Feature Matching Method of Oblique Images Based on Geometric Constraints
-
摘要:
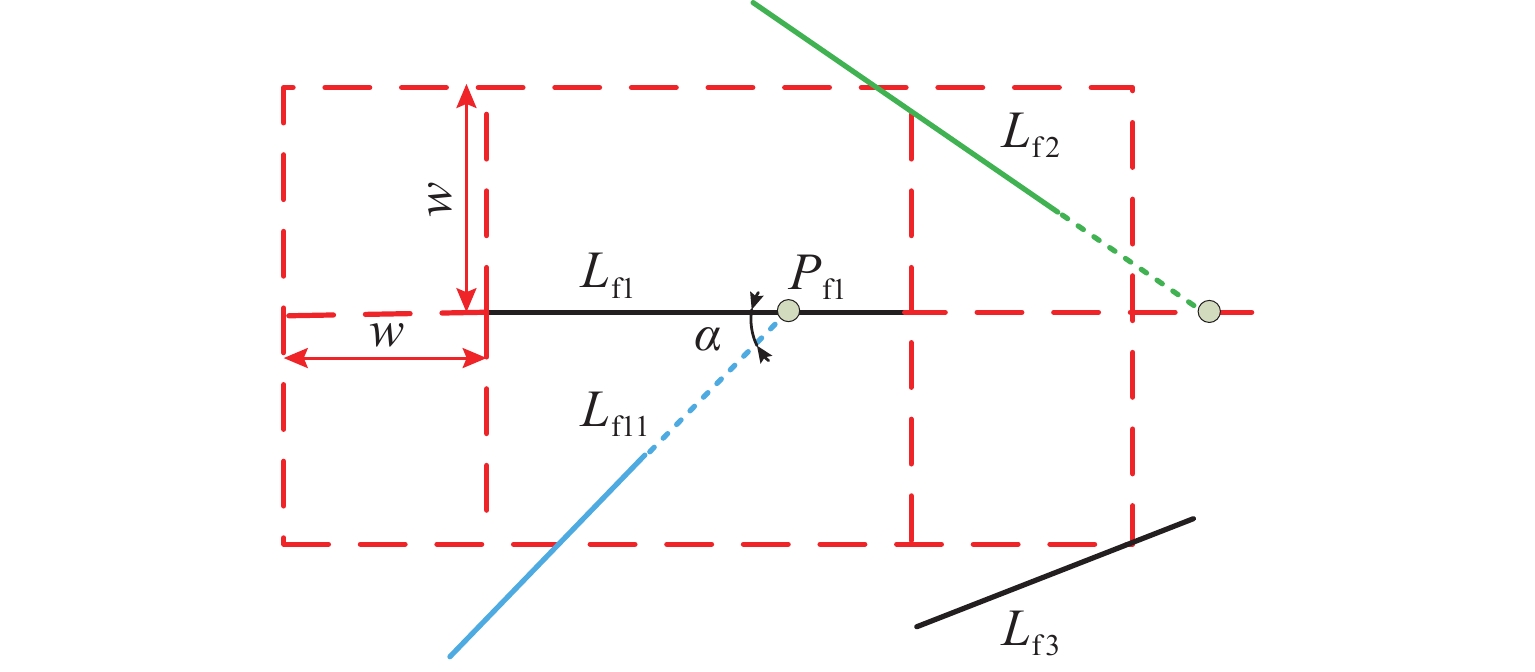
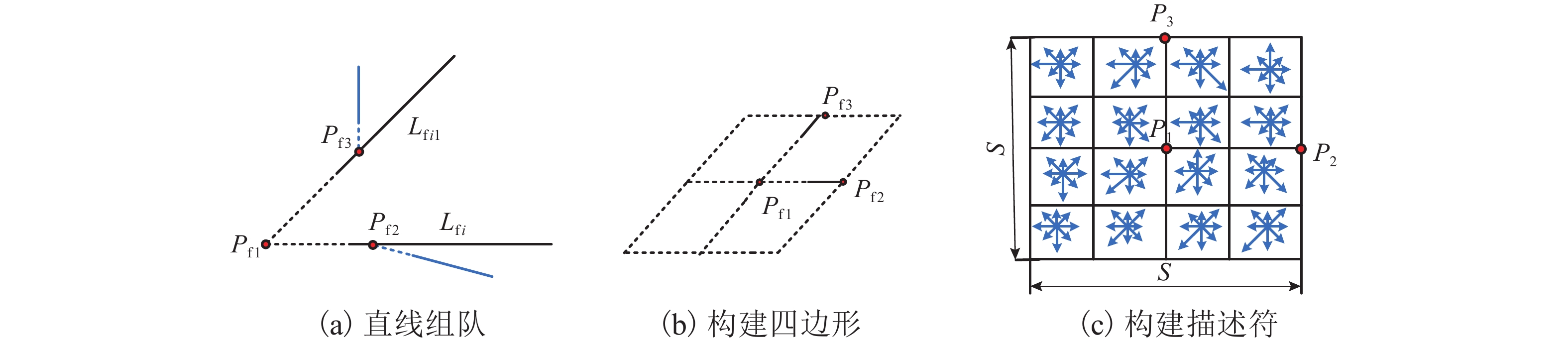
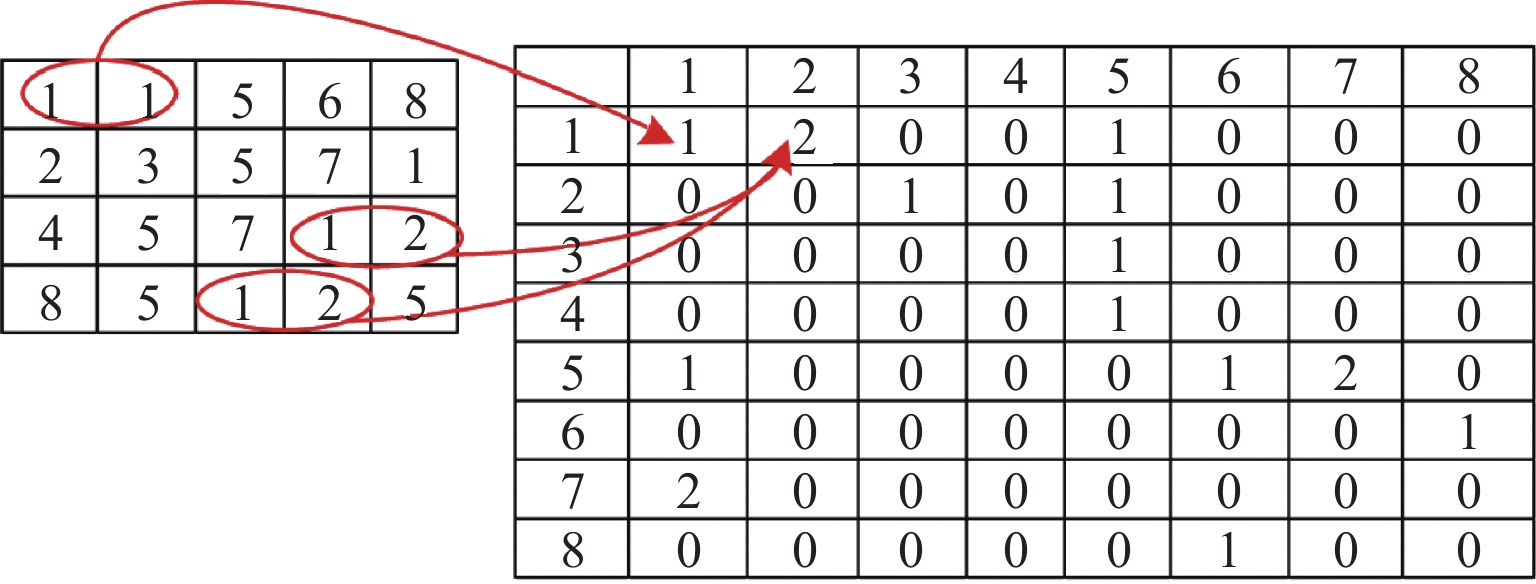
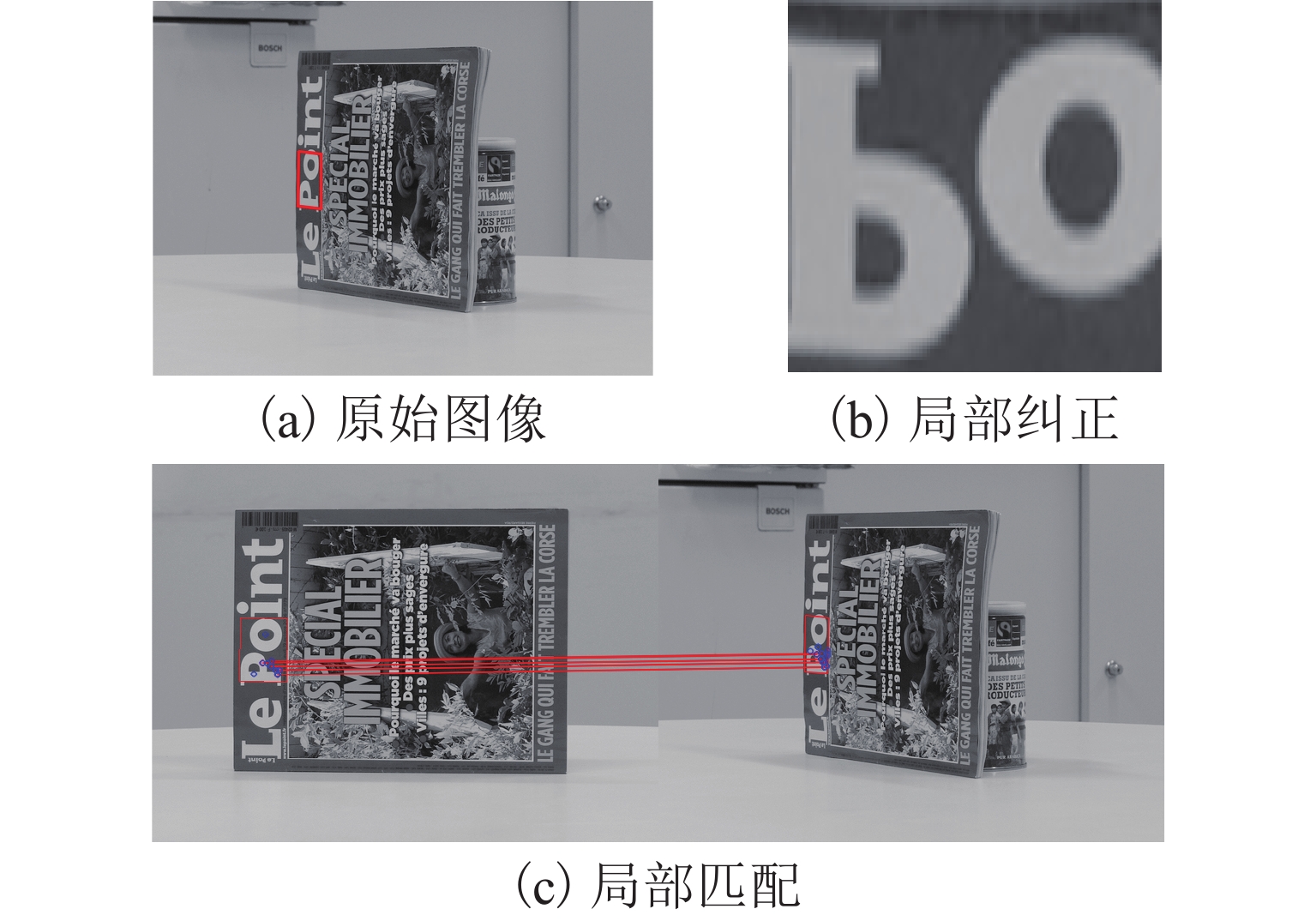
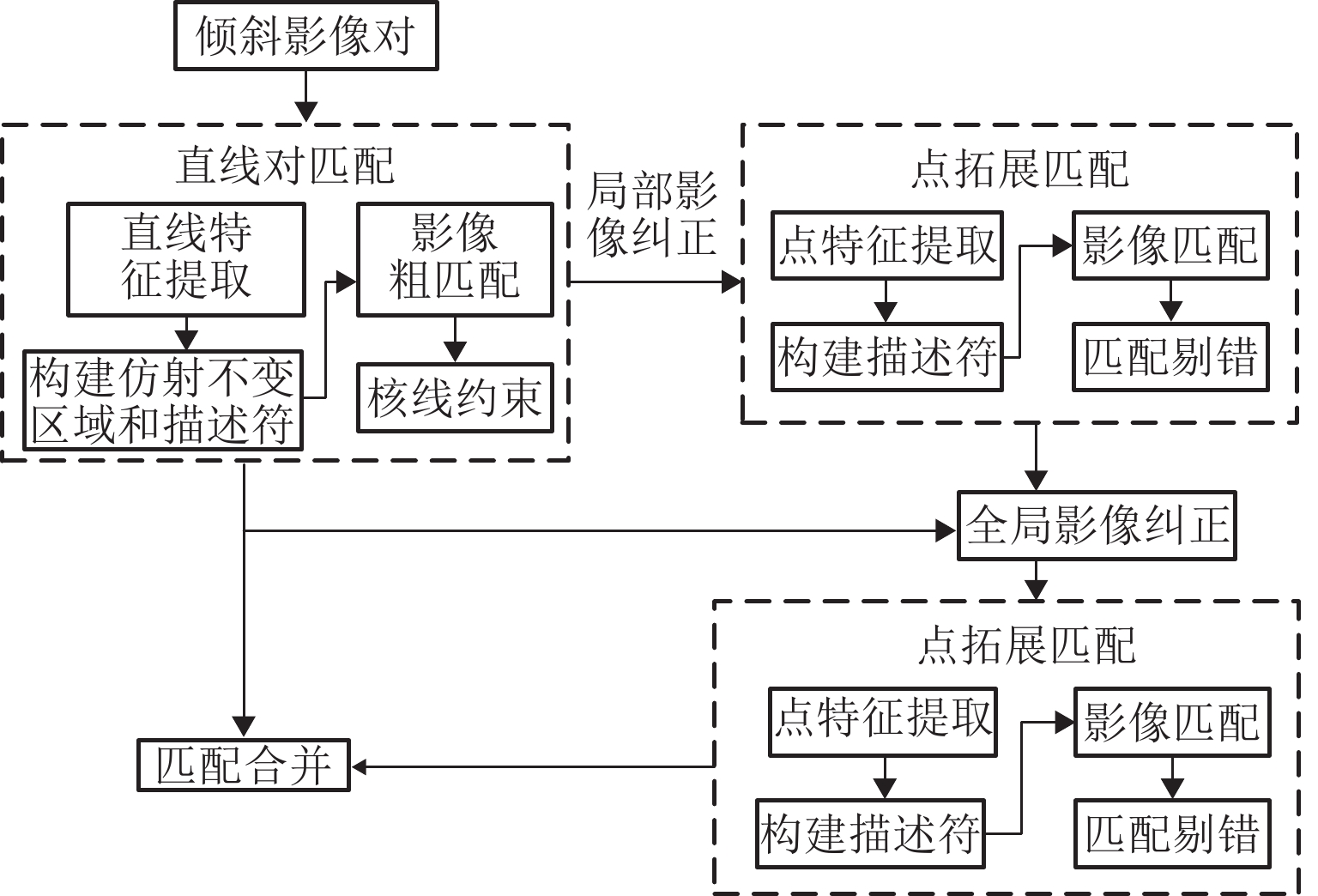
针对倾斜影像视角变换较大、重复纹理导致匹配数量少、匹配精度不高的问题,提出一种适用于倾斜影像的特征点、线分级匹配方法. 首先,用直线提取(检测)算法(LSD)获取影像直线特征,并将直线特征以一定约束进行直线组对,构建直线对区域与改进的SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform)特征描述符进行匹配,使用RANSAC算法剔除误匹配,获得初始匹配结果后再进行核线约束;然后,利用已获得直线对区域进行影像局部纠正,在纠正后的局部影像上采用SIFT匹配并反算回原始影像,利用得到的同名点全局纠正倾斜影像,并进行特征点匹配与采用基于方格的运动统计算法(GMS)剔除误匹配,仍将匹配结果反算回原始影像上;最后,将仿射尺度不变特征变化结果与点拓展匹配结果进行合并,得到最终匹配结果. 试验结果表明:本文方法匹配正确率与经典的仿射不变匹算法(ASIFT)的正确率相差不大,但匹配数量却是ASIFT算法的1倍~3倍.
Abstract:A feature point and line hierarchical matching method is proposed, suitable for oblique images to solve the challenges of large angle in view transformation, a few matches due to repeated texture, and low matching accuracy. Firstly, the line features of images derive from the line extraction (detection) algorithm (LineSegmentDector), follow constraints to pair, and construct line pair regions to match the improved SIFT feature descriptor. Secondly, after RANSAC algorithm eliminates mismatches, the epipolar constraint acts upon the initial matching results. Then, the obtained lines correct the local image, and the corrected local image uses SIFT matching, which contributes to calculating the original image reversely. The obtained matching points are used to globally correct the oblique image, and the feature points are matched; the grid-based motion statistics (GMS) algorithm eliminates the mismatches; the matching results go through reverse calculation and return to the original image. The line matching results and the point expanding matching results combine into final results, showing that the matching accuracy of the proposed method is close to that of ASIFT, but the number of matching is 1-3 times it.
-
Key words:
- oblique image /
- line feature /
- epipolar constraint /
- point expanding matching /
- global correction
-
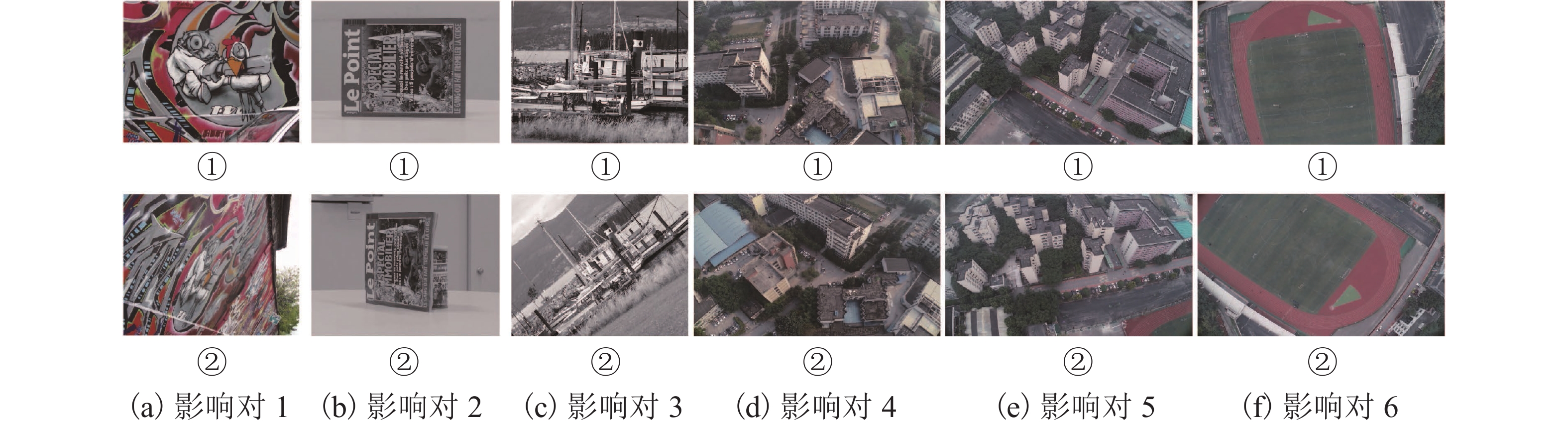
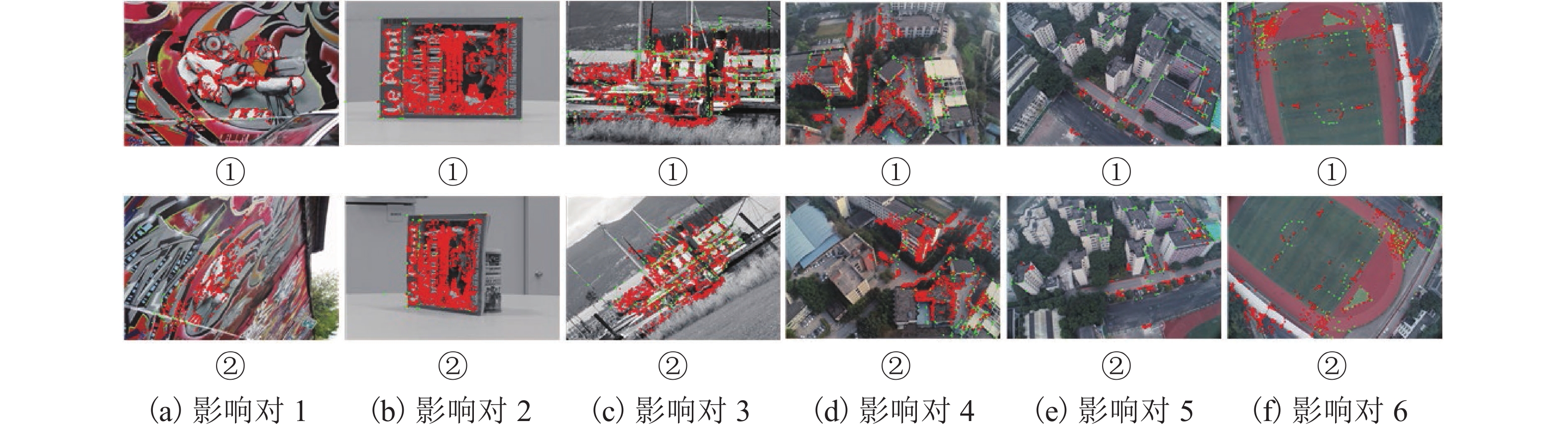
表 1 实验统计结果
Table 1. Statistic results of experiments
对 SIFT Harris-Affine Hessian-Affine ASIFT SuperGlue 本文方法 项目 影像对 RANSAC GMS RANSAC GMS RANSAC GMS RANSAC GMS GMS 匹配总数 1 41 0 20 0 38 0 708 502 0 943 2 235 69 36 0 407 294 2392 2353 168 2228 3 2081 218 79 0 79 0 2437 2181 216 8417 4 227 24 16 0 46 0 1789 1231 208 2235 5 55 0 19 0 40 0 232 56 207 443 6 167 0 13 0 16 0 259 28 2 1086 正确数 1 — 0 — 0 1 0 686 488 0 880 2 84 60 22 0 380 270 2266 2243 160 2163 3 1870 209 — 0 32 0 2383 2095 209 8302 4 198 20 — 0 1 0 1760 1207 199 2175 5 21 0 1 0 4 0 230 53 193 330 6 142 0 — 0 — 0 258 25 — 974 -
[1] 余美. 倾斜立体影像匹配若干问题研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. [2] LOWE D G. Distinctive image feature from scale-invariant key points[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [3] MA J, CHAN C W, CANTERS F. Fully automatic subpixel image registration of multiangle CHRIS/Proba data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2829-2839. [4] MOREL J M, YU G. ASIFT: a new framework for fully affine invariant image comparison[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 438-469. doi: 10.1137/080732730 [5] YU G, MOREL J M. ASIFT: an algorithm for fully affine invariant comparison[J]. Image Processing on Line, 2011, 1: 11-38. doi: 10.5201/ipol.2011.my-asift [6] LI K, YAO J. Line segment matching and reconstruction via exploiting coplanar cues[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 125: 33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.01.006 [7] GIOIR RAFAEL G V, JAKUBOWICZ J , MOREL J M, et al. LSD: a fast line segment detector with a false detection control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(4): 722-732. [8] FAN B, WU F, HU Z. Robust line matching through line-point invariants[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(2): 794-805. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.08.004 [9] MIKOLAJCZYK K, SCHMID C. Scale & affine invariant interest point detectors[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(1): 63-86. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000027790.02288.f2 [10] MIKOLAJCZYK K, TUYTEIAARS T, SCHMID C, et al. A comparison of affine region detectors[J]. International Journal of Computor Vision, 2005, 65: 43-72. doi: 10.1007/s11263-005-3848-x [11] 姚国标,邓喀中,艾海滨,等. 倾斜立体影像自动准稠密匹配与三维重建算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2014,39(7): 843-849.YAO Guobiao, DENG Kazhong, AI Haibin, et al. An algorithm of automatic quasi-dense matching and three-dimensional reconstruction for oblique stereo images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(7): 843-849. [12] 余美,邓喀中,杨化超,等. 基于WαSH局部特征的立体影像匹配[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(3): 685-690.YU Mei, DENG Kazhong, YANG Huachao, et al. Stereo images matching based on WαSH local features[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2018, 47(3): 685-690. [13] 肖雄武,郭丙轩,李德仁,等. 一种具有仿射不变性的倾斜影像快速匹配方法[J]. 测绘学报,2015,44(4): 414-421.XIAO Xiongwu, GUO Bingxuan, LI Deren, et al. A quick and affine invariance matching method for oblique images[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2015, 44(4): 414-421. [14] YU Yinian, HUANG Kaiqi, CHEN Wei, et al. A novel algorithm for view and illumination invariant image matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 21(1): 229-240. [15] XIAO X W, GUO B X, SHI Y R, et al. Robust and rapid matching of oblique UAV images of urban area[C]//Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series. Wuhan: SPIE, 2013: 223-230. [16] LI K, YAO J , XIA M H, et al. Joint point and line segment matching on wide-baseline stereo images[C]//2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). New York: IEEE, 2016: 1-9. [17] 陈敏,朱庆,何海清,等. 面向城区宽基线立体像对视角变化的结构自适应特征点匹配[J]. 测绘学报,2019,48(9): 1129-1140.CHEN Min, ZHU Qing, HE Haiqing, et al. Structureadaptive feature point matching for urban area wide-baseline images with viewpoint variation[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(9): 1129-1140. [18] 张平,王竞雪. 直线对几何特征约束的近景影像特征匹配[J]. 遥感信息,2020,35(4): 124-132.ZHANG Ping, WANG Jingxue. Line matching for close-range images with geometry features of line pairs[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2020, 35(4): 124-132. [19] RAGURAM R, CHUM O, POLLEFEYS M, et al. USAC: a universal framework for random sample consensus[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(8): 2022-2038. [20] 王竞雪,朱庆,王伟玺. 顾及拓扑关系的立体影像直线特征可靠匹配算法[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(11): 1850-1858.WANG Jingxue, ZHU Qing, WANG Weixi. Reliable line matching algorithm for stereo images with topological relationship[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(11): 1850-1858. [21] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona: IEEE, 2011: 2564-2571. [22] LEVI G, HASSNER T. LATCH: learned arrangements of three patch codes[C]//2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). NewYork: IEEE, 2016: 1-9. [23] 李卓,刘洁瑜,李辉,等. 基于ORB-LATCH的特征检测与描述算法[J]. 计算机应用,2017,37(6): 1759-1762.LI Zhuo, LIU Jieyu, LI Hui, et al. Feature detection and description algorithm based on ORB-LATCH[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2017, 37(6): 1759-1762. [24] BIAN J W, LIN W Y, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. GMS: grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra-robust feature correspondence[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(6): 1580-1593. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01280-3 [25] MIKOLAJCZYK K, SCHMID C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(10): 1615-1630. [26] SONG W H, JUNG H G, GWAK I Y, et al. Oblique aerial image matching based on iterative simulation and homography evaluation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 87: 317-331. [27] 杨蒙蒙,张爱华. 基于灰度共生矩阵和同步正交匹配追踪的分形图像压缩[J]. 计算机应用,2021,41(5): 1445-1449.YANG Mengmeng, ZHANG Aihua. Fractal image compression based on gray-level co-occurrence matrix and simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(5): 1445-1449. [28] SARLIN P E, DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, et al. Superglue: Learning feature matching with graph neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020: 4938-4947. -




 下载:
下载: