Experimental Study on Anisotropy Mechanical Properties of Corroded Rock Mass
-
摘要:
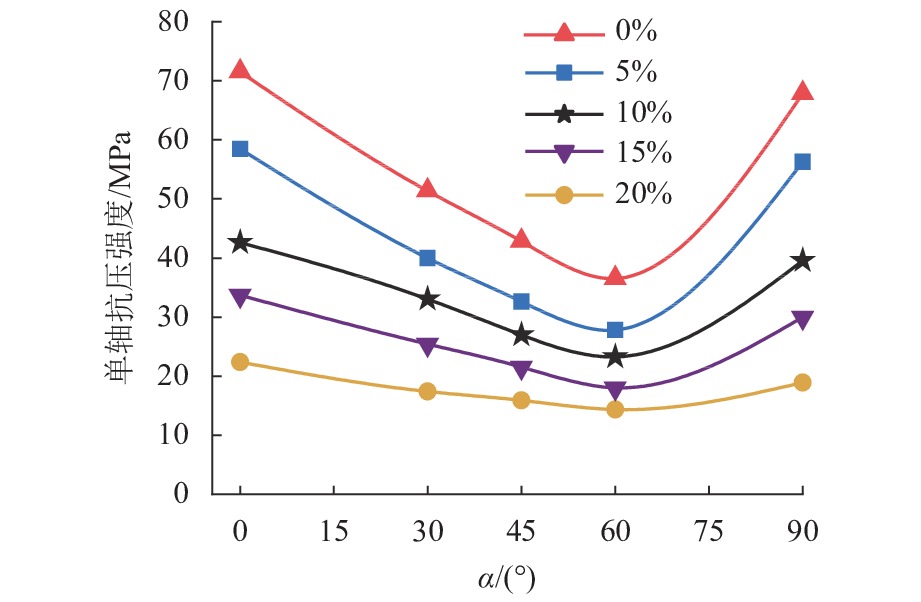
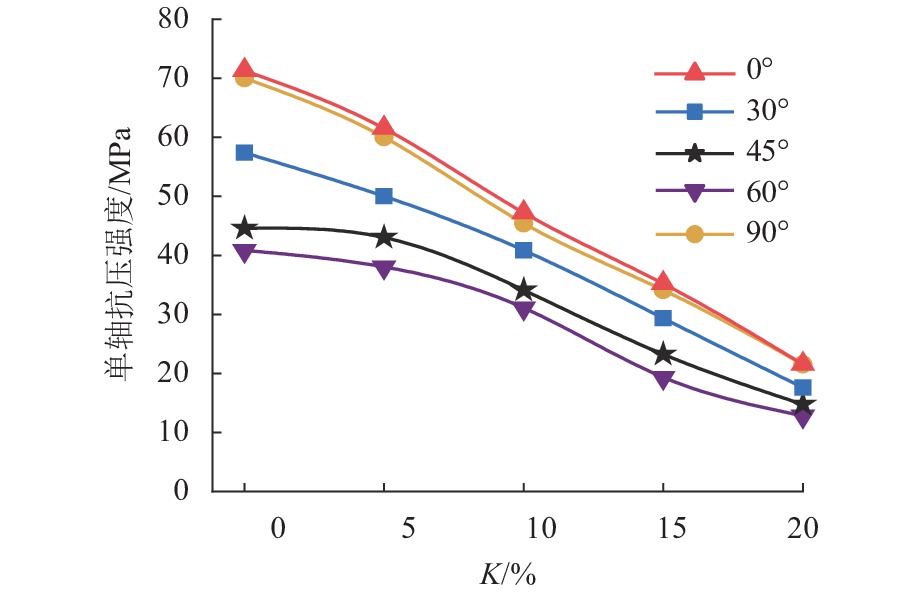
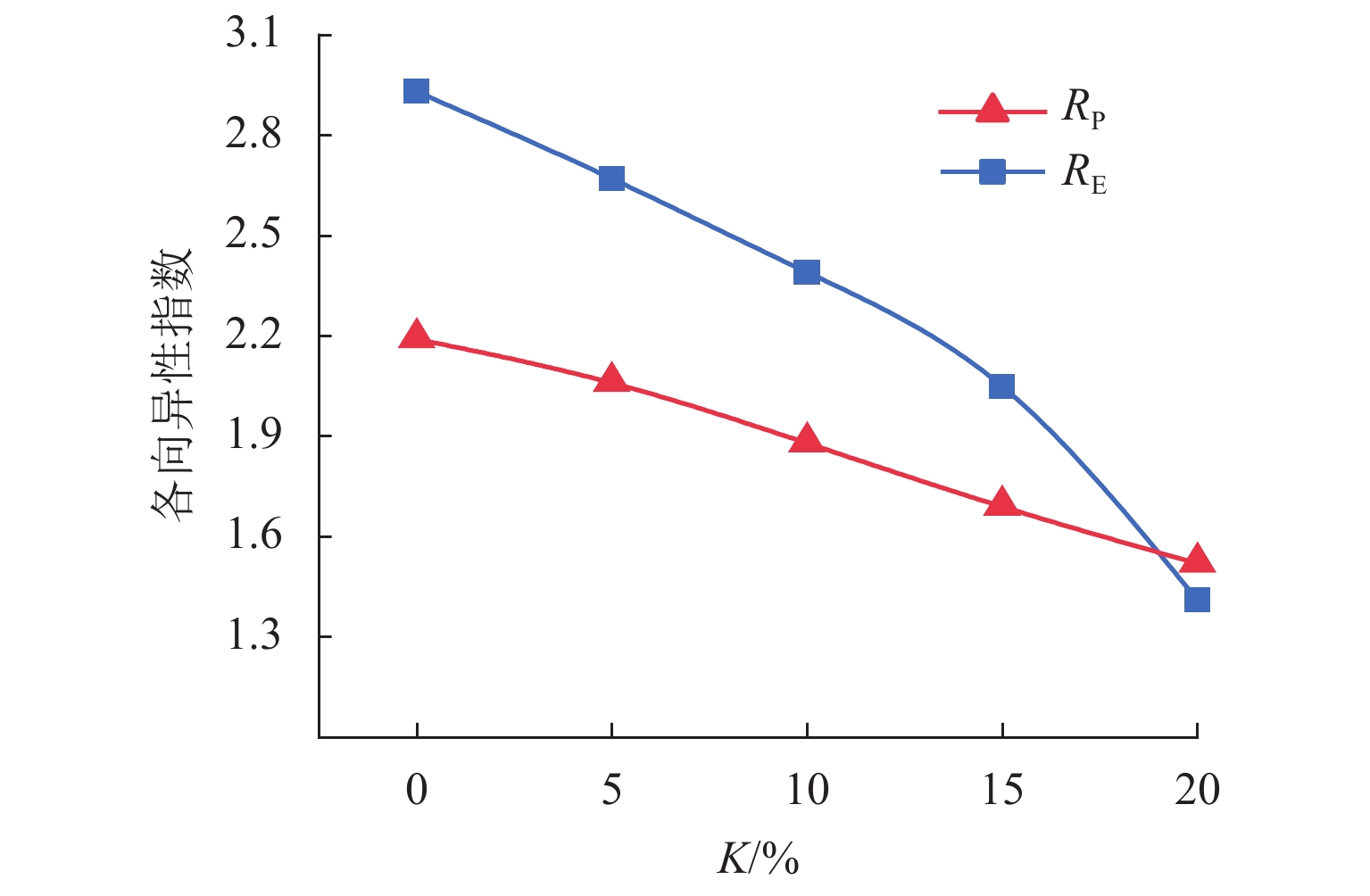
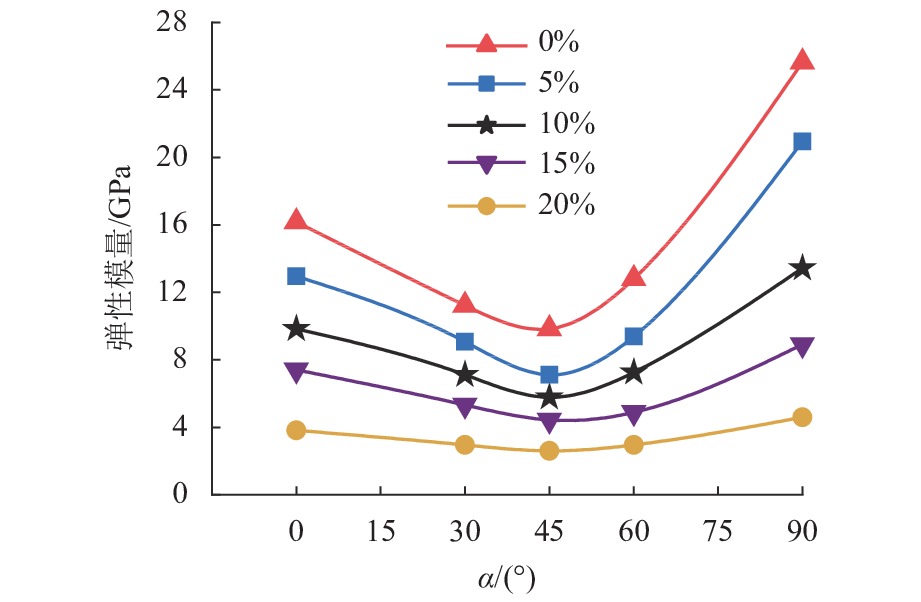
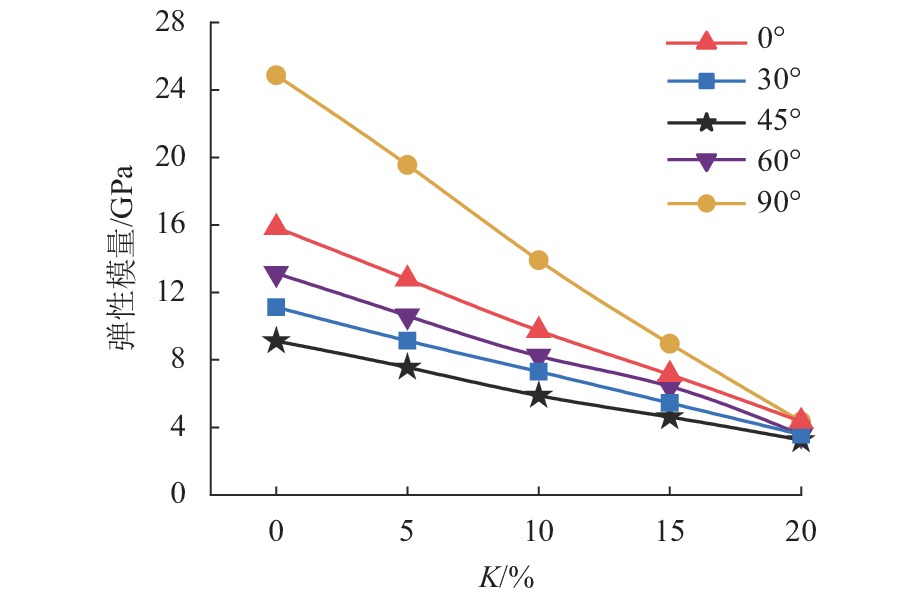
溶蚀岩体通常对岩体工程稳定性具有关键控制作用. 为了揭示富含层理溶蚀岩体各向异性力学性质演化规律,分别针对不同溶蚀率(
K = 0%,5%,10%,15%,20%)的岩体进行室内单轴抗压试验,获取每种溶蚀率条件下不同夹角(α = 0°,30°,45°,60°,90°)抗压强度和弹性模量,分析岩体破坏特征,依据试验结果建立含层理溶蚀岩体抗压强度和弹性模量的预测模型,并进行实验验证. 结果表明:抗压强度在α = 0°,90° 时最大,α = 45° 时最小,整体呈现对称U形;弹性模量在α = 60° 最小,α = 90° 最大,整体呈现不对称U形;完整岩体抗压强度以及弹性模量的各向异性指数最大,分别为1.98、3.05,随着溶蚀率增大其值逐渐减小,K = 20%时,分别为1.10、1.36;溶蚀率较小岩体变形破坏受岩体基质和层理控制,以劈裂、错动剪切和滑动剪切为主;随着溶蚀率增大,变形破坏受溶蚀孔隙和骨架控制明显,以骨架鼓胀剪切错动、压碎破坏为主.Abstract:Corroded rock mass usually plays a key role in controlling the stability of rock mass engineering. In order to reveal the evolution law of anisotropic mechanical properties and failure characteristics of the bedded rock mass suffering corrosions, indoor uniaxial compression tests were carried out on rock masses with different corrosion rates (
K = 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%) to obtain their compressive strength and elastic modulus at different included angles (α = 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°) . Based on the test results, mathematic models for predicting the compressive strength and elastic modulus of the corroded rock mass with beddings were established and then validated by experiment. The results show that the compressive strength achieves its maximum value at the included angleα = 0°, 90°, and achieves its minimum value atα = 45°, presenting a symmetrical U shape as a whole; while the elastic modulus is the smallest atα = 60° and the largest atα = 90°, showing an asymmetric U shape as a whole. The anisotropy indexes of compressive strength and elastic modulus (i.e., RP and RE) of the intact rock mass are the largest, which are 1.98 and 3.05 respectively, and their values gradually decrease with the corrosion rate increasing. WhenK = 20%, RP and RE are 1.10 and 1.36, respectively. The deformation and failure of rock mass with small corrosion rates are controlled by rock matrix and beddings, mainly by splitting, staggered shear and sliding shear. As the corrosion rate increases, the deformation and failure are obviously controlled by dissolution pores and skeleton, and the skeleton swelling, shear dislocation and crushing failure are the main types.-
Key words:
- uniaxial compression /
- corroded rock mass /
- anisotropy /
- failure mode
-
表 1 溶蚀岩体单轴抗压试验变形破坏特征
Table 1. Deformation and failure of corroded rock mass in uniaxial compression test
溶蚀率/% α/(°) 0 30 45 60 90 0 裂纹由两端产生向中间延伸,穿过基质和层理面劈裂张拉破坏 沿层理面错动,发生张剪切性破坏,同时伴随沿轴向应力方向劈裂破坏 沿层理结构面的复合剪切破坏 沿层理结构面剪切滑移破坏 沿层理结构面剪切劈裂破坏 5 穿过基质和层理面劈裂张拉破坏,骨架效应不明显 沿层理面错动,发生张剪切性破坏,骨架效应不明显 层理结构面的复合剪切破坏,骨架效应不明显 沿层理结构面的剪切滑移破坏,骨架效应不明显 沿层理结构面间的剪切劈裂破坏,骨架效应不明显 10 骨架鼓胀剪切,与溶蚀裂隙贯通,张开
宽大沿层理贯穿面发生剪切破坏,骨架压剪破坏 整体呈现张剪复合破坏,裂缝密集宽大,局部骨架压剪碎裂
破坏整体呈现张剪复合破坏,裂缝宽大,局部骨架压剪碎裂破坏 沿层理结构面间的剪切劈裂破坏,局部骨架压剪碎裂破坏 15 骨架鼓胀剪切明显,局部碎裂破坏 骨架剪切破坏,局部碎裂破坏 骨架剪切破坏,局部碎裂破坏 骨架剪切破坏,局部碎裂破坏 骨架剪切破坏,局部碎裂破坏 20 整体碎裂破坏,不存在明显剪切特征 整体碎裂破坏,不存在明显剪切特征 整体碎裂破坏,不存在明显的剪切特征 整体碎裂破坏,不存在明显剪切特征 整体碎裂破坏,不存在明显剪切特征 表 2 模型检验相关数据
Table 2. Data for model validation
组序 K/
%α/
(°)P/MPa E/GPa 误差/% 试验 模型 试验 模型 P E N1 7 25 56.44 57.36 13.68 14.53 1.60 5.85 N2 12 40 42.60 41.10 5.82 6.15 3.65 5.37 N3 15 65 24.76 23.14 6.42 6.88 7.00 6.69 N4 18 75 21.56 23.17 4.64 4.36 6.95 −6.42 -
[1] 刘新荣,袁文,傅晏,等. 干湿循环作用下砂岩溶蚀的孔隙度演化规律[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(3): 527-532. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201803017LIU Xinrong, YUAN Wen, FU Yan, et al. Porosity evolution of sandstone dissolution under wetting and drying cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(3): 527-532. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201803017 [2] 胡巍,柳景华,庞云铭,等. 基于H-B准则的各向异性边坡岩体强度参数修正研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5): 1196-1202.HU Wei, LIU Jinghua, PANG Yunming, et al. Correction of strength parameters for anisotropic slope rock mass based on H-B principles[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(5): 1196-1202. [3] APOLLARO C, MARINI L, CRITELLI T, et al. The standard thermodynamic properties of vermiculites and prediction of their occurrence during water-rock interaction[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 35: 264-278. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.04.018 [4] TALLINI M, PARISSE B, PETITTA M, et al. Long-term spatio-temporal hydrochemical and Rn-222 tracing to investigate groundwater flow and water-rock interaction in the Gran Sasso (central Italy) carbonate aquifer[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2013, 21(7): 1447-1467. doi: 10.1007/s10040-013-1023-y [5] ALT-EPPING P, DIAMOND L W, HÄRING M O, et al. Prediction of water-rock interaction and porosity evolution in a granitoid-hosted enhanced geothermal system, using constraints from the 5 km Basel-1 well[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 38: 121-133. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.09.006 [6] 李苍松,廖烟开,谷婷. 岩溶围岩力学特性试验的初步研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2007,3(7): 1358-1362,1386.LI Cangsong, LIAO Yankai, GU Ting. Preliminary study on mechanical property tests for karst rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2007, 3(7): 1358-1362,1386. [7] 刘海燕,李增学,郭建斌. 泥灰岩溶蚀模型力学效应分析[J]. 人民黄河,2009,31(7): 64-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2009.07.031 [8] 郭佳奇,刘希亮,乔春生. 自然与饱水状态下岩溶灰岩力学性质及能量机制试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(2): 296-308.GUO Jiaqi, LIU Xiliang, QIAO Chunsheng. Experimental study of mechanical properties and energy mechanism of karst limestone under natural and saturated states[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(2): 296-308. [9] 朱雷,王小群,聂德新,等. 基于随机模型溶蚀岩体强度参数研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(6): 1034-1038.ZHU Lei, WANG Xiaoqun, NIE Dexin, et al. Stochastic method based evaluation of corrosion rock strength parameters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(6): 1034-1038. [10] 张社荣,王枭华,王超. 孔隙结构特征及发育程度对溶蚀岩体力学特性的影响[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版),2017,50(10): 1018-1028.ZHANG Sherong, WANG Xiaohua, WANG Chao. Effects of pore structure and its development degree on dissolution rock mechanical characteristics[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2017, 50(10): 1018-1028. [11] 于丽,李哲,王明年,等. 岩溶弱发育对围岩力学参数的影响规律研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2018,15(2): 435-443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2018.02.022YU Li, LI Zhe, WANG Mingnian, et al. Study on the influence of weak karst development on mechanical parameters of surrounding rock[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(2): 435-443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2018.02.022 [12] 黄波林,殷跃平,张枝华,等. 三峡工程库区岩溶岸坡消落带岩体劣化特征研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(9): 1786-1796.HUANG Bolin, YIN Yueping, ZHANG Zhihua, et al. Study on deterioration characteristics of shallow rock mass in water the level fluctuation zone of karst bank slopes in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(9): 1786-1796. [13] 余逍逍,史文兵,王小明,等. 基于数字图像处理技术的溶蚀岩体细观变形破坏机制模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(3): 409-416.YU Xiaoxiao, SHI Wenbing, WANG Xiaoming, et al. Simulation on mesoscopic deformation and failure mechanism of dissolved rock mass using digital image processing technology[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 409-416. [14] TAVALLALI A, VERVOORT A. Effect of layer orientation on the failure of layered sandstone under Brazilian test conditions[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2010, 47(2): 313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.01.001 [15] TAVALLALI A, VERVOORT A. Failure of layered sandstone under brazilian test conditions: effect of micro-scale parameters on macro-scale behaviour[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2010, 43(5): 641-653. doi: 10.1007/s00603-010-0084-7 [16] NIANDOU H, SHAO J F, HENRY J P, et al. Laboratory investigation of the mechanical behaviour of Tournemire shale[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1997, 34(1): 3-16. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(97)80029-9 [17] TIEN Y M, KUO M C. A failure criterion for transversely isotropic rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2001, 38(3): 399-412. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(01)00007-7 [18] 彭剑文,曾飞涛,李长洪,等. 石英砂岩力学特性及各向异性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2017,38(增刊1): 103-112.PENG Jianwen, ZENG Feitao, LI Changhong, et al. Experimental study of anisotropy and mechanical property of quartz sandstone[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(S1): 103-112. [19] 王聪聪,李江腾,林杭,等. 板岩单轴压缩各向异性力学特征[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2016,47(11): 3759-3764.WANG Congcong, LI Jiangteng, LIN Hang, et al. Anisotropic mechanical characteristics of slate in uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(11): 3759-3764. [20] 陈天宇,冯夏庭,张希巍,等. 黑色页岩力学特性及各向异性特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(9): 1772-1779.CHEN Tianyu, FENG Xiating, ZHANG Xiwei, et al. Experimental study on mechanical and anisotropic properties of black shale[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(9): 1772-1779. [21] 邓华锋,王伟,李建林,等. 层状砂岩各向异性力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(1): 112-120.DENG Huafeng, WANG Wei, LI Jianlin, et al. Experimental study on anisotropic characteristics of bedded sandstone[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 112-120. [22] 殷达,孟庆祥,徐建荣,等. 基于微结构张量的岩石各向异性弹塑性本构及其应用[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(9): 1751-1758.YIN Da, MENG Qingxiang, XU Jianrong, et al. Anisotropic elastoplastic constitutive model based on microstructure tensor and its engineering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(9): 1751-1758. [23] 中华人民共和国水利部. 水利水电工程岩石试验规程: SL 264—2001[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2001. [24] SINGH J, RAMAMURTHY T, RAO G V. Strength anisotropies in rocks[J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal, 1989, 19(2): 147-166. -




 下载:
下载: