Effect of Aerodynamic Wings on Lift Force Characteristics of High-Speed Maglev Train
-
摘要:
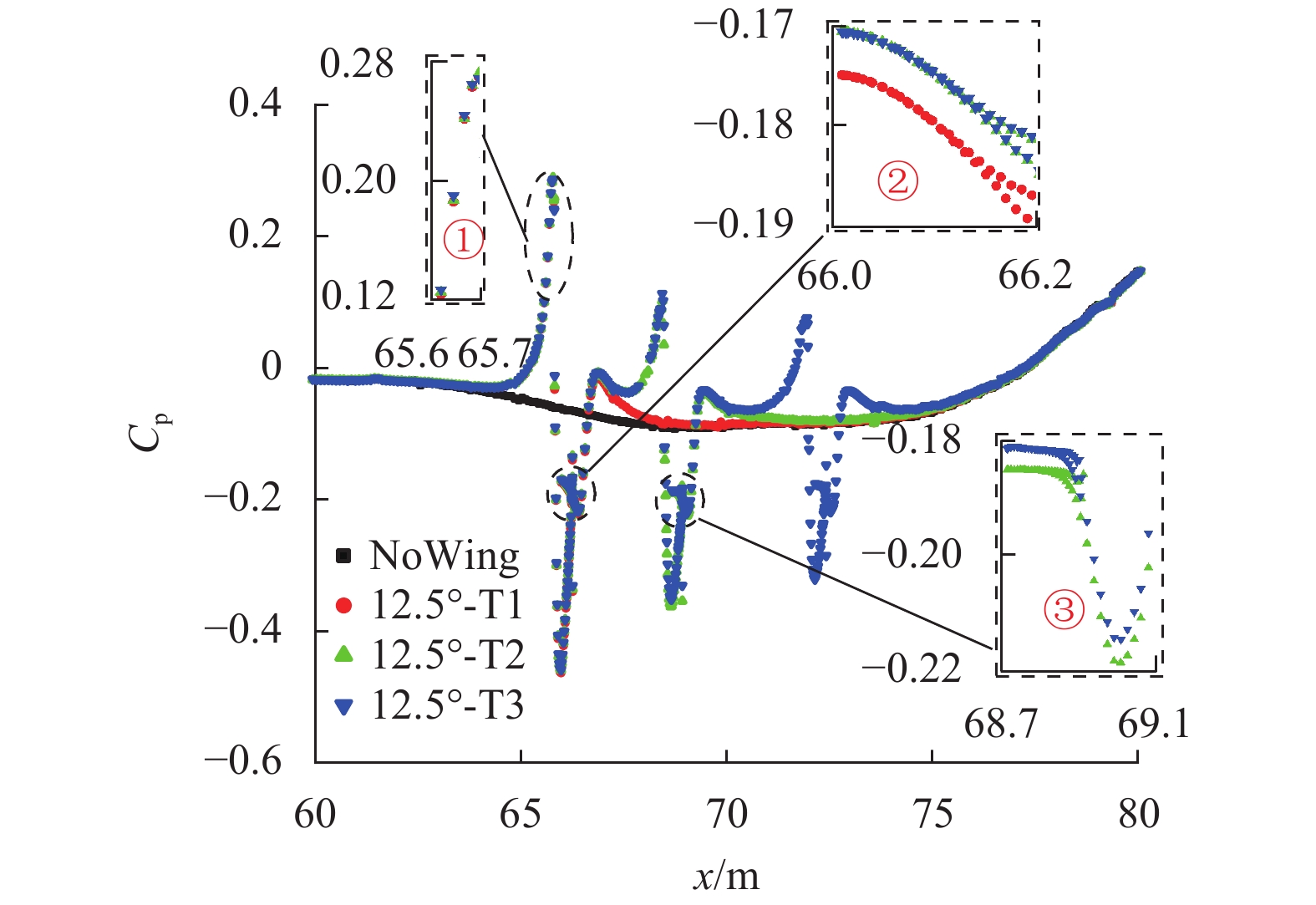
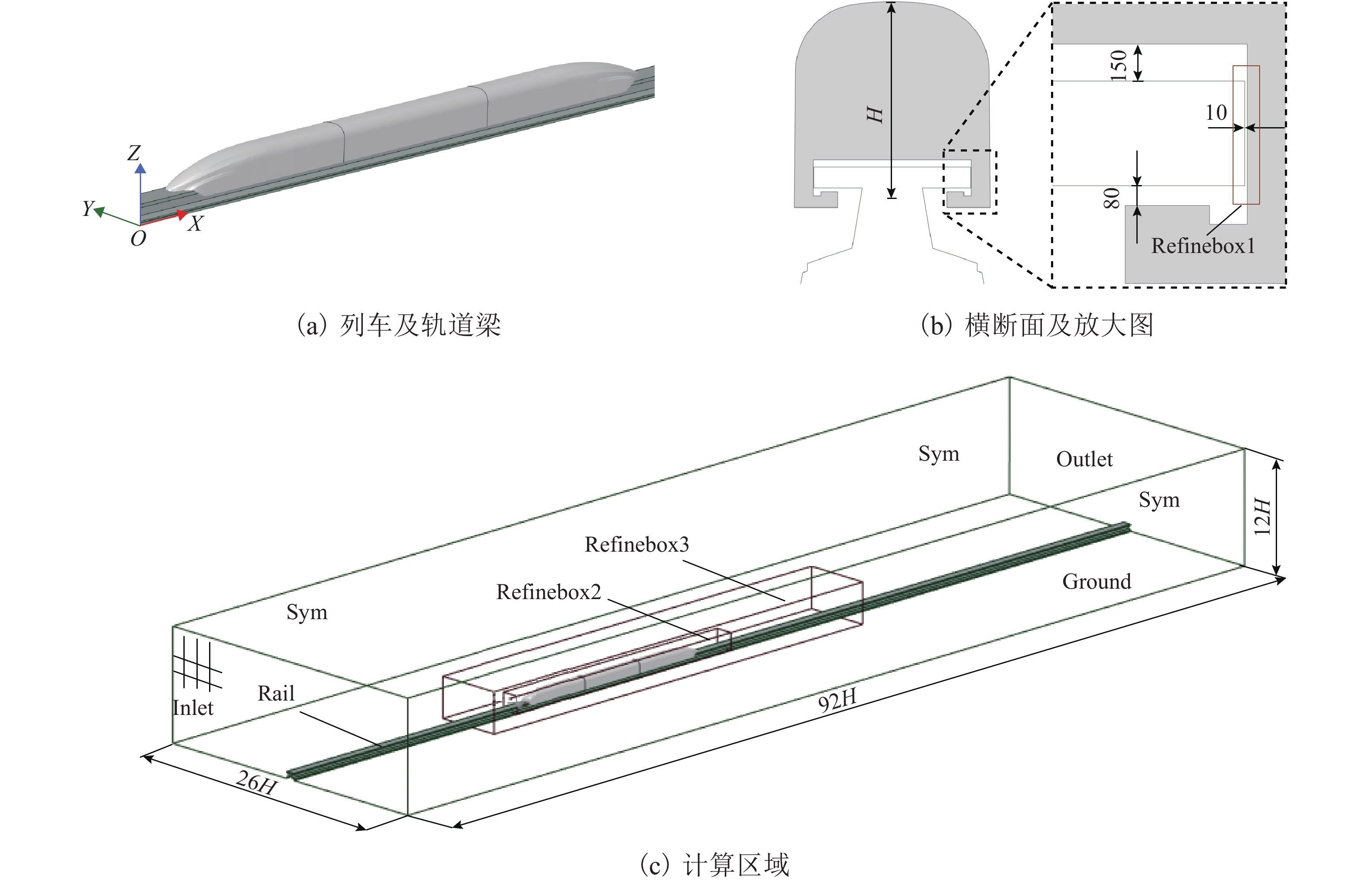
磁悬浮列车高速运行时受到较大气动升力作用,尤其是尾车向上的气动升力较大,易使悬浮性能恶化,甚至导致悬浮控制系统失效,影响列车的乘坐舒适性及运行安全性,因此亟待开展高速磁悬浮列车的尾车升力特性研究及改善工作. 对开展过风洞试验的高速磁悬浮列车进行数值模拟计算,得到的列车表面压力系数与风洞实验数据吻合较好,并加装气动翼改善高速磁悬浮尾车气动升力,研究了气动翼角度、数量对尾车气动性能的影响. 研究结果表明:仅安装一个气动翼时,其自身的气动升力随角度的增加而减小,但尾车气动升力则呈现先减小后增大的规律,气动翼角度为12.5° 时尾车升力最小,与原始磁悬浮列车相比气动升力系数减小3.9%,气动翼及尾车气动阻力略有增加;以气动翼与车体切线角度保持不变为基准在尾车安装多个12.5° 气动翼,不同位置气动翼的气动阻力基本相同,气动翼数量增加后尾车气动阻力随之增大;不同位置气动翼的气动升力存在差异,向鼻尖方向气动翼的气动升力递减,尾车气动升力随气动翼数量增加先减小后趋于稳定;各方案中安装2个气动翼的磁悬浮列车气动性能相对更优,与原始磁悬浮列车相比尾车气动升力减小4.6%,整车阻力仅增加1.4%.
Abstract:Maglev trains are subjected to great aerodynamic lift force when running at high speeds, especially the tail car, which may deteriorate the suspension performance and even cause the suspension control system to fail. All these will affect the ride comfort and operation safety of high-speed maglev trains. Therefore, it is urgent to study and improve the lift force characteristics of the tail car of high-speed maglev trains. To this end, a numerical simulation of the high-speed maglev train is carried out in comparison with a wind tunnel test, and the surface pressure coefficient of the train obtained through numerical simulation is in good agreement with the wind tunnel test results. Then, aerodynamic wings (aero-wings) are installed to improve the aerodynamic lift force performance of the tail car, and the influence of the angle and number of the aero-wings on the aerodynamic characteristics of the tail car is studied. The results show that the aerodynamic lift force of the wing decreases with the increase of angle when only one is installed, but the aerodynamic lift force of the tail car decreases first and then increases. Moreover, the lift force of the tail car is the smallest when the aero-wing angle is 12.5°. Compared with the original maglev train, the aerodynamic lift force coefficient of the winged train is reduced by 3.9%, while the resistance of the aero-wing and the tail car is slightly increased. On the basis that the tangent angle between the aero-wing and the car body remains unchanged, multiple 12.5° aero-wings are installed on the tail car. The aerodynamic resistance of the aero-wings at different positions is basically the same, and the aerodynamic resistance of the tail car increase as the number of aero-wings increases. However, the aerodynamic lift force of the aero-wing at different positions is different, which decreases toward the tip of the nose. The aerodynamic lift force of the tail car first decreases with the increase of the aero-wing number and then stabilizes. Finally, the aerodynamic performance of the maglev train with two aero-wings is found relatively better. Compared with the original maglev train, the aerodynamic lift force of the tail car is reduced by 4.6%, and the resistance of the whole vehicle is only increased by 1.4%.
-
表 1 列车及气动翼的气动力系数
Table 1. Aerodynamic force coefficient of the maglev trian and aerodynamic wings
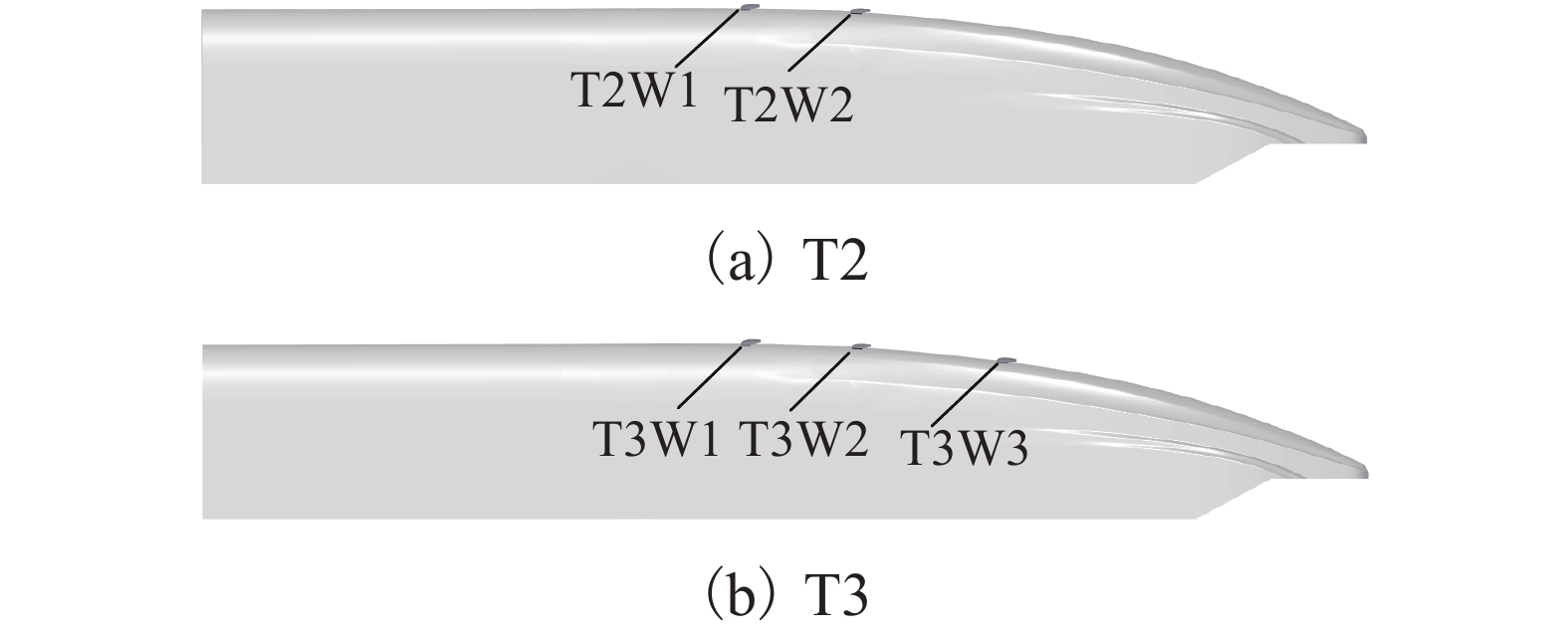
气动翼角度/(°) CdH CdM CdT CdW CdTT ClH ClM ClT ClW ClTT 未安装 0.082 0.051 0.071 0.071 0.232 0.116 0.569 0.569 5.0 0.082 0.051 0.071 0.001 0.072 0.232 0.116 0.560 0.013 0.573 10.0 0.082 0.051 0.071 0.001 0.072 0.232 0.116 0.559 0.010 0.569 12.5 0.082 0.051 0.071 0.002 0.073 0.232 0.116 0.539 0.008 0.547 15.0 0.082 0.051 0.071 0.002 0.073 0.232 0.116 0.561 0.005 0.566 17.5 0.082 0.051 0.071 0.003 0.074 0.232 0.116 0.567 0.003 0.570 表 2 尾车及气动翼的气动力系数
Table 2. Aerodynamic force coefficients of the tail car and aerodynamic wings
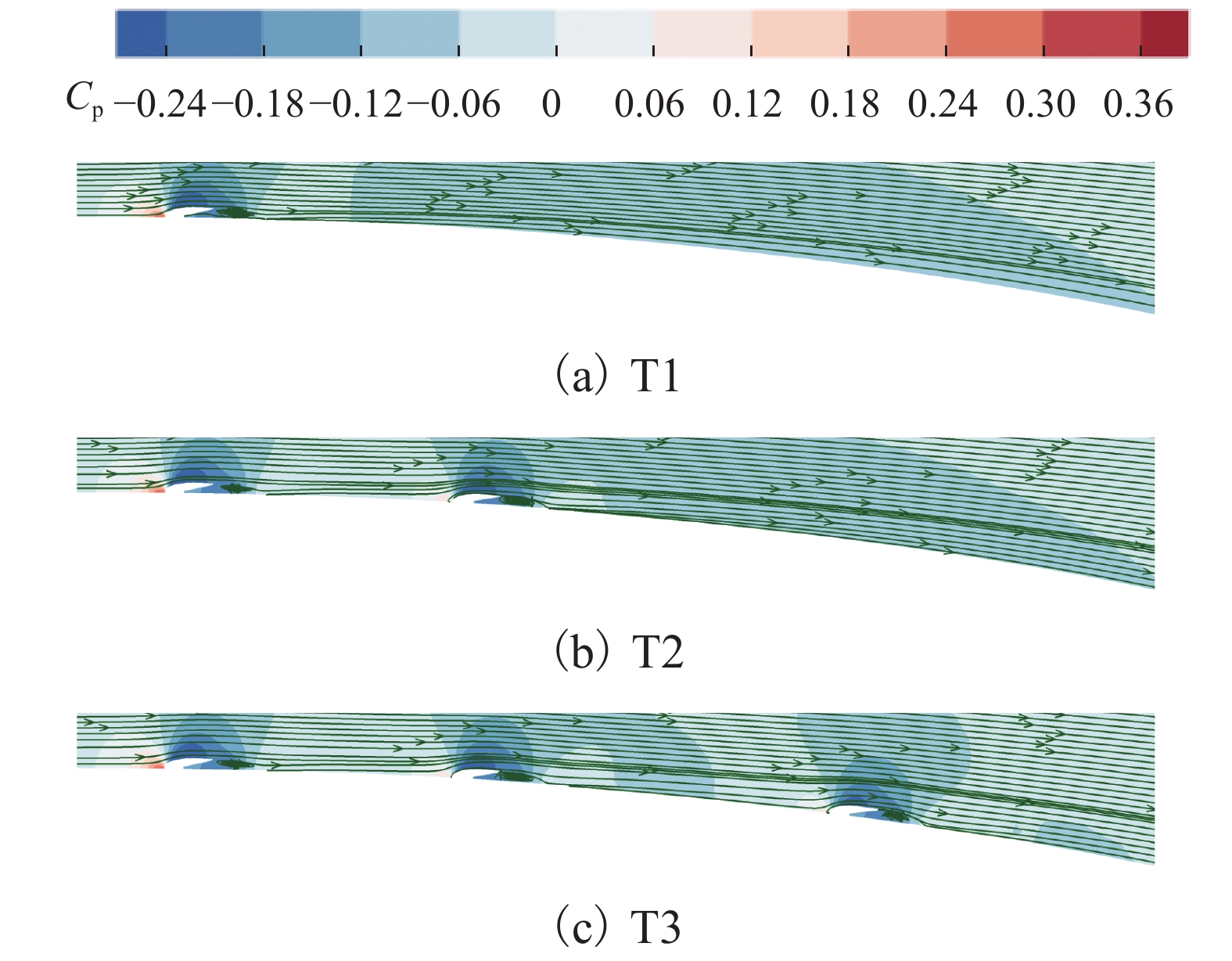
名称 Cd-T Cd-W1 Cd-W2 Cd-W3 Cd-TT Cl-T Cl-W1 Cl-W2 Cl-W3 Cl-TT 未安装 0.071 0.071 0.569 0.569 T1 0.071 0.002 0.073 0.559 0.008 0.547 T2 0.070 0.002 0.002 0.074 0.528 0.008 0.007 0.543 T3 0.069 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.075 0.521 0.008 0.007 0.006 0.543 -
[1] 邓自刚,张勇,王博,等. 真空管道运输系统发展现状及展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(5): 1063-1072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180204DENG Zhigang, ZHANG Yong, WANG Bo, et al. Present situation and prospect of evacuated tube transportation system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1063-1072. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180204 [2] 王家素,王素玉. 高温超导磁悬浮列车研究综述[J]. 电气工程学报,2015,10(11): 1-10. doi: 10.11985/2015.11.001WANG Jiasu, WANG Suyu. High temperature superconducting maglev train[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2015, 10(11): 1-10. doi: 10.11985/2015.11.001 [3] DONG F L, HUANG Z, HAO L N, et al. An on-board 2G HTS magnets system with cooling-power-free and persistent-current operation for ultrahigh speed superconducting maglevs[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 1-12. [4] ZHOU P, LI T, ZHAO C F, et al. Numerical study on the flow field characteristics of the new high-speed maglev train in open air[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University−SCIENCE A, 2020, 21(5): 366-381. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1900412 [5] 沈志云. 关于我国发展真空管道高速交通的思考[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2005,40(2): 133-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.02.001SHEN Zhiyun. On developing high-speed evacuated tube transportation in China[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2005, 40(2): 133-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2005.02.001 [6] 翟婉明,赵春发. 现代轨道交通工程科技前沿与挑战[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001ZHAI Wanming, ZHAO Chunfa. Frontiers and challenges of sciences and technologies in modern railway engineering[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001 [7] 丁叁叁,姚拴宝,陈大伟. 高速磁浮列车气动升力特性[J]. 机械工程学报,2020,56(8): 228-234. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.08.228DING Sansan, YAO Shuanbao, CHEN Dawei. Aerodynamic lift force of high-speed maglev train[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(8): 228-234. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.08.228 [8] 李人宪,刘应清,翟婉明. 高速磁悬浮列车纵向及垂向气动力数值分析[J]. 中国铁道科学,2004,25(1): 8-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.01.002LI Renxian, LIU Yingqing, ZHAI Wanming. Numerical analysis of aerodynamic force in longitudinal and vertical direction for high-speed maglev train[J]. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(1): 8-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2004.01.002 [9] 刘堂红,田红旗,王承尧. 不同磁浮列车外形的气动性能比较[J]. 国防科技大学学报,2006,28(3): 94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2006.03.020LIU Tanghong, TIAN Hongqi, WANG Chenyao. Aerodynamic performance comparison of several kind of nose shape of maglev train[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2006, 28(3): 94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2006.03.020 [10] 舒信伟,谷传纲,梁习锋,等. 高速磁浮列车气动阻力性能数值模拟与参数化评估[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2006,6(2): 6-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2006.02.002SHU Xinwei, GU Chuangang, LIANG Xifeng, et al. Numerical simulation and parameterized investigation of aerodynamic drag performances of high-speed maglev trains[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2006, 6(2): 6-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-1637.2006.02.002 [11] SUN Z X, WANG M Y, WEI L Y, et al. Aerodynamic shape optimization of an urban maglev train[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2021, 37(5): 954-969. [12] 毕海权,雷波,张卫华. 自然风对高速磁浮列车气动特性的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学,2007,28(2): 67-72.BI Haiquan, LEI Bo, ZHANG Weihua. Effects of natural wind on aerodynamic characteristics of high-speed maglev train[J]. China Railway Science, 2007, 28(2): 67-72. [13] 梁习锋,沈娴雅. 环境风与列车交会耦合作用下磁浮列车横向气动性能[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2007,38(4): 751-757. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7207.2007.04.031LIANG Xifeng, SHEN Xianya. Lateral aerodynamic performances of maglev train when two trains meet with wind blowing[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2007, 38(4): 751-757. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7207.2007.04.031 [14] LI T, QIN D, ZHANG J Y. Effect of RANS turbulence model on aerodynamic behavior of trains in crosswind[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 32(5): 85-96. doi: 10.1186/s10033-019-0402-2 [15] LI T, DAI Z Y, YU M G, et al. Numerical investigation on the aerodynamic resistances of double-unit trains with different gap lengths[J]. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 15(1): 549-560. doi: 10.1080/19942060.2021.1895321 -




 下载:
下载: