Optimal Design of Heavy-Haul Rail Grinding Profile Considering Grinding Amount
-
摘要:
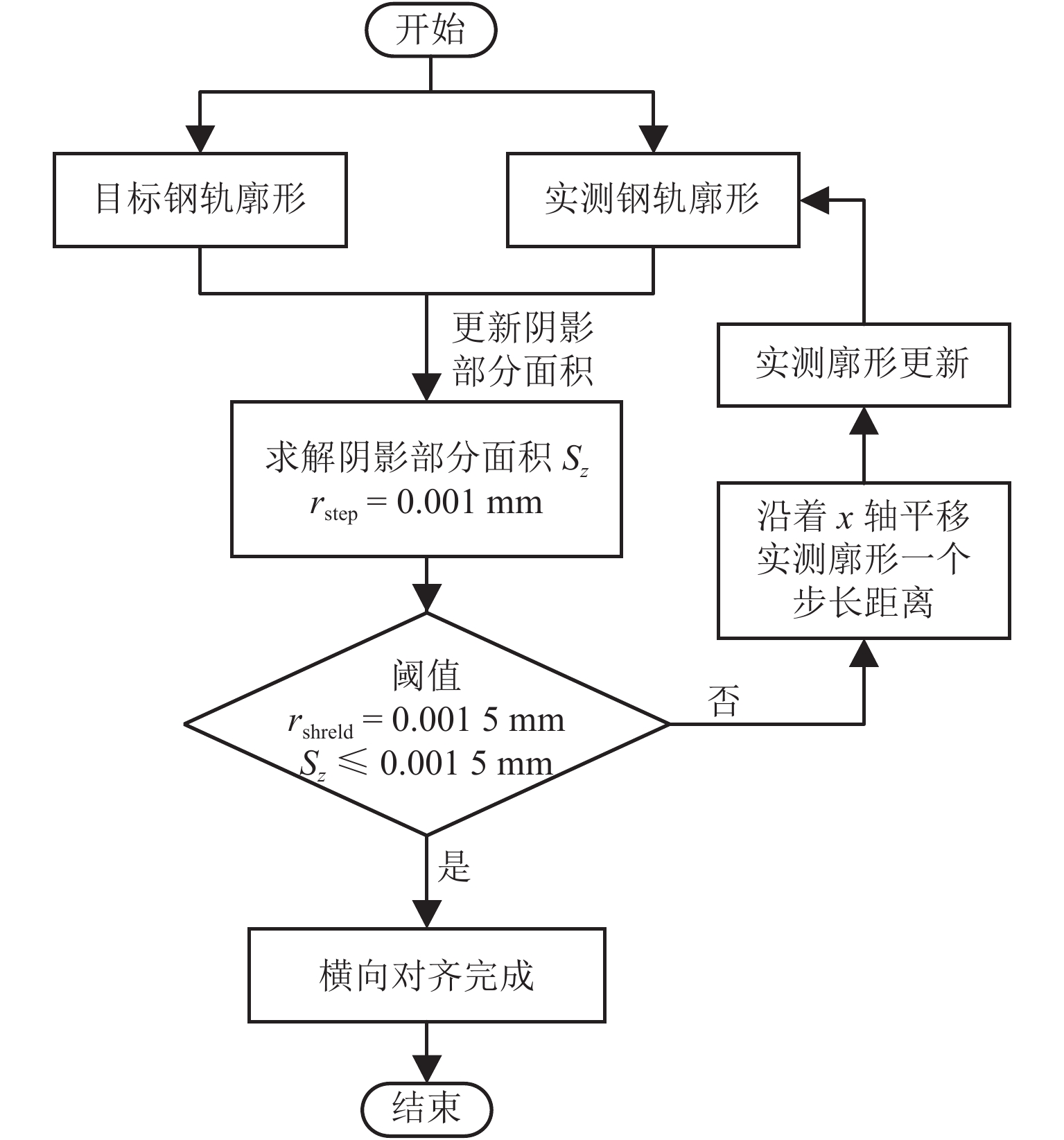
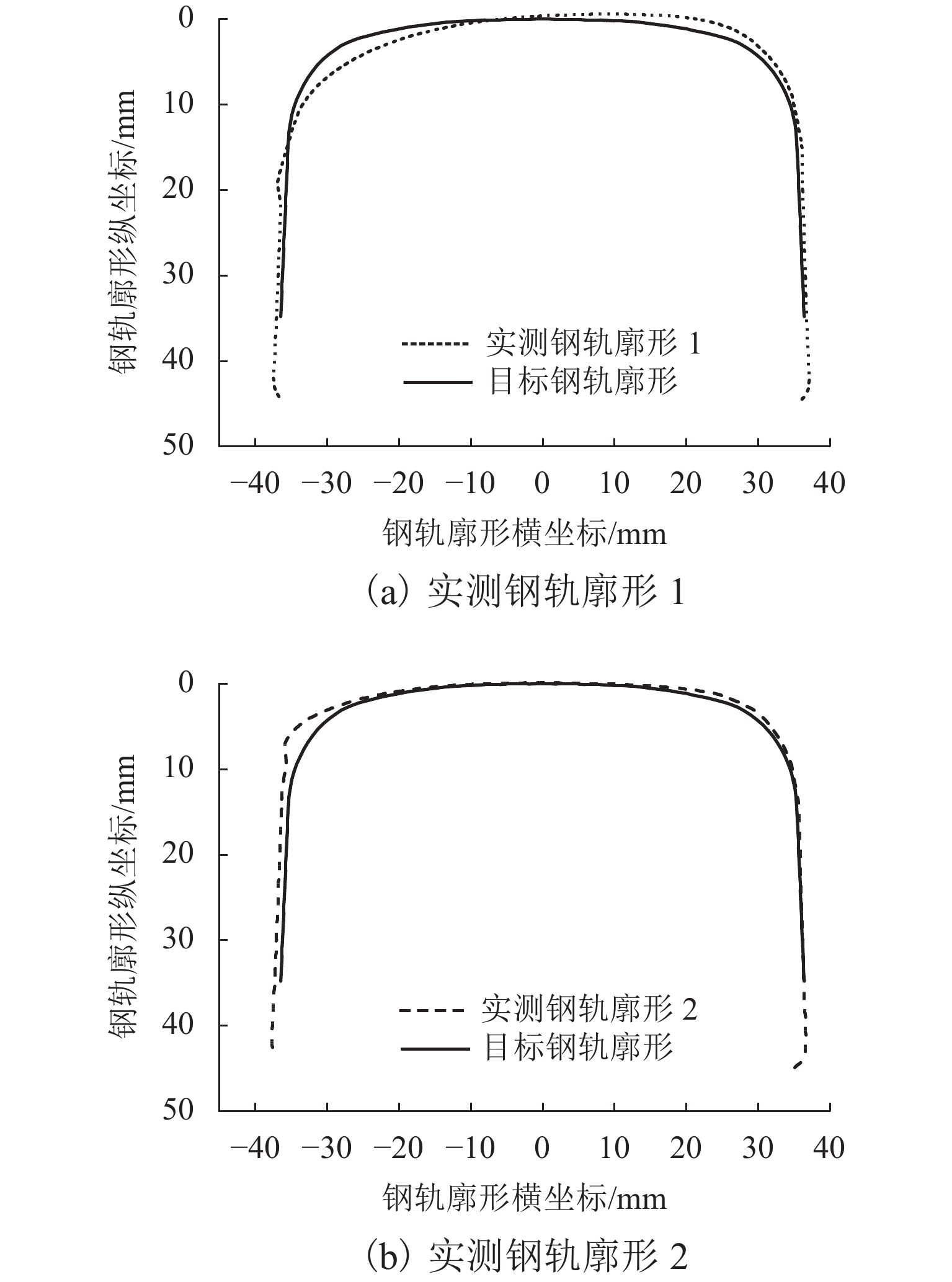
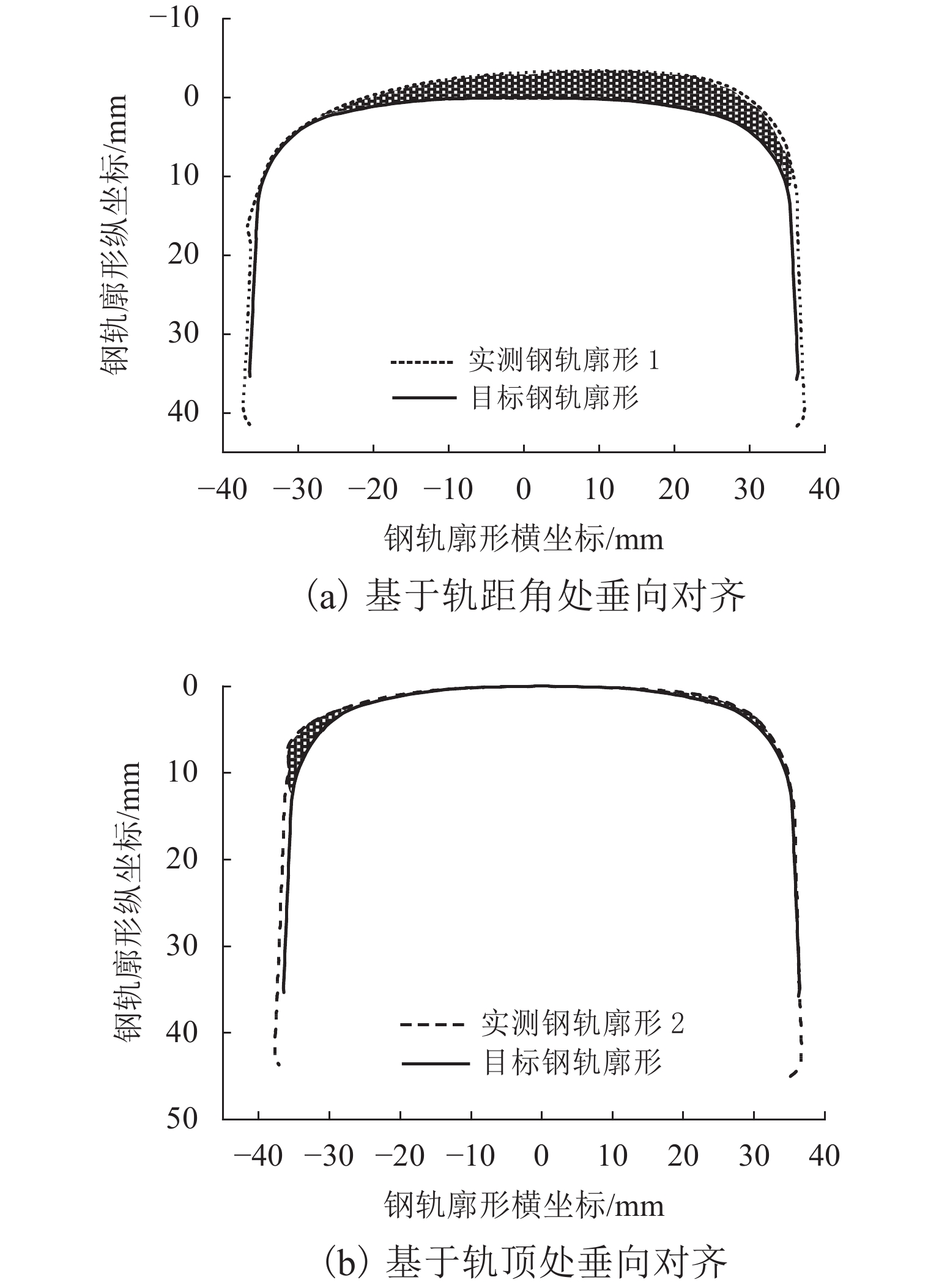
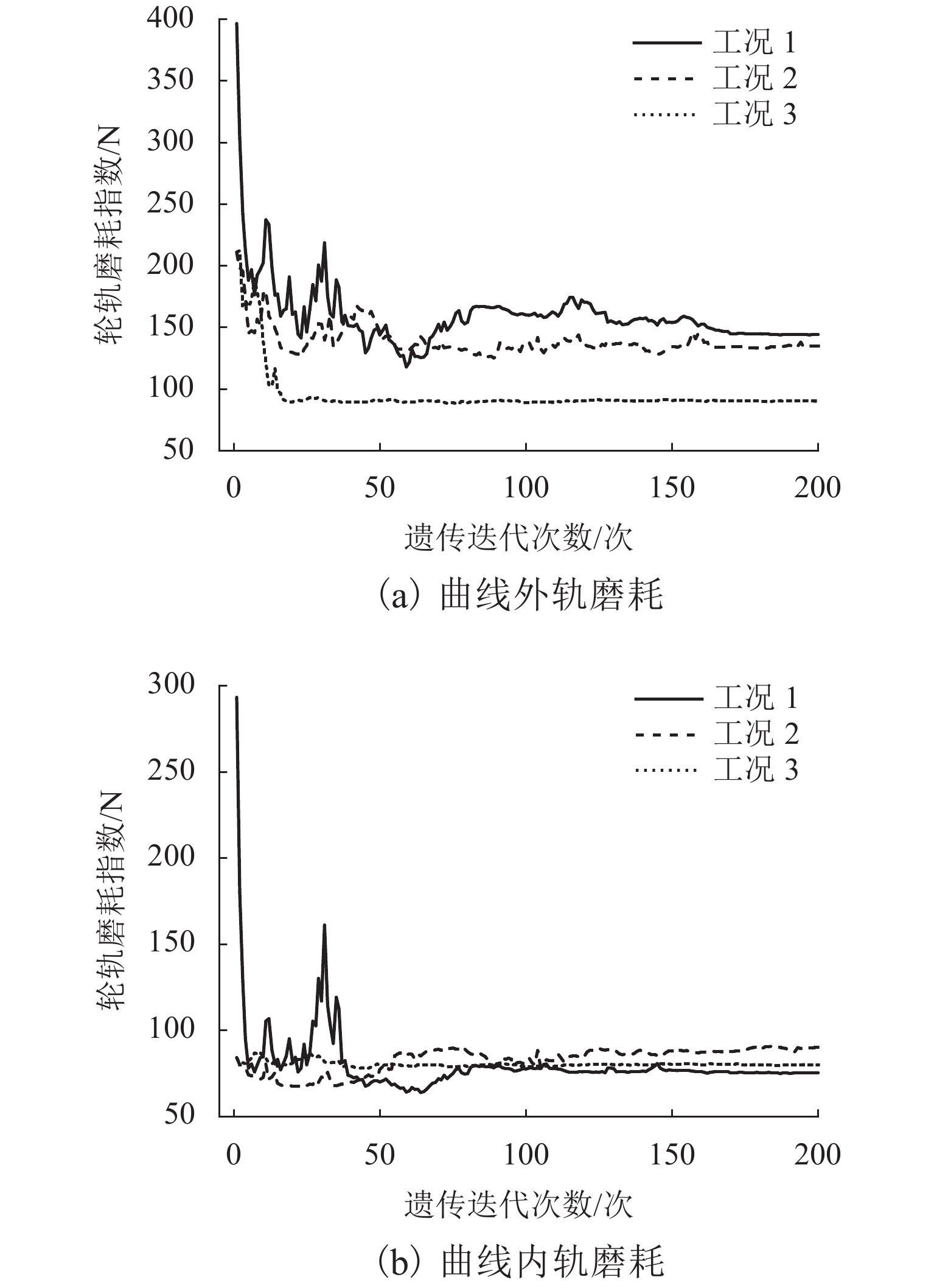
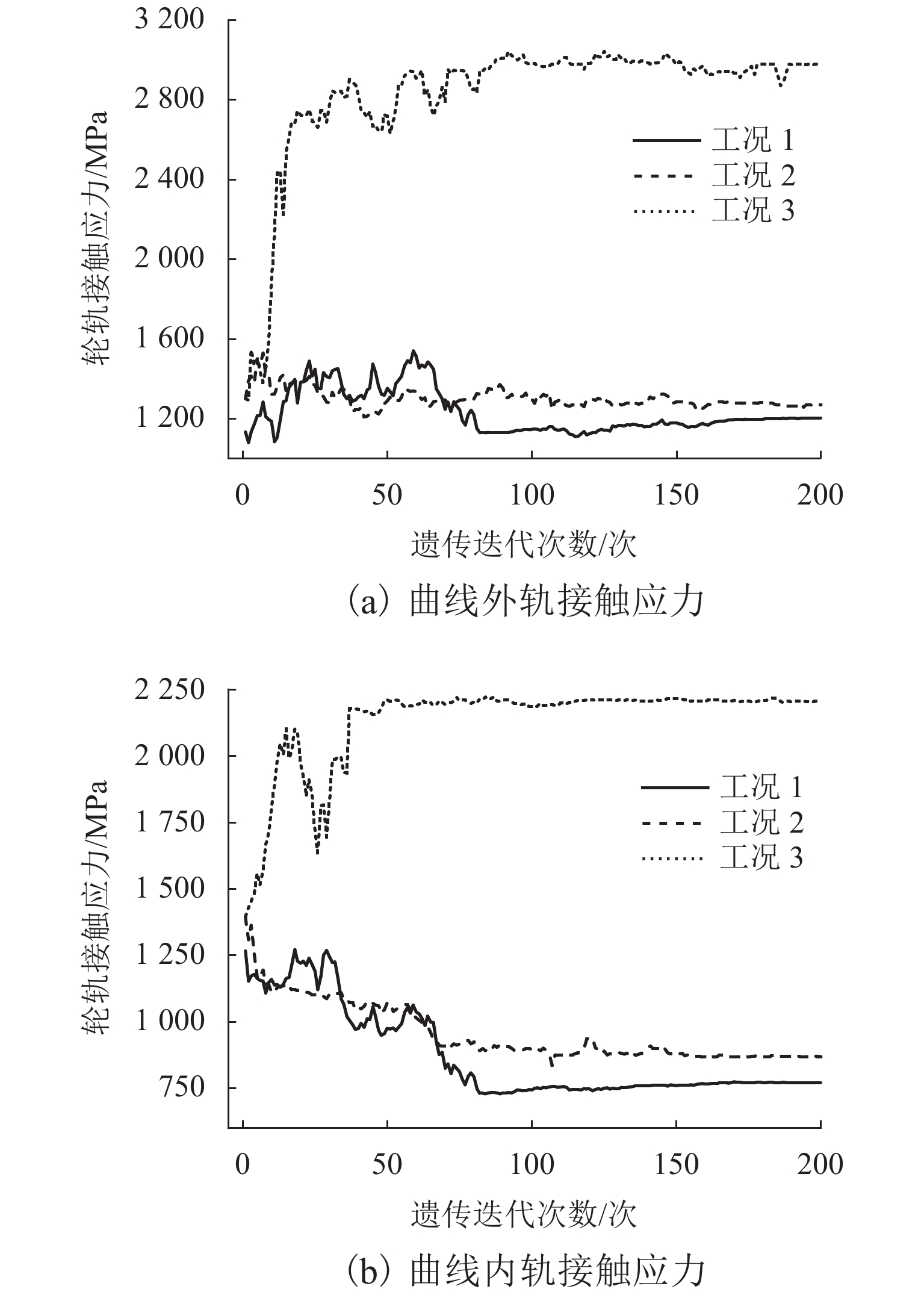
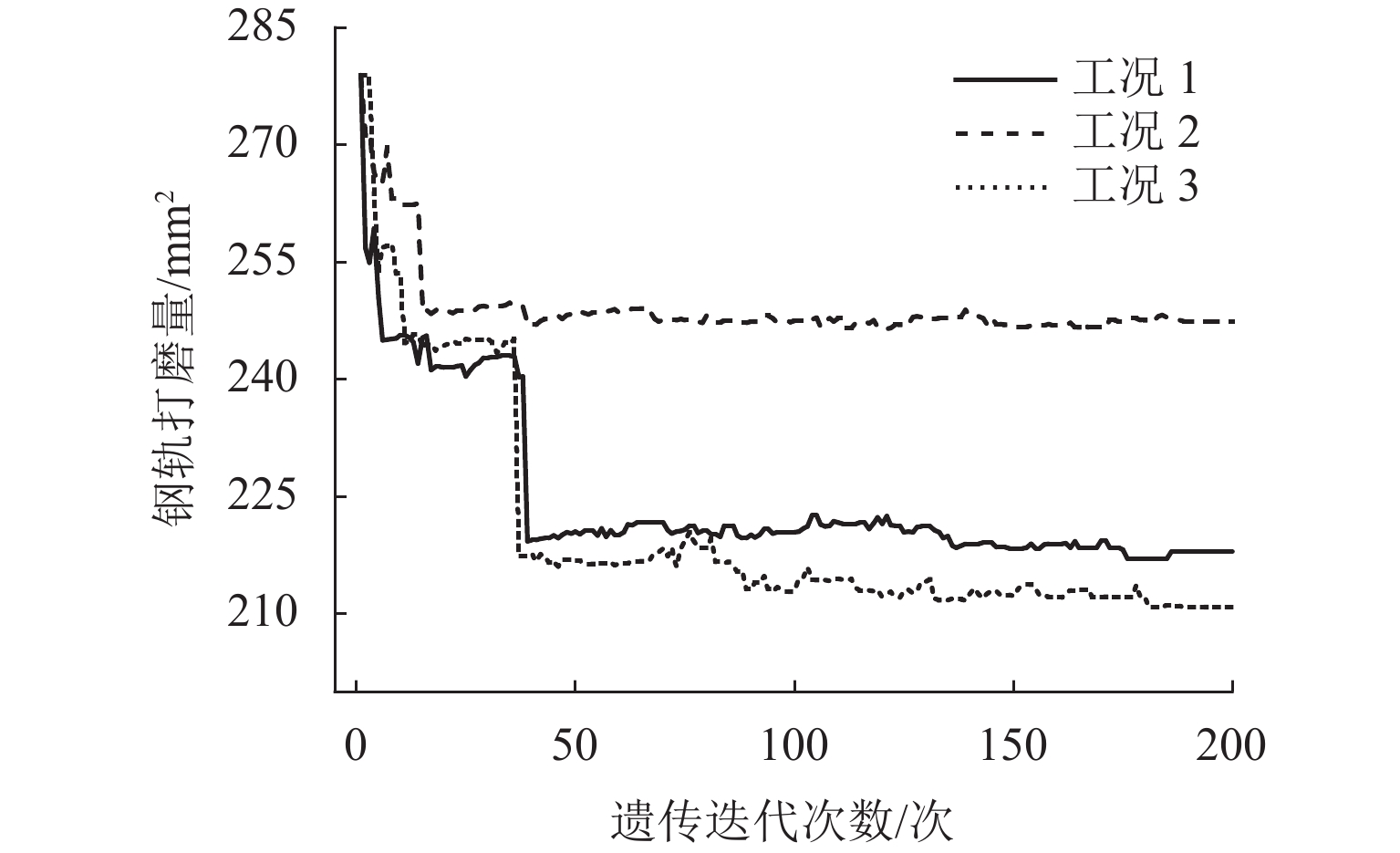
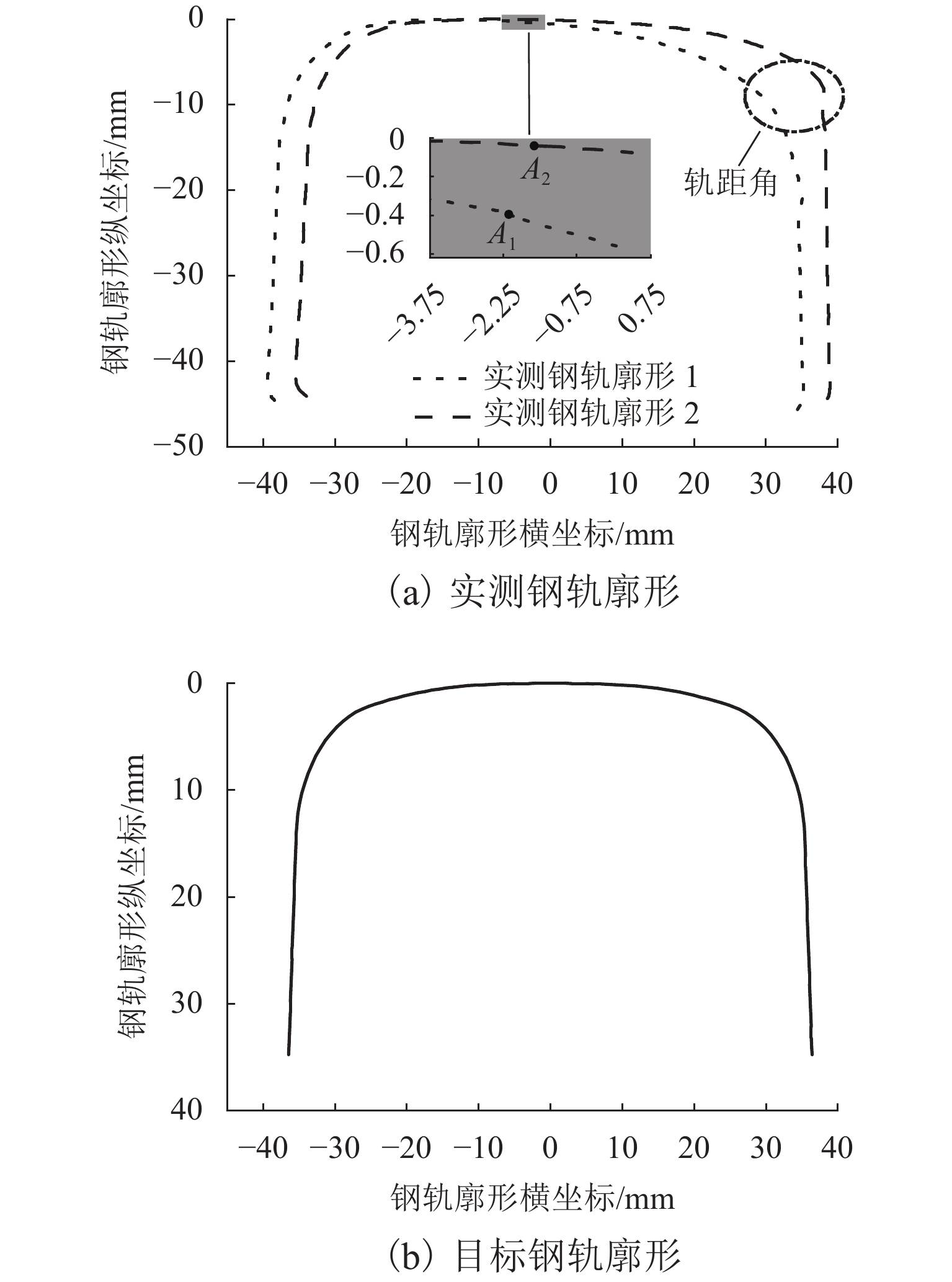
为在重载钢轨打磨廓形优化设计中最小化钢轨打磨量,建立了打磨量的钢轨廓形对齐及计算方法,设计以轮轨磨耗指数、轮轨接触应力以及钢轨打磨量为优化子目标的综合优化评价模型,并对不同优化策略的优化结果进行了分析. 首先,通过矩阵旋转变换、曲线拟合及样条插值等理论建立钢轨廓形自动对齐算法,并计算目标廓形打磨量;其次,考虑轮轨磨耗指数、接触应力以及钢轨打磨量,建立综合优化目标函数,采用遗传算法并联合车辆轨道动力学仿真模型求解优化钢轨打磨廓形;最后,运用所建立的钢轨廓形优化设计模型计算分析不同优化策略的设计结果. 研究结果表明:同时考虑轮轨磨耗、轮轨接触应力和钢轨打磨量,优化后曲线外、内轨廓形平均磨耗指数相比初始廓形下降68.9%,内轨接触应力下降39.1%,打磨量下降21.8%,优化效果最佳;只考虑轮轨磨耗和接触应力时,优化后曲线外轨廓形磨耗指数和内轨接触应力下降较为明显,但打磨量下降速率相对较慢,仅为11.3%;只考虑打磨量时,优化后钢轨廓形打磨量下降最快,为24.4%,但轮轨接触应力显著变大.
Abstract:In order to minimize grinding amount in optimization design of heavy-haul rail grinding profile, an alignment and calculation method of the grinding amount of rail profile was established. Meanwhile, a comprehensive optimization evaluation model was designed. The model regarded wheel-rail wear index, wheel-rail contact stress and rail grinding amount as optimization sub-objectives, and the optimization results of different optimized strategies were analyzed. Firstly, an automatic alignment algorithm for rail profile was established through the theories of matrix rotation transformation, curve fitting and spline interpolation. Then the amount of rail grinding was calculated. Secondly, considering the optimization indicators such as wheel-rail wear index, contact stress and rail grinding amount, a comprehensive optimization objective function was established. The genetic algorithm was used to solve the optimized rail profile in conjunction with the vehicle track dynamics simulation model. Finally, the design results of different optimization strategies were calculated and analyzed by using the established rail profile optimization design model. The results show that, considering wheel-rail wear, wheel-rail contact stress and amount of rail grinding at the same time, the average wear index of the optimized high and low rail profile reduces by 68.9% when compared with the initial profile. The low rail contact stress obtains a decrease of 39.1%. The grinding amount gets a reduction of 21.8%. Thus the optimized effect is the best. After optimization, the high rail profile wear index and low rail contact stress decrease significantly in conditions of only considering wheel-rail wear and contact stress, but the decline rate of the grinding amount is relatively slow, reaching 11.3%. When only considering the grinding amount, the grinding amount of rail profile drops the fastest after optimization, which is 24.4%, while the wheel-rail contact stress is significantly larger.
-
表 1 优化策略
Table 1. Optimization strategies
工况 磨耗权重系数 应力权重系数 打磨量权重系数 1 0.0833 0.1095 0.8072 2 0.4585 0.5515 0 3 0 0 1 表 2 外轨磨耗和内轨接触应力
Table 2. High rail wear and low rail contact stress
工况 外轨磨耗指数/N 内轨应力/MPa 实测廓形 1 2482.0 1294.0 1 105.1 770.5 2 133.8 868.3 3 109.8 2201.0 -
[1] 刘启跃,王文健,周仲荣. 高速与重载铁路钢轨损伤及预防技术差异研究[J]. 润滑与密封,2007,32(11): 11-14,68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2007.11.004LIU Qiyue, WANG Wenjian, ZHOU Zhongrong. An investigation on difference of rail damage and preventive technique of high-speed and heavy-haul railway[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2007, 32(11): 11-14,68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2007.11.004 [2] GERLICI J, LACK T. Contact geometry influence on the rail/wheel surface stress distribution[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 2(1): 2249-2257. [3] 董勇,康彦兵,张华鹏,等. 地铁线路钢轨波磨对车辆振动特性的影响[J]. 机械,2021,48(10): 22-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0316.2021.10.004DONG Yong, KANG Yanbing, ZHANG Huapeng, et al. Effect of rail corrugation in metro line on vibration characteristics of vehicle[J]. Machinery, 2021, 48(10): 22-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0316.2021.10.004 [4] GRASSIE S, NILSSON P, BJURSTROM K, et al. Alleviation of rolling contact fatigue on Sweden's heavy haul railway[J]. Wear, 2002, 253(1/2): 42-53. [5] PERSSON I, NILSSON R, BIK U, et al. Use of a genetic algorithm to improve the rail profile on Stockholm underground[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2010, 48(S1): 89-104. [6] CHOI H Y, LEE D H, SONG C Y, et al. Optimization of rail profile to reduce wear on curved track[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2013, 14(4): 619-625. doi: 10.1007/s12541-013-0083-1 [7] WANG P, GAO L, XIN T, et al. Study on the numerical optimization of rail profiles for heavy haul railways[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2017, 231(6): 649-665. [8] 毛鑫,沈钢. 基于轮径差函数的曲线钢轨打磨廓形设计[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(2): 253-259. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.02.017MAO Xin, SHEN Gang. Curved rail grinding profile design based on rolling radii difference function[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(2): 253-259. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.02.017 [9] 郭战伟. 普速铁路钢轨打磨对轮轨接触关系的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学,2020,41(6): 109-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.06.12GUO Zhanwei. Influence of rail grinding on wheel-rail contact relationship in general speed railway[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(6): 109-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2020.06.12 [10] 王亮,向伟彬,刘宏达,等. 小半径曲线钢轨非对称打磨目标型面优化[J]. 机械科学与技术,2021,40(6): 949-954.WANG Liang, XIANG Weibin, LIU Hongda, et al. Target profile optimization of asymmetrical grinding for rail with sharp-radius curve[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 949-954. [11] 肖杰灵,刘学毅. 钢轨非对称廓型的设计方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(3): 361-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.03.007XIAO Jieling, LIU Xueyi. Design method of rail asymmetric silhouette[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(3): 361-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.03.007 [12] 张金,俞喆,杨超,等. 普速铁路钢轨打磨廓形优化设计及效果评价[J]. 铁道建筑,2020,60(10): 138-141.ZHANG Jin, YU Zhe, YANG Chao, et al. Optimization design and effect evaluation of rail grinding profile for conventional speed railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2020, 60(10): 138-141. [13] 余博. 基于面积信息的钢轨打磨方法研究与实现[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2018. [14] 黄佳乐,桂卫东. 基于MATLAB钢轨廓形法线值计算及现场应用[J]. 铁路技术创新,2020(2): 72-78. [15] 唐彦玲,吴磊,董勇,等. 重载铁路曲线钢轨廓形多目标优化设计[J]. 机械,2020,47(12): 1-9.TANG Yanling, WU Lei, DONG Yong, et al. Multi-objective optimization design of rail profiles on curve tracks of heavy haul railway[J]. Machinery, 2020, 47(12): 1-9. [16] 成棣,胡晓依,刘丰收,等. 基于改进层次分析法的高速列车轮轨型面匹配评价方法及应用[J]. 中国铁道科学,2019,40(3): 80-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2019.03.12CHENG Di, HU Xiaoyi, LIU Fengshou, et al. Evaluation method and application of wheel-rail profile matching for high speed train based on improved analytic hierarchy process[J]. China Railway Science, 2019, 40(3): 80-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2019.03.12 [17] WU L, LIU J Q, DHANASEKAR M, et al. Optimisation of railhead profiles for curved tracks using improved non-uniform rational B-splines and measured profiles[J]. Wear, 2019, 418/419: 123-132. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2018.11.012 -




 下载:
下载: