Undifferenced Precise GPS Processing Software PLAOD and Its Performance Analysis
-
摘要:
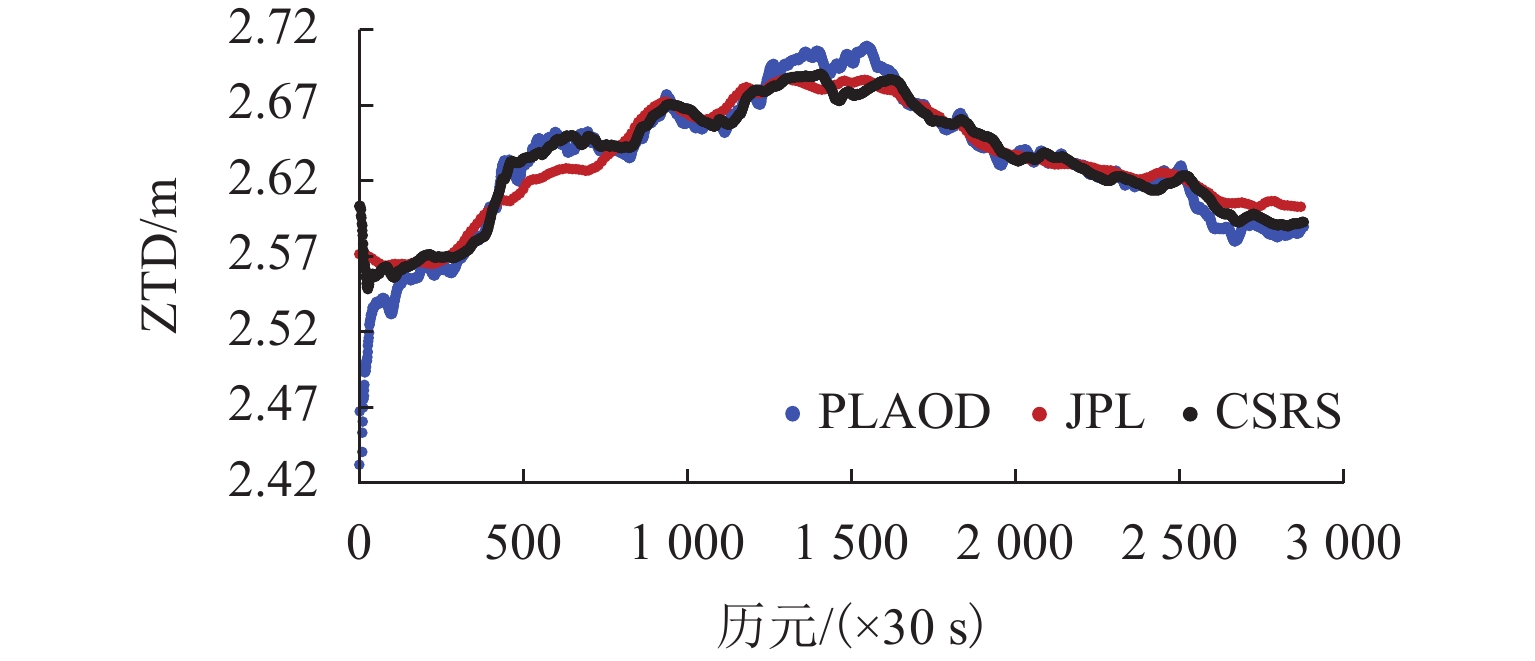
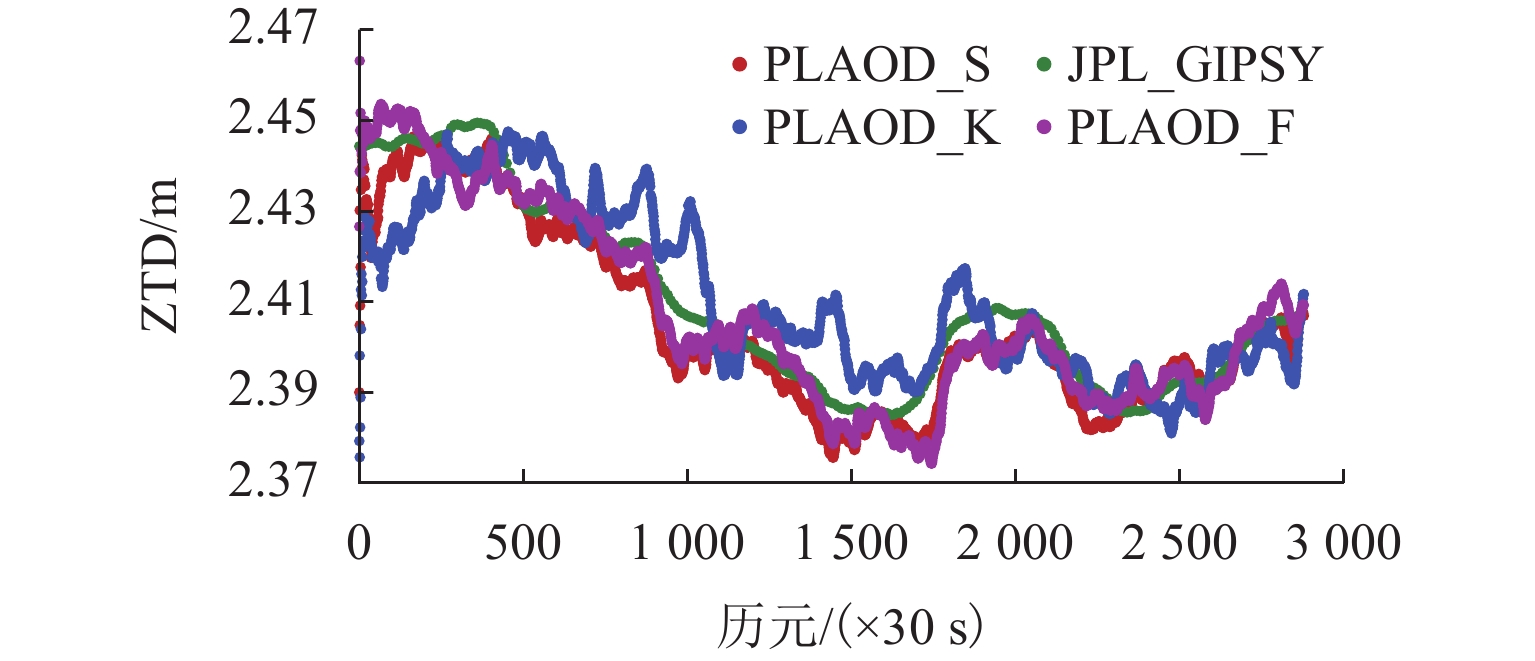
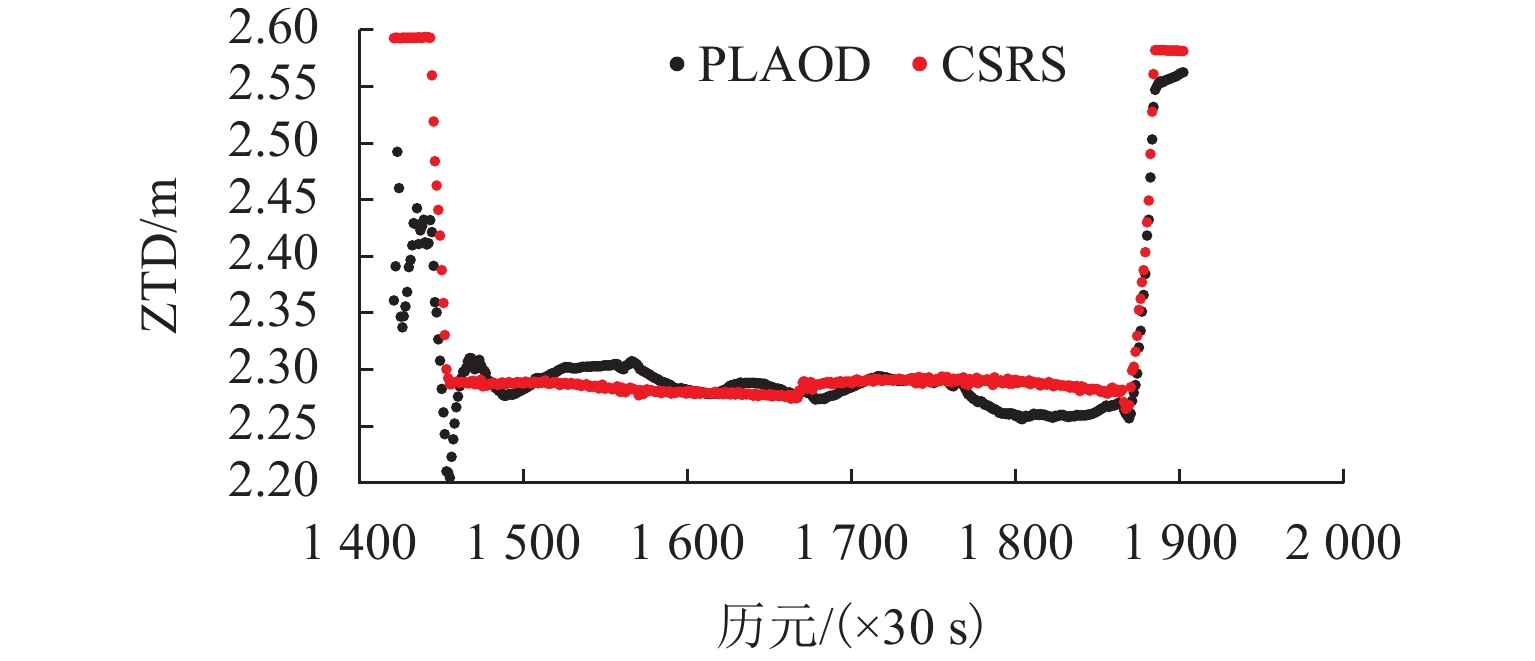
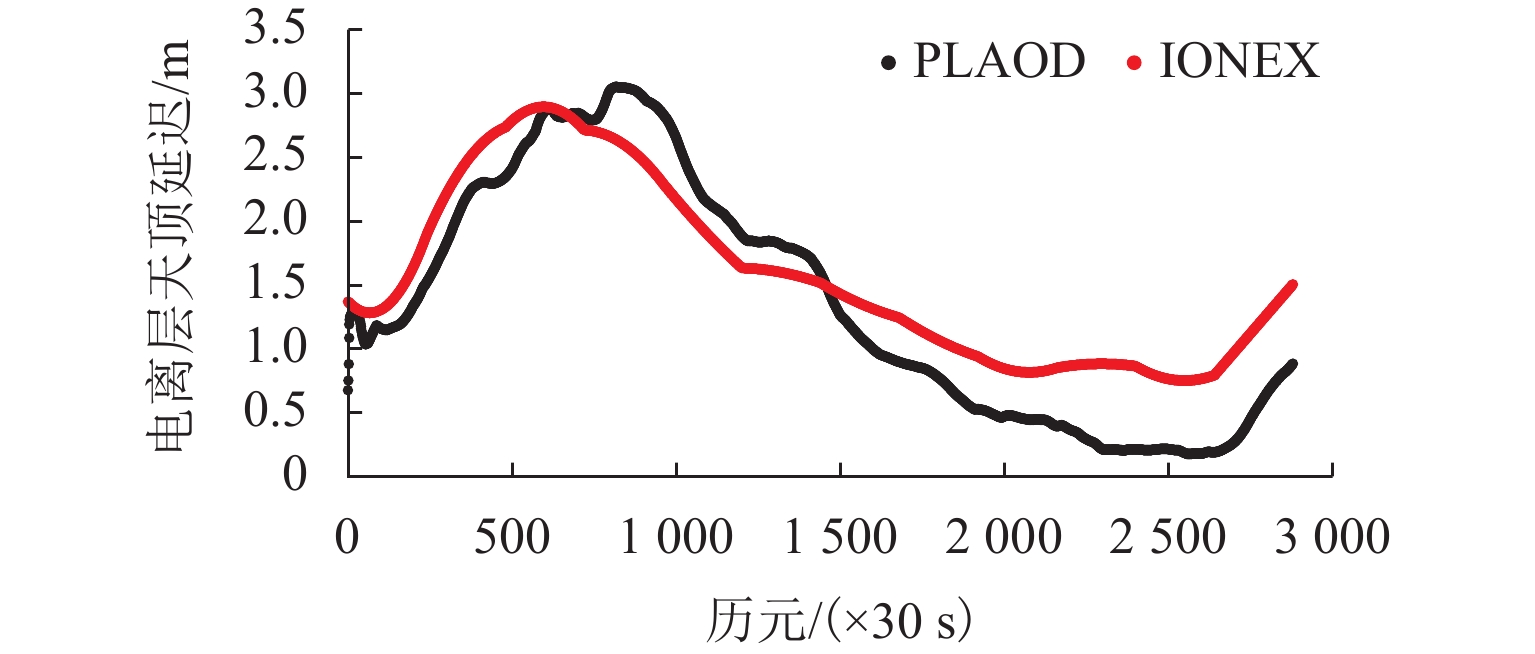
PLAOD (precise location and orbit determination)是西南交通大学自主研发的GPS非差精密定位定轨软件. 该软件目前能够处理GPS观测数据,具有高精度定位、大气反演和低轨卫星轨道确定功能. 本文在介绍PLAOD相关理论的基础之上对其性能进行了分析. 利用多组GPS观测数据进行测试,通过与IGS (international GNSS service)等相关机构精密产品对比,PLAOD具备如下性能:静态定位精度可达毫米级;动态定位精度可达厘米级;静态对流层天顶延迟的估计精度通常优于1 cm,动态对流层天顶延迟的估计精度在2 cm以内;电离层天顶延迟估计结果与IGS的IONEX (ionosphere exchange)产品具有较高的吻合度;与JPL (jet propulsion laboratory)提供的简化动力学低轨卫星轨道相比,几何法确定轨道的准确度可达厘米级.
Abstract:PLAOD (precise location and orbit determination) is an undifferenced precise GPS data processing software for positioning and orbit determination fully developed by Southwest Jiaotong University. Currently, the software can process GPS observation data, and has the functions of precise positioning, atmospheric inversion and orbit determination for low earth obiter. Following the introduction to basic theory of PLAOD, its performance is focused. Multiple sets of GPS observation data were tested. Compared with the precise product provided by IGS (international GNSS service) and other institutes, PLAOD has shown following features. The static positioning accuracy can reach millimeter level, the kinematic positioning accuracy can reach centimeter level, the estimation precision of the tropospheric zenith delay in static mode is usually better than 1 cm, and the one in kinematic mode is better than 2 cm. There is a high consistence between the ionospheric zenith delay results from PLAOD and the IONEX (ionosphere exchange) product of IGS. In comparison with the reduced dynamic orbit of low earth orbiter provided by JPL (jet propulsion laboratory), the accuracy of orbit determined by geometry method is usually at the centimeter level.
-
表 1 误差改正
Table 1. Error correction
表 2 PLAOD参数处理方案
Table 2. Parameter processing strategy of PLAOD
参数 处理方案 测站坐标 静态时过程噪声为 0,动态时先验值源自伪距单点定位 模糊度 过程噪声为 0 对流层 随机游走,过程噪声默认为 4 cm2/h,动态时顾及历元间高差引起的影响 对流层梯度 随机游走 电离层 随机游走 电离层梯度 随机游走 接收机钟差 先验值源自伪距单点定位 卫星钟差 20 min弧段二阶多项式拟合 卫星坐标 10 阶滑动拉格朗日插值 表 3 测试站地理点位置
Table 3. Geographic location of testing stations
站点 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) CHAN(长春) 125.443 43.790 BJFS(北京房山) 115.892 39.609 BJNM(北京) 116.224 40.245 HKSL(香港小冷水) 113.928 22.372 HKWS(香港黄石) 114.335 22.434 JFNG(九峰) 114.491 30.516 LHAZ(拉萨) 91.104 29.657 TWTF(桃园) 121.164 24.954 表 4 站点解算坐标偏差
Table 4. Coordinate bias of solved stations
站点 年积日 dN
/mmdE
/mmdU
/mm收敛时间
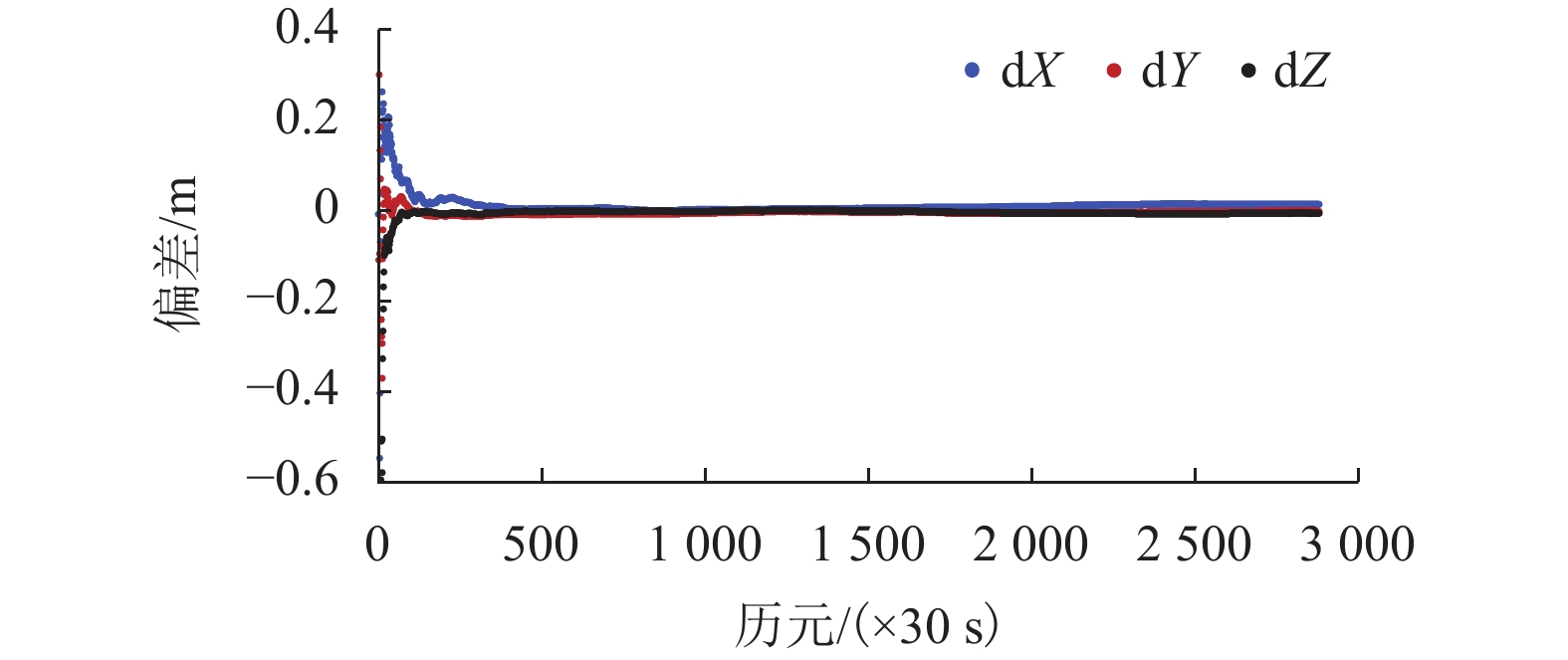
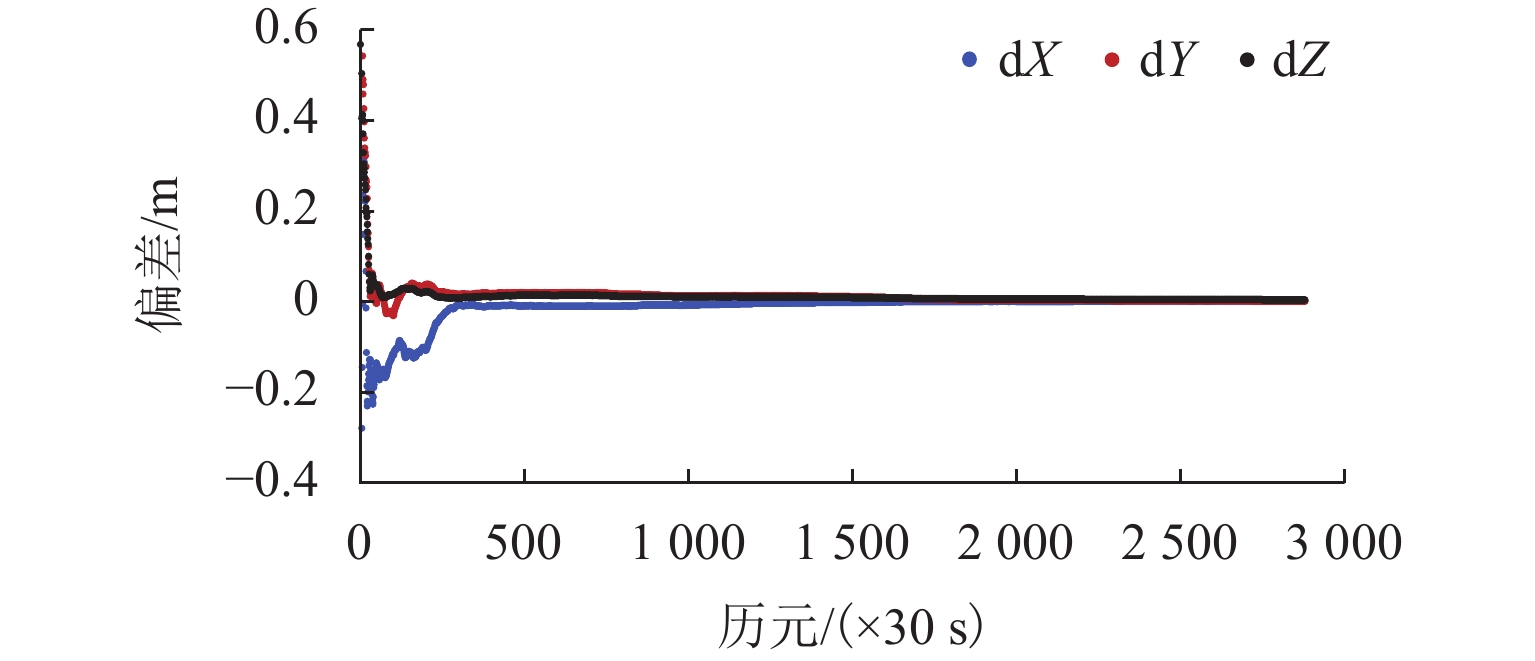
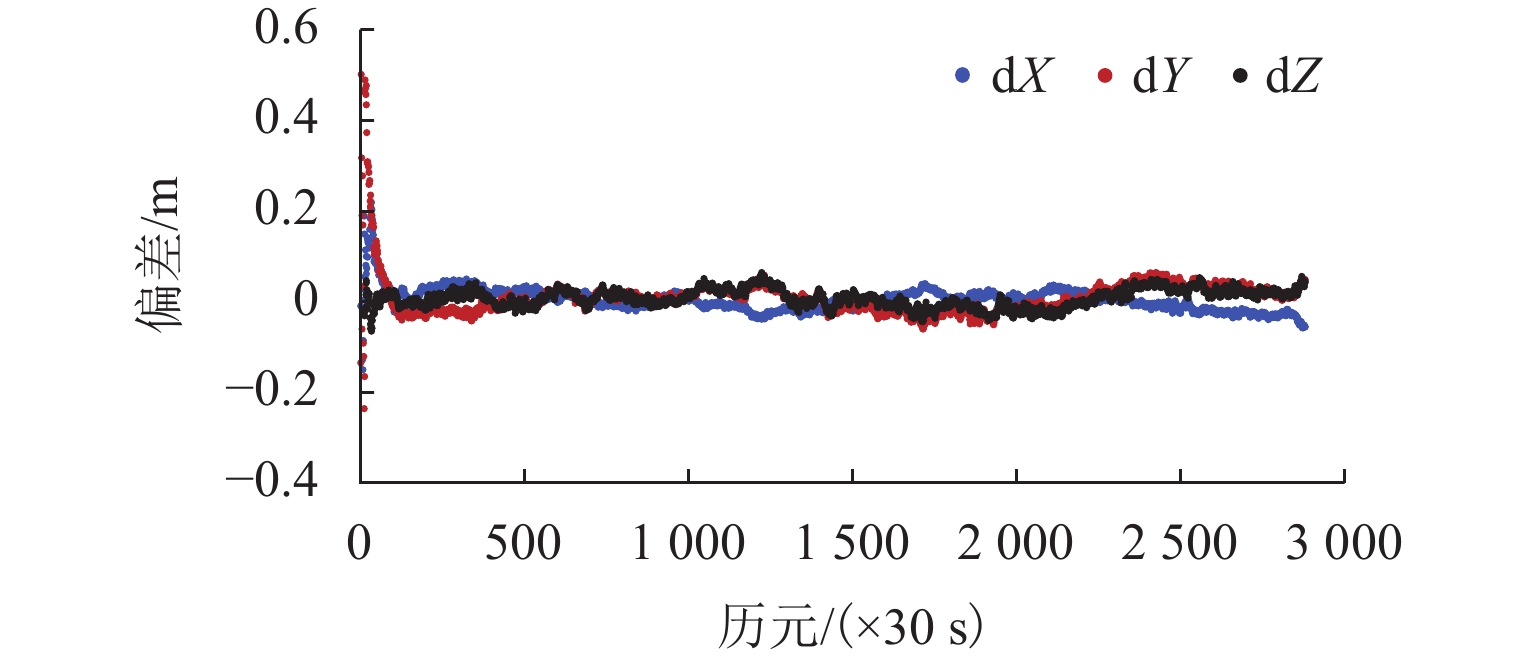
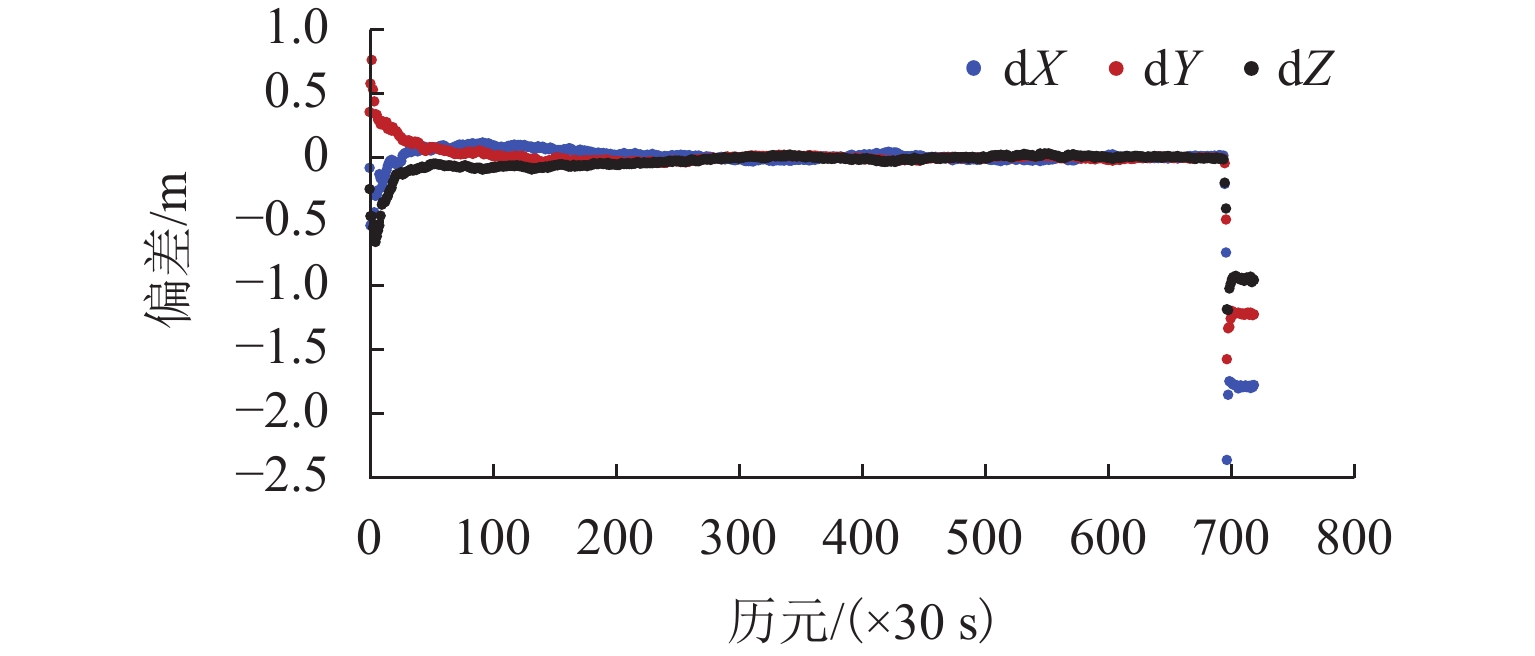
/minCHAN 001 1.9 −9.2 −11.3 32.0 002 2.4 −5.7 −7.5 19.0 003 2.0 −7.1 −9.2 43.0 BJFS 001 2.0 1.2 −1.8 30.0 002 2.5 0.7 −0.5 21.0 003 2.5 −0.2 2.8 23.0 BJNM 001 2.6 −3.6 −0.8 29.0 002 4.5 0.4 1.4 50.0 003 4.0 −4.5 4.3 46.5 HKSL 001 2.0 0.5 −3.9 30.5 002 3.8 0.1 1.7 25.0 003 4.4 −2.5 2.0 20.5 HKWS 001 1.0 1.5 2.2 30.0 002 3.3 1.9 −0.1 52.5 003 3.5 −0.3 1.9 104.5 JFNG 001 2.0 3.2 0.6 20.0 002 2.8 4.4 9.0 13.0 003 3.1 3.4 8.1 19.0 LHAZ 001 3.6 −1.5 −3.8 42.0 002 4.1 1.5 −0.3 57.0 003 3.5 −1.5 −4.4 44.0 TWTF 001 0.8 3.9 −9.3 26.5 002 4.4 1.0 −5.4 21.5 003 4.0 0.1 −6.3 19.0 -
[1] ZUMBERGE J F, HEFLIN M B, JEFFERSON D C, et al. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(B3): 5005-5017. doi: 10.1029/96JB03860 [2] KOUBA J, HÉROUX P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products[J]. GPS Solutions, 2001, 5(2): 12-28. doi: 10.1007/PL00012883 [3] GAO, Y, SHEN, X. A new method for carrier phase based precise point positioning[J]. Navigation, 2002, 49(2): 109-116. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.2002.tb00260.x [4] 张小红,李星星,李盼. GNSS精密单点定位技术及应用进展[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10): 1399-1407. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170327ZHANG Xiaohong, LI Xingxing, LI Pan. Review of GNSS PPP and its application[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1399-1407. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170327 [5] GENG Jianghui. Rapid integer ambiguity resolution in GPS precise point positioning[D]. Nottingham: University of Nottingham, 2010. [6] SIMON B, RICHARD B. L, MARCELO C. S. The precise point positioning software centre: an insight into online PPP services[R]. Buenos Aires: IAG, 2009. [7] IBANEZ D, ROVIRA G A, SANZ J, et al. The GNSS laboratory tool suite (gLAB) updates: SBAS, DGNSS and global monitoring system[C]//9th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing. Noordwijk: IEEE, 2018: 1-11. [8] TAKASU T. RTKLIB: open source program Package for RTK-GPS[R]. Tokyo: Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, 2009. [9] GENG J H, CHEN X Y, PAN Y X, et al. PRIDE PPP-AR: an open-source software for GPS PPP ambiguity resolution[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23(4): 1-10. [10] BANVILLE S, GENG J H, LOYER S, et al. On the interoperability of IGS products for precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00190-019-01332-z [11] ASHBY N. Relativity in the global positioning system[J]. Living Reviews in Relativity, 2003, 6(1): 1-42. doi: 10.12942/lrr-2003-1 [12] PETIT G, LUZUM B. IERS Conventions (2010) [EB/OL]. [2021-7-26]. https://www.iers.org/IERS/EN/Publications/TechnicalNotes/tn36.html. [13] WU J T, WU S C, HAJJ G A, et al. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase[J]. Manuscripta Geodaetica, 1993, 18(2): 91-98. [14] WELCH G, BISHOP G. An introduction to the Kalman filter[EB/OL]. [2021-07-26]. https://www.cs.unc.edu/~welch/media/pdf/kalman_intro.pdf [15] GUO J Y, YUAN Y D, KONG Q L, et al. Deformation caused by the 2011 eastern Japan great earthquake monitored using the GPS single-epoch precise point positioning technique[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2012, 9(4): 483-493. doi: 10.1007/s11770-012-0360-2 [16] KOUBA J. Implementation and testing of the gridded Vienna mapping function 1 (VMF1)[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2008, 82(4/5): 193-205. [17] BOEHM J, NIELL A, TREGONING P, et al. Global mapping function: a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(7): 304-317. [18] BOEHM J, HEINKELMANN R, SCHUH H. Short note: a global model of pressure and temperature for geodetic applications[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2007, 81(10): 679-683. doi: 10.1007/s00190-007-0135-3 -




 下载:
下载: