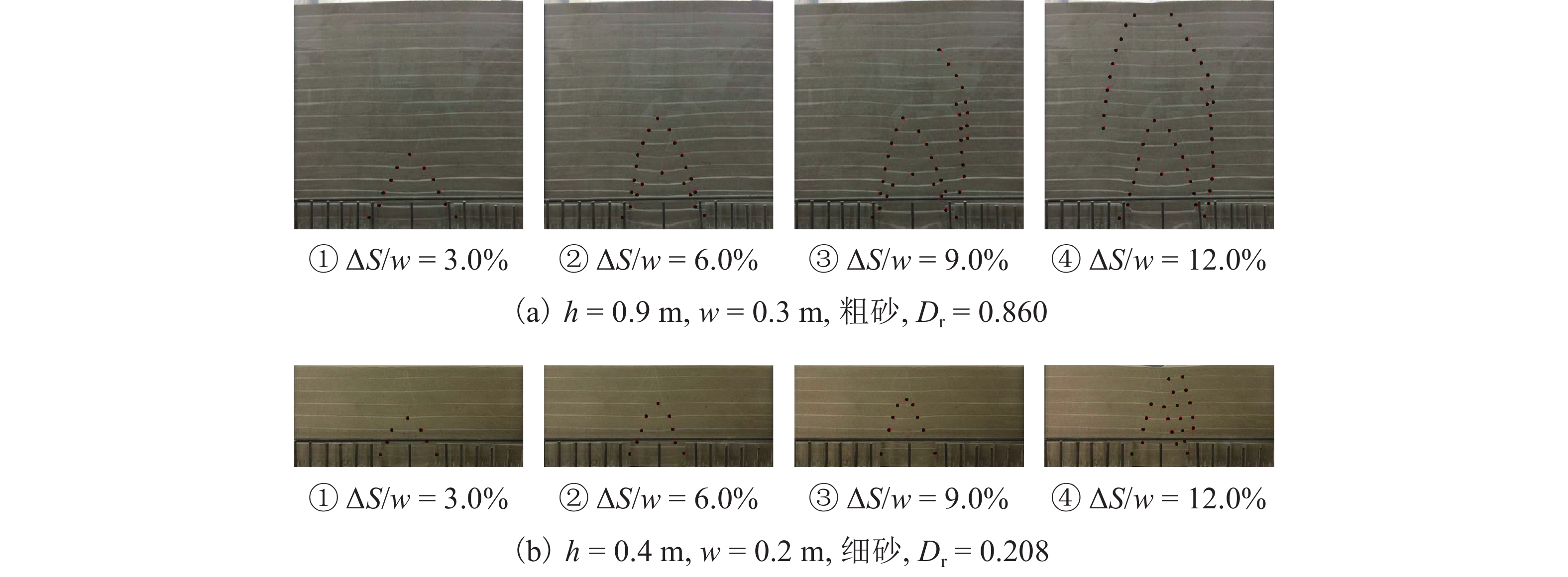
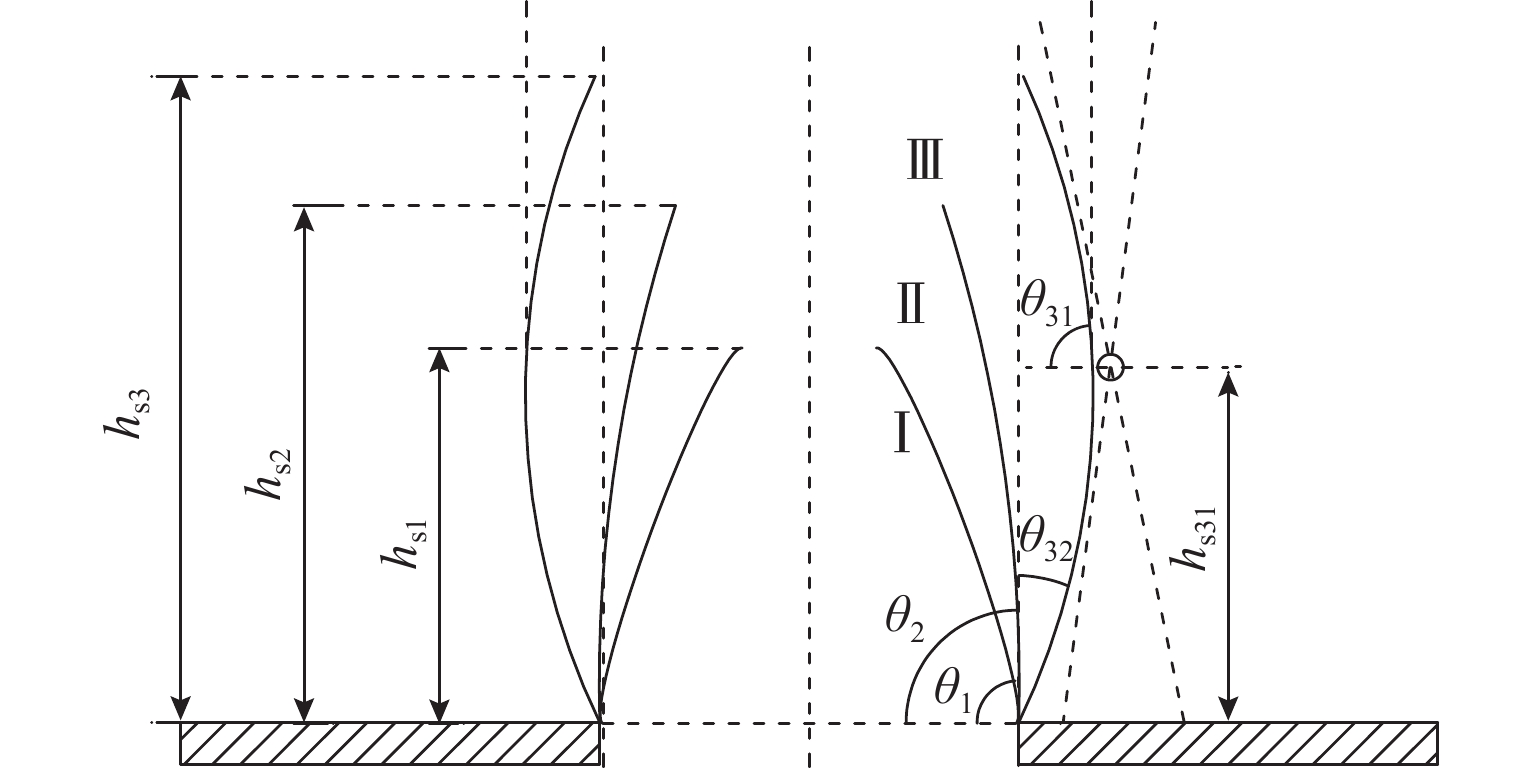
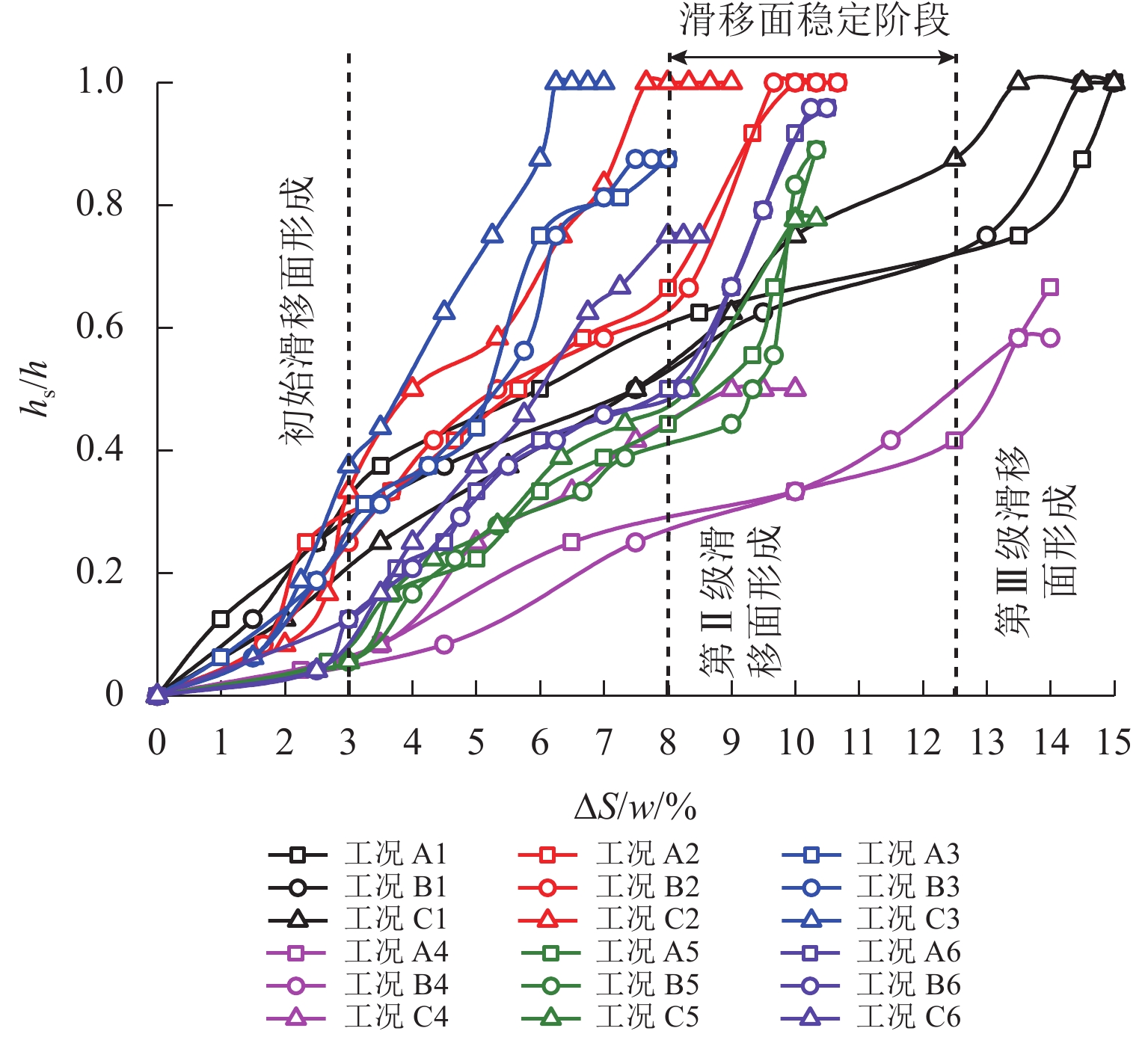
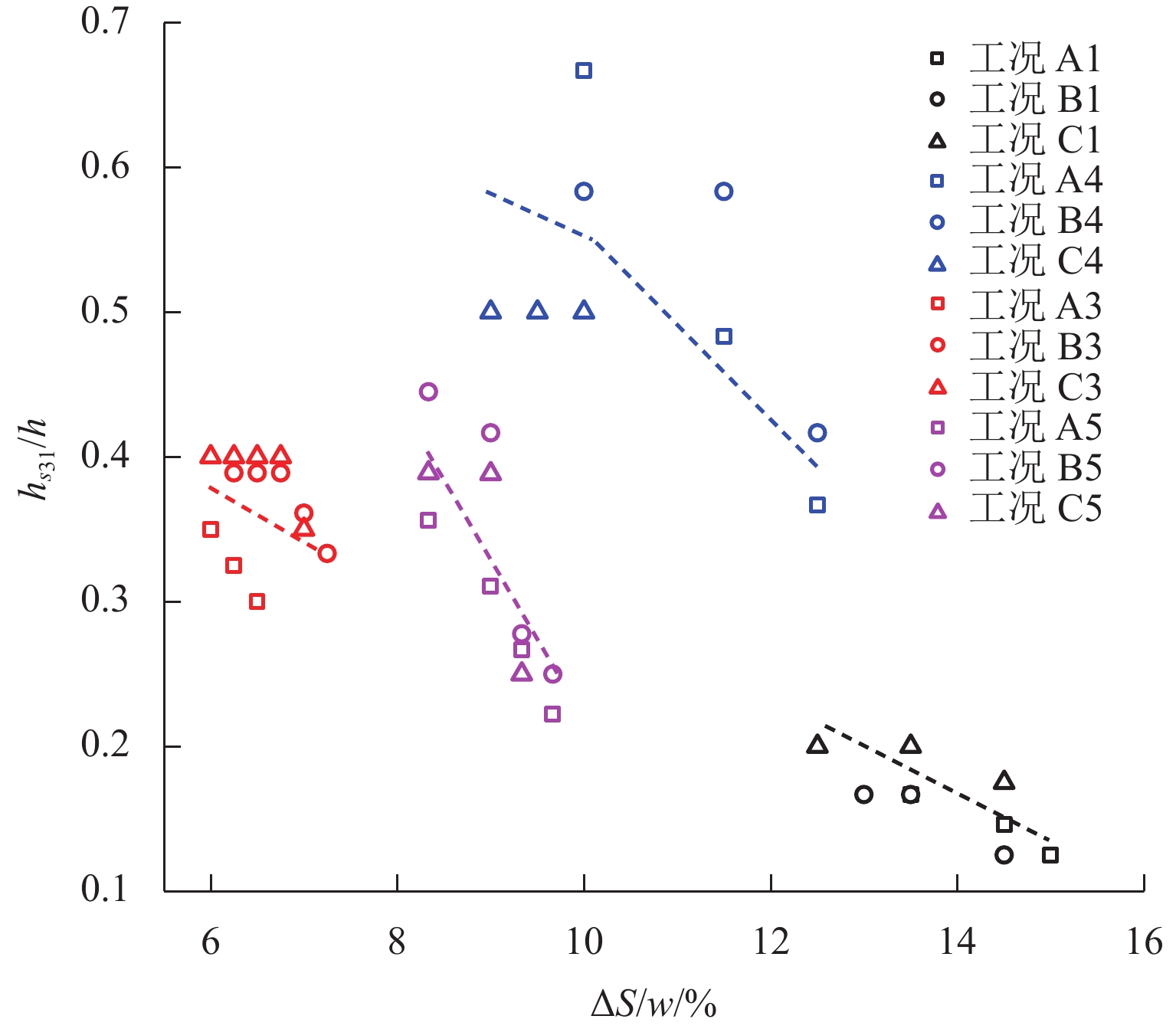
Geometric Contour of Slip Surfaces and Loosening Earth Pressure in Sand Under Soil-Arching Effect
-
摘要:
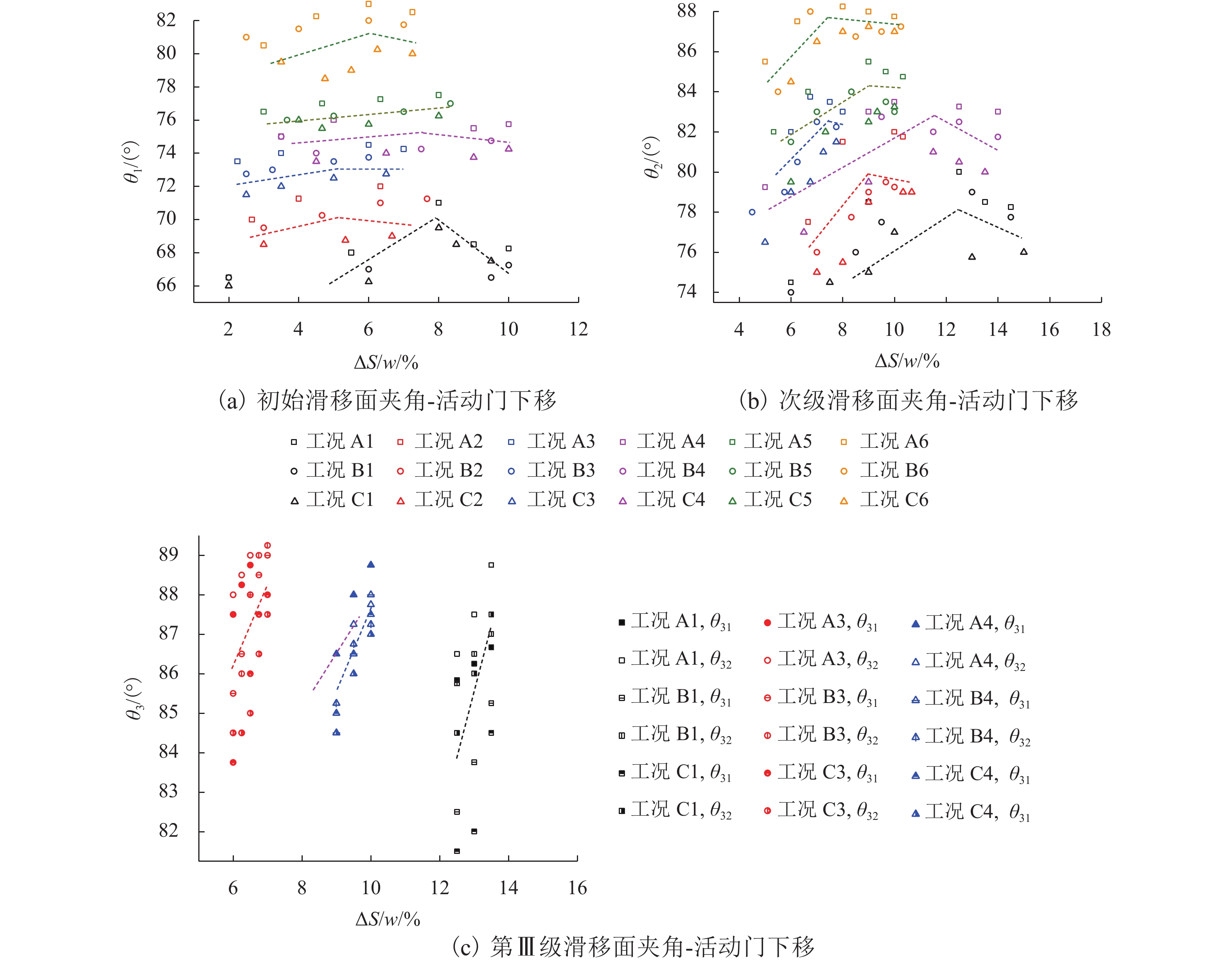
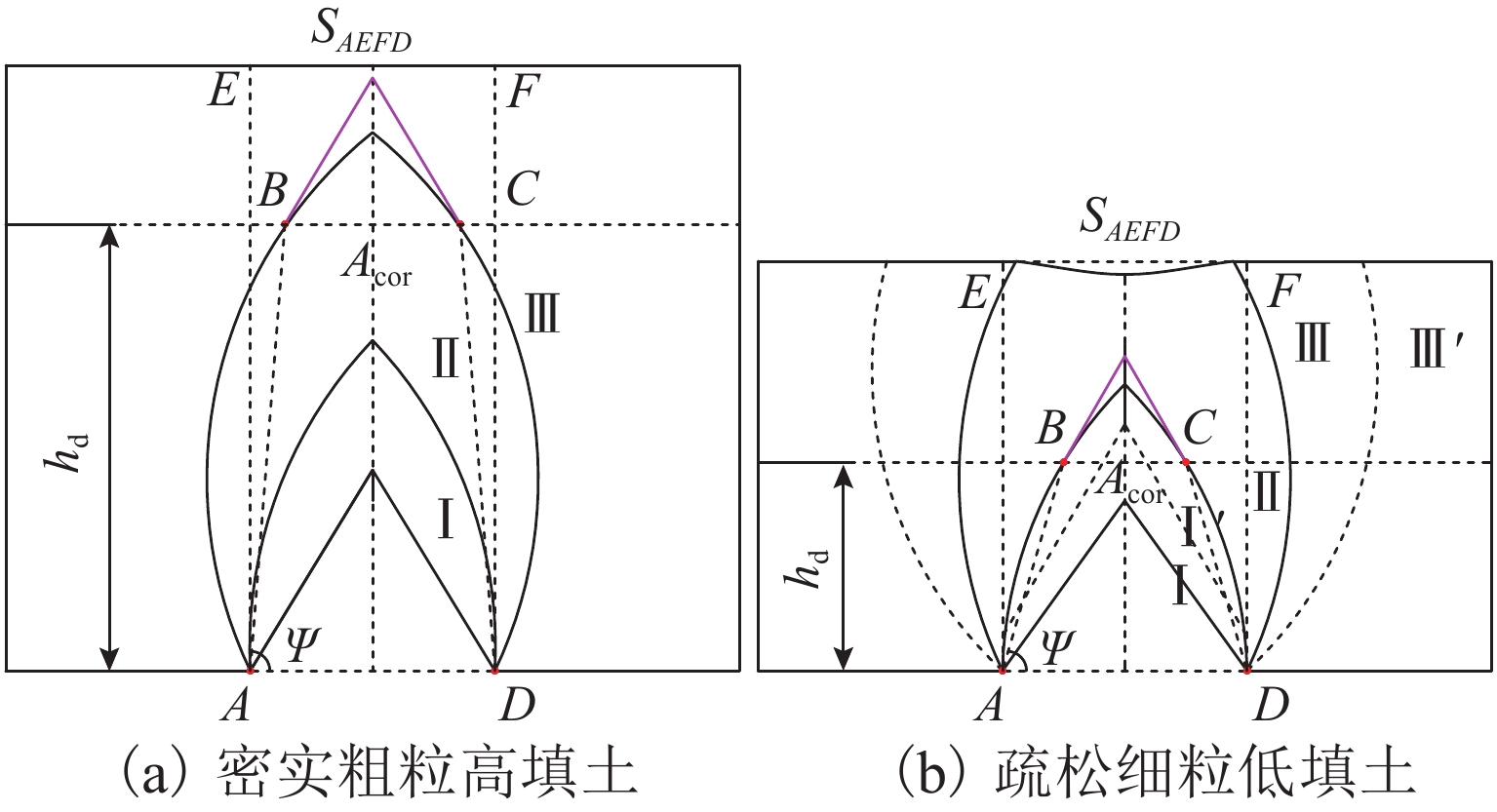
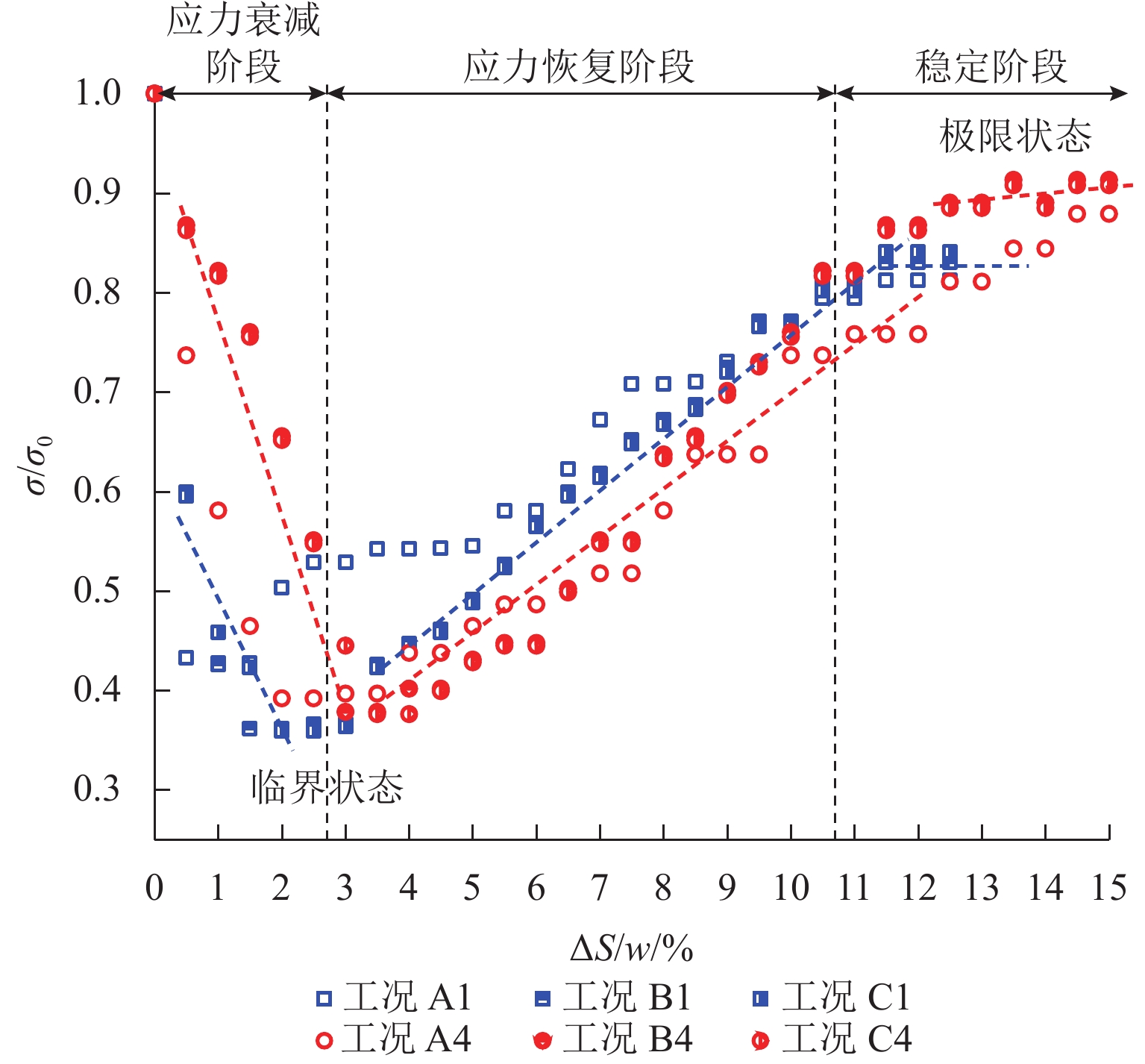
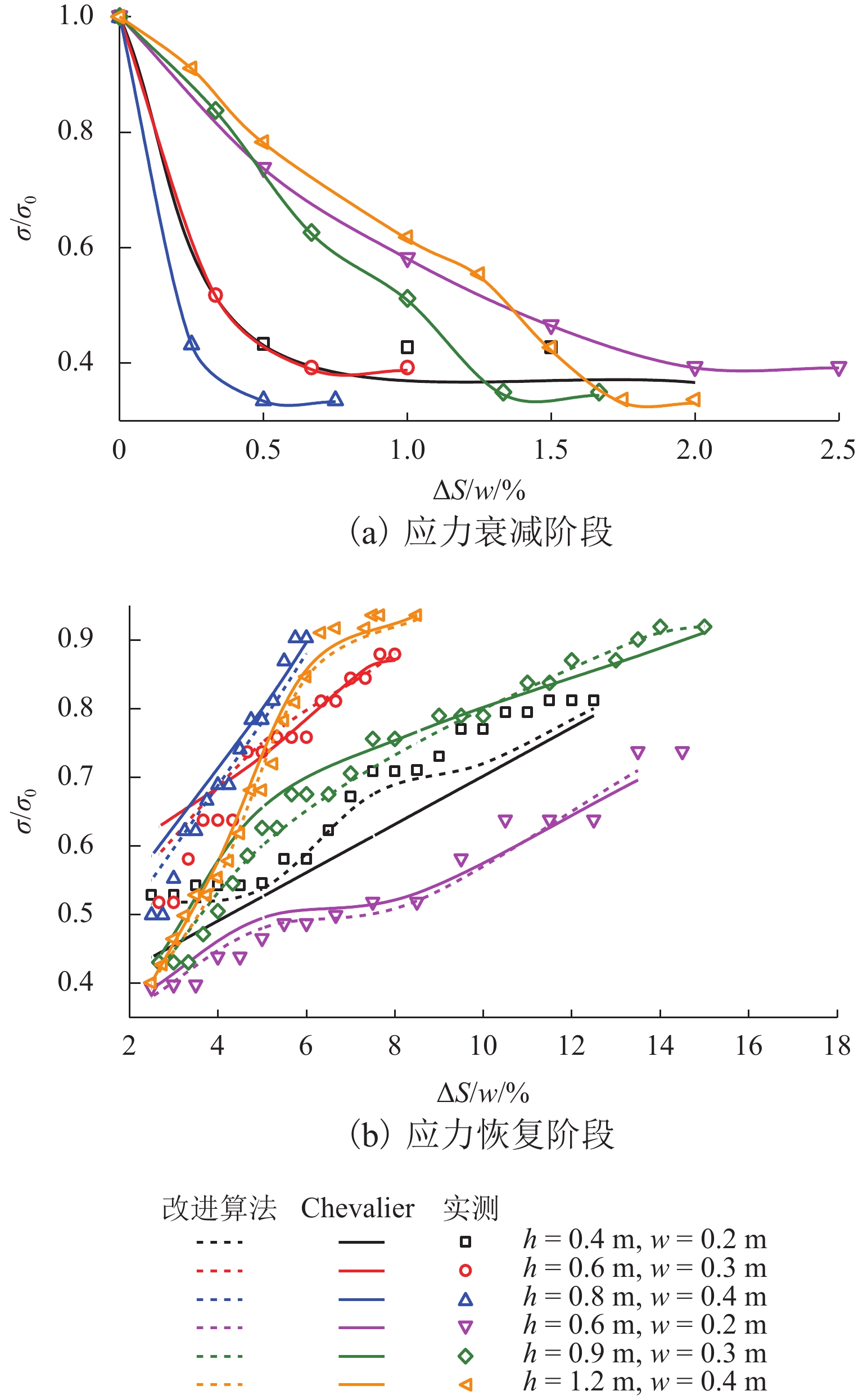
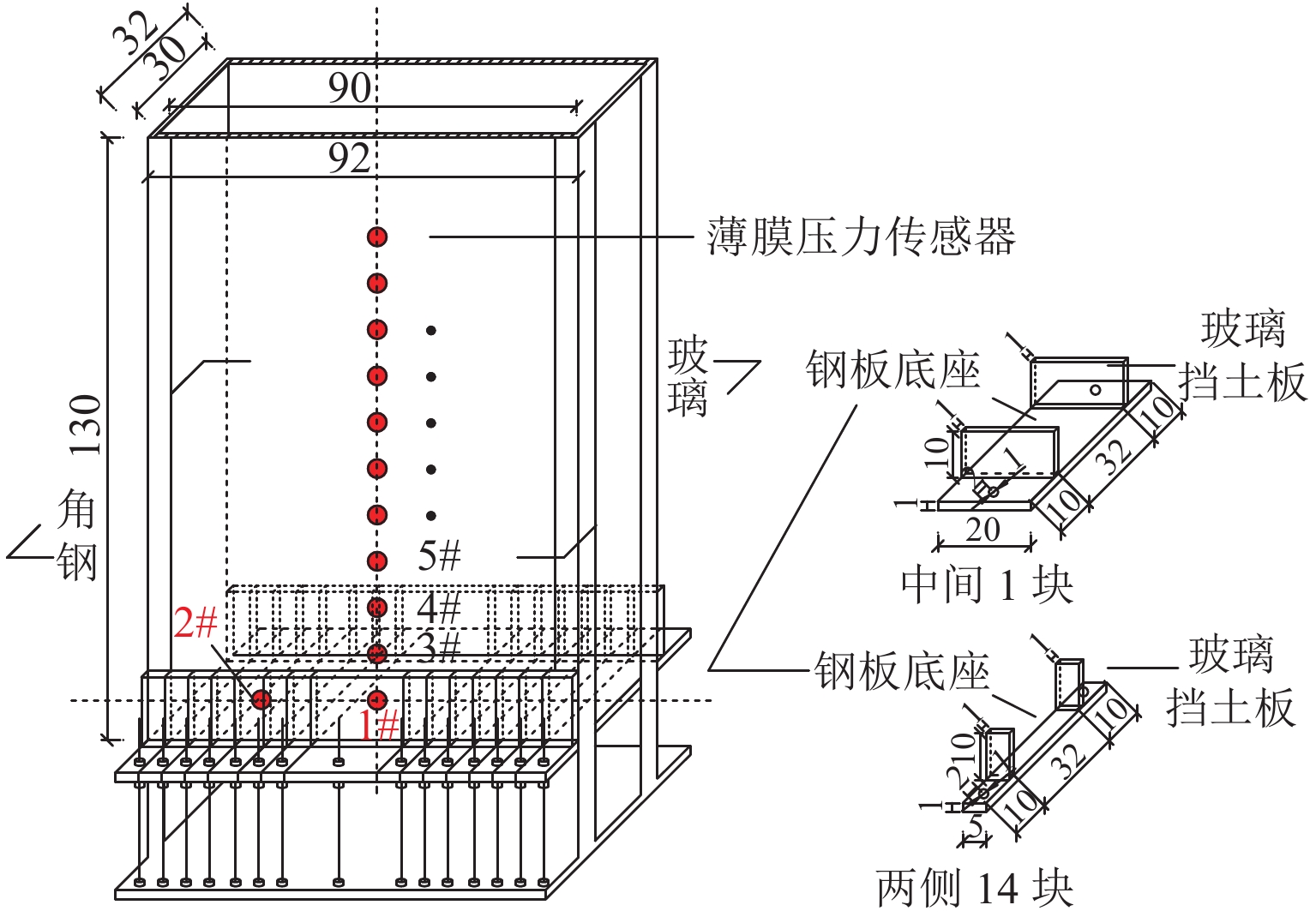
土拱效应本质上是由于土体内部松动引起的应力转移现象,土体松动过程伴随着滑移面的形成和延展,但目前针对滑移面几何轮廓、松动影响范围以及考虑松动区动态演变对松动土压力的影响等方面的研究尤待深入. 利用Trapdoor试验对砂土拱效应滑移面轮廓及演变开展研究,获得滑移面几何轮廓及其演变模式在不同填土高度、活动门下移和宽度以及砂料密度下的表征区别. 通过界定滑移面影响范围内松动核心区域,提出基于核心区几何形状的松动应力计算方法. 分析松动应力-活动门下移曲线特征,以揭示最大、最小拱状态条件下的曲线特征随填土高度、活动门下移和宽度以及砂密度的变化规律. 研究结果表明:1) 滑移面轮廓随活动门下移的演化过程为三角形—子弹头形—椭圆形,填土高度越高,活动门宽度越小,初始和次级滑移面轮廓越尖锐;2) 初始、次级滑移面高度随活动门下移递增,第Ⅲ级滑移面拐点高度随活动门下移递减, 初始、次级滑移面夹角随活动门下移先增后减,第Ⅲ级滑移面上半夹角与下半夹角均随活动门下移递增;3) 随着填土高度的增加,松动核心区形状演化过程为三角形—梯形—矩形,核心区高度为填土高度的0.5倍~0.8倍,核心区夹角与核心区面积均随内摩擦角的增加近似线性递减;4) 基于核心区面积的松动应力计算方法相比,Terzaghi等方法更具适用性,且其适用于计算低填土试验组的临界应力和高填土试验组的极限应力. 研究成果为更精确地描述砂土松动区的位移破坏模式及其界定标准以及松动区稳定性评价提供参考.
-
关键词:
- 土拱效应 /
- Trapdoor试验 /
- 滑移面轮廓 /
- 松动区 /
- 松动土压力
Abstract:The soil-arching effect, in essence, is a stress transfer phenomenon triggered by the loosening of the internal structure of the soil. The loosening process is accompanied by the formation and expansion of slip surfaces. At present, research on the geometric contour of slip surfaces, loosening-affected areas, and influence of the dynamic evolution of loosening zones on the loosening earth pressure remains sparse. Therefore, Trapdoor tests were conducted to investigate the contour of slip surfaces and their evolution in sand under the soil-arching effect. In this way, differences in the characterization of the geometric contour of slip surfaces and their evolution modes under different filling heights, downward movements and widths of trapdoors, and sand densities were obtained. By defining a core loosening zone in the area affected by slip surfaces, a calculation method for the loosening stress based on the geometric contour of the core loosening zone was proposed. In addition, the curve characteristics of the loosening stress and downward movement of the trapdoor were analyzed to reveal the changes in curve characteristics with the filling height, downward movement and width of the trapdoor, and sand density under maximum and minimum arch states. The research results show that: 1) the contour of slip surfaces evolves from a triangle, to a bullet shape, and finally to an ellipse with the downward movement of the trapdoor. As the filling height gets greater, and the trapdoor becomes narrower, the contour of primary and secondary slip surfaces is sharper. 2) with the downward movement of the trapdoor, the height of the primary and secondary slip surfaces increases, while that of inflection points of the level-Ⅲ slip surface decreases. In addition, as the trapdoor moves downward, the angles of the primary and secondary slip surfaces both increase first and then decrease, while the upper and lower half-angles of the level-Ⅲ slip surface both increase. 3) the contour of the core loosening zone changes from a triangle, to a trapezoid, and finally to a rectangle with increasing filling height. The height of the core loosening zone is 0.5–0.8 times the filling height, and the angle and area of the zone both decrease in a quasi-linear manner with increasing internal friction angle. 4) the calculation method for the loosening stress based on the area of the core zone is more applicable than Terzaghi’s method, and it is suggested that it be used to calculate the critical stress of test groups with a low and a high filling height respectively. The research results provide more accurate descriptions and judgment criteria for the displacement and failure modes of the loosening zone in sand. They also provide a reference for evaluating the stability of the loosening zone.
-
表 1 砂物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of sand
种类 d50/mm 不均匀
系数 cu曲率系数 cc 最大干密度
ρdmax/(kg·m−3)最小干密度
ρdmin/(kg·m−3)Dr 内摩擦角 φ/(°) 细砂 0.27 2.67 0.95 1719 1318 0.208 31.4 中砂 0.32 2.57 1.34 1616 1354 0.607 34.5 粗砂 0.53 2.92 0.84 1703 1439 0.860 38.4 表 2 Trapdoor试验组工况
Table 2. Trapdoor test conditions
试验组工况 种类 h/m w/m 传感器埋设间距/m A1 细砂 0.4 0.2 0.1 A2 0.6 0.3 0.1 A3 0.8 0.4 0.2 A4 0.6 0.2 0.1 A5 0.9 0.3 0.2 A6 1.2 0.4 0.2 B1 中砂 0.4 0.2 0.1 B2 0.6 0.3 0.1 B3 0.8 0.4 0.2 B4 0.6 0.2 0.1 B5 0.9 0.3 0.2 B6 1.2 0.4 0.2 C1 粗砂 0.4 0.2 0.1 C2 0.6 0.3 0.1 C3 0.8 0.4 0.2 C4 0.6 0.2 0.1 C5 0.9 0.3 0.2 C6 1.2 0.4 0.2 表 3 稳定滑移面高度-内摩擦角
Table 3. Stable slip surface height-internal friction angle
m φ/(°) h=0.4 m, w=0.2 m h=0.8 m, w=0.4 m h=0.6 m, w=0.2 m h=0.9 m, w=0.3 m hs1 hs2 hs3 hs31 hs1 hs2 hs3 hs31 hs1 hs2 hs3 hs31 hs1 hs2 hs3 hs31 31.4 0.225 0.250 0.400 — 0.625 0.750 — — 0.363 0.425 — — 0.275 0.523 0.875 0.675 34.5 0.238 — — — 0.625 0.788 0.725 0.352 0.338 0.463 0.600 0.425 0.312 — — — 38.4 0.225 0.263 — — 0.688 0.763 — — 0.413 0.488 0.525 0.450 0.337 0.575 0.900 0.708 注:部分试验未形成次级或第Ⅲ级滑移面,以“—”表示. 表 4 松动核心区几何特征
Table 4. Geometric characteristics of core loosening area
φ/(°) h/m w/m hd/m ψ/(°) Acor/m2 Acor/SAEFD 31.4 0.4 0.2 0.40 81.5 0.036 0.45 1.2 0.4 0.85 88.5 0.385 0.80 34.5 0.8 0.4 0.75 88.5 0.231 0.72 0.6 0.2 0.55 85.0 0.057 0.48 38.4 0.6 0.2 0.60 83.5 0.056 0.47 1.2 0.4 0.80 89.0 0.375 0.78 表 5 临界、极限状态特征
Table 5. Characteristics of critical and ultimate states
φ/
(°)h=0.4 m, w=0.2 m h=0.8 m, w=0.4 m h=0.6 m, w=0.2 m h=1.2 m, w=0.4 m σcri/
σ0σult/
σ0ΔScri/w/
%ΔSult/w/
%σcri/
σ0σult/
σ0ΔScri/w/
%ΔSult/w/
%σcri/
σ0σult/
σ0ΔScri/w/
%ΔSult/w/
%σcri/
σ0σult/
σ0ΔScri/w/
%ΔSult/w/
%31.4 0.43 0.81 1.2 11 0.33 0.90 0.5 5.7 0.39 0.89 2.0 14 0.34 0.93 1.8 7.2 34.5 0.36 0.83 1.5 10 0.34 0.92 1.0 5.5 0.38 0.90 3.2 12 0.32 0.95 1.8 6.5 38.4 0.35 0.84 2.0 9 0.33 0.93 1.3 5.2 0.37 0.90 3.3 11 0.31 0.96 2.3 5.8 -
[1] TERZAGHI K. Theoretical soil mechanics[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 1943. [2] COSTA Y D, ZORNBERG J G, BUENO B S, et al. Failure mechanisms in sand over a deep active trapdoor[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(11): 1741-1753. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000134 [3] IGLESIA G R, EINSTEIN H H, WHITMAN R V. Investigation of soil arching with centrifuge tests[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2014, 140(2): 04013005.1-04013005.13. [4] RUI R, VAN TOL A F, XIA Y Y, et al. Investigation of soil-arching development in dense sand by 2D model tests[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2016, 39(3): 20150130.1-20150130.16. [5] ESKIŞAR T, OTANI J, HIRONAKA J. Visualization of soil arching on reinforced embankment with rigid pile foundation using X-ray CT[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2012, 32: 44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2011.12.002 [6] HONG W P, LEE J H, LEE K W. Load transfer by soil arching in pile-supported embankments[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2007, 47(5): 833-843. doi: 10.3208/sandf.47.833 [7] AHMADI A, SEYEDI HOSSEININIA E. An experimental investigation on stable arch formation in cohesionless granular materials using developed trapdoor test[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 137-146. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.02.011 [8] LAI H J, ZHENG J J, ZHANG R J, et al. Classification and characteristics of soil arching structures in pile-supported embankments[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 98: 153-171. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.02.007 [9] SANTICHAIANAINT K. Centrifuge modeling and analysis of active trapdoor in sand[D]. Boulder: University of Colorado at Boulder. [10] GUO P J, ZHOU S H. Arch in granular materials as a free surface problem[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2013, 37(9): 1048-1065. doi: 10.1002/nag.1137 [11] CHEVALIER B, COMBE G, VILLARD P. Experimental and discrete element modeling studies of the trapdoor problem: influence of the macro-mechanical frictional parameters[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2012, 7(1): 15-39. doi: 10.1007/s11440-011-0152-5 [12] DEWOOLKAR M M, SANTICHAIANANT K, KO H Y. Centrifuge modeling of granular soil response over active circular trapdoors[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2007, 47(5): 931-945. doi: 10.3208/sandf.47.931 [13] HAN J, WANG F, AL-NADDAF M, et al. Progressive development of two-dimensional soil arching with displacement[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 17(12): 04017112.1-04017112.12. [14] IGLESIA G R, EINSTEIN H H, WHITMAN R V. Validation of centrifuge model scaling for soil systems via trapdoor tests[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2011, 137(11): 1075-1089. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000517 [15] KEAWSAWASVONG S, UKRITCHON B. Undrained stability of an active planar trapdoor in non-homogeneous clays with a linear increase of strength with depth[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2017, 81: 284-293. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.08.027 [16] PARDO G S, SÁEZ E. Experimental and numerical study of arching soil effect in coarse sand[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2014, 57: 75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.01.005 [17] HAN G X, GONG Q M, ZHOU S H. Soil arching in a piled embankment under dynamic load[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2015, 15(6): 4014094.1-4014094.11. [18] SADREKARIMI J, ABBASNEJAD A. Arching effect in fine sand due to base yielding[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2010, 47(3): 366-374. doi: 10.1139/T09-107 [19] KHOSRAVI M H, PIPATPONGSA T, TAKEMURA J. Theoretical analysis of earth pressure against rigid retaining walls under translation mode[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2016, 56(4): 664-675. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2016.07.007 [20] YAO Q Y, DI H G, JI C, et al. Ground collapse caused by shield tunneling in sandy cobble stratum and its control measures[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(10): 5599-5614. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01878-9 [21] 陈强,董桂城,王超,等. 基于透明土技术的桩后土拱效应特征分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(3): 509-522.CHEN Qiang, DONG Guicheng, WANG Chao, et al. Characteristics analysis of soil arching effect behind pile based on transparent soil technology[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(3): 509-522. [22] 周思危. 砂土平面土拱形状及沉降特性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2019. [23] TAYLOR Z J, GURKA R, KOPP G A, et al. Long-duration time-resolved PIV to study unsteady aerodynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2010, 59(12): 3262-3269. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2010.2047149 [24] HADAD T, GURKA R. Effects of particle size, concentration and surface coating on turbulent flow properties obtained using PIV/PTV[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2013, 45: 203-212. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2012.11.006 [25] 郑云,刘志祥,余志祥,等. 基于PIV试验的积雪平屋面风场特性研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(2): 430-437,461.ZHENG Yun, LIU Zhixiang, YU Zhixiang, et al. Wind field characteristics of snow-covered low-rise building roof based on PIV experiments[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 430-437,461. -




 下载:
下载: