Interfacial Stress and Failure Criteria of Steel Structure Coatings Under Wind-Sand Erosion
-
摘要:
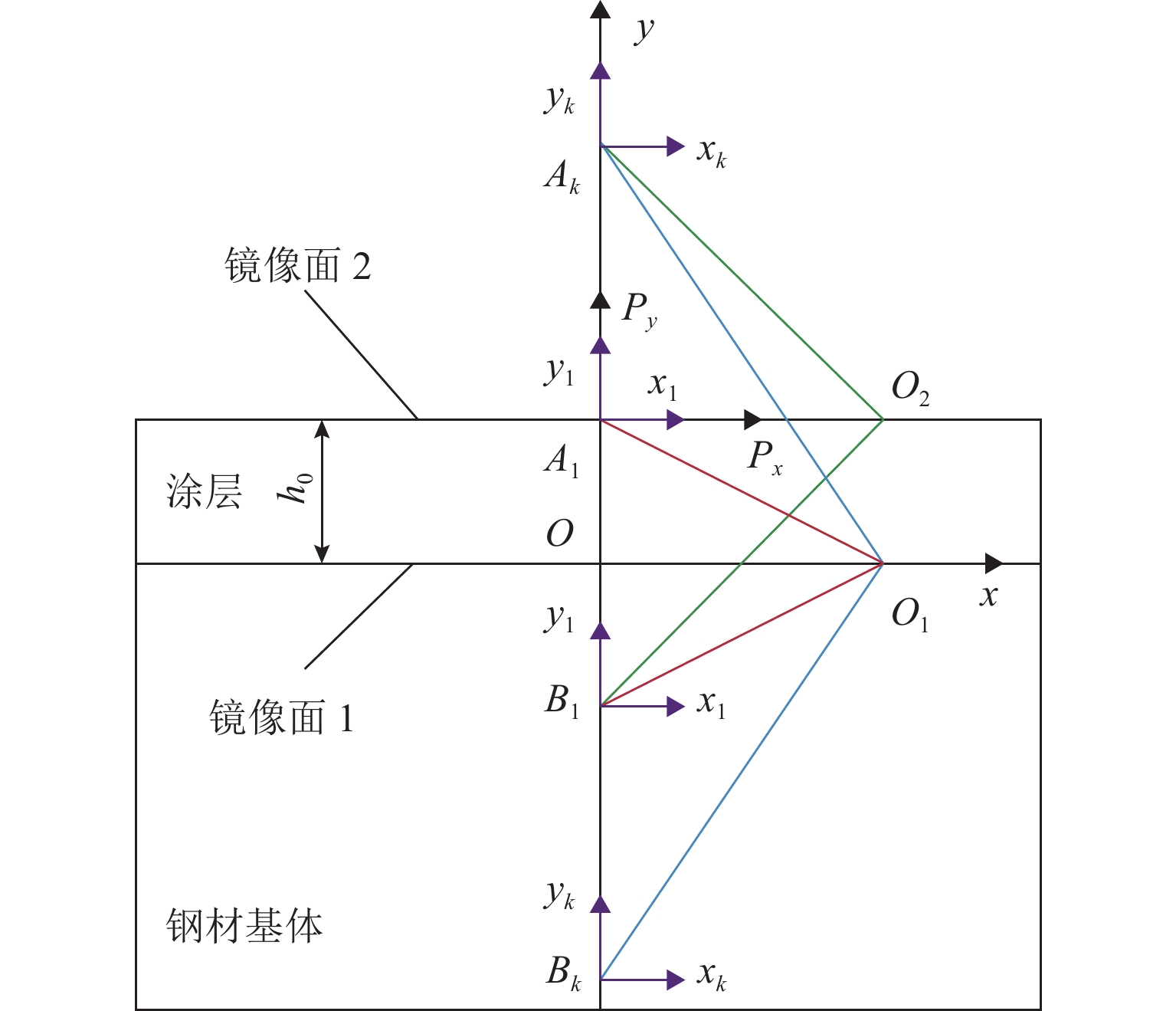
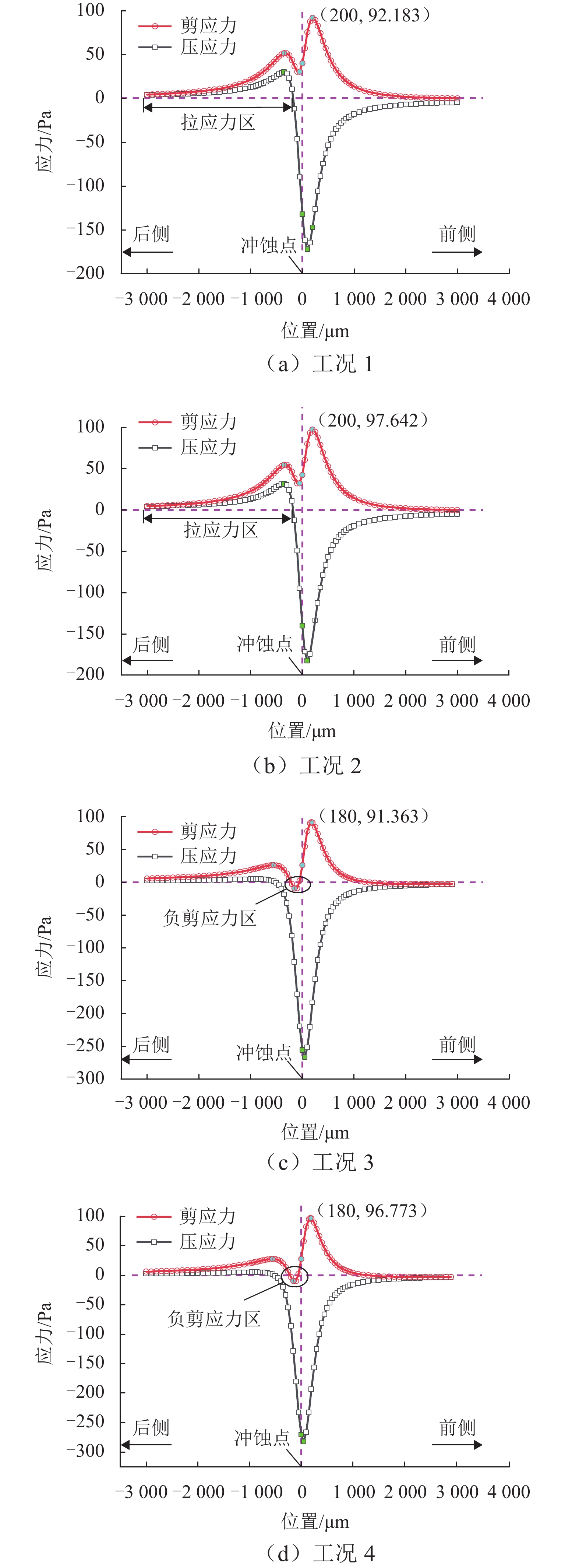
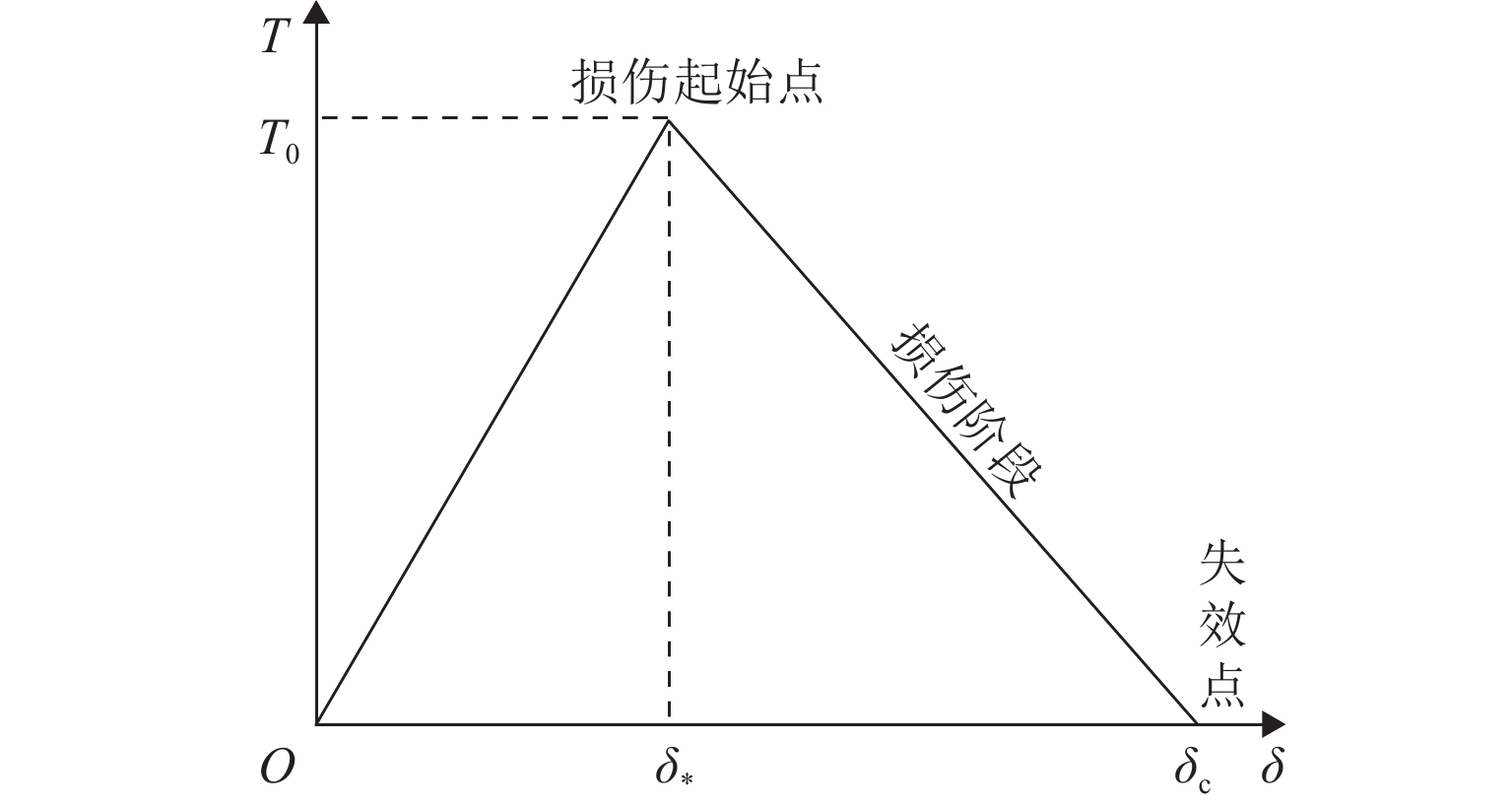
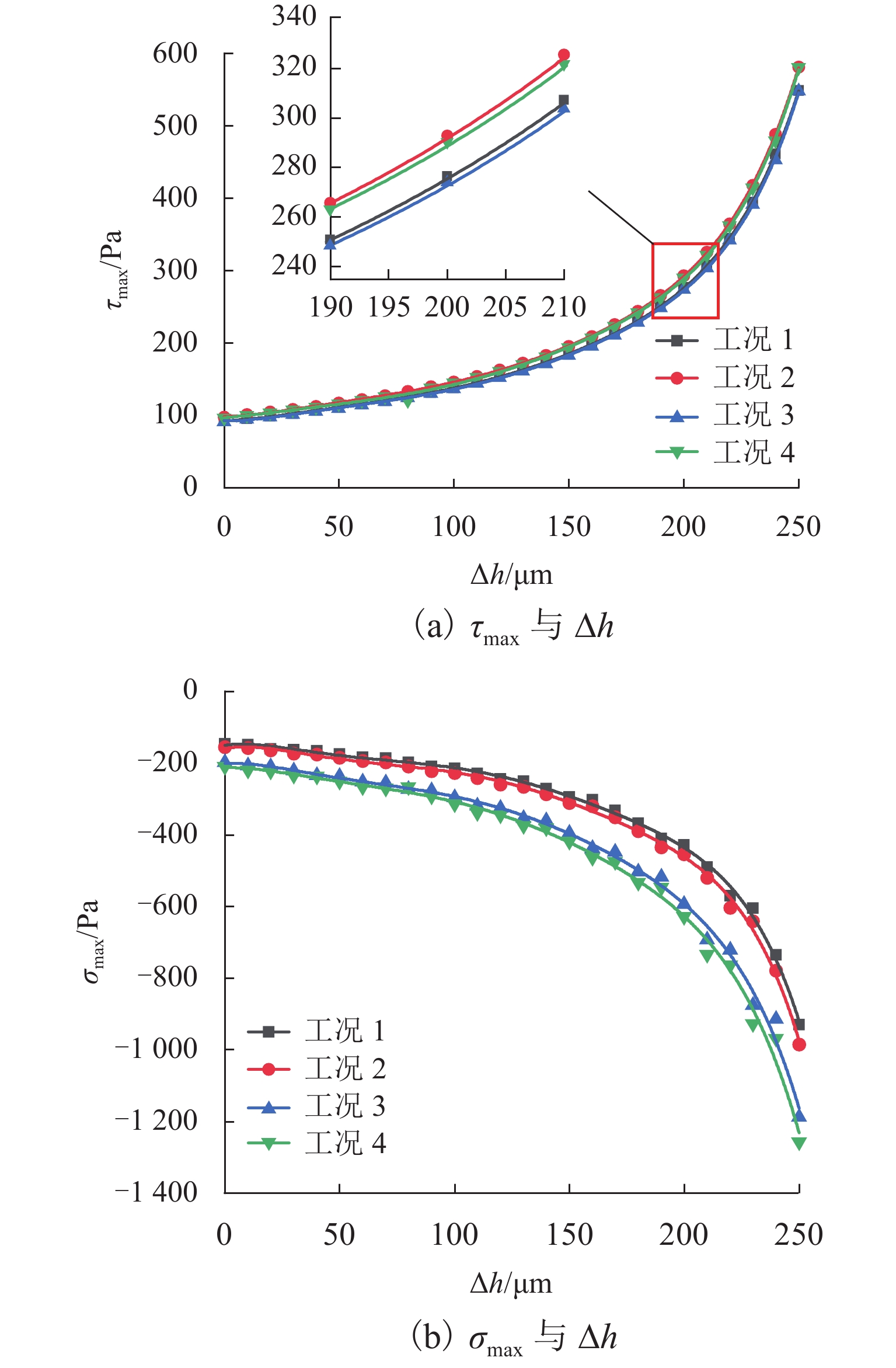
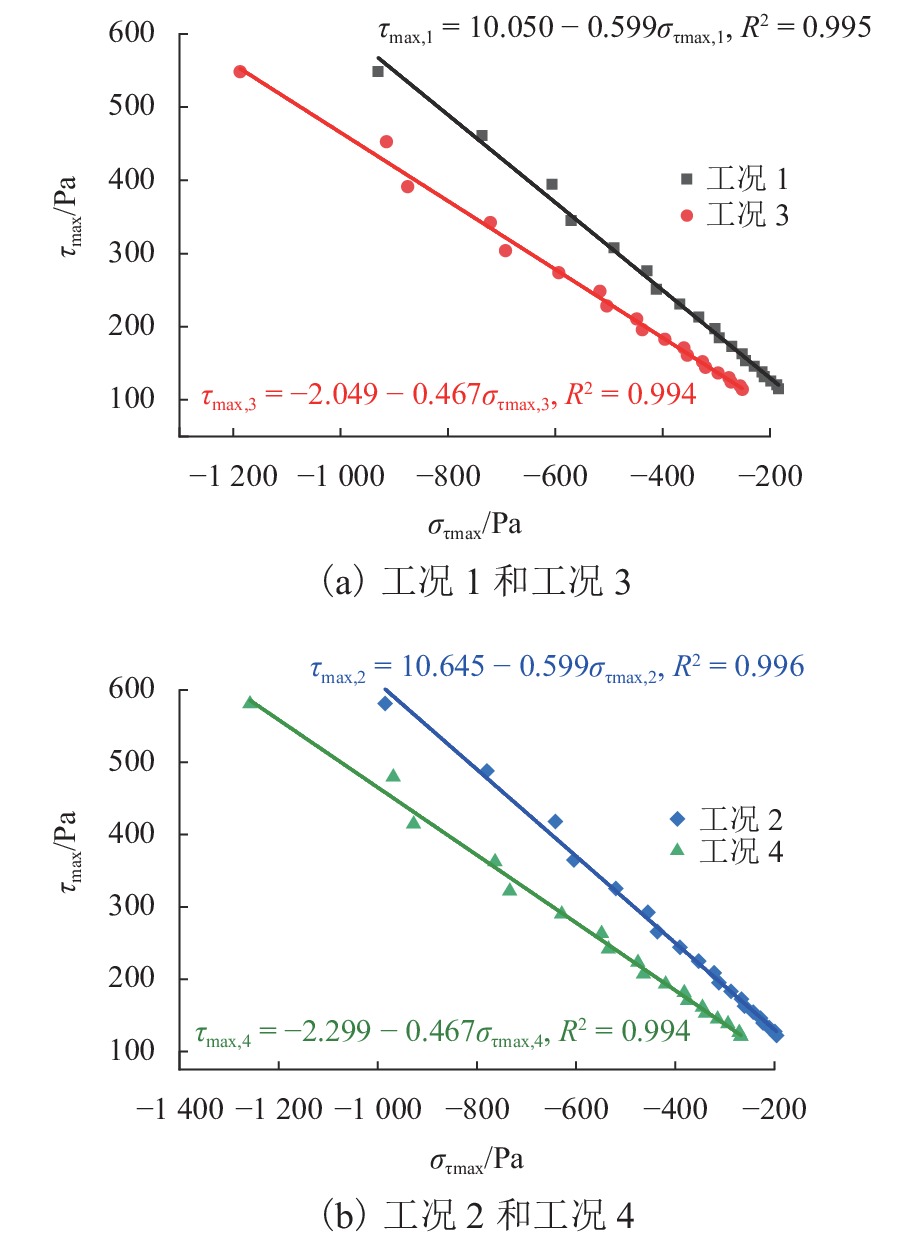
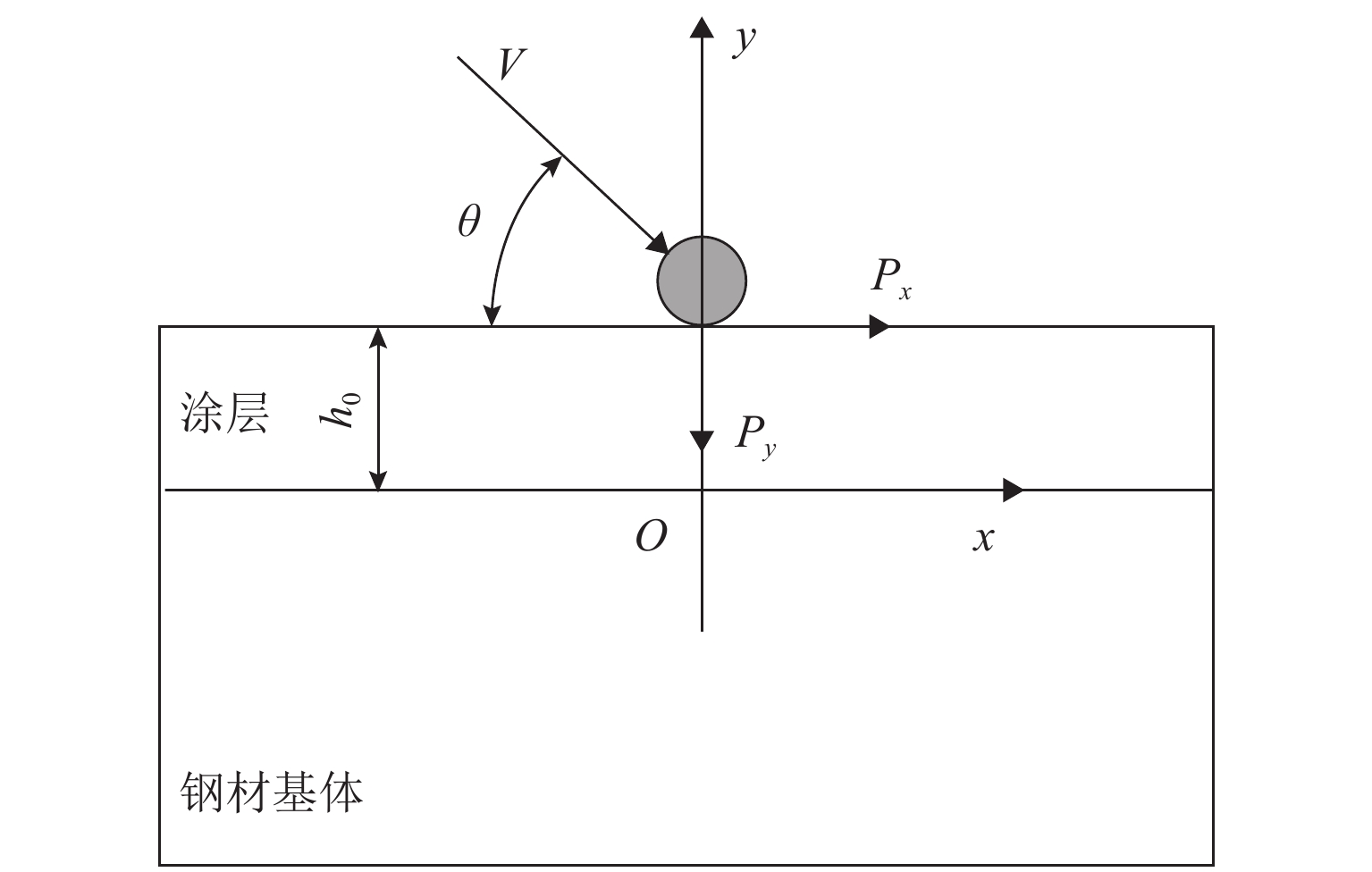
为表征和评价风沙冲蚀作用下钢结构涂层界面结合强度,以西北地区风沙流特征为背景,利用接触力学和界面力学理论建立了在风沙冲蚀作用下钢结构涂层的界面应力表达式. 结合断裂力学理论和有限元分析方法,确定了钢结构涂层的界面起裂位置. 在起裂位置处建立了考虑压应力影响的界面应力破坏准则.研究结果表明:当冲蚀角度为30° 和60° 时,最大界面剪应力分别位于冲蚀点前侧200 mm和180 mm处,最大界面压应力分别位于冲蚀点前侧100 mm和50 mm处,涂层界面的起裂位置为最大界面剪应力处. 风沙冲蚀作用下涂层的界面应力破坏准则与莫尔-库伦强度准则相似,斜率的大小取决于沙粒的冲蚀角度,且当冲蚀角度为30° 和60° 时,斜率大小分别为 −0.599和 −0.467.
Abstract:In order to characterize and assess the interfacial bonding strength of steel structure coatings under wind-sand erosion, expressions for calculating interfacial stresses of the steel structure coating under wind-sand erosion are established using theories of contact mechanics and interface mechanics, based on the typical sandstorm background of Northwest China. The interface crack initiation position of steel structure coating is determined by combined use of the fracture mechanics theory and finite element analysis method. The interfacial stress failure criterion considering the influence of compressive stress is established at the crack position. The results show that when the erosion angle is 30° and 60°, the maximum interfacial shear stress is located at 200 mm and 180 mm in front of the erosion point, and the maximum interfacial compressive stress is located at 100 mm and 50 mm in front of the erosion point, respectively. The interface crack in the coating initiates at the position of the maximum interfacial shear stress. In addition, the proposed interfacial stress failure criterion for coatings under wind-sand erosion is similar to the Mohr-Coulomb strength criterion. The slope depends on the erosion angle of the sand particles. When the erosion angle is 30° and 60°, the slope magnitude is −0.599 and −0.467, respectively.
-
Key words:
- steel structure /
- coating /
- failure criterion /
- interface stress /
- wind and sand
-
表 1 西北地区沙尘暴强度划分等级
Table 1. Classification of sandstorm intensity in Northwest China
强度等级 风力
等级瞬时极大风速vmax/(m·s−1) 最小能见度
smin/m特强 ≥ 10 ≥ 25 < 50 强 ≥ 8 ≥ 20 [50, 200) 中 6~8 ≥ 17 [200, 500) 弱 4~6 ≥ 10 [500, 1000) 表 2 各材料的力学参数
Table 2. Mechanical parameters of materials
名称 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 沙粒 40.00 0.25 涂层 0.77 0.40 钢材基体 206.00 0.30 表 3 沙粒冲蚀工况
Table 3. Sand erosion cases
工况 V/(m·s−1) θ/(°) r/mm 1 20 30 0.075 2 20 30 0.100 3 20 60 0.075 4 20 60 0.100 表 4 工况2下界面应力的理论解与数值解对比
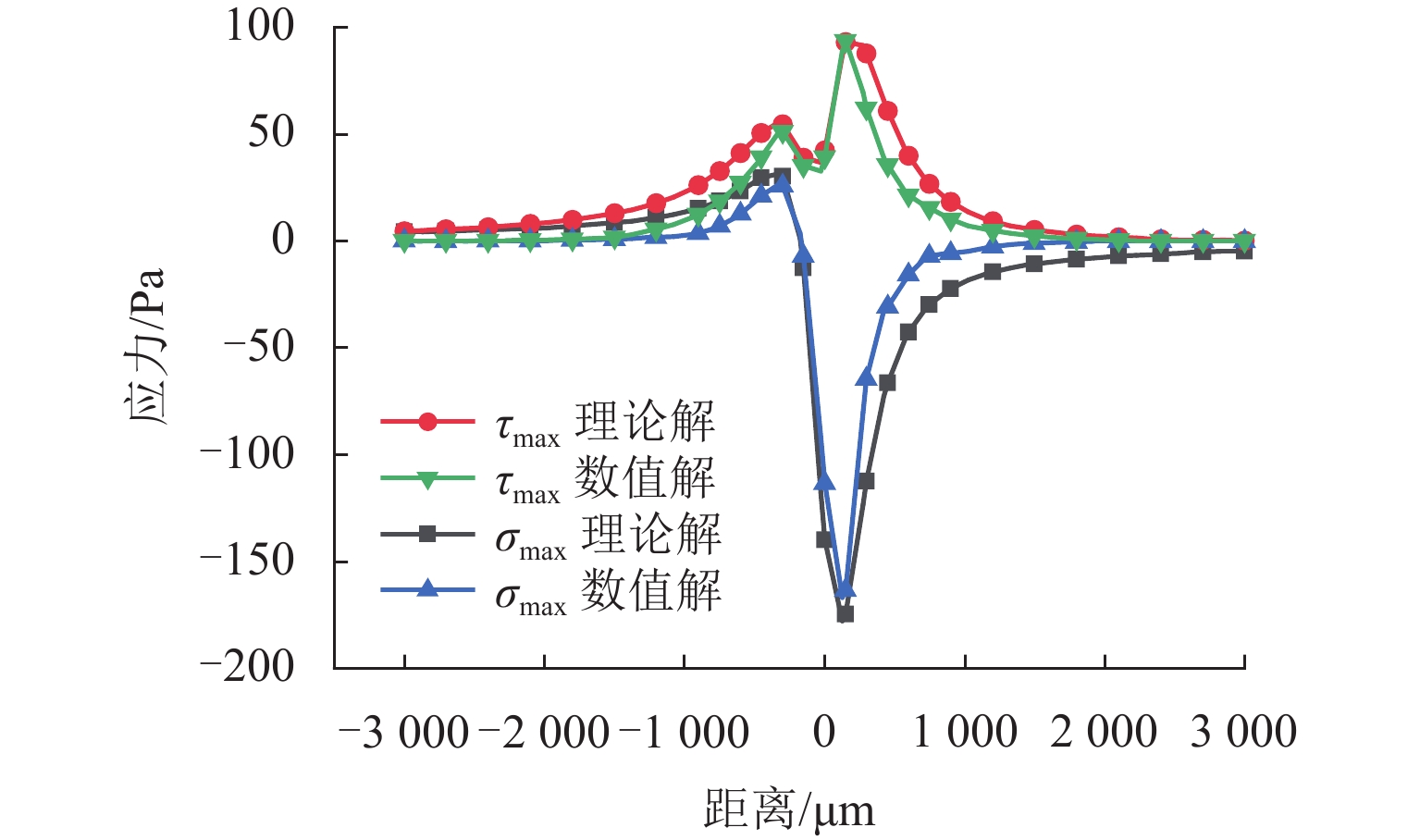
Table 4. Comparison of theoretical and numerical solutions of interfacial stress in case 2
类型 τmax/Pa σmax/Pa 理论解 93.170 −174.605 数值解 93.565 −163.360 相对误差/% 0.42 6.44 表 5 裂纹尖端Ⅱ型应力强度因子
Table 5. Type Ⅱ stress intensity factor at the crack tip
工况 2 号裂纹 1 号裂纹 3 号裂纹 1 0.321 0.646 0.545 2 0.338 0.680 0.574 3 0.186 0.552 0.440 4 0.202 0.593 0.473 表 6 工况1下界面应力点的拟合表达式参数
Table 6. Fitting expression parameters of interfacial stress point in case 1
变量 B1/(× 10−11) B2/(× 10−8) B3/(× 10−6) B4/(× 10−4) B5/(× 10−2) B6/(× 10−2) d R2 τmax 1.794 −1.061 2.452 −2.578 1.400 7.800 92.754 0.999 σmax −7.562 4.943 −12.310 10.000 −7.400 90.300 −150.778 0.997 表 7 不同界面剪应力所对应的界面压应力
Table 7. Interfacial compressive stresses corresponding to different interfacial shear stresses
Δh/μm τmax/MPa |στmax|/MPa 0 92 147 50 184 294 200 276 429 220 344 571 240 461 736 250 549 930 表 8 各工况下界面应力破坏准则表达式
Table 8. Expressions of interfacial stress failure criterion in various cases
冲蚀工况 破坏准则表达式 决定系数 R2 1 ${\tau _{\max } } = 10.050 - 0.599{\sigma _{ {\text{max} } } }$ 0.995 2 ${\tau _{\max } } = 10.645 - 0.599{\sigma _{ {\text{max} } } }$ 0.996 3 ${\tau _{\max } } = - 2.049 - 0.467{\sigma _{ {\text{max} } } }$ 0.994 4 ${\tau _{\max } } = - 2.299 - 0.467{\sigma _{ {\text{max} } } }$ 0.994 -
[1] 卞达,王永光,倪自丰,等. 涂层厚度对硬脆涂层结合强度的影响[J]. 计算力学学报,2016,33(1): 103-106.BIAN Da, WANG Yongguang, NI Zifeng, et al. Effect of the coating thickness on the bond strength for brittle coating substrate system[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2016, 33(1): 103-106. [2] BENJAMIN P, WEAVER C. Measurement of adhesion of thin films[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A, 1960, 254(1277): 163-176. [3] 杨班权,陈光南,张坤,等. 涂层/基体材料界面结合强度测量方法的现状与展望[J]. 力学进展,2007,37(1): 67-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2007.01.010YANG Banquan, CHEN Guangnan, ZHANG Kun, et al. A review on measurement methods for interfacial bonding strength between coating and substrate[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2007, 37(1): 67-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2007.01.010 [4] OLLENDORF H, SCHNEIDER D. A comparative study of adhesion test methods for hard coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 1999, 113(1/2): 86-102. [5] STEINMANN P A, TARDY Y, HINTERMANN H E. Adhesion testing by the scratch test method: the influence of intrinsic and extrinsic parameters on the critical load[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1987, 154(1/2): 333-349. [6] TANG W, XU K W, WANG P, et al. Scratch behavior of multi-layered metallic thin films on Al2O3 substrates[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 182(2/3): 143-148. [7] BEYDON R, BERNHART G, SEGUI Y. Measurement of metallic coatings adhesion to fibre reinforced plastic materials[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2000, 126(1): 39-47. doi: 10.1016/S0257-8972(00)00516-8 [8] GUO S Q, MUMM D R, KARLSSON A M, et al. Measurement of interfacial shear mechanical properties in thermal barrier coating systems by a barb pullout method[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 53(9): 1043-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.07.012 [9] PERERA D Y. On adhesion and stress in organic coatings[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 1996, 28(1): 21-23. doi: 10.1016/0300-9440(95)00585-4 [10] 许金泉. 界面力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. [11] 卓杨,许金泉. 基于分子动力学模拟结果的界面破坏准则[J]. 工程力学,2008,25(2): 46-51.ZHUO Yang, XU Jinquan. An interface fracture criterion based on simulation of molecular dynamics[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2008, 25(2): 46-51. [12] 于秦,许金泉. 薄膜涂层材料界面纯剪破坏标准试验法的开发[J]. 力学季刊,2005,26(4): 618-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0053.2005.04.017YU Qin, XU Jinquan. Development of pure shearing destructive standard test method for coating materials[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2005, 26(4): 618-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0053.2005.04.017 [13] 郝贠洪,邢永明,杨诗婷,等. 风沙环境下钢结构涂层的冲蚀磨损力学性能研究[J]. 应用力学学报,2013,30(3): 350-355, 473. doi: 10.11776/cjam.30.03.B119HAO Yunhong, XING Yongming, YANG Shiting, et al. The erosion-wear mechanical properties of the coating of steel structure subject to sandstorm[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2013, 30(3): 350-355, 473. doi: 10.11776/cjam.30.03.B119 [14] 郝贠洪,朱敏侠,冯玉江,等. 风沙冲击作用下钢结构表面涂层与基体界面应力研究[J]. 固体力学学报,2014,35(5): 485-492. doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2014.05.007HAO Yunhong, ZHU Minxia, FENG Yujiang. et al. Interface stress between steel surface coating and substrate under the sand shock[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2014, 35(5): 485-492. doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2014.05.007 [15] 徐启运,胡敬松. 我国西北地区沙尘暴天气时空分布特征[J]. 应用气象学报,1996,7(4): 479-482.XU Qiyun, HU Jingsong. Featurures of spatial and temporal distributions of the dust storms in northwest China[J]. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorological, 1996, 7(4): 479-482. [16] 赵富康,蔺鹏臻,颜维毅,等. 钢箱-混凝土组合桥梁防腐涂层的疲劳应力分析[J]. 涂料工业,2020,50(10): 7-14. doi: 10.12020/j.issn.0253-4312.2020.10.7ZHAO Fukang, LIN Pengzhen, YAN Weiyi. et al. Fatigue stress analysis of anti-corrosion coatings on steel box-concrete composite beam bridge[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2020, 50(10): 7-14. doi: 10.12020/j.issn.0253-4312.2020.10.7 [17] 胡振虎. 基于内聚力模型的复合材料胶接接头界面失效机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [18] 解德, 钱勤, 李长安. 断裂力学中的数值计算方法及工程应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. [19] 王自强, 陈少华. 高等断裂力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. [20] MUTOH Y, XU J Q MIYASHITA Y, et. al. On evalution of adhesive strength in scratch test of coating materials[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2002, 68(6): 909-915. [21] 李广信. 高等土力学[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016. -




 下载:
下载: