Shrinkage Characteristics and Anti-Crack Technology of Early-Age Concrete under Large Dry-Cold Temperature Difference
-
摘要:
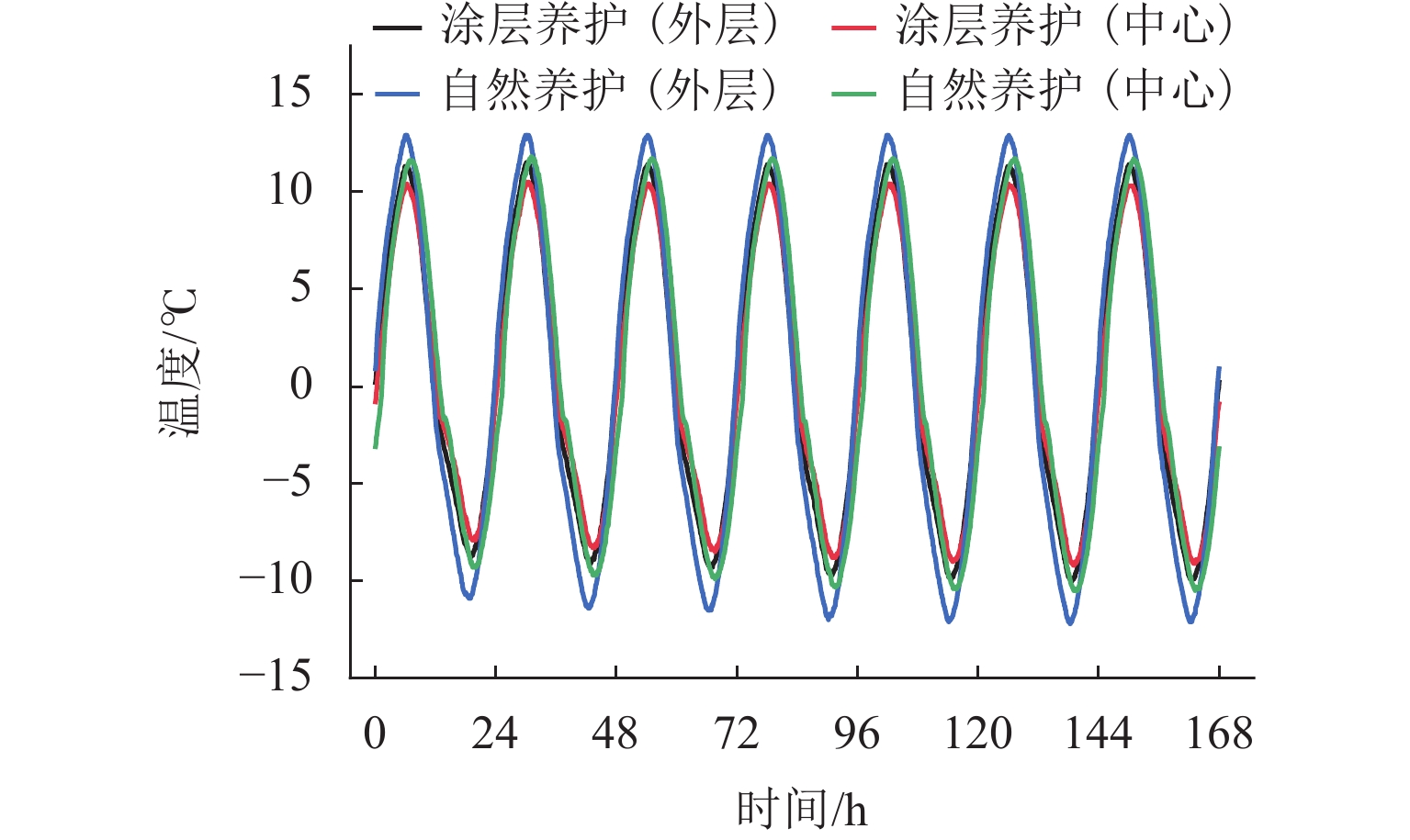
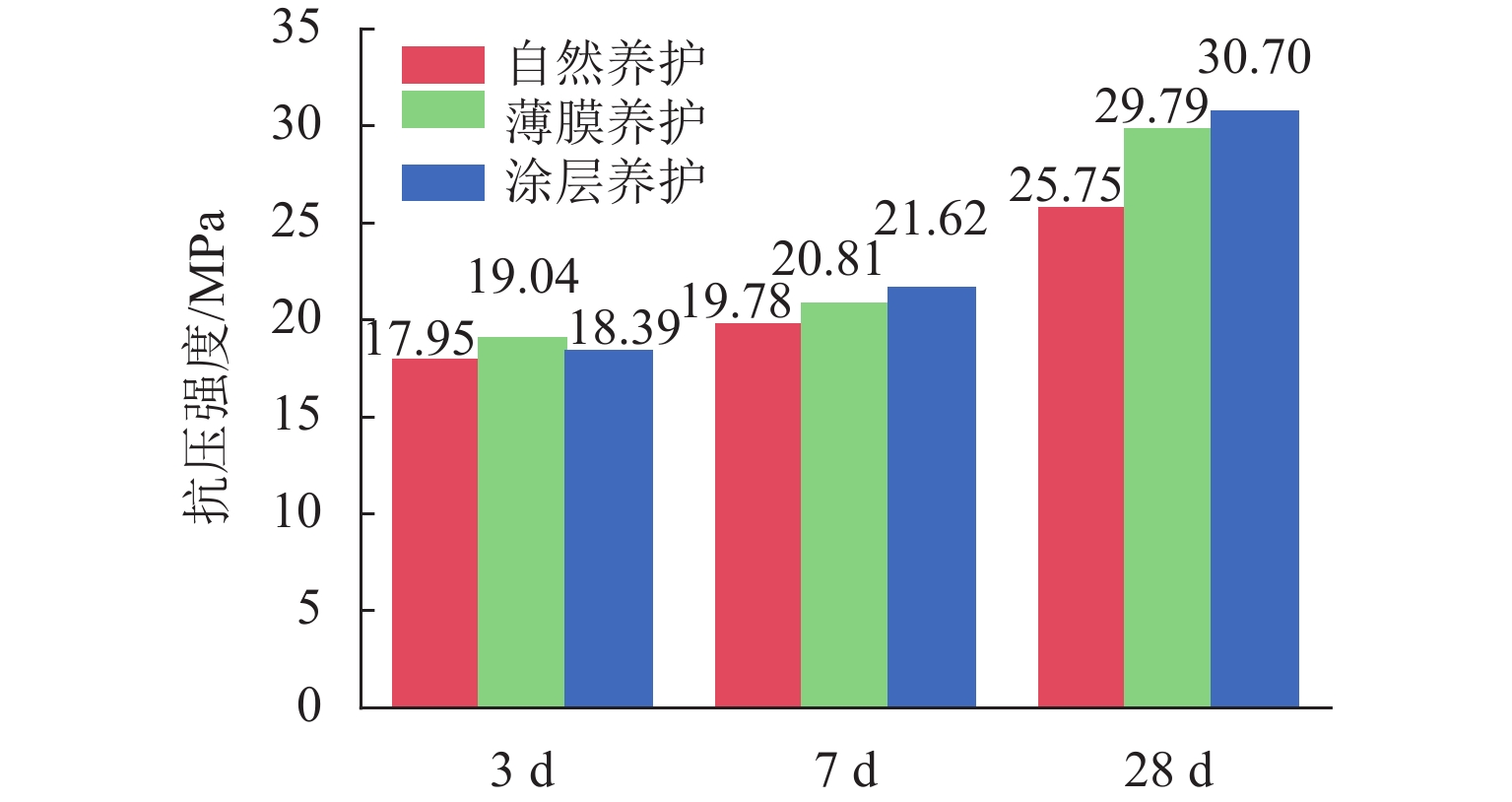
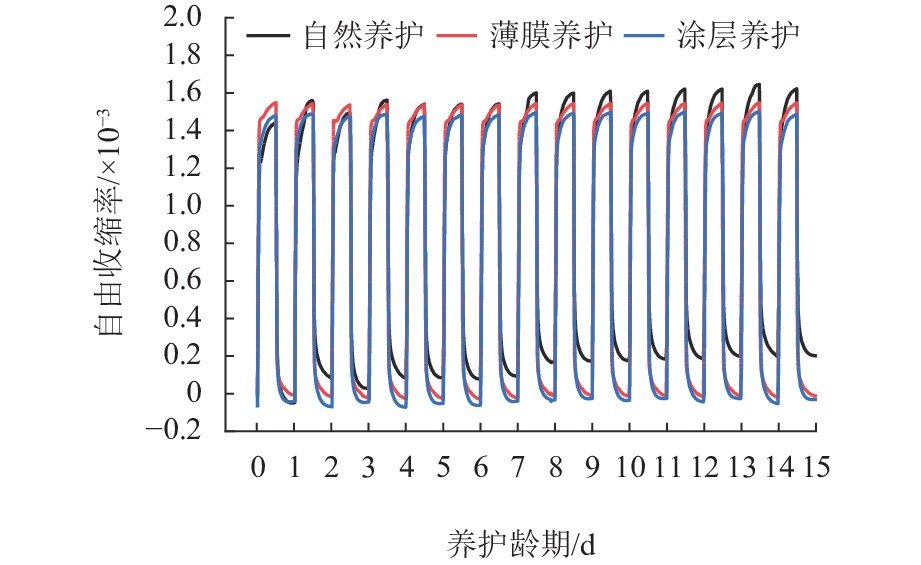
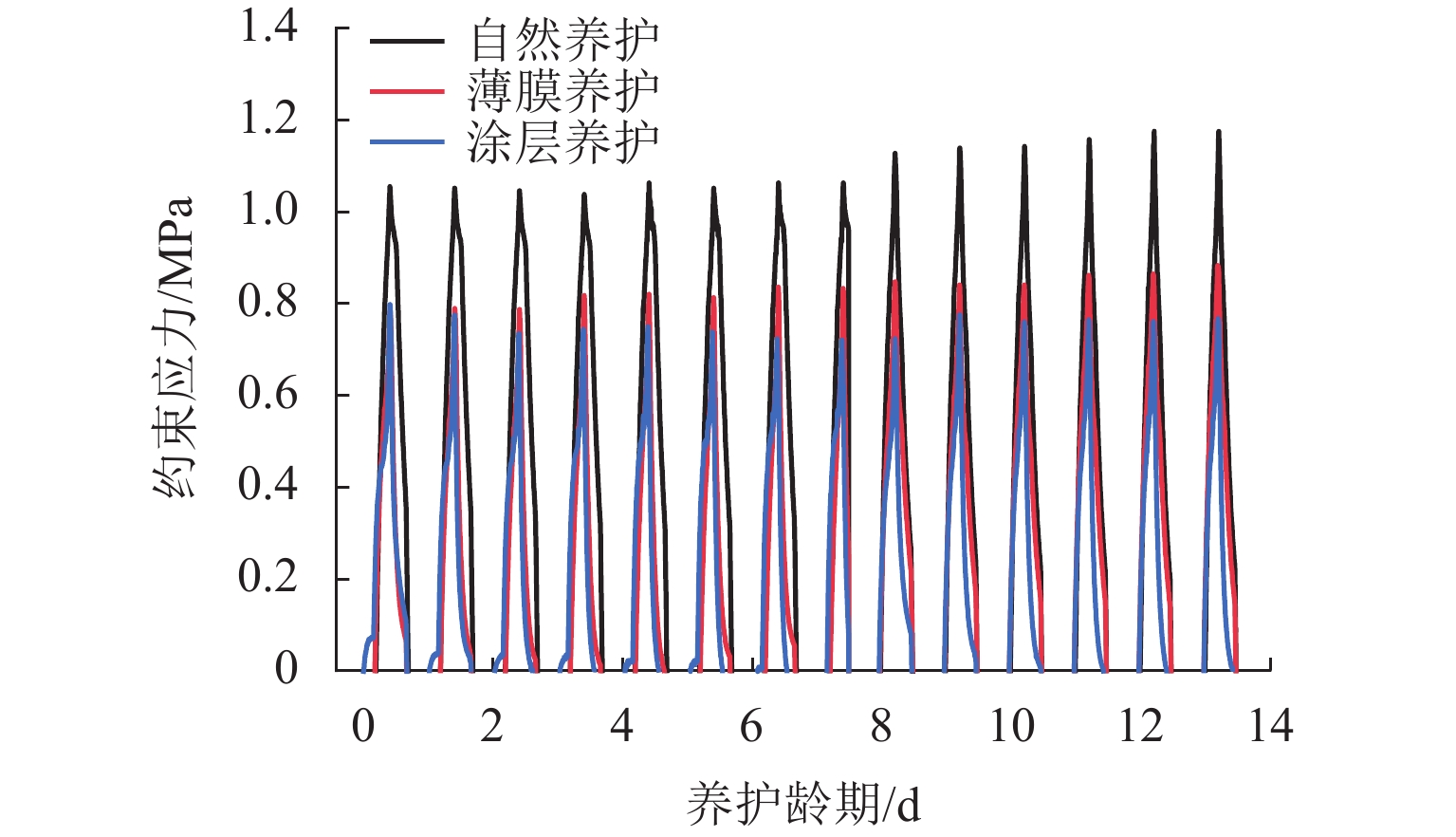
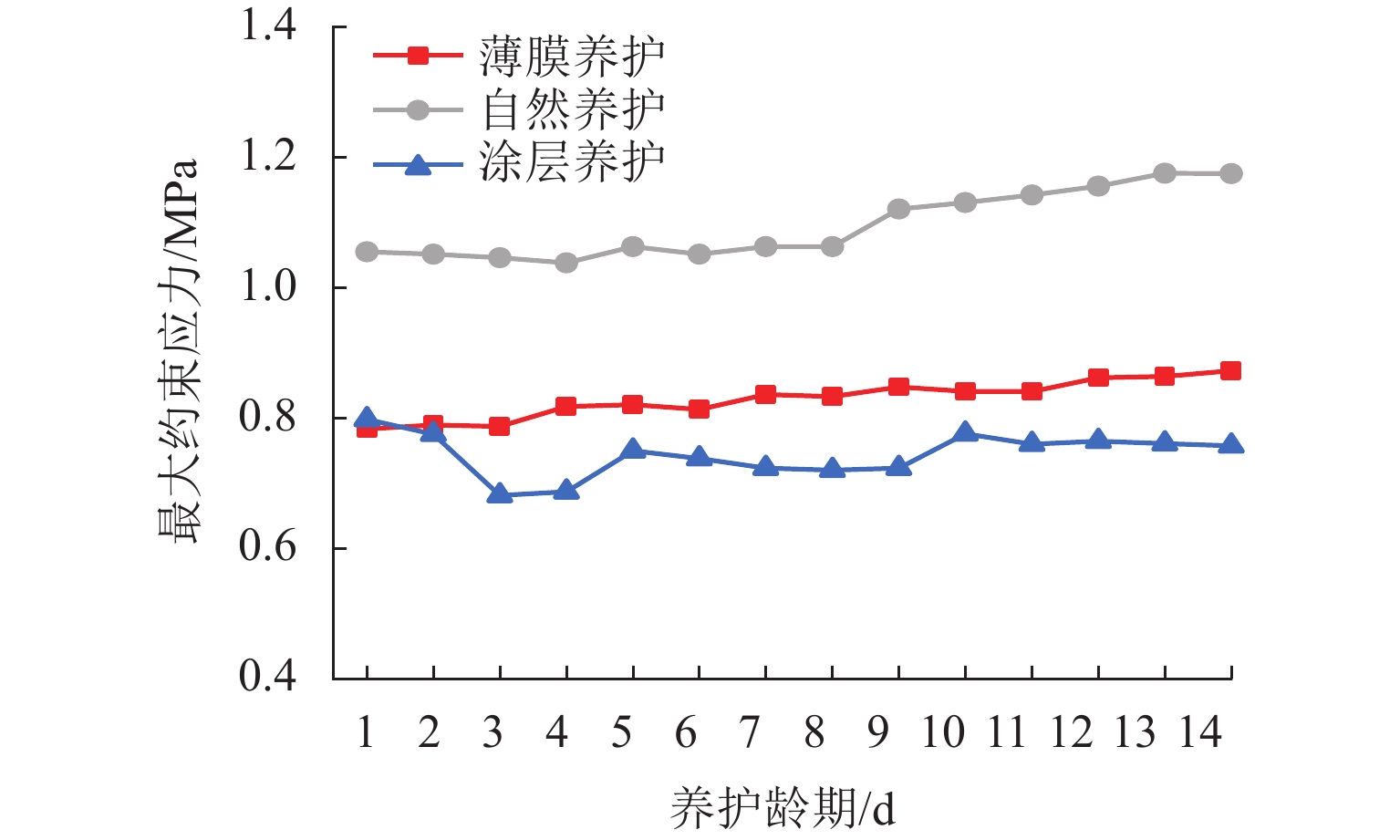
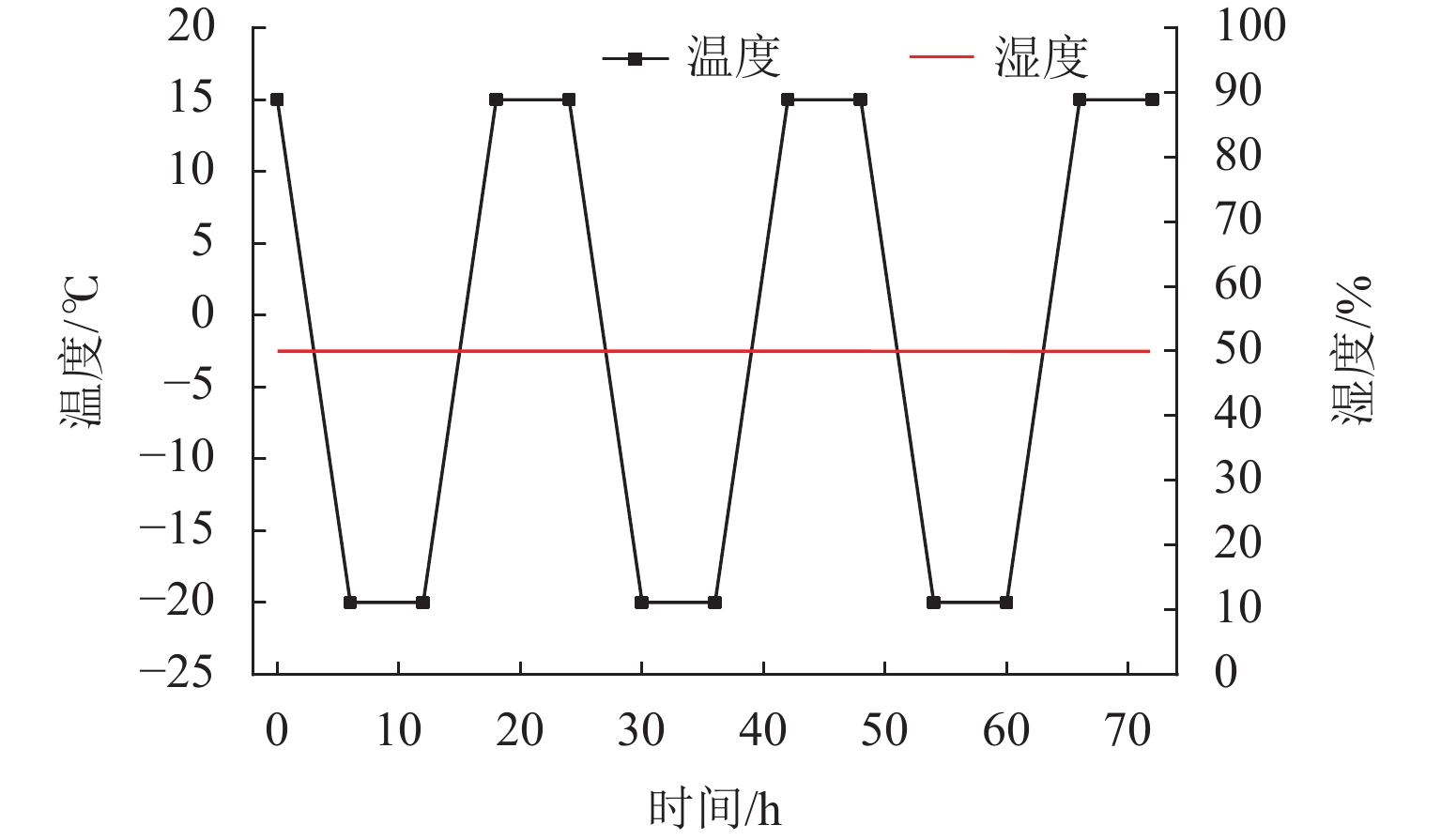
为探究干寒大温差下早龄期混凝土收缩变形规律,降低开裂风险,采用3种养护方法对混凝土进行早龄期养护,以抗压强度、劈裂抗拉强度、自由收缩率及最大约束应力为表征手段,设置了基本力学性能试验、自由收缩试验与约束收缩试验,并采用综合型多指标的灰色关联法分析了不同养护方式下混凝土的抗裂性能. 同时,设计了纳米涂层保温性能试验,探究其对混凝土的保温隔热性能. 试验结果表明:在−20.0~15.0 ℃的循环温度中,采用纳米涂层使得圆柱体混凝土试件内部平均温差降低2.95 ℃;相比于标准养护,3种养护方式下混凝土抗压及劈裂抗拉强度均有显著降低,干寒大温差不利于混凝土的强度发展;自由收缩率随温度变化明显,呈现出温度降低,自由收缩率增大,反之,温度升高自由收缩率减小,并在−20.0 ℃与15.0 ℃时出现极值;最大约束应力受到养护方式影响,自然养护下最大约束应力发展最快,终值最大,薄膜养护次之,涂层养护最大约束应力发展最慢,终值最小;涂层养护下灰色关联度高达0.9149,明显高于自然养护与薄膜养护,表现出优异的抗裂性能.
Abstract:In order to explore the shrinkage and deformation laws of early-age concrete under large dry-cold temperature differences and reduce the risk of cracking, three curing methods were used for early-age curing of concrete. The compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, free shrinkage rate, and maximum restraint stress were used as the characterization methods. Basic mechanical performance test, free shrinkage test, and restraint shrinkage test were designed. The comprehensive multi-index grey correlation method was adopted to analyze the anti-cracking performance of concrete under different curing methods. In addition, a nano-coating thermal insulation performance test was designed to explore its thermal insulation performance on concrete. The test results show that the use of nano-coating reduces the average temperature difference inside the cylindrical concrete specimen by 2.95 ℃ in the circulating temperature of ‒20.0–15.0 ℃; compared with those under standard curing, the compressive and splitting tensile strengths of concrete under the three curing methods are significantly reduced, and the large dry-cold temperature difference is not conducive to the strength development of concrete. The free shrinkage rate changes significantly with temperature. Specifically, as the temperature decreases, the free shrinkage rate increases, and as the temperature rises, the free shrinkage rate decreases. In addition, extreme values appear at ‒20.0 ℃ and 15.0 ℃; the maximum restraint stress is affected by the curing method. Under natural curing, the maximum restraint stress develops the fastest, with the largest final value, followed by that under film curing. Under coating curing, the maximum restraint stress develops the slowest, with the smallest final value. The gray correlation degree under coating curing is as high as 0.9149, which is significantly higher than that under natural curing and film curing, showing excellent anti-cracking performance.
-
Key words:
- early-age concrete /
- curing method /
- strength /
- shrinkage /
- anti-cracking performance
-
表 1 涂层保温性能试验设计表
Table 1. Test design table of coating thermal insulation performance
试件编号 循环温度/℃ 保温隔热涂层厚度/mm 测试时长/d 试件个数/个 底涂层 中涂层 面涂层 总厚度 1 −20.0~15.0 0.1 1.0 0.1 1.2 7 2 2 −20.0~15.0 7 2 表 2 混凝土各项性能测试结果汇总
Table 2. Summary of concrete performance test results
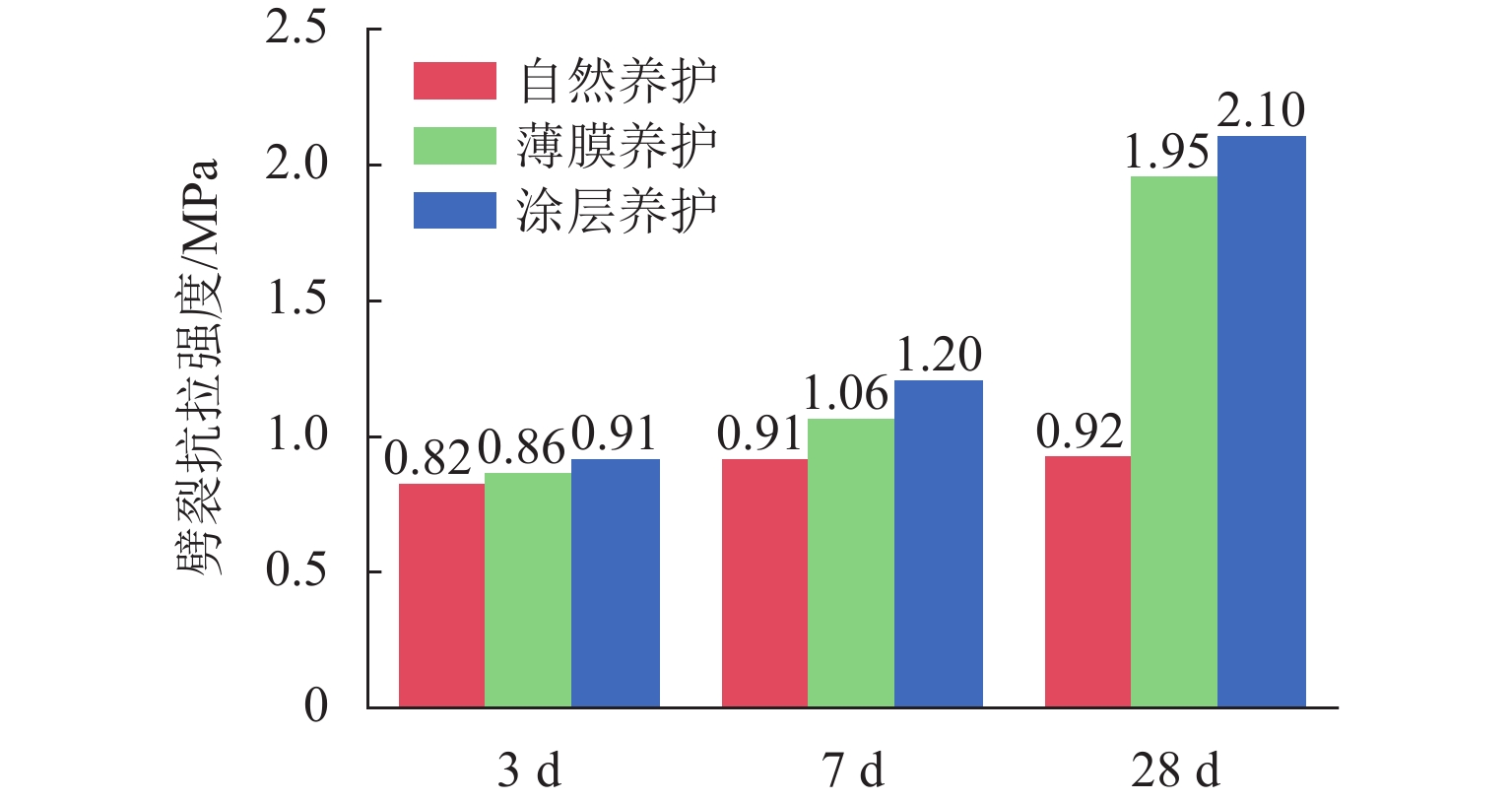
养护方式 劈裂抗拉
强度/MPa抗压强
度/MPa最大自由
收缩率/ × 10−3最大约束
应力/MPa自然养护 0.91 19.78 1.601 1.06 薄膜养护 1.06 20.81 1.544 0.84 涂层养护 1.20 21.62 1.494 0.72 表 3 矩阵判断各元素选取标准[24]
Table 3. Judgement matrix criteria for selecting each element
标度值 意义 1 X ai 与 Xjb 重要性相同 3 Xai 比 Xjb 稍重要 5 X ai 比 Xjb 明显重要 2、4 Xai 比 Xjb 重要性介于相邻标度值之间 上面各行标度
值的倒数相比于 X ai、Xjb 的重要性 -
[1] 赵文斌,刘建勋,张戎令,等. 强风、干寒、大温差地区混凝土箱梁早期抗裂性分析[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2016,35(10): 3253-3257,3273.ZHAO Wenbin, LIU Jianxun, ZHANG Rongling, et al. Strongly windy and dry cold large temperature difference analysis on early cracking of concrete box girder[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 35(10): 3253-3257,3273. [2] 陈华鑫,王铜,何锐,等. 高原复杂气候环境对混凝土气孔结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(2): 30-37.CHEN Huaxin, WANG Tong, HE Rui, et al. Effect of complex climatic environment on pore structure and mechanical properties of concrete[J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 40(2): 30-37. [3] 胡玉兵,曹瑞普. 高原地区混凝土内外部结构性能的差异性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2017,36(增1): 213-218.HU Yubing, CAO Ruipu. Differences of internal and external structural properties of concrete in the plateau area[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 36(S1): 213-218. [4] AL-SALEH S A, AL-ZAID R Z. Effects of drying conditions, admixtures and specimen size on shrinkage strains[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2006, 36(10): 1985-1991. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.11.005 [5] TORRENTI J M, GRANGER L, DIRUY M, et al. Modeling concrete shrinkage under variable ambient conditions[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1999, 96(1): 35-39. [6] EMBORG M, BERNANDER S. Assessment of risk of thermal cracking in hardening concrete[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1994, 120(10): 2893-2912. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1994)120:10(2893) [7] TENG L W, HUANG R, CHEN J, et al. A study of crystalline mechanism of penetration sealer materials[J]. Materials, 2014, 7(1): 399-412. doi: 10.3390/ma7010399 [8] SALAZAR-HERNÁNDEZ C, ALQUIZA M J P, SALGADO P, et al. TEOS-colloidal silica-PDMS-OH hybrid formulation used for stone consolidation[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2010, 24(6): 481-488. [9] CERVANTES J, ZARRAGA R, SALAZAR-HERNANDEZ C. ChemInform abstract: organotin catalysts in organosilicon chemistry[J]. ChemInform, 2012, 43(39): 157-163. [10] 张戎令,王起才,刘树红,等. 极端大温差、干旱戈壁地区桥墩养护方法研究[J]. 兰州交通大学学报,2014,33(4): 49-55.ZHANG Rongling, WANG Qicai, LIU Shuhong, et al. Research on method of pier maintenance in gobi region of extreme large temperature difference and drought[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2014, 33(4): 49-55. [11] 高鹏,陈阳,黄浩良,等. 干燥环境下混凝土内部损伤的量化[J]. 硅酸盐学报,2021,49(2): 312-322.GAO Peng, CHEN Yang, HUANG Haoliang, et al. Quantification of damage in concrete under drying condition[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2021, 49(2): 312-322. [12] 魏亚,郑小波,郭为强. 干燥环境下内养护混凝土收缩、强度及开裂性能[J]. 建筑材料学报,2016,19(5): 902-908.WEI Ya, ZHENG Xiaobo, GUO Weiqiang. Shrinkage, strength development and cracking of internally cured concrete exposed to dry conditions[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2016, 19(5): 902-908. [13] 中国建筑科学研究院有限公司. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019. [14] 中国建筑科学研究院. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. [15] QIN Y, YI Z J, WANG W N, et al. Time-dependent behavior of shrinkage strain for early age concrete affected by temperature variation[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 2017: 1-7. [16] 曾启. 温度循环作用后混凝土力学性能试验研究及破坏机理分析[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. [17] 邵爽爽. 蒸养混凝土超早龄期性能与开裂分析[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2019. [18] 苏安双. 高性能混凝土早期收缩性能及开裂趋势研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008. [19] CORTAS R, ROZIÈRE E, STAQUET S, et al. Effect of the water saturation of aggregates on the shrinkage induced cracking risk of concrete at early age[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014, 50: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.02.006 [20] LI H, LIU J P, WANG Y J, et al. Deformation and cracking modeling for early-age sidewall concrete based on the multi-field coupling mechanism[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 88: 84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.03.005 [21] 王树和,水中和,玄东兴. 大温差环境条件下混凝土表面裂缝损伤[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),2006,36(增2): 122-125.WANG Shuhe, SHUI Zhonghe, XUAN Dongxing. Investigation on surface cracking damage of concrete under big temperature difference[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 36(S2): 122-125. [22] ALY T, SANJAYAN J G. Mechanism of early age shrinkage of concretes[J]. Materials and Structures, 2009, 42(4): 461-468. doi: 10.1617/s11527-008-9394-6 [23] 张强勇,王保群,向文. 盐岩地下储气库风险评价层次分析模型及应用[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(8): 2299-2306.ZHANG Qiangyong, WANG Baoqun, XIANG Wen. Hierarchical analytical model of risk evaluation for underground salt rock gas storage and its application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(8): 2299-2306. [24] 王卓甫. 工程项目风险管——理论、方法与应用[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2003. -




 下载:
下载: