Real-Time Enhancement Algorithm Based on DenseNet Structure for Railroad Low-Light Environment
-
摘要:
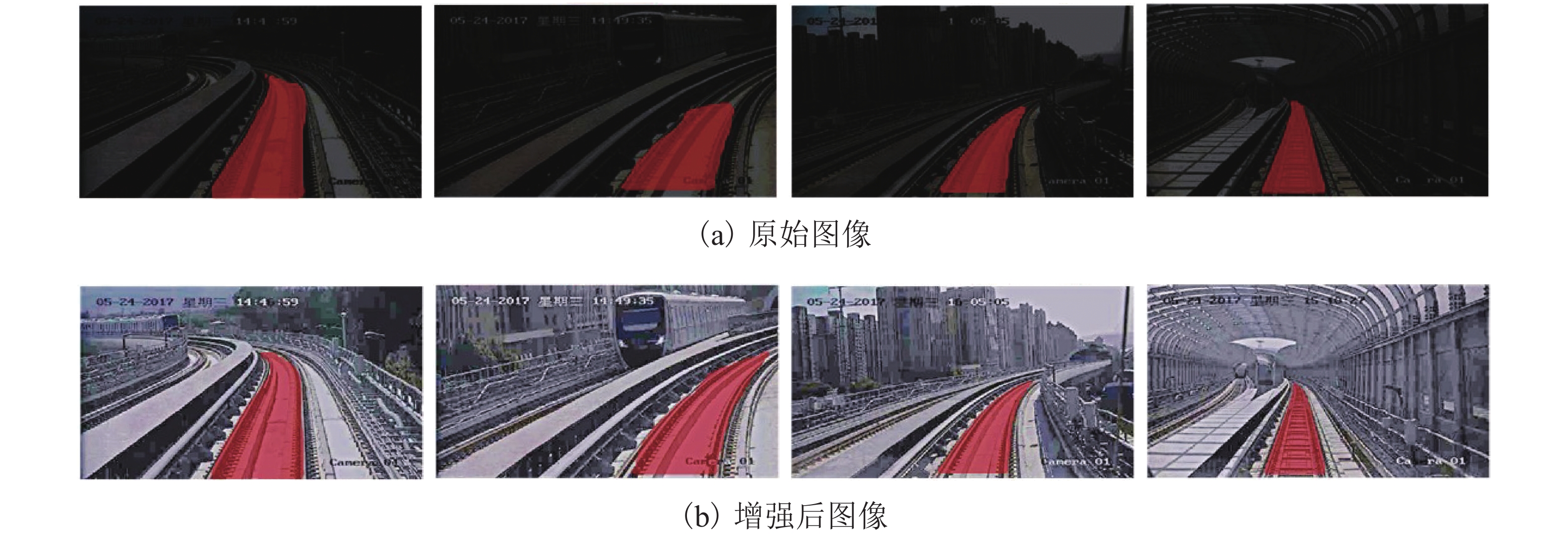
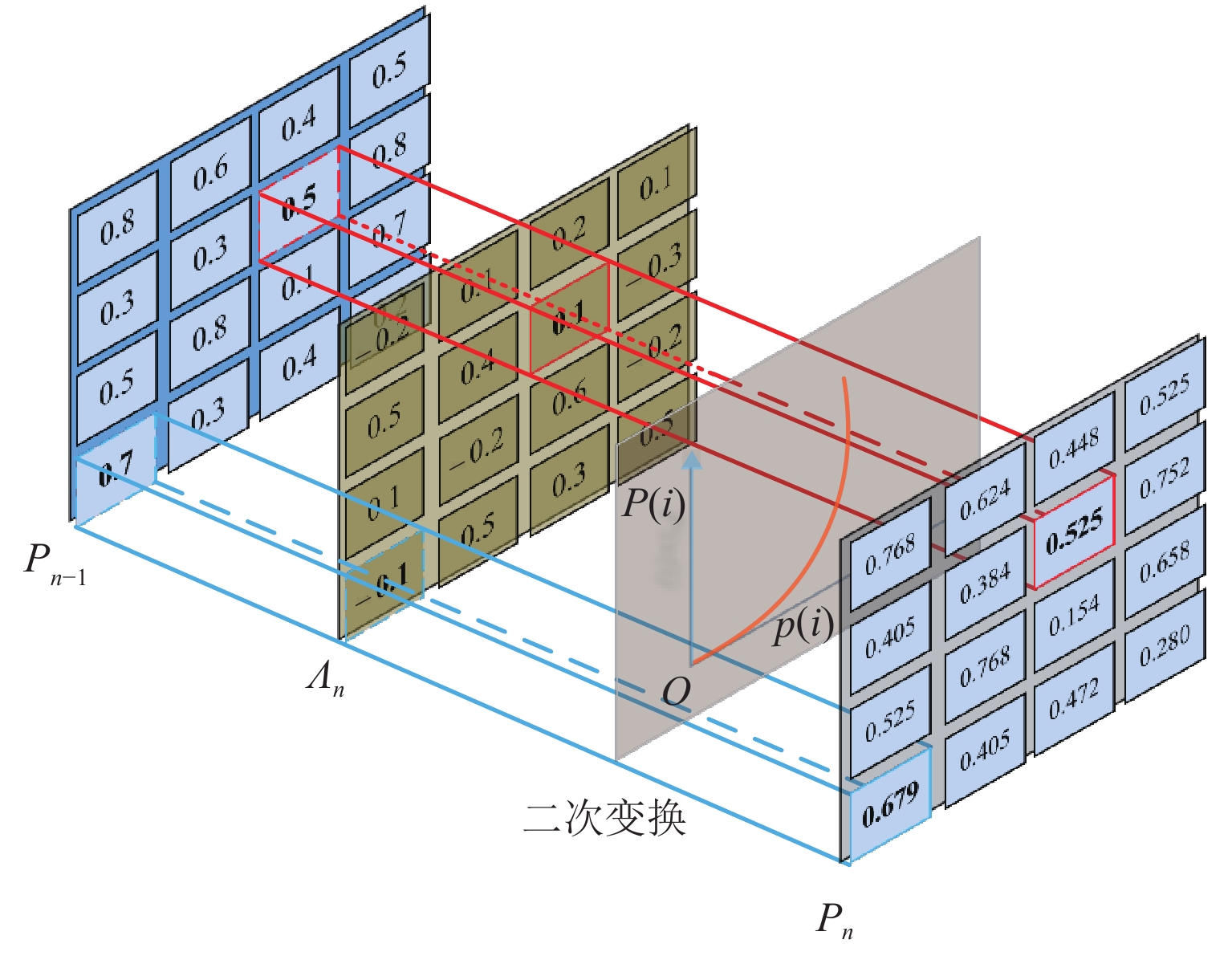
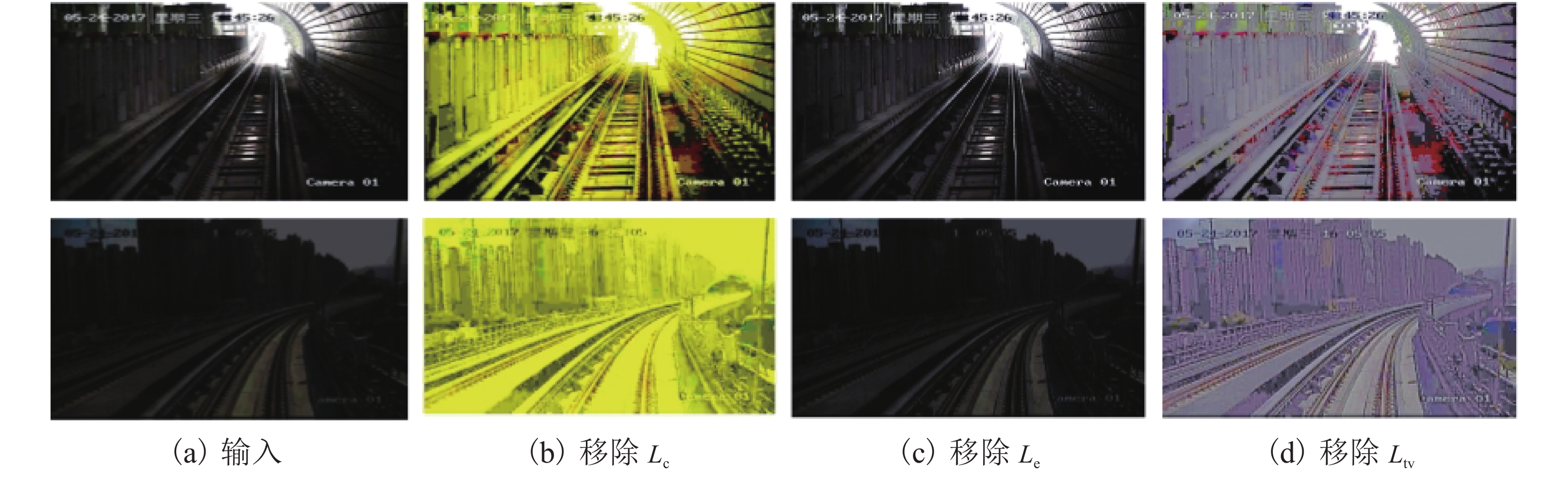
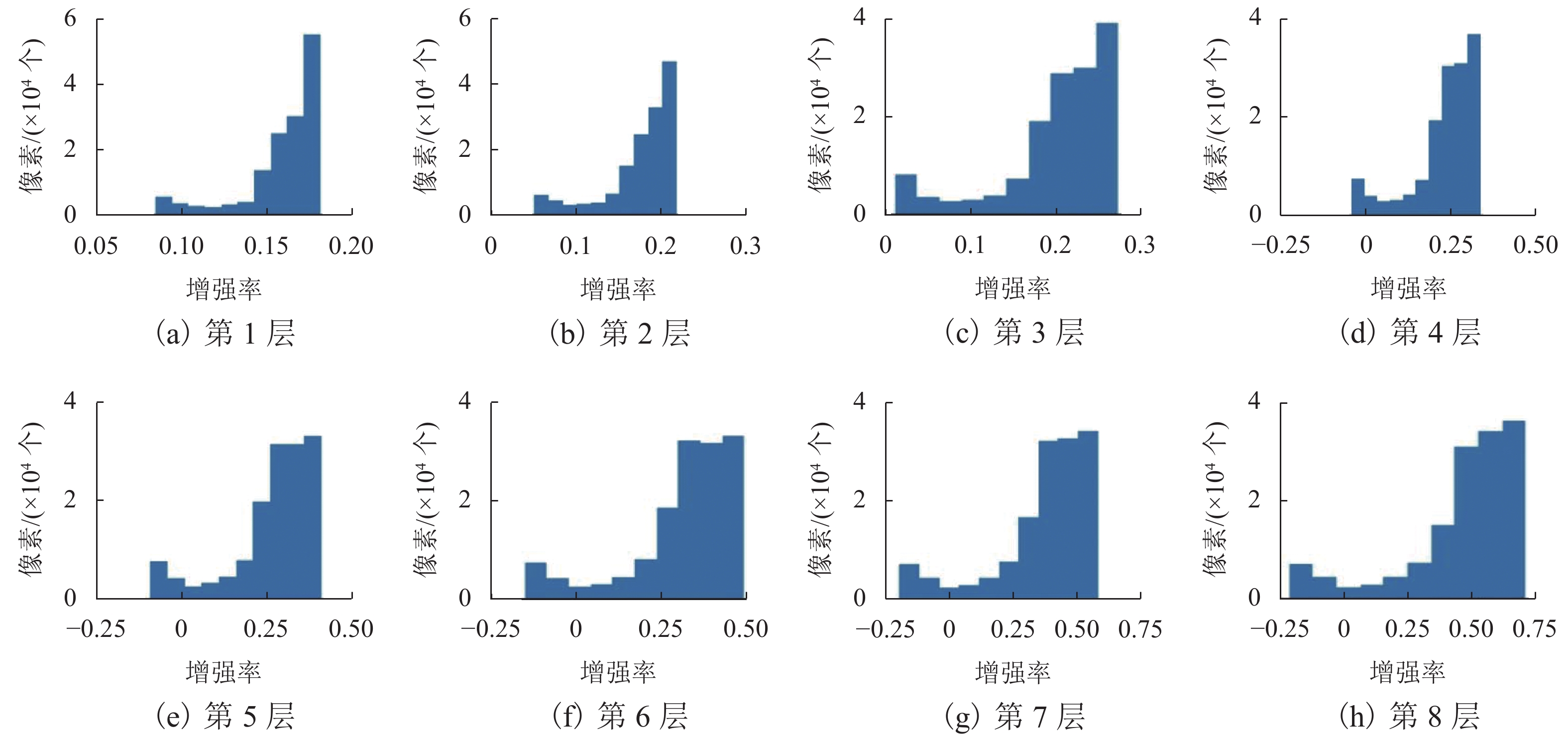
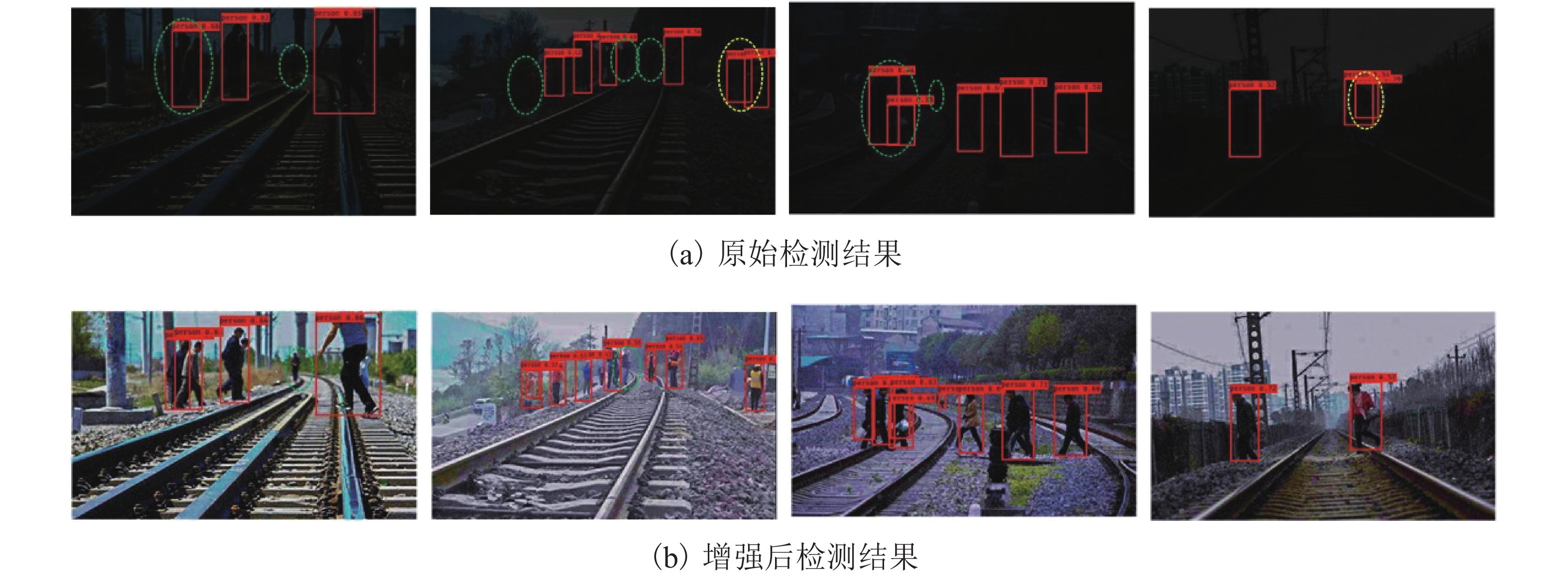
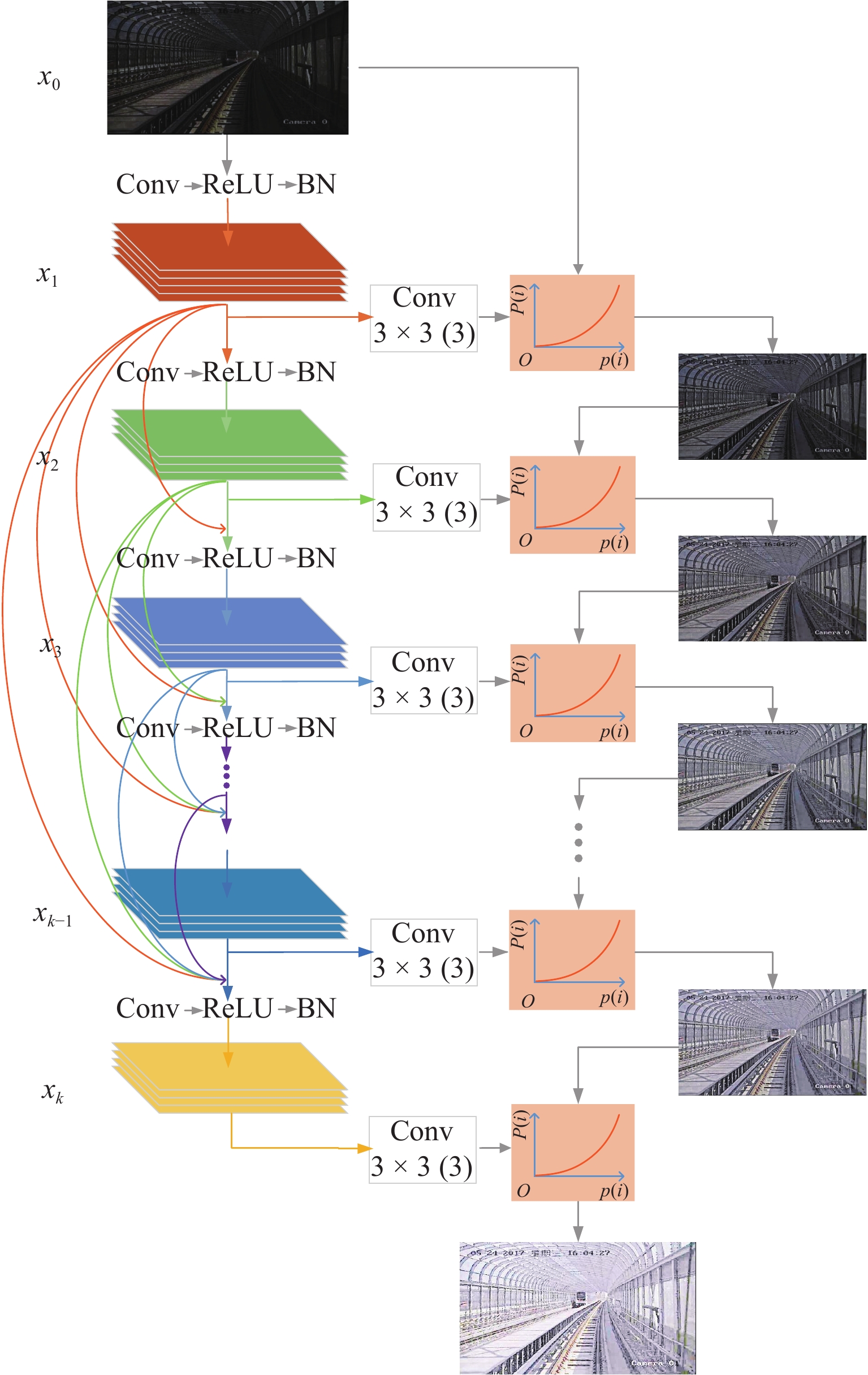
车载视觉系统是未来城市轨道交通安全运行的重要保障,列车在封闭环境或夜间运行时所处的弱光照环境会严重影响车载视觉系统的检测效果. 为此,提出了一种针对铁路封闭环境或夜间行车环境下低照度图像的实时视觉增强算法. 该算法以密集连接网络(densely connected network,DenseNet)结构为骨干网建立特征尺寸不变网络,提取图像光照、颜色等信息输出光照增强率图,并基于非线性映射函数调整每个像素的光照强度,通过分级结构将低照度输入图像的曝光率由低层到高层不断增强. 建立的深度学习网络模型采用自监督的方式训练网络参数,利用低照度图像自身特征和先验知识构建损失函数,其由曝光损失、色彩恒定损失及光照平滑度损失3个分量组成. 多种场景下的低照度增强实验结果显示:本文算法能够对输入图像曝光值进行自适应,对低曝光以及高曝光区域动态调整曝光率从而改善低照度图像的可视化效果,处理速度能够达到160帧/s,满足实时性处理的要求;通过在低照度增强前后的轨道分割及行人检测算法性能对比实验证明:所提出的算法能够大大提高暗光环境下的视觉检测效果,在RSDS (railroad segmentation dataset)数据集中轨道分割
F 值提高5%以上,在轨道场景下行人检测误检率及漏检率均有效降低.Abstract:Train on-board vision system is an important guarantee for the safety of future urban rail transit operations. The detection effect of the on-board vision system will be seriously affected by the low-light environment when the train operates in a closed environment or at night. To this end, a real-time visual enhancement algorithm is proposed for low-light images in a closed railway environment or night driving environment. The algorithm uses a densely connected network (DenseNet) structure as the backbone network to establish a feature-size invariant network. The network extracts image illumination, color, and other information and predicts the light enhancement rate images. These rate maps adjust the light intensity of each pixel on the basis of the nonlinear mapping function. The network enhances the exposure rate of low-light input images through a hierarchical structure from low level to high level. The developed deep learning network model uses self-supervised learning to train the network parameters. The chracteristics of the low-light image and the prior knowledge are utilized to construct the loss function, which consist of three components: exposure loss, colour constancy loss and illumination smoothness loss. The experimental results of low-light enhancement in multiple scenes show that the algorithm can adapt to the exposure value of input images, dynamically adjust the exposure rate for low-exposure and high-exposure regions to improve the visualization of low-light images, and the processing speed can reach 160 fps to meet the requirements of real-time processing. The comparative experiments of railroad segmentation and pedestrian detection before and after low-light enhancement prove that the proposed algorithm can improve the visual detection in a low-light environment. As for testing on the RSDS (railroad segmentation dataset) datasets, the
F -value of railroad segmentation is increased by more than 5%, and the false detection rate and missed detection rate of pedestrians in multiple railroad scenes are effectively reduced. -
表 1 不同分割算法在暗光增强前、后的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different segmentation algorithms before and after low-light enhancement
-
[1] 董昱,郭碧. 基于Hu不变矩特征的铁路轨道识别检测算法[J]. 铁道学报,2018,40(10): 64-70.DONG Yu, GUO Bi. Railway track detection algorithm based on Hu invariant moment feature[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(10): 64-70. [2] WANG Y, WANG L D, HU Y H, et al. RailNet:a segmentation network for railroad detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 143772-143779. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2945633 [3] 王尧,余祖俊,朱力强,等. 基于高阶全连接条件随机场的高速铁路异物入侵检测方法[J]. 铁道学报,2019,41(5): 82-92.WANG Yao, YU Zujun, ZHU Liqiang, et al. Incursion detection method based on higher-order fully-connected conditional random fields[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2019, 41(5): 82-92. [4] 史红梅,柴华,王尧,等. 基于目标识别与跟踪的嵌入式铁路异物侵限检测算法研究[J]. 铁道学报,2015,37(7): 58-65.SHI Hongmei, CHAI Hua, WANG Yao, et al. Study on railway embedded detection algorithm for railway intrusion based on object recognition and tracking[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(7): 58-65. [5] 王银,王立德,邱霁,等. 一种基于多层RBM网络和SVM的行人检测方法研究[J]. 铁道学报,2018,40(3): 95-100.WANG Yin, WANG Lide, QIU Ji, et al. Research on pedestrian detection method based on multilayer RBM network and SVM[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(3): 95-100. [6] REZA A M. Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement[J]. Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology, 2004, 38(1): 35-44. doi: 10.1023/B:VLSI.0000028532.53893.82 [7] CHEN S D, RAMLI A R. Minimum mean brightness error bi-histogram equalization in contrast enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2003, 49(4): 1310-1319. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2003.1261234 [8] LAND E H. The retinex theory of color vision[J]. Scientific American, 1977, 237(6): 108-128. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1277-108 [9] LI M, LIU J, YANG W, et al. Joint Denoising and enhancement for low-light images via retinex model[C]//International Forum on Digitial TV and Wireless Multimedia Communications. Shanghai: [s.n.], 2017: 91-99. [10] LI M D, LIU J Y, YANG W H, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828-2841. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539 [11] LORE K G, AKINTAYO A, SARKAR S. LLNet:a deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 650-662. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.008 [12] WEI C, WANG W J, YANG W H, et al. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[DB/OL]. (2018-08-14). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1808.04560 [13] CHEN C, CHEN Q F, XU J, et al. Learning to see in the dark[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 3291-3300. [14] CAI J R, GU S H, ZHANG L. Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27: 2049-2062. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2794218 [15] JIANG Y F, GONG X Y, LIU D. EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2340-2349. [16] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 2261-2269. [17] BUCHSBAUM G. A spatial processor model for object colour perception[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1980, 310(1): 1-26. doi: 10.1016/0016-0032(80)90058-7 [18] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation [C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston: IEEE, 2015: 3431-3440. [19] NOH H, HONG S, HAN B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago: IEEE, 2015: 1520-1528. [20] HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice: IEEE, 2017: 2980-2988. -




 下载:
下载: