Inversion Method of Vortex-Induced Vibration Amplitude for Long-Span Bridges with Partially Installed Noise Barrier
-
摘要:
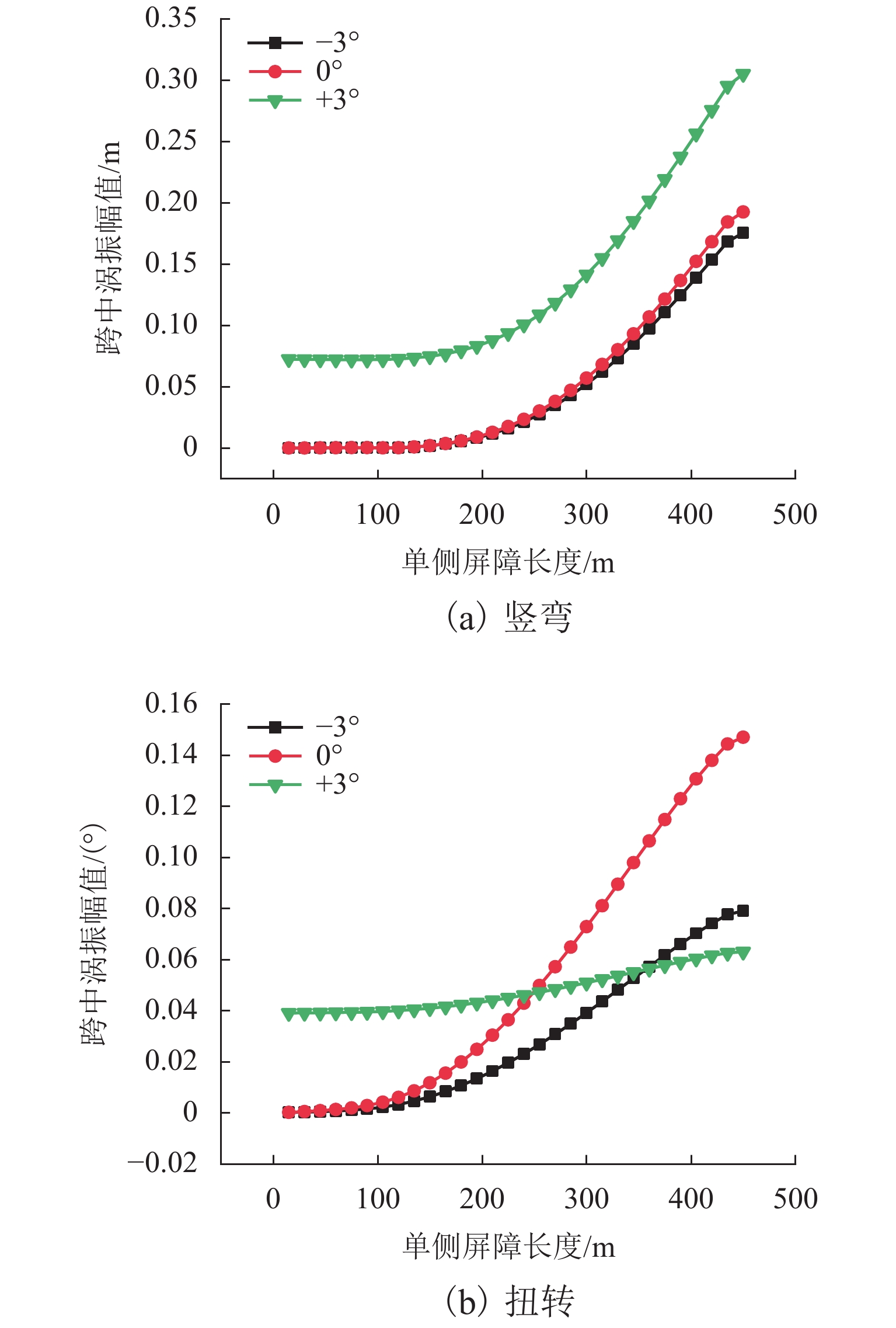
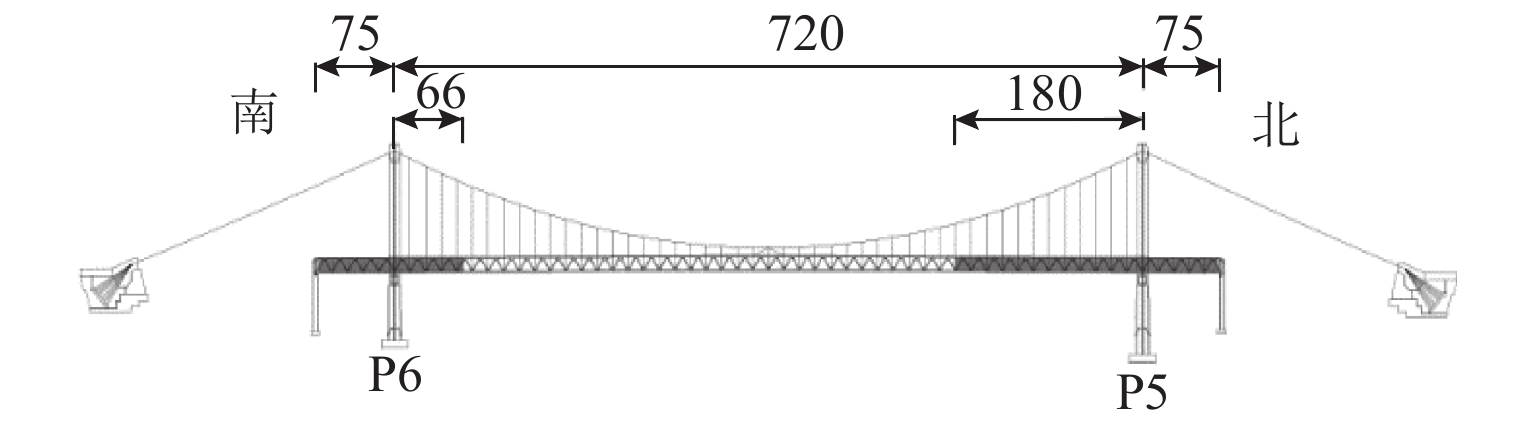
大跨桥梁的涡激共振常采用节段模型风洞试验进行测量,但节段模型试验建立在二维理论上,当桥梁由于分段式声屏障导致沿跨向存在多种气动外形时,涡振响应难以通过节段试验直接测量. 本文基于线性涡激力模型提出考虑多气动外形影响的节段-实桥涡振幅值反演方法. 首先,分别对带屏障与无屏障段截面进行节段模型风洞试验;然后,通过ANSYS谐响应分析,反演全跨布置与不布置屏障两种工况的实桥涡振幅值,获得对应的涡激荷载幅值;最后,根据声屏障实际布置位置分段施加涡激荷载,得到设置分段式声屏障桥梁的实桥涡振响应,并基于本文方法对不同声屏障布置方案进行了参数分析与讨论. 试验结果表明:全封闭声屏障会显著降低主梁抗风性能,屏障的分段布置对整体涡振影响较大;本文方法可通过节段模型试验结果直接估算多气动外形桥梁的全桥涡振响应,声屏障布置应在满足降噪条件下尽量布置于边跨,若布置长度超过桥塔位置,须尽量缩短布置长度以减小涡振响应.
Abstract:The sectional model test in wind tunnels is often used to measure the vortex-induced vibration (VIV) of long-span bridges. Since the sectional model test is based on two-dimensional theory, when the bridge has different aerodynamic configurations along the span due to the partial installation of noise barriers, it is difficult to measure the VIV response directly through the sectional model test. Based on the empirical linear VIV model, an assessment method of VIV between the sectional model and prototype bridge that considers the effects of multiple aerodynamic configurations is proposed. Firstly, the sectional model test is performed on the models with and without barriers respectively. Then, the prototype response of the noise barriers installed and not installed along the span is investigated by ANSYS harmonic analysis, and the corresponding amplitude of the vortex-induced force is obtained. Finally, according to the actual installation position of the noise barrier along the span, the vortex-induced force is imposed on the bridge and the prototype response with the partially installed noise barrier is obtained. In addition, based on the method in this paper, various noise barrier installation schemes are numerically simulated. The results indicate that fully enclosed noise barrier will significantly reduce the aerodynamic performance of the main girder and the overall VIV will be affected by partial installation of barrier to a large degree. The method in this paper can estimate the prototype response of multi-aerodynamic configurations bridges through the results of sectional model tests. The installation of the noise barrier should be arranged on the side span as far as possible under the conditions of noise reduction. If the arrangement length exceeds the position of the bridge tower, it should be shortened as much as possible to reduce the vortex-induced response.
-
表 1 涡激力反演结果
Table 1. Amplitude of vortex induced force
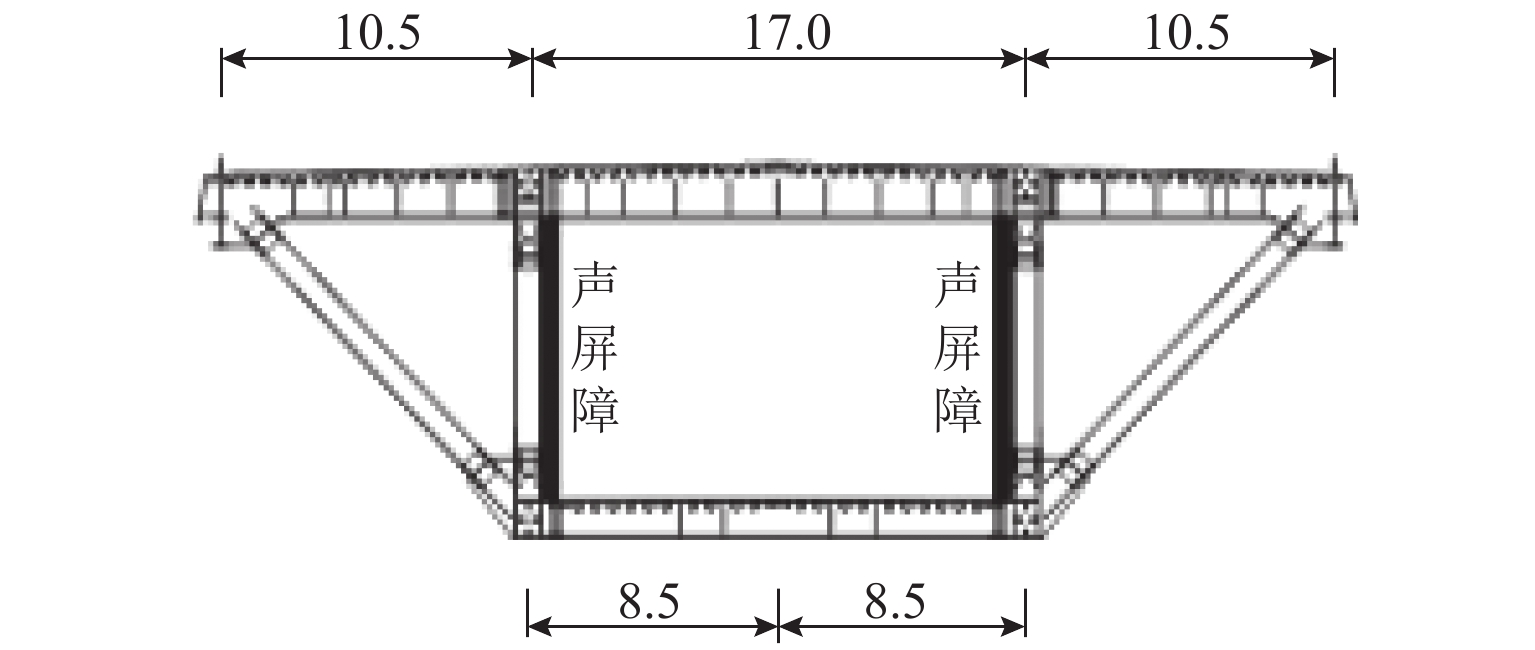
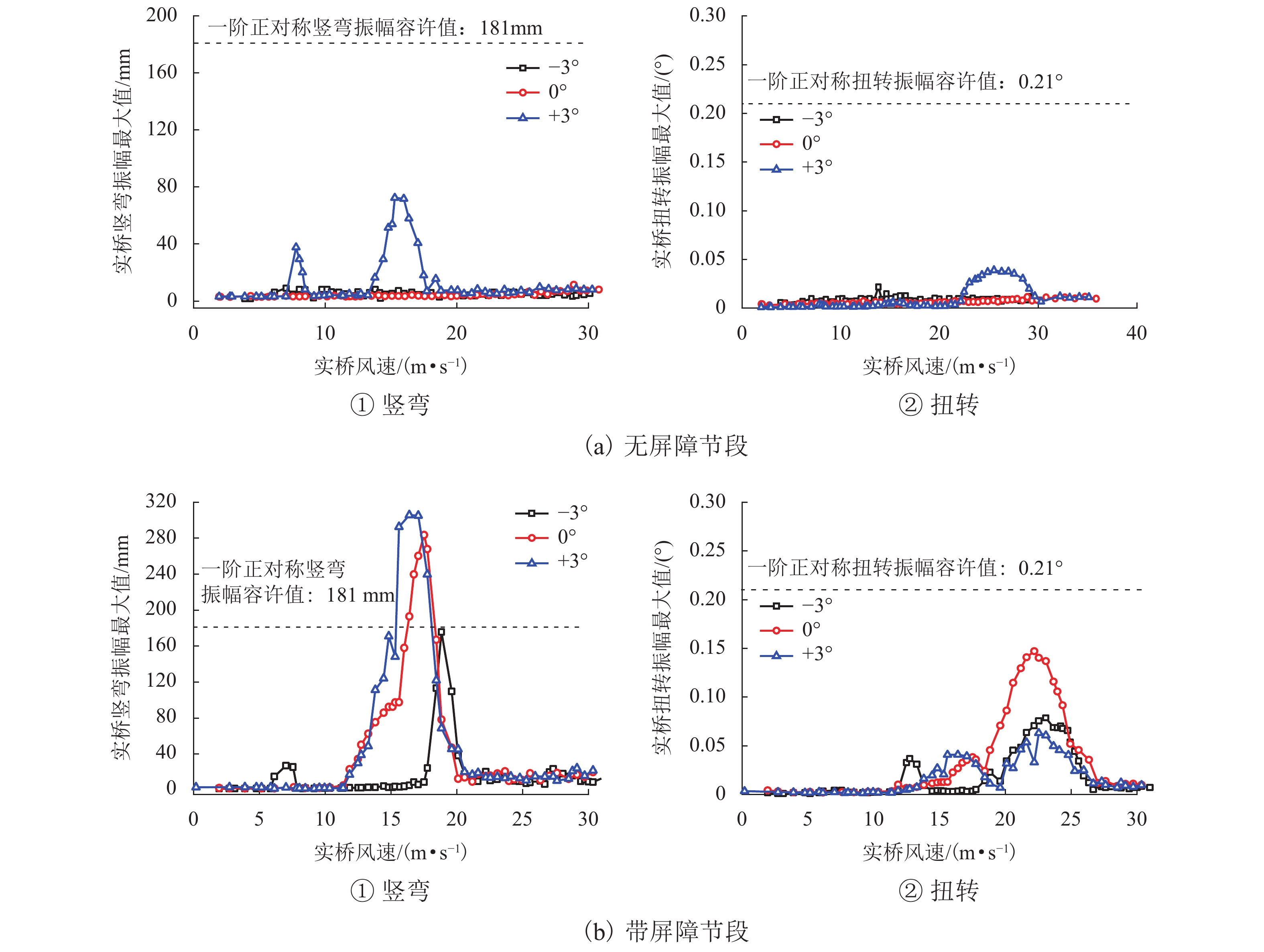
风攻角/(°) 对应风速/(m·s−1) $A_1^* $/kN $A_0^* $/kN −3 18.8 6566.2 0 0 17.5 7198.1 0 +3 15.9 11404.8 2706.8 表 2 实桥跨中涡振幅值
Table 2. Amplitude of VIV at mid-span
风攻角/
(°)全跨无屏障幅值 全跨带屏障幅值 分段布置幅值 竖弯/
mm扭转/
(°)竖弯/
mm扭转/
(°)竖弯/
mm扭转/
(°)−3 未起振 未起振 175.6 0.079 10.4 0.017 0 未起振 未起振 192.5 0.147 11.4 0.031 +3 72.4 0.039 305.0 0.063 86.1 0.044 -
[1] 苏洋. 公铁两用双层桥梁风屏障气动机理及优化研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. [2] 韩旭,彭栋,向活跃,等. 横风作用下高速铁路桥梁全封闭声屏障气动特性的风洞试验研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2019,59(7): 151-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2019.07.35HAN Xu, PENG Dong, XIANG Huoyue, et al. Research on wind tunnel tests for aerodynamic characteristics of closed noise barriers on high speed railway bridges under crosswinds[J]. Railway Engineering, 2019, 59(7): 151-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2019.07.35 [3] 孙延国,廖海黎,李明水. 基于节段模型试验的悬索桥涡振抑振措施[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2012,47(2): 218-223,264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.02.008SUN Yanguo, LIAO Haili, LI Mingshui. Mitigation measures of vortex-induced vibration of suspension bridge based on section model test[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012, 47(2): 218-223,264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2012.02.008 [4] SIMIU E S R H. Wind effects on structures[M]. New York: Wiley, 1986. [5] EHSAN F, SCANLAN R H. Vortex-induced vibrations of flexible bridges[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1990, 116(6): 1392-411. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1990)116:6(1392) [6] HARTLEN R T, CURRIE IAIN G. Lift-oscillator model of vortex-induced vibration[J]. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division, 1970, 96(5): 577-91. doi: 10.1061/JMCEA3.0001276 [7] 周帅,陈克坚,陈政清,等. 大跨桥梁涡激共振幅值估算方法的理论基础与应用[J]. 高速铁路技术,2019,10(5): 25-31. doi: 10.12098/j.issn.1674-8247.2019.05.006ZHOU Shuai, CHEN Kejian, CHEN Zhengqing, et al. Theoretical basis and practical applications of various vortex-induced vibration amplitudes estimation methods for large-span bridges[J]. High Speed Railway Technology, 2019, 10(5): 25-31. doi: 10.12098/j.issn.1674-8247.2019.05.006 [8] 张志田,陈政清. 桥梁节段与实桥涡激共振幅值的换算关系[J]. 土木工程学报,2011,44(7): 77-82. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2011.07.009ZHANG Zhitian, CHEN Zhengqing. Similarity of amplitude of sectional model to that of full bridge in the case of vortex-induced resonance[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(7): 77-82. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2011.07.009 [9] 周奇,孟晓亮,朱乐东. 基于非线性涡激力广义模型的涡振幅值换算[J]. 土木工程学报,2020,53(10): 82-88. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2020.10.008ZHOU Qi, MENG Xiaoliang, ZHU Ledong. Amplitude conversion of vortex-induced vibration based on generalized model of nonlinear vortex-induced force[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(10): 82-88. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2020.10.008 [10] SUN Y G, LI M S, LIAO H L. Nonlinear approach of vortex-induced vibration for line-like structures[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 124: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2013.10.011 [11] IRWIN P. Full aeroelastic model tests[M]. [S.l.]: Routledge, 2017: 125-35. [12] HJORTH-HANSEN E. Section model tests[M]. [S.l.]: Routledge, 2017: 95-112. [13] 秦浩,廖海黎,李明水. 变截面连续钢箱梁桥典型施工阶段涡激振动[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(5): 760-765,786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.05.003QIN Hao, LIAO Haili, LI Mingshui. Vortex-induced vibration of continuous steel box-girder bridge with variable cross-sections at typical erection stages[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(5): 760-765,786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.05.003 [14] DUAN J L, HUANG W P. CFD-based numerical analysis of a variable cross-section cylinder[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2014, 13(4): 584-588. doi: 10.1007/s11802-014-2048-0 [15] 陈政清. 工程结构的风致振动、稳定与控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. [16] 王新敏. ANSYS结构动力分析与应用 [M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2014. -




 下载:
下载: