Optimization of Shared Parking Capacity Based on Urban Traffic Network Equilibrium
-
摘要:
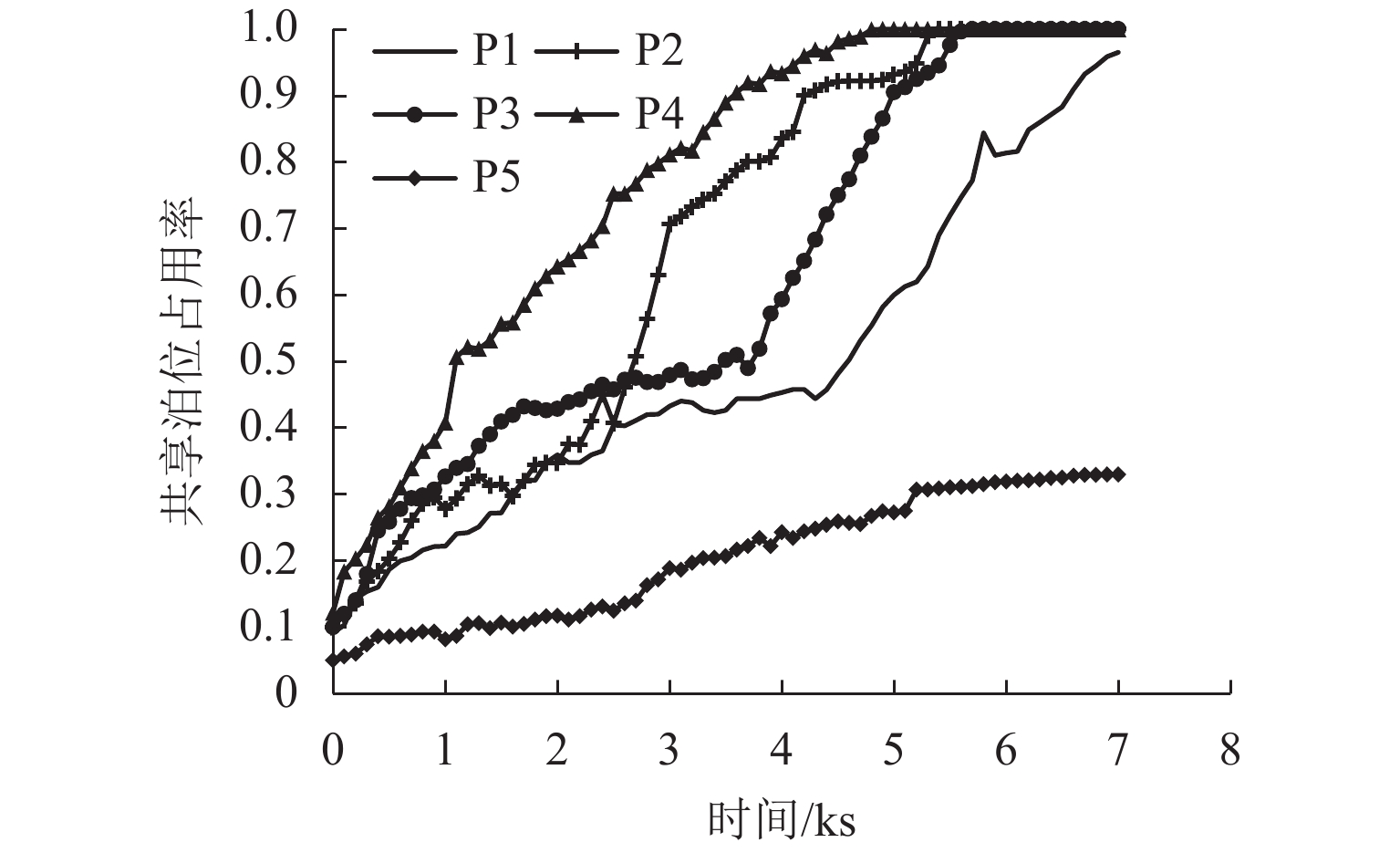
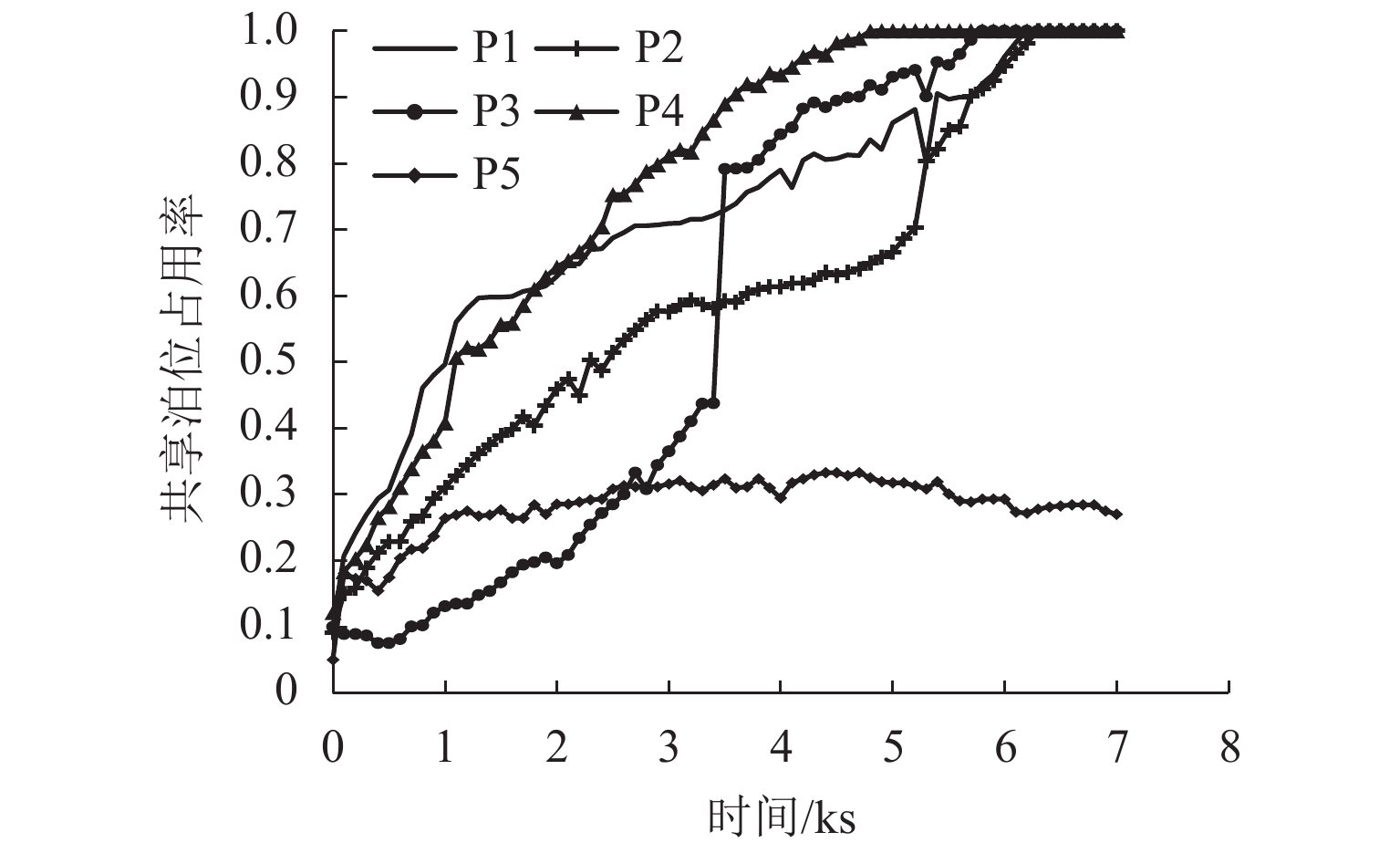
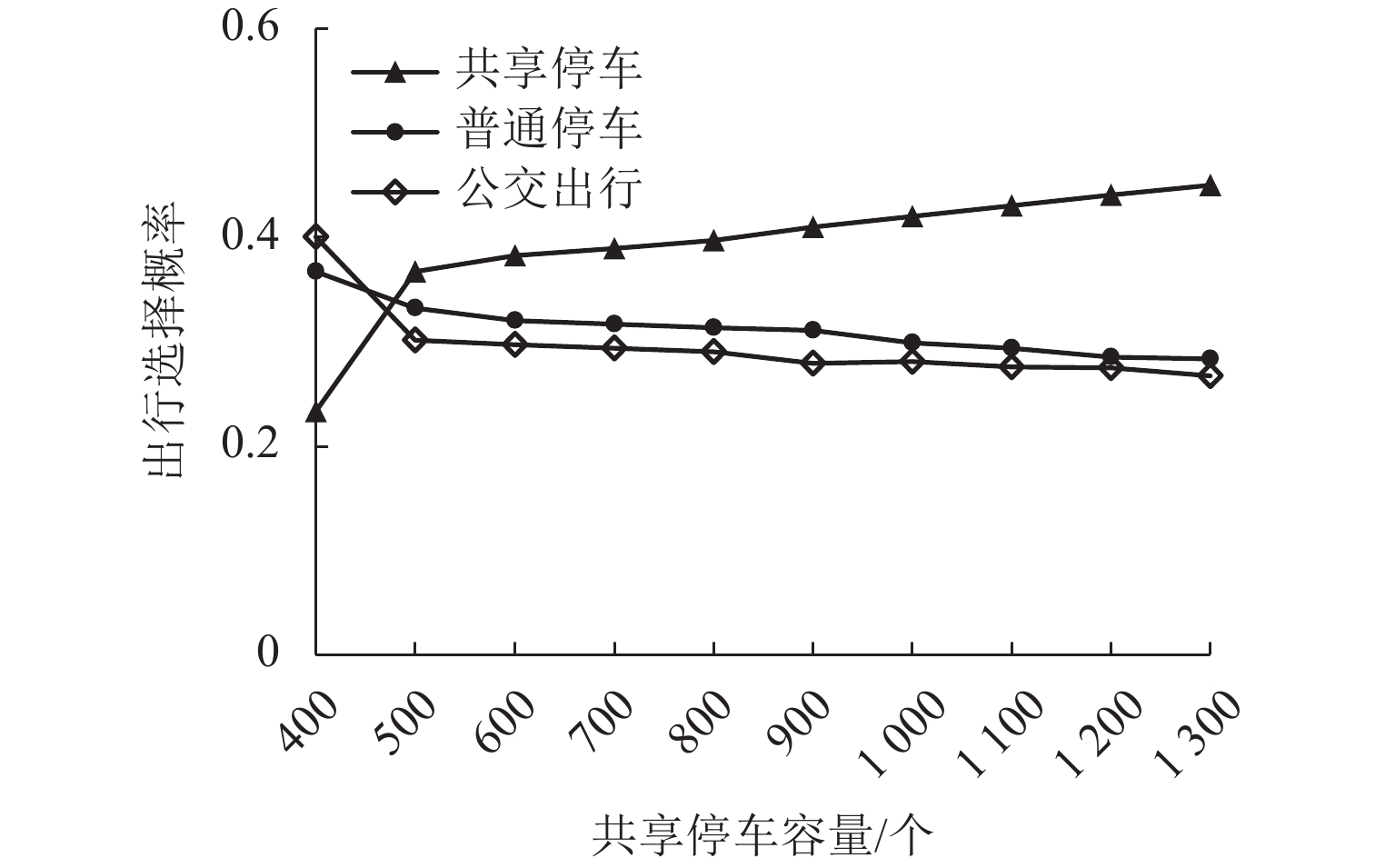
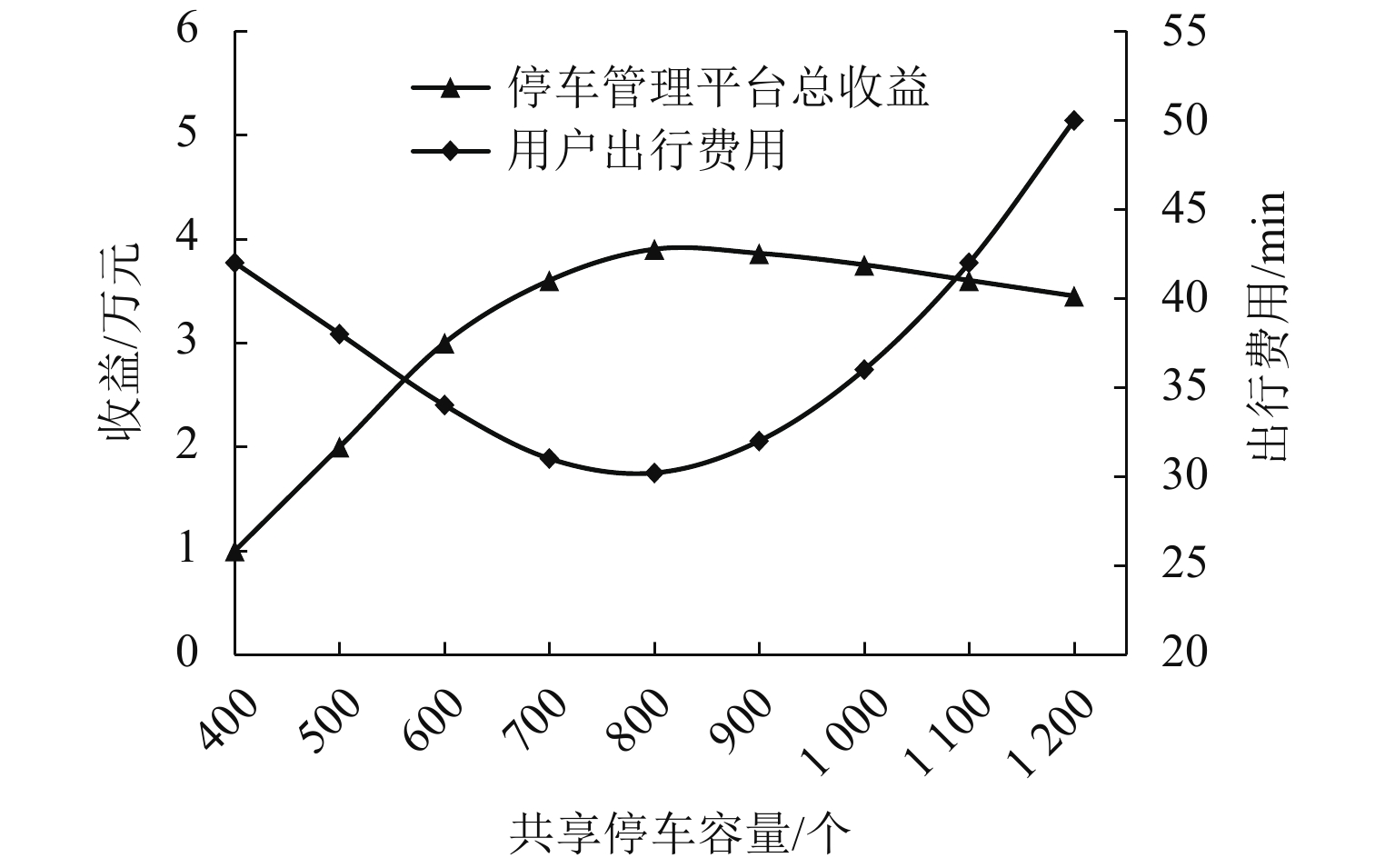
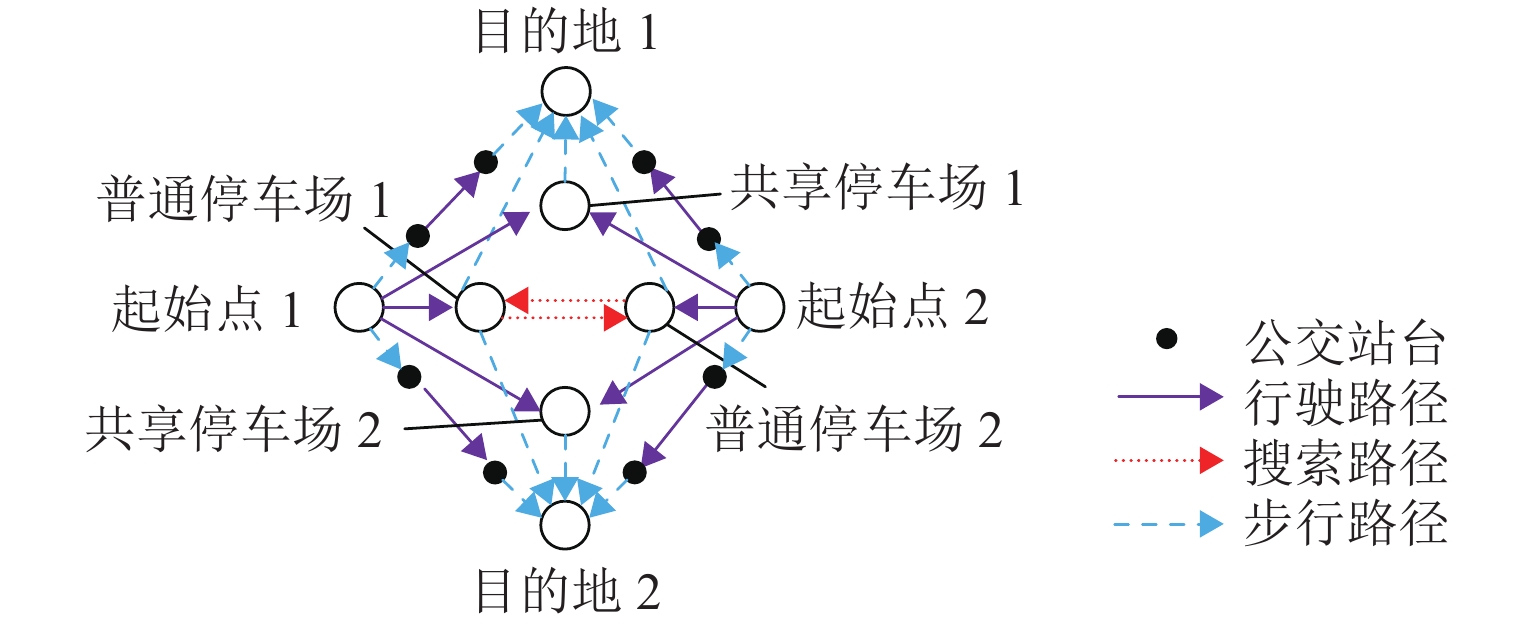
为研究共享停车容量优化分配对用户出行选择的影响,建立了双层规划模型,上层模型根据停车管理平台总收益与步行费用最小确定共享停车用地的最优停车容量,下层建立共享停车、普通停车与乘坐公交出行的多用户均衡分配模型,用于描述共享停车用户出行方式的选择,通过共享停车选择概率实现上、下层模型之间的联系;设计了相继平均算法求解下层模型,并内嵌于差分进化算法,进而求解上层模型. 对常州市金坛区CBD区域的部分路网进行模拟测试. 研究表明:在不同共享停车容量分配下,停车管理平台收益随着容量的增加呈先递增后减少的趋势,而用户的出行费用随着共享停车容量的增加呈先减少后上升的趋势,说明合理地分配共享停车容量可以实现停车管理平台收益与共享停车需求之间的均衡.
Abstract:In order to study the impact of optimal allocation of shared parking capacity on user travel choices, a two-level planning model is established. The upper model determines the optimal parking capacity of shared parking land based on the total revenue of the parking management platform and the minimum walking cost. The lower layer establishes a multi-user balanced allocation model of shared parking, ordinary parking and public transportation to describe the choice of shared parking users’ travel modes. The connection between the upper and lower models is realized through the shared parking selection probability. The successive average algorithm is designed to solve the lower model, and it is embedded in the differential evolution algorithm to solve the upper model. A simulation test is conducted on part of the road network in the CBD area of Jintan District, Changzhou City. The result show that under different shared parking capacity allocations, the revenue of the parking management platform increases with the increase of capacity and then decrease, while the user’s travel expenses decrease with the increase of capacity and then rising, which shows that reasonable allocation of shared parking capacity can achieve a balance between the revenue of the parking management platform and the demand for shared parking.
-
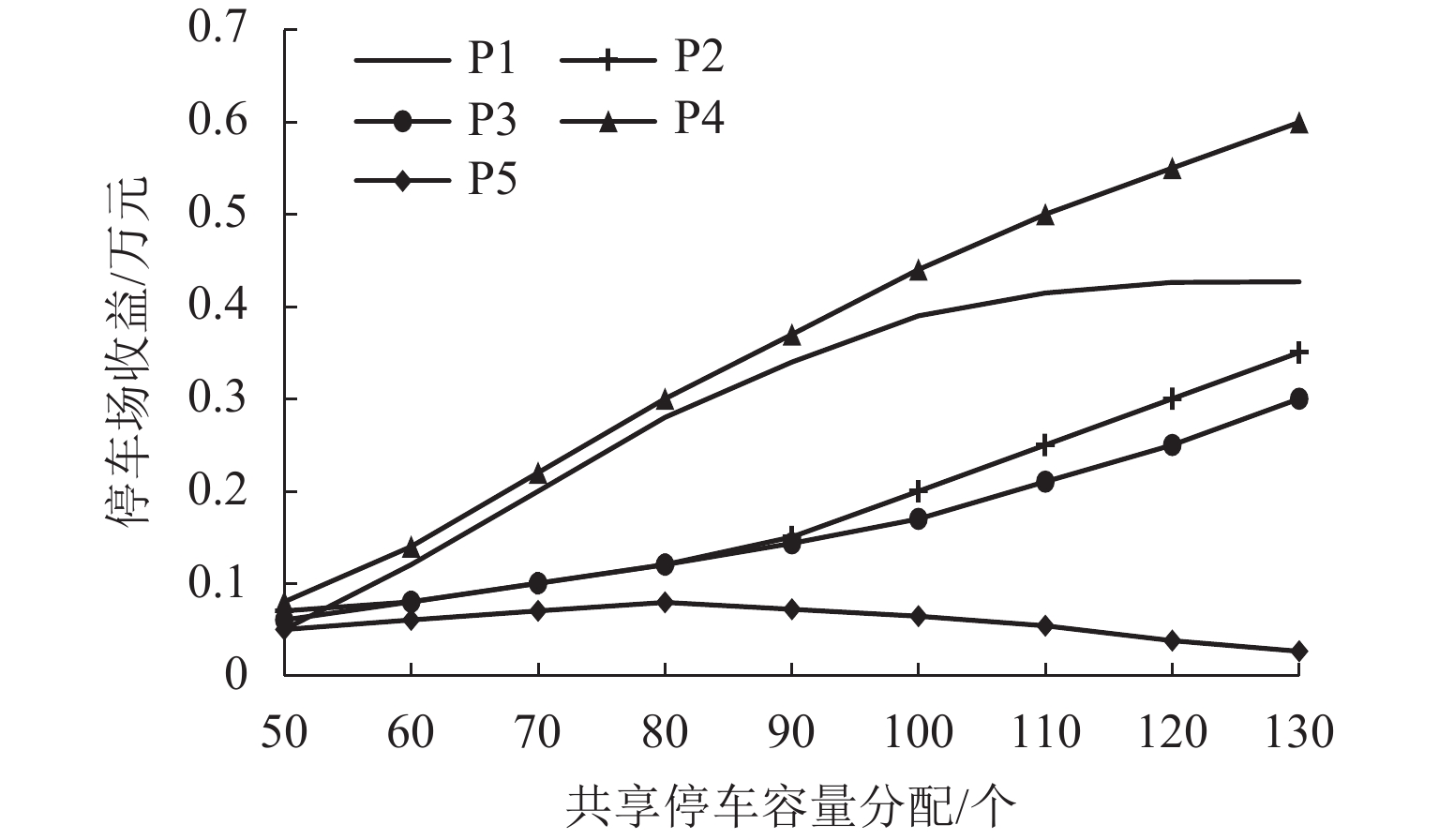
表 1 共享泊位用地的停车容量
Table 1. Parking capacity of shared berth land
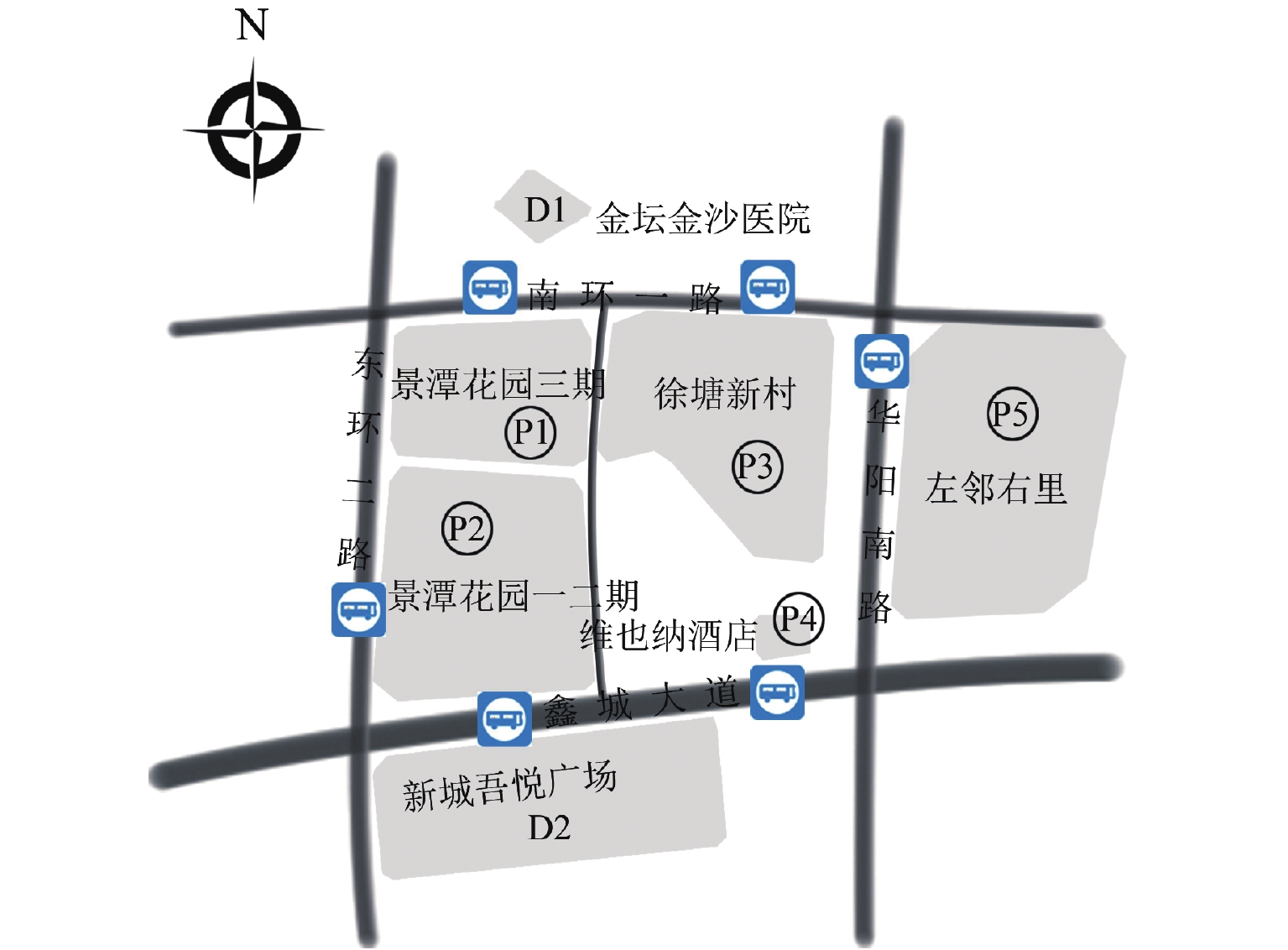
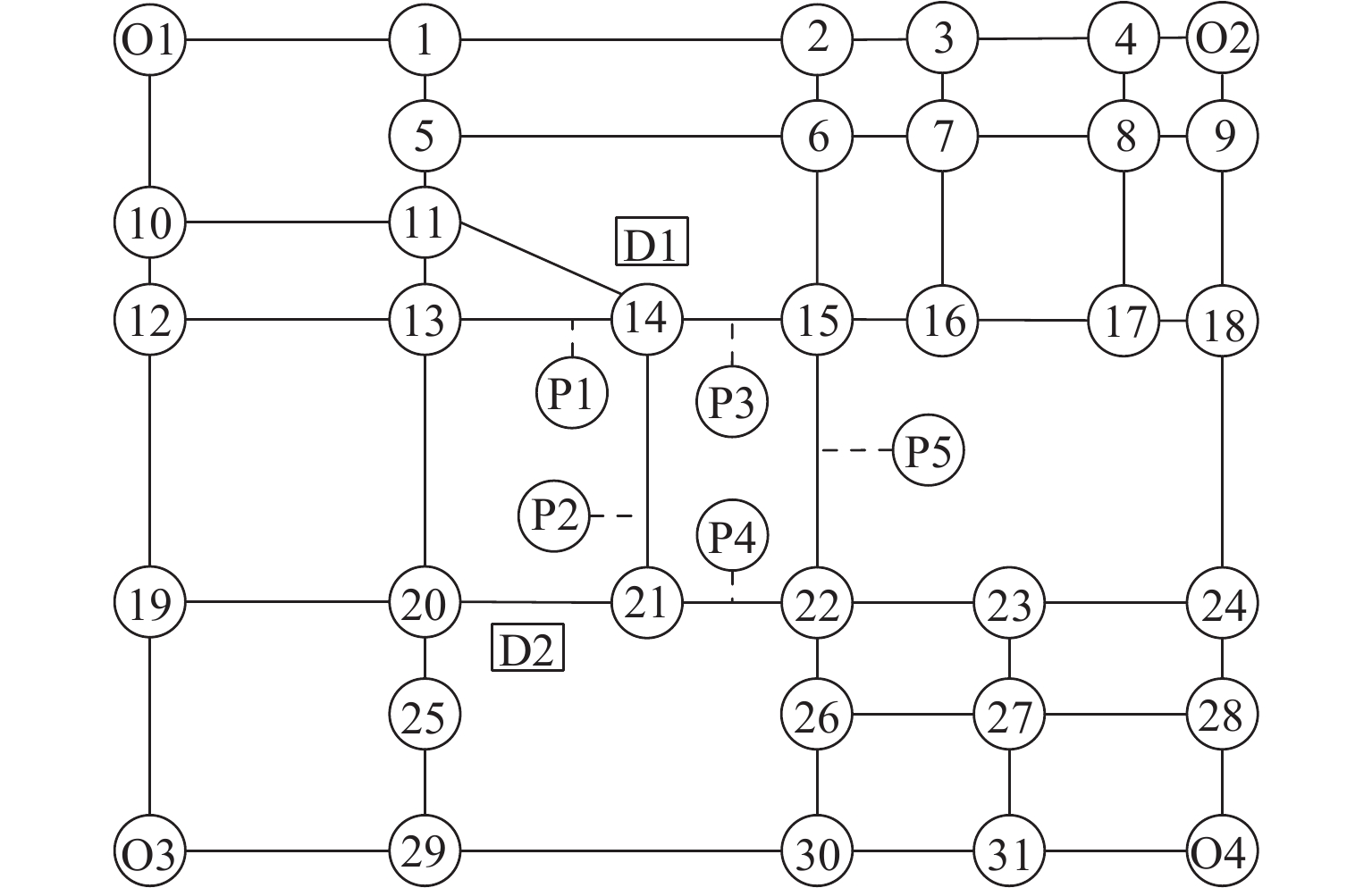
个 停车场 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 容量 460 270 392 166 620 表 2 停车场到目的地的步行距离
Table 2. Distance between parking lot and destination
m 目的地 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 D1 120 452 130 650 540 D2 390 125 350 110 650 表 3 共享停车场剩余及分配的泊位容量
Table 3. Remaining and allocated berth capacity of shared parking lot
个 停车场 剩余泊位 分配泊位 P1 360 110 P2 213 180 P3 350 300 P4 133 130 P5 431 80 合计 1486 800 -
[1] 李亚辉. 基于泊位共享的城市综合体停车需求预测方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016. [2] 王庆刚. 允许泊位共享的城市综合体停车需求分析方法研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018. [3] 徐志豪,马健霄. 基于行为选择特性的泊位共享需求预测[J]. 物流科技,2019,42(7): 27-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3100.2019.07.008XU Zhihao, MA Jianxiao. Parking sharing demand forecasting based on behavior selection[J]. Logistics Sci-Tech, 2019, 42(7): 27-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3100.2019.07.008 [4] ALKHEDER S A, AL RAJAB M M, ALZOUBI K. Parking problems in Abu Dhabi, UAE toward an intelligent parking management system “ADIP:Abu Dhabi Intelligent Parking”[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2016, 55(3): 2679-2687. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2016.06.012 [5] JIANG B W, FAN Z P. Optimal allocation of shared parking slots considering parking unpunctuality under a platform-based management approach[J]. Transportation Research Part E:Logistics and Transportation Review, 2020, 142: 102062.1-102062.16. [6] SHAO C Y, YANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. A simple reservation and allocation model of shared parking lots[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2016, 71: 303-312. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2016.08.010 [7] 段满珍,杨兆升,张林,等. 个性化诱导下的居住区共享停车泊位分配模型[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(2): 174-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2017.02.005DUAN Manzhen, YANG Zhaosheng, ZHANG Lin, et al. Parking spaces allocation model of residential areas sharing parking based on personalized guidance[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2017, 38(2): 174-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2017.02.005 [8] 孙会君,傅丹华,吕莹,等. 基于共享停车的车位租用与分配模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(3): 130-136.SUN Huijun, FU Danhua, LV Ying, et al. Parking spaces renting and allocation model for shared parking[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(3): 130-136. [9] 张水潮,蔡逸飞,黄锐,等. 基于预约需求的共享停车平台泊位分配方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(3): 137-143,162.ZHANG Shuichao, CAI Yifei, HUANG Rui, et al. Shared parking space allocation method considering reservation demand[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(3): 137-143,162. [10] XIAO H H, XU M, GAO Z Y. Shared parking problem:a novel truthful double auction mechanism approach[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2018, 109: 40-69. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2018.01.008 [11] LEI C, OUYANG Y F. Dynamic pricing and reservation for intelligent urban parking management[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2017, 77: 226-244. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2017.01.016 -




 下载:
下载: