Stability Control of Electrodynamic Suspension with Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet Hybrid Halbach Array
-
摘要:
为了研究不同控制方法下永磁电磁混合Halbach阵列的电动悬浮稳定性,首先,利用电磁场理论对系统悬浮力2D解析式进行了推导,并搭建有限元模型对其进行了验证;其次,建立了系统垂向动力学模型,设计了基于气隙反馈的定气隙PID控制器和变气隙PID控制器;最后,仿真分析了系统受到外界扰动时的悬浮气隙及线圈电流波形. 研究结果表明:当系统受到1 mm轨道沉降扰动时,两种控制器均能使系统稳定运行于额定状态,且动态过程一致;当系统受到 ±1000 N扰动力作用时,定气隙PID控制器可使系统稳定悬浮于额定气隙30 mm位置,且稳态线圈电流分别为2.12 A/mm2和 −2.17 A/mm2,变气隙PID控制器则使系统分别稳定悬浮于28.5 mm及31.6 mm位置,且稳态线圈电流均为0.
Abstract:In order to study the suspension stability of the electrodynamic suspension (EDS) with permanent magnet (PM) and electromagnet hybrid halbach array under different control methods, Firstly, the 2D levitation force analytical expression was derived by using the electromagnetic field theory and the corresponding finite element model (FEM) was built to verify the suspension force analytical expression. Secondly, the vertical dynamic model of the system was established, and the fixed air gap PID controller and variable air gap PID controller based on the air gap feedback were designed respectively. Finally, the system suspension air gap and current density waveforms under external disturbances were simulated and analyzed. The simulation results indicate that both controllers can make the system suspend stably at the rated state and have the same dynamic process under the 1 mm track settlement disturbance. When the system is disturbed by the ± 1000 N disturbing force, the fixed air gap PID controller can make the system suspend stably at the 30 mm rated air gap, and apply the steady state coil current of 2.12 A/mm2 and −2.17 A/mm2 respectively. The variable air gap PID controller makes the system suspend stably at 28.5 mm and 31.6 mm respectively, and applies the steady-state coil current of 0.
-
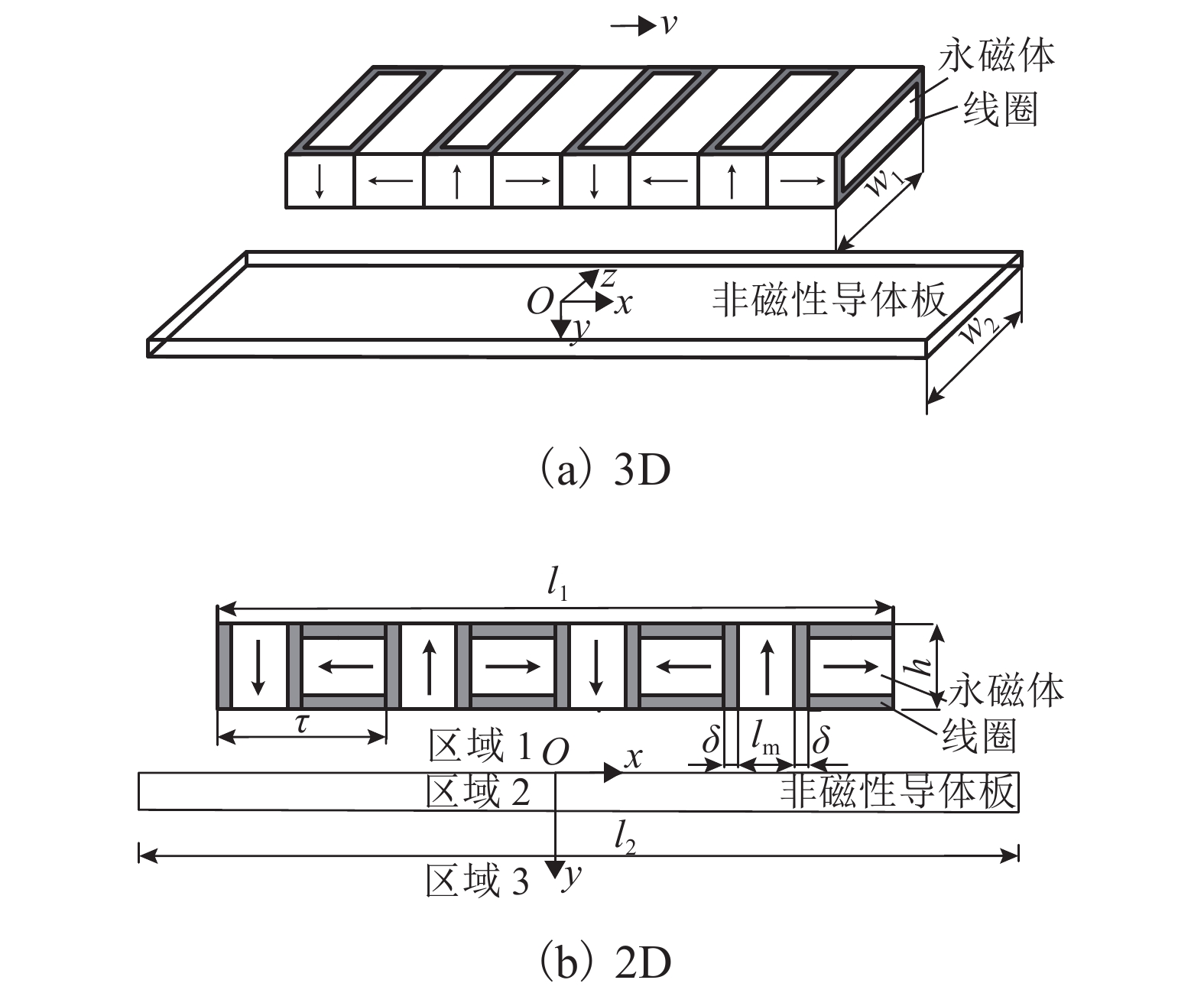
表 1 模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 永磁体剩磁 Br/T 1.25 线圈宽度/mm 10 永磁体横向宽度/mm 200 线圈电流体密度 J/
( A•mm−2))6 永磁体长度/mm 80 导体板横向宽度/mm 200 永磁体高度/mm 100 导体板长度/mm 1600 一对极模块数 m 4 导体板厚度 d/mm 20 阵列总长度/mm 800 导体板电导率/
(S•m−1)3.8 × 107 阵列模块数 N 8 气隙 g/mm 30 -
[1] POST R F, RYUTOV D. The Inductrack concept: A new approach to magnetic levitation[R]. Springfield: Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 1996. [2] 罗成,张昆仑,靖永志. 新型Halbach阵列永磁电动悬浮系统垂向稳定性[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2019,19(2): 101-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2019.02.010LUO Cheng, ZHANG Kunlun, JING Yongzhi. Vertical stability of permanent magnet EDS system with novel Halbach array[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2019, 19(2): 101-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2019.02.010 [3] CHENG Y W, HE G, LONG Z Q. Vertical dynamic stability analysis of EDS levitation systems based on Halbach magnet arrays[C]//2009 Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Guilin: IEEE, 2009: 3726-3730. [4] 郑杰. 感应线圈对磁浮系统性能影响研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2006. [5] CHEN S S, ZHU S, CAI Y. On the unsteady-motion theory of magnetic forces for maglev[R]. Argonne : Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 1996. [6] ZHU S, CAI Y, ROTE D M, et al. Magnetic damping for maglev[J]. Shock and Vibration, 1998, 5: 119-128. doi: 10.1155/1998/480273 [7] HAN Q H. Analysis and modeling of the EDS maglev system based on the Halbach permanent magnet array[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 2004. [8] KO W. Modeling and analysis of the EDS maglev system with the Halbach magnet array[D]. Orlando: University of Central Florida, 2007. [9] HAN C, KO W, LIN K C, et al. Study of a hybrid magnet array for an electrodynamic maglev control[J]. Journal of Magnetics, 2013, 18(3): 370-374. doi: 10.4283/JMAG.2013.18.3.370 [10] 贺光. 基于Halbach结构的永磁电动与电磁混合悬浮技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2010. [11] LONG Z Q, HE G, XUE S. Study of EDS & EMS hybrid suspension system with permanent-magnet halbach array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2011, 47(12): 4717-4724. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2011.2159237 [12] 闫宇壮,李云钢,程虎. 电动电磁混合磁浮悬浮稳定性及技术特性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2007,27(6): 53-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2007.06.012YAN Yuzhuang, LI Yungang, CHENG Hu. Analysis of levitation stability and technology characters of EDS and EMS hybrid maglev[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2007, 27(6): 53-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2007.06.012 [13] 陈殷,张昆仑. Halbach永磁阵列空间磁场的解析计算[J]. 磁性材料及器件,2014,45(1): 1-4,9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3830.2014.01.001CHEN Yin, ZHANG Kunlun. Analytic calculation of the magnetic field created by Halbach permanent magnets array[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices, 2014, 45(1): 1-4,9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3830.2014.01.001 [14] LUO C, ZHANG K L, DUAN J H, et al. Study of permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension system with a novel halbach array[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, 2020, 15(2): 969-977. [15] 陈殷,张昆仑. 板式双边永磁电动悬浮电磁力计算[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(24): 150-156.CHEN Yin, ZHANG Kunlun. Calculation of electromagnetic force of plate type null double side permanent magnet electrodynamic suspension[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(24): 150-156. [16] 雷银照. 时谐电磁场解析方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000. [17] MELCHER J R. Continuum electromechanics[M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 1981. [18] KIM W J. High-precision planar magnetic levitation[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute Technology, 1997. [19] 宋玉晶,张鸣,朱煜. Halbach永磁阵列磁场解析求解及推力建模[J]. 电工技术学报,2014,29(11): 61-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.11.008SONG Yujing, ZHANG Ming, ZHU Yu. Modeling of halbach array magnetic field and motor thrust[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(11): 61-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.11.008 [20] 赵博, 张洪亮. Ansoft12在工程电磁场中的应用[M]. 北京: 水利水电出版社, 2010. [21] 王莉,张昆仑. 基于零功率控制策略的混合磁悬浮系统[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2005,40(5): 667-672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.05.022WANG Li, ZHANG Kunlun. Hybrid magnetic suspension system based on zero power control strategy[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2005, 40(5): 667-672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.05.022 [22] 王莉. 混合EMS磁悬浮系统研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006. -




 下载:
下载:







