Experimental Study on Hydro-Abrasion Performance of Polyvinyl Alcohol Fiber Cementitious Composites
-
摘要:
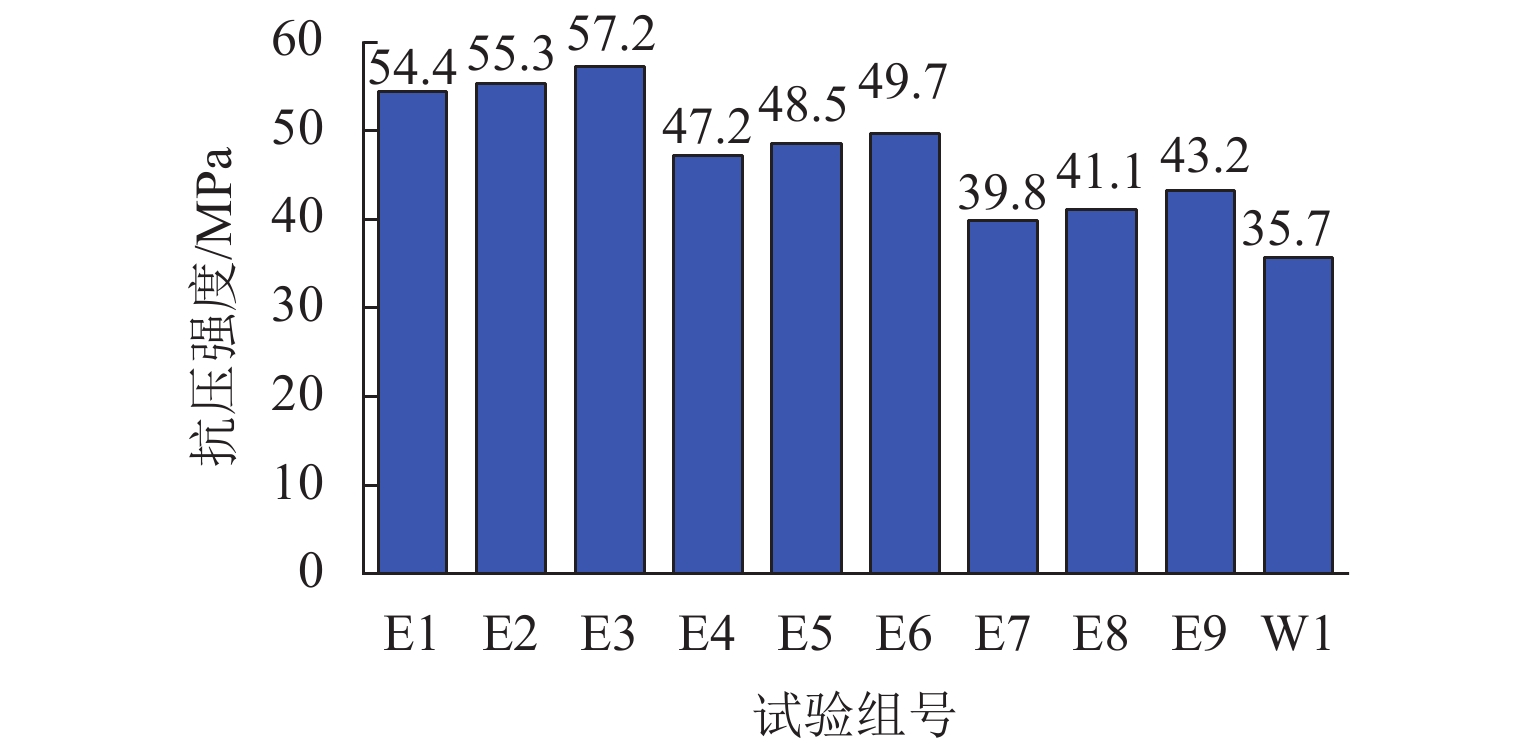
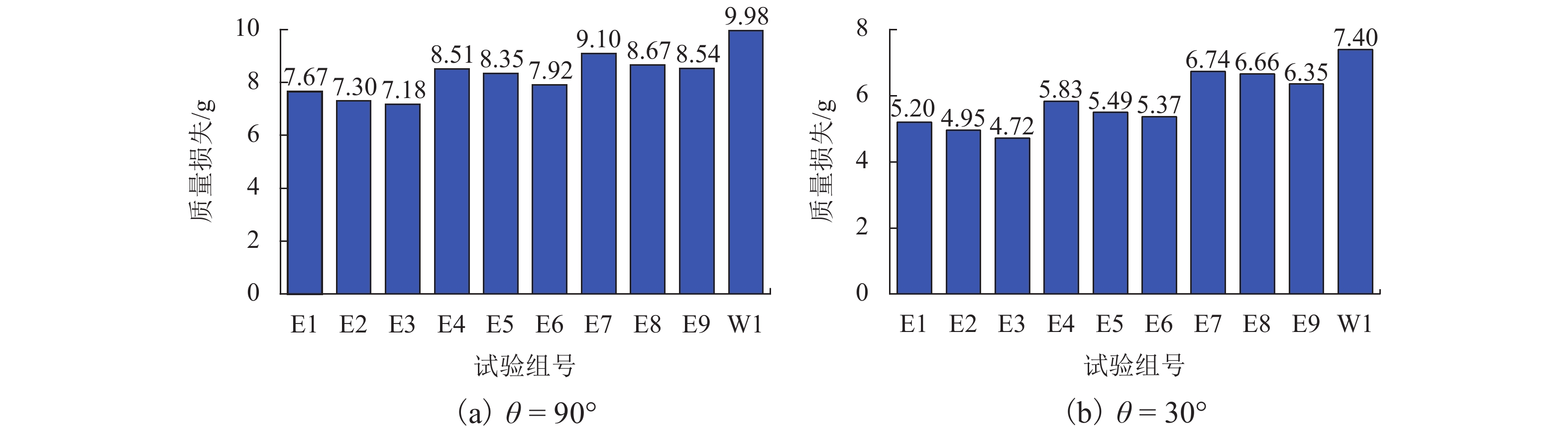
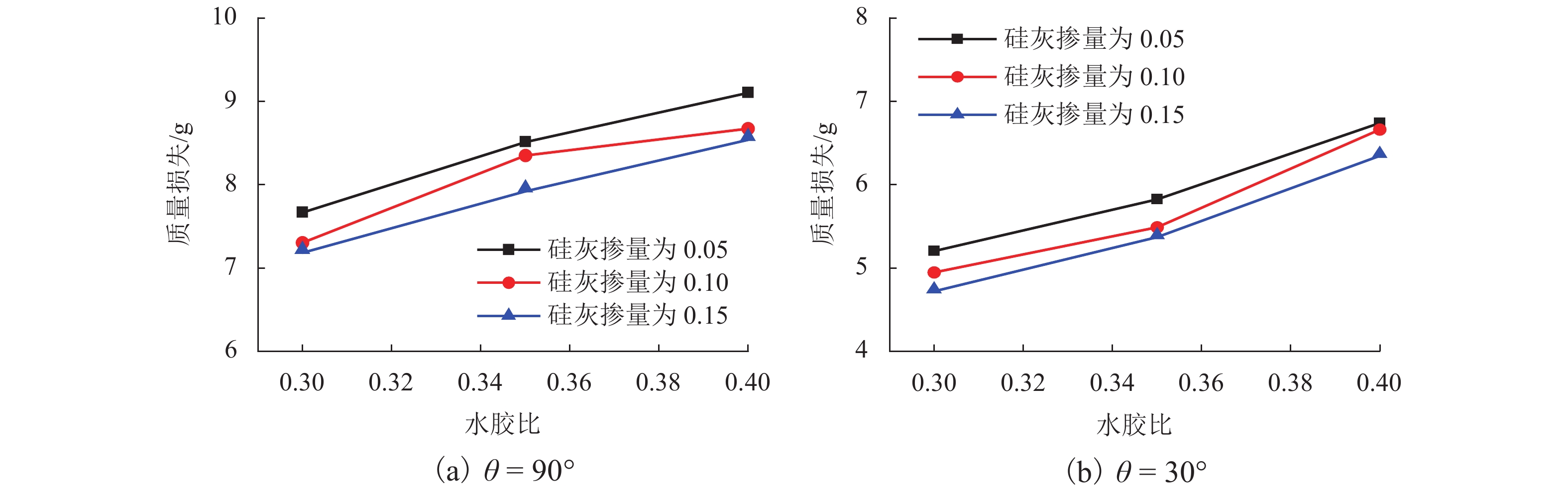
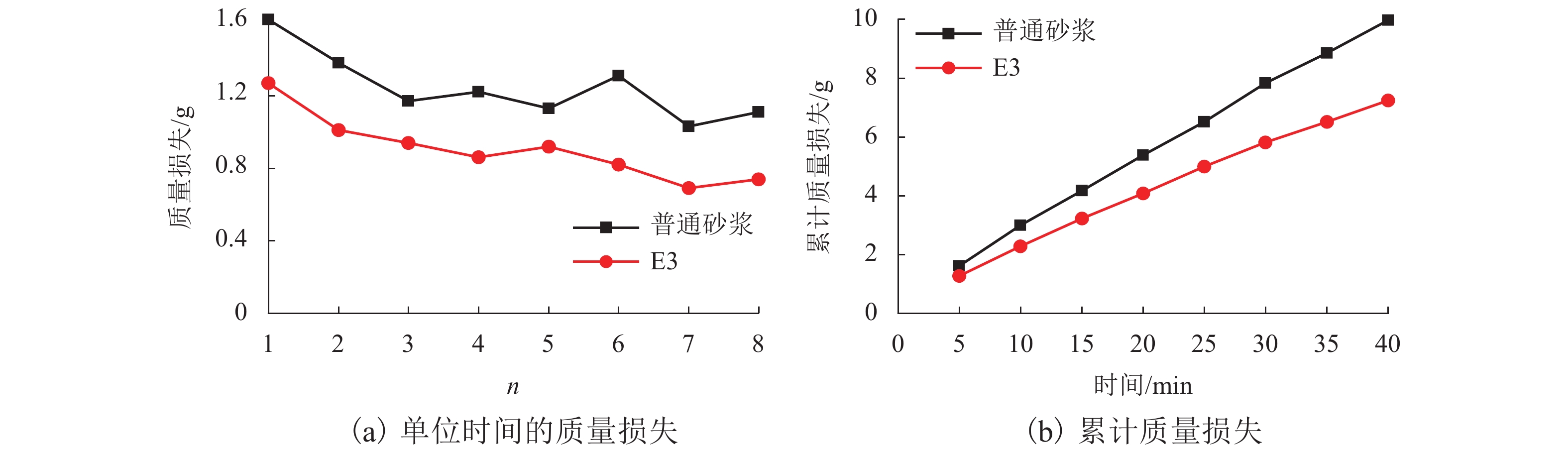
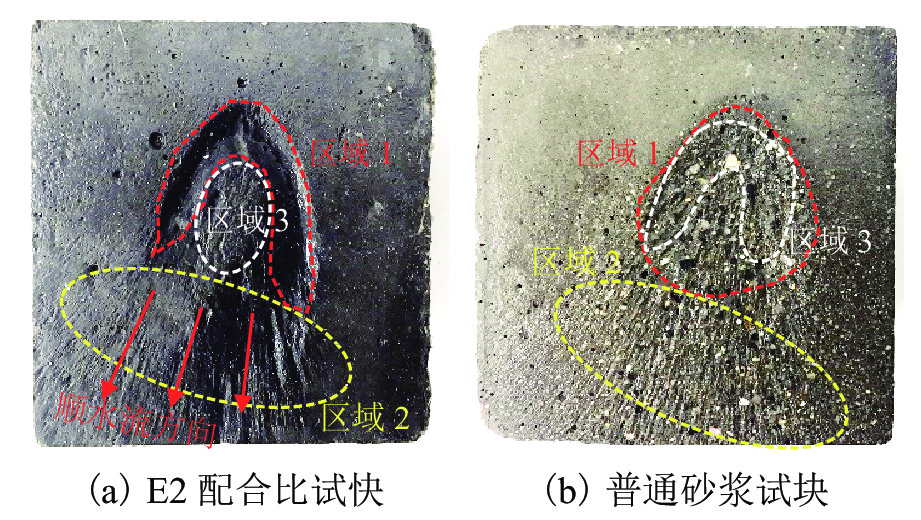
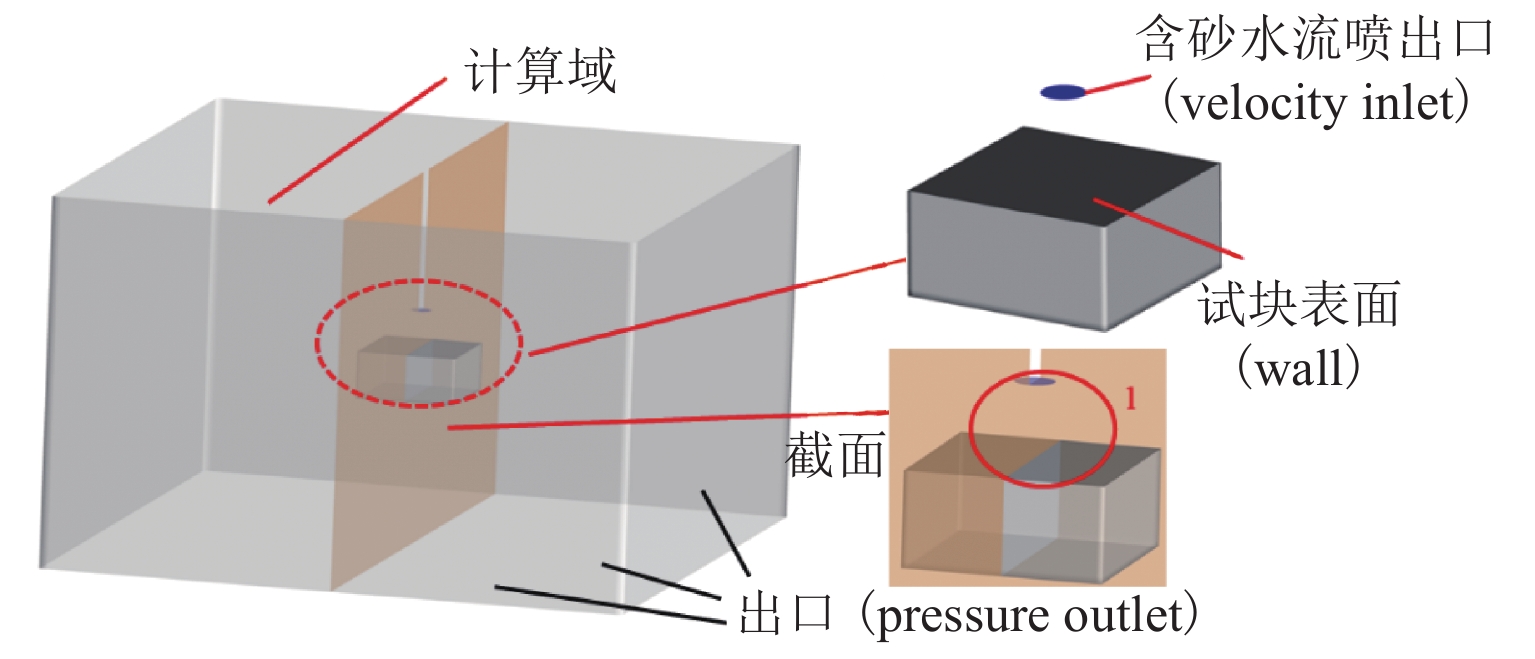
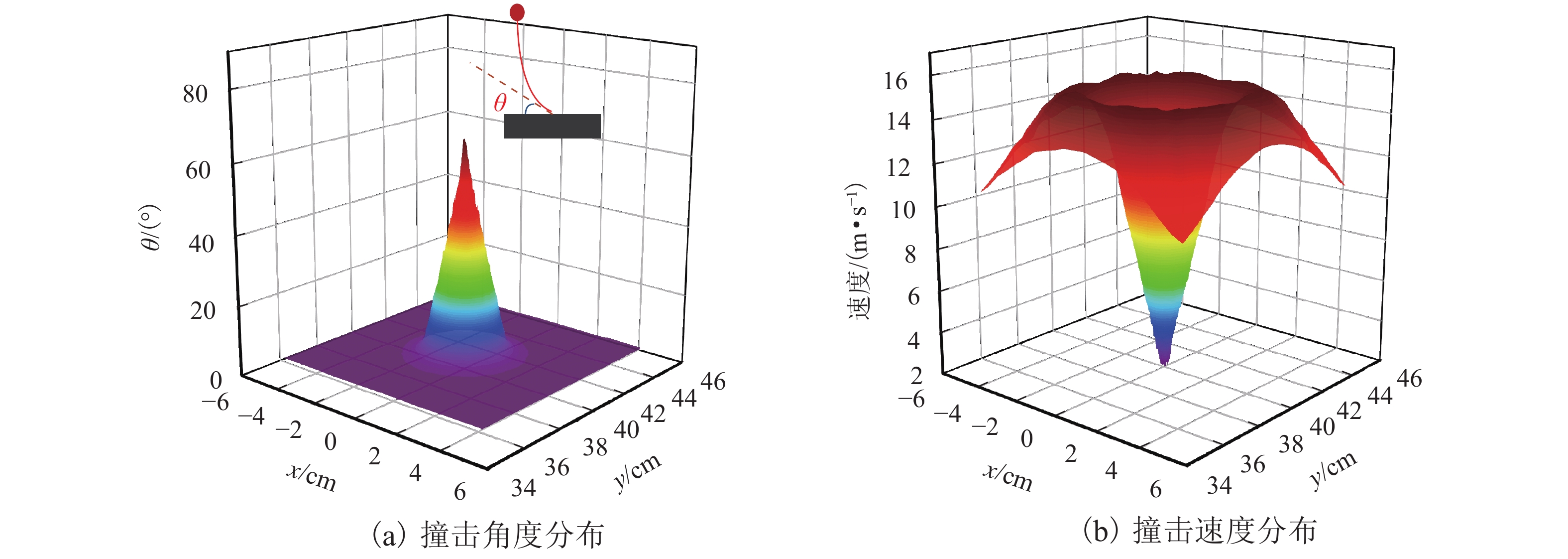
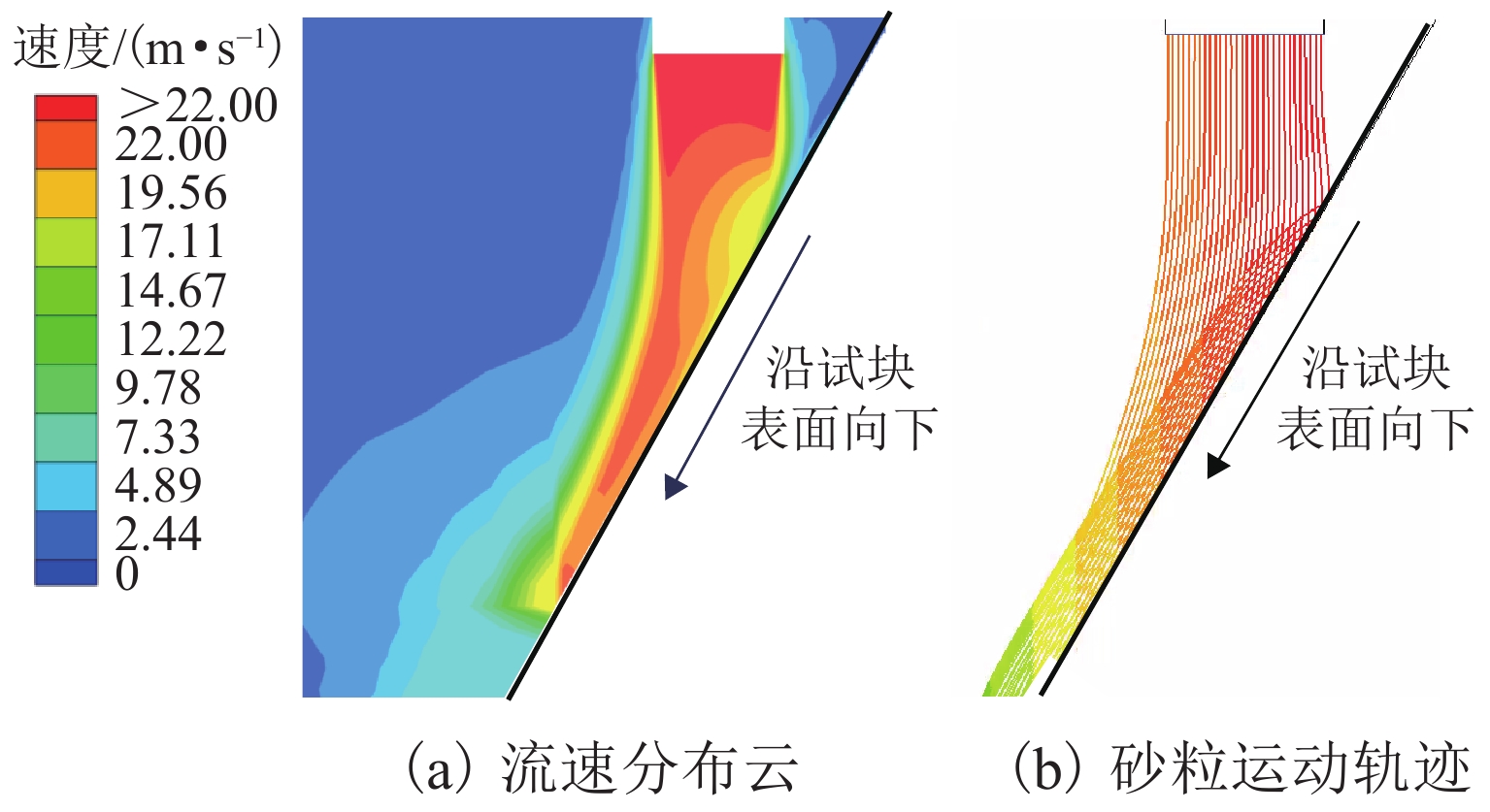
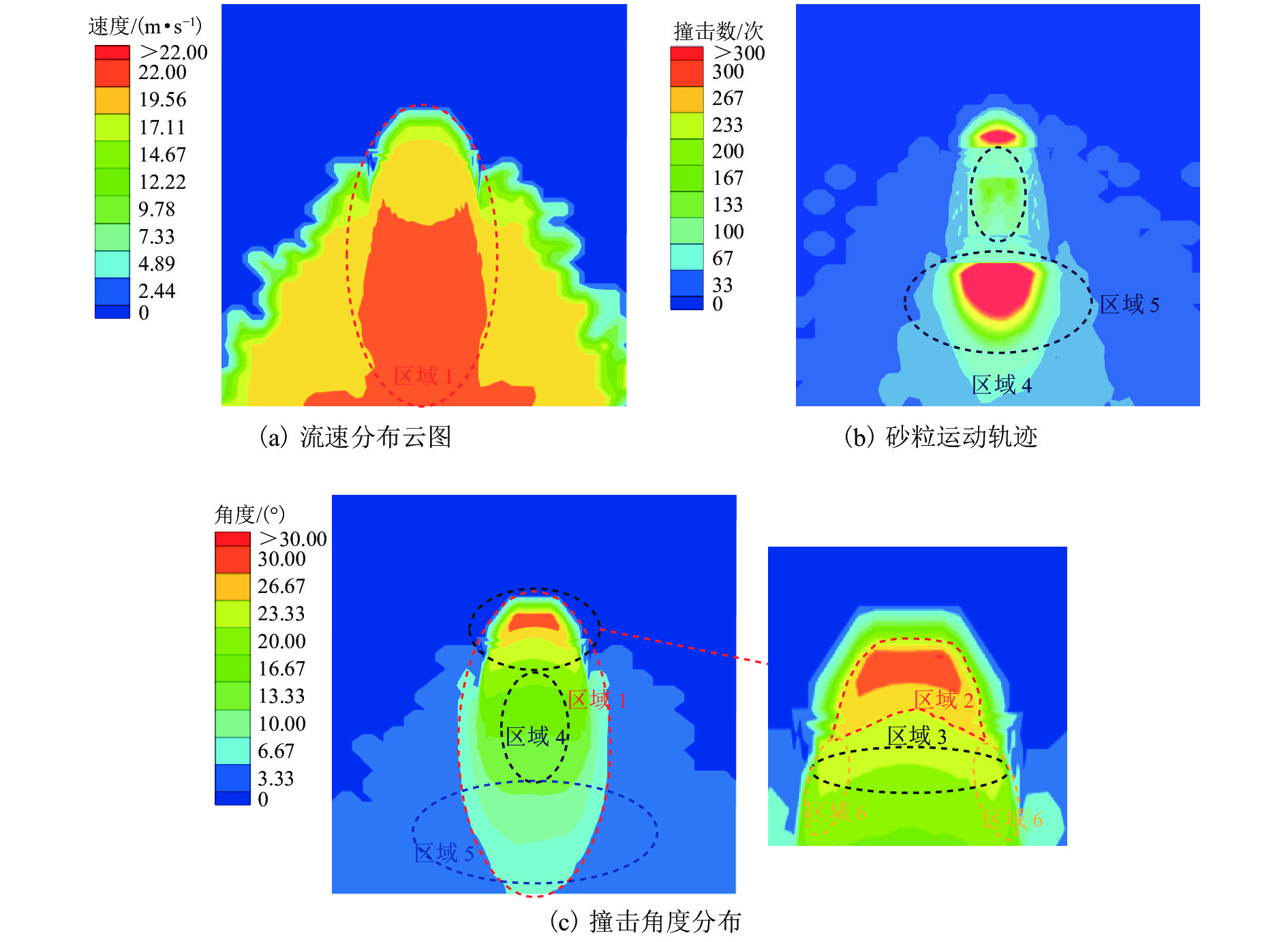
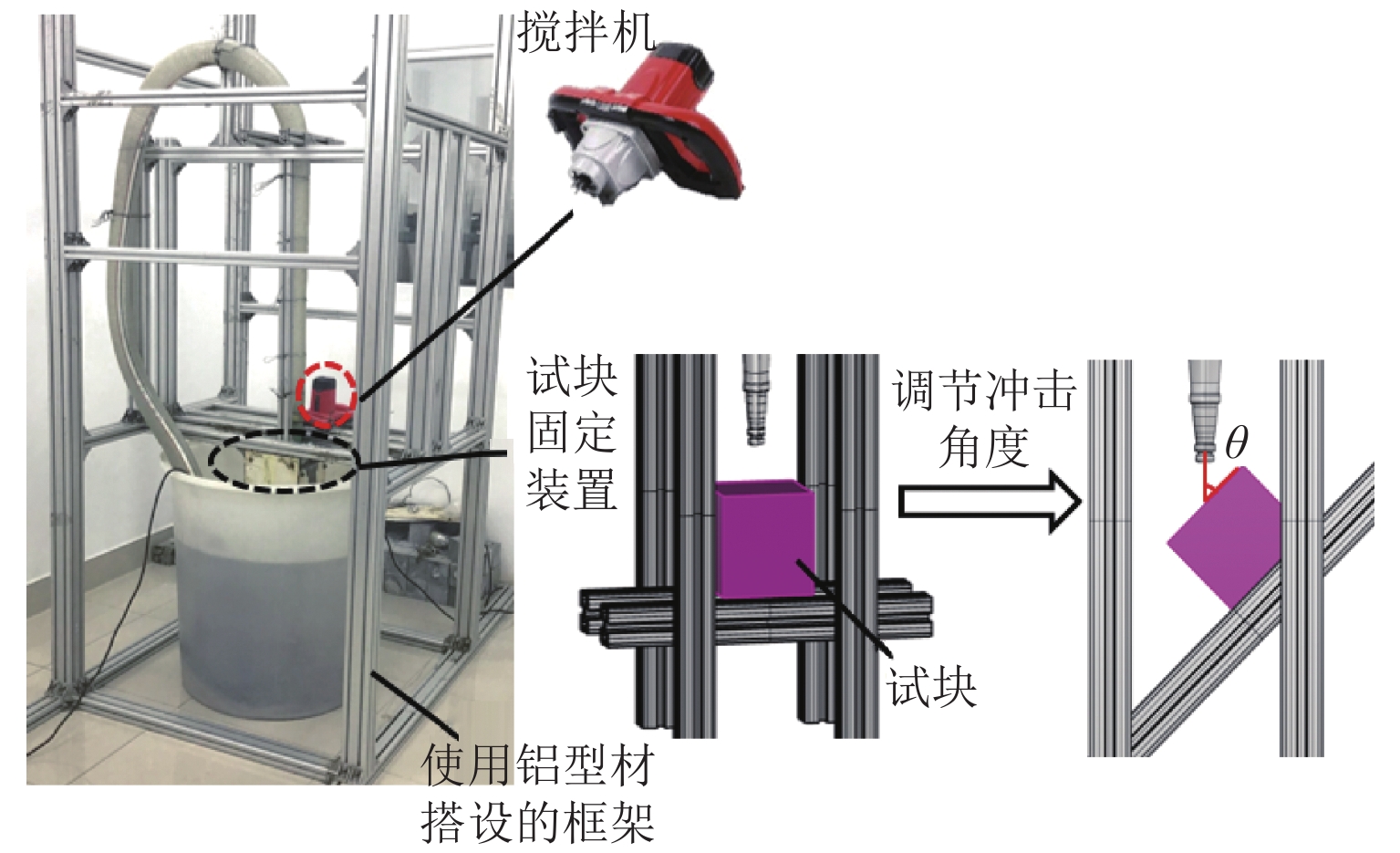
挟沙水流对桥墩的冲蚀磨损严重,继而影响桥梁的安全服役. 为此,采用自主研制的冲蚀磨损试验装置,对一种桥墩抗冲蚀磨损材料——聚乙烯醇(polyvinyl alcohol,PVA)纤维水泥基复合材料进行冲蚀磨损试验. 以普通砂浆为参照,首先,测试了普通砂浆试块和PVA纤维水泥基复合材料试块的抗压强度;然后,测量了冲蚀引起的质量损失,并分析了两类材料在不同冲击角度下的冲蚀磨损特点;最后,采用计算流体力学程序开展数值模拟,从流场角度对冲蚀磨损机理开展了深入分析. 研究结果表明:水胶比对材料抗冲蚀磨损性能影响最大,水胶比越低,材料的强度越高和抗冲蚀磨损性能越好;在不同的冲击角度下,试块表面的冲蚀坑形状不同,在90° 冲击条件下,冲蚀坑呈圆环状,在30° 冲击条件下,冲蚀坑呈马蹄形;普通砂浆和E3配合比试块随冲击时间增加,单位时间(5 min)的质量损失逐渐减小,但两者的冲蚀过程不同.
Abstract:Bridge safety during service is greatly influenced by hydro-abrasion caused by waterborne sand. An independently developed testing device was employed to conduct hydro-abrasion tests on a type of anti-abrasion material, i.e., polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber reinforced cement based composites. Ordinary mortar was selected as the reference material. Firstly, the compressive strengths of the two types of materials were tested and then the weight losses caused by hydro-abrasion were measured. The hydro-abrasion characteristics of the two materials under different impacting angles were analyzed. Finally, the computational fluid dynamics program was used to conduct numerical simulation and the generation mechanisms of abrasion pits were explored on the basis of flow field analysis. Results show that water-binder ratio has the most influence on the anti-abrasion performance; the smaller the water-binder ratio, the larger the material compressive strength and the better the anti-abrasion performance. Abrasion pits on the specimen surfaces have different shapes when suffering impacting of different angles, i.e., the abrasion pit is circular when the impacting angle is 90°, and it is in horseshoe shape when the impacting angle is 30°. The abrasion weight loss of the ordinary mortar specimen and the E3 mix-proportion specimen increases with impacting time. However, the abrasion weight per unit time (5 minutes) of the two types of materials deceases with the increase of the unit time, and their abrasion processes are different.
-
表 1 PVA纤维水泥基复合材料抗冲蚀性能正交试验方案配合比
Table 1. Mix proportion of PVA fiber reinforced cement based composites in orthogonal test scheme on anti-abrasion performance
编号 材料/(kg•m−3) 掺量比重 水 水泥 硅灰 微珠 砂 减水剂 PVA纤维 水胶比 硅灰 微珠 El 381 1080 64 127 457 19 26 0.30 0.05 0.10 E2 381 953 127 191 457 19 26 0.30 0.10 0.15 E3 381 826 191 254 457 19 26 0.30 0.15 0.20 E4 432 987 62 185 444 19 26 0.35 0.05 0.15 E5 432 864 123 247 444 19 26 0.35 0.10 0.20 E6 432 925 185 123 444 19 26 0.35 0.15 0.10 E7 480 899 60 240 432 18 26 0.40 0.05 0.20 E8 480 959 120 120 432 18 26 0.40 0.10 0.10 E9 480 839 180 180 432 18 26 0.40 0.15 0.15 注:PVA纤维掺量占其余材料总体积的百分数为 2%. -
[1] 黄细彬,袁银忠,王世夏. 含沙掺气高速水流对壁面磨蚀的分析[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版),2000,28(2): 27-31.HUANG Xibin, YUAN Yinzhong, WANG Shixia. Analysis of abrasion of wall material by high velocity sediment laden and aerated flow[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2000, 28(2): 27-31. [2] 王前. 流水冲击作用下桥梁承台及桩基础冲蚀数值模拟研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2017. [3] 余志祥,张蓬勃,赵雷,等. 山区桥梁墩柱水沙磨蚀损伤调查与仿真分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2016,36(6): 919-926.YU Zhixiang, ZHANG Pengbo, ZHAO Lei, et al. Investigation and numerical calculation of bridge pier in mountain area under erosion of flow and sediment[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2016, 36(6): 919-926. [4] 郑德路. 聚乙烯醇纤维水泥基复合材料抗冲击性能试验研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2013. [5] 许有俊,李明浩,张治华,等. PVA纤维对混凝土抗压强度和轴心抗压强度的影响[J]. 化工新型材料,2020,48(1): 250-252.XU Youjun, LI Minghao, ZHANG Zhihua, et al. Influence of PVA fiber on compressive strength and axial compression strength of concrete[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2020, 48(1): 250-252. [6] LI V C, WANG S, WU C. Tensile strain-hardening behavior of polyvinyl alcohol engineered cementitious composite[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2001, 98(6): 483-492. [7] SHAFIQ N, AYUB T, KHAN S U. Investigating the performance of PVA and basalt fibre reinforced beams subjected to flexural action[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 153: 30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.06.008 [8] WOO A, WON B, SONG C. A study on the enhancement of durability performance of faced slab concrete in CFRD[C]//18th International Conference on Composite Materials. Jeju: [s.n.], 2011: 5847-5852. [9] WOO S K, SONG Y C, WON J P. Enhanced durability performance of face slab concrete in concrete-faced rock-filled dam using fly ash and PVA fibre[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2011, 15(5): 875-882. doi: 10.1007/s12205-011-1231-8 [10] ABID S R, SHAMKHI M S, MAHDI N S, et al. Hydro-abrasive resistance of engineered cementitious composites with PP and PVA fibers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 187: 168-177. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.194 [11] 王彦平,陈昶旭,张戎令,等. PVA纤维增强水泥基修补砂浆冲蚀磨损性能试验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2019,38(12): 3752-3758.WANG Yanping, CHEN Changxu, ZHANG Rongling, et al. Experimental study on erosion wear properties of PVA fiber reinforced cement matrix mortar[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2019, 38(12): 3752-3758. [12] 中国建筑材料科学研究总院. 混凝土外加剂: GB 8076—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [13] 冯乃谦. 新实用混凝土大全[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. [14] 中国建筑科学研究院有限公司. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019. [15] TEWARI U S, HARSHA A P, HÄGER A M, et al. Solid particle erosion of carbon fibre- and glass fibre-epoxy composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2003, 63: 549-557. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00210-5 [16] MANSOURI A, ARABNEJAD H, SHIRAZI S A, et al. A combined CFD/experimental methodology for erosion prediction[J]. Wear, 2015, 332/333: 1090-1097. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2014.11.025 -




 下载:
下载: