Study on Surface Uplift Caused by Construction of Shallow-Buried Soil Rectangular Pipe Jacking at Subway Entrance and Exit
-
摘要:
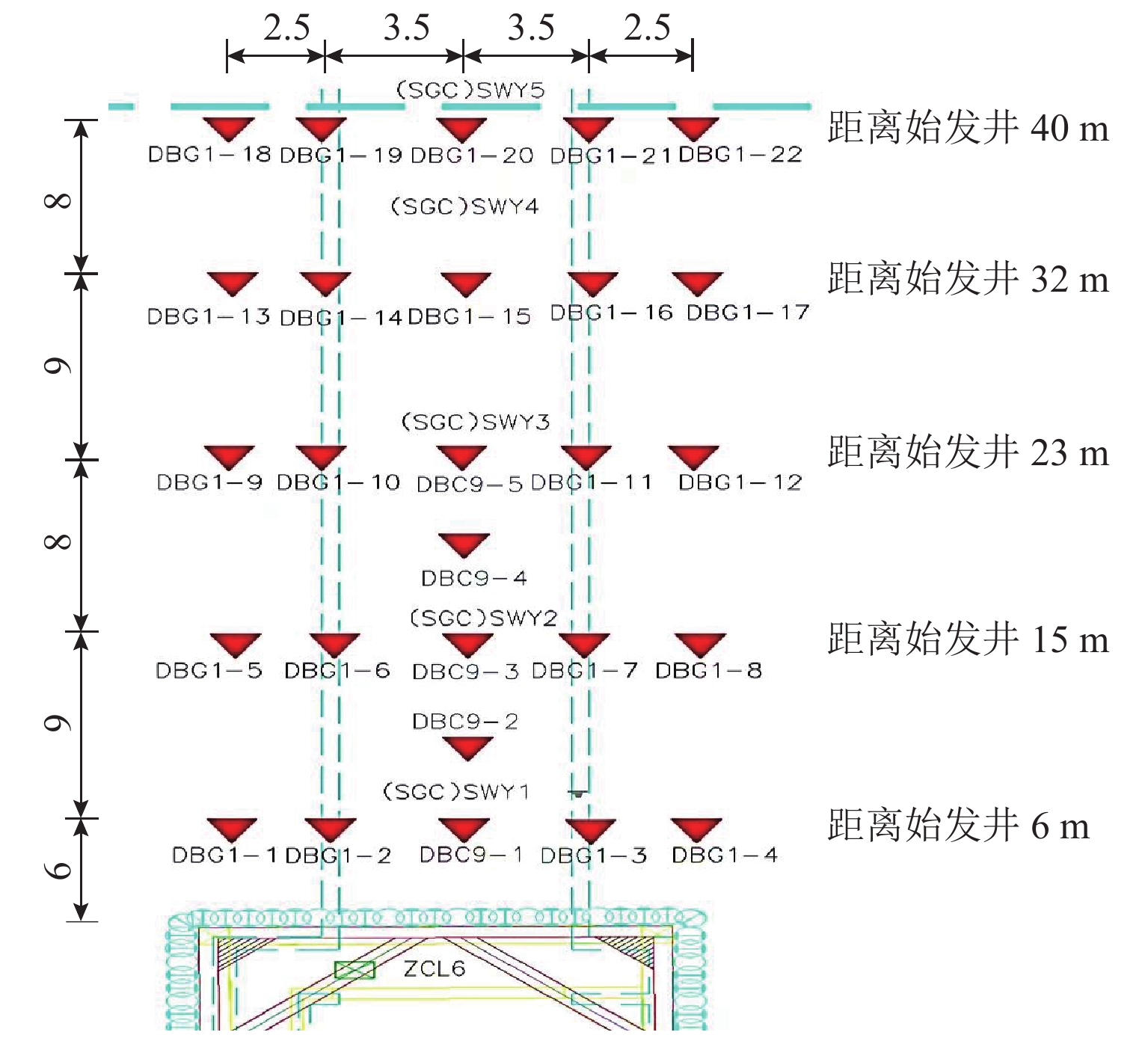
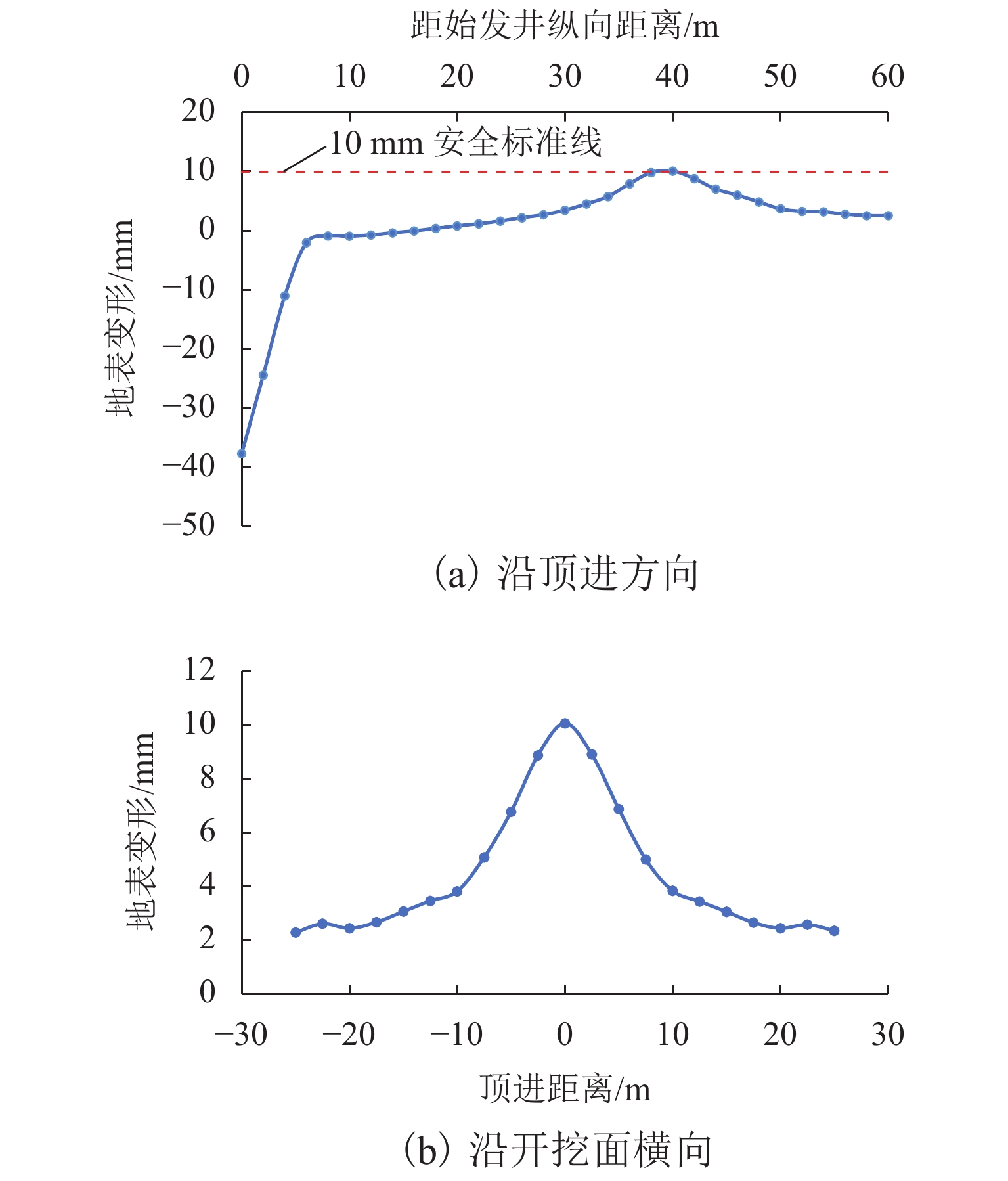
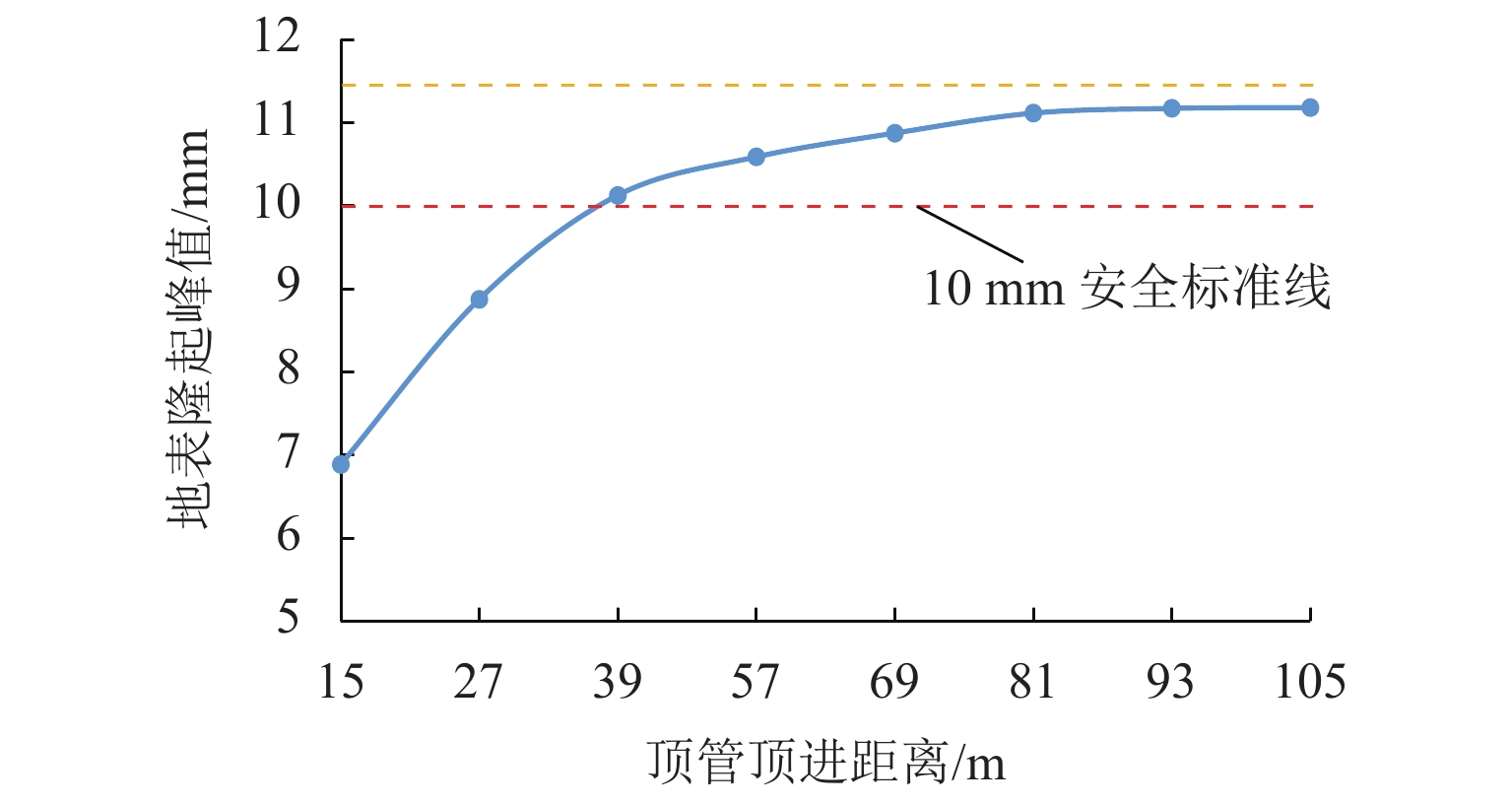
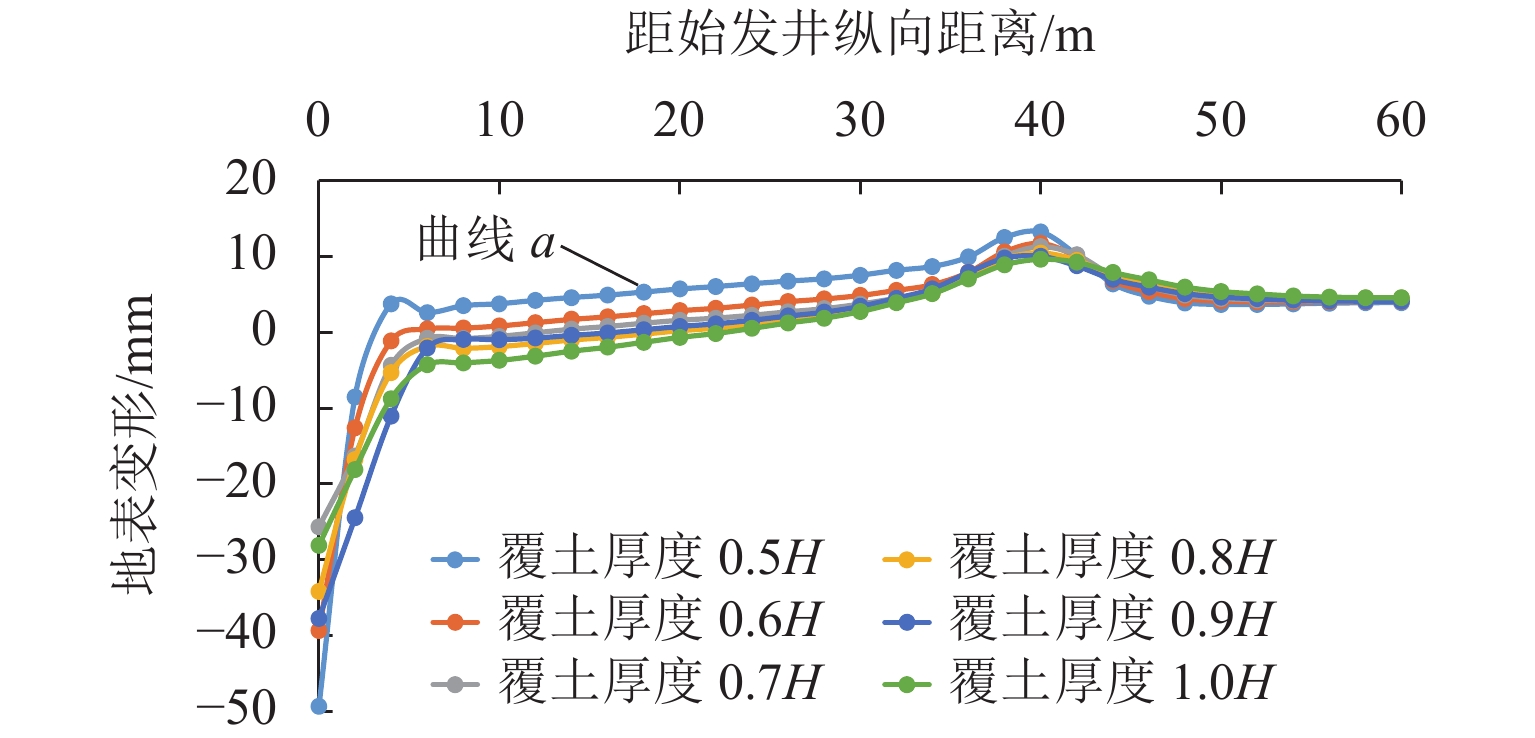
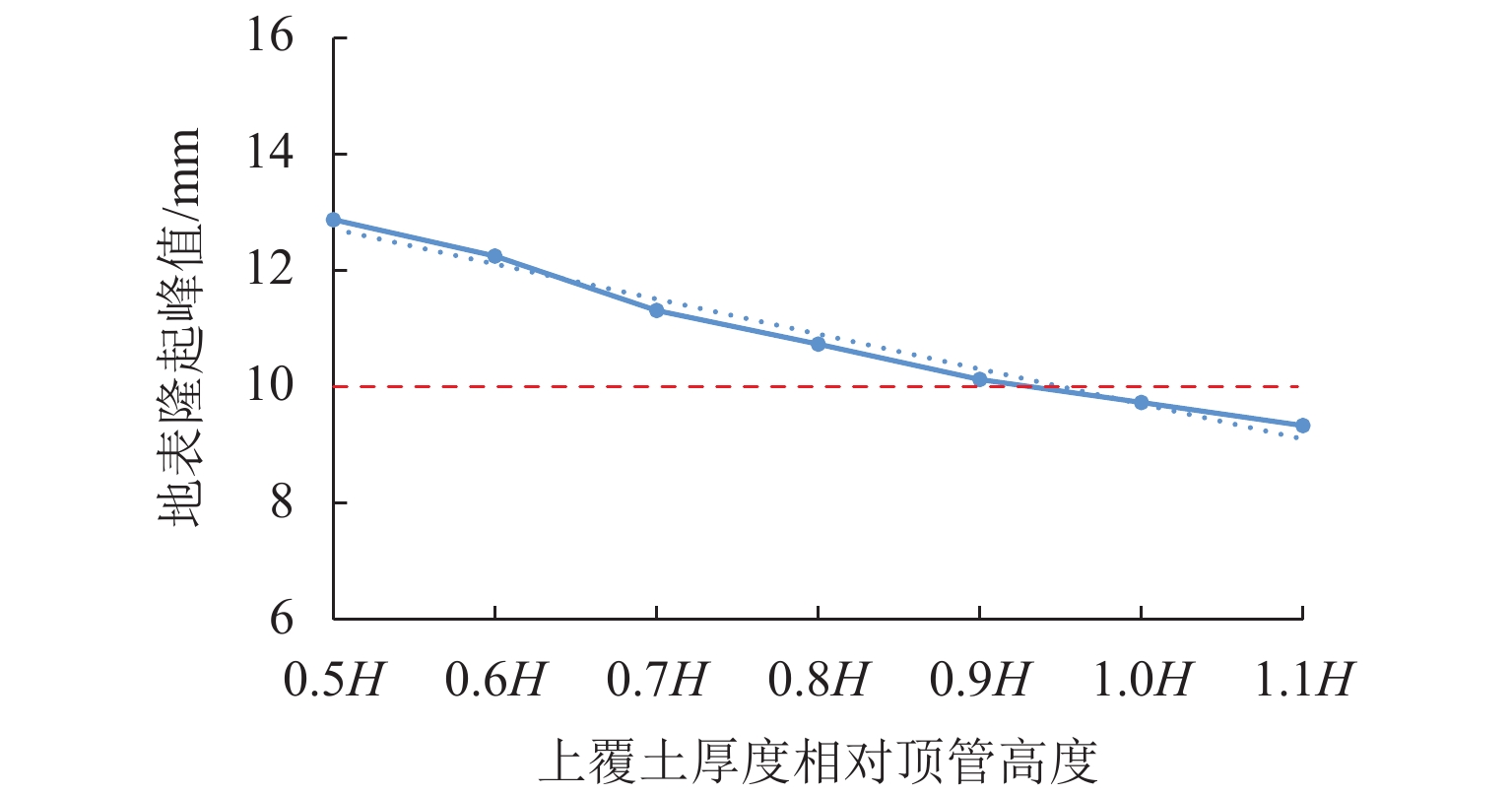
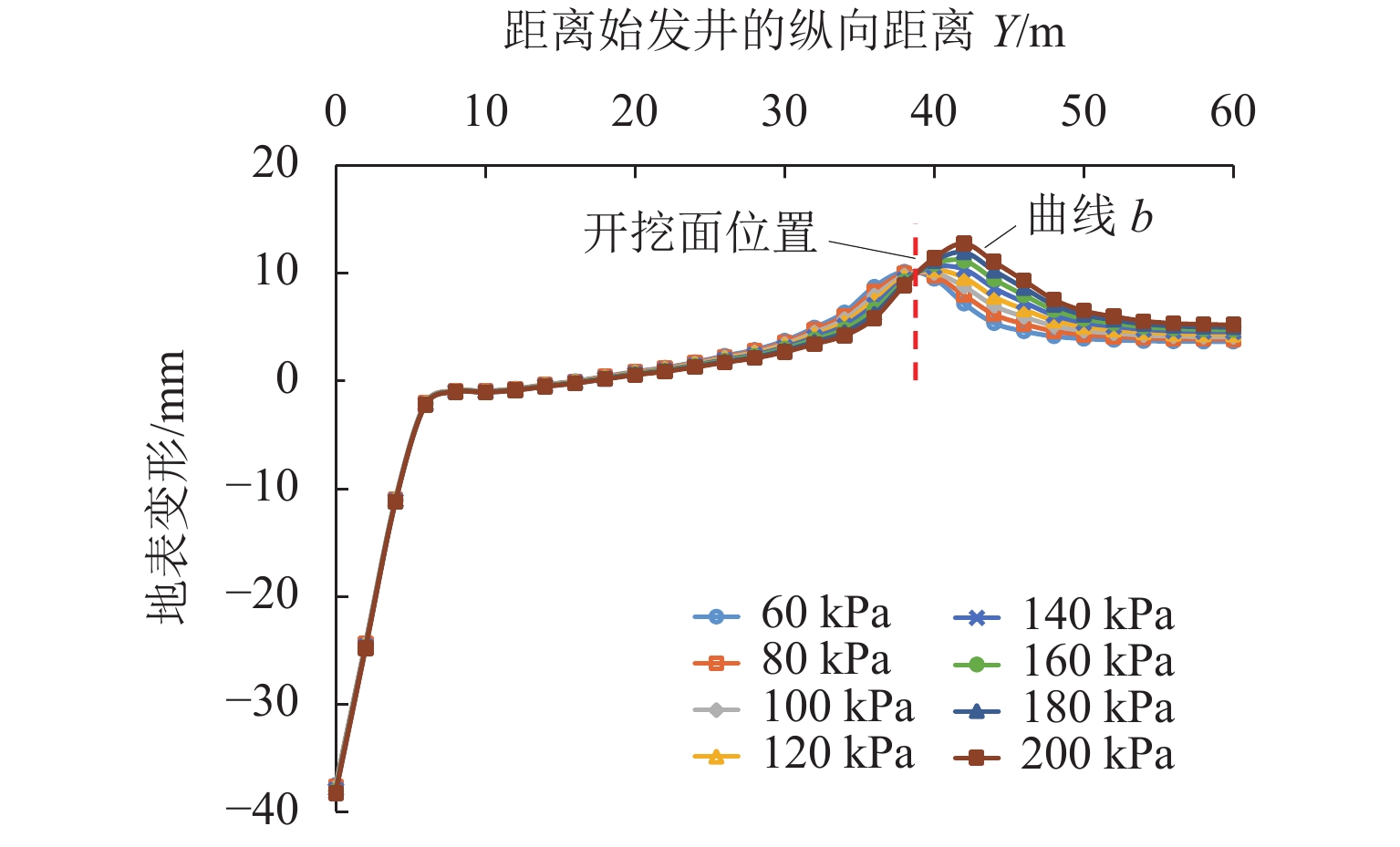
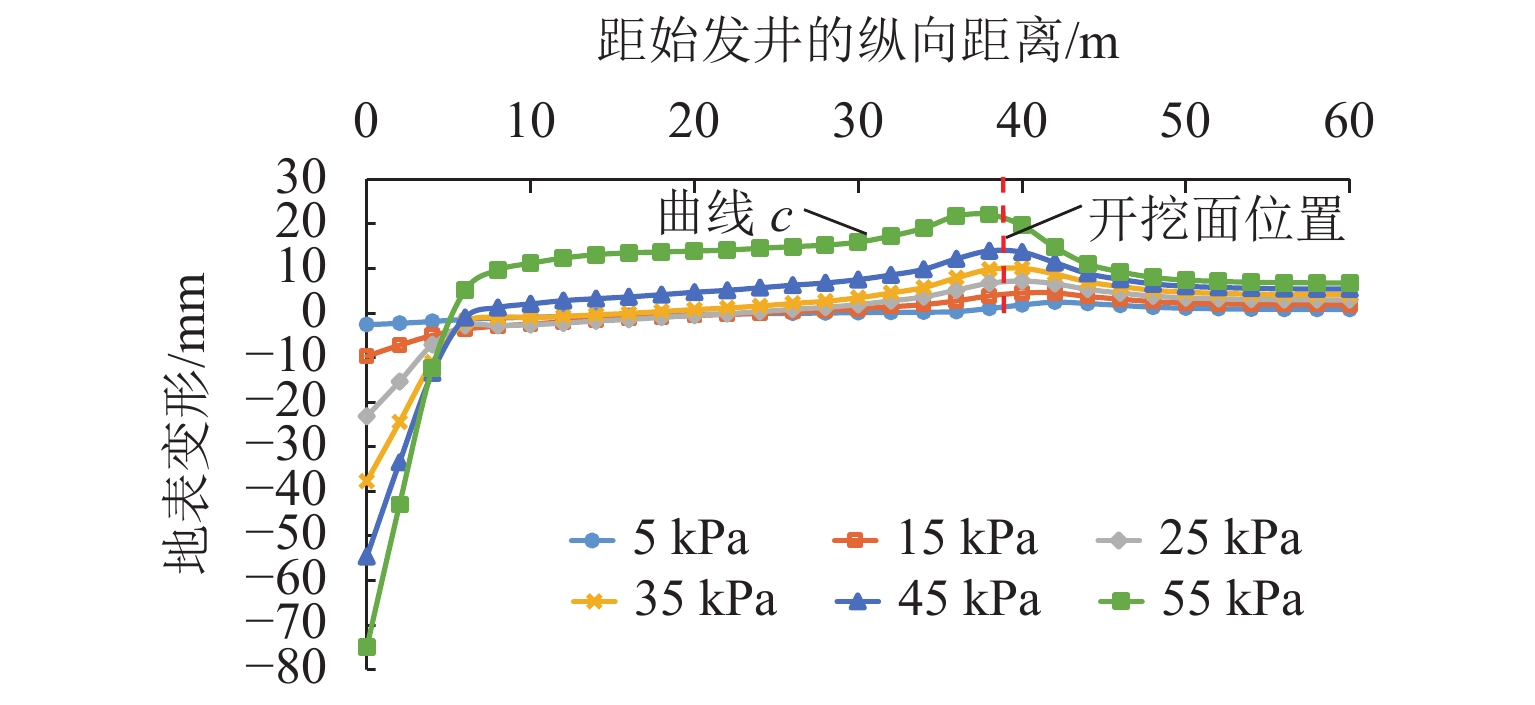
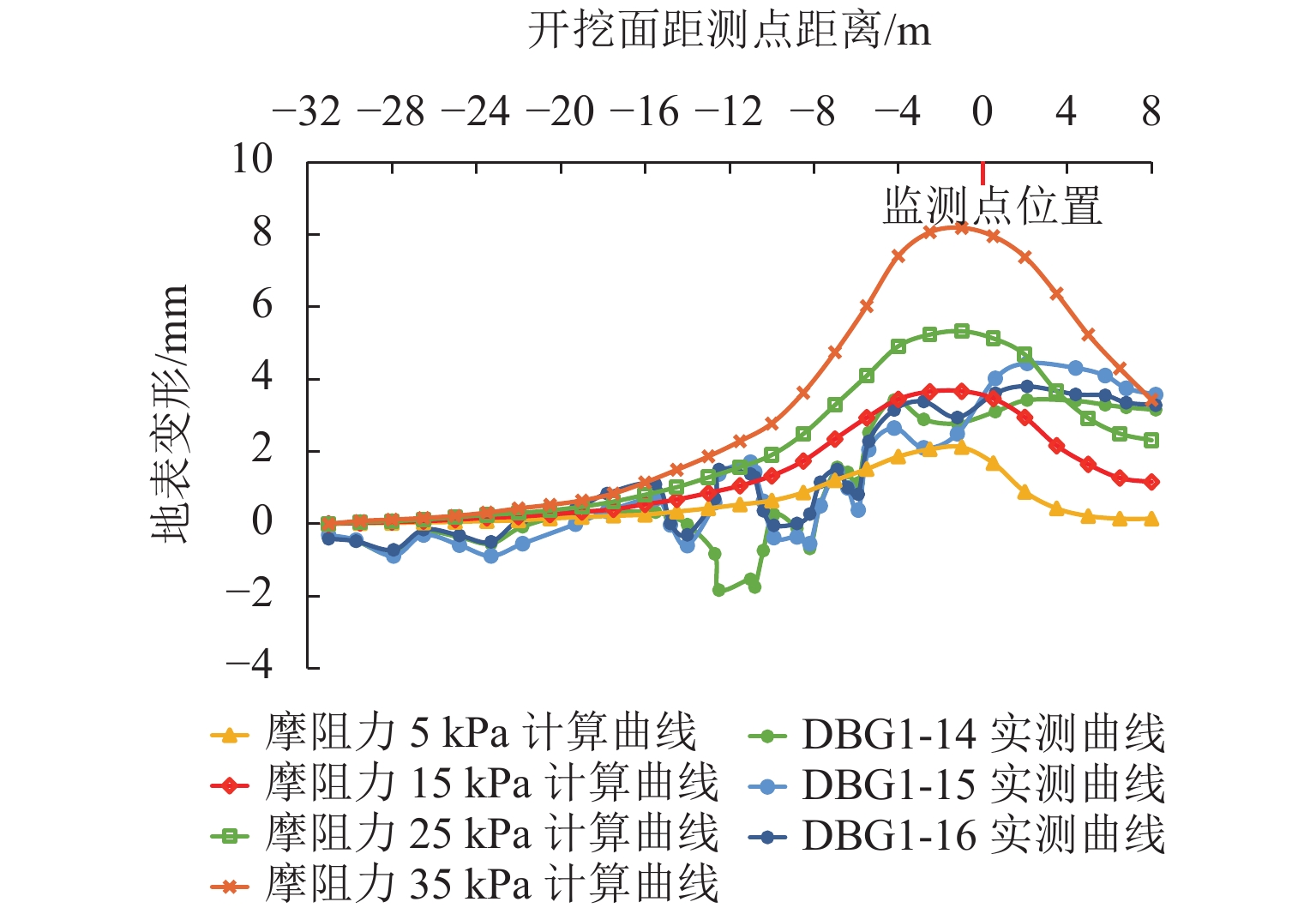
针对浅覆土矩形顶管施工时存在地表隆起过大的风险,应用MIDAS GTS岩土数值软件动态模拟大口径矩形顶管掘进施工过程,探究其在不同覆土厚度、开挖面顶进压力、摩擦阻力下引起的地表隆起规律,并与现场监测数据进行对比分析. 结果表明:顶管顶进时地表监测点的隆起规律与数值计算结果基本吻合;顶管开挖面顶进压力、管节与地层的摩阻力引起的地表隆起在开挖面附近叠加达到峰值;地表的隆起峰值随覆土厚度的减小而线性增加,当开挖面顶进压力为100 kPa、管节摩阻力为35 kPa时,顶管覆土厚度每减小0.1
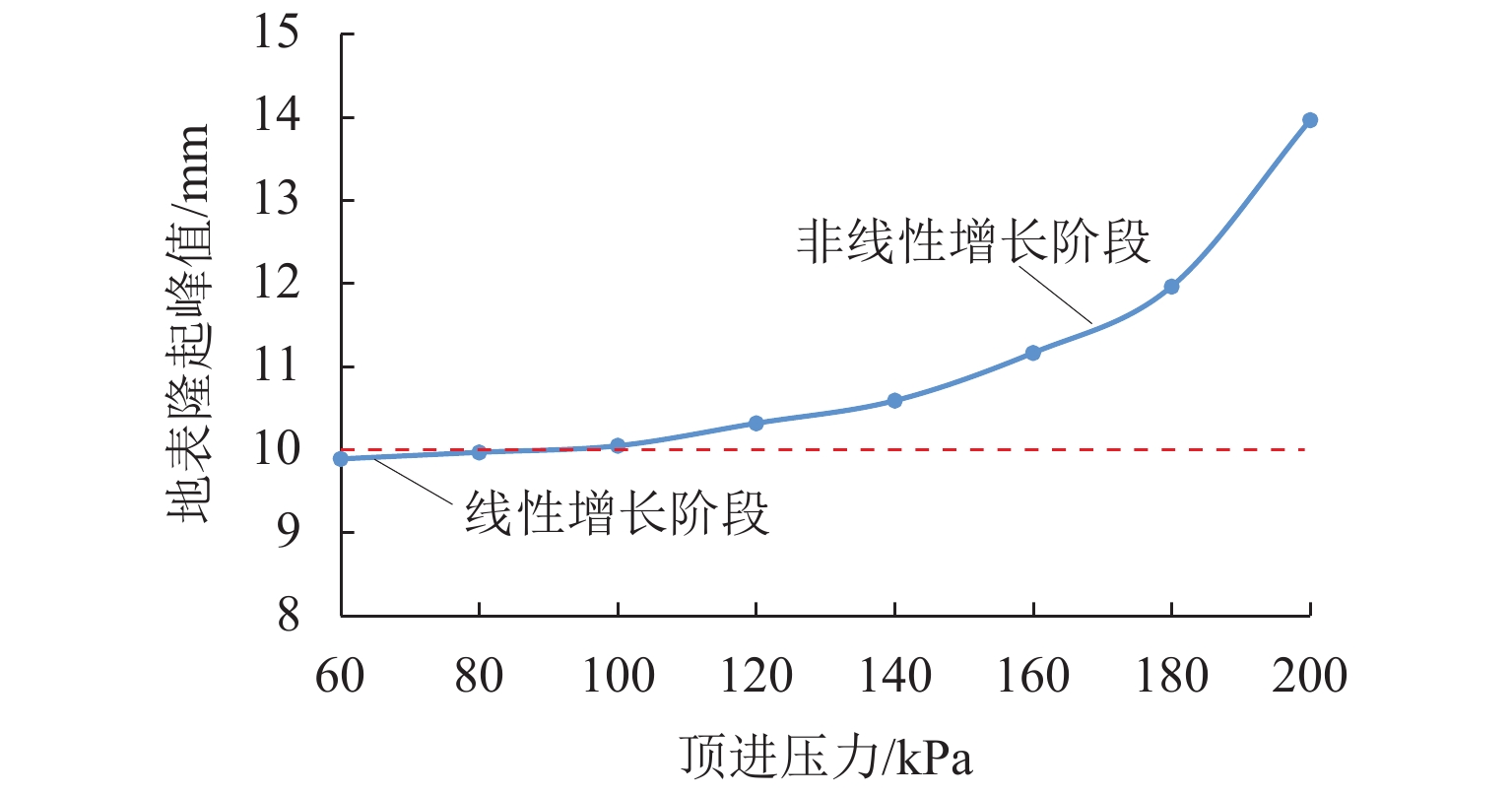
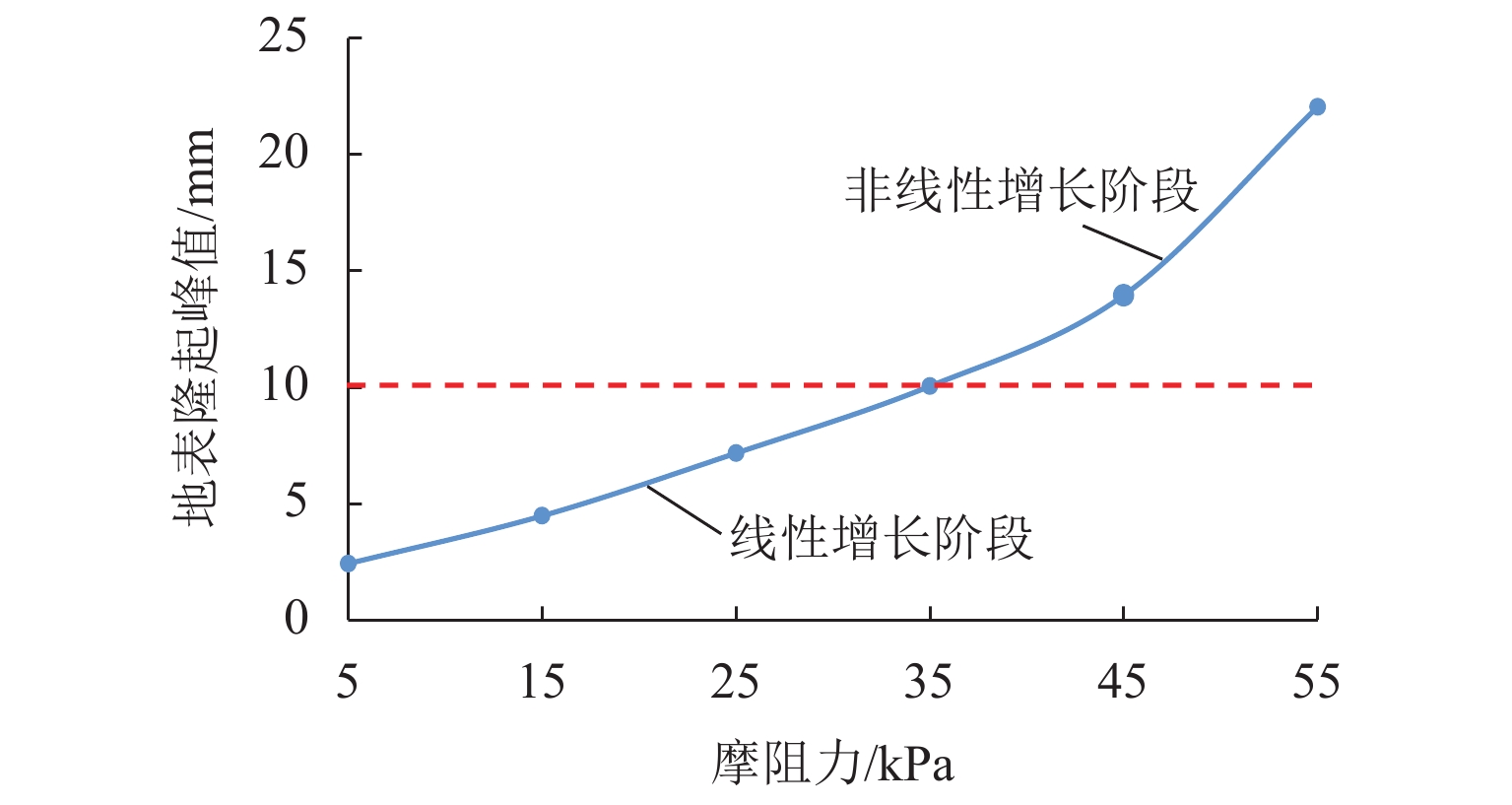
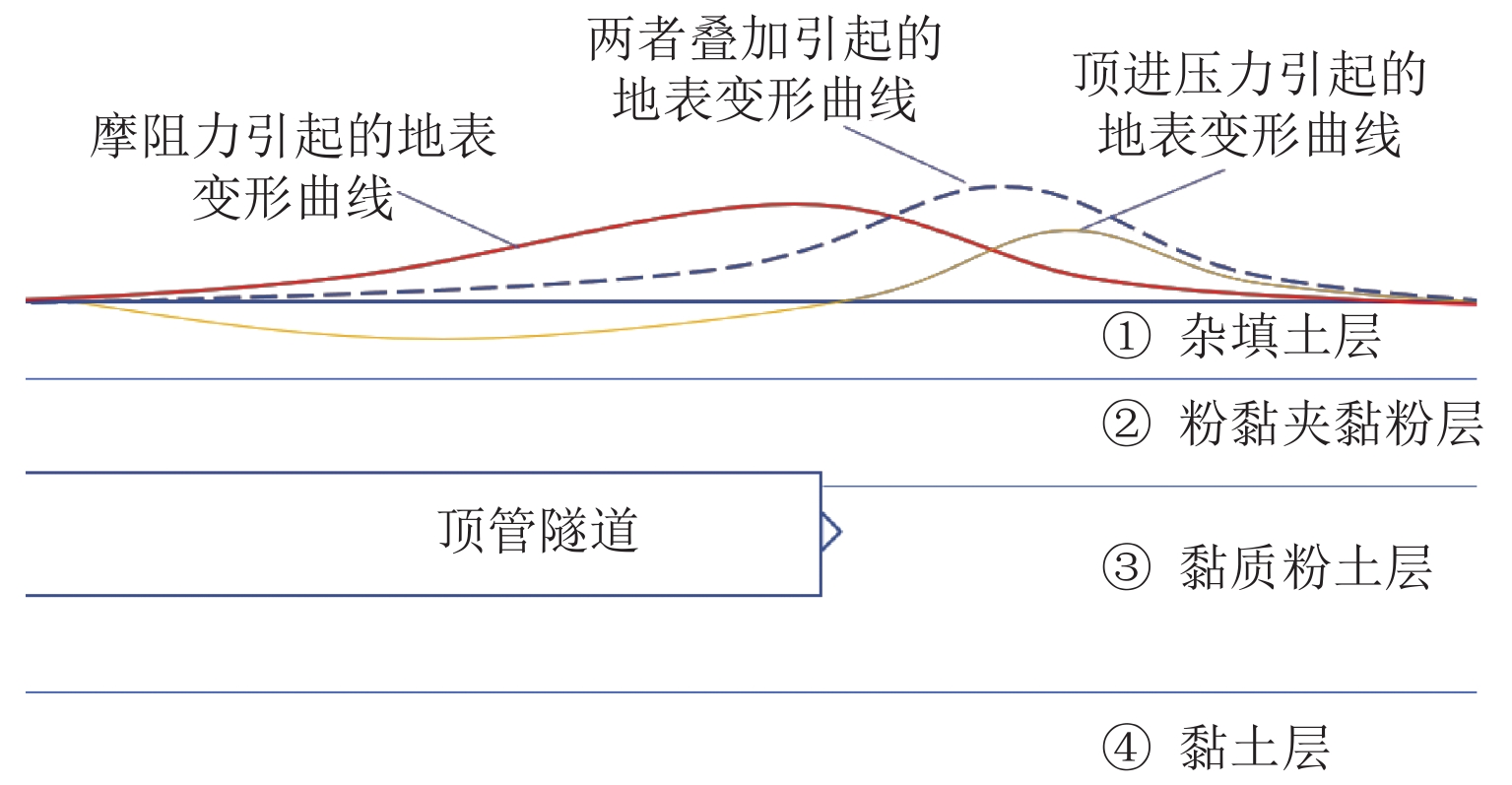
H (H 为矩形顶管高度),地表隆起峰值增大约6.00 mm;浅覆土顶管地表隆起随顶进压力和管节摩阻力的增长规律可分为缓慢增长阶段和非线性快速增长阶段;为降低浅覆土顶管工程上覆土被顶破的风险,需要合理控制开挖面顶进压力及其波动、在管节外周形成厚度均匀的减摩泥浆套,确保地层稳定和顶管工程的安全.Abstract:In view of the risk of excessive surface uplift in rectangular pipe jacking construction under the condition of shallow-buried soil, the finite element software MIDAS GTS was applied to simulate the dynamic process of large-diameter rectangular pipe jacking, and to explore the law of surface uplift caused by different thickness of soil covering, different jacking pressure of excavation face and different friction between pipe joint and soil, and to compare and analyze with the field monitoring data. The results show that the uplifting rule of surface monitoring points during pipe jacking is basically consistent with the numerical calculation results. The surface uplift caused by the jacking pressure on the excavation surface of the pipe jacking and the frictional resistance between the pipe joints and the formation is superimposed to reach a peak value near the excavation surface. As the thickness of the overburden decreases, the peak value of the surface uplift increases linearly. When the jacking pressure of excavation face is 100 kPa and the friction resistance of the pipe joint is 35 kPa, the peak value of surface uplift increases about 6.00 mm when the soil jacking thickness decreases for 0.1
H (H is the height of rectangular pipe jacking). The growth law of surface uplift in shallow-buried soil jacking pipe with the increase of jacking pressure and joint friction can be divided into two stages: slow growth stage and nonlinear rapid growth stage. In order to reduce the risk of overburden soil being broken in shallow-buried soil pipe jacking project, it is necessary to take reasonable measures to control the jacking pressure and its fluctuation on the excavation surface, and to form an antifriction slurry sleeve with uniform thickness around the pipe joint, so as to ensure the stability of stratum and the safety of pipe jacking project.-
Key words:
- shallow-buried soil /
- numerical simulation /
- rectangular pipe jacking /
- surface uplift
-
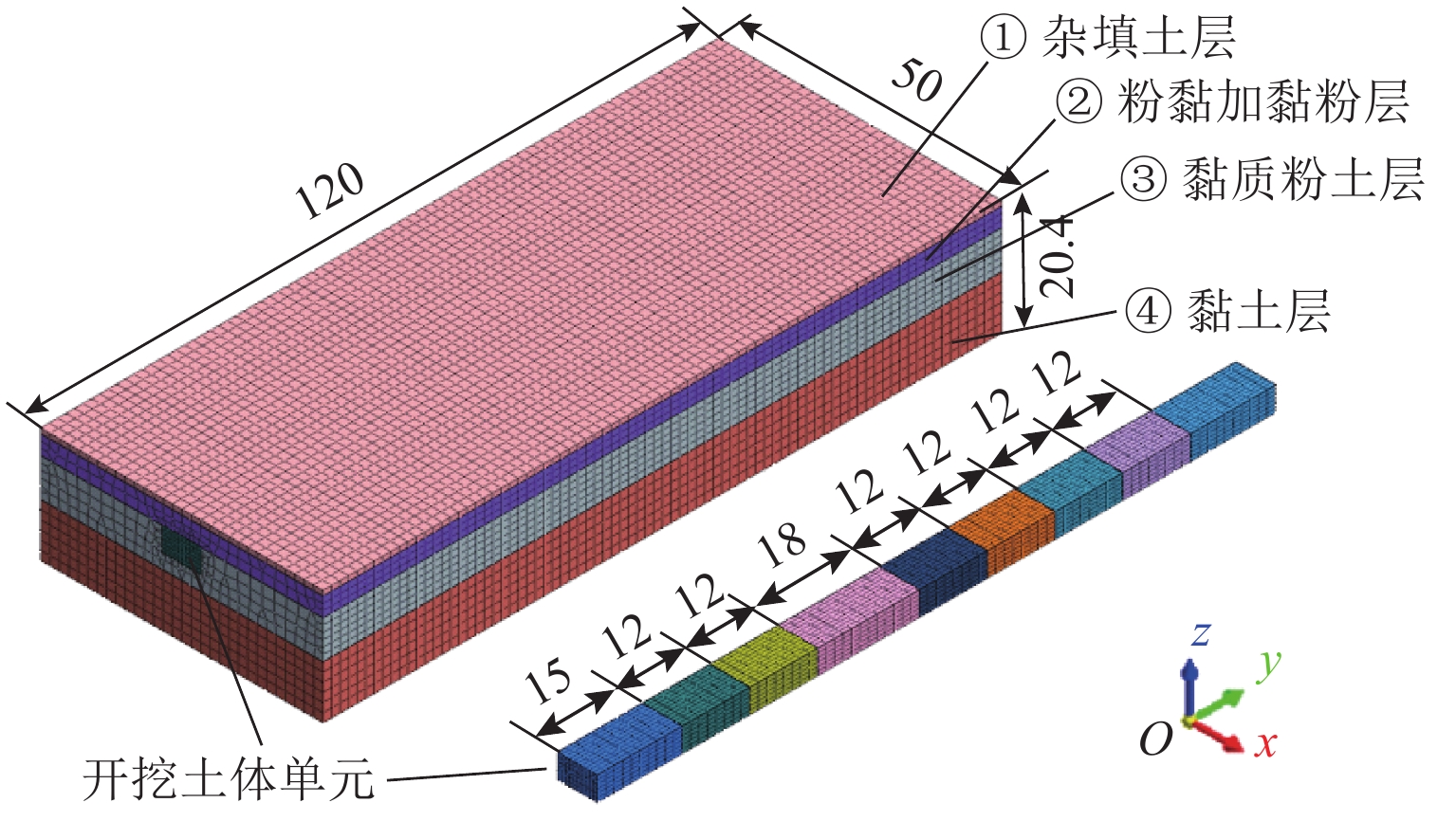
表 1 土层物理力学参数
Table 1. Soil physical and mechanical parameters
土 层 土层厚度
/m重度
/(kN·m−3)压缩模量
/MPa泊松比 侧压力
系数内摩擦角
/(°)黏聚力
/kPa① 杂填土 0.92 18.5 2500 0.30 0.49 12.0 5.0 ② 粉黏夹黏粉 3.30 20.2 7290 0.33 0.59 13.4 59.3 ③ 黏质粉土 6.80 19.0 10330 0.31 0.61 29.4 8.6 ④ 黏土 17.00 20.2 7400 0.32 0.67 11.1 51.5 -
[1] 彭立敏,王哲,叶艺超,等. 矩形顶管技术发展与研究现状[J]. 隧道建设,2015,35(1): 1-8.PENG Limin, WANG Zhe, YE Yichao, et al. Technological development and research status of rectangular pipe jacking method[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2015, 35(1): 1-8. [2] 贾连辉. 矩形顶管在城市地下空间开发中的应用及前景[J]. 隧道建设,2016,36(10): 1269-1276.JIA Lianhui. Application of rectangular pipe jacking machine to urban underground space development and its prospects[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2016, 36(10): 1269-1276. [3] NG R M C, LO K Y, ROWE R K. Analysis of field performance—the Thunder Bay tunnel[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1986, 23(1): 30-50. doi: 10.1139/t86-005 [4] LEE K M, ROWE R K. Finite element modelling of the three-dimensional ground deformations due to tunnelling in soft cohesive soils: part 2—results[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 1990, 10(2): 111-138. doi: 10.1016/0266-352X(90)90002-D [5] BEER G, WATSON J O, SWOBODA G. Three-dimensional analysis of tunnels using infinite boundary elements[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 1987, 3(1): 37-58. doi: 10.1016/0266-352X(87)90031-0 [6] SHI J S, ORTIGAO J A R, BAI J L. Modular neural networks for predicting settlements during tunneling[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1998, 124(5): 389-395. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1998)124:5(389) [7] YEH I C. Application of neural networks to automatic soil pressure balance control for shield tunneling[J]. Automation in Construction, 1997, 5(5): 421-426. doi: 10.1016/S0926-5805(96)00165-3 [8] 黄宏伟,胡昕. 顶管施工力学效应的数值模拟分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2003,22(3): 400-406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.03.012HUANG Hongwei, HU Xin. 3D numerical analysis on construction mechanics effect of pipe-jacking[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(3): 400-406. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.03.012 [9] 魏纲,张鑫海,徐银锋. 考虑多因素的类矩形盾构施工引起土体竖向位移研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(1): 199-208. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1032WEI Gang, ZHANG Xinhai, XU Yinfeng. Deriving vertical displacement of ground due to quasi-rectangular shield tunneling considering multiple factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 199-208. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1032 [10] 许有俊,王雅建,冯超,等. 矩形顶管施工引起的地面沉降变形研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2018,14(1): 192-199.XU Youjun, WANG Yajian, FENG Chao, et al. Research on ground deformation caused by rectangular pipe jacking construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2018, 14(1): 192-199. [11] 许有俊,史明,李育发,等. 大断面土压平衡矩形顶管施工引起地表竖向变形研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版),2020,53(7): 597-604. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2020-07-005XU Youjun, SHI Ming, LI Yufa, et al. Study on vertical deformation of ground surface caused by construction of large section soil pressure balanced rectangular pipe jacking[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2020, 53(7): 597-604. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2020-07-005 [12] 曹宇春,诸葛恒源,曾阳,等. 大口径顶管施工对地表沉降的影响分析[J]. 科技通报,2019,35(6): 75-79. doi: 10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2019.06.013CAO Yuchun, ZHUGE Hengyuan, ZENG Yang, et al. Influence of large diameter pipe jacking construction on ground surface settlement[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2019, 35(6): 75-79. doi: 10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2019.06.013 [13] 张治华. 矩形顶管施工引起的非对称附加推力作用下地表隆起及控制[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2019. [14] 中国地质大学(武汉). 顶管施工技术及验收规范(试行)[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2007. [15] 肖云之. 粉质黏土地层渣土改良试验研究[J]. 甘肃科技纵横,2019,48(9): 51-54,65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6375.2019.09.015XIAO Yunzhi. Experimental study on residual soil improvement in a silty clay layer[J]. Scientific & Technical Information of Gansu, 2019, 48(9): 51-54,65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6375.2019.09.015 [16] 王明胜,路军富,罗奥雷. 粉质黏土地层隧道盾构施工渣土改良剂试验[J]. 铁道工程学报,2020,37(5): 74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.05.014WANG Mingsheng, LU Junfu, LUO Aolei. Experiment on soil improver for shield tunnel construction in silty clay stratum[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2020, 37(5): 74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2020.05.014 [17] ZUMSTEG R, PLÖTZE M, PUZRIN A. Reduction of the clogging potential of clays: new chemical applications and novel quantification approaches[J]. Géotechnique, 2013, 63(4): 276-286. [18] 王福芝,曾聪,孔耀祖. 大直径长距离顶管润滑泥浆方案研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2016,35(2): 49-52.WANG Fuzhi, ZENG Cong, KONG Yaozu. Mud scheme for a large diameter and long distance pipe jacking project[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(2): 49-52. [19] 唐培文. 大断面矩形顶管减阻技术应用研究:以苏州综合管廊矩形顶管为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(2): 198-203.TANG Peiwen. Application of drag reduction technology of large section rectangular pipe jacking: a case study of rectangular jacking of Suzhou comprehensive pipe rack[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 198-203. -





 下载:
下载: