Influence of Track Parameters on Wheel/Rail Contact Behavior of High-Speed Turnout
-
摘要:
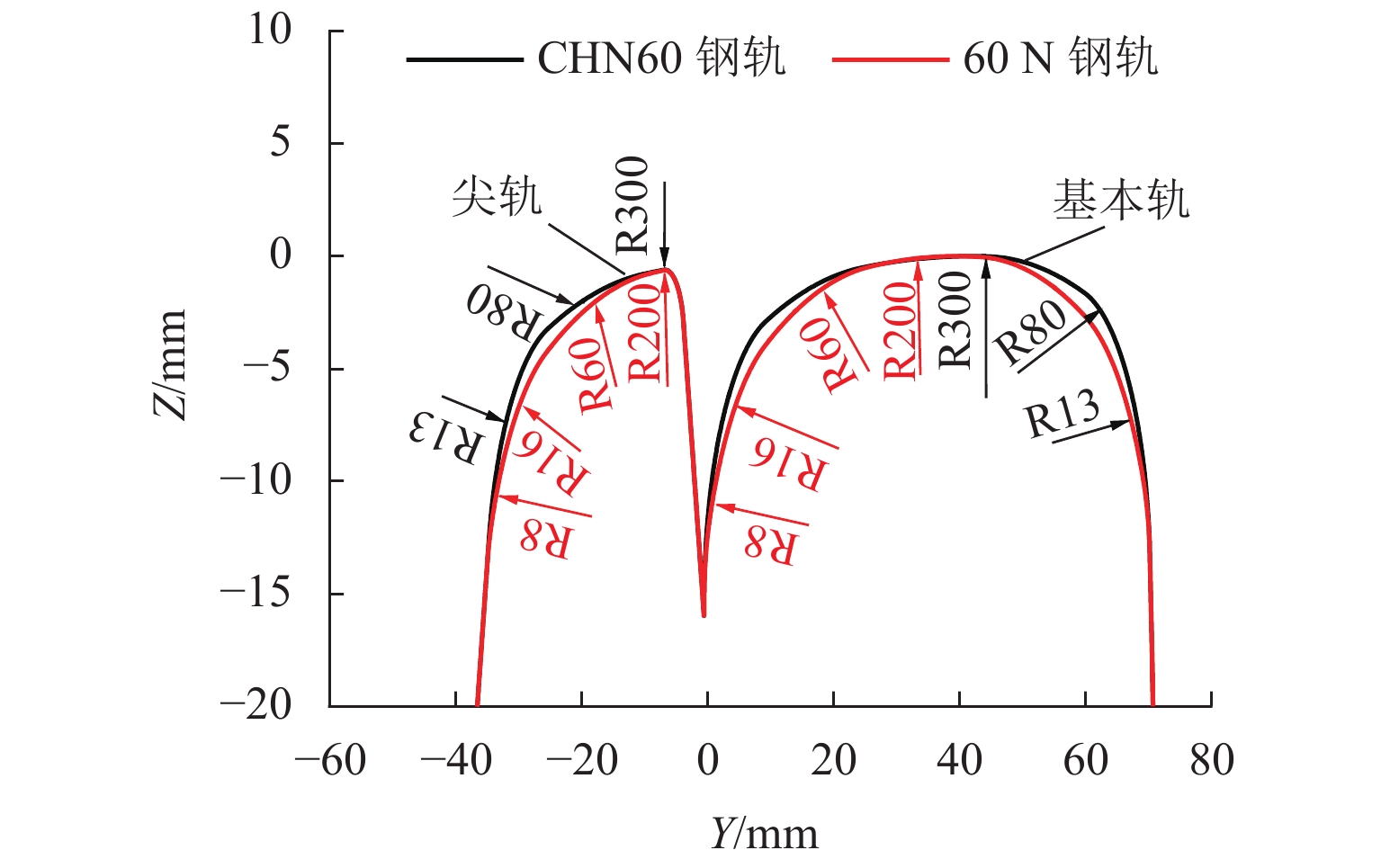
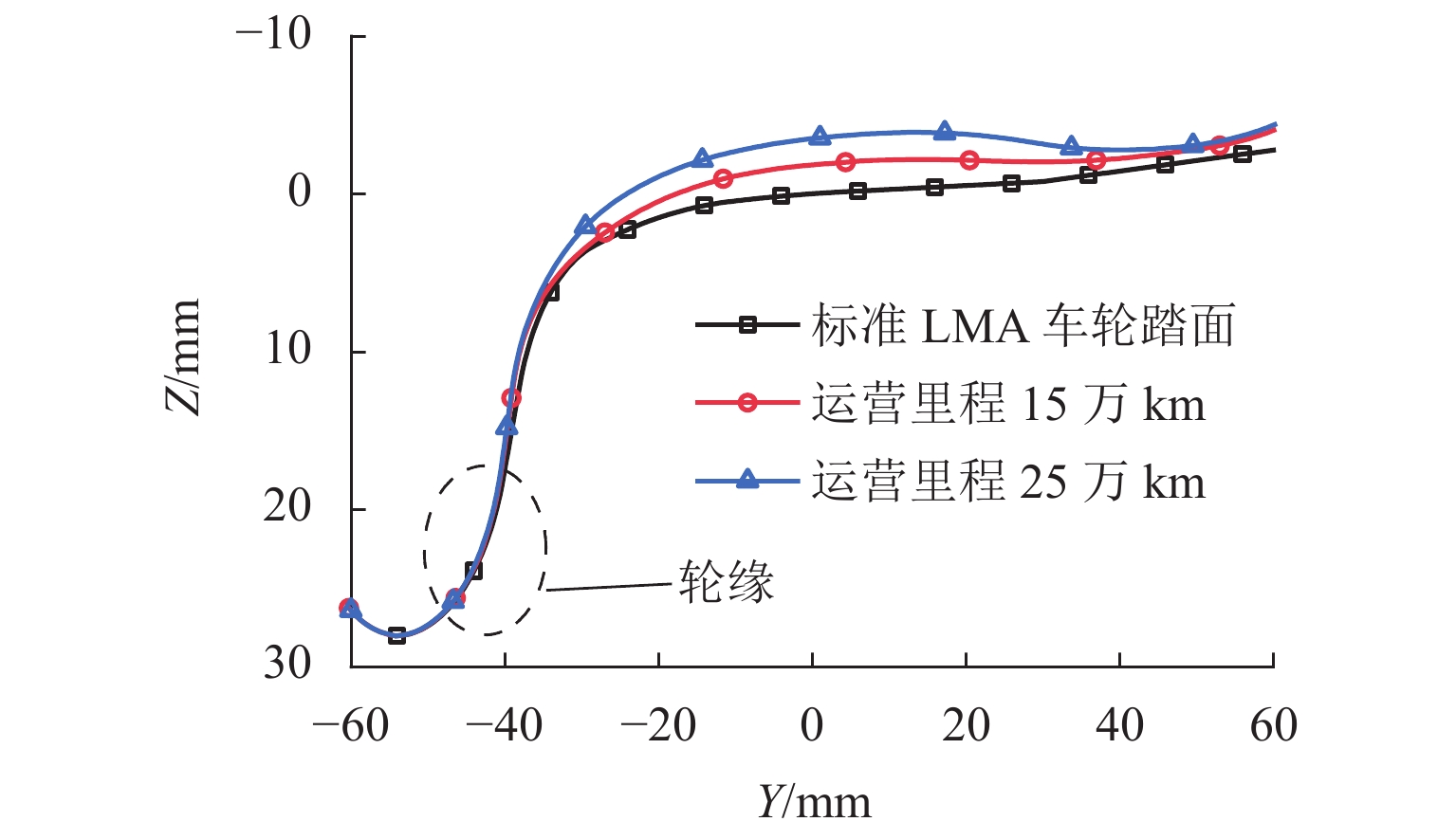
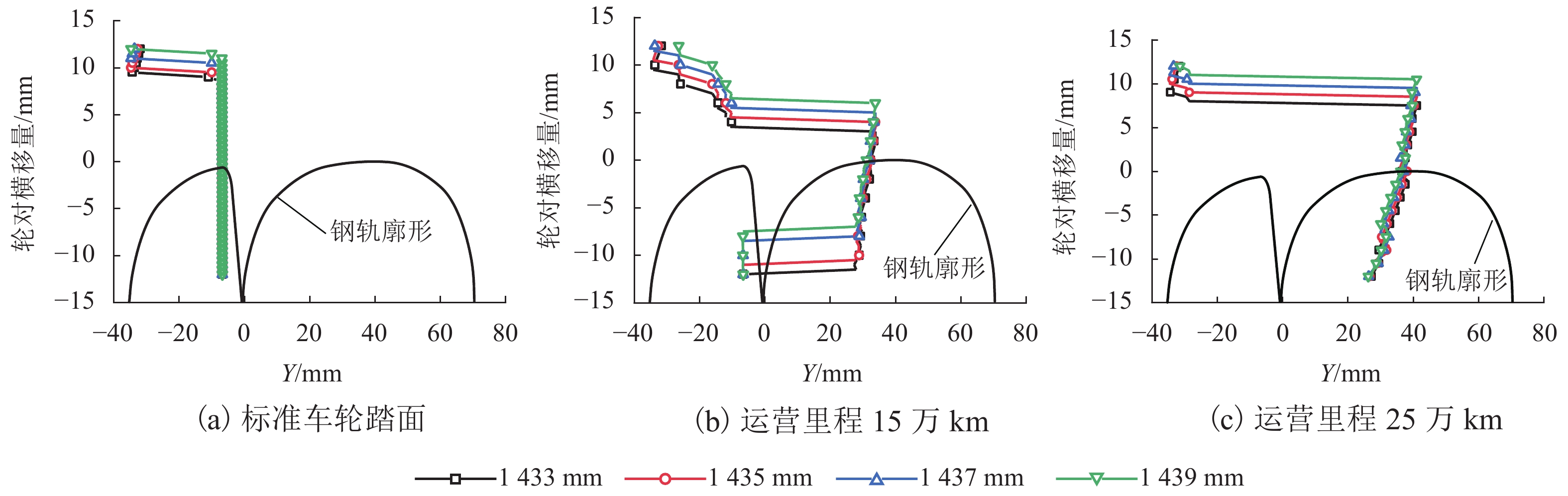
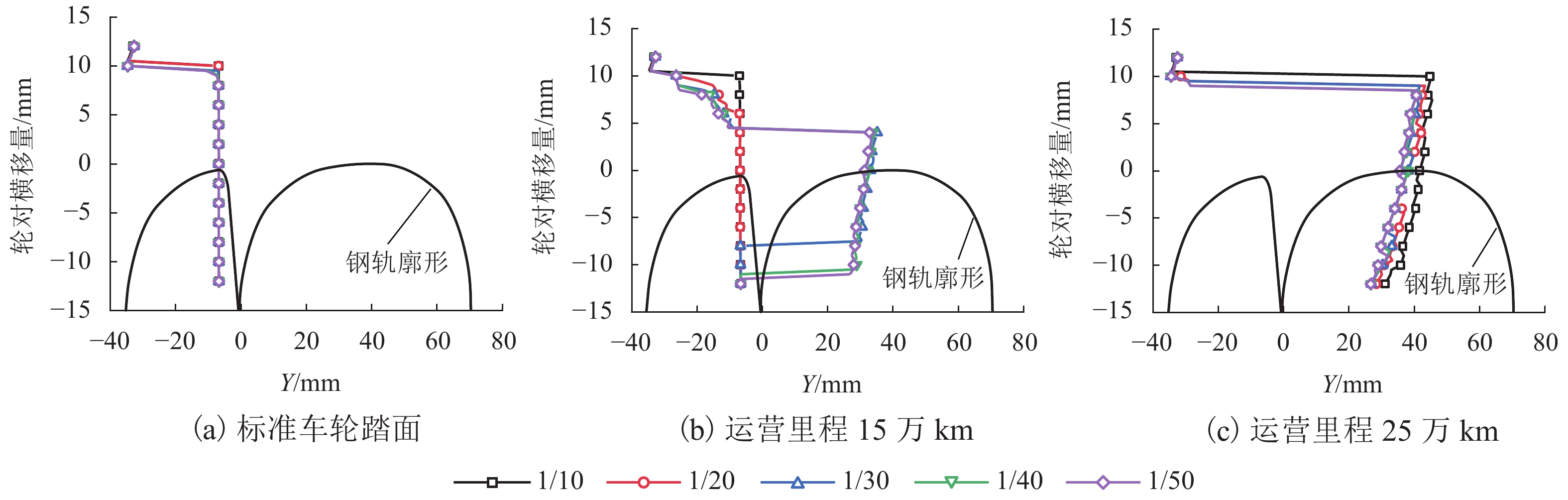
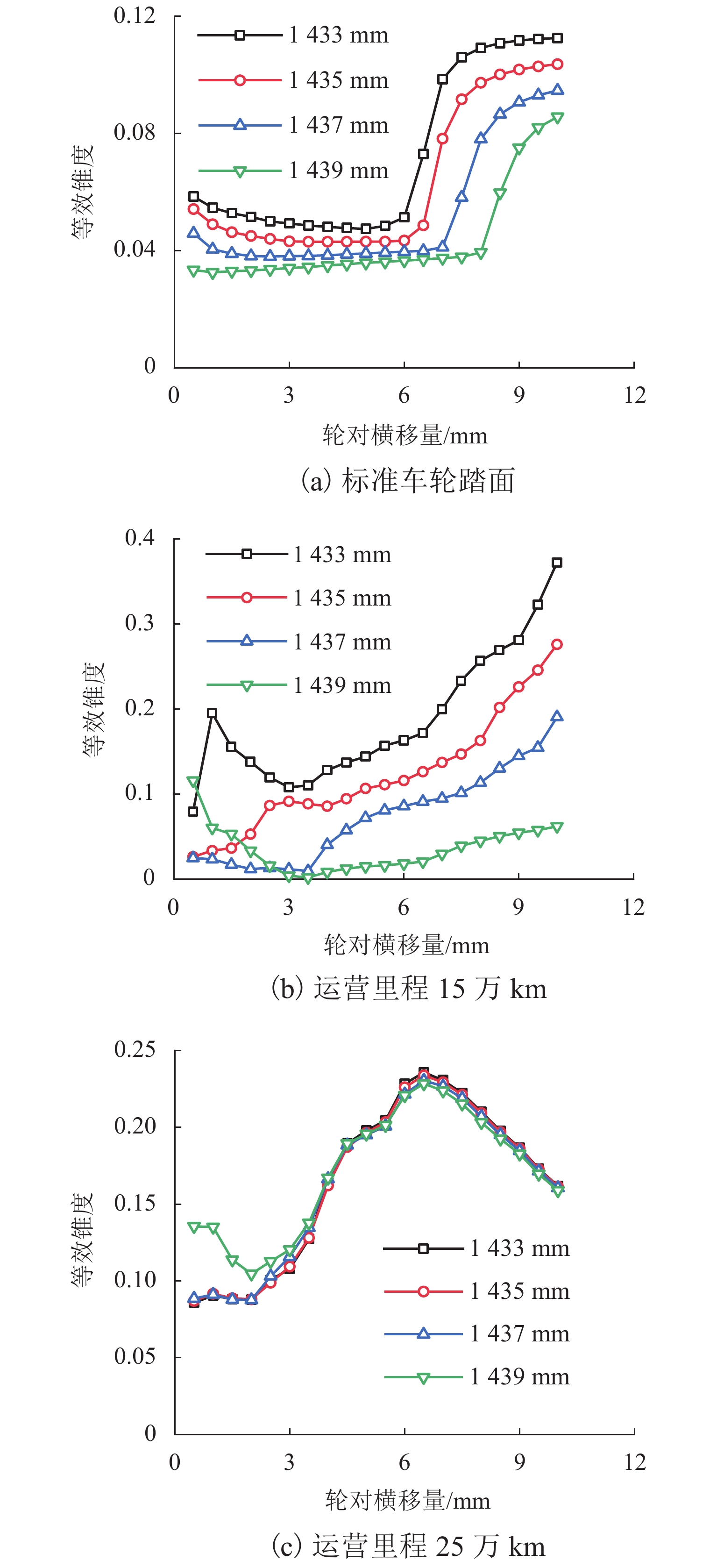
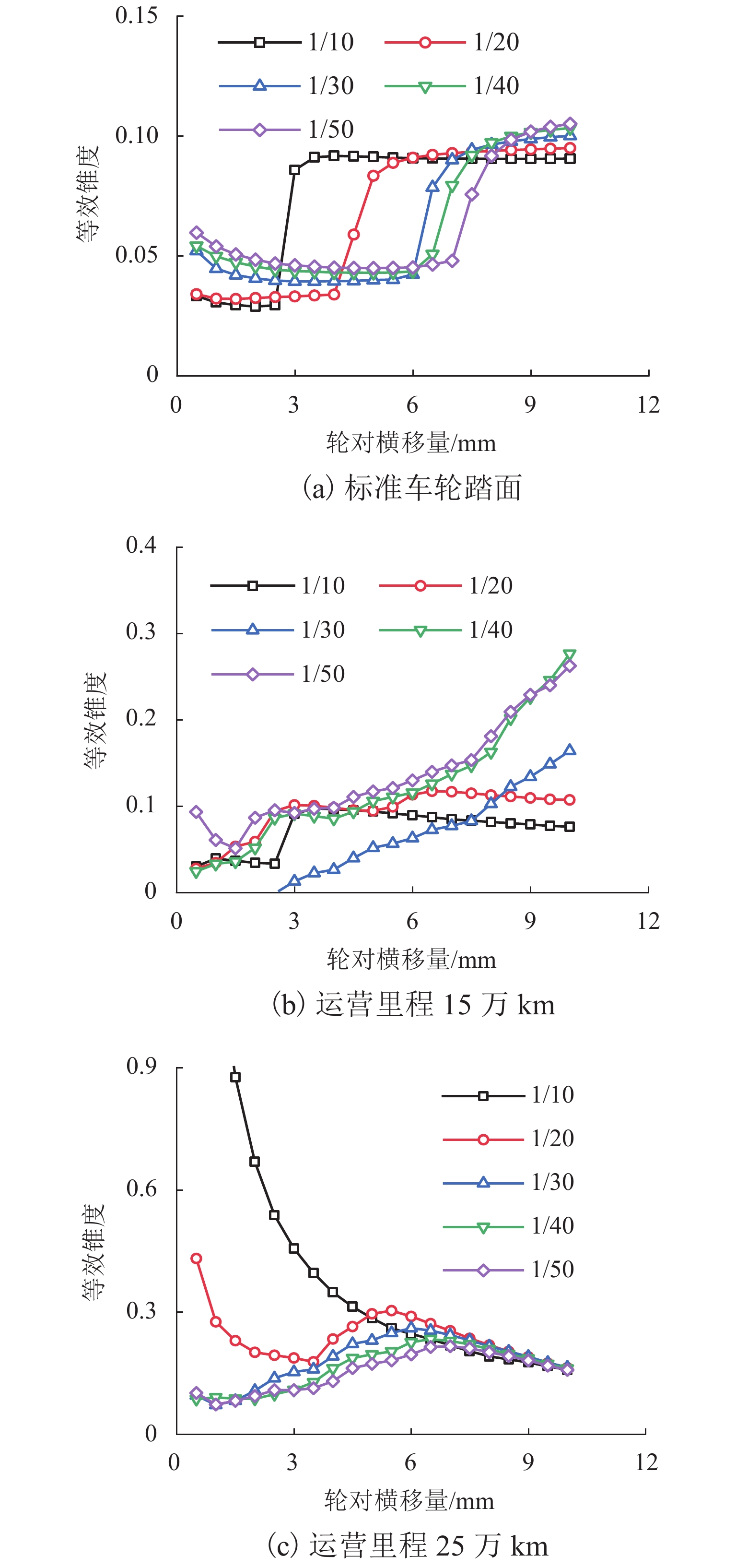
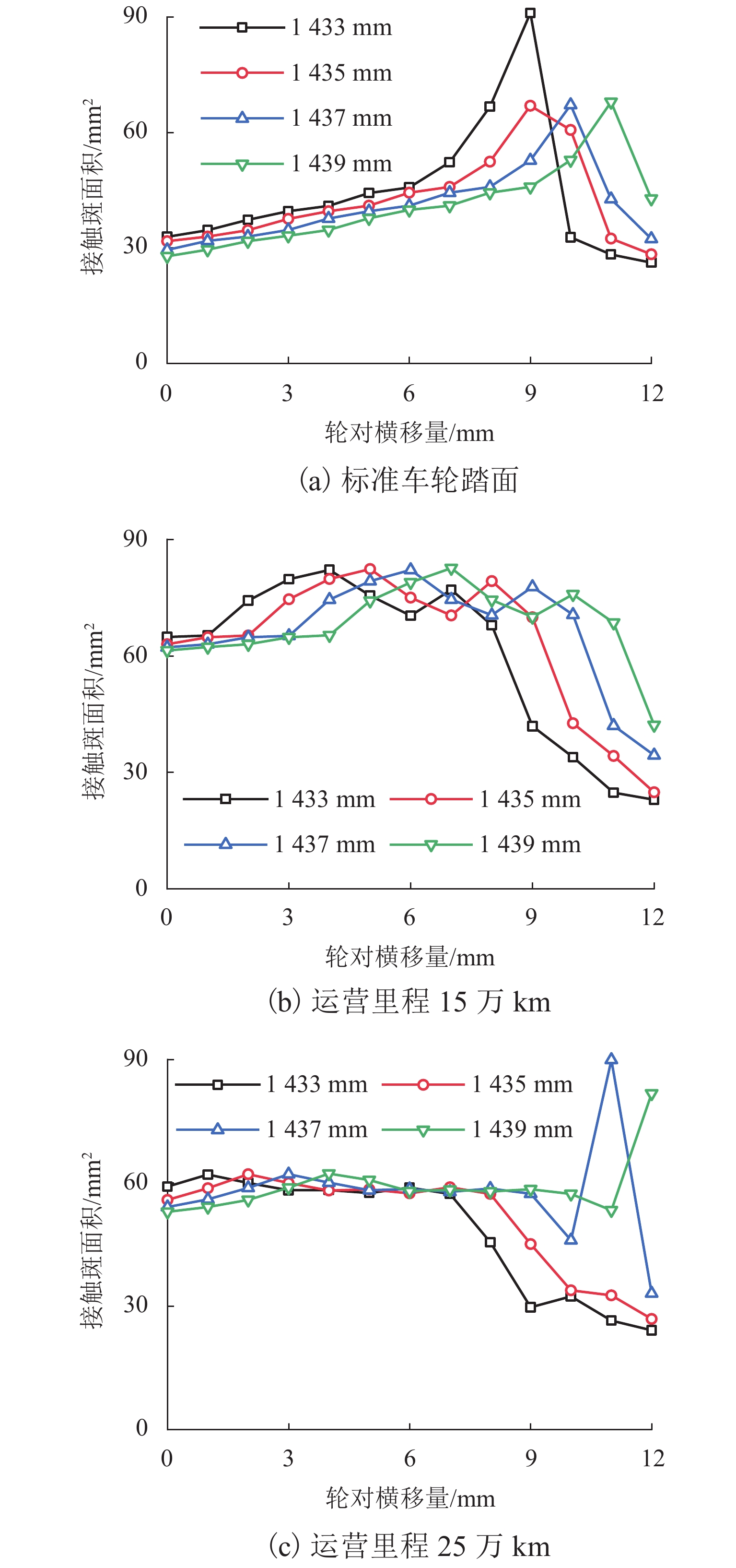
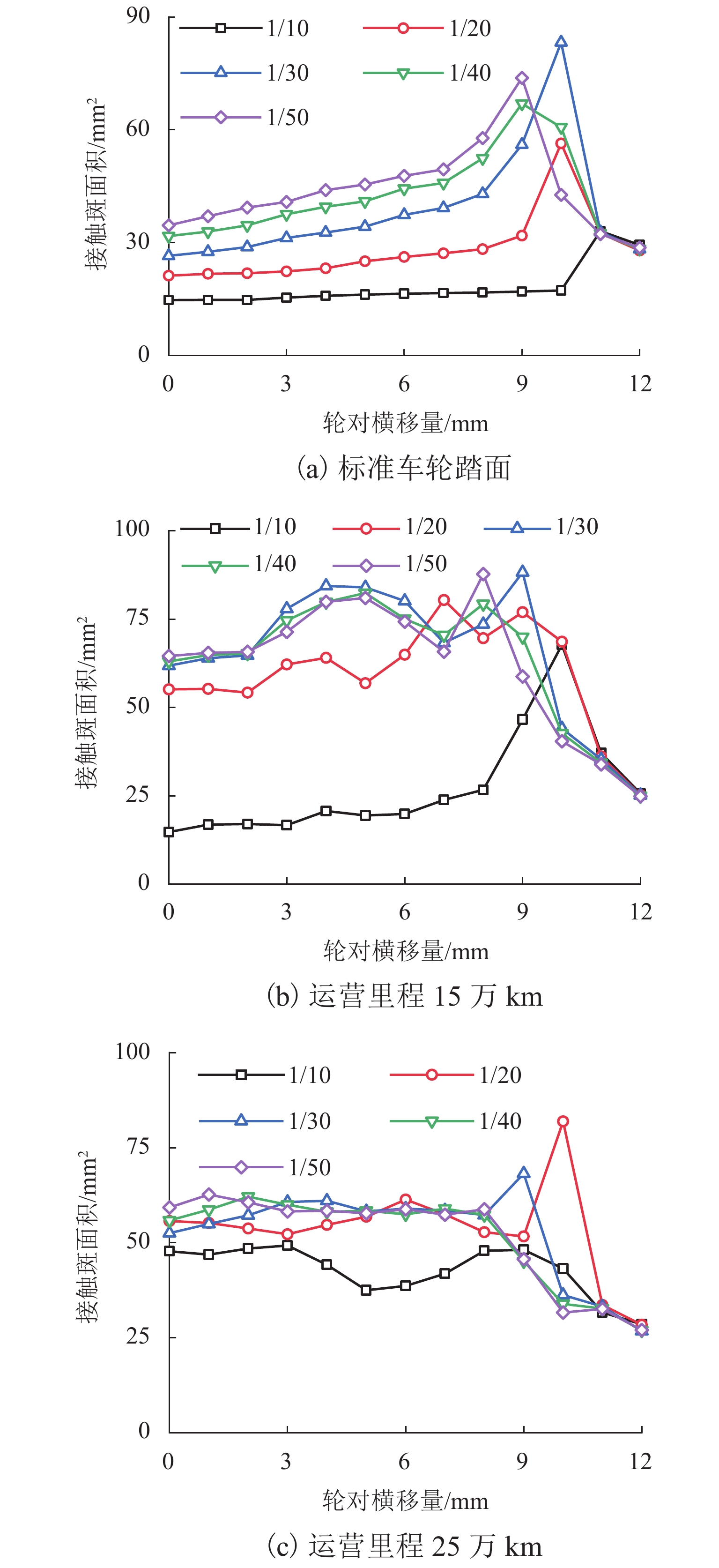
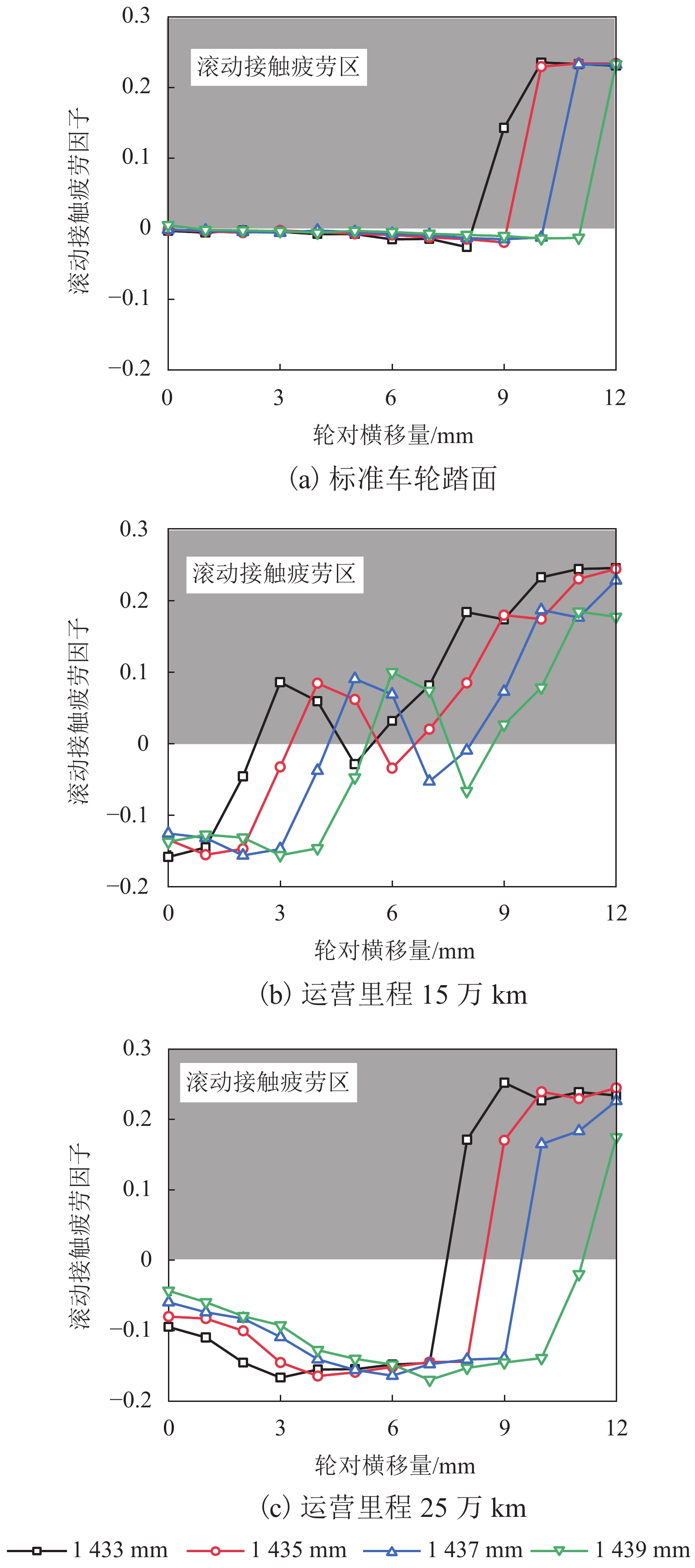
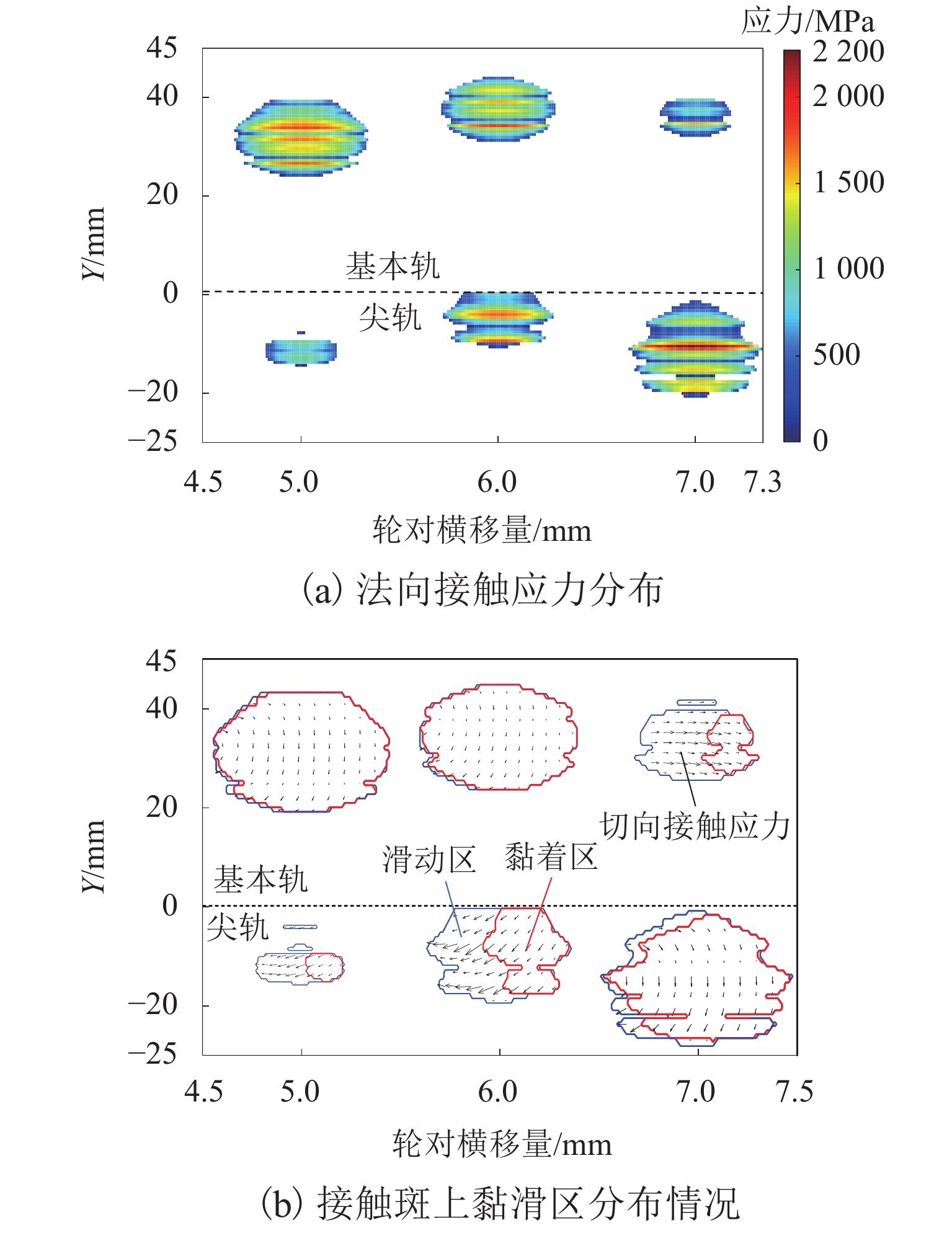
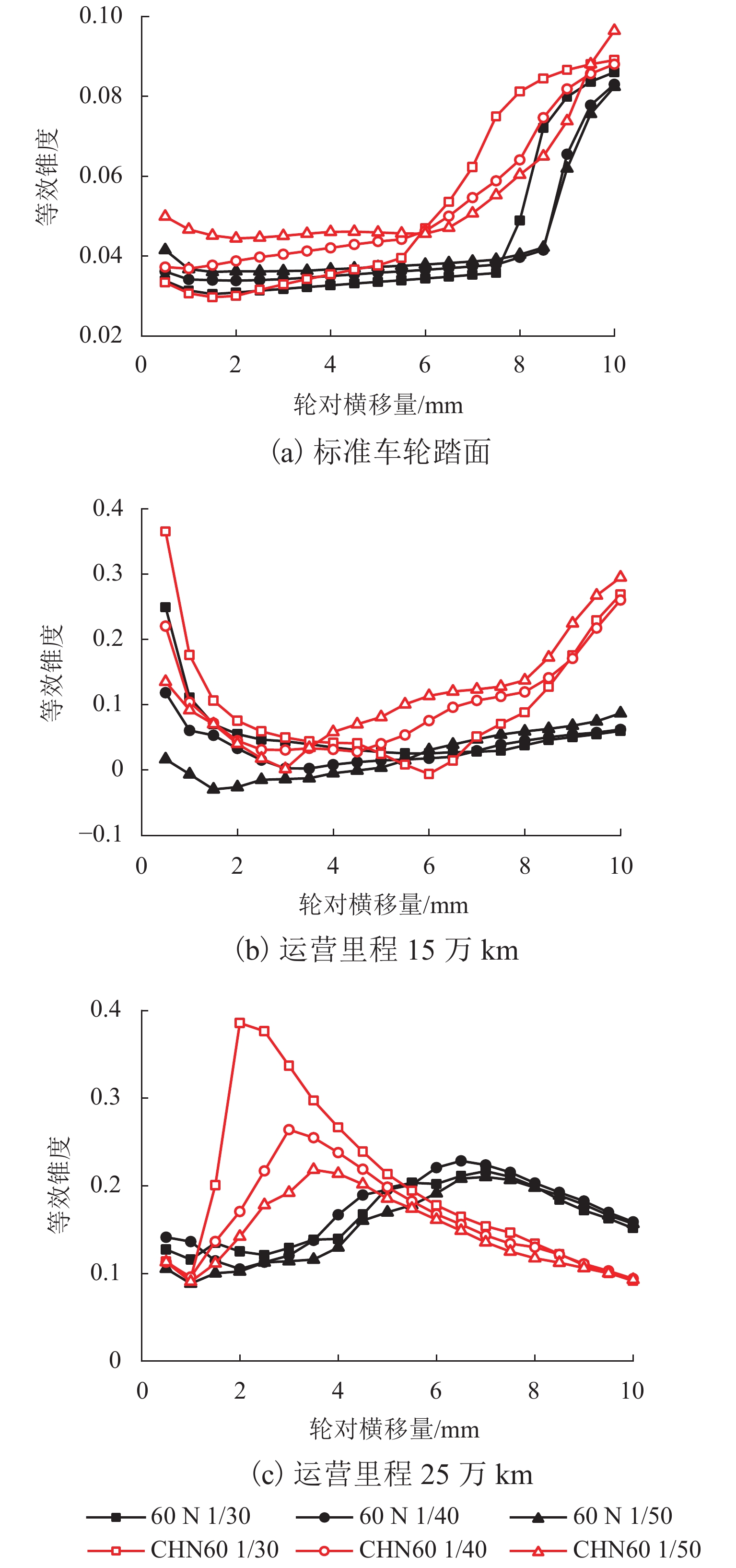
为研究60N钢轨350 km/h 18号高速道岔合理的轨距和轨底坡,利用60N钢轨高速道岔关键断面和实测LMA磨耗车轮,基于迹线法原理和Kalker三维非赫兹滚动接触理论,分析不同轨距和轨底坡参数下的轮轨接触几何和力学特性,并与CHN60钢轨高速道岔计算结果进行对比. 结果表明:在保证安全的前提下适当将轨距加宽可改善轮轨匹配关系,提升列车过岔平稳性,减小轮对横移量大于8 mm时的轮轨接触应力和表面滚动接触疲劳因子,延长尖轨使用寿命;轨底坡为1/30、1/40和1/50时,轮轨接触参数相差较小,匹配性能较优;轨底坡为1/10和1/20时,横向不平顺和轮轨滚动接触疲劳因子普遍较大,且1/10轨底坡对车轮磨耗的适应性较差;与CHN60钢轨高速道岔相比,60N钢轨高速道岔的等效锥度普遍更小,列车过岔平稳性更优;车轮磨耗易导致车轮在轮轨过渡区段空转,引起尖轨伤损.
Abstract:In order to investigate reasonable rail gauge and rail cant of No.18 turnout with 60N rail under the straight passing speed 350 km/h, based on the track line method and Kalker’s 3D non-Herz rolling contact theory, key sections of 60N rail turnout and measured LMA worn wheels were used to analyzed the wheel-rail contact geometric and mechanical characteristics under different rail gauges and different rail cant parameters. The calculation results were compared with those of CHN60 rail turnout. The results show that under the premise of ensuring safety, properly widening the rail gauge can improve the wheel-rail matching relationship, improve the stability of the train went through the turnout, reduce the wheel-rail contact stress and surface rolling contact fatigue factor when the wheelset-lateral displacement is greater than 8 mm, and extend the service life of the rail. When the rail cant is 1/30, 1/40 and 1/50, the wheel-rail contact parameters have little difference and the matching performance is better. When the rail cant is 1/10 and 1/20, the lateral irregularity and wheel-rail rolling contact fatigue factors are generally large, and the adaptability of 1/10 rail cant to wheel wear is poor. Compared with CHN60 rail turnout, the equivalent conicity of 60N rail turnout is generally smaller, and the stability of the train went through the turnout is better. Wheel wear is easy to lead to wheelspin in the wheel-rail transition section, resulting in switch rail damage.
-
Key words:
- rail gauge /
- rail cant /
- 60N rail /
- worn wheel /
- high-speed turnout /
- wheel-rail contact
-
[1] 王平,陈嵘,徐井芒,等. 高速铁路道岔系统理论与工程实践研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 357-372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.015WANG Ping, CHEN Rong, XU Jingmang, et al. Theories and engineering practices of high-speed railway turnout system: survey and review[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 357-372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.015 [2] 杜星,陶功权,杨城,等. 轨底坡变化对高速车辆运行行为的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(2): 286-294.DU Xing, TAO Gongquan, YANG Cheng, et al. Influence of different rail cants change on dynamical characteristics of high-speed railway vehicles[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(2): 286-294. [3] 钱瑶,王平,苏谦,等. 轨底坡对高速铁路轮轨接触行为影响分析[J]. 铁道工程学报,2018,35(3): 18-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2018.03.004QIAN Yao, WANG Ping, SU Qian, et al. Effect analysis of rail cant on the wheel-rail contact behavior of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2018, 35(3): 18-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2018.03.004 [4] 陈嵘,温静,于浩,等. 地铁线路轨距对轮轨接触行为的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2020,51(3): 824-831. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.03.028CHEN Rong, WEN Jing, YU Hao, et al. Influence of rail gauge on wheel-rail contact behavior of metro line[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(3): 824-831. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.03.028 [5] 陈嵘,温静,李博,等. 考虑非对称轨底坡的轮轨滚动接触应力分析[J]. 铁道工程学报,2019,36(5): 13-19,70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.05.003CHEN Rong, WEN Jing, LI Bo, et al. Analysis of wheel/rail rolling contact stress considering asymmetric rail cant[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2019, 36(5): 13-19,70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.05.003 [6] CUI D B, LI L, JIN X S, et al. Wheel-rail profiles matching design considering railway track parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 23(4): 410-417. doi: 10.3901/CJME.2010.04.410 [7] SÁNCHEZ R A, SANJUÁN E L, BRAVO J L. Experimental validation of track inspection trolley using a rigorous self-checking procedure[J]. Journal of Surveying Engineering, 2020, 146(3): 0000315.1-0000315.8. [8] 李超,张军,李霞,等. 动态轨距优化技术在重载道岔上的应用[J]. 大连交通大学学报,2015,36(S1): 55-61.LI Chao, ZHANG Jun, LI Xia, et al. Research on dynamic gauge optimization of heavy haul switch rail[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University, 2015, 36(S1): 55-61. [9] YE Y G, SUN Y. Reducing wheel wear from the perspective of rail track layout optimization[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part K: Journal of Multi-Body Dynamics, 2021, 235(2): 217-234. doi: 10.1177/1464419320956831 [10] 闫正,陈嘉胤,徐井芒,等. 不同车轮踏面与高速60N钢轨道岔静态接触特性研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2021,52(4): 1358-1370. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.04.032YAN Zheng, CHEN Jiayin, XU Jingmang, et al. Study of static contact properties of diverse wheel treads and high-speed 60N rail turnout[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(4): 1358-1370. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.04.032 [11] 陈嵘,方嘉晟,汪鑫,等. 车轮型面演变对高速道岔区轮轨接触行为影响分析[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(5): 101-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.05.012CHEN Rong, FANG Jiasheng, WANG Xin, et al. Influence of wheel profile evolution on wheel-rail contact behavior in high-speed turnout area[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(5): 101-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2019.05.012 [12] 王晨,罗世辉,邬平波,等. 动车组踏面凹型磨耗对车辆稳定性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 84-91.WANG Chen, LUO Shihui, WU Pingbo, et al. Effect of hollow worn tread of electric multiple units on vehicle stability[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 84-91. [13] British Standards Institution. BS EN 15302: 2008 Railway applications—method for determining the equivalent conicity[S]. London: British Standards Institution, 2008. [14] International Union of Railways. UIC code 519 method for determining the equivalent conicity[S]. Paris: International Union of Railways, 2004. [15] 马晓川,王平,徐井芒,等. 铁路道岔轮轨非赫兹滚动接触算法对比与分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(18): 95-103. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.18.095MA Xiaochuan, WANG Ping, XU Jingmang, et al. Analysis and comparison of different wheel-rail non-hertzian rolling contact approaches in railway turnout[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(18): 95-103. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.18.095 [16] 干锋,戴焕云,高浩,等. 铁道车辆不同踏面等效锥度和轮轨接触关系计算[J]. 铁道学报,2013,35(9): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.09.004GAN Feng, DAI Huanyun, GAO Hao, et al. Calculation of equivalent conicity and wheel-rail contact relationship of different railway vehicle treads[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2013, 35(9): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2013.09.004 -





 下载:
下载: