Energy Management and Capacity Allocation Scheme for Co-phase Traction Power Supply and Energy Storage System in Electrified Railways
-
摘要:
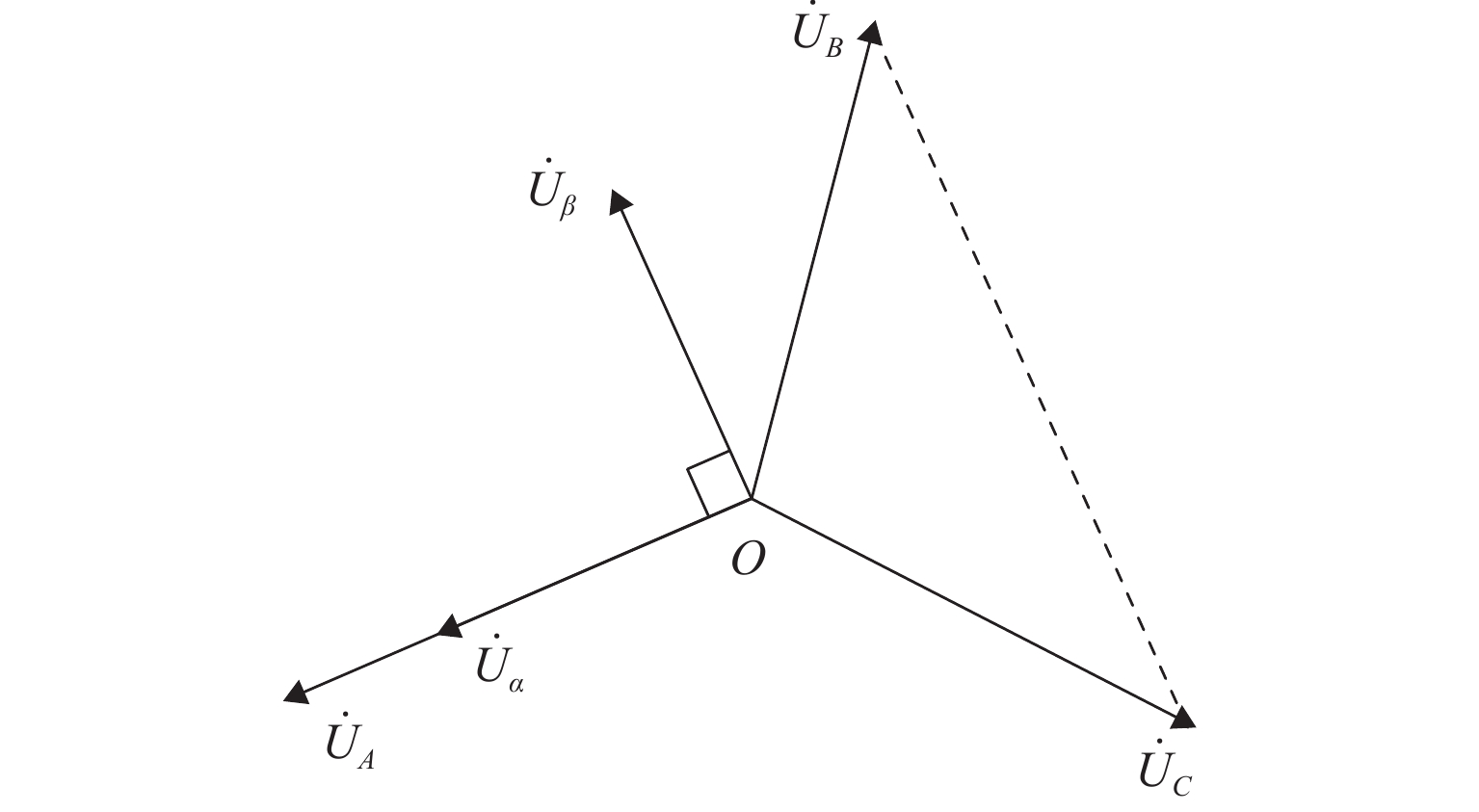
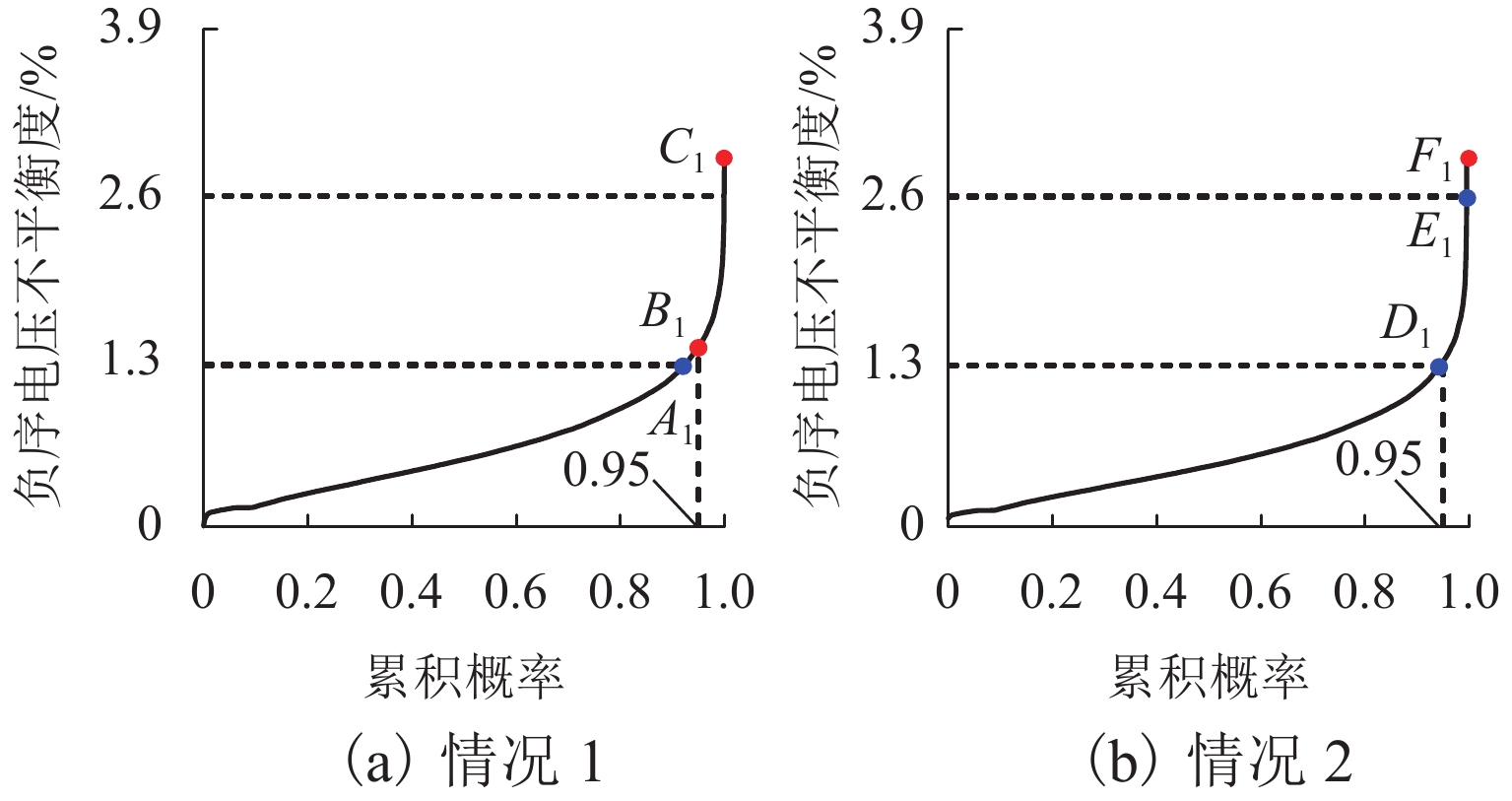
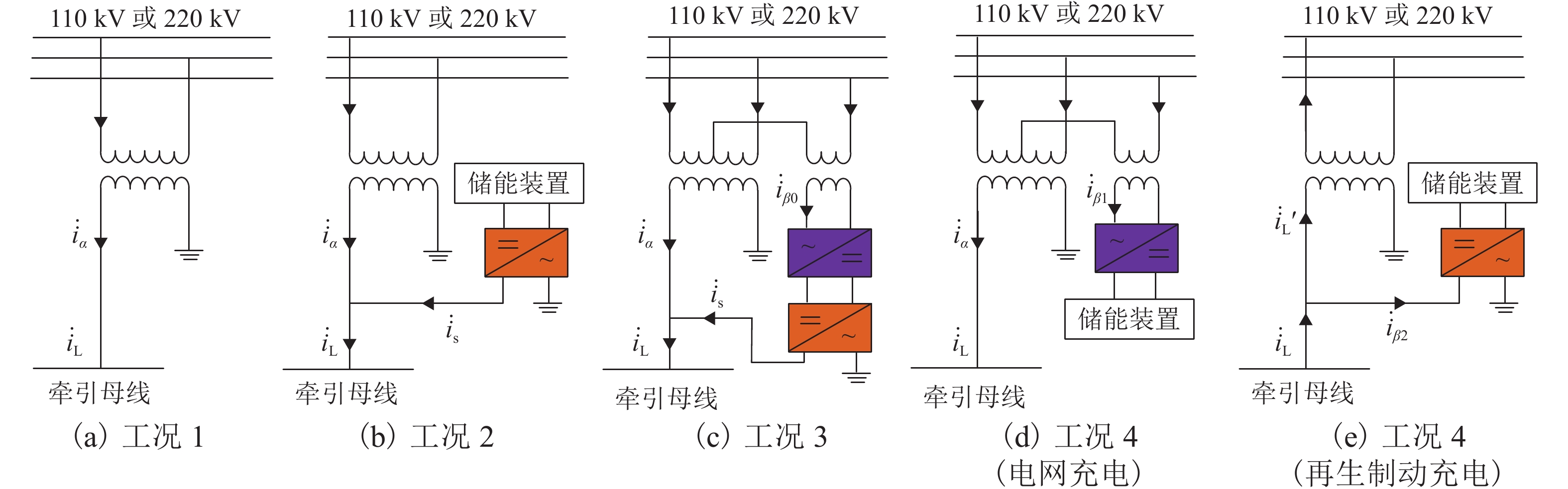
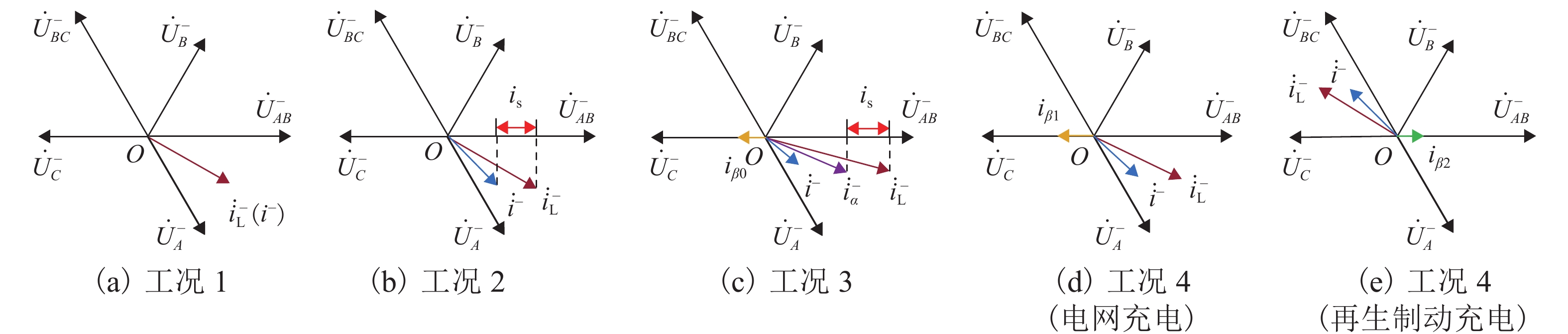
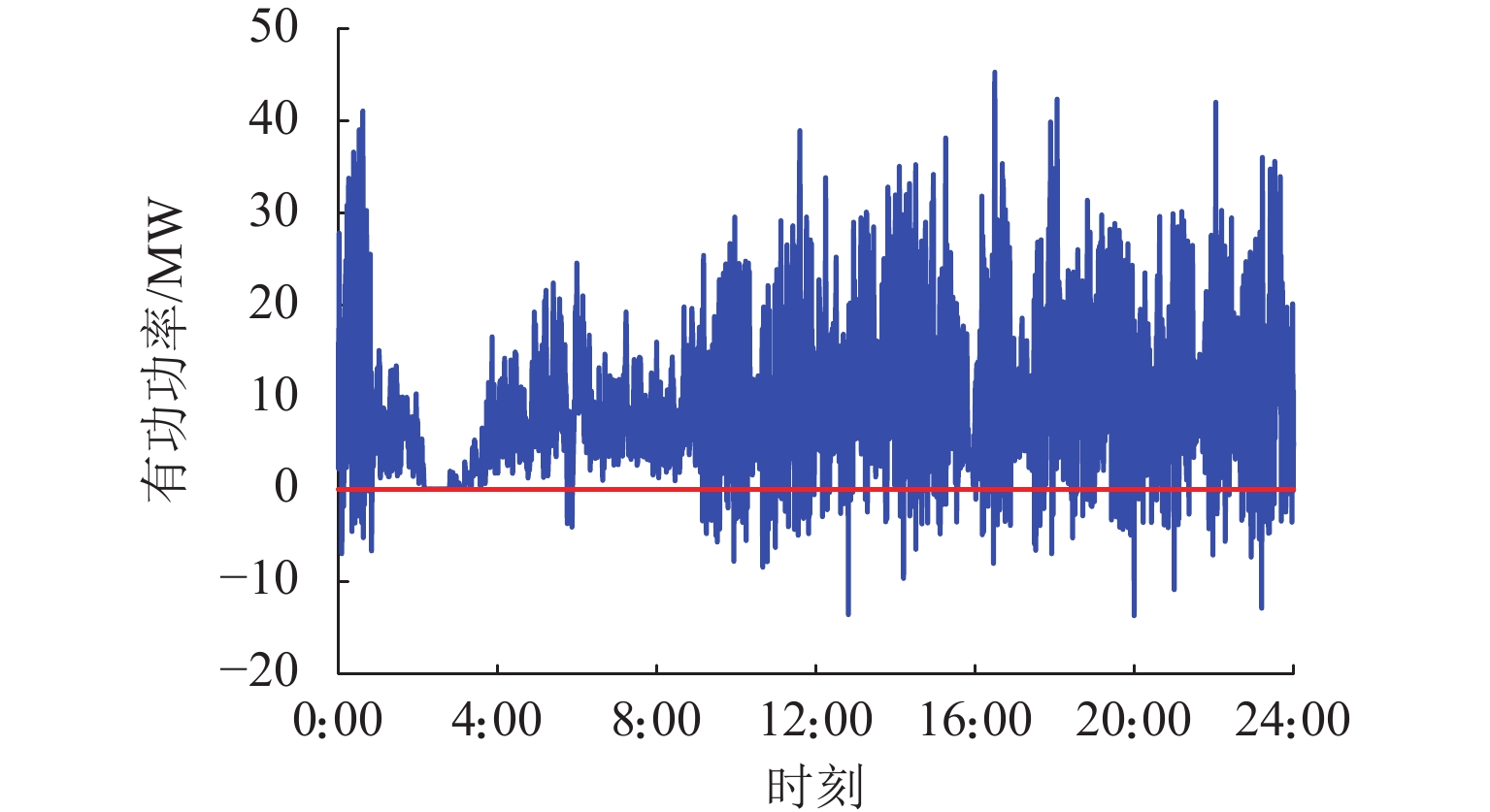
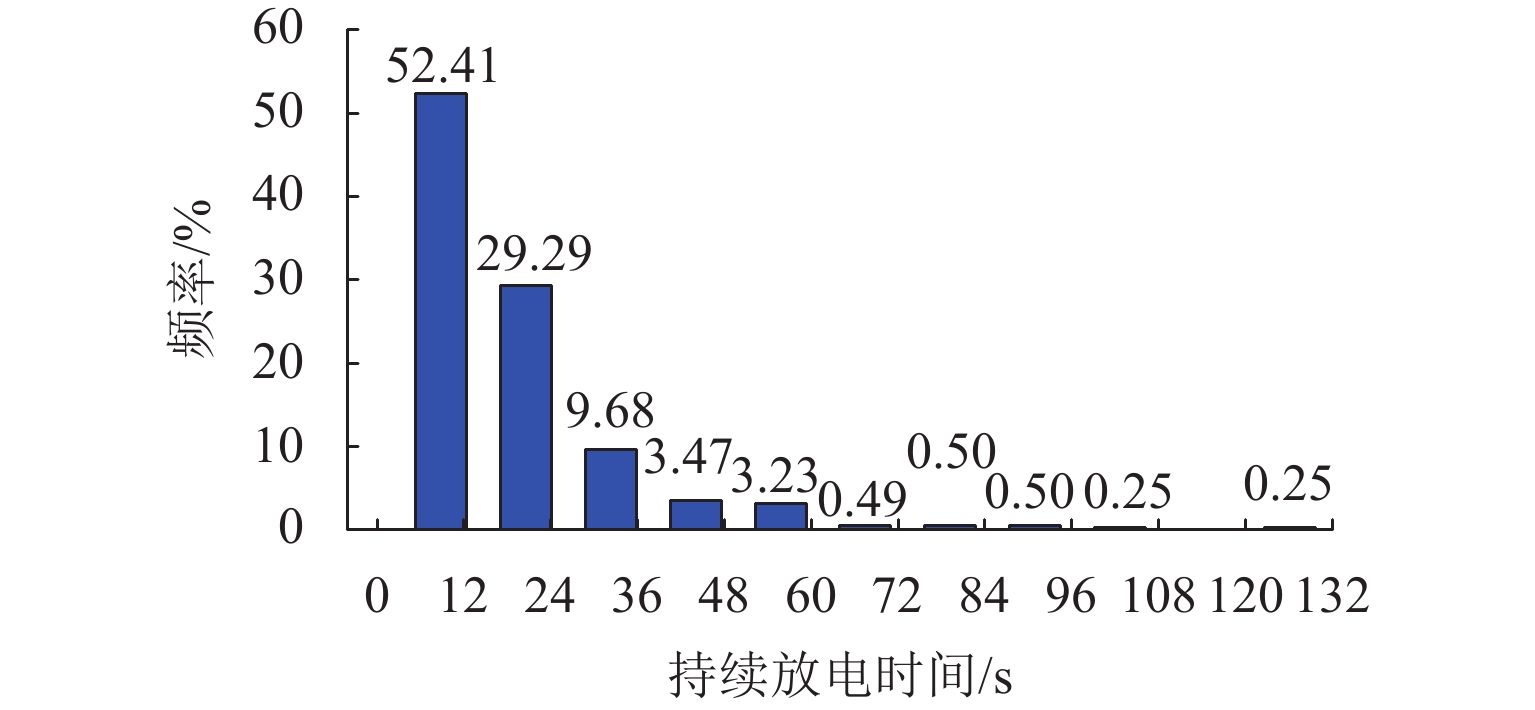
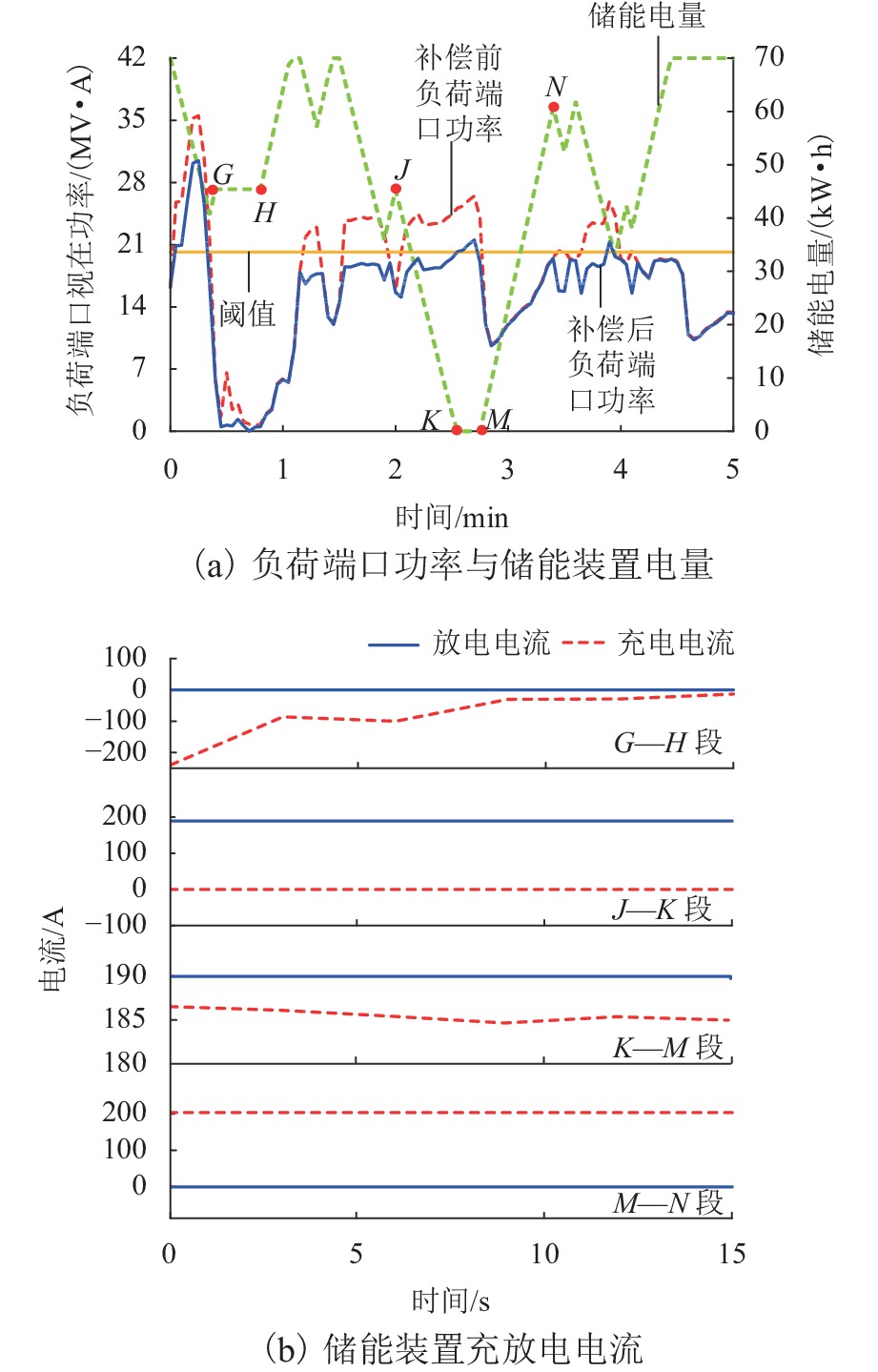
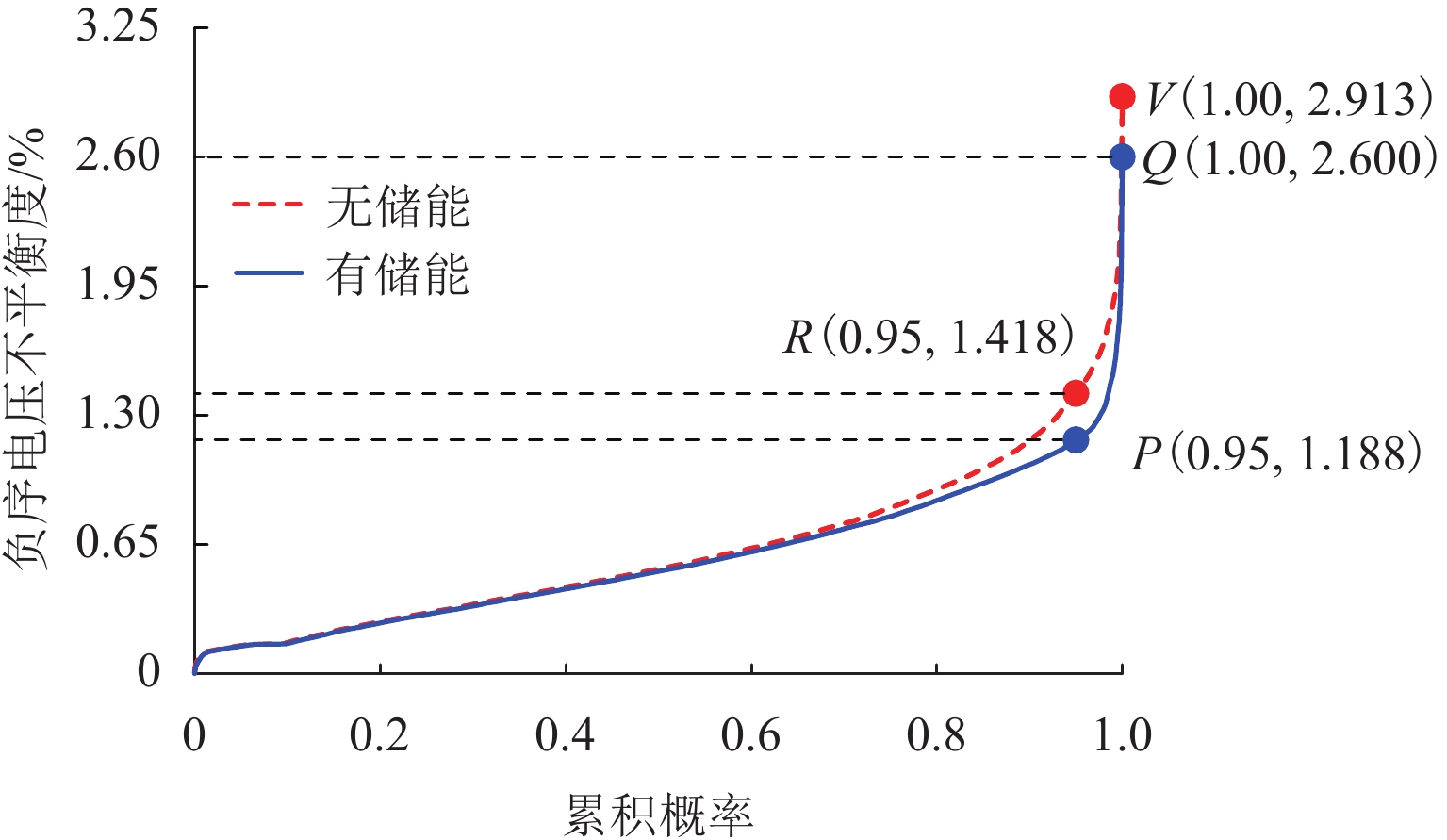
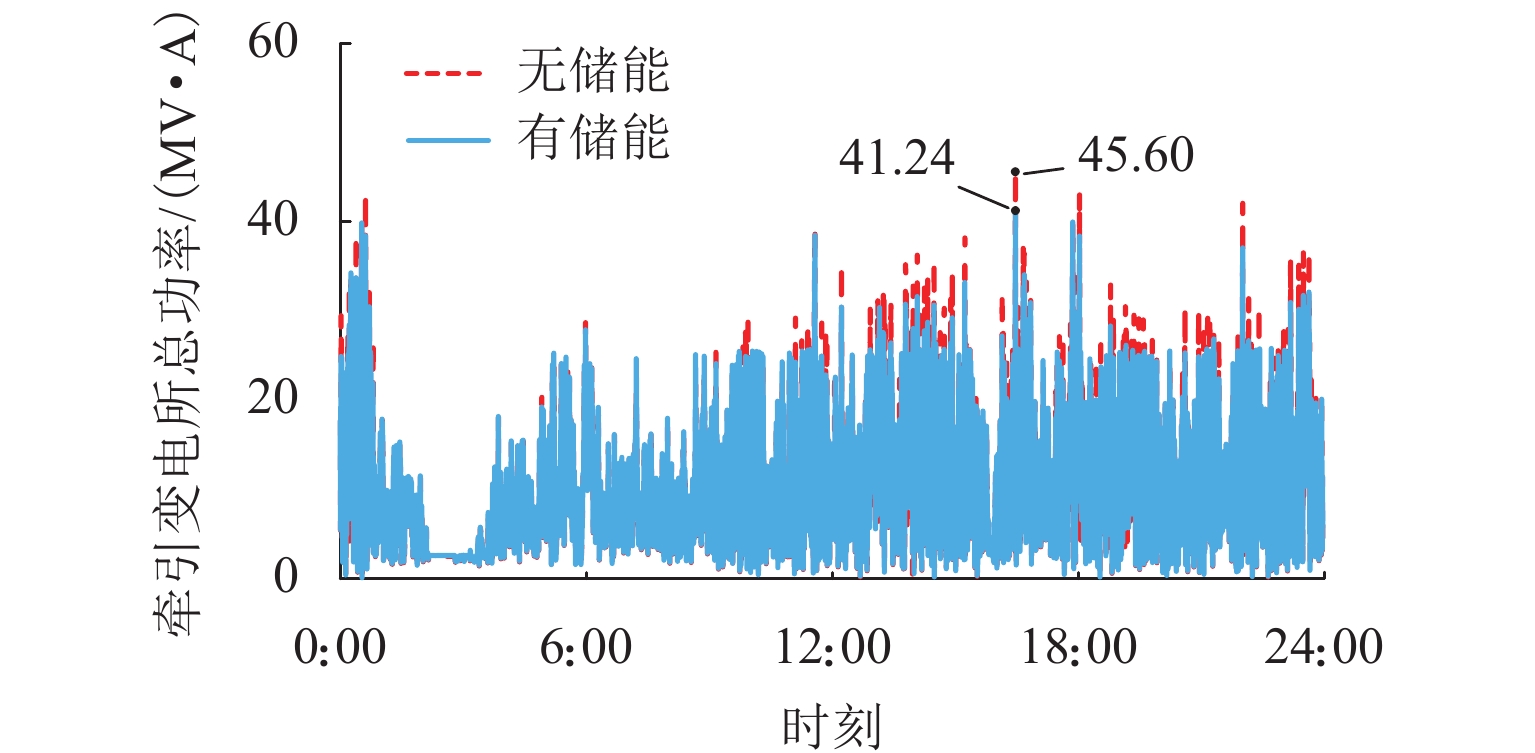
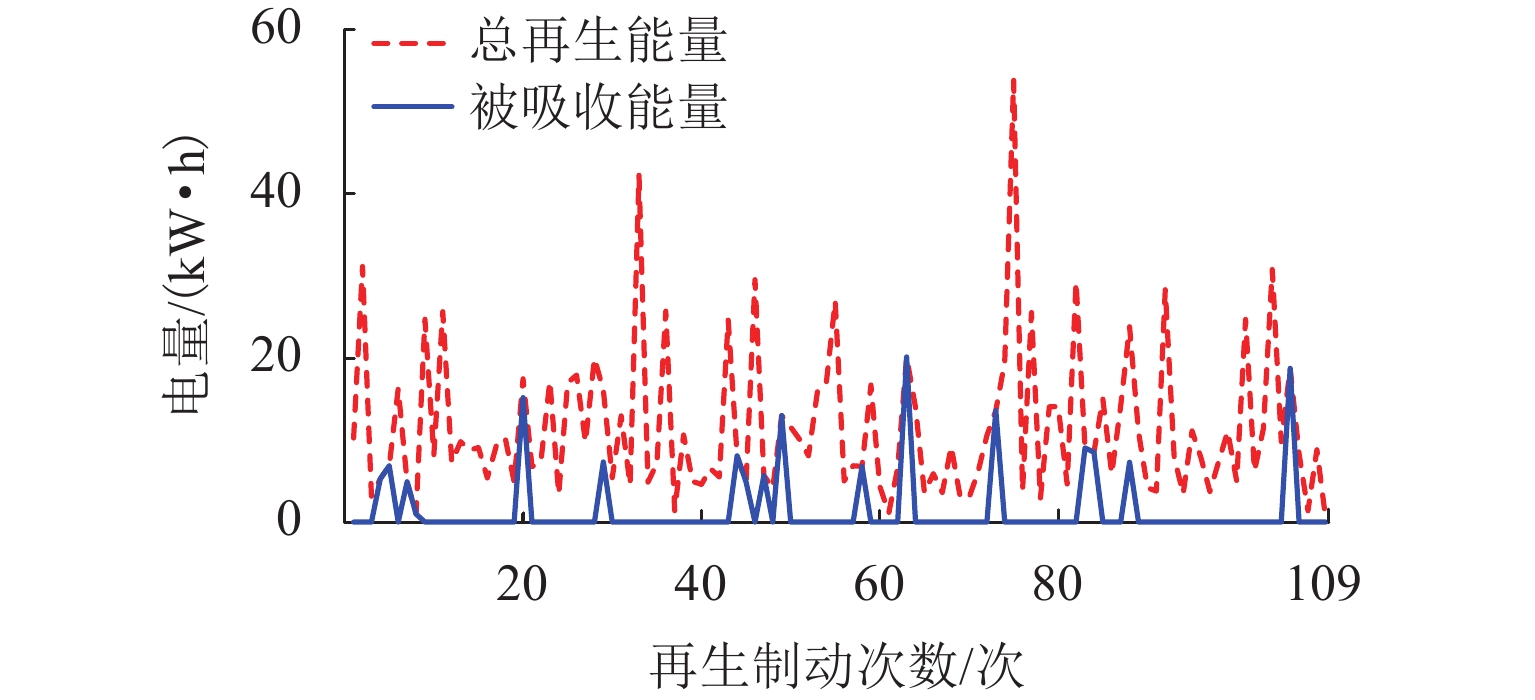
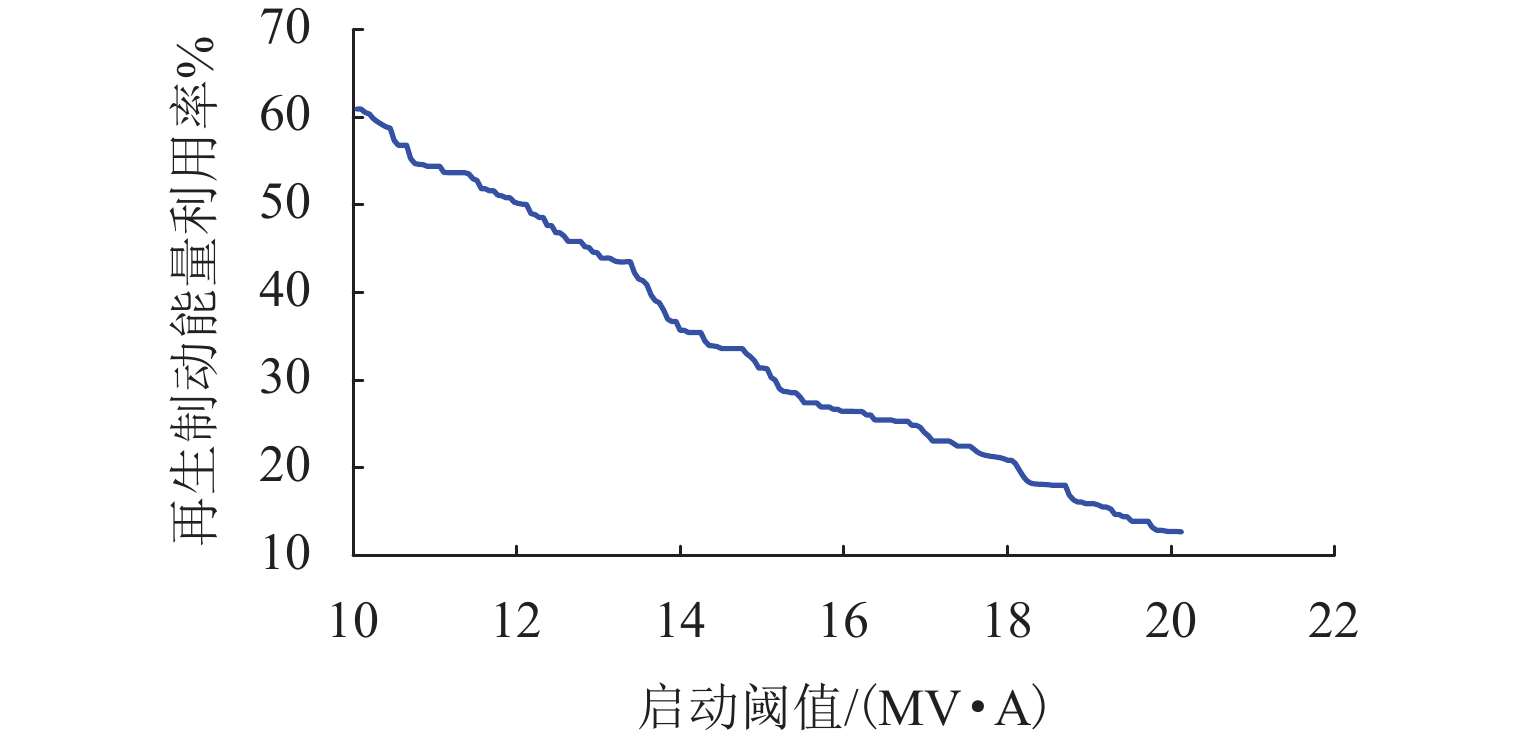
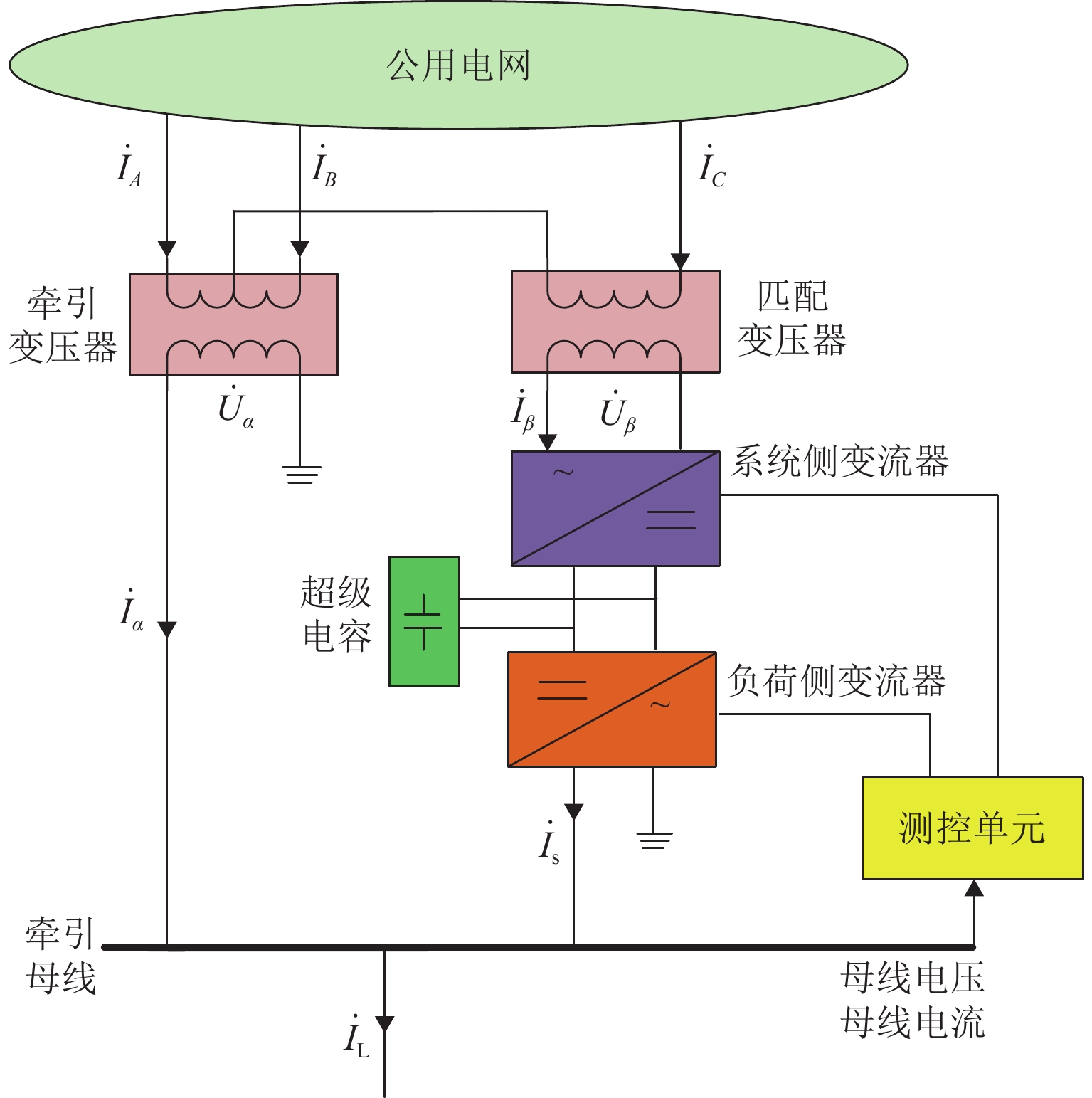
为进一步降低电气化铁路对三相电网的负序影响,兼顾牵引变电所节能经济运行,提出了一种电气化铁路同相储能供电系统能量管理策略和容量配置方案. 首先,以三相电压不平衡度限值为约束,确定了不同负序超标情况下储能装置启动阈值;而后,建立了储能供电系统负序补偿模型,计算储能装置充放电电流;最后,以牵引变电所实测数据为例,给出储能装置容量配置方案,并计算验证了所提能量管理策略的可行性和正确性. 研究结果表明:该同相储能供电系统通过实时控制储能装置充放电,可实现负序满意度补偿、负荷削峰填谷、兼顾再生能量利用,负序补偿度由储能装置放电功率决定,削峰填谷效果和再生能量利用率由储能装置启动阈值和储能容量决定;储能容量一定时,越小阈值,再生制动能量利用率越高.
Abstract:In order to reduce the impact of electrified railways on the negative sequence of three-phase power grid, and consider energy-saving and economic operation of traction substations, an energy management strategy and capacity allocation scheme is proposed for the co-phase traction power supply and energy storage system in electrified railways. Firstly, with the constraint of the three-phase voltage unbalance limit, the starting threshold of the energy storage device is determined in the cases of the negative sequence exceeding standard. Then the negative-sequence compensation model of the power supply and energy storage system is established to calculate its charging and discharging current. The measured data of traction substations are used to develop the capacity allocation scheme of the energy storage device, which are then validated by the calculation. The results show that the co-phase traction power supply and energy storage system can control the charge and discharge of the energy storage device in real time to realize negative-sequence satisfaction compensation, load peak shaving and valley filling, and regenerative energy utilization. The degree of negative sequence compensation is determined by the discharge power of the energy storage device. The peak-shaving and valley-filling effect and regenerative energy utilization rate are determined by the starting threshold and the capacity of the energy storage device. When the energy storage capacity is constant, the smaller the threshold, the higher the utilization rate of regenerative braking energy.
-
-
[1] 李群湛, 贺建闽. 牵引供电系统分析[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2007. [2] 冯晓云. 电力牵引交流传动及其控制系统[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. [3] 徐千鸣,马伏军,何志兴,等. 双星型多电平铁路功率调节器及其控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(13): 3609-3619, 3380. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.151180XU Qianming, MA Fujun, HE Zhixing, et al. A railway power conditioner and its control method based on double star bridge cells[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(13): 3609-3619, 3380. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.151180 [4] GHASSEMI A, MAGHSOUD I, FARSHAD S, et al. Power quality improvement in Y/△ electric traction system using a railway power conditioner[C]//2013 12th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering. Wroclaw: IEEE, 2013: 489-494. [5] 李群湛. 论新一代牵引供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001LI Qunzhan. On new generation traction power supply system and its key technologies for electrification railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001 [6] 王辉,李群湛,李晋,等. 基于YNd变压器与静止无功发生器的电气化铁路同相供电综合补偿方案[J]. 电工技术学报,2020,35(17): 3739-3749. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.190957WANG Hui, LI Qunzhan, LI Jin, et al. Comprehensive compensation schemes of cophase power supply of electrified railway based on YNd transformer and static var generator[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(17): 3739-3749. doi: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.190957 [7] 胡海涛,陈俊宇,葛银波,等. 高速铁路再生制动能量储存与利用技术研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(1): 246-256,391. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.190650HU Haitao, CHEN Junyu, GE Yinbo, et al. Research on regenerative braking energy storage and utilization technology for high-speed railways[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(1): 246-256,391. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.190650 [8] SHAFIGHY M, KHOO S Y, KOUZANI A Z. Energy efficiency methods in electrified railways based on recovery of regenerated power[M]//Electrical Engineering and Control. Berlin: Springer, 2011: 69-77. [9] 黄小红,赵艺,李群湛,等. 电气化铁路同相储能供电技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(4): 856-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20181083HUANG Xiaohong, ZHAO Yi, LI Qunzhan, et al. Co-phase traction power supply and energy storage technology for electrified railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 856-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20181083 [10] 王喜军. 电气化铁路飞轮储能充放电管理及其控制策略研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019. [11] 赵亚杰,夏欢,王俊兴,等. 基于动态阈值调节的城轨交通超级电容储能系统控制策略研究[J]. 电工技术学报,2015,30(14): 427-433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.14.057ZHAO Yajie, XIA Huan, WANG Junxing, et al. Control strategy of ultracapacitor storage system in urban mass transit system based on dynamic voltage threshold[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(14): 427-433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.14.057 [12] 西南交通大学. 一种电气化铁路储能同相供电装置: CN 201720805482.7[P]. 2018-02-05. [13] 刘若飞. 储能式同相供电系统的建模与优化控制策略研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019. [14] 徐政, 屠卿瑞, 管敏渊. 柔性直流输电系统[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2013. [15] 全国电压电流等级和频率标准化技术委员会. 电能质量 三相电压不平衡: GB/T 15543—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [16] 张丽艳. 新建电气化铁路对电网电能质量影响的预测与对策分析研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2012. [17] 李群湛. 牵引变电所供电分析及综合补偿技术[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2006. [18] 孟彦京,张商州,陈景文,等. 充电方式对超级电容能量效率的影响[J]. 电子器件,2014,37(1): 13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2014.01.004MENG Yanjing, ZHANG Shangzhou, CHEN Jingwen, et al. The impact of charging mode pairs of super-capacitor energy efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Electron Devices, 2014, 37(1): 13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2014.01.004 -




 下载:
下载: