Characteristic Identification of Aerodynamic Noise Sources in High-Speed Train Bogie Area
-
摘要:
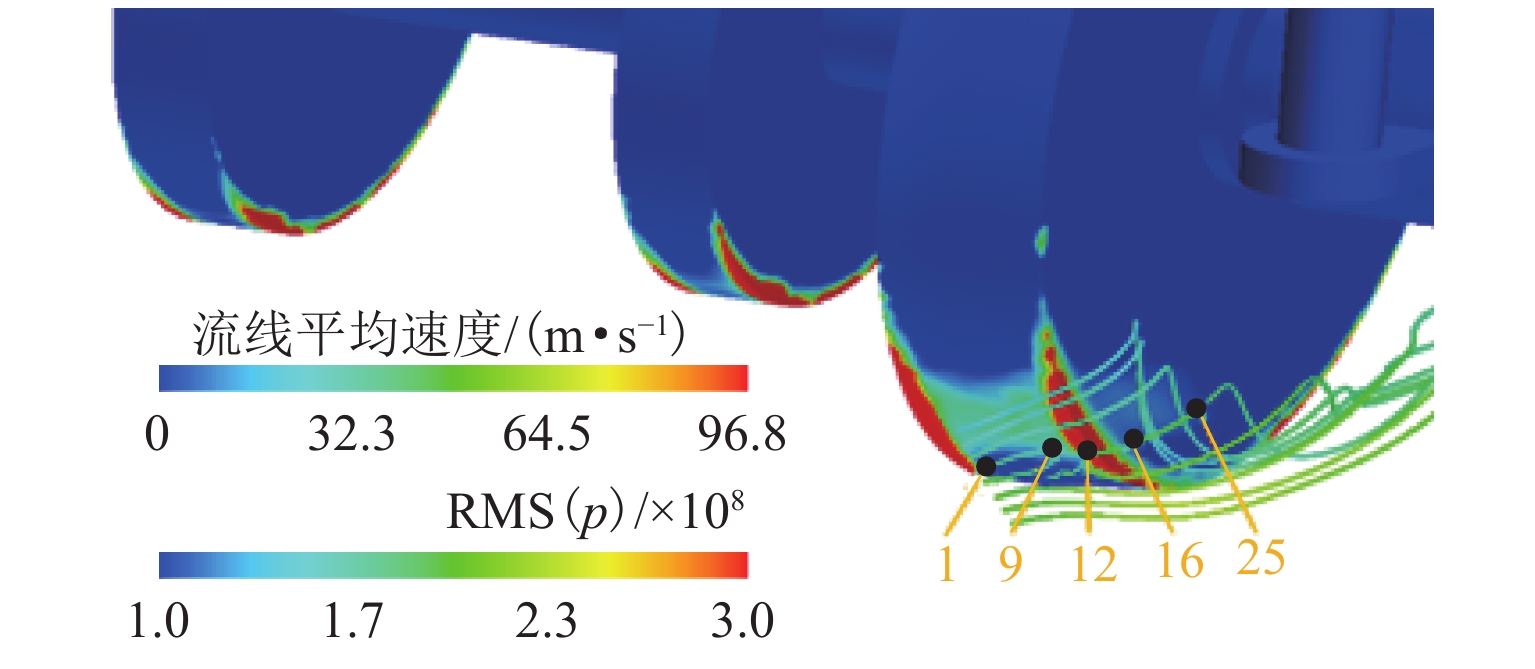
为了创建高速列车气动噪声源识别方法,以气动声学基本波动方程为基础,将高速列车气动声源等效为无数微球形声源组成,利用声辐射和流场物理量之间的关系,并结合高速列车气动数值仿真技术,建立了高速列车偶极子声源和四极子声源的识别方法,从全新的角度对某高速列车头车气动噪声源进行识别;基于涡声方程声源项特征,进一步揭示了偶极子声源和流场流动的关系. 研究结果明确了高速列车主要偶极子和四极子声源的强弱和分布特征,表明了气流的直接撞击和分离现象是产生声源的主要原因,头车及转向架区域气动噪声源以偶极子声源为主;偶极子声源强度较大位置出现在边沿较为尖锐的地方,在绝大多数情况下流体经过时涡量急剧增加,成为其形成强声源的主要原因.
Abstract:In order to create an identification method of aerodynamic noise source of high-speed trains, based on the wave equation of aeroacoustics, the high-speed train aerodynamic sound source was equivalent to countless micro-spherical sound sources. Using the relationship between sound radiation and physical quantities of the flow field, combined with the high-speed train aerodynamic numerical simulation technology, identification methods of dipole sound source and quadrupole sound source of high-speed train were established. The aerodynamic noise sources of a high-speed train head coach were identified from a new perspective by the methods. Based on the characteristics of the sound source term of the vortex sound equation, the relationship between the dipole sound source and the flow field was revealed. The research results clarify the strength and distribution characteristics of the main dipole and quadrupole sound sources of high-speed train, and indicate that the direct impact and separation of the airflow are the main reasons for the sound sources. The aerodynamic noise sources in the head coach and bogie area are mainly dipole sound sources. The strong dipole sound sources appear at the sharp edges of the parts. In most cases, the vorticity increases sharply when the fluid passes by those sharp edges, which becomes the main reason for the formation of a strong sound source.
-
表 1 网格独立性测试结果
Table 1. Grid independence test results
网格量/万 图 4 中测点 3/
总声压级与风洞实验
总声压级差值3800 79.8 2.3 4000 80.2 2.7 4500 78.6 1.1 7000 78.4 0.9 -
[1] LIGHTHILL M J. On sound generated aerodynamically Ⅰ: general theory[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1952, 211(1107): 564-587. [2] LIGHTHILL M J. On sound generated aerodynamically Ⅱ: turbulence as a source of sound[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1954, 222(1148): 1-32. [3] CURLE N. The influence of solid boundaries upon aerodynamic sound[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1955, 231(1187): 505-514. [4] FFOWCS W J E, HAWKINGS D L. Boundary-layer pressure and the corcos model: a development to incorporate low-wavenumber constraints[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1965, 22: 505-519. [5] FFOWCS W J E, HAWKINGS D L. Sound generation by turbulence and surfaces in arbitrary motion[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series A (1934-1990), 1969, 264(1151): 321-342. [6] POWELL A. Theory of vortex sound[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1964, 36(1): 177-195. doi: 10.1121/1.1918931 [7] BOGEY C, BAILLY C, JUVÉ D. Computation of flow noise using source terms in linearized Euler’s equations[J]. AIAA Journal, 2002, 40(2): 235-243. doi: 10.2514/2.1665 [8] EWERT R, SCHRÖDER W. Acoustic perturbation equations based on flow decomposition via source filtering[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 188(2): 365-398. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00168-2 [9] 王毅刚,黄晓胜,危巍,等. 涡声理论在汽车A柱气动噪声优化中的应用[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2017,37(2): 107-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2017.02.022WANG Yigang, HUANG Xiaosheng, WEI Wei, et al. Aerodynamic noise optimization of vehicle’s A-pillar based on vortex sound theory[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2017, 37(2): 107-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2017.02.022 [10] 杨志刚,刘洋,王毅刚. 有限长圆柱绕流气动噪声源特性分析[J]. 声学技术,2019,38(1): 5-14.YANG Zhigang, LIU Yang, WANG Yigang. Study of aeroacoustic noise source induced by a cylindrical flow of finite length[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2019, 38(1): 5-14. [11] MELLET C, LÉTOURNEAUX F, POISSON F, et al. High speed train noise emission: latest investigation of the aerodynamic/rolling noise contribution[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 293(3/4/5): 535-546. [12] 张卫华. 高速列车顶层设计指标研究[J]. 铁道学报,2012,34(9): 15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.09.003ZHANG Weihua. Study on top-level design specifications of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(9): 15-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.09.003 [13] 张曙光. 350 km·h−1高速列车噪声机理、声源识别及控制[J]. 中国铁道科学,2009,30(1): 86-90.ZHANG Shuguang. Noise mechanism, sound source localization and noise control of 350 km·h−1 high-speed train[J]. China Railway Science, 2009, 30(1): 86-90. [14] 高阳,王毅刚,王金田,等. 声学风洞中的高速列车模型气动噪声试验研究[J]. 声学技术,2013,32(6): 506-510.GAO Yang, WANG Yigang, WANG Jintian, et al. Testing study of aerodynamic noise for high speed train model in aero-acoustic wind tunnel[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2013, 32(6): 506-510. [15] NAGAKURA K. Localization of aerodynamic noise sources of Shinkansen trains[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, 293(3/4/5): 547-556. [16] HE B, JIN X S. Investigation into external noise of a high-speed train at different speeds[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science A, 2014, 15: 1019-1033. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1400307 [17] LAUTERBACH A, EHRENFRIED K, LOOSE S, et al. Microphone array wind tunnel measurements of Reynolds number effects in high-speed train aeroacoustics[J]. International Journal of Aeroacoustics, 2012, 11(3/4): 411-446. [18] ATSUSHI Y N I. Evaluation methods for aerodynamic noise from a high-speed train bogie in a wind tunnel test[C]//INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, 2011(6): 1543-1553. [19] 张亚东,张继业,张亮,等. 高速列车动车转向架气动噪声数值分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 870-877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.008ZHANG Yadong, ZHANG Jiye, ZHANG Liang, et al. Numerical analysis of aerodynamic noise of motor car bogie for high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 870-877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.008 [20] 黄莎,杨明智,李志伟,等. 高速列车转向架部位气动噪声数值模拟及降噪研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2011,42(12): 3899-3904.HUANG Sha, YANG Mingzhi, LI Zhiwei, et al. Aerodynamic noise numerical simulation and noise reduction of high-speed train bogie section[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2011, 42(12): 3899-3904. [21] 朱剑月,王毅刚,杨志刚,等. 高速列车转向架区域裙板对流场与气动噪声的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2017,45(10): 1512-1521. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.10.014ZHU Jianyue, WANG Yigang, YANG Zhigang, et al. Effect of bogie fairing on flow and aerodynamic noise behaviour around bogie of high-speed train[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2017, 45(10): 1512-1521. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.10.014 [22] HAN J, LAN J. Research on the radiation characteristics of aerodynamic noises of a simplified bogie of the high-speed train[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2017, 19(3): 2280-2293. doi: 10.21595/jve.2017.18229 [23] 高阳,李启良,陈羽,等. 高速列车头型近场与远场噪声预测[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(1): 124-129. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2019.01.018GAO Yang, LI Qiliang, CHEN Yu, et al. Prediction of near field and far field noise for high-speed train head shape[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2019, 47(1): 124-129. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2019.01.018 [24] 张强. 气动声学基础[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012. -





 下载:
下载: