Permanent World-Leading Position of High-Speed Railways in China in Engineering
-
摘要:
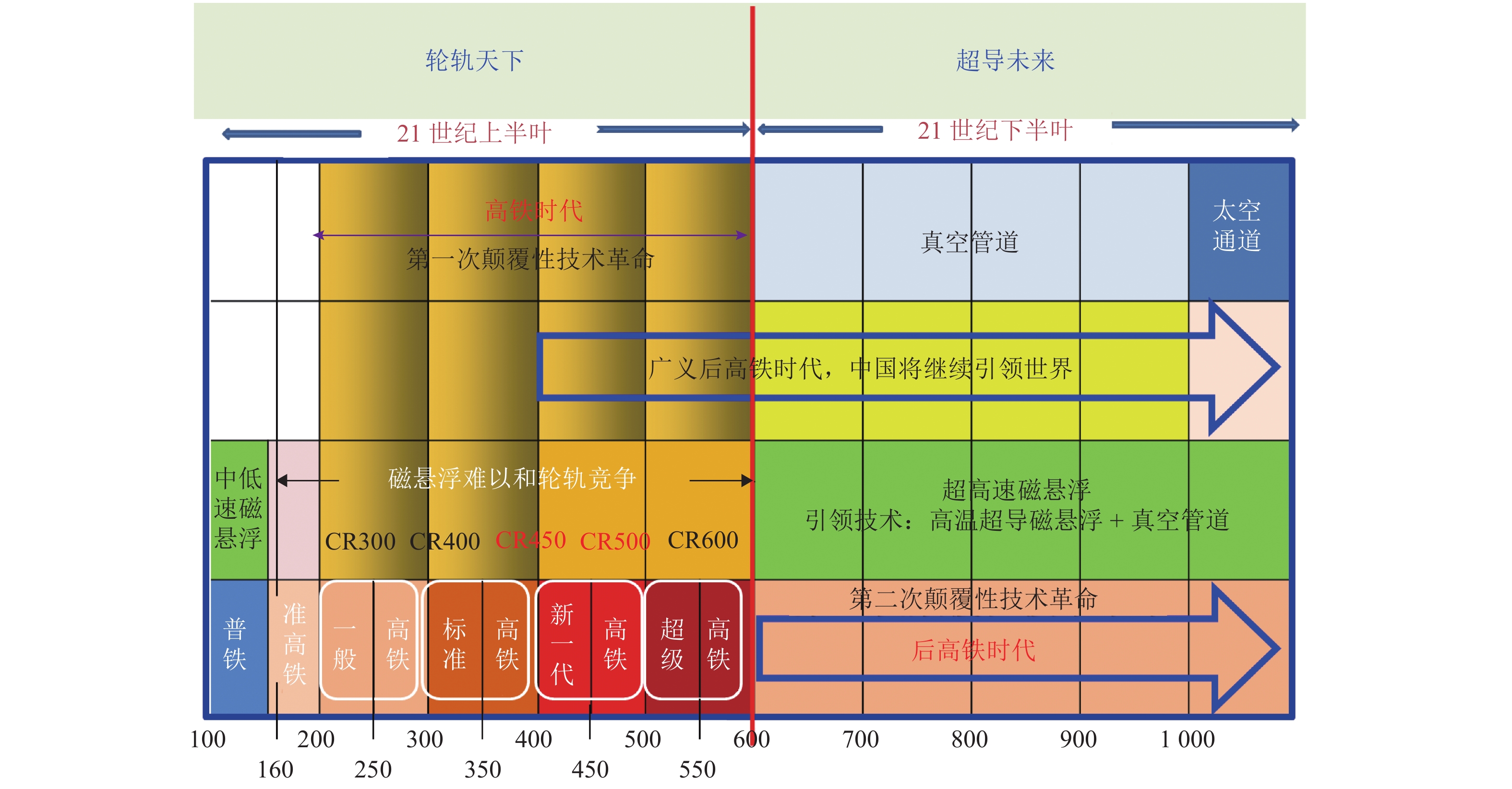
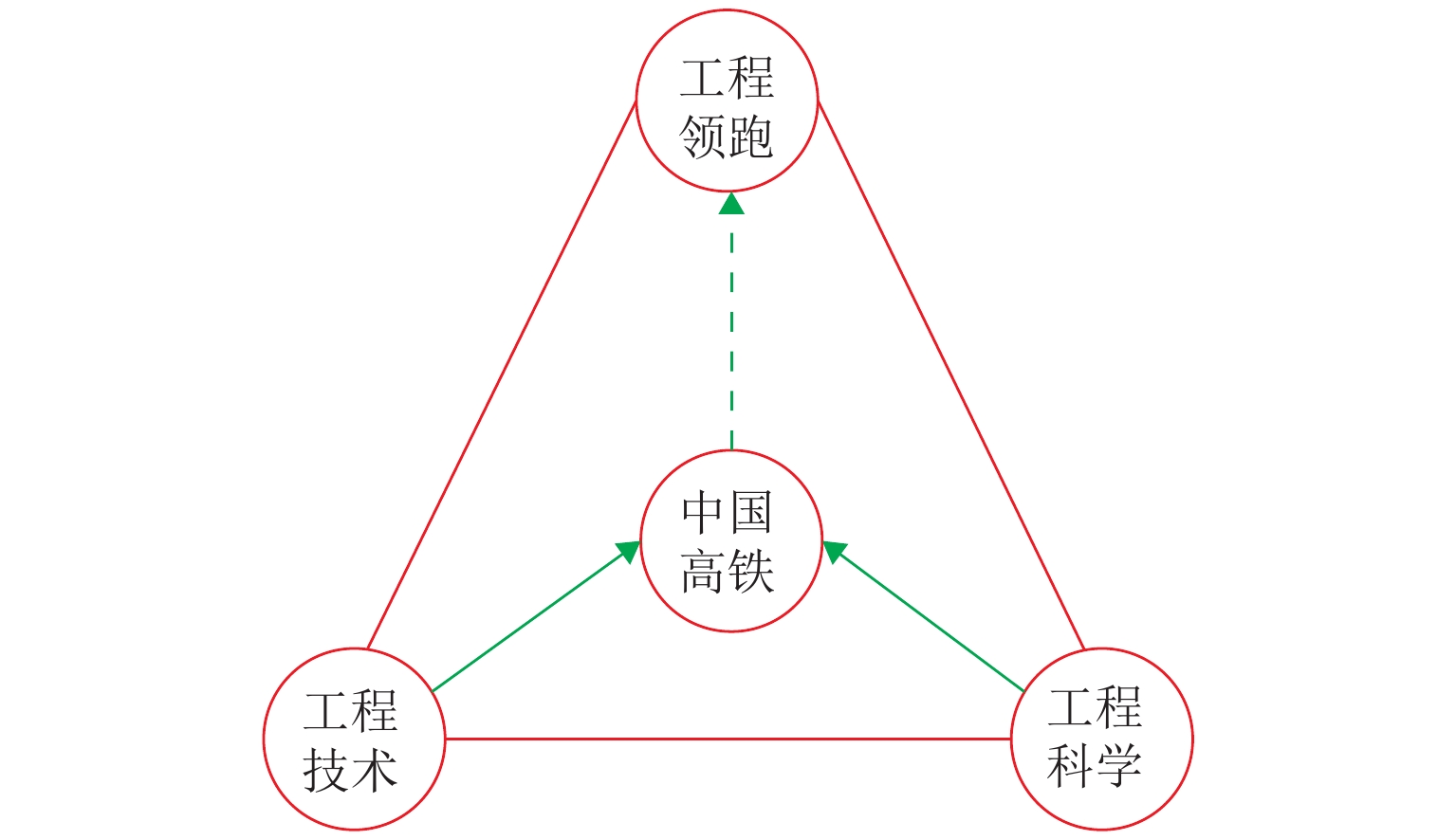
本文从高铁工程发展的角度出发,陈述了中国高铁工程发展概况,解读了只有工程技术和工程科学的紧密结合才能实现高铁工程领跑,才能保持中国高铁工程继续领跑世界;回顾了中国高铁快速崛起、领跑世界的历程,包括酝酿期、探索期、成熟期和发展期;复兴号高速列车已经成为中国高铁自主创新的成功范例,标志着中国高铁工程由跟跑、并跑到领跑,初步实现了工程领跑. 分析了中国高铁工程领跑面临德国、法国和日本等国家轮轨高铁更高速度、数字化转型以及日本和美国等国家高速及超高速管道磁悬浮高铁发展的严峻挑战. 提出了围绕“轮轨天下,超导未来”等应对严峻挑战的积极对策,并展望了高铁时代和后高铁时代轮轨高铁的发展趋势和磁悬浮高铁的未来发展,力求中国高铁继续保持工程领跑的最佳境界.
Abstract:From the perspective of the development of high-speed railway engineering, the development of high-speed railways in China was briefly reviewed to demonstrate that China must closely combine engineering technology and engineering science, so as to take a lead in high-speed railway engineering. The rapid rising of high-speed railways in China and their paths to the world-leading position were reviewed in terms of incubation, exploration, maturation, and evolution stages. The Fuxing high-speed train is a successful example of indigenous innovation of high-speed railways in China, and it marks a milestone for high-speed railways in China from lagging behind and catching up with, to overtaking high-speed railways in other countries, which initially occupies a world-leading position. The severe challenges to the world-leading position of high-speed railways in China were analyzed, which came from the transformation to higher speed and digitalization in high-speed railways of Germany, France, and Japan and from the high-speed and super high-speed pipeline magnetic levitation systems of Japan and the United States. Proactive countermeasures to these challenges were proposed centered on the strategy of “the wheel/rail connects the world, and superconducting maglev will shape the future”. The trend of development in the high-speed railway age and post-high-speed railway age and the future development of high-speed maglev were looked forward to striving for the best status that high-speed railway in China will retain world-leading position in engineering.
-
表 1 CRH380典型高速列车
Table 1. CRH380 typical high-speed train
型号 运营速度/
(km·h−1)适应环境
温度/℃使用寿命/年 编组形式
(动拖)轴重/t 牵引总
功率/kW全列定员/
人列车总长/
mCRH380A 350 −25~+ 40 20 6M2T ≤15 9120 494 203.00 CRH380AL 350 −25~+ 40 20 14M2T ≤15 20482 1027 403.00 CRH380B 350 −40~+ 40 20 4M4T ≤17 9200 490 200.65 CRH380BL 350 −25~+ 40 20 8M8T ≤17 18400 1004 399.25 -
[1] 陆东福. 打造中国高铁亮丽名片[J]. 中国科技奖励,2021(8): 6-11.LU Dongfu. Create a beautiful business card for China high-speed rail[J]. China Awards for Science and Technology, 2021(8): 6-11. [2] 杜善义. 强起来的重要标志是领跑[J]. 科技导报,2021,39(12): 19-20.DU Shanyi. An important symbol of a country’s strength is to lead[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2021, 39(12): 19-20. [3] 贾玉树. 从工程技术走向工程科学[J]. 建设机械技术与管理,2020,33(3): 16-17.JIA Yushu. From engineering technology to engineering science[J]. Construction Machinery Technology & Management, 2020, 33(3): 16-17. [4] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 中长期铁路网规划[EB/OL].(2004-01-21)[2021-08-18]. https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E4%B8%AD%E9%95%BF%E6%9C%9F%E9%93%81%E8%B7%AF%E7%BD%91%E8%A7%84%E5%88%92/62609349?fr=aladdin. [5] 张卫华,罗仁,宋春元,等. 基于电机动力吸振的高速列车蛇行运动控制[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2020,20(5): 125-134.ZHANG Weihua, LUO Ren, SONG Chunyuan, et al. Hunting control of high-speed train using traction motor as dynamic absorber[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(5): 125-134. [6] 田睿. 世界高速列车的发展(中)[J]. 国外铁道机车与动车,2020(5): 1-7,28.TIAN Rui. The development of high-speed trains in the world[J]. Foreign Railway Locomotive and Motor Car, 2020(5): 1-7,28. [7] 轨道世界. Avelia Horizon-阿尔斯通 SNCF联合打造的法国下一代超高速列车[EB/OL]. (2018-08-01)[2021-09-18]. https://www.sohu.com/a/244677391_180330. [8] 王同军. 中国智能高铁发展战略研究[J]. 中国铁路,2019(1): 9-14. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2019.01.009WANG Tongjun. Study on the development strategy of China intelligent high speed railway[J]. China Railway, 2019(1): 9-14. doi: 10.19549/j.issn.1001-683x.2019.01.009 [9] 国务院办公厅. 关于进一步做好铁路规划建设工作意见[EB/OL].(2021-03-15)[2021-08-18].https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%85%B3%E4%BA%8E%E8%BF%9B%E4%B8%80%E6%AD%A5%E5%81%9A%E5%A5%BD%E9%93%81%E8%B7%AF%E8%A7%84%E5%88%92%E5%BB%BA%E8%AE%BE%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C%E7%9A%84%E6%84%8F%E8%A7%81/56523390?fr=ge_ala. [10] 李仁涵. 人工智能技术属性及其社会属性[J]. 上海交通大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2020,28(4): 19-22. doi: 10.13806/j.cnki.issn1008-7095.2020.008LI Renhan. Technical and social attributes of artificial intelligence[J]. Journal of Shanghai JiaoTong University (Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2020, 28(4): 19-22. doi: 10.13806/j.cnki.issn1008-7095.2020.008 [11] 田睿. 世界高速列车的发展(下)[J]. 国外铁道机车与动车,2020(6): 27-29.TIAN Rui. The development of high-speed trains in the world[J]. Foreign Railway Locomotive and Motor Car, 2020(6): 27-29. [12] 熊嘉阳,邓自刚. 高速磁悬浮轨道交通研究进展[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 177-198.XIONG Jiayang, DENG Zigang. Research progress of high-speed maglev rail transit[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 177-198. [13] 中国铁道科学研究院科学技术信息研究所. 2020世界高速铁路发展动向[EB/OL]. (2021-03-03)[2021-08-18]. https://view.inews.qq.com/a/20210303A09D3Q00 [14] 谢毅,肖杰. 高速铁路发展现状及趋势研究[J]. 高速铁路技术,2021,12(2): 23-26.XIE Yi, XIAO Jie. Research on high-speed railway development status and trend[J]. High Speed Railway Technology, 2021, 12(2): 23-26. [15] 熊嘉阳,沈志云. 中国高速铁路的崛起和今后的发展[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(5): 6-29. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.05.002XIONG Jiayang, SHEN Zhiyun. Rise and future development of Chinese high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(5): 6-29. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.05.002 -




 下载:
下载: