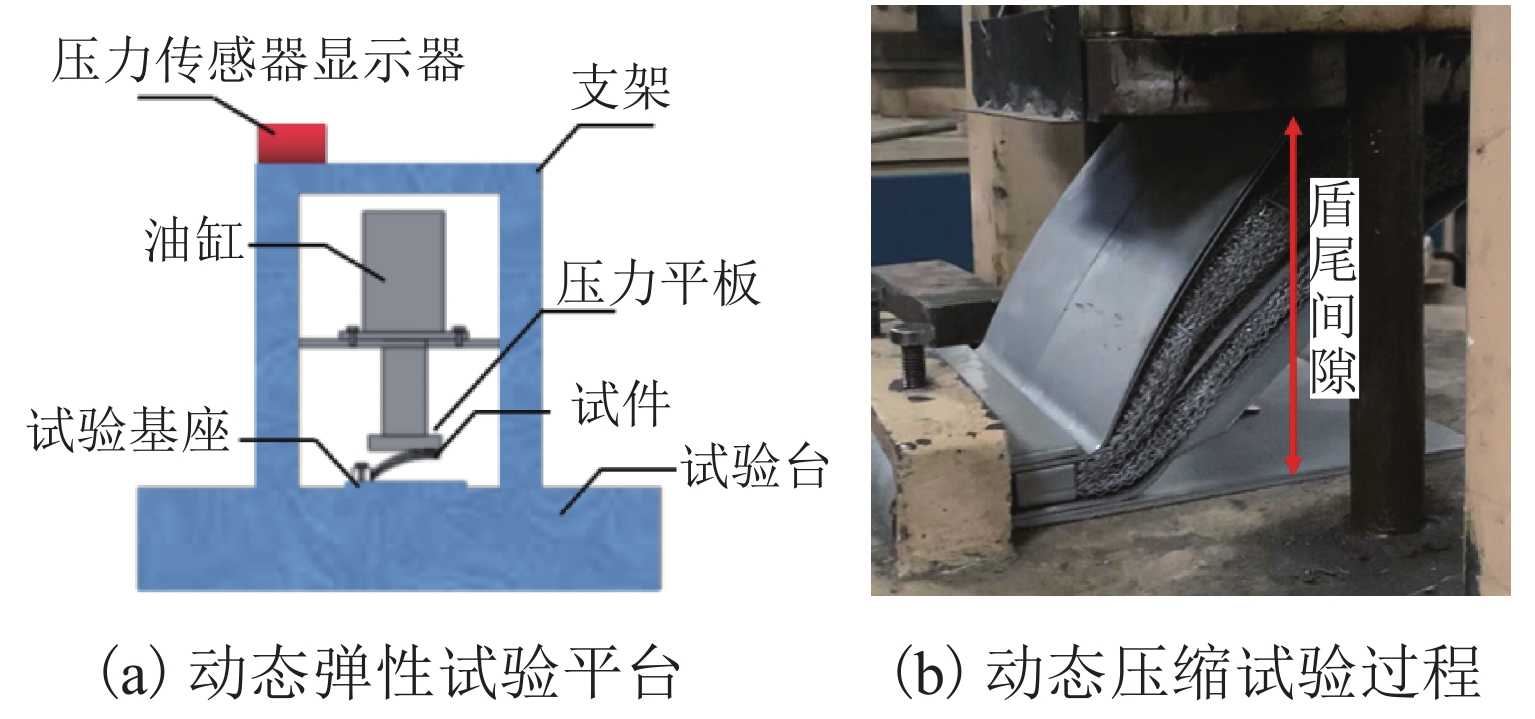
Analysis of Sealing Performance of Shield Tail Brush Based on Compression and Grease Escape Test
-
摘要:
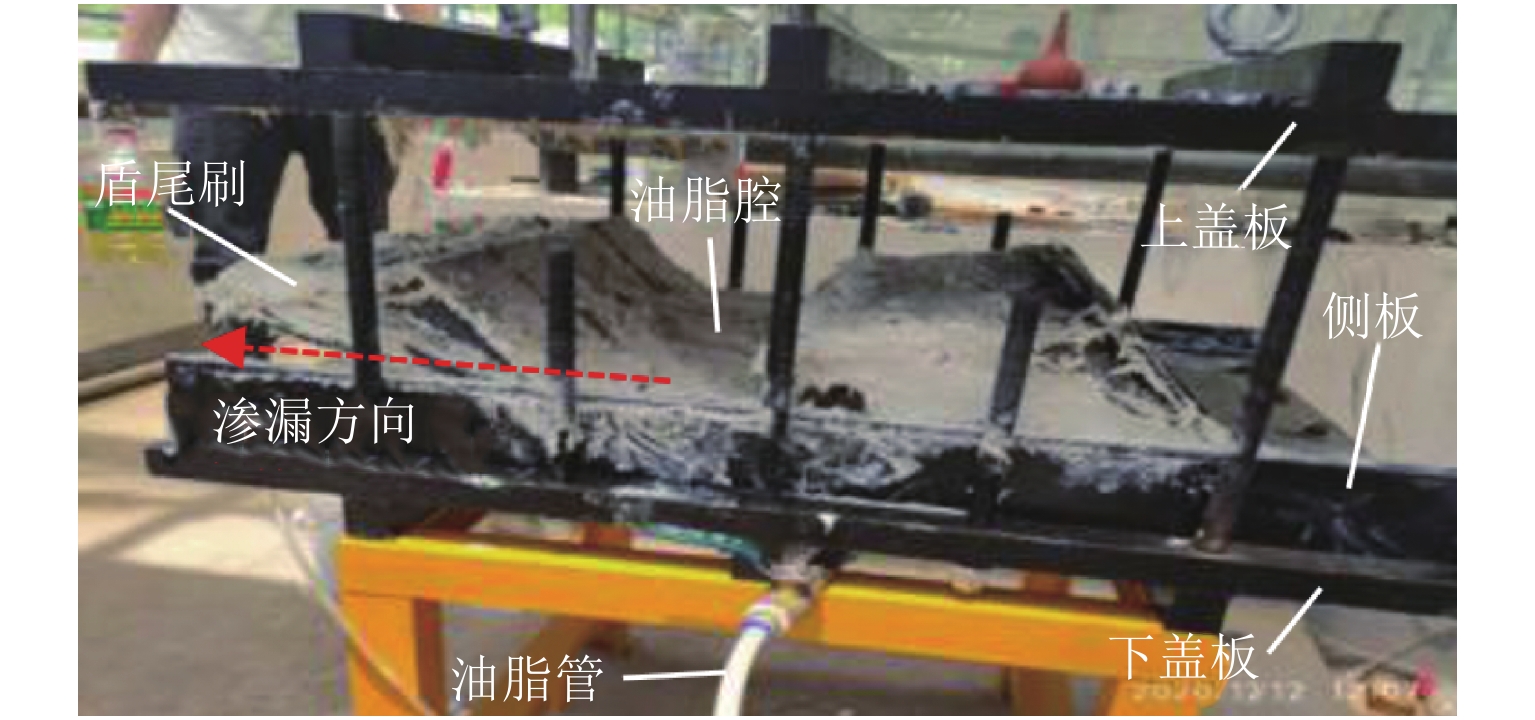
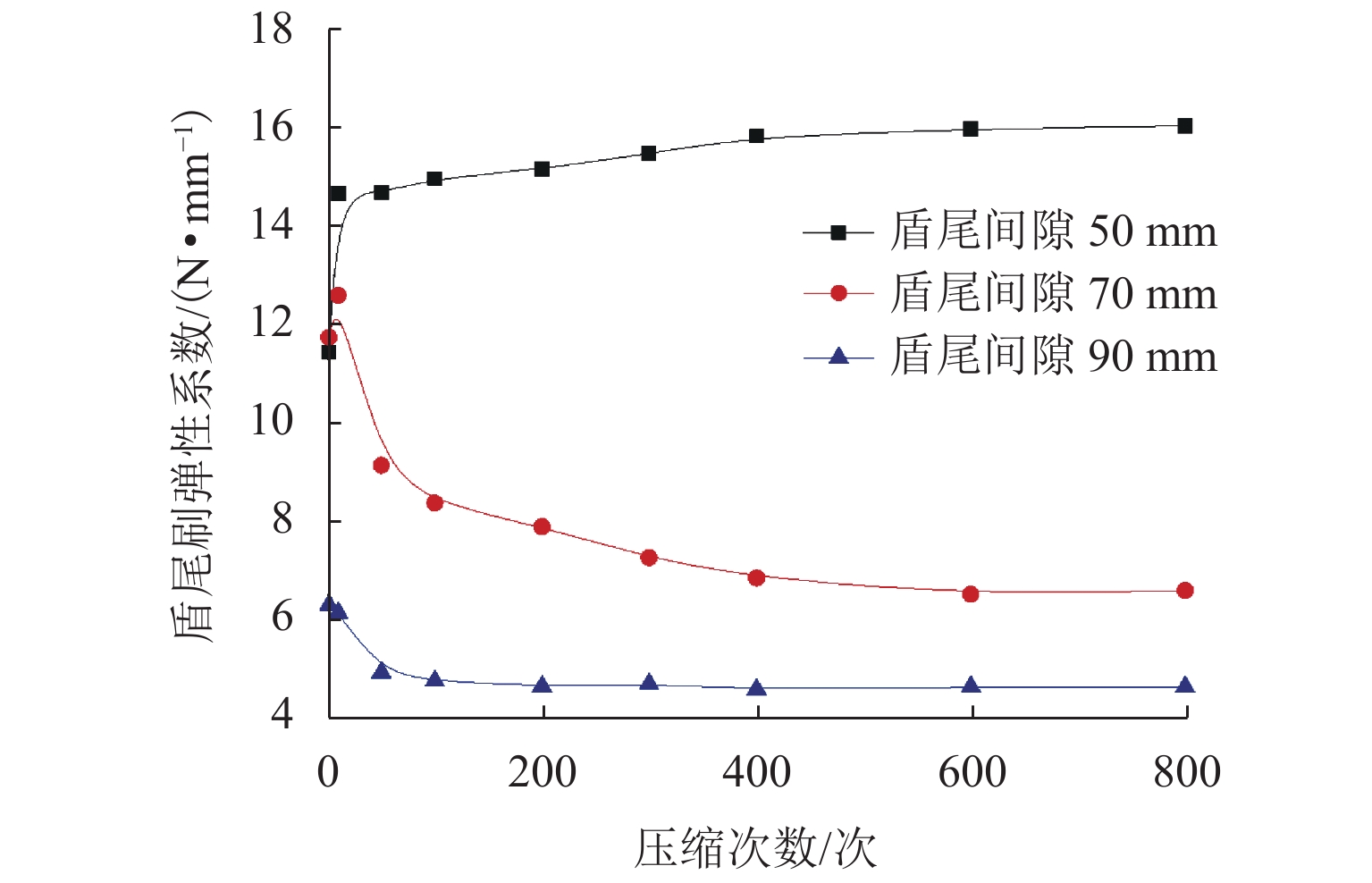
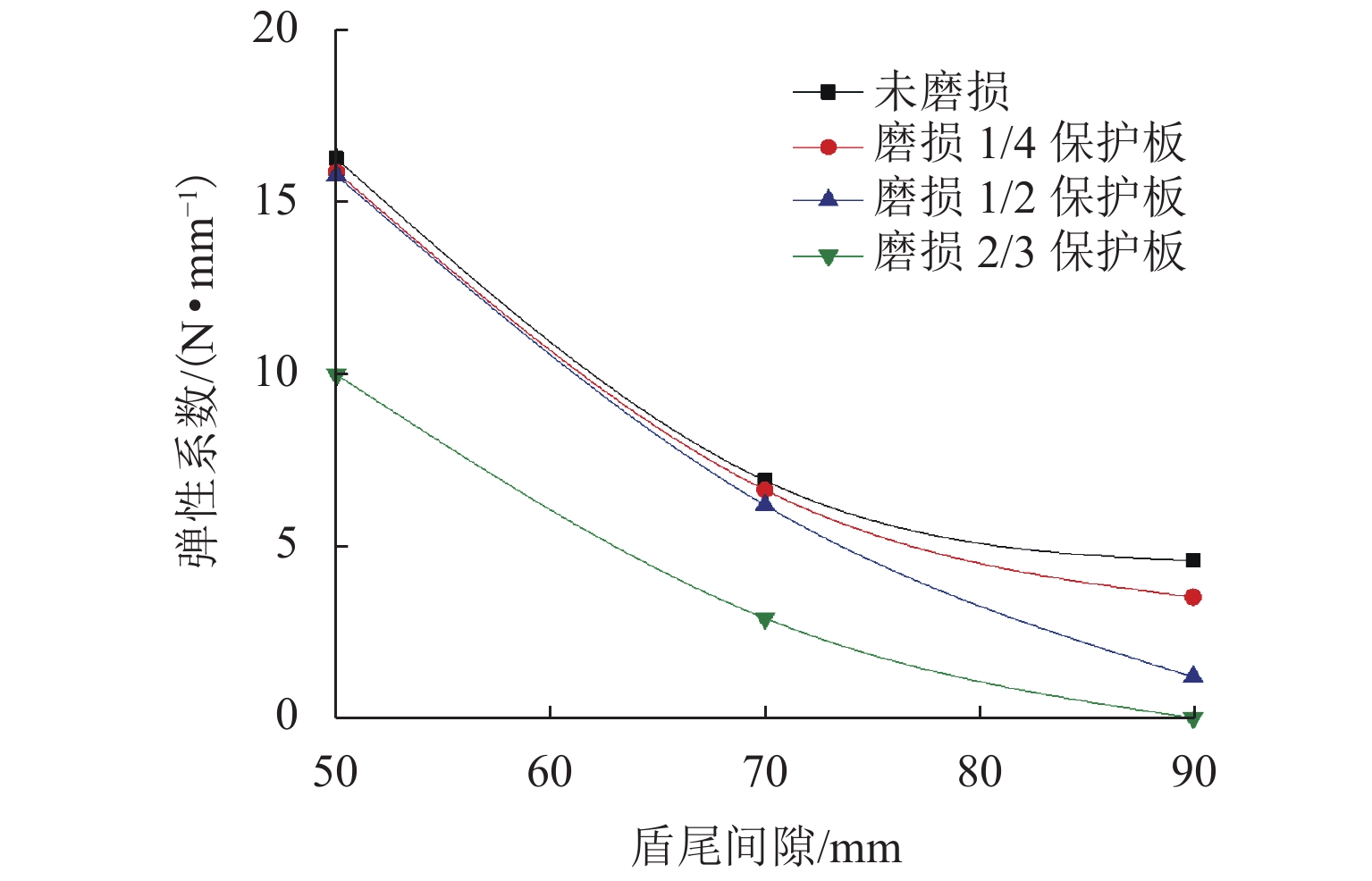
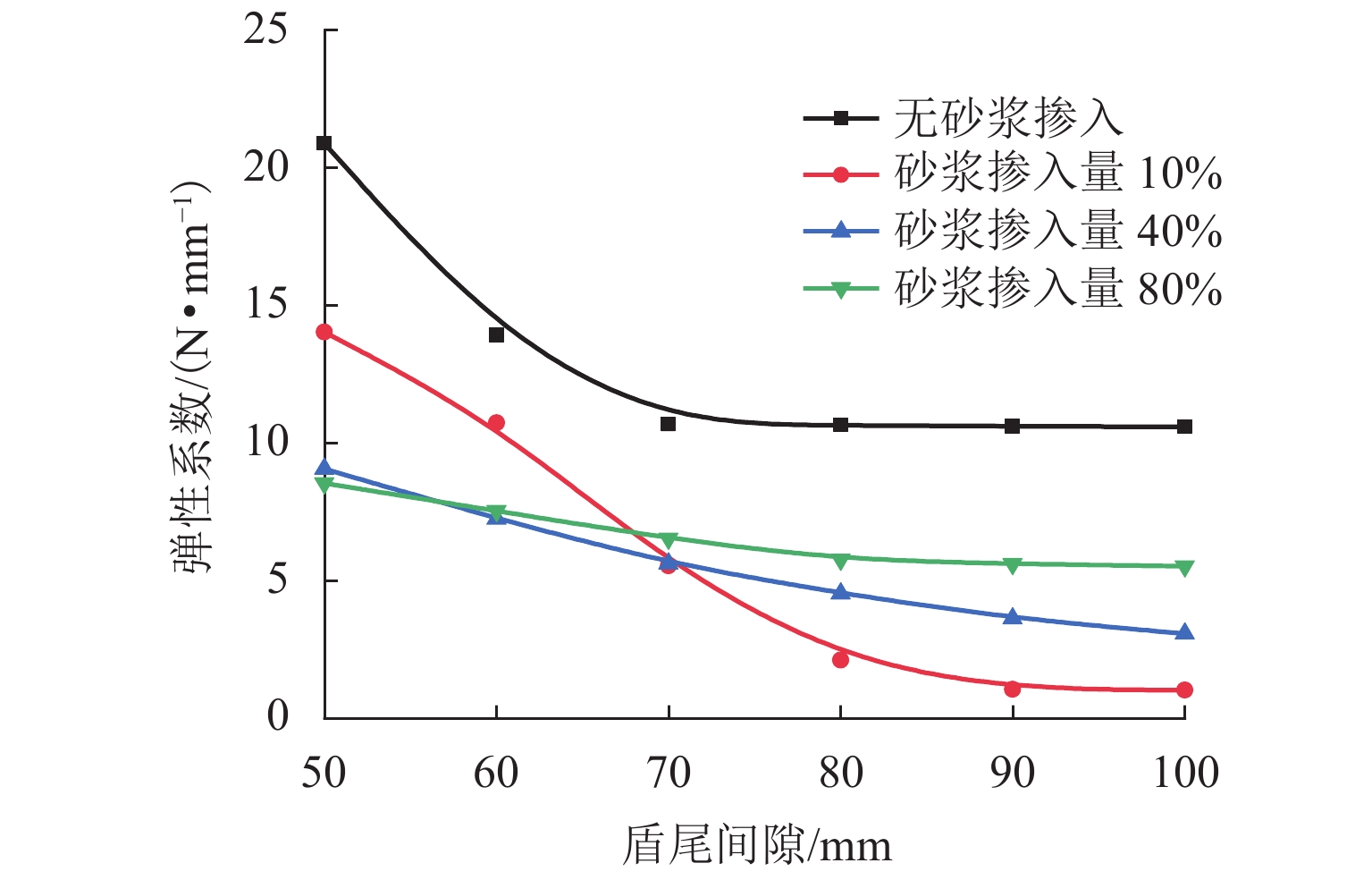
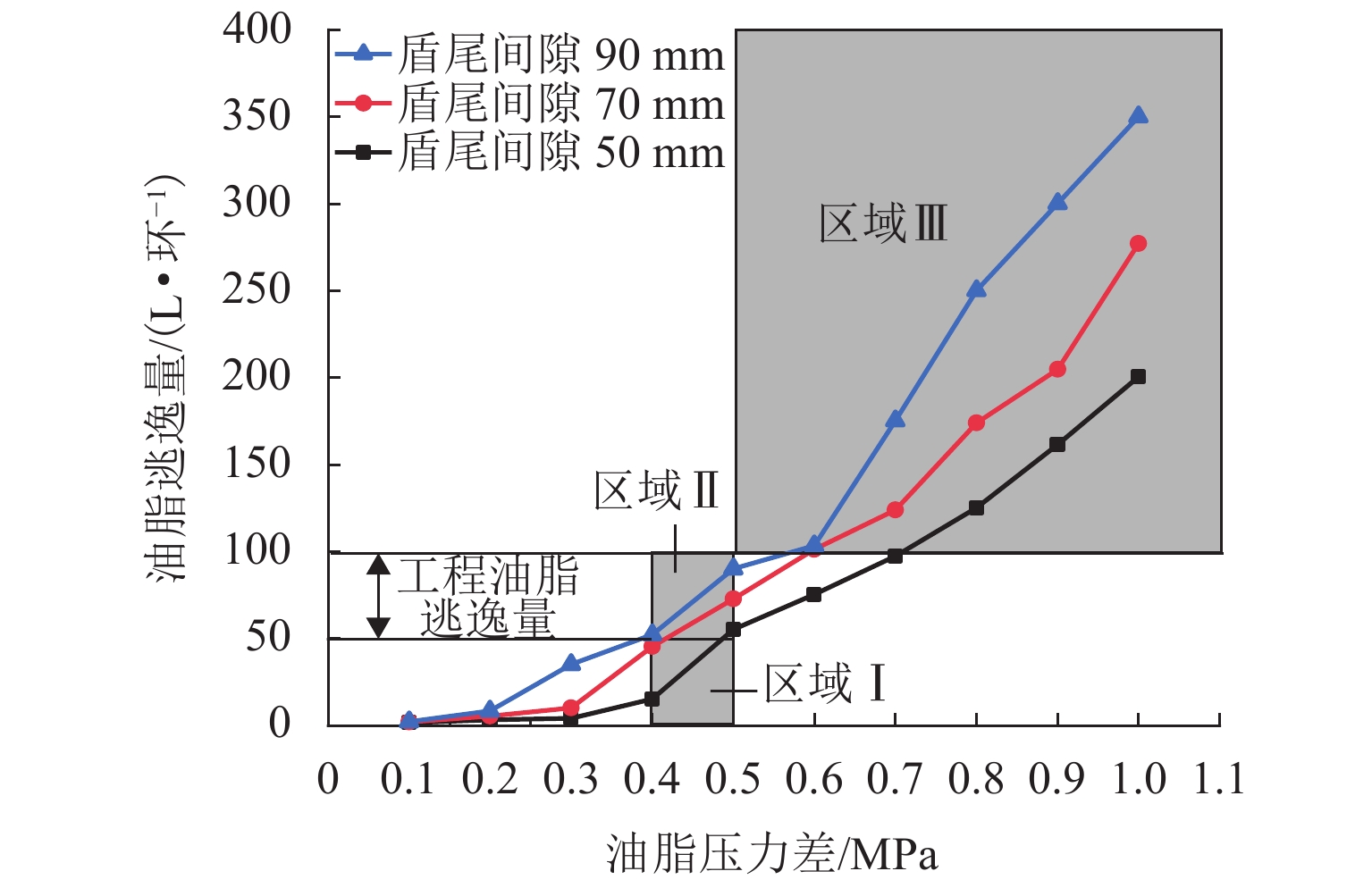
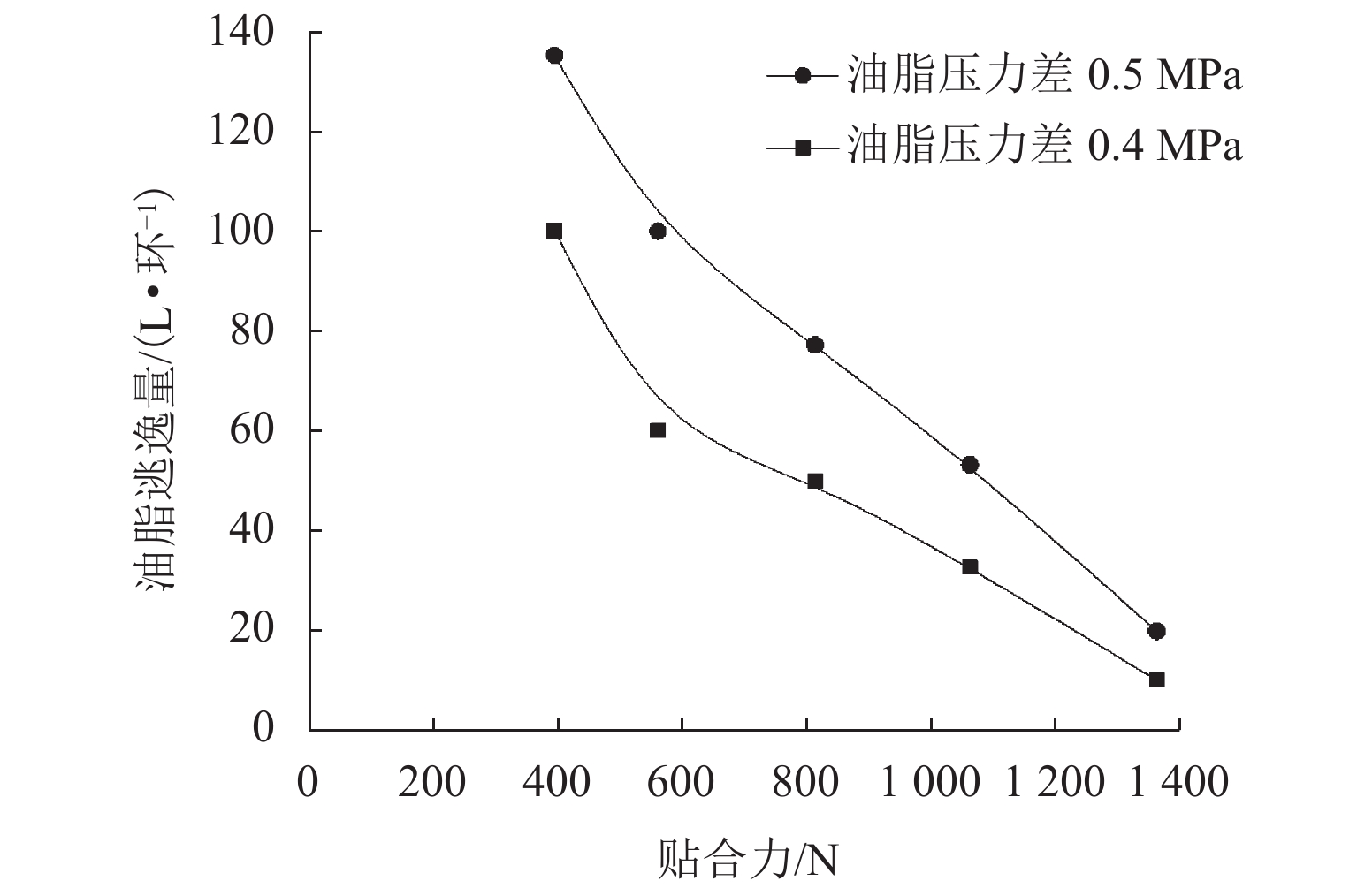
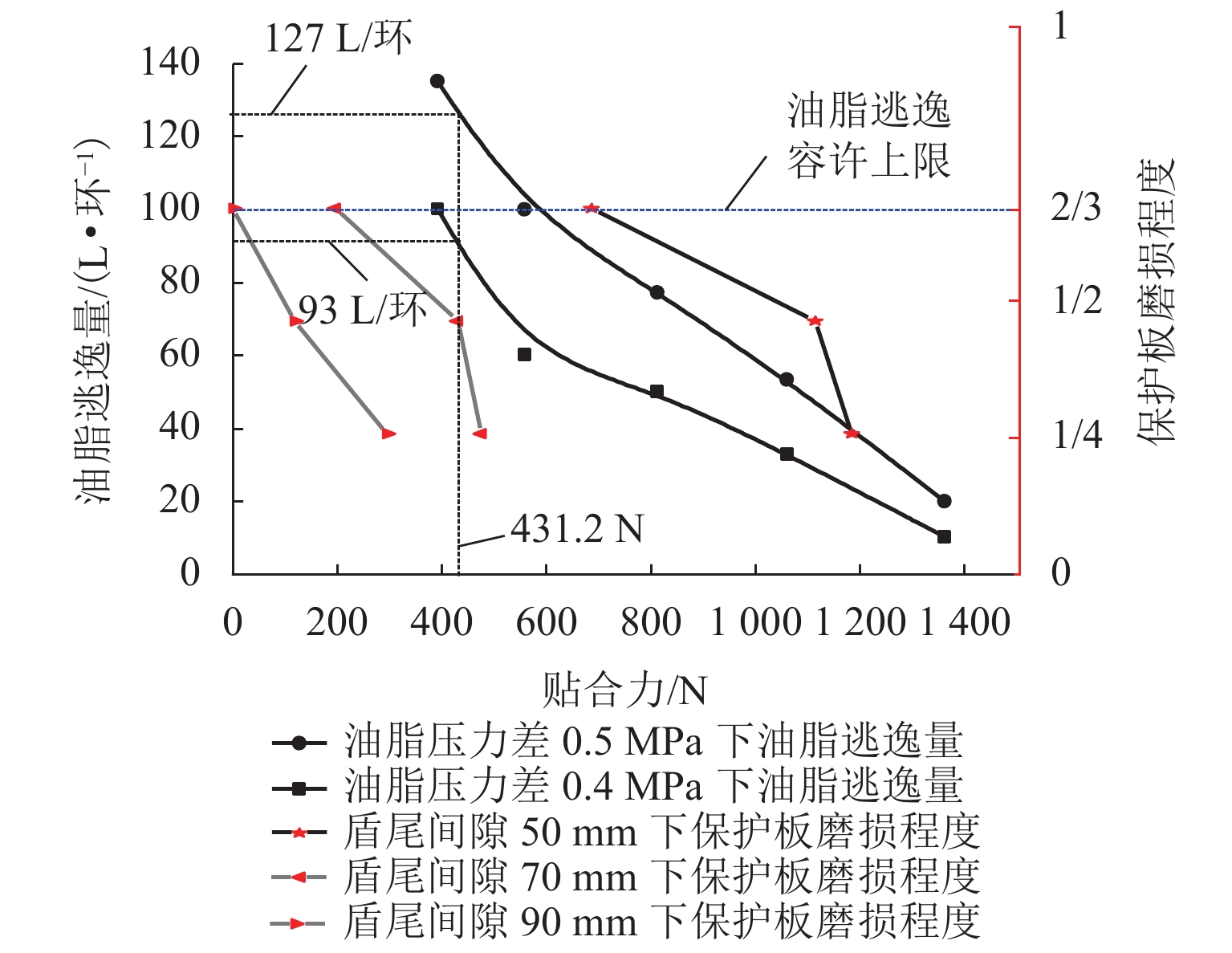
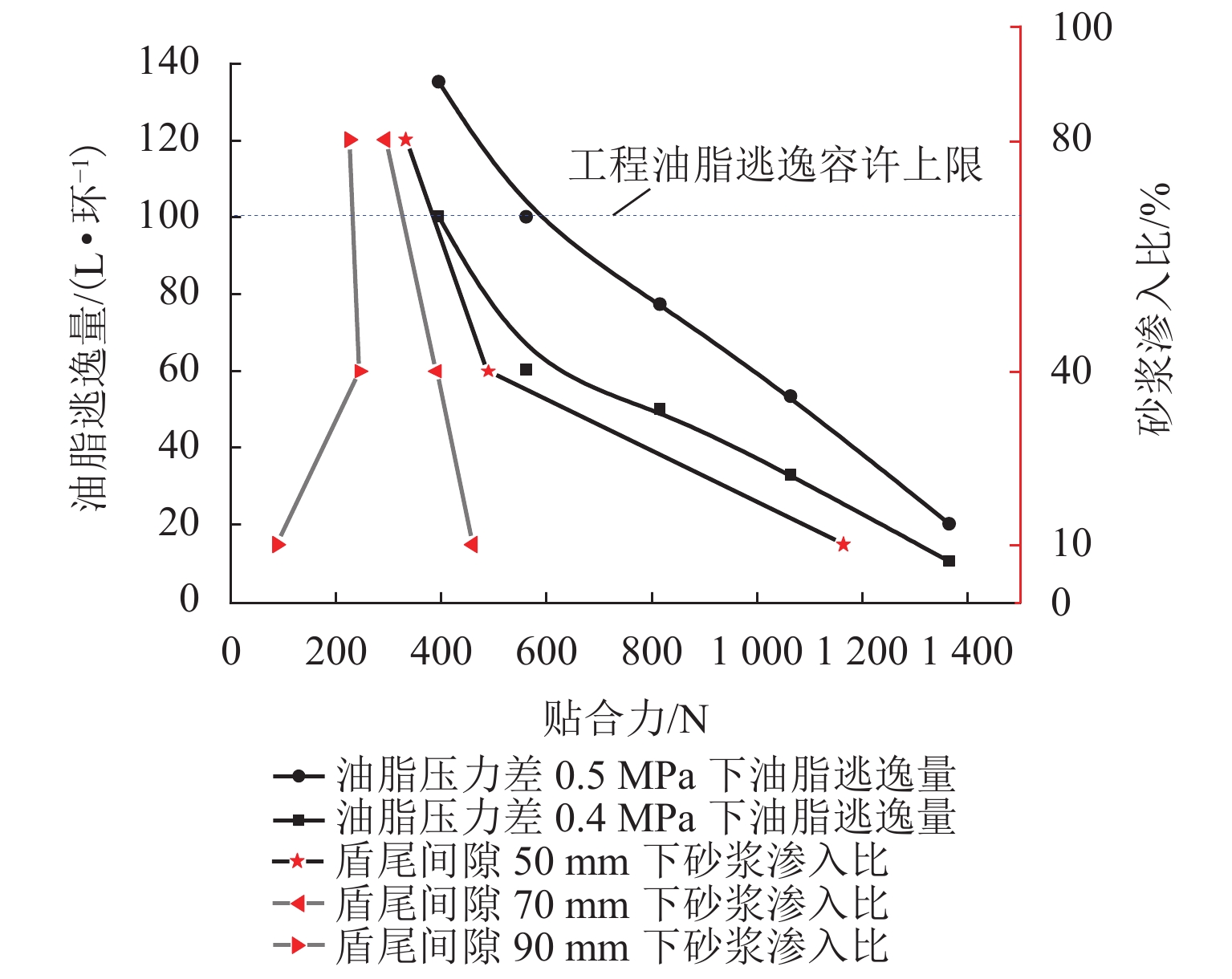
为研究盾尾刷质量问题对盾尾刷密封系统工作性能的影响,基于动态压缩试验与油脂逃逸试验,探讨了盾尾刷长期挤压、磨损程度、砂浆渗入对盾尾刷密封性能的影响机理. 首先,通过动态压缩试验,获得各个影响因素下盾尾刷贴合力变化规律;其次,利用油脂逃逸试验获取不同工况下盾尾刷的油脂逃逸量;最后,以贴合力为媒介,将影响盾尾刷质量的因素与油脂逃逸量联系起来,探讨盾尾刷的密封性能. 研究结果表明:长期挤压、盾尾刷磨损程度、砂浆渗入等因素对盾尾刷弹性性能的影响显著,尤其是砂浆渗入,盾尾刷弹性性能损失最大可达90%;油脂压力存在一临界压力,盾尾间隙为50、70、90 mm的临界油脂压力分别为0.4、0.3、0.2 MPa,低于临界压力时油脂逃逸量极少,超过临界压力时油脂逃逸量陡增,油脂压力增加0.1 MPa,油脂逃逸量增加4倍以上;在盾构平均盾尾间隙(70 mm)条件下,当保护板磨损超过1/2与砂浆渗入比超过10%时,油脂逃逸将超过工程容许上限.
Abstract:In order to study the effect of the quality of shield tail brush on the working performance of shield tail sealing system, based on dynamic compression test and grease escape test, the influence mechanism of long-term extrusion, wear degree of shield tail brush and mortar penetration on sealing performance of shield tail brush are revealed. Firstly, the variation law of the adhesion force of shield tail brush under various influencing factors is discussed based on the dynamic compression test. Secondly, the grease escape volume of shield tail brush under different working conditions is obtained by grease escape test. Finally, taking the adhesion force as the medium, the factors affecting the quality of shield tail brush are connected with the volume of grease escape, and the sealing performance of shield tail brush is discussed. The results show that, long-term extrusion, wear degree of shield tail brush and mortar penetration ratio have significant effects on the elastic properties of shield tail brush, especially the mortar penetration ratio can cause the elastic property loss up to 90%. There is a critical pressure in the grease pressure, and the critical grease pressure with shield tail clearance of 50, 70, 90 mm is 0.4, 0.3, 0.2 MPa respectively. When grease pressure is lower than the critical pressure, the volume of grease escape is very small. When it exceeds the critical pressure, the volume of grease escape increases sharply. The grease pressure further increases by 0.1 MPa, the volume of grease escape increases by more than 4 times. Under the condition of average shield tail clearance (70 mm), the volume of grease escape exceeds the allowable upper limit when the wear of protective plate exceeds 1/2 and the mortar penetration ratio exceeds 10%.
-
Key words:
- shield tunnel /
- shield tail brush /
- dynamic compression /
- grease escape /
- sealling
-
表 1 正常盾尾刷的贴合力与残余高度
Table 1. Adhesion force and residual height of normal shield tail brush
压缩次数/次 盾尾间隙 50 mm 盾尾间隙 70 mm 盾尾间隙 90 mm 贴合力/N 残余高度/mm 贴合力/N 残余高度/mm 贴合力/N 残余高度/mm 1 1509.2 182.0 1303.4 186.0 588.0 183.0 10 1479.8 151.0 1195.6 170.0 548.8 179.0 50 1430.8 147.5 850.6 168.0 431.2 177.0 100 1421.0 145.0 754.6 165.0 411.6 176.0 200 1401.4 142.5 695.8 163.0 401.8 176.0 300 1391.6 140.0 637.0 162.5 401.8 175.0 400 1391.6 138.0 597.8 162.0 392.0 175.0 600 1372.0 136.0 558.6 160.5 392.0 174.0 800 1362.2 135.0 558.6 159.5 392.0 174.0 表 2 磨损盾尾刷的贴合力与残余高度
Table 2. Adhesion force and residual height of worn shield tail brush
保护板磨损程度 盾尾间隙 50 mm 盾尾间隙 70 mm 盾尾间隙 90 mm 贴合力/N 残余高度/mm 贴合力/N 残余高度/mm 贴合力/N 残余高度/mm 未磨损 1392.4 136.0 597.8 157.0 382.2 174.0 磨损 1/4 1185.0 125.0 475.2 142.0 294.0 174.0 磨损 1/2 1114.7 121.0 431.2 140.0 117.6 189.0 磨损 2/3 686.0 119.0 196.0 138.0 0 190.0 表 3 不同工况下的盾尾刷贴合力
Table 3. Adhesion force of shield tail brush under different working conditions
N 盾尾间隙/mm 砂浆渗入比/% 0 10 40 80 50 1391.6 1164.8 490.0 333.2 60 1136.8 891.8 490.0 333.2 70 602.3 460.0 392.2 294.2 80 502.1 176.4 303.8 254.8 90 391.2 88.2 245.0 225.4 100 245.0 85.4 196.0 219.3 表 4 盾尾刷密封性统计
Table 4. Sealing performance statistics of shield tail brush
盾尾刷弹性影响因素 油脂逃逸量/(L•环−1) 磨损程度 保护板磨损 1/4 75~110 保护板磨损 1/2 80~125 保护板磨损 2/3 120~200 渗入比 砂浆渗入 10% 80~125 砂浆渗入 40% 90~130 砂浆渗入 80% 105~150 -
[1] 崔玖江. 盾构隧道施工风险与规避对策[J]. 隧道建设,2009,29(4): 377-396.CUI Jiujiang. Risks and countermeasures for construction of shield-bored tunnels[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2009, 29(4): 377-396. [2] 潘国庆. 隧道施工中盾构盾尾密封渗漏风险源分析[J]. 中国市政工程,2008(5): 59-60,93.PAN Guoqing. Analysis of risk sources in seal leakage at shield tail during tunneling[J]. China Municipal Engineering, 2008(5): 59-60,93. [3] KAWASAKI M, YOSHIZAKI K, SUGIMOTO M. Water sealing by wire brush with grease for pneumatic caisson method at great depth underground[J]. Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 48(2): 64-71. [4] 任广艳. 透水涌砂冒险堵漏隧道坍塌撤人不及: 广东省佛山市轨道交通2号线“2·7”透水坍塌重大事故分析[J]. 吉林劳动保护,2019(8): 40-42. [5] 李奕,钟志全. 一种新型盾尾刷的设计与应用[J]. 建筑机械化,2011,32(1): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1366.2011.01.020LI Yi, ZHONG Zhiquan. Design and application of a new type of shield tail brush[J]. Construction Mechanization, 2011, 32(1): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1366.2011.01.020 [6] 霍志光. 新型盾尾刷设计与应用分析[J]. 价值工程,2011,30(8): 87-88.HUO Zhiguang. Design and application analysis of new shield tail brush[J]. Value Engineering, 2011, 30(8): 87-88. [7] 沈桂丽,刘金祥,李剑雄,等. 盾尾密封刷实验平台的设计与研究[J]. 隧道建设,2015,35(8): 851-854.SHEN Guili, LIU Jinxiang, LI Jianxiong, et al. Design of and study on tail brush experimental platform[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2015, 35(8): 851-854. [8] 李大伟,刘金祥,赵新合. 盾尾刷综合实验平台的研制[J]. 建筑机械化,2015,36(2): 70-72.LI Dawei, LIU Jinxiang, ZHAO Xinhe. Development of tail sealing brushes comprehensive testing bench[J]. Construction Mechanization, 2015, 36(2): 70-72. [9] MAIDL B, HERRENKNECHT M, MAIDL U, et al. Mechanised shield tunnelling[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Ernst and Sohn, 2012: 87-99. [10] 魏林春. 盾尾钢丝刷受力性能模拟试验研究[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2021,41(2): 206-211.WEI Linchun. Experimental study on mechanical bahavior of wire brushes on shield tail[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(2): 206-211. [11] LI F, YANG Y Y, TAO M J, et al. A cement paste-tail sealant interface modified with a silane coupling agent for enhancing waterproofing performance in a concrete lining system[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(13): 7165-7175. doi: 10.1039/C8RA10457C [12] 李光,王宁. 基于多相流数值模拟的盾尾密封系统密封性研究[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2021,41(增1): 490-496.LI Guang, WANG Ning. Sealing performance of shield tail sealing system based on multiphase flow numerical simulation[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2021, 41(S1): 490-496. [13] 钭婧. 盾构机盾尾密封系统压力分布特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2021. -





 下载:
下载: