Risk Evaluation Model of Blockchain Integration Based on CKKS Encryption Scheme
-
摘要:
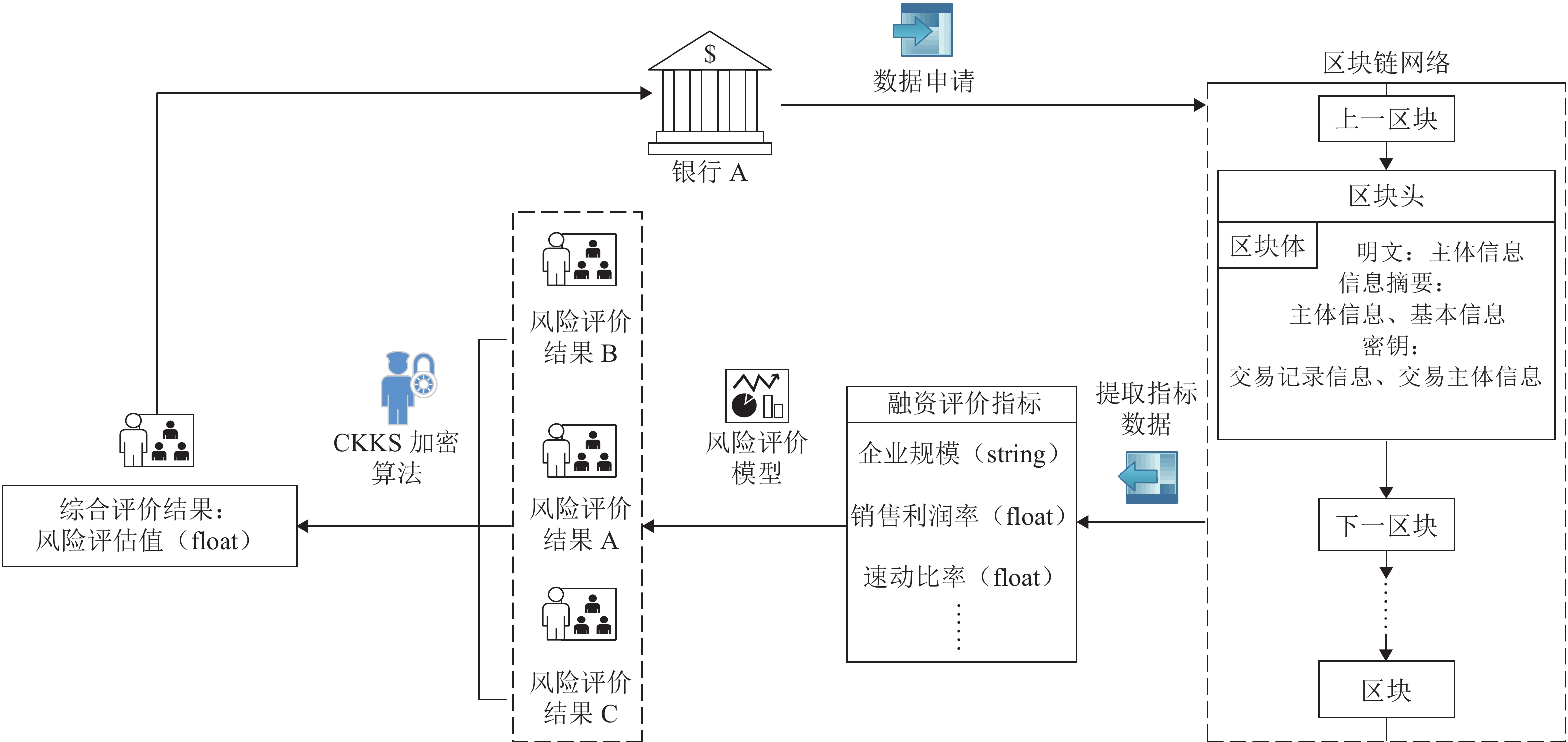
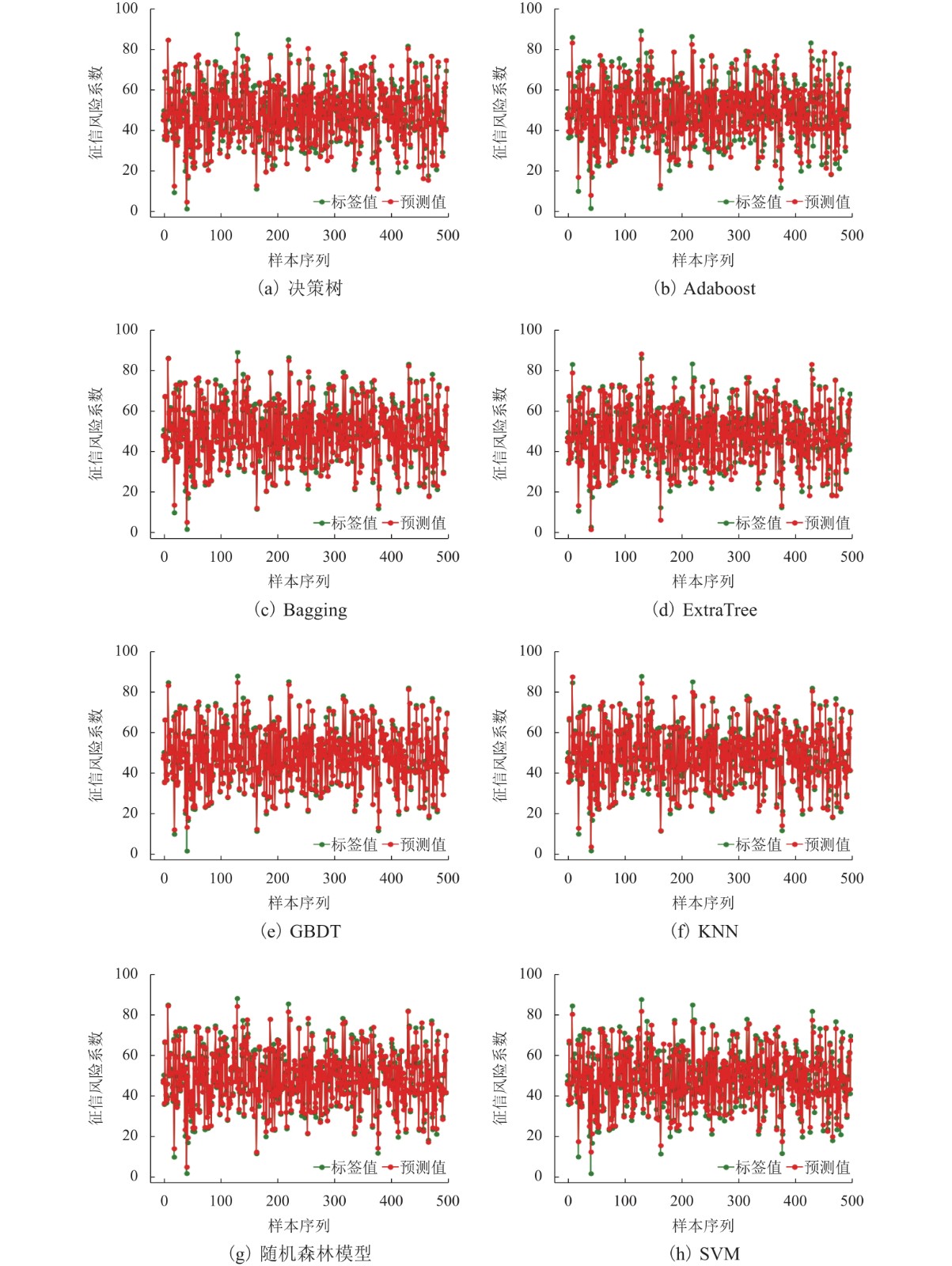
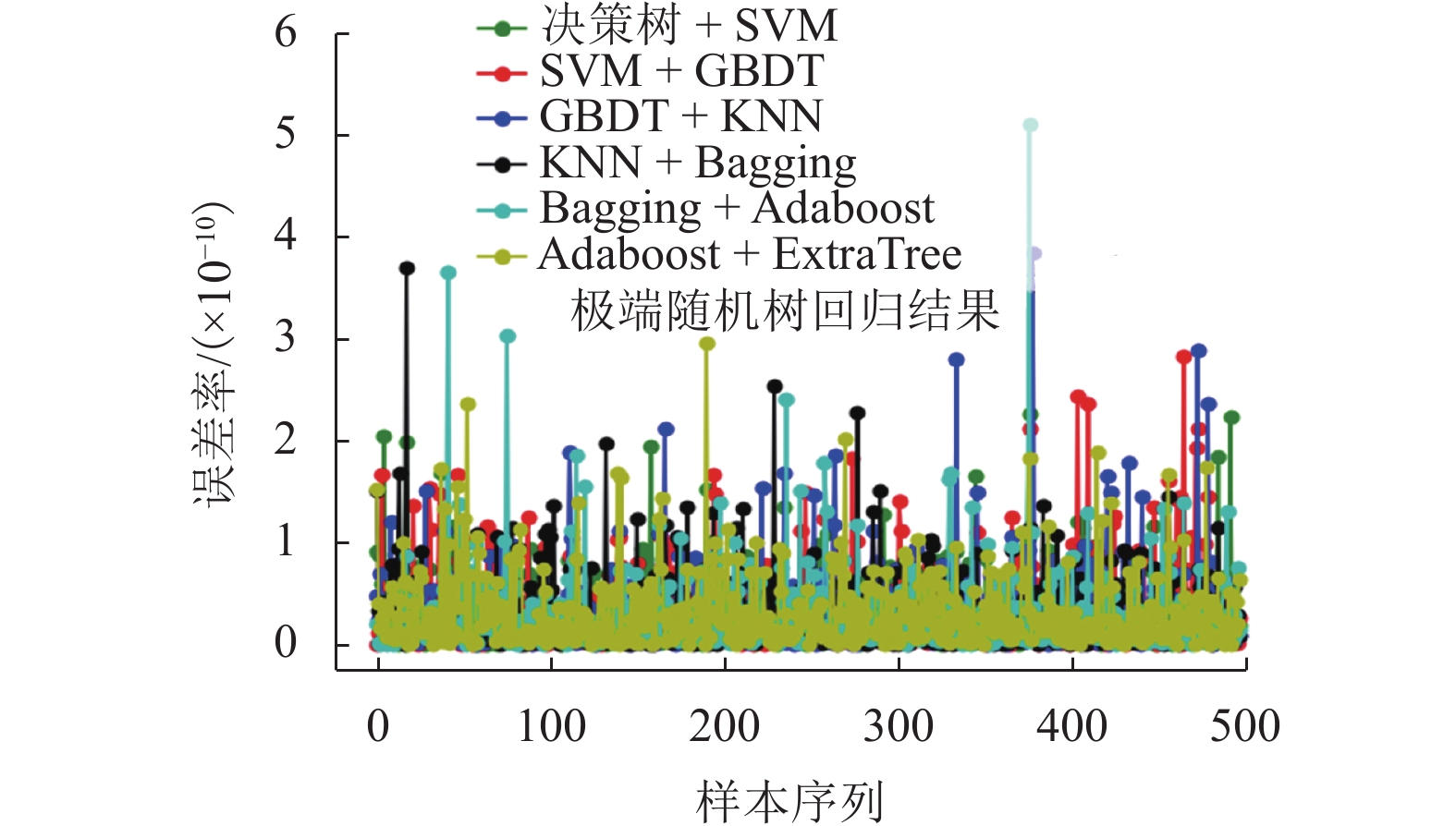
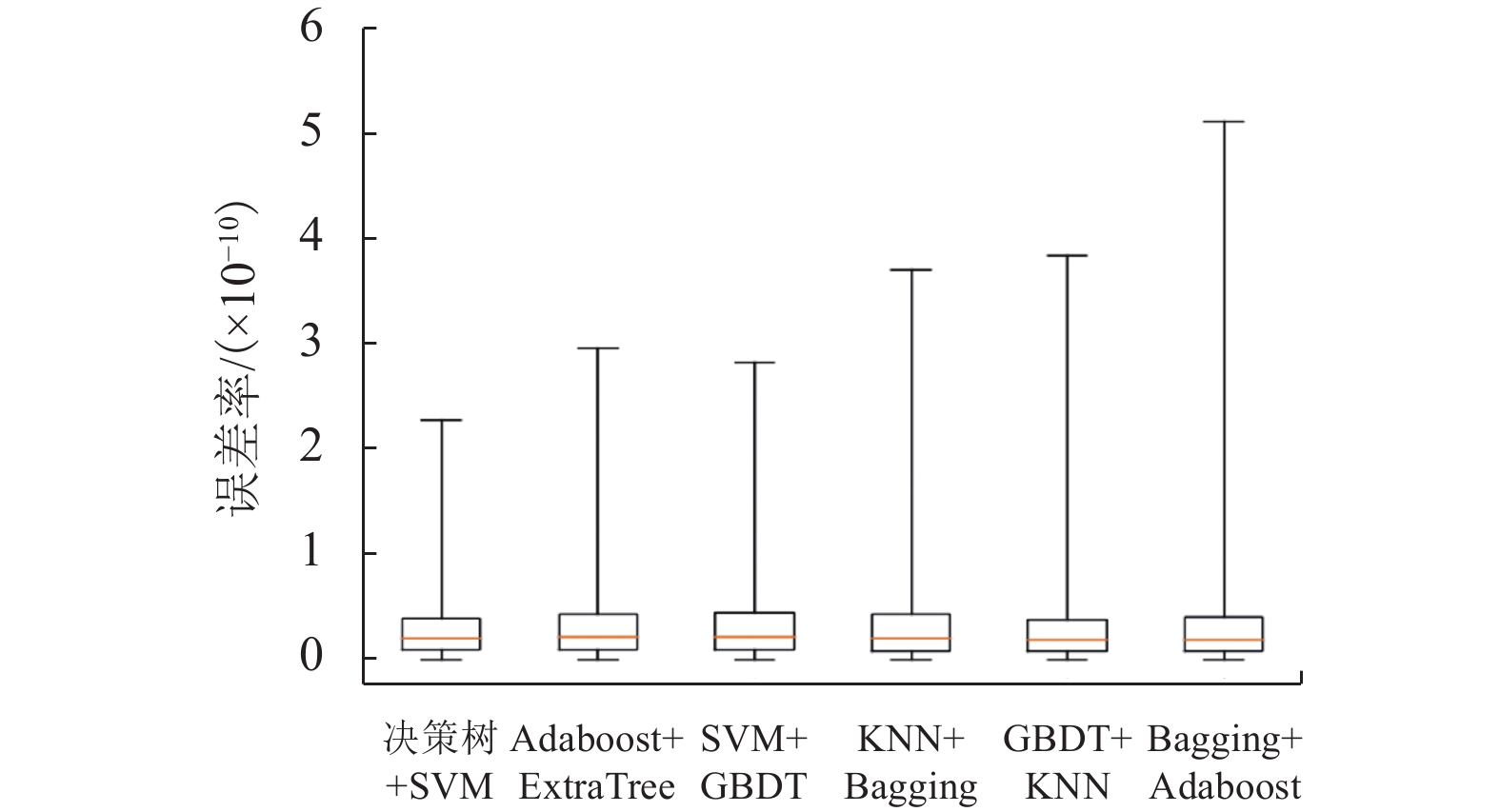
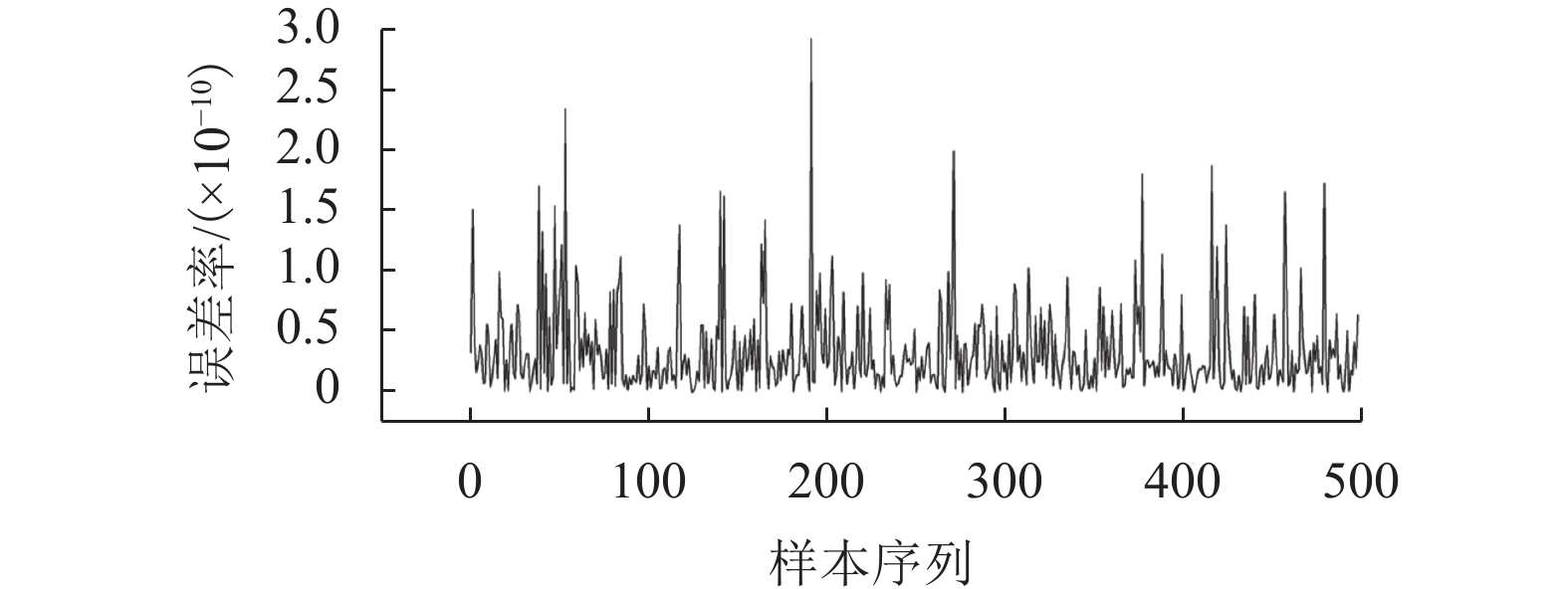
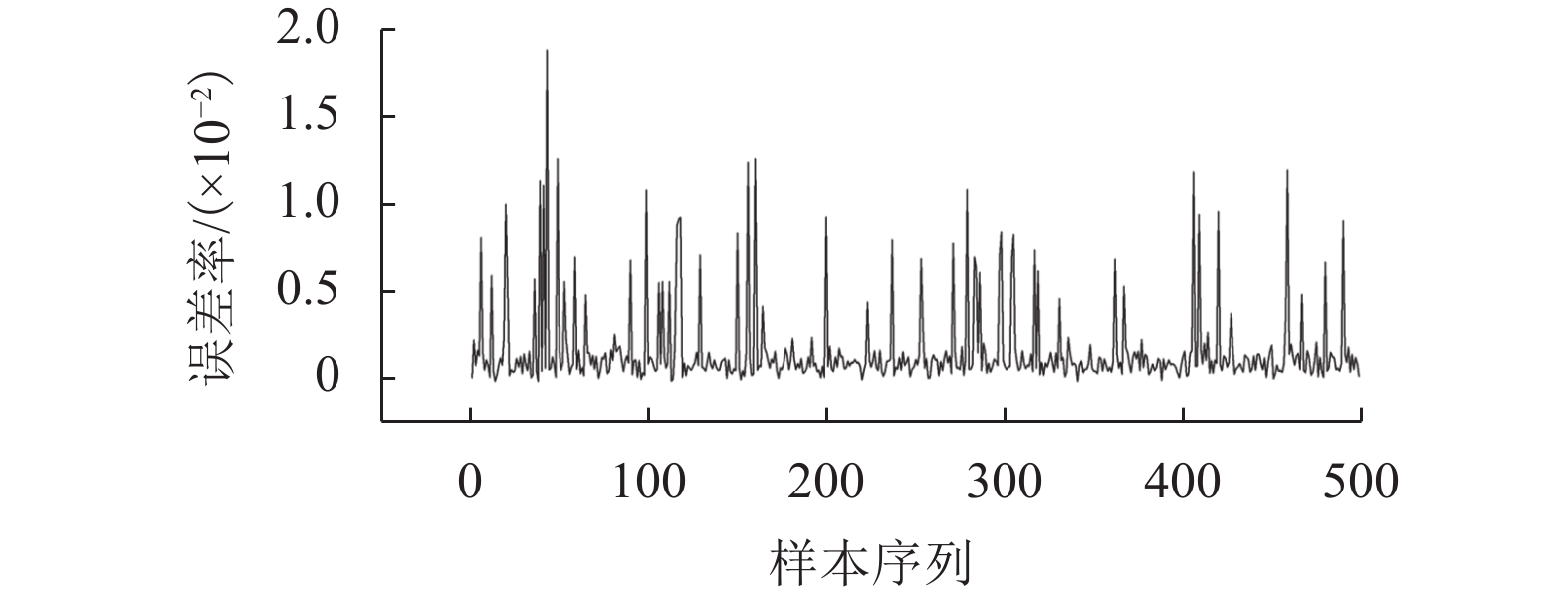
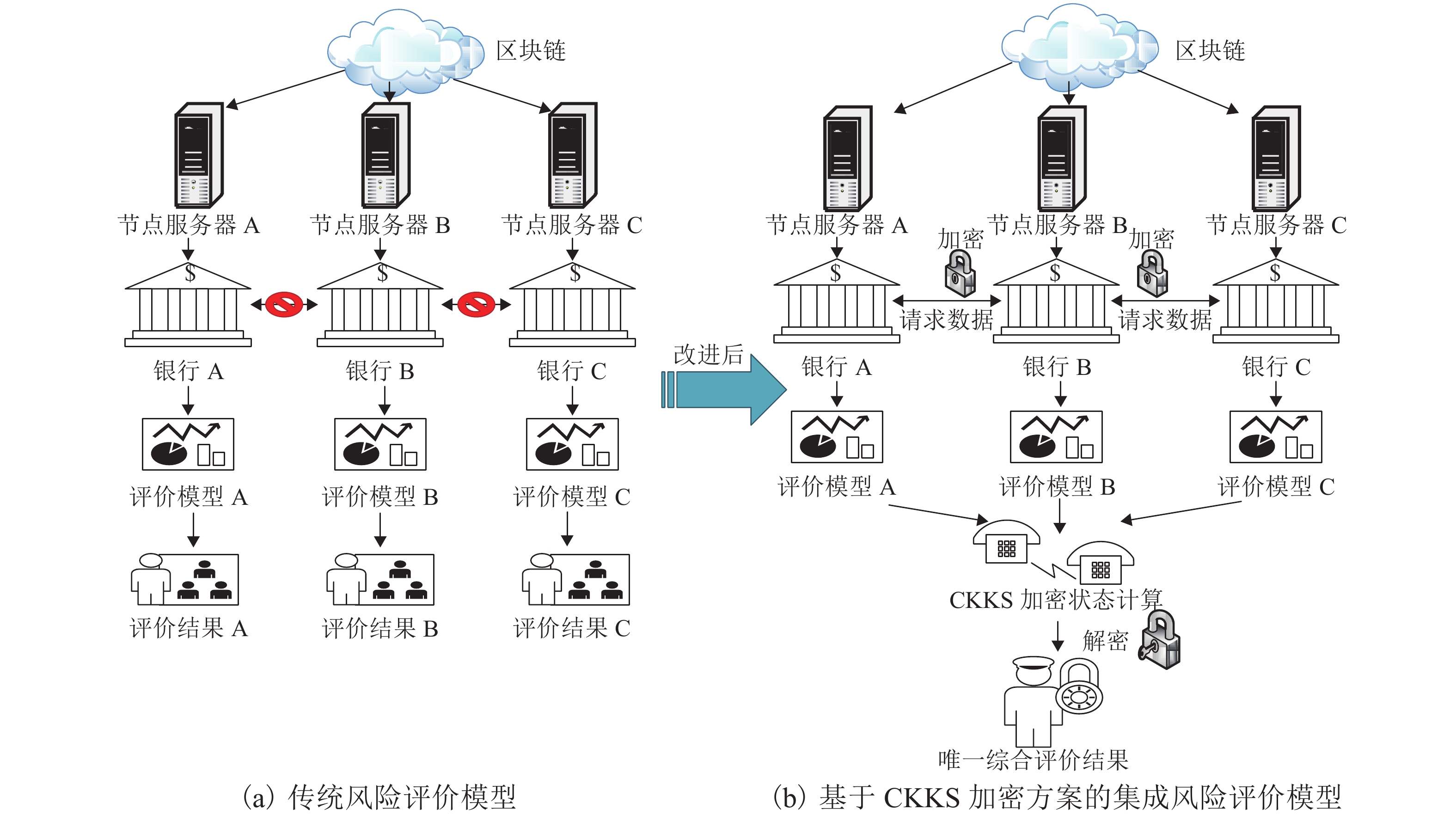
针对区块链平台中存在的多方数据交互不可信以及隐私数据易泄露等问题,基于CKKS (Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song)全同态加密方案,提出了一种集成风险评价模型,把同态加密算法应用到风险评价中,将多种评价模型与同态加密结合起来. 首先,利用三角模糊综合评价方法确定各评价指标的权重,通过多种评价方法处理分布式数据库中的样本数据,获得相关节点对同一交易事件的风险评价结果;其次,利用公钥对评价结果进行加密并进行同态运算,获得密文综合评价结果,以避免风险评价过程中的数据泄露;再次,利用私钥对评价结果进行解码,获得明文综合评价结果;最后,选取5 000个中欧班列企业的样本数据作为案例,利用决策树模型、Adaboost模型、Bagging模型、ExtraTree极端随机数模型、GBDT (gradient boosting regression trees)模型、KNN(K-nearest neighbor)模型、随机森林模型、SVM (support vector machine)模型等最为常见的评价模型进行风险评价,并将经CKKS方案加密后的综合评价结果与明文直接计算的综合评价结果和经BFV (Brakerski-Fan-vercauteren)方案加密后的综合评价结果进行了对比. 结果表明:该集成风险评价模型具有普适性,对较为常见的评价模型均能适用;模型的综合评价结果误差率较小,与实际结果的误差率均在10−9以内;与BFV方案加密后的结果相比,经CKKS方案加密后的结果误差率小于前者的十万分之一,评价结果更为准确.
Abstract:Aiming at solving problems of distrust in the data interaction between multiple parties and leakage of privacy data, an integrated risk assessment model based on the Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song (CKKS) fully homomorphic encryption scheme is proposed by using homomorphic encryption algorithm in combination with multiple assessment models for risk assessment. Firstly, the triangular fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method is used to determine weights of evaluation indexs, and a variety of evaluation methods are used to process the sample data in the distributed database to obtain the risk evaluation results of related nodes for the same transaction event. Secondly, the public key is used to encrypt the evaluation results, and then homomorphic operation is performed to obtain the encrypted comprehensive evaluation results, so as to avoid data leakage in the process of risk assessment. Thirdly, the private key is used to decode the evaluation results to obtain decrypted comprehensive evaluation results. Finally, 5000 samples from China Railway Express companies are taken as cases to evaluate the risk with eight common evaluation models, including the decision tree model, Adaboost model, Bagging model, ExtraTree model, gradient boosting regression tree (GBDT) model, K-nearest neighbor (KNN) model, random forest model, and support vector machine (SVM) model. In addition, the comprehensive evaluation results encrypted by CKKS scheme are compared with the results directly calculated by plaintext and encrypted by BFV scheme. The findings show that: the integrated risk assessment model is universal and applicable to more common assessment models; the error rates of the comprehensive evaluation results obtained by the integrated risk assessment model are small, within 10−9 against the actual results; compared with the result encrypted by BFV scheme, the error rate of the result encrypted by CKKS scheme is less than 1/100000 of the former, and the evaluation result is more accurate.
-
Key words:
- Blockchain /
- data leakage /
- fully homomorphic encryption scheme /
- risk assessment /
- integrated model
-
表 1 0.1~0.9标度的含义
Table 1. Meaning of scale 0.1~0.9
标度 对应的三角模糊数 含义 0.1 (0.1,0.1,0.2) 指标 i 相对于指标 j 极端不重要 0.3 (0.2,0.3,0.4) 指标 i 相对于指标 j 明显不重要 0.5 (0.4,0.5,0.6) 指标 i 与指标 j 同样重要 0.7 (0.6,0.7,0.8) 指标 i 相对于指标 j 明显重要 0.9 (0.8,0.9,0.9) 指标 i 相对于指标 j 极端重要 表 2 定性指标量化评分表
Table 2. Quantitative scoring of qualitative indices
定性指标 评价指标分档/分 [8, 10] [4, 8) [0, 4) 交易履约情况(X8) 好 中 差 核心企业的对外担保状况(X9) 几乎无 少量 较多 供应链关系的强度(X10) 高 中 低 表 3 三角模糊打分表
Table 3. Triangular fuzzy scoring results
k B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 1 (0.1,0.2,0.3) (0,0.1,0.3) (0.1,0.3,0.5) (0.5,0.2,0.3) (0.6,0.8,0.9) 2 (0.2,0.3,0.3) (0.4,0.7,0.8) (0.3,0.2,0.2) (0.7,0.8,0.9) (0.1,0.2,0.4) 3 (0.4,0.5,0.3) (0.1,0.3,0.5) (04,0.5,0.7) (0.1,0.4,0.6) (0.1,0.6,0.7) 4 (0.5,0.7,0.3) (0.3,0.6,0.9) (0.4,0.6,0.8) (0.3,0.5,0.7) (0.1,0.3,0.4) 5 (0.6,0.4,0.3) (0.2,0.4,0.5) (0.5,0.8,0.9) (0.5,0.6,0.8) (0.2,0.4,0.5) wm (0.15, 0.21,0.32) (0.13,0.22,0.35) (0.11,0.18,0.28) (0.18,0.25,0.39) (0.09,0.14,0.24) 表 4 指标赋权结果
Table 4. Index weighting results
指标名称 变量 权重 指标名称 变量 权重 企业规模 X1 0.0246 核心企业对外担保情况 X9 0.1512 销售利润率 X2 0.0833 供应链关系强度 X10 0.0014 速动比率 X3 0.0255 赊销周期 X11 0.1146 存货周转率 X4 0.0117 产品可替代性 X12 0.0884 资产负债率 X5 0.0140 权益乘数 X13 0.0176 交易量 X6 0.0748 质押物变现能力 X14 0.0799 交易金额 X7 0.0363 总资产周转率 X15 0.1329 交易履约情况 X8 0.1437 表 5 CKKS方案和BFV方案同态加密结果及误差率
Table 5. Homomorphic encryption results and error rates of CKKS and BFV schemes
编号 KNN 模型 +
随机森林模型CKKS 全同态加密
评价结果CKKS 方案
误差率BFV 全同态加密
评价结果BFV 方案
误差率1 48.6117737805 48.6117737789 3.34 × 10−11 48.6094744655 4.73 × 10−5 2 38.4173642857 38.4173642916 1.53 × 10−10 38.3934853887 6.22 × 10−4 3 66.6095043478 66.6095043506 4.09 × 10−11 66.6003539367 1.37 × 10−4 4 40.7277690992 40.7277690999 1.66 × 10−11 40.7098999864 4.39 × 10−4 5 36.0318162194 36.0318162184 2.58 × 10−11 36.0170565909 4.10 × 10−4 6 39.2235467290 39.2235467305 3.98 × 10−11 39.1413627605 2.10 × 10−3 7 45.2551751634 45.2551751619 3.20 × 10−11 45.2384881180 3.69 × 10−4 8 85.5722701987 85.5722701993 7.54 × 10−12 85.5655826327 7.82 × 10−5 9 59.7378161329 59.7378161324 8.14 × 10−12 59.7254652272 2.07 × 10−4 10 49.4582034252 49.4582034281 5.74 × 10−11 49.4489389677 1.87 × 10−4 11 50.6262683040 50.6262683016 4.62 × 10−11 50.6237741777 4.93 × 10−5 12 59.0855247219 59.0855247221 4.30 × 10−12 59.0248410817 1.03 × 10−3 13 50.8218075188 50.8218075195 1.39 × 10−11 50.8154754434 1.25 × 10−4 14 51.5208750000 51.5208750014 2.77 × 10−11 51.5204698244 7.86 × 10−6 15 40.6476813842 40.6476813860 4.43 × 10−11 40.6440481786 8.94 × 10−5 16 41.8885428177 41.8885428182 1.16 × 10−11 41.8792671831 2.21 × 10−4 17 37.0070685441 37.0070685404 1.01 × 10−10 36.9933666065 3.70 × 10−4 18 66.6304171240 66.6304171283 6.33 × 10−11 66.6209557226 1.42 × 10−4 19 14.8742302481 14.8742302472 6.03 × 10−11 14.8490706101 1.69 × 10−3 20 38.9383642857 38.9383642857 3.34 × 10−11 38.8372207385 2.60 × 10−5 -
[1] ELGHAISH F A K, ABRISHAMI S, HOSSEINI M R. Integrated project delivery with blockchain: an automated financial system[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 114(1): 209-224. [2] LIU H, ZHANG Y, YANG T. Blockchain-enabled security in electric vehicles cloud and edge computing[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(3): 78-83. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1700344 [3] 邰雪,孙宏斌,郭庆来. 能源互联网中基于区块链的电力交易和阻塞管理方法[J]. 电网技术,2016,40(12): 3630-3638.TAI Xue, SUN Hongbin, GUO Qinglai. Electricity transactions and congestion management based on blockchain in energy internet[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(12): 3630-3638. [4] 张宁,王毅,康重庆,等. 能源互联网中的区块链技术:研究框架与典型应用初探[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(15): 4011-4023.ZHANG Ning, WANG Yi, KANG Chongqing, et al. Blockchain technique in the energy Internet: preliminary research framework and typical applications[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(15): 4011-4023. [5] 袁勇,王飞跃. 区块链技术发展现状与展望[J]. 自动化学报,2016,42(4): 481-494.YUAN Yong, WANG Feiyue. Blockchain: the state of the art and future trends[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4): 481-494. [6] OMRAN Y, HENKE M, HEINES R, et al. Blockchain-driven supply chain finance: towards a conceptual framework from a buyer perspective[C]//2017: 26th Annual Conference of the International Purchasing and Supply Education and Research Association. Budapest: [s.n.], 2017: 1-15. [7] 徐忠,邹传伟. 区块链能做什么、不能做什么?[J]. 金融研究,2018(11): 1-16.XU Zhong ZOU Chuanwei. What can blockchain do and cannot do?[J]. Journal of Financial Research, 2018(11): 1-16. [8] 龚强,班铭媛,张一林. 区块链、企业数字化与供应链金融创新[J]. 管理世界,2021,37(2): 3,22-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2021.02.004GONG Qiang, BAN Mingyuan, ZHANG Yilin. Blockchain, enterprise digitalization and supply chain finance innovation[J]. Journal of Management World, 2021, 37(2): 3,22-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2021.02.004 [9] RIVEST RL, ADLEMAN L M, DERTOUZOS M L. On databanks and privacy homomorphisms[J]. Foundations of Secure Computation, 1978, 76(4): 169-179. [10] GOLDWASSER S, MICALI S. Probabilistic encryption[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1984, 28(2): 270-299. doi: 10.1016/0022-0000(84)90070-9 [11] GENTRY C. Fully homomorphic encryption using ideal lattices[C]//In Proceedings of the Forty-First Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of computing, Association for Computing Machinery. New York: ACM Press, 2009: 169-178. [12] GENTRY C. A fully homomorphic encryption scheme[M]. Ann Arbor: [s.n.], 2009. [13] CHEON J H , KIM A , KIM M , et al. Homomorphic encryption for arithmetic of approximate numbers[C]//International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security. Hong Kong: Springer, 2017: 409-437. [14] 郑尚文,刘尧,周潭平,等. 优化的基于错误学习问题的CKKS方案[J]. 计算机应用,2021,41(6): 1723-1728.ZHENG Shangwen, LIU Yao, ZHOU Tanping, et al. Optimized CKKS scheme based on learning with errors problem[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(6): 1723-1728. [15] NAKASUMI M. Information sharing for supply chain management based on block chain technology[C]//2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics. Thessaloniki: IEEE, 140-149. [16] 刘彦松,夏琦,李柱,等. 基于区块链的链上数据安全共享体系研究[J]. 大数据,2020,6(5): 92-105.LIU Yansong, XIA Qi, LI Zhu, et al. Research on secure data sharing system based on blockchain[J]. Big Data Research, 2020, 6(5): 92-105. [17] 钱萍,吴蒙. 同态加密隐私保护数据挖掘方法综述[J]. 计算机应用研究,2011,28(5): 1614-1617,1622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2011.05.004QIAN Ping, WU Meng. Survey of privacy preserving data mining methods based on homomorphic encryption[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2011, 28(5): 1614-1617,1622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2011.05.004 [18] DU M X, CHEN Q J, XIAO J, et al. Supply chain finance innovation using blockchain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2020, 67(4): 1045-1058. doi: 10.1109/TEM.2020.2971858 [19] 王竹泉,宋晓缤,王苑琢. 我国实体经济短期金融风险的评价与研判——存量与流量兼顾的短期财务风险综合评估与预警[J]. 管理世界,2020,36(10): 156-170,216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2020.10.012WANG Zhuquan, SONG Xiaobin, WANG Yuanzhuo. Objective evaluation and rational judgment of short-term financial risk in China’s real economy: comprehensive assessment and early warning of short-term financial risk considering stock and flow[J]. Management World, 2020, 36(10): 156-170,216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5502.2020.10.012 [20] 廖礼坤,张炜. 导入期风险企业的风险综合评价[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2004,39(5): 590-594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2004.05.008LIAO Likun, ZHANG Wei. Synthetical evaluation of risks of venture business during start-up period[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2004, 39(5): 590-594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2004.05.008 [21] 龙云飞. 基于熵值法的中小企业供应链融资信用风险评价[J]. 统计与决策,2013(13): 177-179. [22] 程昔武,丁忠明. 高校负债融资风险及其评价方法研究[J]. 财贸研究,2009,20(6): 131-138,152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6260.2009.06.022CHENG Xiwu, DING Zhongming. Research on risk of debt financing to colleges & universities and it’s evaluating[J]. Finance and Trade Research, 2009, 20(6): 131-138,152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6260.2009.06.022 [23] 曹清玮,戴丽芳,孙琪,等. 社会网络环境下基于分布式信任的在线评价方法[J]. 控制与决策,2020,35(7): 1697-1702.CAO Qingwei, DAI Lifang, SUN Qi, et al. A distributed trust based online evaluation under social network[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(7): 1697-1702. [24] 仇文革,李俊松,胡兰,等. 基于WebGIS的地下工程安全风险管理系统[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2011,46(6): 953-959,965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.06.011QIU Wenge, LI Junsong, HU Lan, et al. WebGIS-based safety risk management system of underground engineering[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011, 46(6): 953-959,965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2011.06.011 [25] 胡兰,胡培. 基于概率论-逻辑学的隧道各方关系与风险研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(6): 1122-1128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.06.024HU Lan, HU Pei. Relation and risk in owner and contractors of tunnel projects based on probability and logic theories[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(6): 1122-1128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.06.024 [26] 何正友,冯玎,林圣,等. 高速铁路牵引供电系统安全风险评估研究综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(3): 418-429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.002HE Zhengyou, FENG Ding, LIN Sheng, et al. Research on security risk assessment for traction power supply system of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(3): 418-429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.03.002 [27] 吴波前,蔡伯根,陆德彪,等. 基于GNSS/INS的列车定位风险评估方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(6): 1191-1198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190981WU Boqian, CAI Baigen, LU Debiao, et al. GNSS/INS based risk assessment in train localization[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1191-1198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190981 [28] 刘曙阳. CI 系统开发技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1997. [29] 刘颖,张丽娟,韩亚男,等. 基于粒子群协同优化算法的供应链金融信用风险评价模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版),2018,56(1): 119-125.LIU Ying, ZHANG Lijuan, HAN Yanan, et al. Financial credit risk evaluation model of supply chain finance based on particle swarm cooperative optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Science Edition), 2018, 56(1): 119-125. -




 下载:
下载: