Influence of Different Rail Cants on Dynamical Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Vehicles
-
摘要:
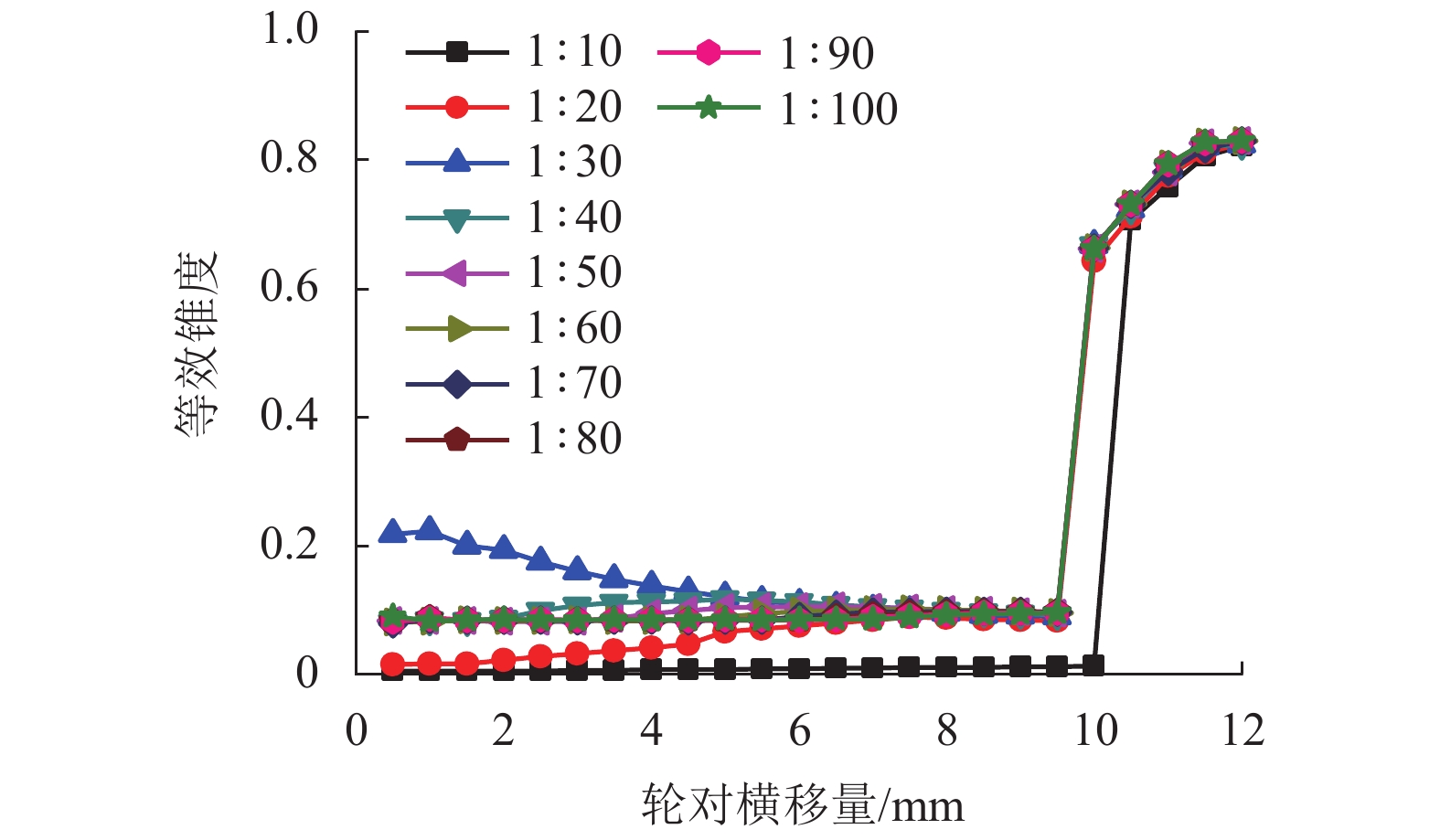
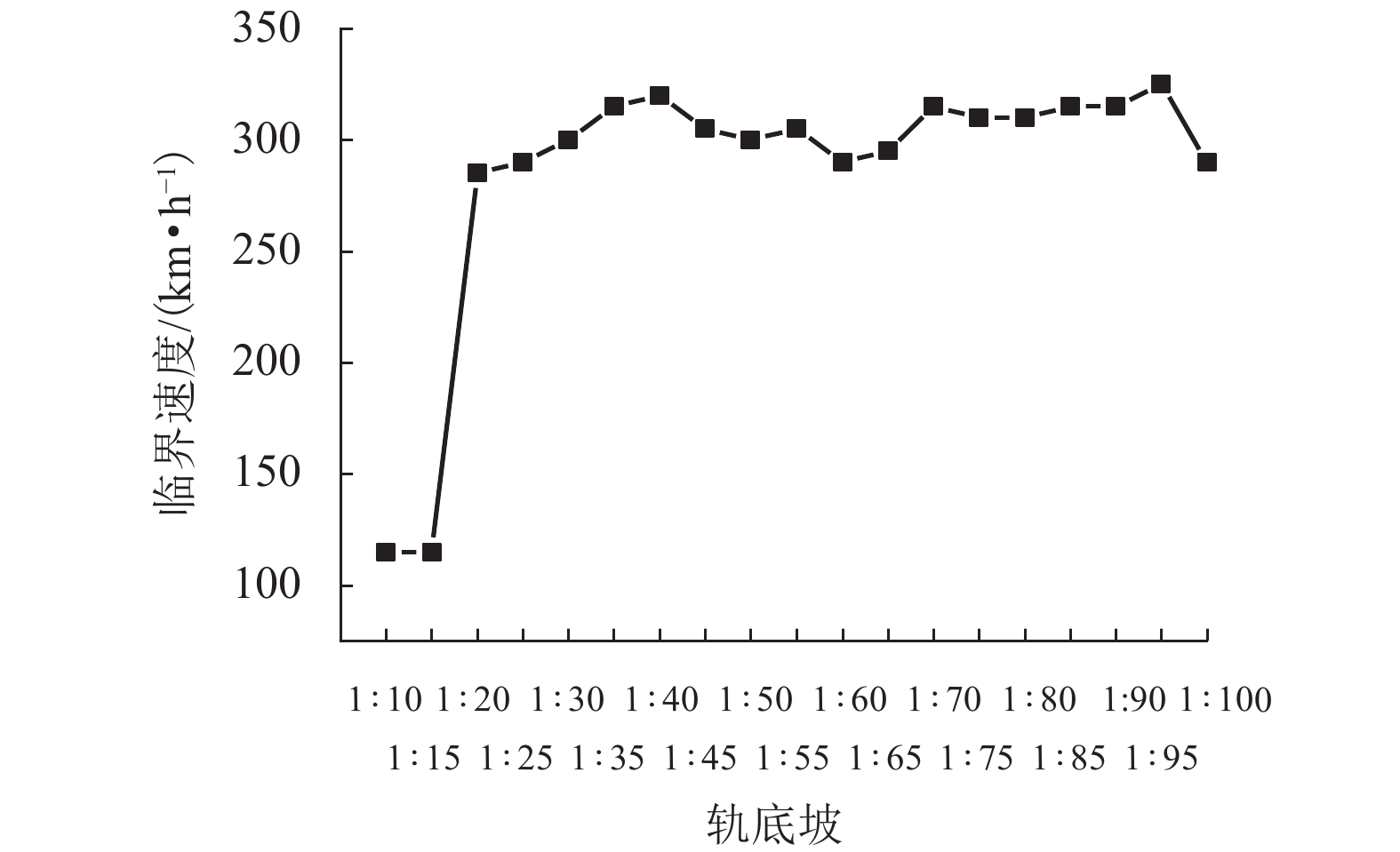
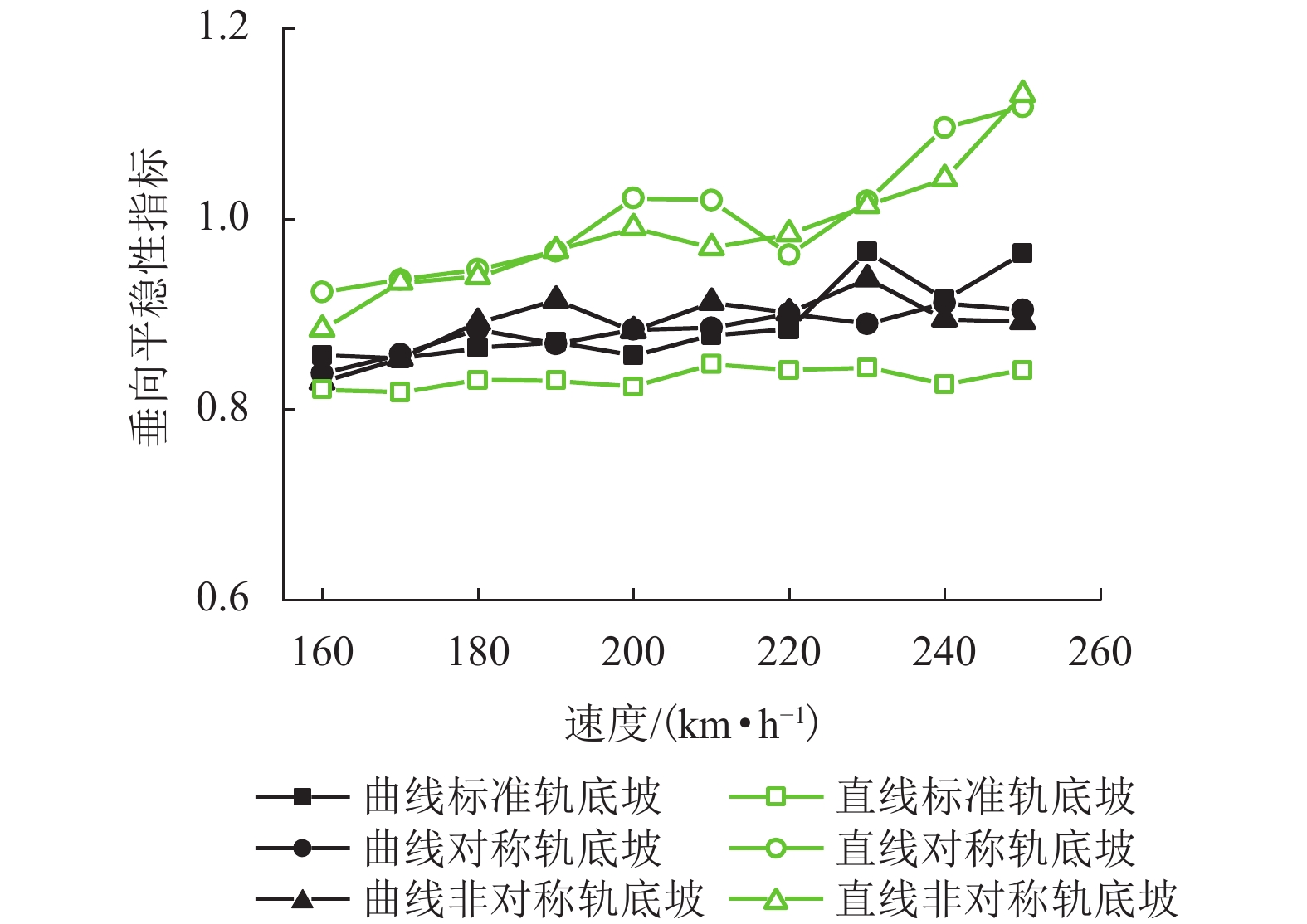
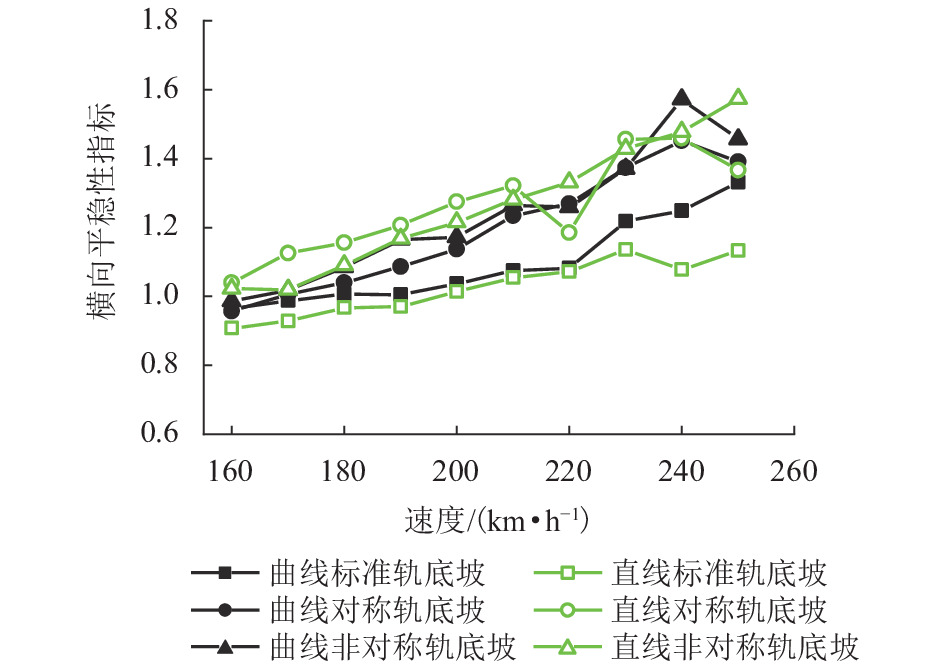
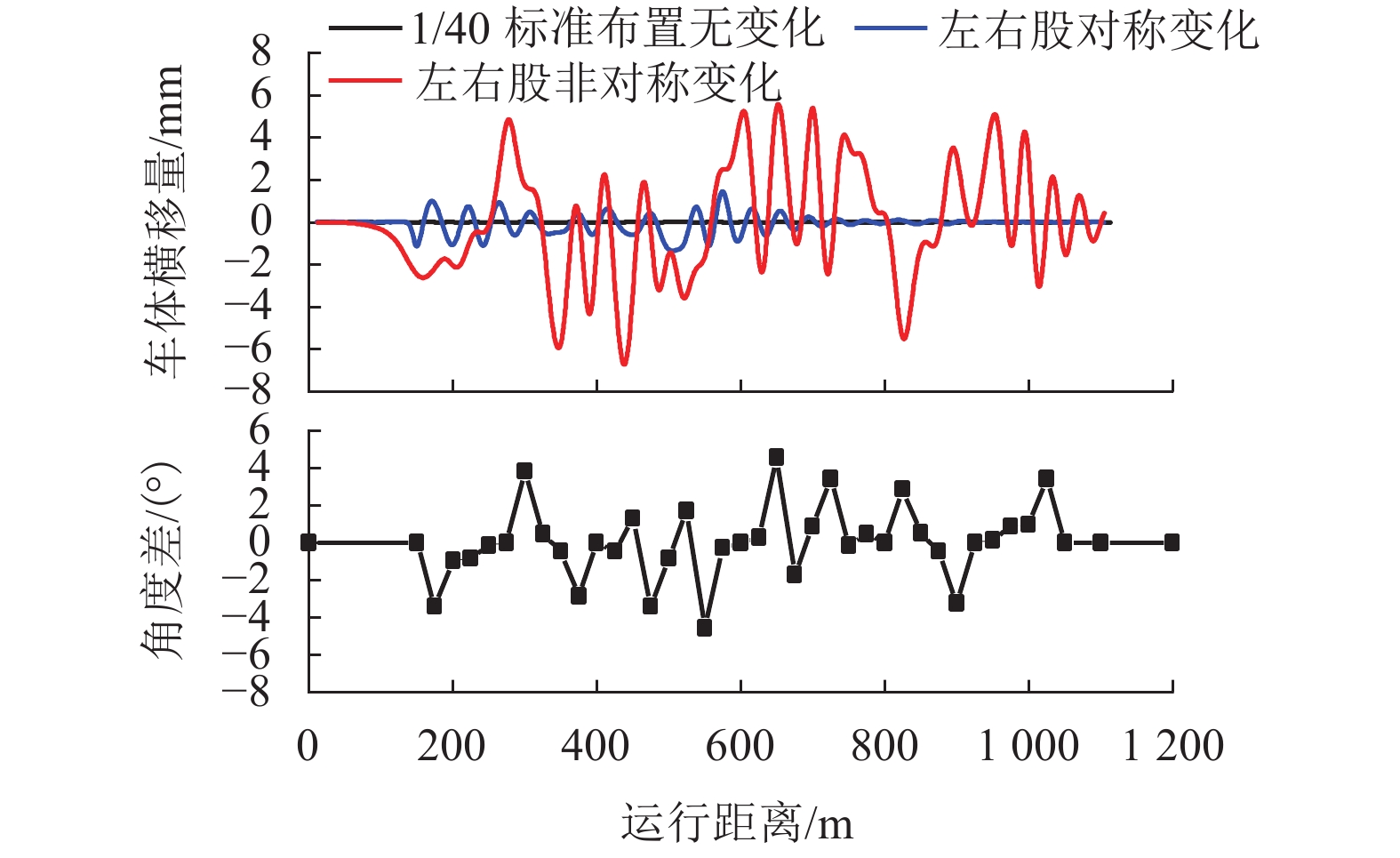
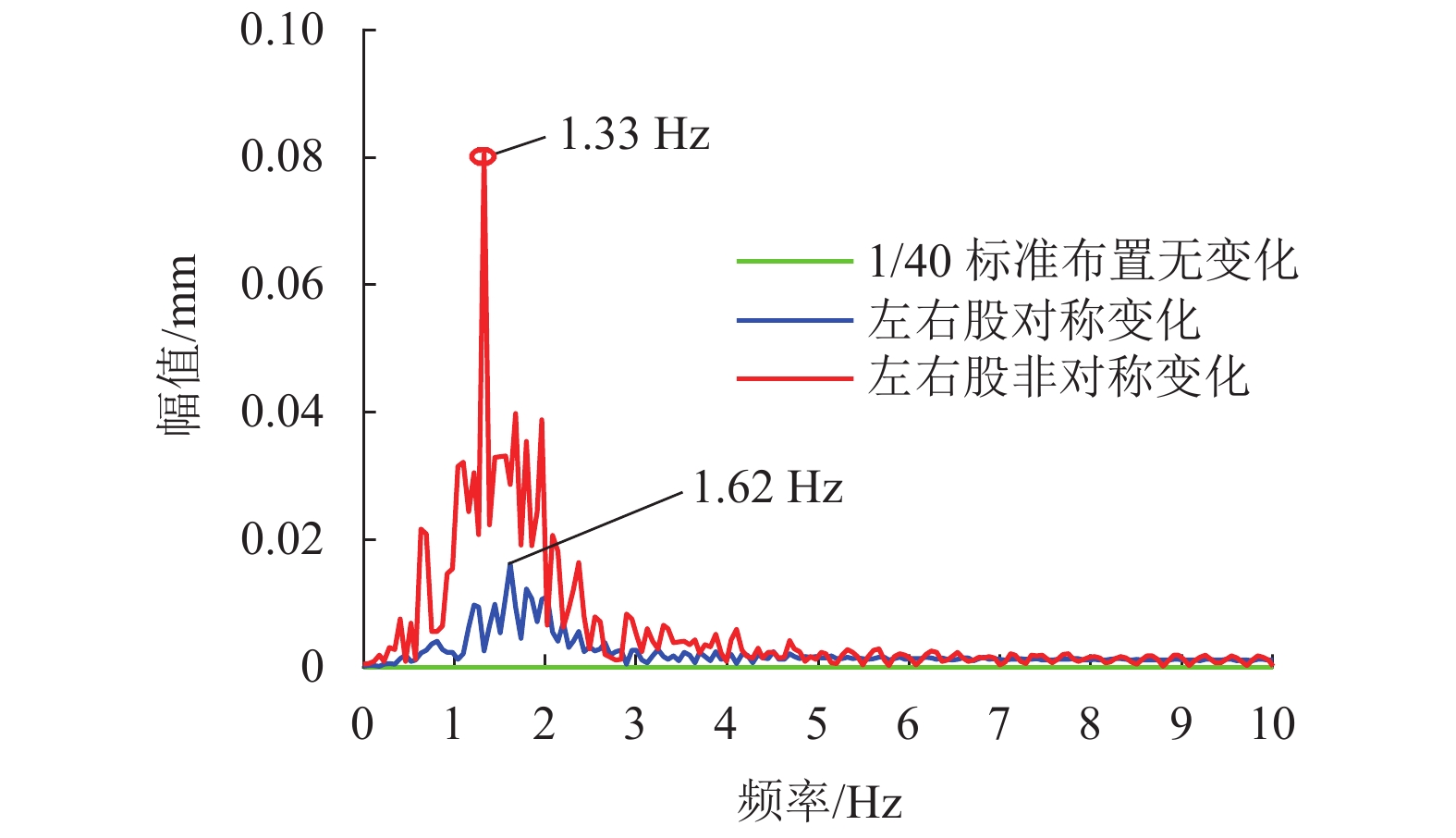
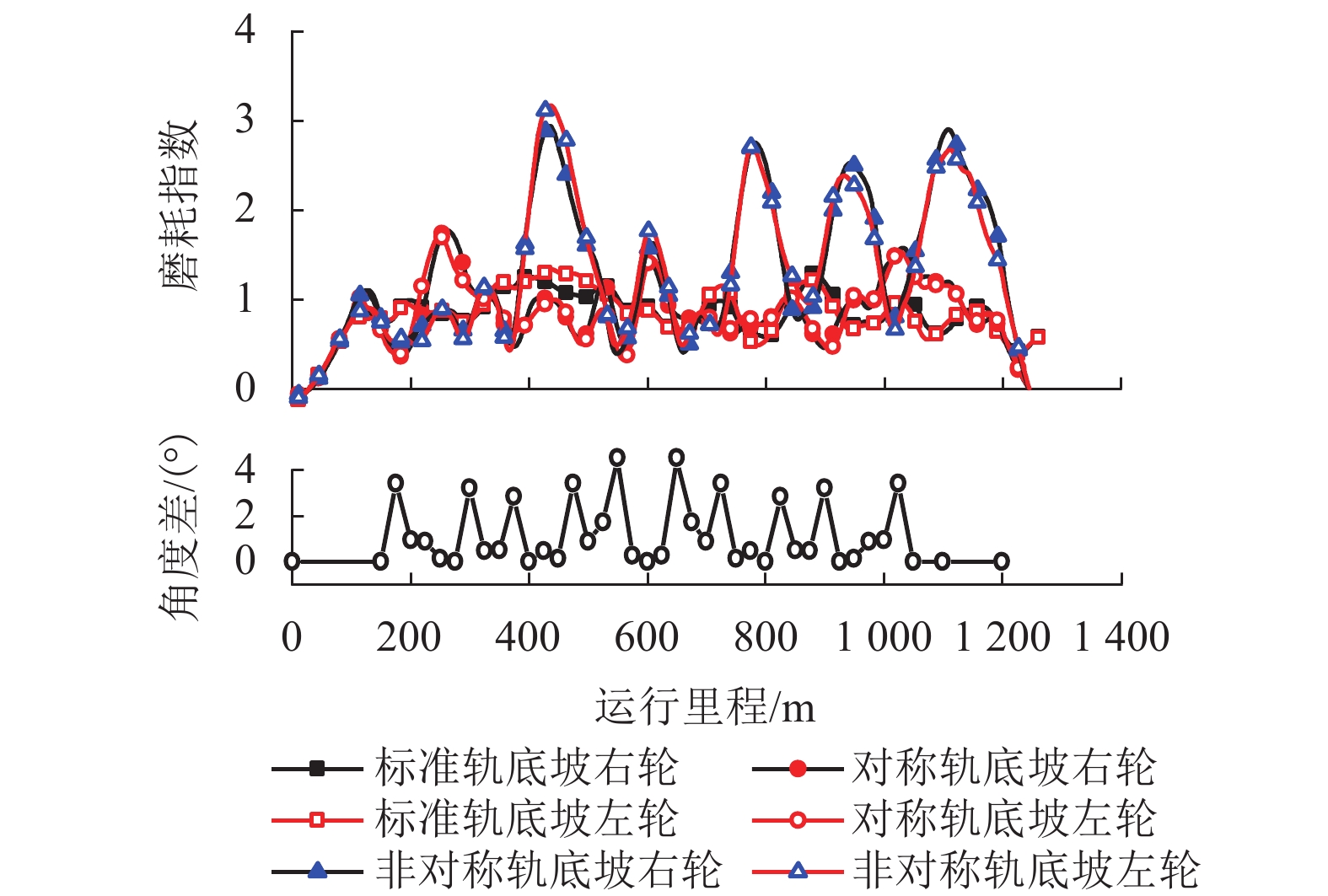
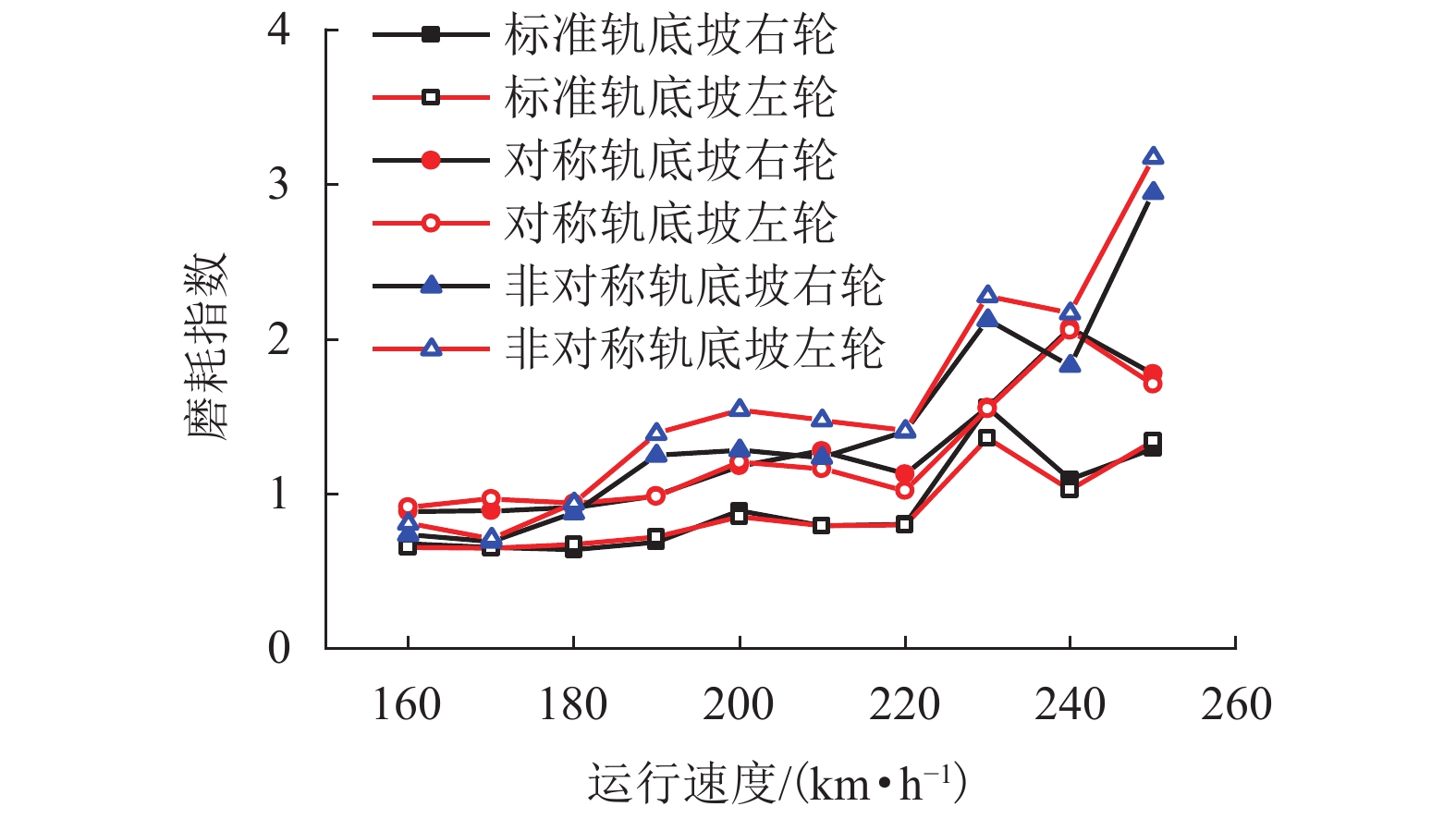
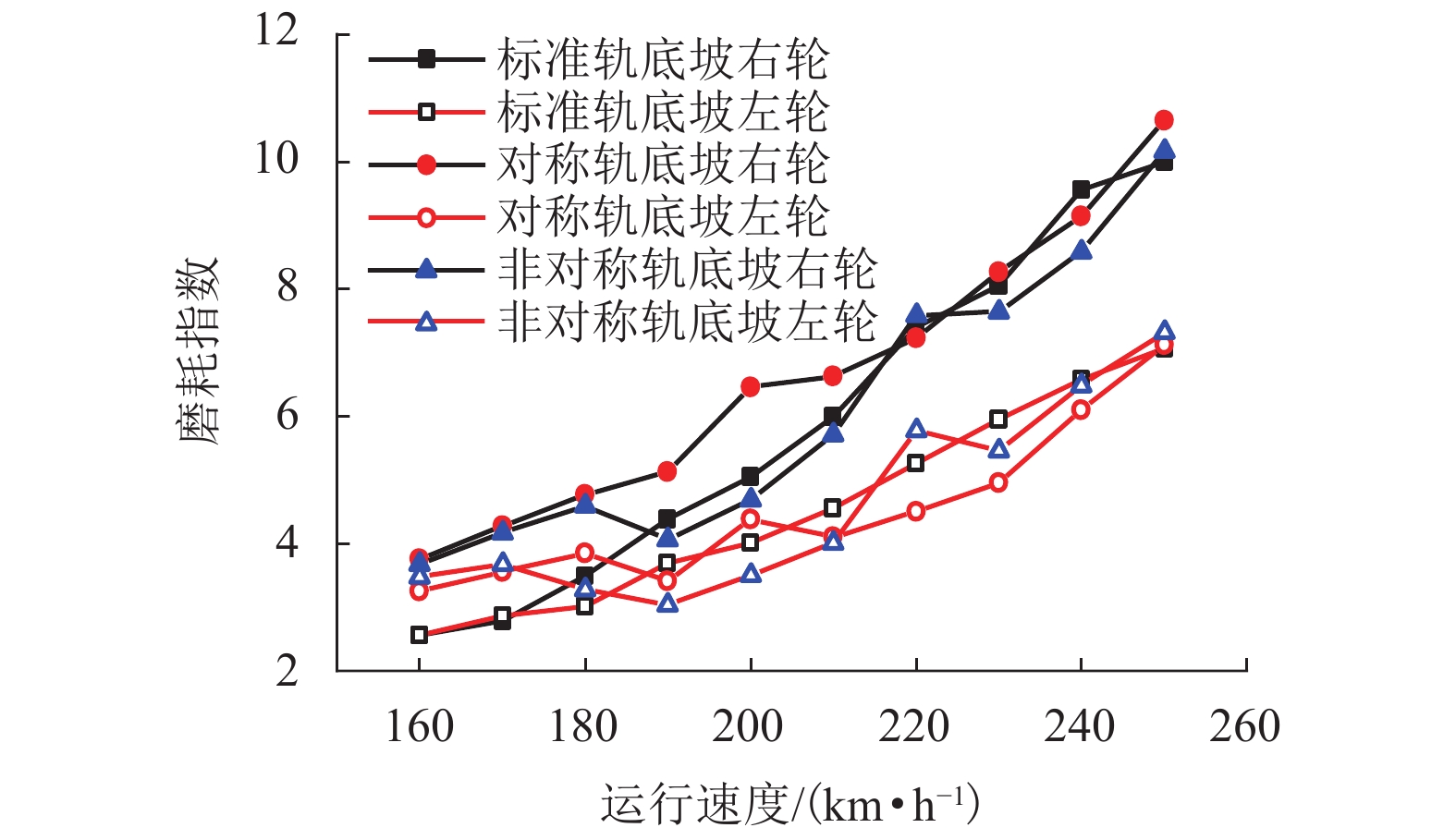
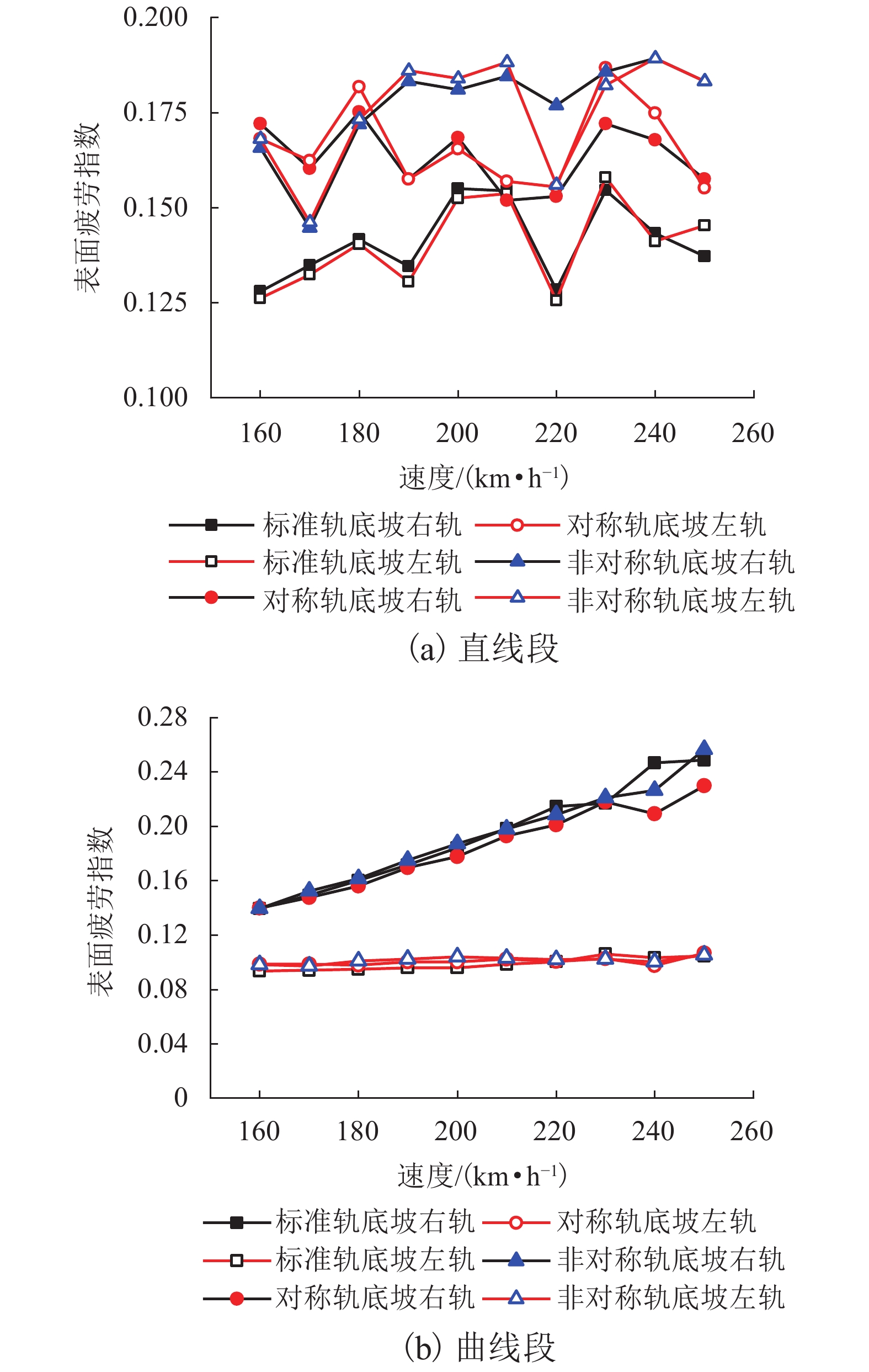
现有轨道精调和养护维修过程中往往只针对轨道的高低、方向、水平、扭曲等相关因素进行调整,对轨底坡的相关规定较少. 对现有客运专线同一轨道的一段区间进行轨底坡现场测量,发现轨底坡变化较大. 通过建立国内某时速250 km动车组车辆模型,考虑LMD车轮型面与标准60 kg/m (CHN60)钢轨匹配,分析了在同一轨道具有标准轨底坡(1∶40)、对称变化轨底坡和非对称变化实测轨底坡条件下的车辆动力学行为. 计算结果表明:轨底坡对称变化和非对称变化对车辆直线运行时的平稳性、舒适性影响很大,较标准轨底坡(1∶40)布置时车辆垂向平稳性指标分别增加了32.96%和34.52%,横向平稳性最大值增加了40.65%;直线段的标准、对称变化与非对称变化轨底坡布置对车轮的磨耗影响逐渐增大;直线段非对称、对称变化轨底坡情况较标准轨底坡最大磨耗指数分别增加136.71%和27.65%,最大表面损伤指数分别增加25.14%和15.86%. 车辆曲线通过对称变化与非对称变化轨底坡布置时,增大车辆横向晃动;曲线段轨底坡变化对车轮磨耗和疲劳指数相对于标准布置情况影响较小,但曲线段轨底坡变化对车轮磨耗和疲劳指数均大于直线段. 最后根据以上结论给出了针对轨底坡的工程化建议.
Abstract:In the process of fine adjustment, maintenance and repair to tracks, it is frequent to adjust only the height, direction, level, distortion and other relevant factors, but there are few relevant regulations on rail cants. It is found that the measured rail cants on a section of a passenger dedicated line vary greatly. By establishing a model of a 250 km/h EMU vehicle, given that the LMD wheel profile matches the standard 60 kg/m (CHN60) rail, the vehicle dynamic behavior is analyzed in the condition of the same track with standard (1∶40), symmetrically changing, and asymmetrically changing rail cants. The calculation results show that the symmetrical and asymmetric changes of the rail cant have a great impact on the stability and comfort of the vehicle when it runs in a straight line. Compared with the standard rail cant (1∶40), the symmetrically and asymmetrically changing rail cants increase vertical stability index by 32.96% and 34.52%, respectively, and the maximum lateral stability index by 40.65%. Wheel wear increases gradually with the sequence of the standard, symmetrical changing, and asymmetric changing rail cants. Compared with the standard rail cant, the asymmetrically and symmetrically changing rail cants on the straight section increases the maximum wear index by 136.71% and 27.65% respectively, and the maximum surface fatigue index by 25.14% and 15.86% respectively. For the symmetrically and asymmetrically changing rail cants, the vehicle lateral shaking is increased. In contrast to the standard rail cant, wheel wear and fatigue index on the curved section are less affected by the variation of rail cants, but they are more influenced on the curved section than those on the straight section. Finally, according to the above conclusions, the practical suggestions for rail cants are put forward.
-
Key words:
- dynamics of high-speed trains /
- rail cant /
- vehicle stability /
- surface fatigue index /
- wear
-
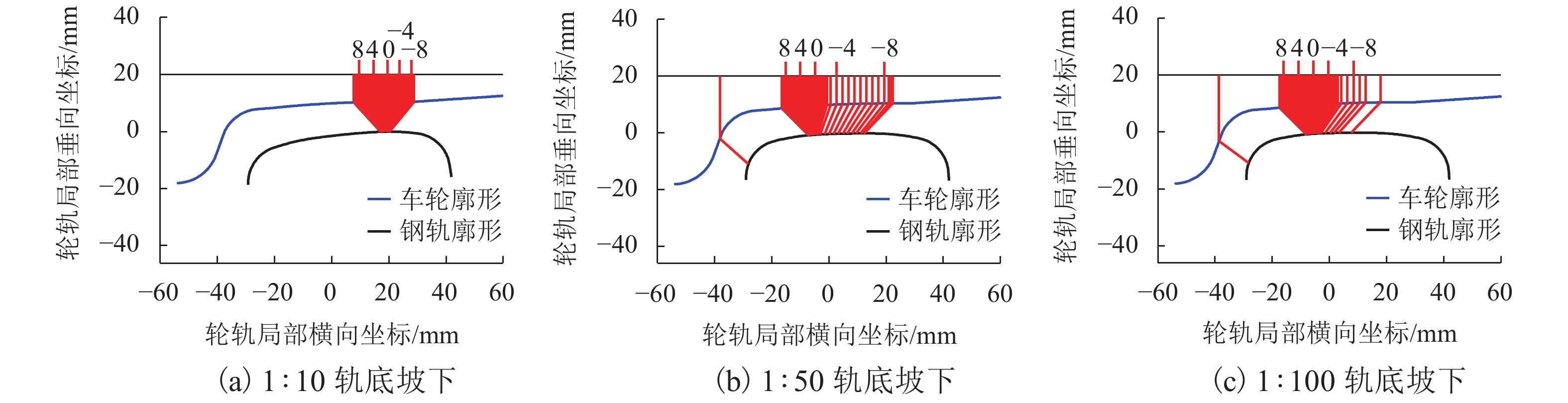
表 1 实测线路轨底坡
Table 1. Measured cants on tracks
距离 /m 曲/直线段 距离 /m 曲/直线段 左轨 左轨 左轨 左轨 0 1∶40 1∶40 625 1∶35 1∶30 150 1∶40 1∶40 650 1∶50 1∶10 175 1∶10 1∶25 675 1∶20 1∶50 200 1∶15 1∶20 700 1∶40 1∶25 225 1∶25 1∶40 725 1∶25 1∶10 250 1∶45 1∶50 750 1∶45 1∶50 275 1∶65 1∶65 775 1∶40 1∶30 300 1∶100 1∶15 800 1∶40 1∶40 325 1∶40 1∶30 825 1∶20 1∶10 350 1∶35 1∶50 850 1∶50 1∶35 375 1∶10 1∶20 875 1∶30 1∶40 400 1∶40 1∶40 900 1∶15 1∶100 425 1∶30 1∶40 925 1∶65 1∶65 450 1∶50 1∶45 950 1∶50 1∶45 475 1∶10 1∶25 975 1∶40 1∶25 500 1∶25 1∶40 1000 1∶20 1∶15 525 1∶50 1∶20 1025 1∶25 1∶10 550 1∶10 1∶50 1050 1∶40 1∶40 575 1∶30 1∶35 1100 1∶40 1∶40 600 1∶20 1∶20 1200 1∶40 1∶40 -
[1] 曾向荣,李文英,高晓新. 城市轨道交通工程钢轨轨底坡取值的探讨[J]. 都市快轨交通,2006,19(6): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2006.06.016ZENG Xiangrong, LI Wenying, GAO Xiaoxin. On the rail base inclination in urban rail transit project[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2006, 19(6): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2006.06.016 [2] 中国人民共和国铁道部. 铁路轨道设计规范: TB 10082—2005[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2005. [3] 陶功权,温泽峰,陆文教,等. 不同轨底坡下地铁车辆轮轨型面匹配的动力学分析[J]. 铁道学报,2016,38(5): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.05.003TAO Gongquan, WEN Zefeng, LU Wenjiao, et al. Dynamic analysis of wheel and rail profile matching relationship for metro vehicle under different rail cant conditions[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38(5): 16-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.05.003 [4] 陶功权,温泽峰,陆文教,等. 不同轨底坡下地铁车辆轮轨型面匹配的静态接触分析[J]. 铁道学报,2015,37(9): 82-89.TAO Gongquan, WEN Zefeng, LU Wenjiao, et al. Static contact analysis of matching relationship of metro vehicle wheel and rail profiles under different rail cant conditions[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(9): 82-89. [5] 陈超. 城市轨道交通曲线几何参数对行车性能的影响及优化[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015. [6] 周宇,王少锋,张杰,等. 轨底坡对曲线线路钢轨疲劳裂纹萌生寿命的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学,2015,36(1): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2015.01.04ZHOU Yu, WANG Shaofeng, ZHANG Jie, et al. Effect of rail cant on fatigue crack initiation life of curve rail[J]. China Railway Science, 2015, 36(1): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2015.01.04 [7] 都敏,张军,王春艳,等. 城市轨道交通线路轨底坡对钢轨磨耗的影响[J]. 铁道机车与动车,2014,484(6): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1820.2014.06.001 [8] 刘鹏飞,王开云,翟婉明,等. 30 t 轴重重载货车轮轨接触几何关系及动态匹配关系[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,27(9): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2013.09.005LIU Pengfei, WANG Kaiyun, ZHAI Wanming, et al. Investigation of wheel-rail contact geometry and dynamic matching for heavy freight wagon with 30 t axle load[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2013, 27(9): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2013.09.005 [9] 邓建辉,陈朝阳,邓勇,等. 轨底坡和轨头廓面对钢轨接触疲劳伤损的影响研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2011,51(8): 109-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2011.08.035 [10] 司道林,王继军,孟宏. 钢轨轨底坡对重载铁路轮轨关系影响的研究[J]. 铁道建筑,2010,435(5): 108-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2010.05.034 [11] 李霞,温泽峰,张剑,等. 轨底坡对轮轨滚动接触行为的影响[J]. 机械强度,2009,31(3): 475-480. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2009.03.026LI Xia, WEN Zefeng, ZHANG Jian, et al. Effect of rail cant on wheel/rail rolling contact behavior[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2009, 31(3): 475-480. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2009.03.026 [12] 关庆华,赵鑫,温泽峰,等. 基于 Hertz 接触理论的法向接触刚度计算方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(4): 883-890.GUAN Qinghua, ZHAO Xin, WEN Zefeng, et al. Calculation method of Hertz normal contact stiffness[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(4): 883-890. [13] 李霞,温泽峰,金学松. 钢轨轨底坡对LM和LMA两种轮对接触行为的影响[J]. 机械工程学报,2008,44(3): 64-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2008.03.011LI Xia, WEN Zefeng, JIN Xuesong. Effect of rail cant on the rolling contact behavior of LM and LMA wheelsets[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 44(3): 64-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2008.03.011 [14] 沈钢,张定贤. 轨底坡对曲线钢轨侧磨影响的研究[J]. 铁道学报,1994,16(3): 95-99.SHEN Gang, ZHANG Dingxian. Research on readjusting rail inclinations for reducing rail side-cutting[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1994, 16(3): 95-99. [15] SADEGHI J, FATHALI M, BOLOUKIAN N. Development of a new track geometry assessment technique incorporating rail cant factor[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2009, 223(3): 255-263. doi: 10.1243/09544097JRRT237 [16] 王开文. 车轮接触点迹线及轮轨接触几何参数的计算[J]. 西南交通大学学报,1984,19(1): 89-99.WANG Kaiwen. The track of wheel contact points and the calculation of wheel/rail geometric contact parameters[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1984, 19(1): 89-99. [17] 金学松, 刘启跃. 轮轨摩擦学[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2004: 9-43 [18] 王晨,罗世辉,邬平波,等. 动车组踏面凹型磨耗对车辆稳定性的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 84-91.WANG Chen, LUO Shihui, WU Pingbo, et al. Effect of hollow worn tread of electric multiple units on vehicle stability[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 84-91. [19] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 机车车辆动力学性能评定及试验鉴定规范: GB/T 5599—2019[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019. [20] International Union of Railways. Guidelines for evaluation passenger comfort in relation to vibration in railway vehicles: UIC 513: 1994[S]. Paris: Traction and Rolling Stock Committee, 1994. -




 下载:
下载: