Study on Characteristics of Water Seepage in Chest of Leshan Giant Buddha
-
摘要:
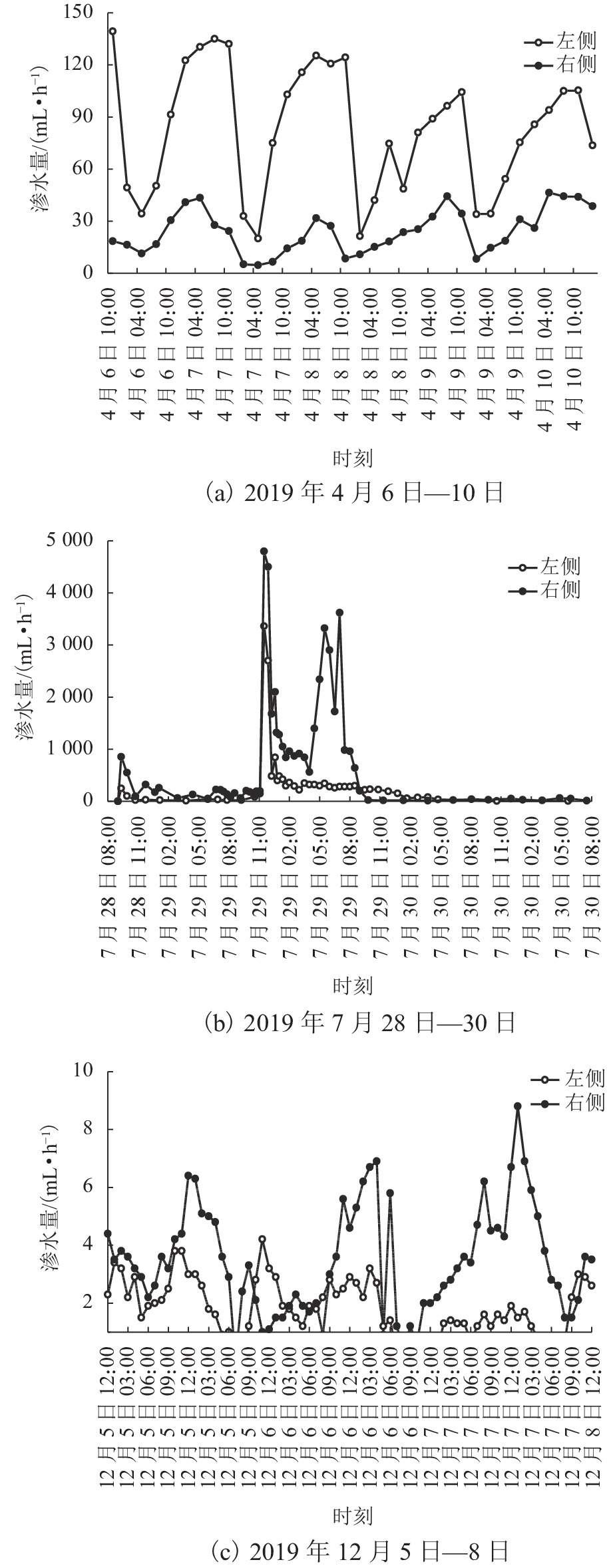
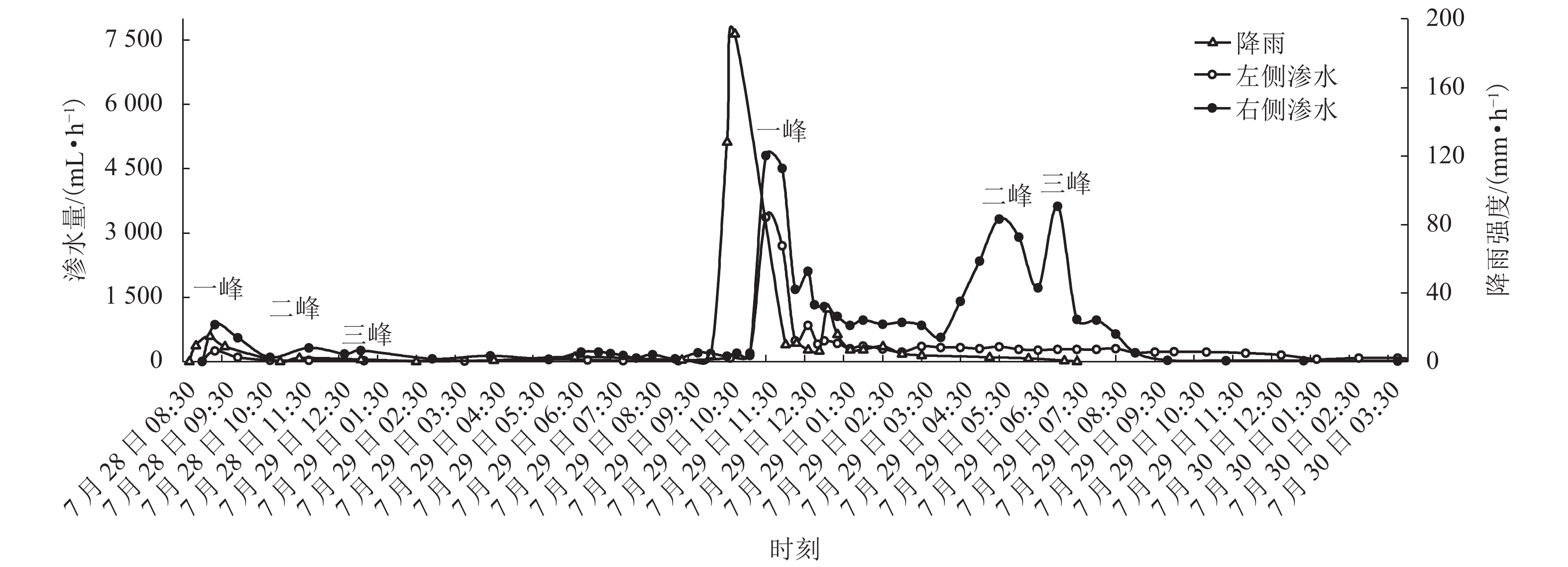
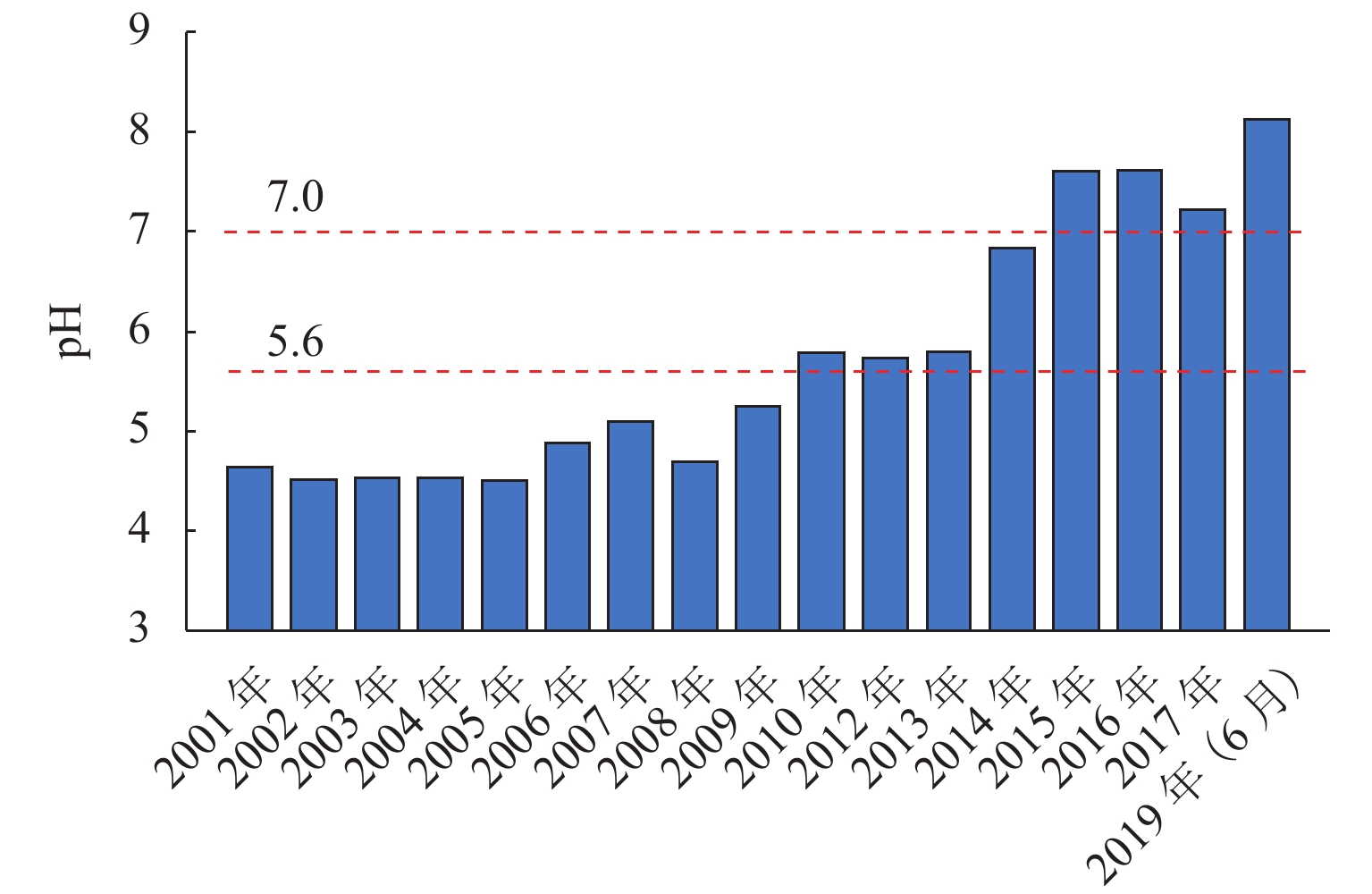
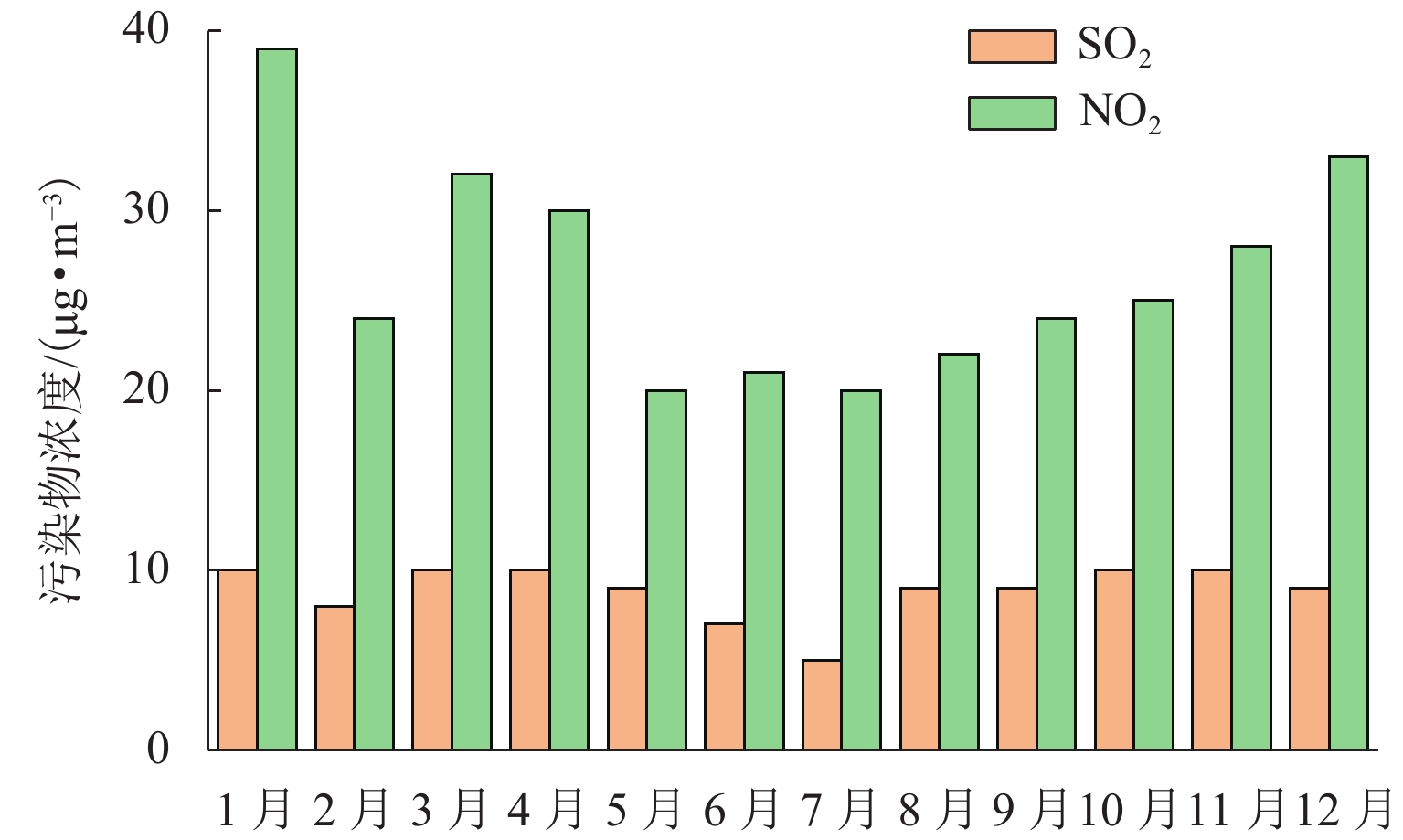
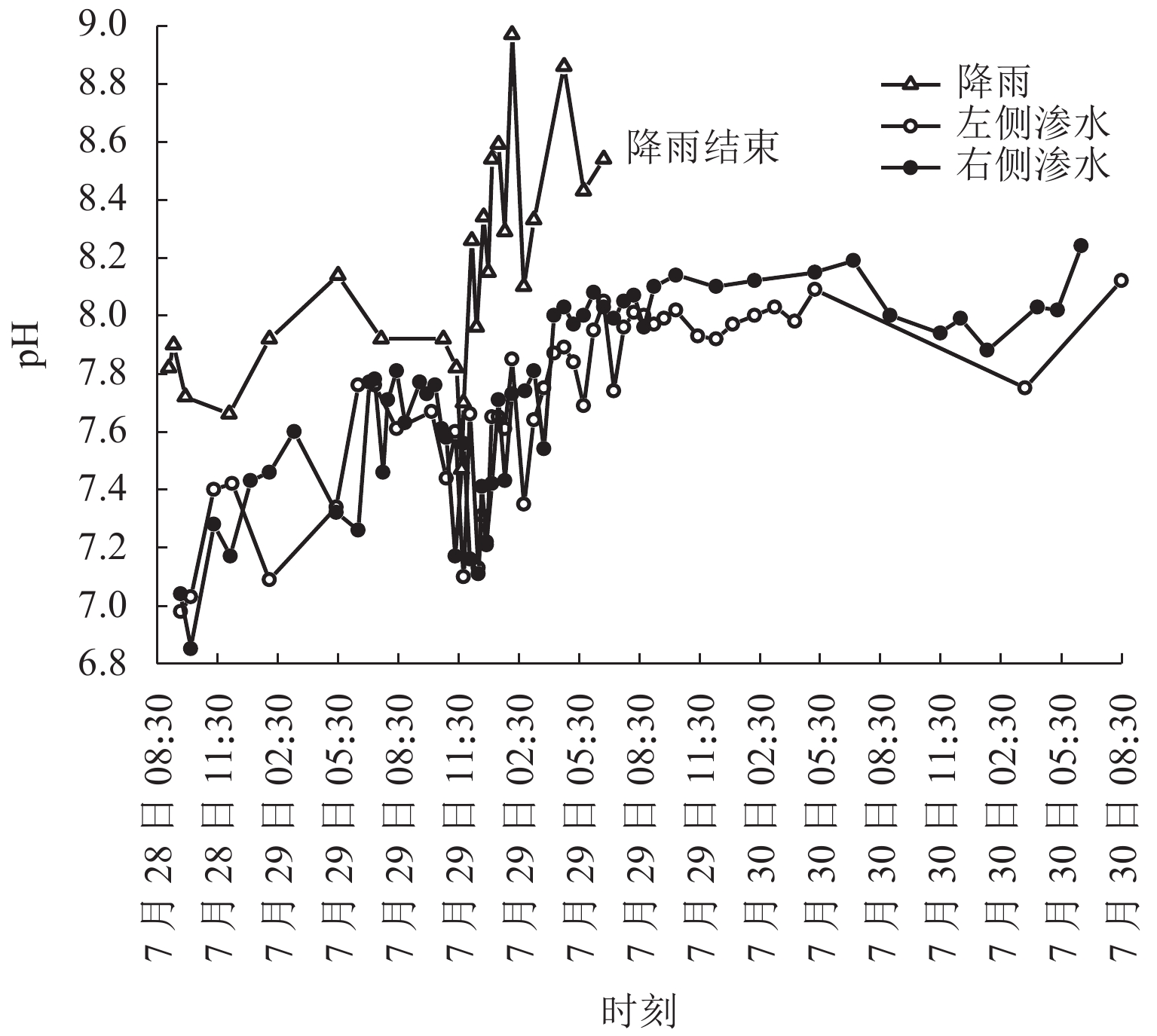
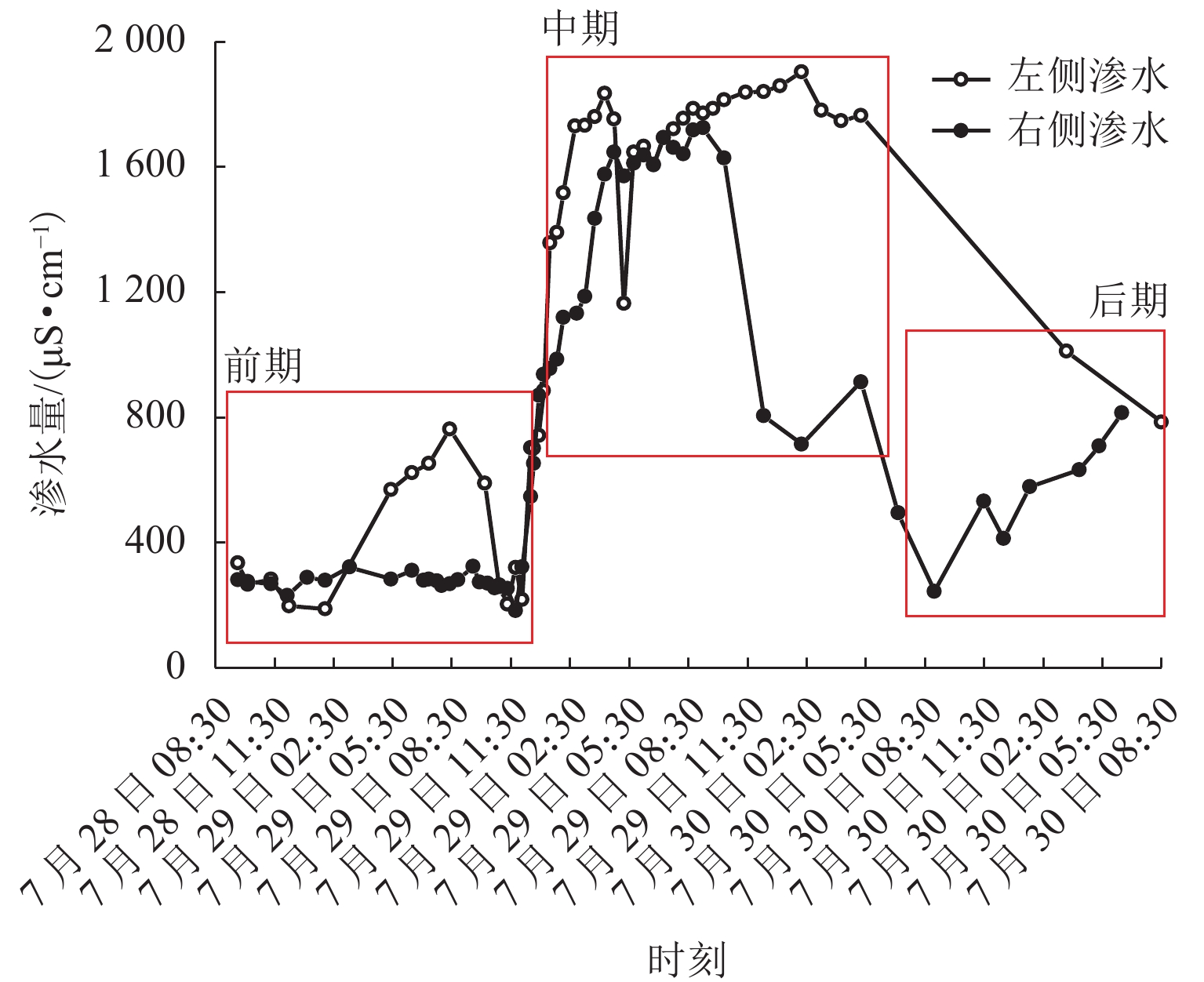
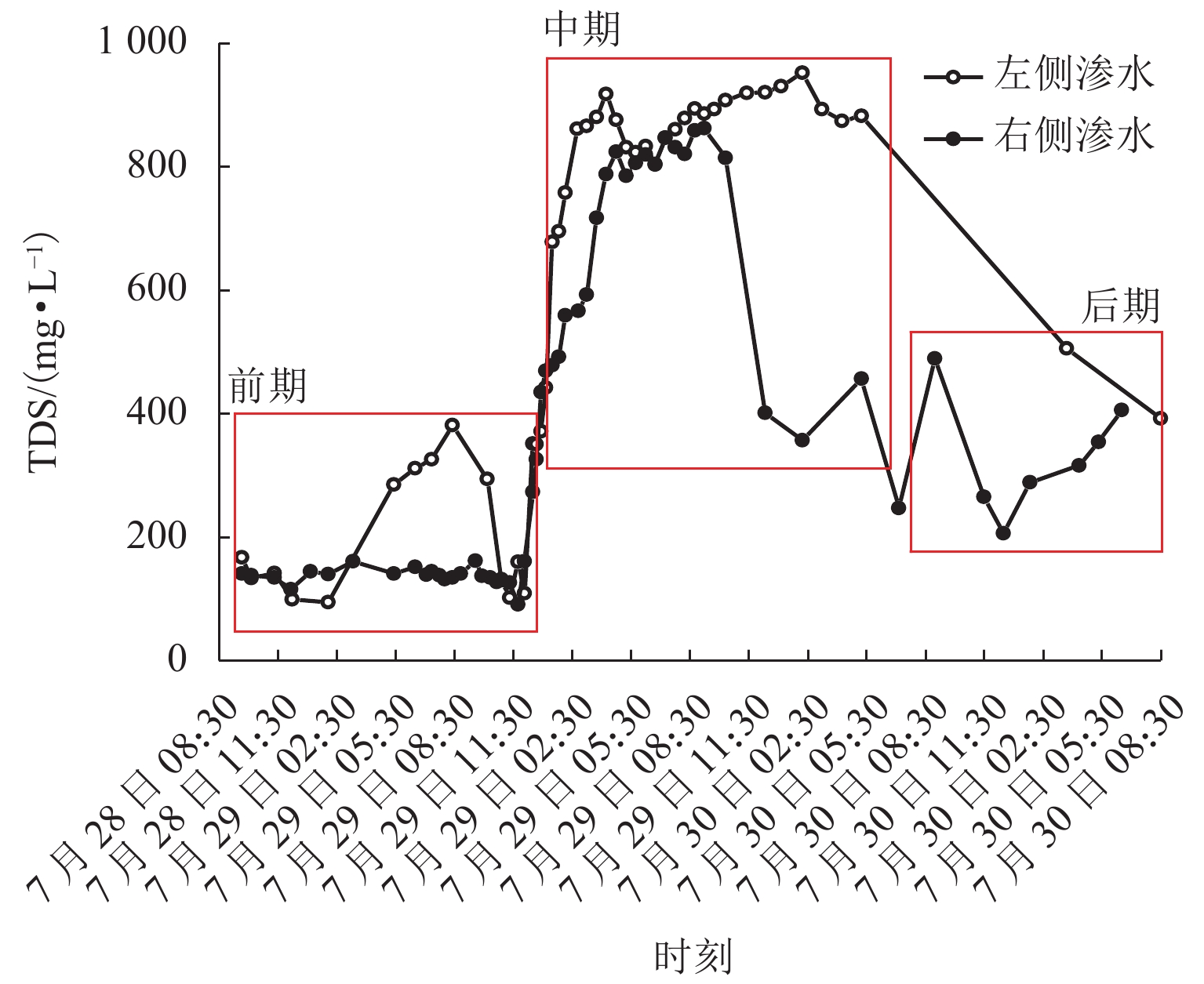
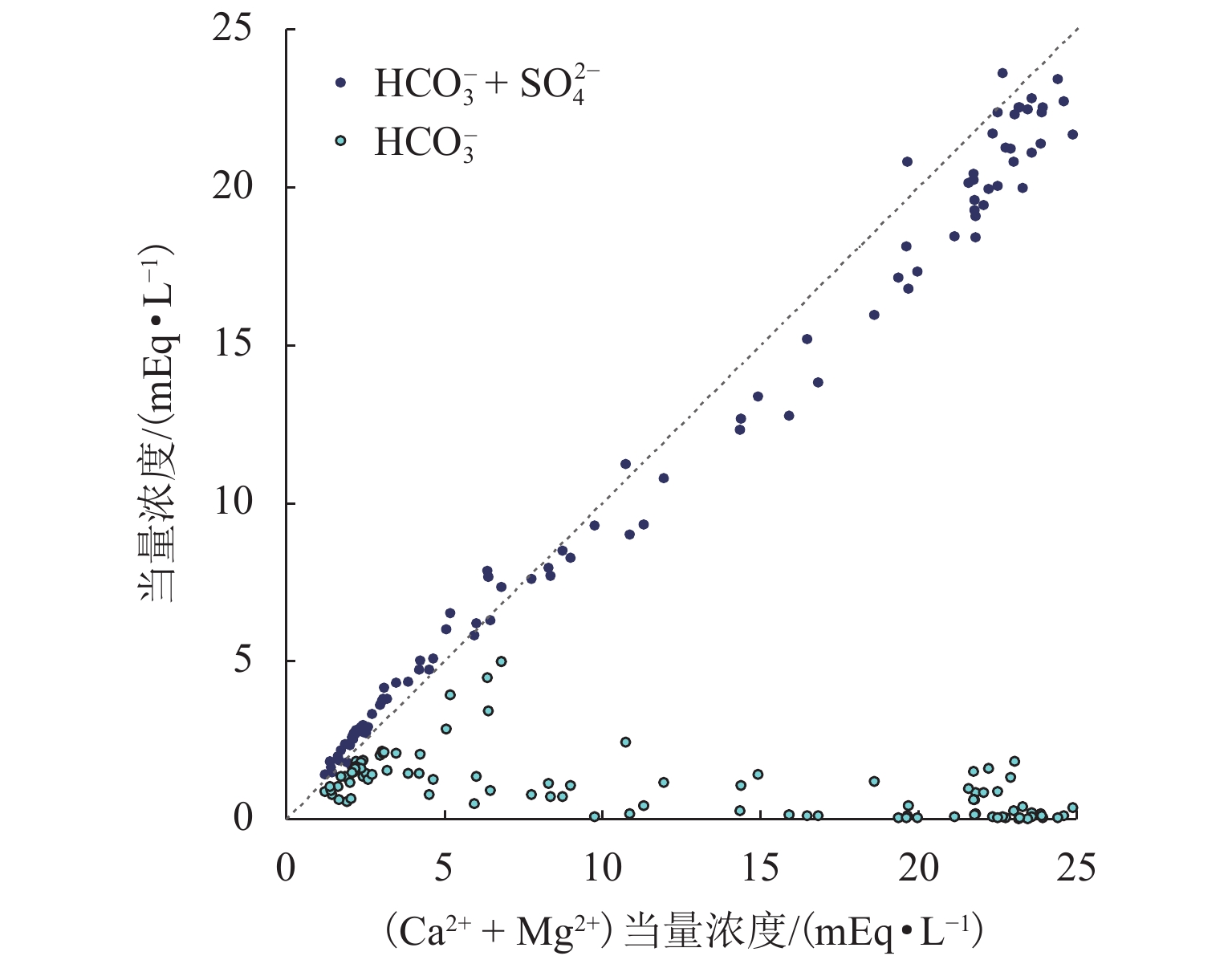
为给乐山大佛渗水病害治理及后期保护研究提供科学依据,本研究首次对乐山大佛渗水及大气降水进行定量监测采样,分析大佛渗水来源及其特征,并结合水化学性质和岩石组成对“大佛砂岩”风化机理进行了研究. 研究表明:乐山大佛胸部渗水在平水期与枯水期主要补给来源为地下水,丰水期主要补给来源为大气降水;大佛胸部渗水含有大量溶解质组分,pH平均值为7.70,2009年之后乐山市降水年平均pH>5.60且逐年增高,至2015年全年降水pH平均值大于7.00,降水已由酸性转为碱性;大佛胸部渗水水化学类型为碳酸盐类-钙组-Ⅱ型与硫酸盐类-钙组-Ⅲ型,阳离子以Ca2 + 为主,阴离子以SO42− 与HCO3− 为主;大佛胸部岩石主要成分为CaCO3和SiO2,在空气和水存在的情况下容易发生溶蚀,岩石风化对大佛渗水中离子贡献超过90%,H2CO3与H2SO4共同参与了“大佛砂岩”的风化.
Abstract:In order to provide a scientific basis for water seepage control and later protection research of Leshan Giant Buddha, this study conducts quantitative monitoring and sampling of water seepage and atmospheric precipitation of Leshan Giant Buddha for the first time, analyzes the source and characteristics of water seepage, and studies the weathering mechanism of sandstone combined with water chemical properties and rock composition.The study shows that groundwater is the main source of water supply to water seepage in the chest of Leshan Giant Buddha during the level and dry periods, and atmospheric precipitation is the main source of water supply during the wet period. Abundant solute compositions are found in water seepage samples, with the pH value being 7.70. Since 2009, the annual average pH value of precipitation in Leshan City is higher than 5.60 and increases year by year. Until 2015, the annual average pH value of precipitation is higher than 7.00, and the precipitation has changed from acidic to alkaline. The hydrochemical type of water seepage in the chest of Leshan Giant Buddha is carbonate-calcium-type Ⅱ and sulfate-calcium-type Ⅲ. The cation is mainly Ca2 + , and the anion is SO42− and HCO3−. The rock in the chest of Leshan Giant Buddha is mainly composed of CaCO3 and SiO2. Therefore, the rock is prone to being corroded after being exposed to air and water. Rock weathering contributes more than 90% of the ions in the seepage water sample, and H2CO3 and H2SO4 jointly affect the weathering of sandstone in Buddha.
-
表 1 渗水离子贡献
Table 1. Contributions to seepage ions
离子 渗水/
(mmol•L)−1大气降水/
(mmol•L)−1降水
贡献/%岩石风化
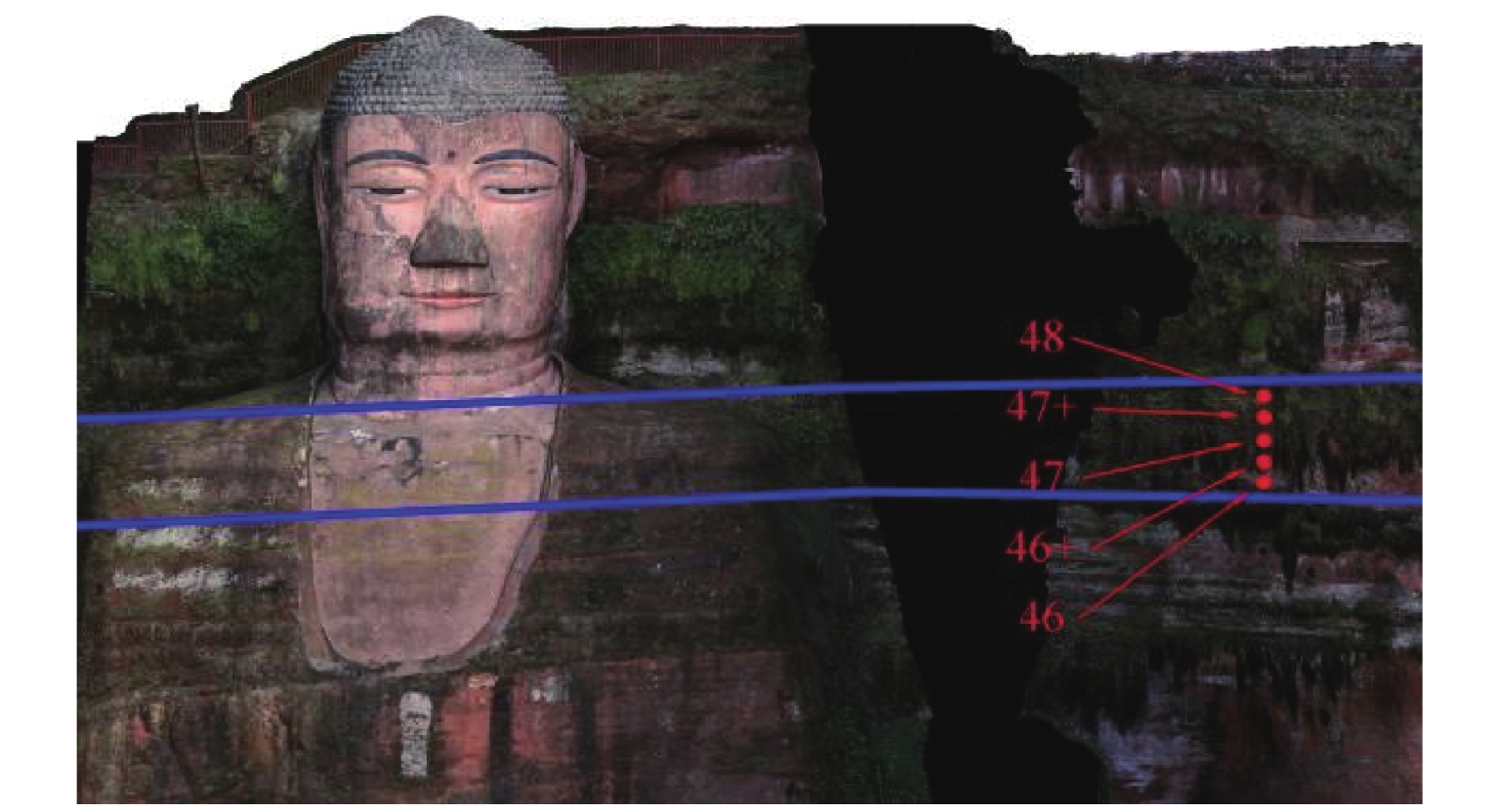
贡献/%Ca2 + 19.92 0.034 1 99 K + 0.88 0 0 100 Mg2 + 2.72 0 0 100 Na + 1.24 0.028 6 94 CI− 1.19 0.033 9 91 NO3− 1.80 0.018 14 86 HCO3− 1.07 0.031 11 89 SO42− 19.00 0.132 4 96 注:0代表离子浓度低于仪器检测限. 表 2 X射线荧光
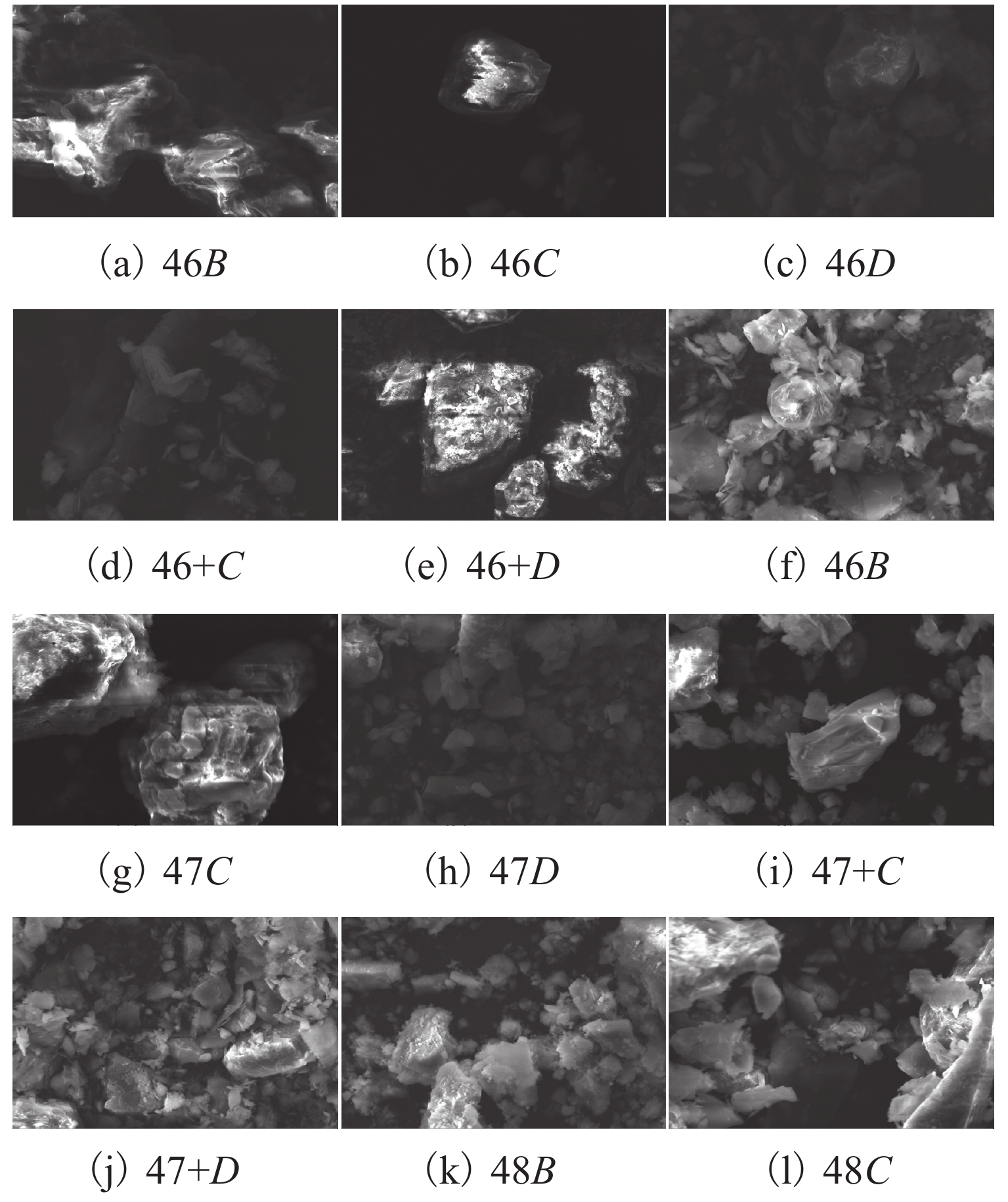
Table 2. X-Ray fluorescence
% 样品 SiO2 CaO Al2O3 MgO Na2O K2O Fe2O 46B 55.41 13.28 9.87 2.08 1.46 1.96 2.59 46C 56.32 15.25 8.85 2.75 2.65 1.45 2.32 46D 56.32 15.25 8.85 2.75 2.65 1.45 2.32 46+B 49.53 15.06 9.81 2.77 1.54 1.69 2.73 46+C 52.35 13.16 10.54 2.26 1.60 1.89 2.94 46+D 52.54 13.52 10.28 2.02 1.63 1.78 3.08 47B 55.84 10.15 12.03 3.78 1.51 2.26 3.35 47C 50.36 9.99 14.31 2.75 1.45 1.79 2.85 47D 59.49 10.39 8.85 2.98 1.53 2.08 2.98 47+B 55.08 10.65 11.61 3.14 1.51 2.06 3.53 47+C 55.09 10.65 11.61 3.14 1.51 2.06 3.59 47+D 54.36 11.45 10.67 3.08 1.55 2.11 3.72 48B 55.62 11.49 10.29 2.04 1.57 1.86 2.66 48C 55.09 10.65 11.61 3.14 1.51 2.06 3.53 48D 54.36 10.67 11.45 3.08 1.55 2.11 3.72 -
[1] 四川省文物考古研究所, 乐山大佛乌尤文物保护管理局. 治理乐山大佛的前期研究[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 2002. [2] 方云,邓长青,李宏松. 石质文物风化病害防治的环境地质问题[J]. 现代地质,2001,15(4): 458-461.FANG Yun, DENG Changqing, LI Hongsong. Environment geological problems in prevention and cure of weathering diseases of carved stone relics[J]. Geoscience, 2001, 15(4): 458-461. [3] 黄继忠. 云冈石窟主要病害及治理[J]. 雁北师范学院学报,2003,19(5): 57-59.HUANG Jizhong. Main damages and preservation of the Yungang grottoes[J]. Journal of Yanbei Normal University, 2003, 19(5): 57-59. [4] 严绍军,方云,孙兵,等. 渗水对龙门石窟的影响及治理分析[J]. 现代地质,2005,19(3): 475-478.YAN Shaojun, FANG Yun, SUN Bing, et al. Influence of water permeation and analysis of treatment for the Longmen grottoes[J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(3): 475-478. [5] 俞剑清,张秉坚,邵浦建,等. 浙江省石窟寺及石刻类文物健康评估调研综述[J]. 石材,2018(3): 29-36.YU Jianqing, ZHANG Bingjian, SHAO Pujian, et al. Survey on health assessment of cave temples and stone carvings in Zhejiang Province[J]. Stone, 2018(3): 29-36. [6] 秦中,张捷,彭学艺,等. 四川乐山大佛风化的初步探讨[J]. 地理研究,2005,24(6): 928-934.QIN Zhong, ZHANG Jie, PENG Xueyi, et al. A study on weathering processes of Leshan Grand Buddha, Sichuan, China[J]. Geographical Research, 2005, 24(6): 928-934. [7] 舒代宁, 邓雪锋. 世界遗产乐山大佛景区酸沉降及防治对策研究[C]//2007中国可持续发展论坛暨中国可持续发展学术年会论文集(3). 北京: [出版者不详], 2007: 1-5. [8] 程远琼, 欧山. 乐山大佛景区酸雨污染趋势及成因分析[C]//2015年中国环境科学学会学术年会论文集. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2015: 1159-1162. [9] LIU X Y, XIAO H W, XIAO H Y, et al. Stable isotope analyses of precipitation nitrogen sources in Guiyang, southwestern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 230: 486-494. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.010 [10] CALVO-FERNÁNDEZ J, MARCOS E, CALVO L. Bulk deposition of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen in mountainous heathland ecosystems in North-Western Spain[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 183: 237-244. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.09.006 [11] SONG X F, LIU X C, XIA J, et al. A study of interaction between surface water and groundwater using environmental isotope in Huaisha River Basin[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2006, 49(12): 1299-1310. doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-1299-z [12] MOON S, HUH Y, QIN J H, et al. Chemical weathering in the Hong (Red) River Basin: rates of silicate weathering and their controlling factors[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(6): 1411-1430. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.12.004 [13] 高蔺云,黄晓荣,奚圆圆,等. 基于云模型的四川盆地气候变化时空分布特征分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(1): 1-7.GAO Linyun, HUANG Xiaorong, XI Yuanyuan, et al. Analysis on characteristics of temporal-spatial climate distribution in Sichuan basin based on cloud model[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 38(1): 1-7. [14] FULLER B M, SKLAR L S, COMPSON Z G, et al. Ecogeomorphic feedbacks in regrowth of travertine step-pool morphology after dam decommissioning, Fossil Creek, Arizona[J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 126(3/4): 314-332. [15] ZHANG Q Q, JIN Z D, ZHANG F, et al. Seasonal variation in river water chemistry of the middle reaches of the Yellow River and its controlling factors[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 156: 101-113. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.05.008 -





 下载:
下载: