increasing by 30% compared with the case of the non-laminated F-rail.
-
Key words:
- magnetic levitation vehicle /
- electromagnet /
- electromagnetic force /
- eddy current
-
表 1 电磁铁主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of electromagnet
参数 取值 极板、轨道厚度/mm 28 铁芯长度/mm 400 极板长度/mm 2 720 线圈匝数/匝 360 线圈电流/A 35 气隙/mm 10 -
[1] 钱清泉, 高仕斌. 中低速磁浮交通发展战略研究[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2019. [2] PRASAD N, JAIN S, GUPTA S. Electrical components of maglev systems: emerging trends[J]. Urban Rail Transit, 2019, 5(2): 67-79. doi: 10.1007/s40864-019-0104-1 [3] GOU J S. Development status and global competition trends analysis of maglev transportation technology based on patent data[J]. Urban Rail Transit, 2018, 4(3): 117-129. doi: 10.1007/s40864-018-0087-3 [4] DONG F L, HUANG Z, LI X F, et al. R&D of no-insulation HTS magnets using 2G wires in a prototype for maglev applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2019, 29(5): 1-5. [5] 曾国保. 中低速磁浮交通的适应性及工程化发展方向[J]. 铁道工程学报,2016,33(10): 111-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.10.023ZENG Guobao. The adaptability and the improvement in engineering of the lower-medium speed maglev transit system[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2016, 33(10): 111-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.10.023 [6] YAMAMURA S, ITO T. Analysis of speed characteristics of attracting magnet for magnetic levitation of vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1975, 11(5): 1504-1507. [7] LI G C, JIA Z, HE G, et al. Analysis of eddy current induced in track on medium-low speed maglev train[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2017, 69(1): 012184.1-012184.10. [8] 罗芳,张昆仑. 常导磁悬浮车悬浮电磁铁的电磁场分析[J]. 机车电传动,2002(1): 27-28,34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2001.01.008LUO Fang, ZHANG Kunlun. Electromagnetic field analysis on suspension magnet of EMS maglev vehicle[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotive, 2002(1): 27-28,34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-128X.2001.01.008 [9] 杨志华. 中低速磁浮列车悬浮系统仿真研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014. [10] BORCHERTS R, DAVIS L. Lift and drag forces for the attractive electromagnetic suspension systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1974, 10(3): 425-428. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.1974.1058452 [11] DU J, OHSAKI H. Numerical analysis of eddy current in the EMS-maglev system[C]//Sixth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems. Beijing: IEEE, 2003: 761-764. [12] 郑丽莉,李杰,李金辉. 钢轨涡流对磁浮列车悬浮电磁力影响的研究[J]. 计算机仿真,2011,28(8): 328-331,336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.08.080ZHENG Lili, LI Jie, LI Jinhui. Research on influence of eddy current induced in steel rails on levitation force of maglev[J]. Computer Simulation, 2011, 28(8): 328-331,336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.08.080 [13] ZHANG M, LUO S H, GAO C, et al. Research on the mechanism of a newly developed levitation frame with mid-set air spring[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(12): 1797-1816. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2018.1435892 [14] 梁潇,戴小冬,谭超,等. 既有长沙磁浮线路桥梁结构提速适用性研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(6): 1493-1498. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.2019.06.019LIANG Xiao, DAI Xiaodong, TAN Chao, et al. Study on the speed-increasing adaptation of the bridge structures in the existing maglev lines in Changsha[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(6): 1493-1498. doi: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.2019.06.019 [15] 詹佳雯. 中低速磁浮列车直线感应电机及悬浮电磁铁分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: