Attack-Sample Generation Method for Train Communication Network Under Few-Shot Condition
-
摘要:
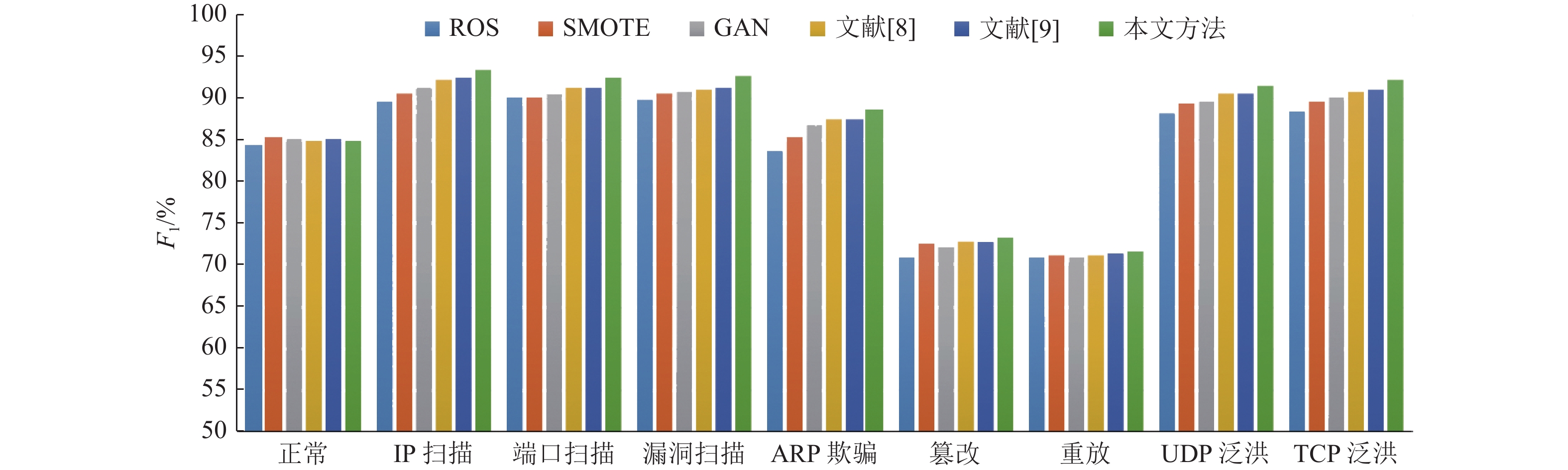
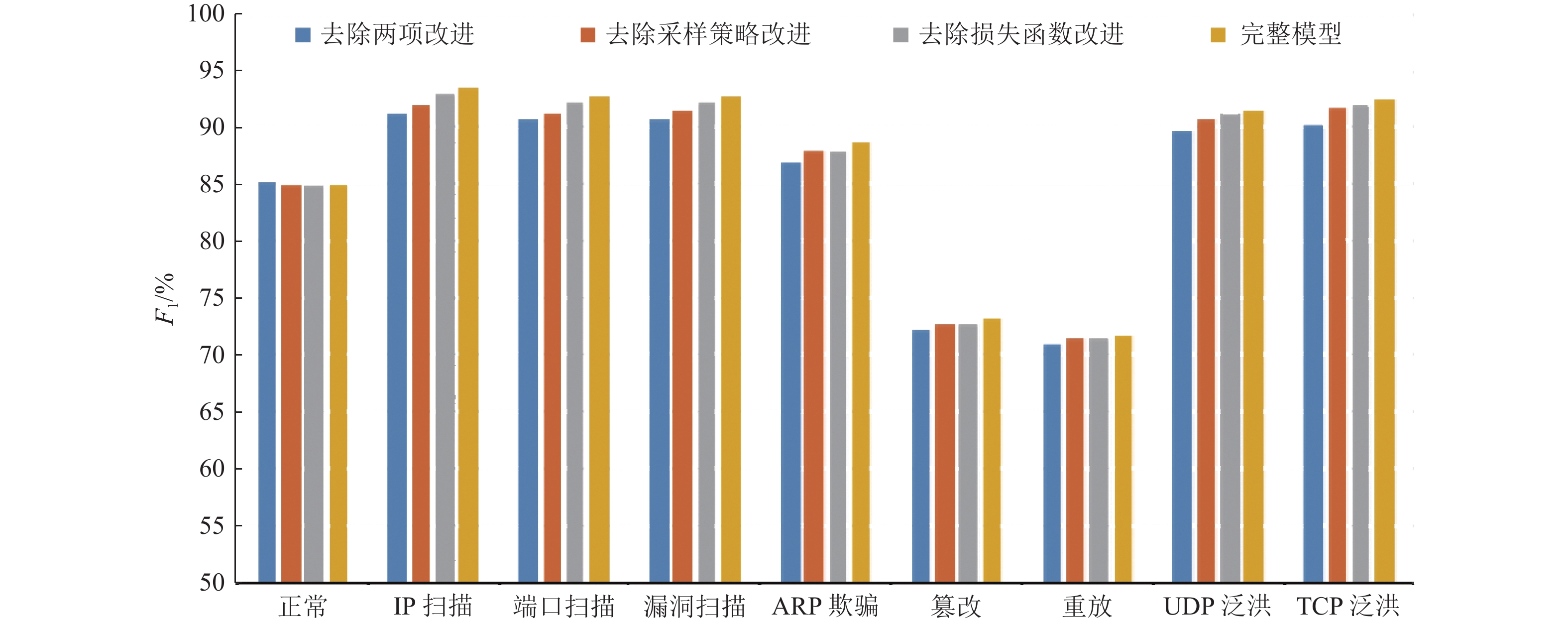
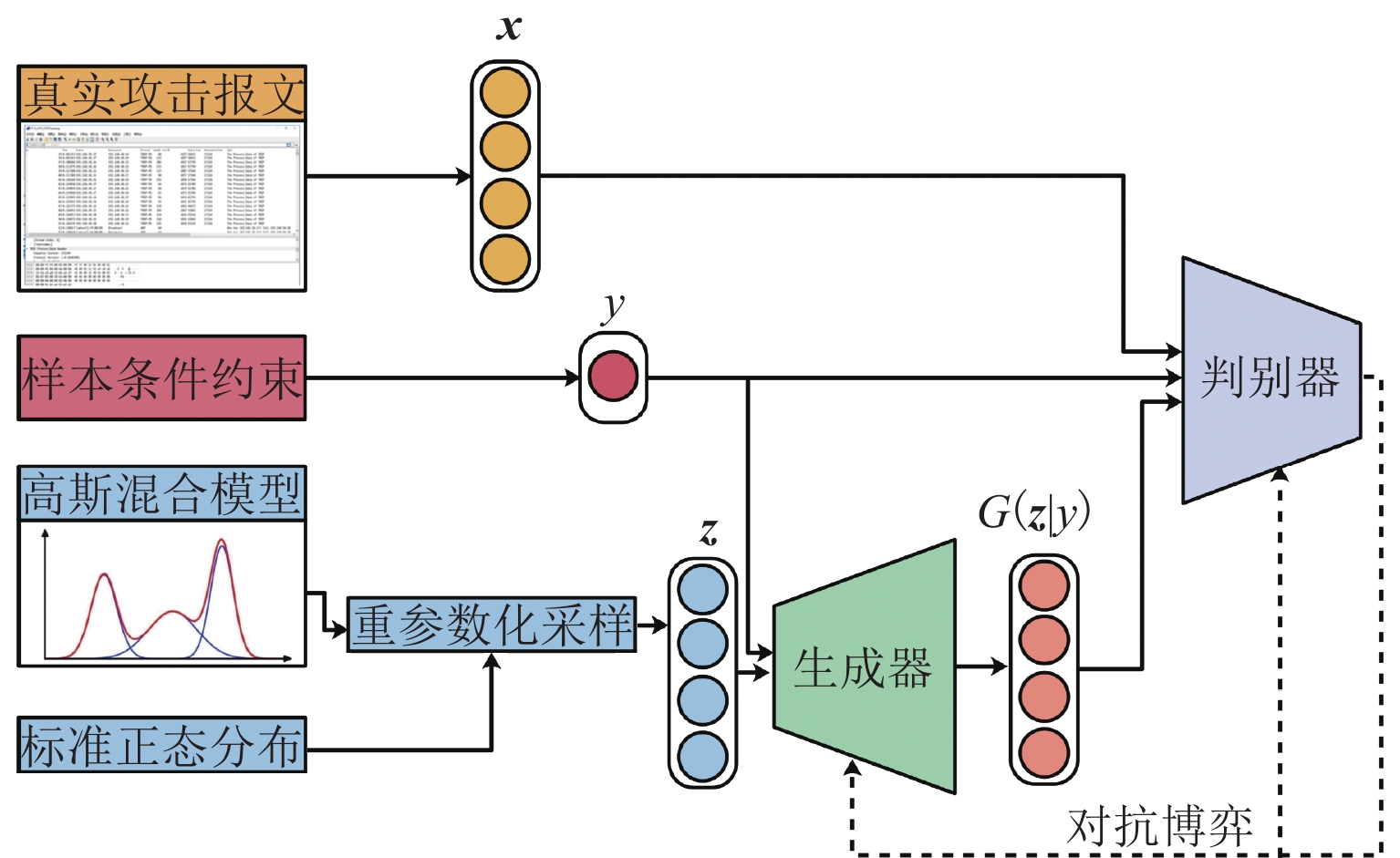
基于深度学习的列车通信网络入侵检测需要充足的训练样本支撑,然而实际可获取的列车通信网络攻击样本非常少. 本文将生成对抗网络(GAN)应用于攻击样本生成任务中,对GAN的采样策略、约束条件与损失函数进行改进,设计了基于卷积神经网络的生成器与判别器,提出一种基于改进GAN的攻击样本生成方法. 基于此方法开展了样本生成实验与入侵检测实验. 结果表明,该方法能够生成有效的攻击样本,改进模型的训练效果,模型的
F 1分数平均增加了4.23%.Abstract:Deep learning-based intrusion detection for the train communication network requires sufficient training samples, but there are few available attack samples in the actual scenario. Generative adversarial network (GAN) thus operates to generate attack samples. Also, the sampling strategy, constraint condition and loss function of GAN are improved; and a generator based on convolutional neural network and a discriminator are designed. Then an improved GAN-based method is proposed for attack sample generation. Sample generation experiments and intrusion detection experiments are conducted to test the proposed method, indicating that it can generate effective attack samples. When applying these generated samples in the training process of the intrusion detection model, the average
F 1 score increase by 4.23%, which means that the detection capability is effectively improved. -
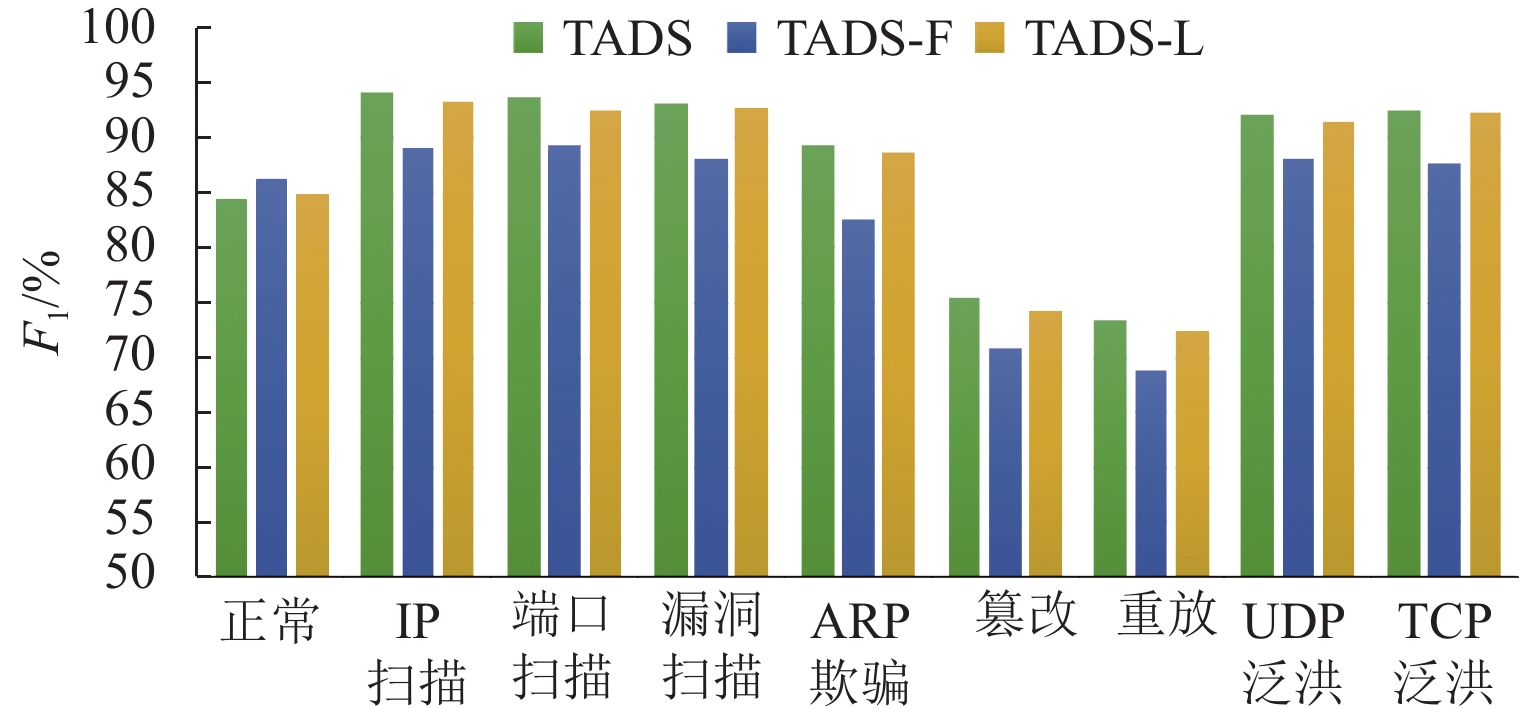
表 1 TADS的样本分布
Table 1. Sample distribution of TADS
攻击类别 样本数量/个 比例/% IP 扫描 10648 44.89 端口扫描 9562 漏洞扫描 11257 篡改 9301 重放 8872 ARP 欺骗 9525 正常报文 72643 55.11 表 2 TADS-F的样本分布
Table 2. Sample distribution of TADS-F
攻击类别 样本数量/个 比例/% IP 扫描 500 3.97 端口扫描 500 漏洞扫描 500 篡改 500 重放 500 ARP欺骗 500 正常报文 72643 96.03 表 3 TADS-L的样本分布
Table 3. Sample distribution of TADS-L
攻击类别 样本数量/个 比例/% IP 扫描 10000 45.23 端口扫描 10000 漏洞扫描 10000 篡改 10000 重放 10000 ARP 欺骗 10000 正常报文 72643 54.77 -
[1] 简捷. 基于以太网的列车通信网络多业务调度优化策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020. [2] FENG J, LU X, YANG W, et al. Survey of development and application of train communication network[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies for Rail Transportation. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 843-854. [3] KUROSE J F, ROSS K W. Computer networking: a top-down approach. 7th edition[M]. [S.l.]: Cenveo Publishing Services, 2017. [4] 赵凯琳,靳小龙,王元卓. 小样本学习研究综述[J]. 软件学报,2021,32(2): 349-369.ZHAO Kailin, JIN Xiaolong, WANG Yuanzhuo. Survey on few-shot learning[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(2): 349-369. [5] TAN X, SU S, HUANG Z, et al. Wireless sensor networks intrusion detection based on SMOTE and the random forest algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(203): S19010203.1-S19010203.15. doi: 10.3390/s19010203 [6] 刘金平,周嘉铭,刘先锋,等. 基于聚类簇结构特性的自适应综合采样法在入侵检测中的应用[J]. 控制与决策,2021,36(8): 1920-1928.LIU Jinping, ZHOU Jiaming, LIU Xianfeng, et al. Toward intrusion detection via cluster structure-based adaptive synthetic sampling approach[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(8): 1920-1928. [7] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 27: 2672-2680. [8] ANDRESINI G, APPICE A, DE ROSE L, et al. GAN augmentation to deal with imbalance in imaging-based intrusion detection[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2021, 123: 108-127. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2021.04.017 [9] HUANG S, LEI K. IGAN-IDS: an imbalanced generative adversarial network towards intrusion detection system in ad-hoc networks[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2020, 105: 102177.1-102177.11. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102177 [10] REYNOLDS D A. Gaussian mixture models[J]. EncycLopedia of Biometrics, 2009, 741: 659-663. [11] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]// Proceedings of the 3th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney: [s.n.], 2017: 214-223. [12] VILLANI C. Optimal transport: old and new[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2009. [13] MAAS A L, HANNUN A Y, NG A Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[C]// Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlauta: ICML, 2013: 3-9. [14] YUE C, WANG L, WANG D, et al. An ensemble intrusion detection method for train ethernet consist network based on CNN and RNN[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 59527-59539. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3073413 [15] GIBERT D, MATEU C, PLANES J. The rise of machine learning for detection and classification of malware: research developments, trends and challenges[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 153: 102526.1-102526.22. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2019.102526 [16] VAN DER MAATEN L, HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2009, 9(11): 2579-2605. -




 下载:
下载: