Calculation of Power Generation Characteristics of Linear Harmonic Generator for Electrodynamic Suspension Maglev Train
-
摘要:
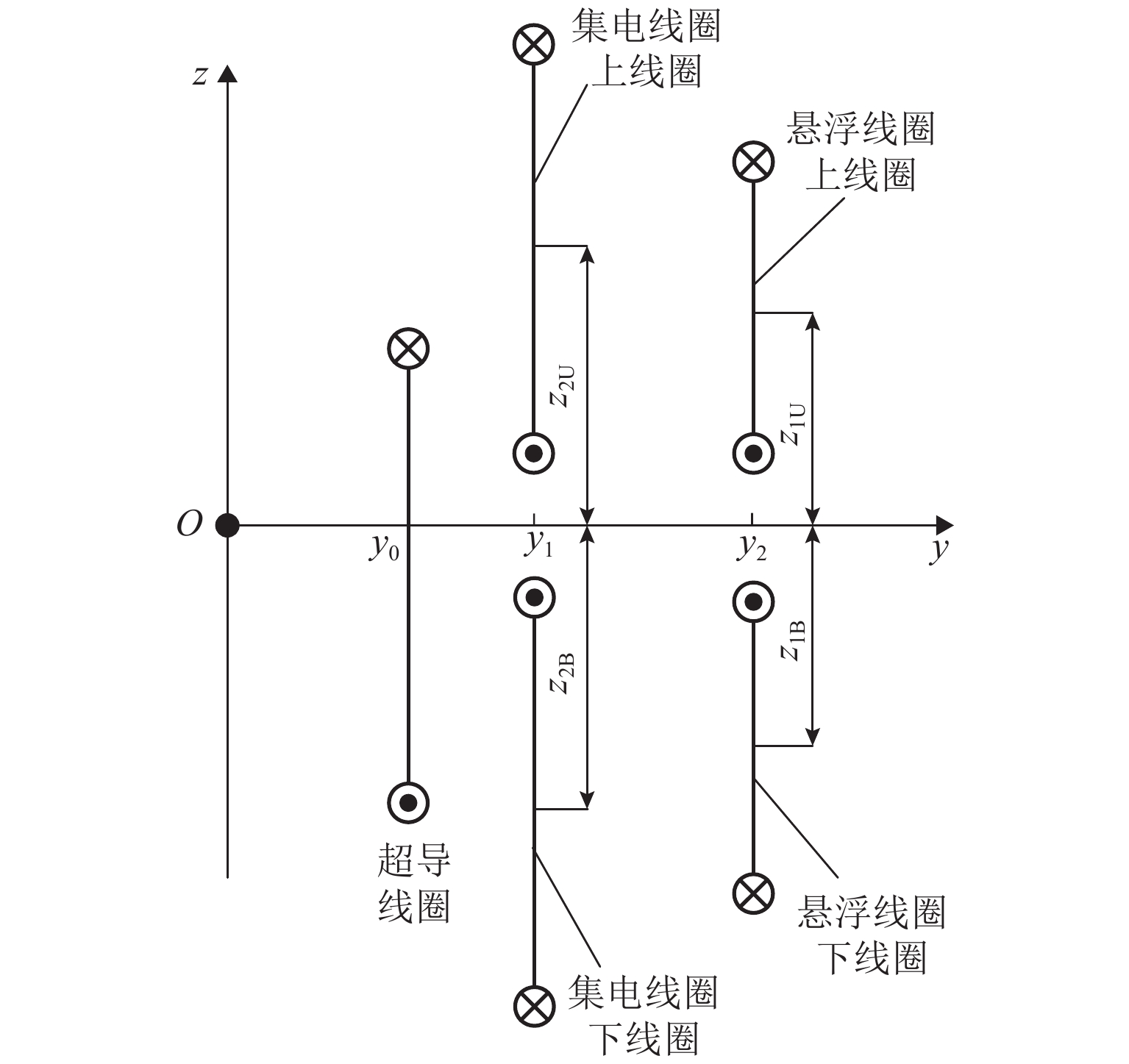
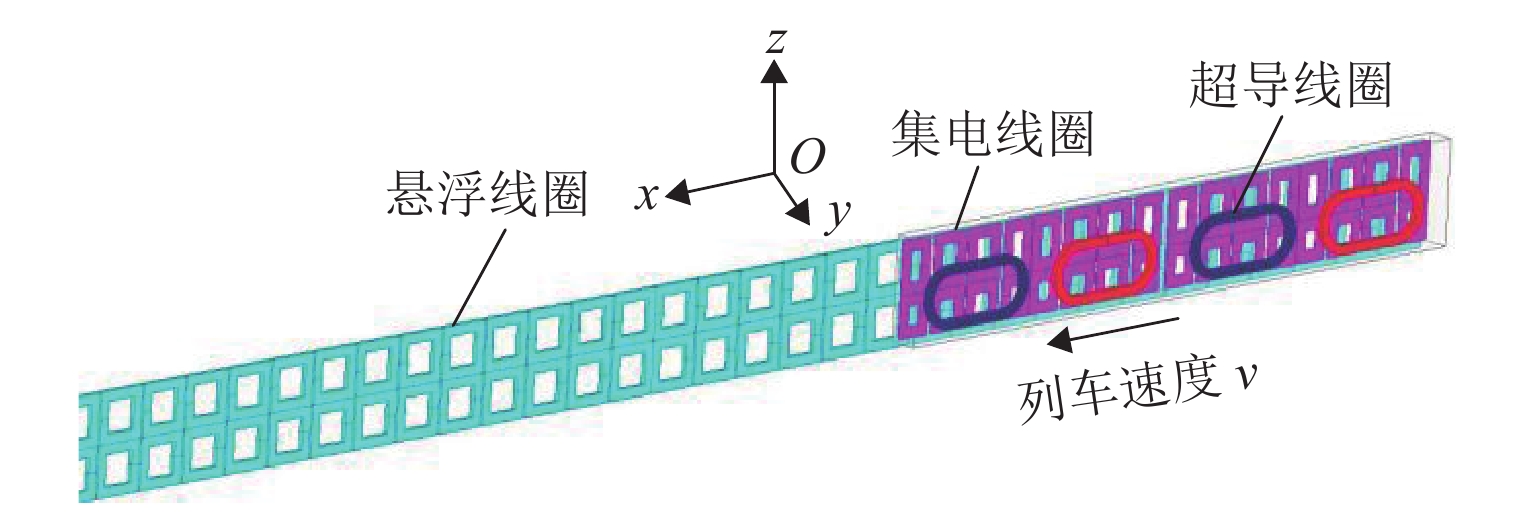
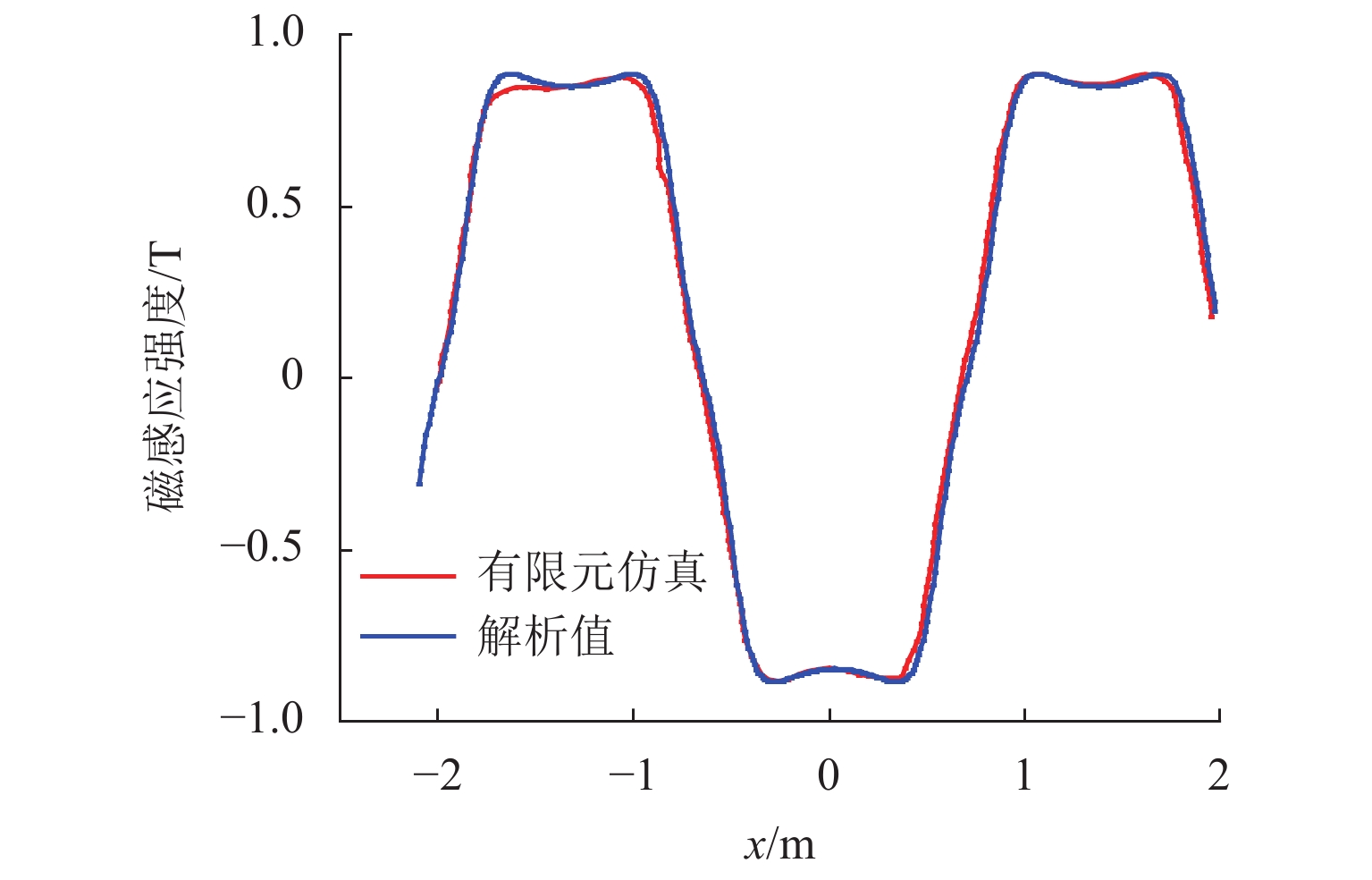
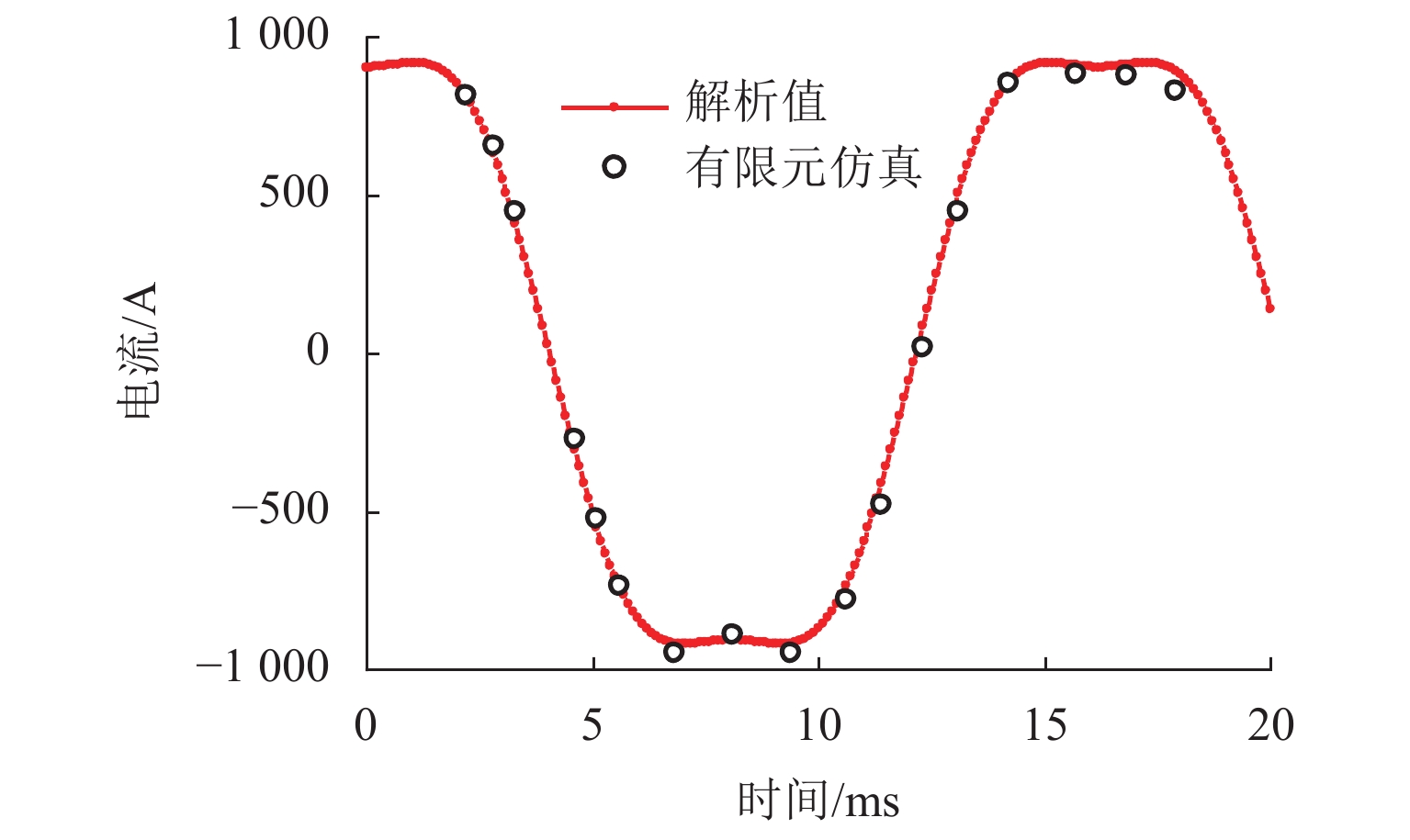
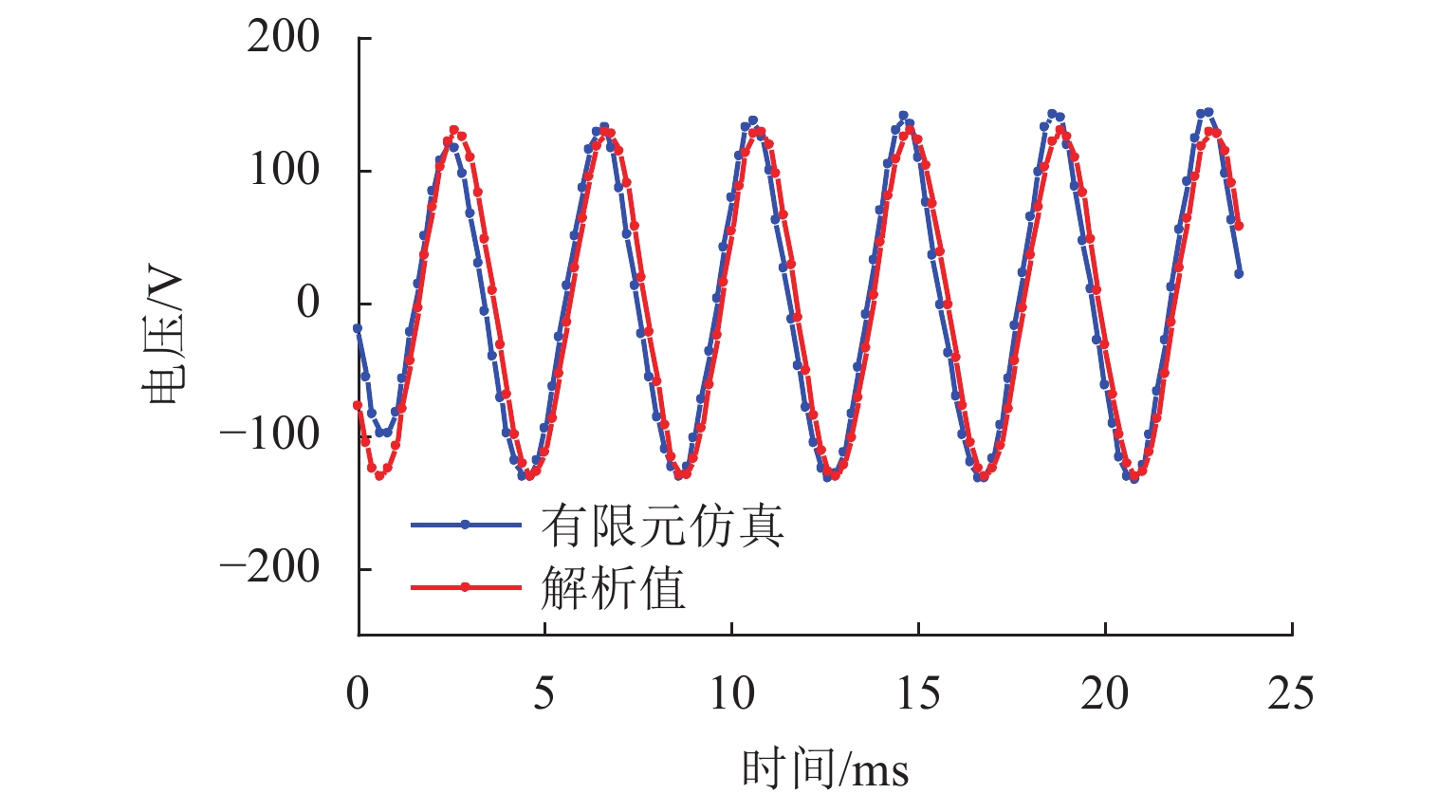
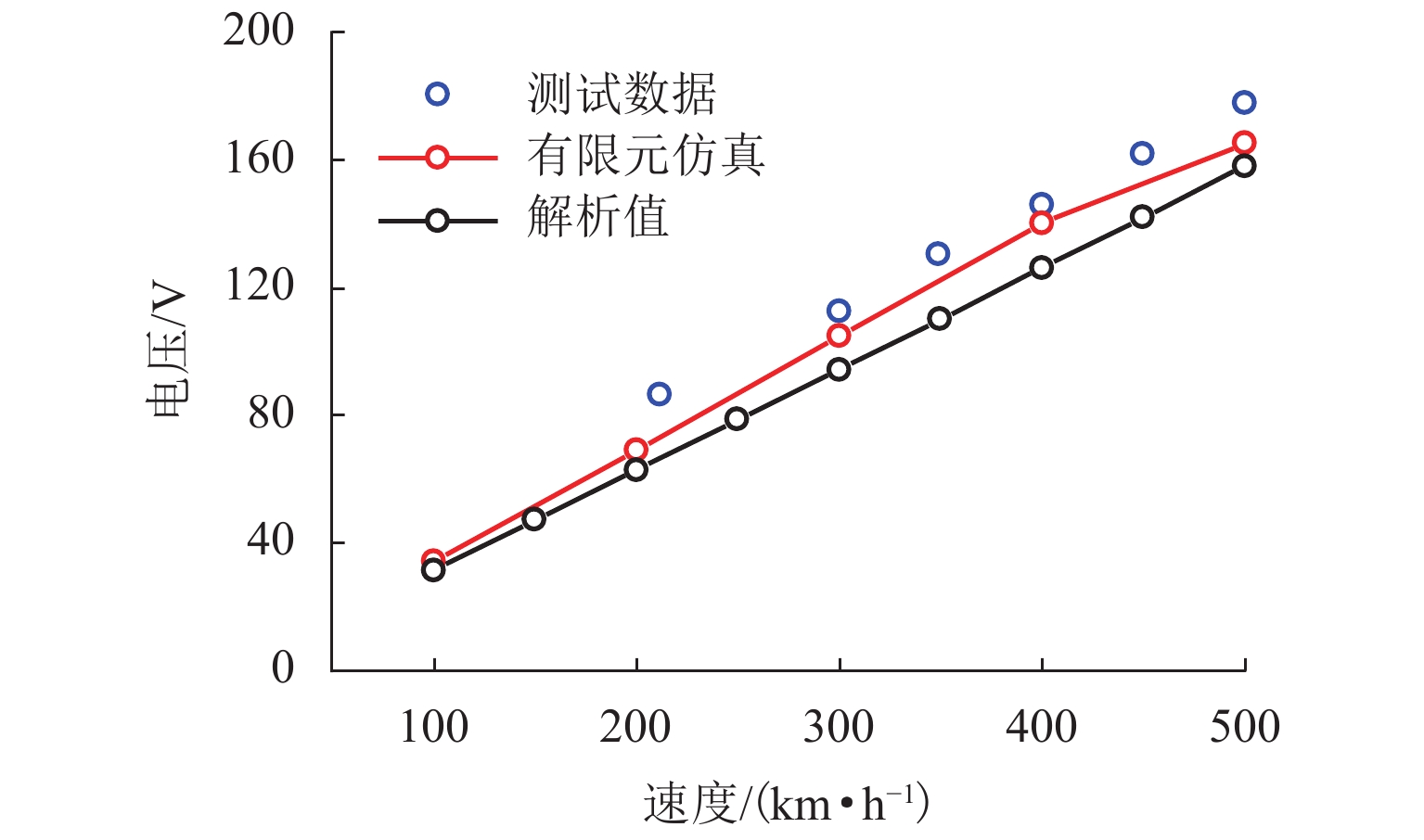
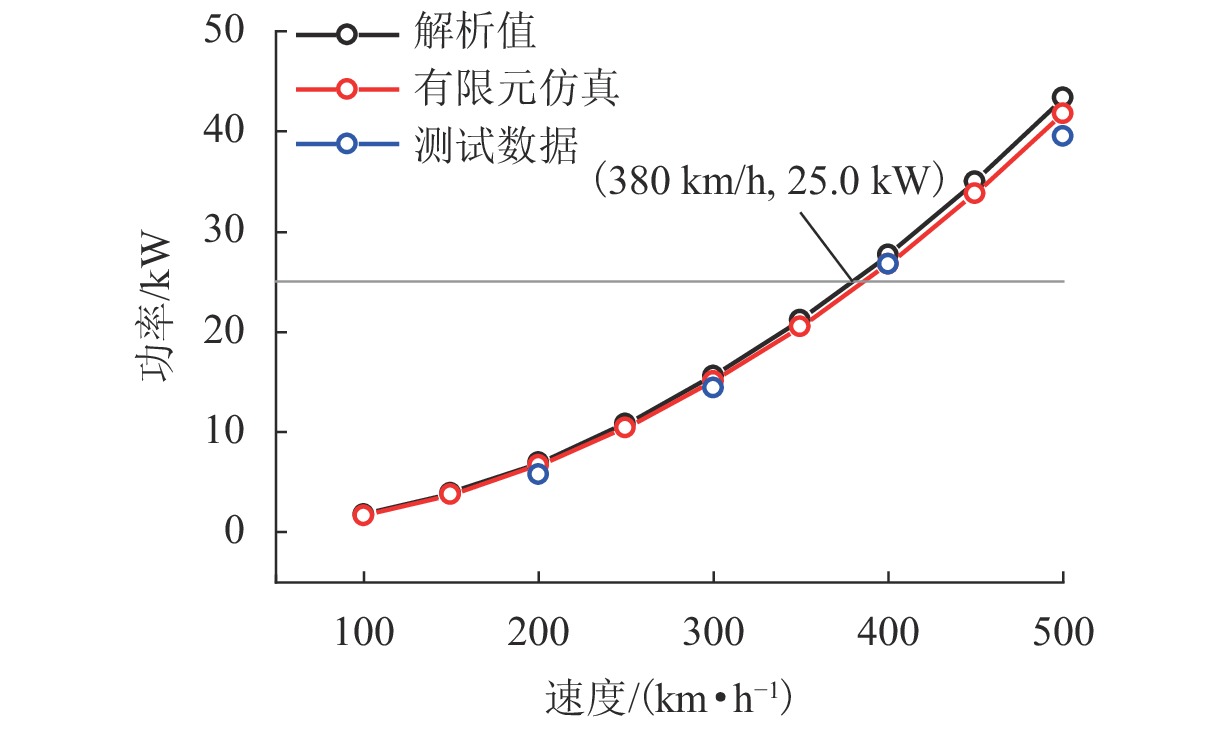
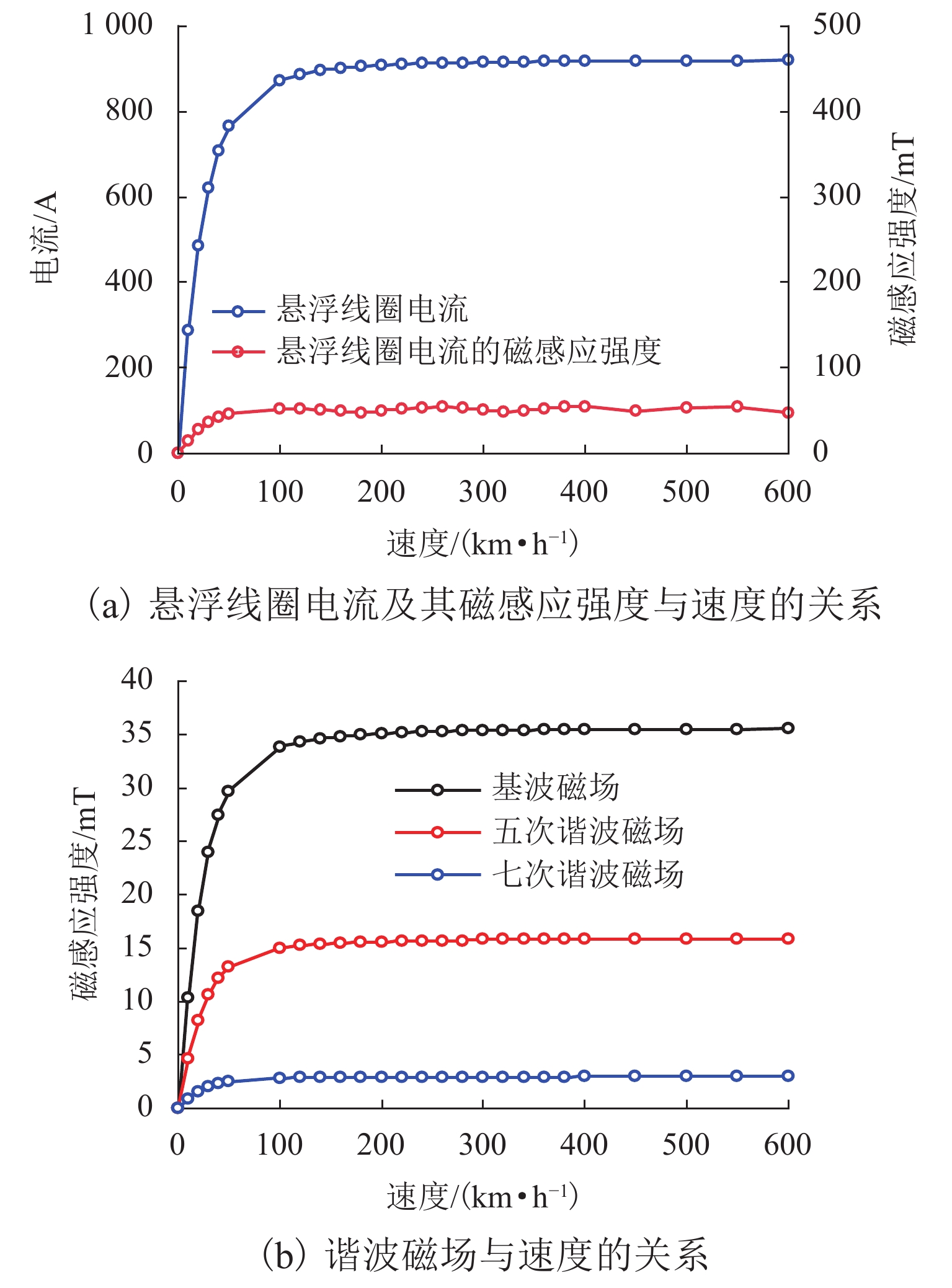
为研究高速磁悬浮车辆直线谐波发电机的发电特性,首先,基于空间谐波法,提出超导线圈的磁动势分布模型,并推导超导线圈在三维空间内磁感应强度分布公式;其次,基于悬浮线圈与超导线圈间的电磁耦合关系,计算悬浮线圈电流的感应磁场,分析得知悬浮线圈五次谐波磁场用于感应集电;然后,将悬浮线圈五次谐波磁场作为集电线圈的激励,推导集电线圈感应电动势的解析式;最后,以日本山梨线MLX01型磁浮列车为工程背景,利用数值解析值、有限元仿真和日本山梨线实测数据进行了对比分析. 研究结果表明:超导线圈磁感应强度、感应电动势和集电功率的解析值与有限元仿真、实测数据的相对误差均在10%以内,验证了磁动势分布模型和解析模型的有效性;列车速度大于100 km/h时,悬浮线圈电流及其感应磁场趋于饱和;集电线圈感应电动势与列车运行速度近似呈线性关系,集电功率与速度呈二次非线性关系;列车速度500 km/h时,集电功率为43.3 kW;列车速度在380 km/h时达到25.0 kW的目标集电功率,保证了磁悬浮车辆车载供电的可靠性.
Abstract:To study the power generation characteristics of linear harmonic generators for high-speed maglev trains, based on the space harmonic method, the magnetomotive force distribution model of superconducting coils is proposed, and the magnetic induction intensity distribution formula of superconducting coils in three-dimensional space is deduced. Secondly, the induced magnetic field of the suspension coil current is calculated based on the electromagnetic coupling relationship between the suspension coil and the superconducting coil, and the fifth harmonic magnetic field of the suspension coil is analyzed that to be used for collecting the inductive current. Further, the fifth harmonic magnetic field of the suspension coil is used as the excitation of the collector coil, and the analytical expression of the induced electromotive force of the collector coil is deduced. Finally, taking the MLX01 maglev train on the Yamanashi line in Japan as the engineering background, the numerical analysis value, finite element simulation and the measured data of the Yamanashi line in Japan are used for comparison. The research results show that the relative errors between the analytical values of the magnetic induction intensity, the induced electromotive force and collecting power of the superconducting coil, the finite element simulation and the measured data are all within 10%, which verifies the validity of the magnetomotive force distribution model and the analytical model. When the train speed is more than 100 km/h, the current of the suspension coil and its induced magnetic field tend to be saturated; the induced electromotive of the collecting force coil is approximately linear with the running speed of the train, and the collecting power has a quadratic nonlinear relationship with the speed; when the train speed is 500 km/h, the collecting power is 43.3 kW; the train speed reaches the target collecting power of 25.0 kW at 380 km/h, which ensures the reliability of the on-board power supply of the maglev train.
-
Key words:
- maglev train /
- numerical analysis /
- linear generator /
- space harmonic method
-
表 1 直线谐波发电机基本参数
Table 1. Parameters of linear harmonic generator
线圈 参数 数值 集电线圈 a2R/mm 200 a2S/mm 245 a2T/mm 245 b2U/mm 435 b2B/mm 245 与超导线圈间距/mm 75 悬浮线圈 a1/mm 350 b1/mm 340 N1/匝 24 τ1/mm 450 与超导线圈间距/mm 185 超导线圈 a0/mm 1070 b0/mm 500 Ns/匝 1400 τ/mm 1350 Is/A 500 -
[1] 张昆仑. 高速磁浮铁路技术[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2021: 1-17. [2] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001 [3] 吴冬华,冯程程,余进. 磁浮列车非接触式供电技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 522-530.WU Donghua, FENG Chengcheng, YU Jin. Contactless power supply technology for maglev trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 522-530. [4] 王一宇,蔡尧,宋旭亮,等. 零磁通式电动悬浮等效模拟系统的特性分析与实验[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(8): 1628-1635.WANG Yiyu, CAI Yao, SONG Xuliang, et al. Characteristic analysis and experiment of the equivalent simulation system for null-flux electrodynamic suspension[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(8): 1628-1635. [5] LEE H W, KIM K C, LEE J. Review of maglev train technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(7): 1917-1925. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.875842 [6] 胡道宇,冯馨月,张志华. 超导电动悬浮系统阻尼特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2021,41(13): 4679-4688.HU Daoyu, FENG Xinyue, ZHANG Zhihua. Study on the damping characteristics of superconducting electrodynamic suspension system[J]. Proceedings of The CSEE, 2021, 41(13): 4679-4688. [7] 王志涛,蔡尧,龚天勇,等. 基于场–路–运动耦合模型的超导电动悬浮列车特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(4): 1162-1171.WANG Zhitao, CAI Yao, GONG Tianyong, et al. Characteristic studies of the superconducting electrodynamic suspension train with a field-circuit-motion coupled model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(4): 1162-1171. [8] 陈敏,周邓燕,徐德鸿. 注入高次谐波电流的磁悬浮列车非接触供电方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2005,25(6): 104-108.CHEN Min, ZHOU Dengyan, XU Dehong. Contactless power supply of maglev using harmonic injection method[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25(6): 104-108. [9] ANDRIOLLO M, MARTINELLI G, MORINI A, et al. Optimization of the on-board linear generator in EMS-maglev trains[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1997, 33(5): 4224-4226. doi: 10.1109/20.619717 [10] 刘志浩. 电磁式高速磁浮系统直线谐波发电机特性分析[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021. [11] 郭亮,卢琴芬,叶云岳. 磁浮列车用直线发电机感应电动势的分析计算[J]. 电工技术学报,2005,20(11): 1-5.GUO Liang, LU Qinfen, YE Yunyue. Analysis and calculation of the linear generator EMF in maglev[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2005, 20(11): 1-5. [12] 刘慧娟,张奕黄. 磁悬浮列车中直线发电机电枢绕组电阻和电感的计算[J]. 北方交通大学学报,2003,27(4): 94-96.LIU Huijuan, ZHANG Yihuang. Calculation of armature resistance and inductance for linear generator used in magnetic levitation vehicle[J]. Journal of Northern Jiaotong University, 2003, 27(4): 94-96. [13] 吴寒玉. 高速磁浮列车多运行姿态下车载直线发电机的性能分析[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020. [14] 高雨晴. 多姿态工况下高速磁浮系统直线发电机特性分析[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021. [15] KASHIWAGI T, MURAI T, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Control of the output power and power factor in a converter of a linear generator for the maglev system[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 2004, 124(10): 1029-1035. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.124.1029 [16] MURAI T, SAKAMOTO Y. High power factor converter control by instantaneous single-phase current for a maglev system linear generator[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 2006, 126(2): 186-191. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.126.186 [17] FUJIWARA S, MURAI T, HASEGAWA H. Magnetic damping method of EDS system using power collection coil[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 1999, 119(2): 254-259. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.119.254 [18] MURAI T, HASEGAWA H, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Active magnetic damper using linear generator[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 1999, 119(11): 1371-1376. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.119.1371 [19] SAKAMOTO Y, MURAI T, KASHIWAGI T, et al. The development of linear generator system combined with magnetic damping function[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 2006, 126(2): 192-198. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.126.192 [20] MURAI T, SAKAMOTO Y. Sensor-less combined vertical and lateral magnetic damper by using linear generator[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Industry Applications, 2006, 126(3): 269-275. doi: 10.1541/ieejias.126.269 [21] TERAI M, IGARASHI M, KUSADA S, et al. The R&D project of HTS magnets for the superconducting maglev[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2006, 16(2): 1124-1129. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2006.871342 [22] YAMAMOTO T, MURAI T, HASEGAWA H, et al. Development of distributed-type linear generator with damping control[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2000, 41(2): 83-88. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.41.83 [23] HASEGAWA H, MATSUE H. Development of a linear generator integrated into an existing superconducting magnet of a yamanashi maglev vehicle[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2004, 45(1): 21-25. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.45.21 -





 下载:
下载: