SAR Image Generation Method via PCGAN for Ship Detection
-
摘要:
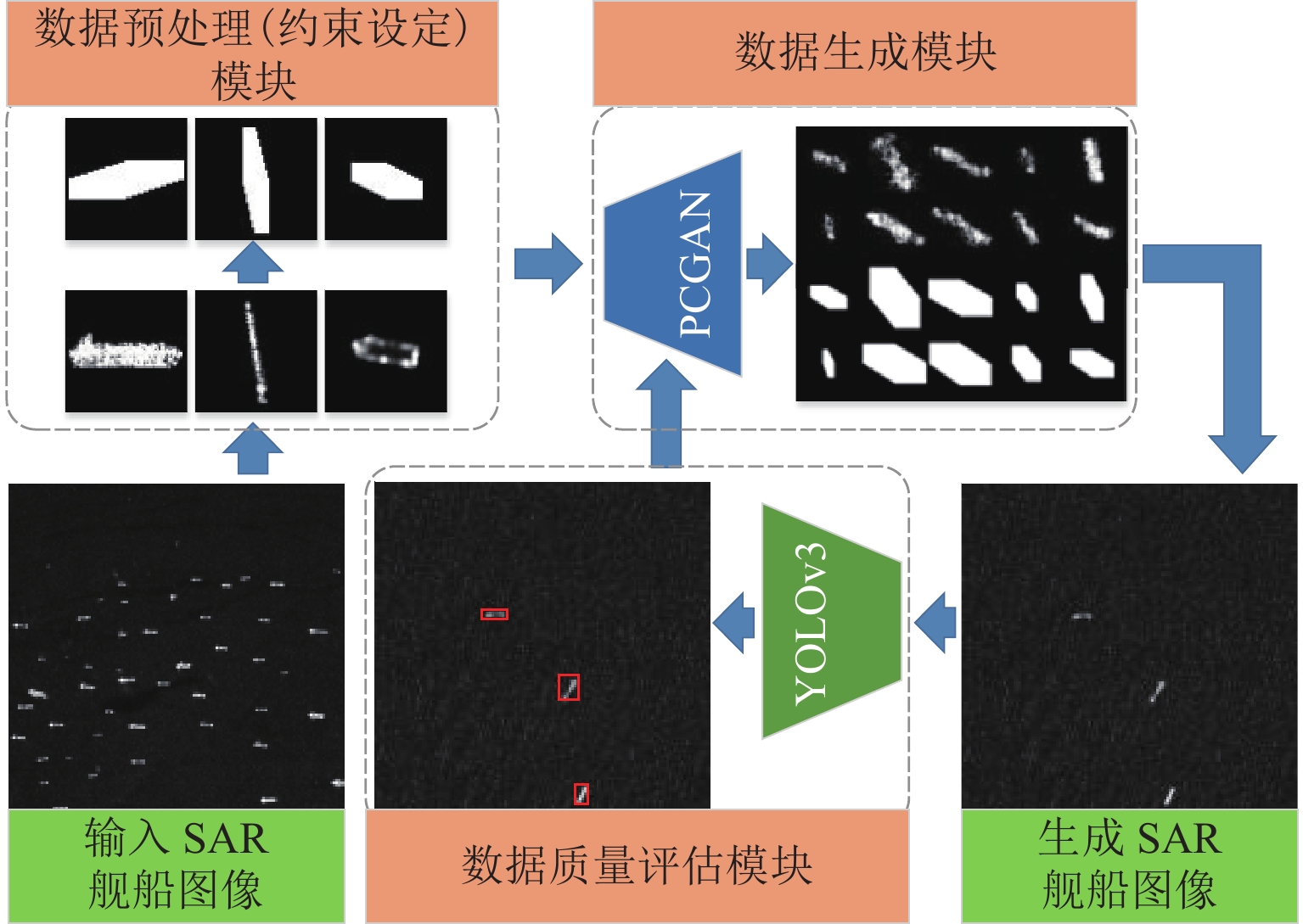
针对现有合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像数据生成方法大多无法同时生成舰船图像及其检测标签的问题,面向SAR舰船图像生成及目标检测任务,构建基于位置信息的条件生成对抗网络(PCGAN). 首先,提出将舰船位置信息作为约束条件用于限制生成图像中舰船的位置,并将其作为舰船图像的检测标签;随后,引入Wasserstein距离稳定PCGAN的训练过程;最后,利用生成的SAR舰船图像及对应检测标签完成YOLOv3网络的端到端训练,实现舰船数据增强与目标检测的协同学习,进而获得更耦合目标检测实际应用的多样性数据. 在HRSID (high resolution SAR image dataset)数据集上的实验结果表明,PCGAN方法能生成清晰、鲁棒的SAR舰船数据,舰船检测准确度最高提升1.01%,验证了所提出方法的有效性.
Abstract:Most of existing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image generation methods fail to generate SAR images and their detection labels simultaneously. A position-based conditional generative adversarial network (PCGAN) is constructed for SAR ship image generation and target detection. Firstly, ship position information is used as a constraint and a detection label to restrict its position in the generated image. Then, the Wasserstein distance is further introduced to stabilize the training process of PCGAN. Finally, the generated SAR images and their corresponding labels are applied for the end-to-end training of YOLOv3, so as to realize the cooperative learning of data enhancement and ship detection, and further obtain the diversified ship data more coupled with the practical application of ship detection. Experimental results conducted on HRSID dataset illustrate that PCGAN can generate clear and robust SAR ship data, and the accuracy of ship detection can be improved by up to 1.01%, thus verifying the proposed method.
-
表 1 不同尺寸内舰船目标比重
Table 1. Proportion of ship targets in different sizes
尺寸/像素 32 × 32 64 × 64 128 × 128 比例/% 14.18 78.88 99.33 表 2 不同训练集下的实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results under different training sets
% 条件 I/幅 100 200 300 增强前 91.01 92.91 93.11 增强 1.0 倍 91.88 93.61 94.06 增强 1.5 倍 91.79 93.73 94.12 增强 2.0 倍 91.46 93.31 93.93 增强 3.0 倍 91.48 93.33 94.00 表 3 不同GAN网络的生成图像质量
Table 3. Image quality of different GANs
不同
生成网络FID SWD 舰船
图像增强
图像舰船
图像增强
图像GAN 221.9 126.3 3665 2519 WGAN 66.06 96.92 181.7 1692 条件 WGAN 157.1 102.8 448.3 1699 条件 WGAN+方向 99.61 99.07 440.0 1620 PCGAN 86.94 95.62 434.2 1513 表 4 消融实验结果
Table 4. Results of ablation experiments
不同生成网络 准确度/% 无生成网络 93.11 条件 WGAN 93.71 条件 WGAN+方向 93.88 PCGAN 94.12 -
[1] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767. [2] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[EB/OL]. (2015-12-08)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.02325. [3] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. [4] DING J, CHEN B, LIU H W, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364-368. [5] 朱柳. 高分辨SAR场景分布的重建方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学,2013. [6] 刘鹏程. 基于特征调制的SAR欺骗干扰方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学,2013. [7] BALZ T, STILLA U. Hybrid GPU-based single- and double-bounce SAR simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(10): 3519-3529. [8] HAMMER H, SCHULZ K. Coherent simulation of SAR images[C]//Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering 7477. Berlin: [s.n.], 2009: 406-414. [9] VAN DEN OORD A, KALCHBRENNER N, KAVUKCUOGLU K. Pixel recurrent neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: [s.n.],2016: 1747-1756. [10] KINGMA D P, WELLING M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[EB/OL]. (2013-12-20)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114. [11] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal:MIT Press, 2014: 2672-2680. [12] RADFORD A, METZ L, CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2015-11-19)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434. [13] KARRAS T, AILA T, LAINE S, et al. Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation[EB/OL]. (2017-10-27)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10196. [14] MIRZA M, OSINDERO S. Conditional generative adversarial nets[EB/OL]. (2014-11-06)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.1784. [15] ARJOVSKY M, BOTTOU L. Towards principled methods for training generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2017-01-17)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.04862. [16] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L. Wasserstein GAN[EB/OL]. (2017-01-26)[2020-10-13]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.07875. [17] 徐永士,贲可荣,王天雨,等. DCGAN模型改进与SAR图像生成研究[J]. 计算机科学,2020,47(12): 93-99. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200700109XU Yongshi, BEN Kerong, WANG Tianyu, et al. Study on DCGAN model improvement and SAR images generation[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(12): 93-99. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.200700109 [18] HUANG H H, ZHANG F, ZHOU Y S, et al. High resolution SAR image synthesis with hierarchical generative adversarial networks[C]//IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Yokohama: IEEE, 2019: 2782-2785. [19] GUO J Y, LEI B, DING C B, et al. Synthetic aperture radar image synthesis by using generative adversarial nets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1111-1115. [20] LU Q L, JIANG H Y, LI G J, et al. Data augmentation method of SAR image dataset based on Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]//2019 International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Informatics (EEI). Nanjing: IEEE, 2019: 488-490. [21] GAO F, YANG Y, WANG J, et al. A deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs)-based semi-supervised method for object recognition in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 846.1-846.21. [22] WEI S J, ZENG X F, QU Q Z, et al. HRSID: a high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120234-120254. [23] HEUSEL M, RAMSAUER H, UNTERTHINER T, et al. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. California: ACM, 2017: 6629-6640. -





 下载:
下载: