Dynamic Characteristics for Evolution Process of Semi-closed Coal Fire
-
摘要:
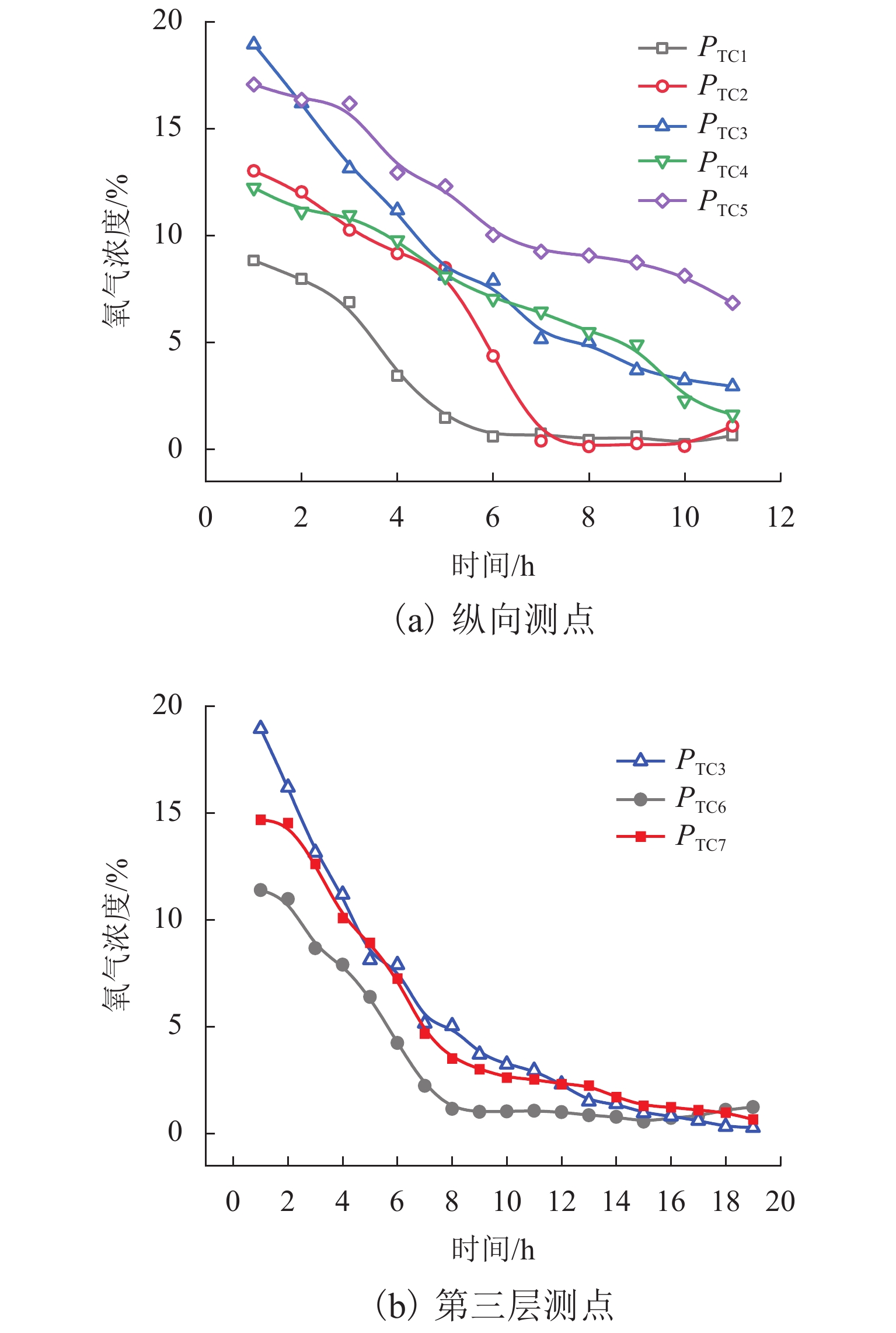
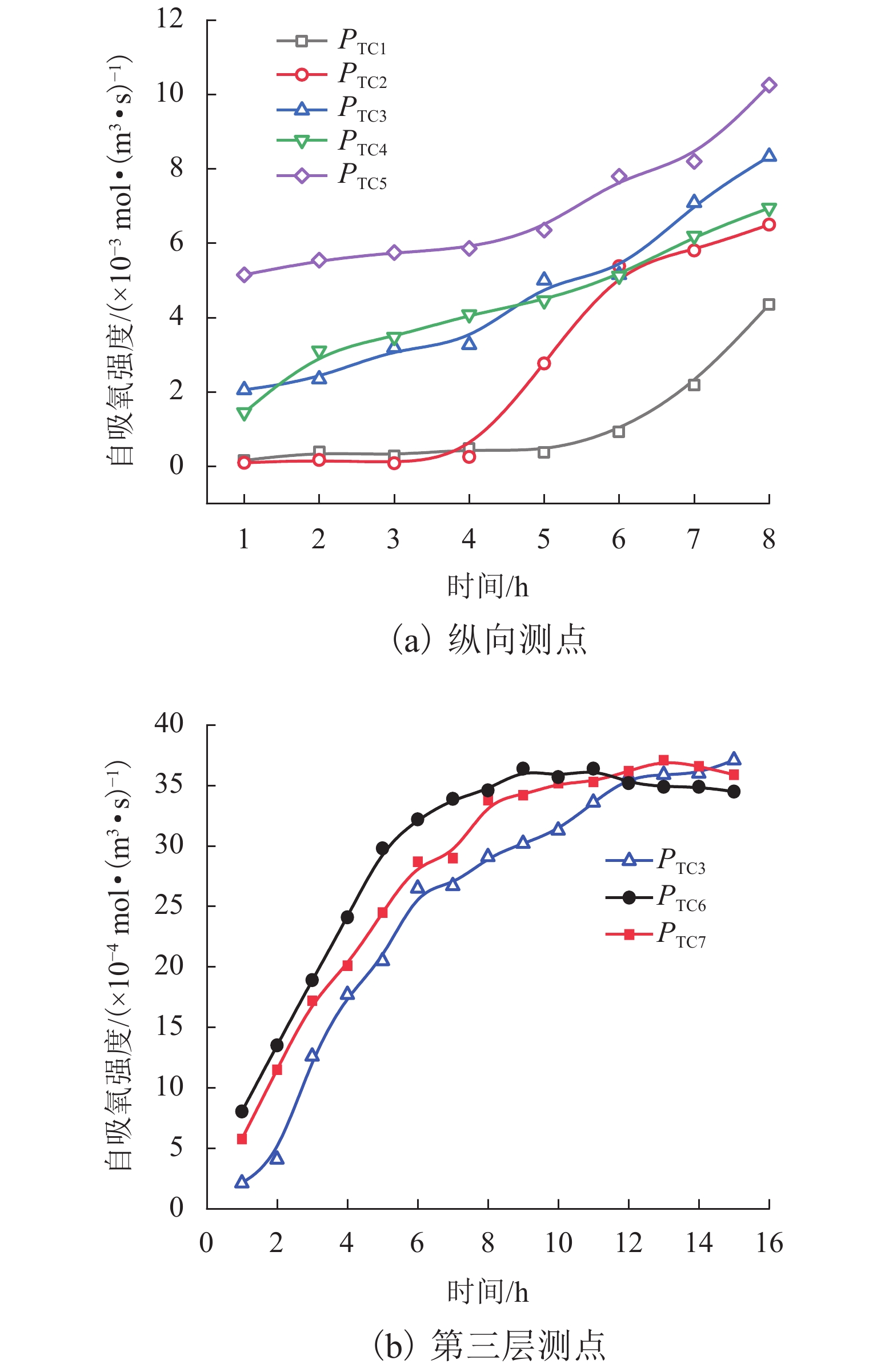
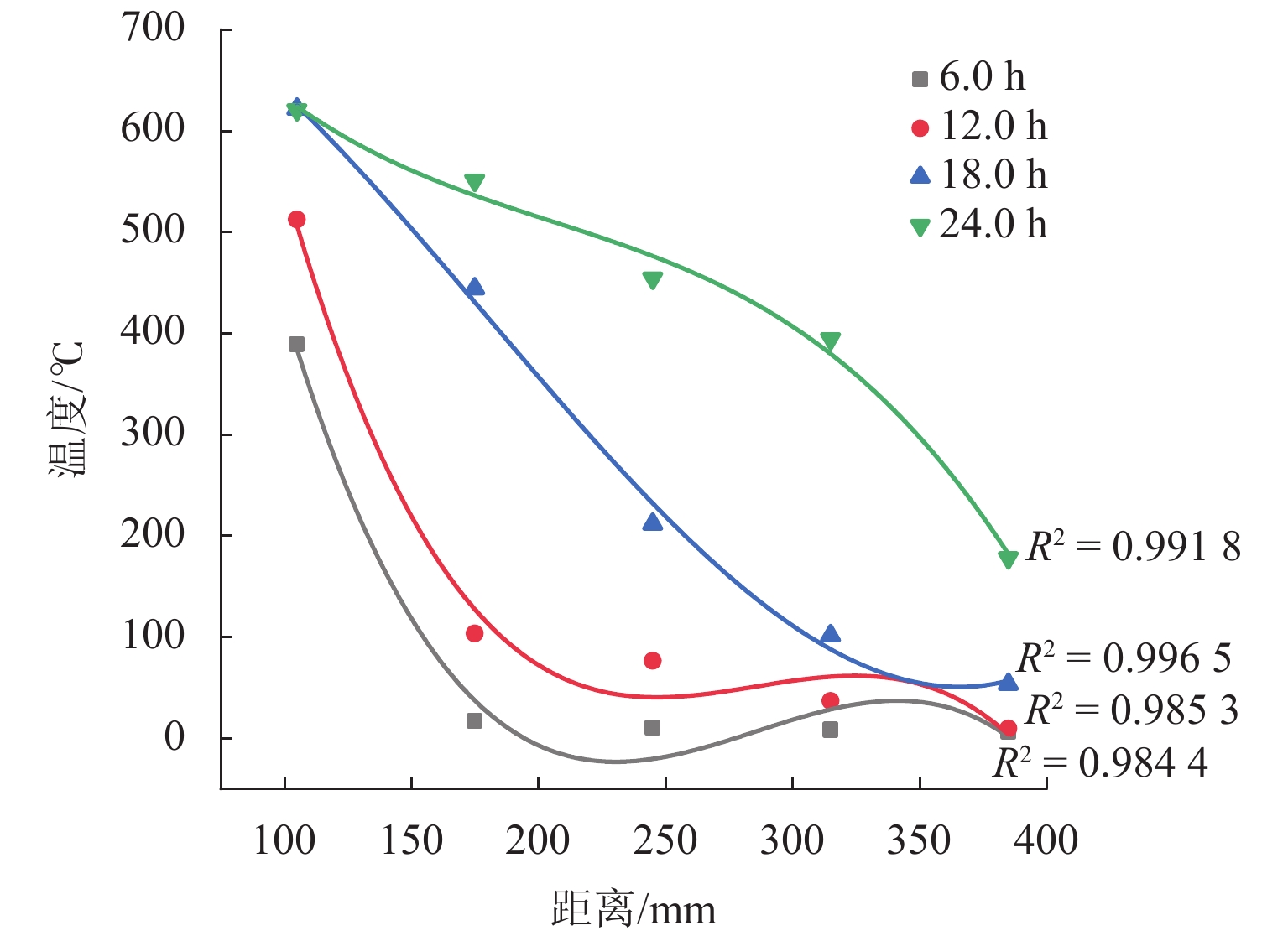
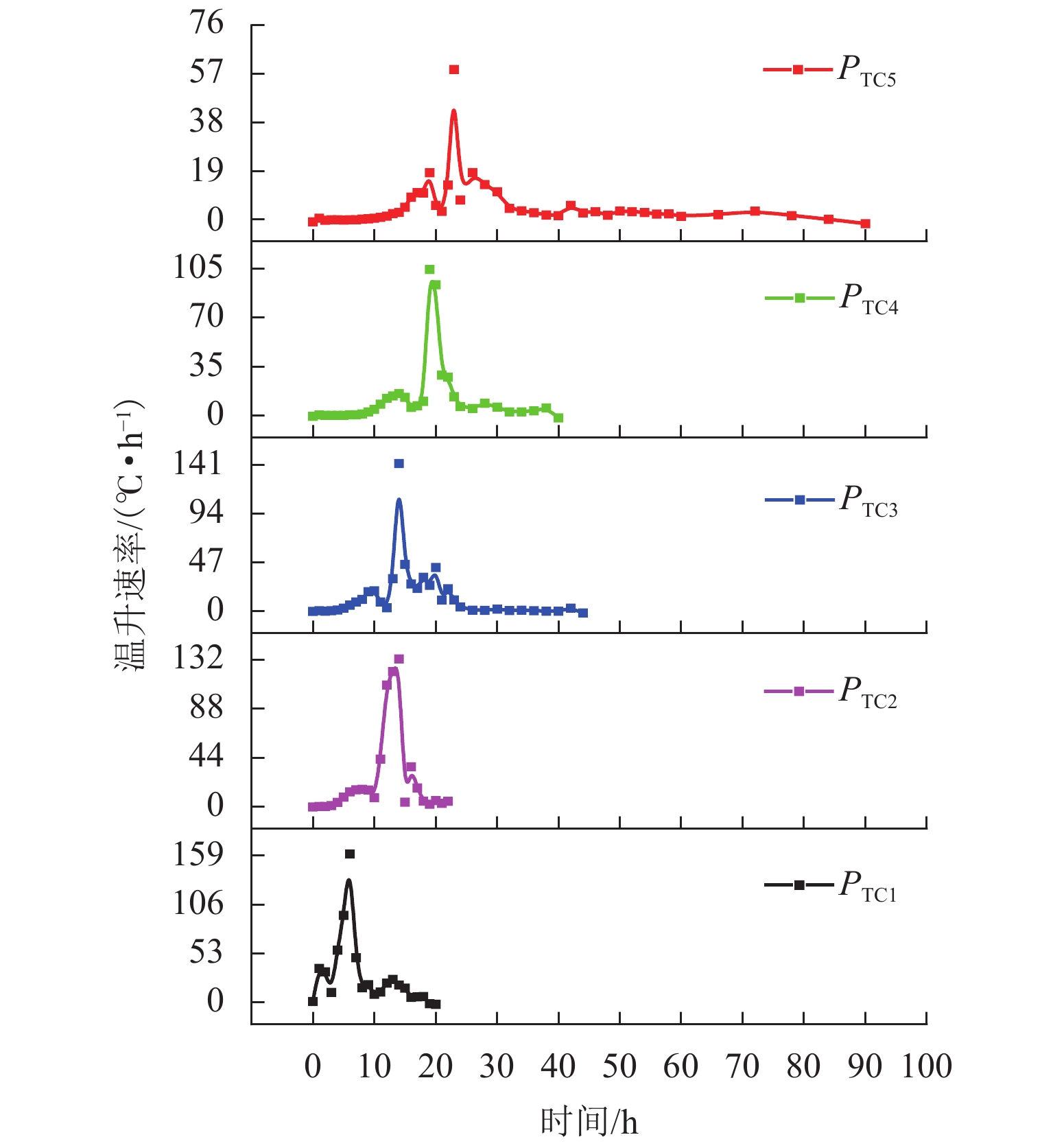
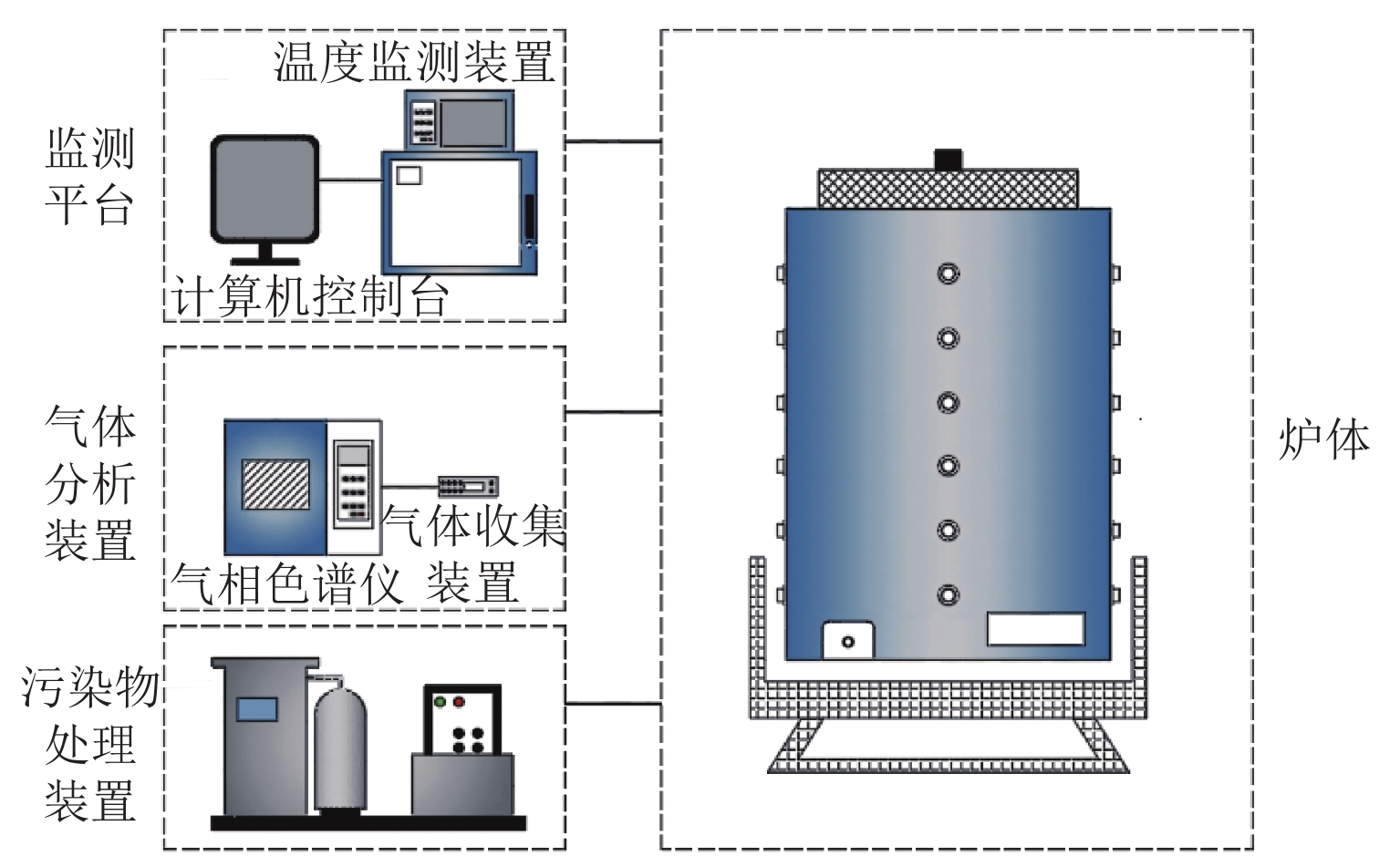
为研究松散煤体自然发火过程中氧气及温度阶段性的演化规律,搭建了半封闭煤火演化实验系统,探究煤体从常温到燃点过程中氧气浓度及温度变化情况,建立松散煤体自燃蔓延过程自然吸氧强度模型,分析自燃过程中氧气分布特征和温度场水平与纵向阶段性移动特征. 结果表明:半封闭煤火演化实验系统能够较好地再现煤自燃“自然吸氧”过程,验证了自然吸氧效应为煤体自燃蔓延提供动力;煤体自然发火过程中,温度变化时间滞后于氧气浓度变化时间,其滞后时间差随煤层纵深变化的增加而增加;在水平方向上高温区域迁移趋势主要受煤体内部裂隙与孔隙分布的影响;自然吸氧强度与测点峰值温度随煤体纵深增加而降低,未发生自燃区域的下方氧气浓度大于其上层氧气浓度. 研究成果对开采、运输、储存状态下的松散煤体自然发火的防治提供理论基础.
Abstract:In order to study the evolution law of oxygen and temperature in the process of spontaneous combustion of loose coal, an experimental system for semi-closed coal fire evolution was built to explore the changes of oxygen concentration and temperature in the process of coal from normal temperature to ignition point, and to establish the natural oxygen absorption intensity model for the spontaneous combustion process of loose coal. The model analyzes the characteristics of oxygen distribution and the horizontal and longitudinal phase movement characteristics of the temperature field during the spontaneous combustion. The results show that the semi-closed coal fire evolution experimental system can better reproduce the natural oxygen absorption process in coal spontaneous combustion, which proves that the natural oxygen absorption effect contributes to the spontaneous combustion of coal mass. During the spontaneous combustion of coal mass, the temperature change time lags behind oxygen concentration change time, and the lag time difference increases with the coal seam depth. The migration trend in the high-temperature area in the horizontal direction is mainly affected by the distribution of cracks and pores at coal body. The natural oxygen absorption intensity and the peak temperature at measuring points decrease with the coal body depth growing, and the oxygen concentration in the lower area without spontaneous combustion is greater than that in the upper layer. The research results provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of spontaneous combustion of loose coal under mining, transportation and storage conditions.
-
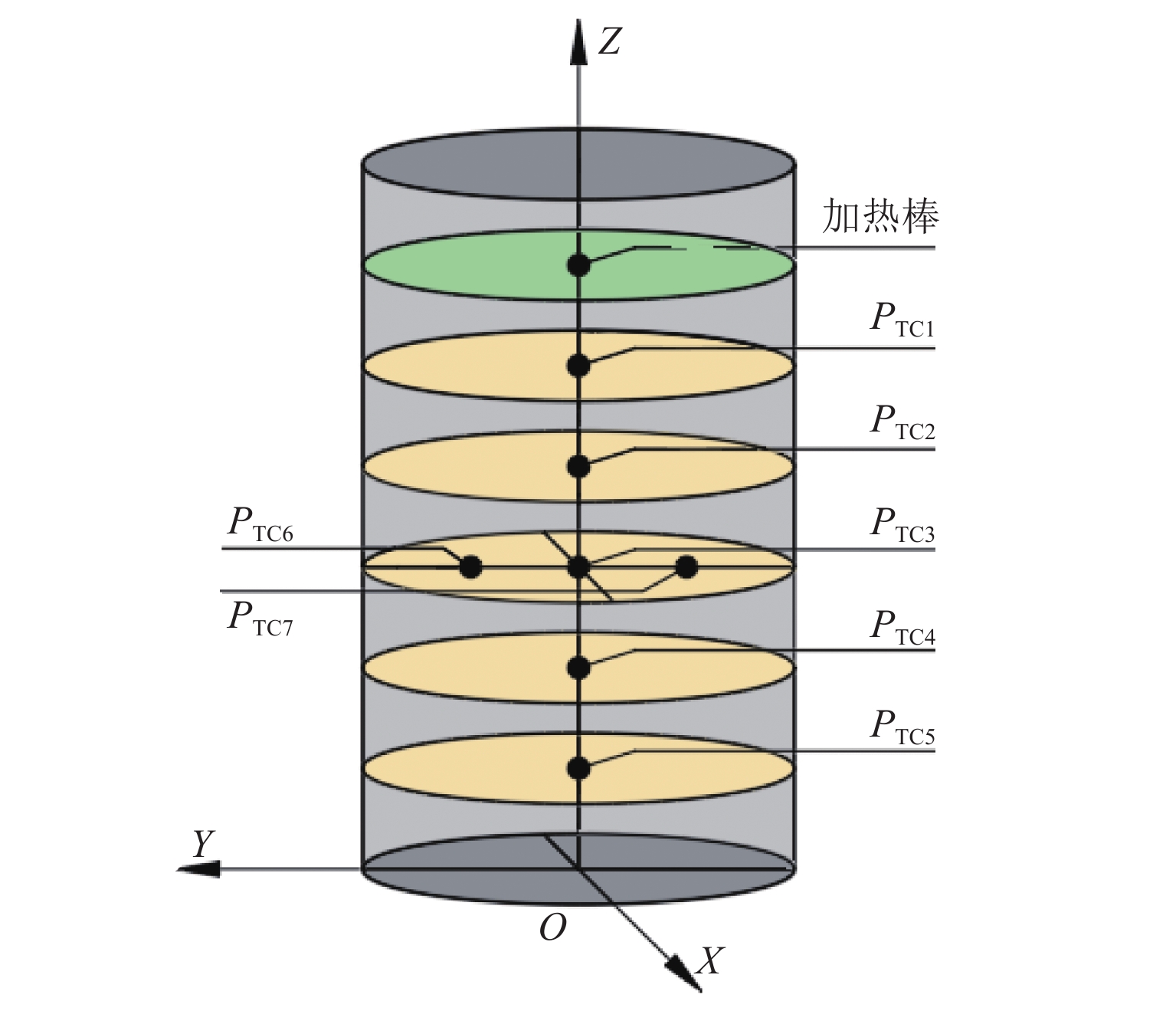
表 1 实验条件
Table 1. Experimental conditions
项目 煤样 粒径/mm 室温/℃ 湿度/% 煤高/mm 装煤量/kg 参数 孟村 10 6 68 480 57.7 表 2 煤质分析
Table 2. Coal quality analysis
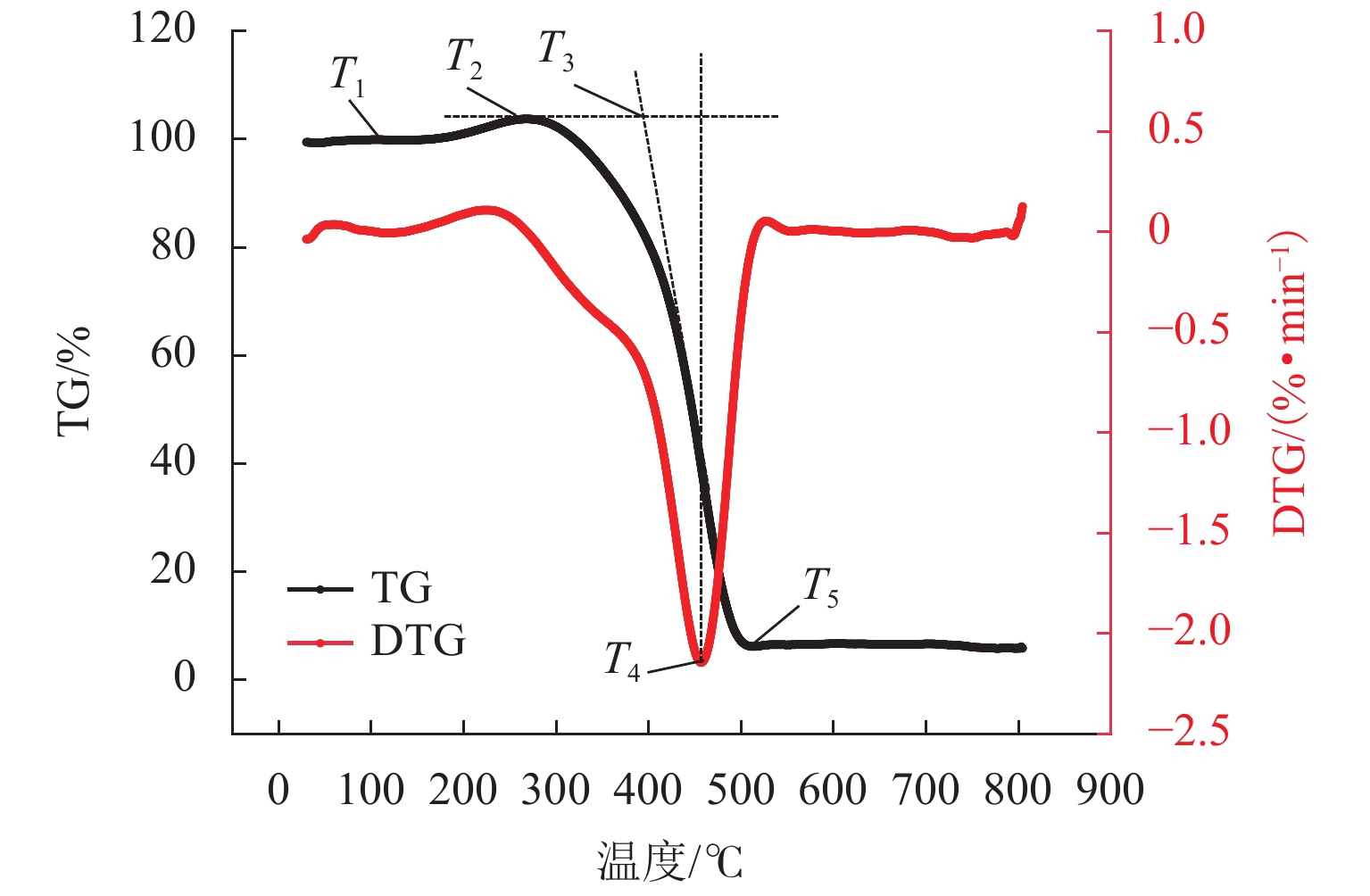
% 工业分析 元素成分分析 Mad Aad Vad FCad C H O N S 4.4 14.0 33.5 48.0 78.8 4.7 14.2 1.3 0.8 表 3 不同氧化自燃阶段温度划分
Table 3. Temperature levels in oxidized spontaneous combustion
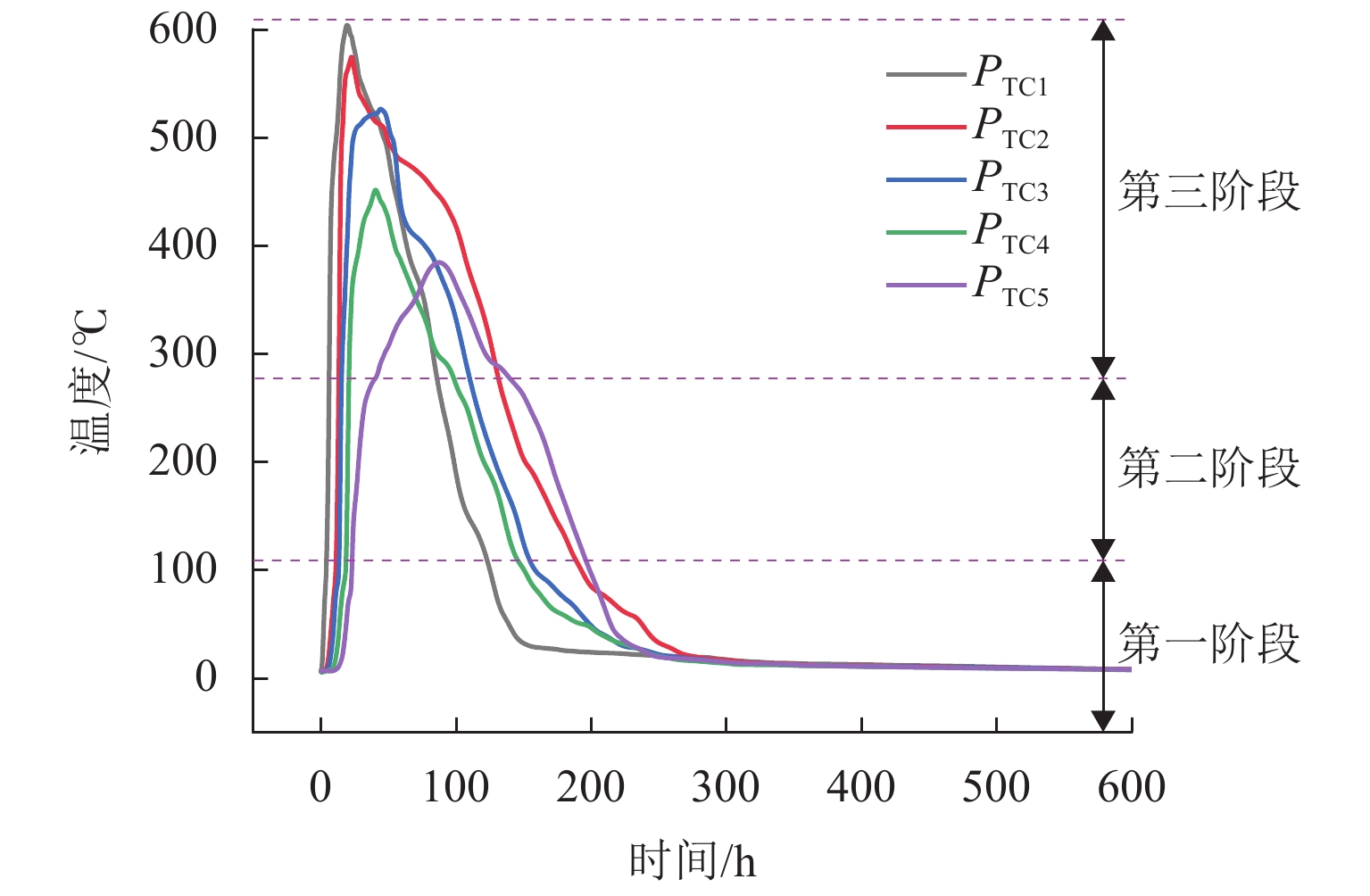
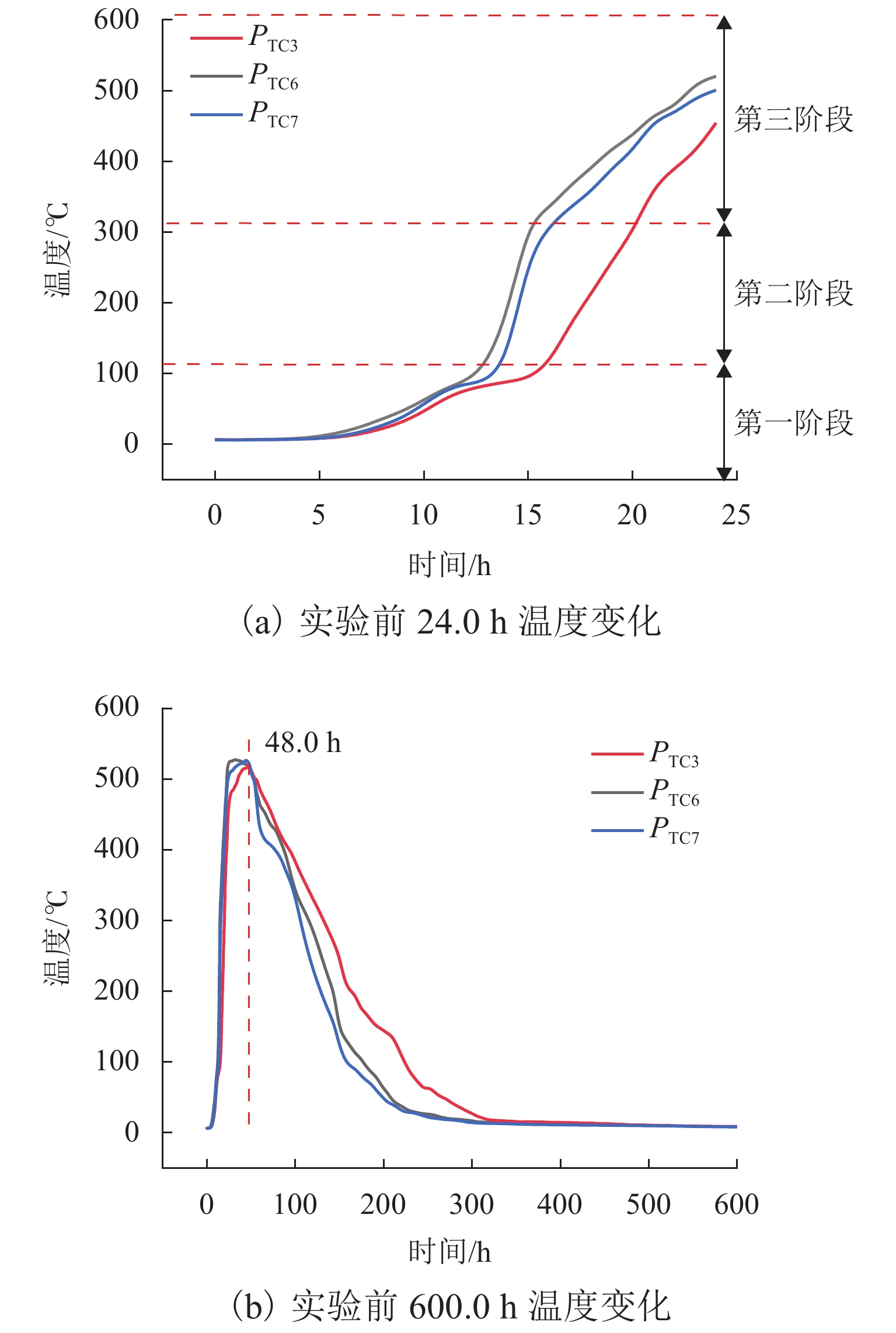
阶段 氧化自燃阶段 平均温度范围/℃ 第一阶段 缓慢氧化阶段 0~111.0 第二阶段 快速升温阶段 112.0~303.0 第三阶段 高温自燃阶段 304.0~604.0 表 4 纵向测点到达各阶段的时间与温度
Table 4. Time and temperature of longitudinal measuring points at each phase
阶段 PTC1 PTC2 PTC3 PTC4 PTC5 时段/h 温度/℃ 时段/h 温度/℃ 时段/h 温度/℃ 时段/h 温度/℃ 时段/h 温度/℃ 第一阶段 0~4.5 121.0 0~12.0 132.0 0~14.0 120.0 0~19.5 115.0 0~32.5 121.0 第二阶段 4.5~6.5 316.0 12.0~13.5 314.0 14.0~16.0 308.0 19.5~21.0 301.0 23.5~48.0 302.0 第三阶段 6.5~23.0 602.0 13.5~24.0 598.0 16.0~48.0 577.0 21.0~43.0 492.0 48.0~73.0 476.0 -
[1] XU J P, GAO W, XIE H P, et al. Integrated tech-paradigm based innovative approach towards ecological coal mining[J]. Energy, 2018, 151: 297-308. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.02.090 [2] 邓军,赵婧昱,张嬿妮,等. 不同变质程度煤二次氧化自燃的微观特性试验[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(5): 1164-1172.DENG Jun, ZHAO Jingyu, ZHANG Yanni, et al. Micro-characteristics of spontaneous combustion of second oxidation with different rank coals[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(5): 1164-1172. [3] 王佟,张博,王庆伟,等. 中国绿色煤炭资源概念和内涵及评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2017,45(1): 1-8,13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.01.001WANG Tong, ZHANG Bo, WANG Qingwei, et al. Green coal resources in China: concept, characteristics and assessment[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2017, 45(1): 1-8,13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.01.001 [4] 邓军,李贝,王凯,等. 我国煤火灾害防治技术研究现状及展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2016,44(10): 1-7,101. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2016.10.001DENG Jun, LI Bei, WANG Kai, et al. Research status and outlook on prevention and control technology of coal fire disaster in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(10): 1-7,101. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2016.10.001 [5] 曾强,聂静,蒲燕. 地下煤火土壤典型重金属分布特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(8): 1989-1996.ZENG Qiang, NIE Jing, PU Yan. Characteristics of the distribution of typical heavy metals in the soils of underground coal fire[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(8): 1989-1996. [6] 聂静,曾强,蒲燕,等. 地下煤火土壤典型重金属砷迁移规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(2): 527-537.NIE Jing, ZENG Qiang, PU Yan, et al. Migration of typical heavy metal as in the soil of underground coal fire[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(2): 527-537. [7] 文虎,程小蛟,许延辉,等. 松散煤体自然发火过程氡析出及运移规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(9): 2816-2823.WEN Hu, CHENG Xiaojiao, XU Yanhui, et al. Law of radon precipitation and migration in loose coal during spontaneous combustion process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(9): 2816-2823. [8] SONG Z Y, ZHU H Q, TAN B, et al. Numerical study on effects of air leakages from abandoned galleries on hill-side coal fires[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2014, 69: 99-110. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2014.08.011 [9] QIN B T, WANG H T, YANG J Z, et al. Large-area goaf fires: a numerical method for locating high-temperature zones and assessing the effect of liquid nitrogen fire control[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(21): 1396.1-1396.14. [10] 邓军,徐精彩,张辛亥. 综放面采空区温度场动态数学模化及应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,1999,28(2): 179-181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.1999.02.023DENG Jun, XU Jingcai, ZHANG Xinhai. Dynamic computer simulation of temperature field in goaf areas of fully mechanized roof coal caving face[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 1999, 28(2): 179-181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.1999.02.023 [11] 褚廷湘,李品,余明高. 水分相变下松散煤体导热系数的数值模拟研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2017,42(7): 1782-1789.CHU Tingxiang, LI Pin, YU Minggao. Simulation study of water phase transition effects on thermal conductivity of loose coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(7): 1782-1789. [12] 蔡灿凡. 煤田火灾温度场及应力场演化过程相似模拟实验研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2017. [13] 赵晓虎,孙鹏帅,杨眷,等. 应用于煤自燃指标气体体积分数在线监测系统[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(增1): 319-327. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.1368ZHAO Xiaohu, SUN Pengshuai, YANG Juan, et al. Online monitoring system of index gases concentration applied to coal sponta-neous combustion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(S1): 319-327. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2020.1368 [14] 赵婧昱,张永利,邓军,等. 影响煤自燃气体产物释放的主要活性官能团[J]. 工程科学学报,2020,42(9): 1139-1148.ZHAO Jingyu, ZHANG Yongli, DENG Jun, et al. Key functional groups affecting the release of gaseous products during spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(9): 1139-1148. [15] 赵婧昱,宋佳佳,郭涛,等. 基于煤火发展演化的松散煤体自燃温度纵深蔓延特征[J]. 煤炭学报,2021,46(6): 1759-1767.ZHAO Jingyu, SONG Jiajia, GUO Tao, et al. Temperature field migration characteristics of loose coal based on experimental scale[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(6): 1759-1767. [16] 李林,陈军朝,姜德义,等. 煤自燃全过程高温区域及指标气体时空变化实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2016,41(2): 444-450.LI Lin, CHEN Junchao, JIANG Deyi, et al. Experimental study on temporal variation of high temperature region and index gas of coal spontaneous combustion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(2): 444-450. [17] 张九零,朱定,朱壮. 煤变质程度对煤自燃特性的影响[J]. 矿业安全与环保,2020,47(3): 42-44.ZHANG Jiuling, ZHU Ding, ZHU Zhuang. The influence of metamorphism degree on spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2020, 47(3): 42-44. [18] 王海燕,周心权,张红军,等. 煤田露头自燃的渗流-热动力耦合模型及应用[J]. 北京科技大学学报,2010,32(2): 152-157.WANG Haiyan, ZHOU Xinquan, ZHANG Hongjun, et al. Seepage-thermal dynamical coupling model for spontaneous combustion of coalfield outcrop and its application[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2010, 32(2): 152-157. [19] 陈晓坤,李海涛,王秋红,等. 高温松散煤体自吸氧试验装置研制及应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报,2015,25(10): 29-34.CHEN Xiaokun, LI Haitao, WANG Qiuhong, et al. Development and application of experimental device for studying oxygen absorption by high temperature loose coal[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(10): 29-34. [20] 吴国光,张永建,王光友,等. 松散煤体中空气渗流规律的试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2009,37(8): 42-45.WU Guoguang, ZHANG Yongjian, WANG Guangyou, et al. Test and study on air transfusion law in loose coal mass[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2009, 37(8): 42-45. [21] ONIFADE M, GENC B. A review of research on spontaneous combustion of coal[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2020, 30(3): 303-311. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2020.03.001 [22] 郭兴明,徐精彩,惠世恩. 松散煤体中氧气输运过程的理论分析[J]. 煤炭学报,2001,26(6): 643-648. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.06.016GUO Xingming, XU Jingcai, HUI Shien. Theoretical analysis on law of transporting oxygen in the loose coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2001, 26(6): 643-648. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2001.06.016 [23] 张英华,周佩玲,黄志安,等. 联络巷对采空区氧化升温带影响的多场耦合模拟研究[J]. 工程科学学报,2016,38(8): 1050-1058.ZHANG Yinghua, ZHOU Peiling, HUANG Zhian, et al. Multi-field coupling numerical simulation of the crossheading effect on oxidization and heat accumulation zones in gob areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(8): 1050-1058. [24] 周佩玲,张英华,黄志安,等. 非均质孔隙率采空区氧化升温规律四维动态模拟[J]. 工程科学学报,2016,38(10): 1350-1358.ZHOU Peiling, ZHANG Yinghua, HUANG Zhian, et al. 4D dynamic simulation of coal oxidation heating law in gobs with heterogeneous porosity[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(10): 1350-1358. [25] 邓军,徐精彩,李莉,等. 不同氧气浓度煤样耗氧特性实验研究[J]. 湘潭矿业学院学报,2001,16(2): 12-14,18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9102.2001.02.004DENG Jun, XU Jingcai, LI Li, et al. Experimental investigation on the relationship of oxygen consumption rate of coal and the concentration of oxygen[J]. Journal of Xiangtan Mining Institute, 2001, 16(2): 12-14,18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9102.2001.02.004 [26] 朱红青,王海燕,沈静,等. 氧浓度对松散煤耗氧速率影响的实验研究[J]. 煤炭工程,2013,45(8): 110-112,115.ZHU Hongqing, WANG Haiyan, SHEN Jing, et al. Experiment study on oxygen concentration affected to oxygen consumption rate of loose coal[J]. Coal Engineering, 2013, 45(8): 110-112,115. [27] 谭波,牛会永,和超楠,等. 回采情况下采空区煤自燃温度场理论与数值分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,44(1): 381-387.TAN Bo, NIU Huiyong, HE Chaonan, et al. Goaf coal spontaneous combustion temperature field theory and numerical analysis under mining conditions[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(1): 381-387. [28] 曹代勇,樊新杰,吴查查,等. 内蒙古乌达煤田火区相关裂隙研究[J]. 煤炭学报,2009,34(8): 1009-1014. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.08.001CAO Daiyong, FAN Xinjie, WU Chacha, et al. Study on the fractures related with coalfield fire area in Wuda coalfield, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(8): 1009-1014. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.08.001 [29] KRISHNASWAMY S, BHAT S, GUNN R D, et al. Low-temperature oxidation of coal: a single-particle reaction-diffusion model[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(3): 333-343. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00180-8 -




 下载:
下载: