Study on Validation Conditions of Rail Corrugation Prediction Models
-
摘要:
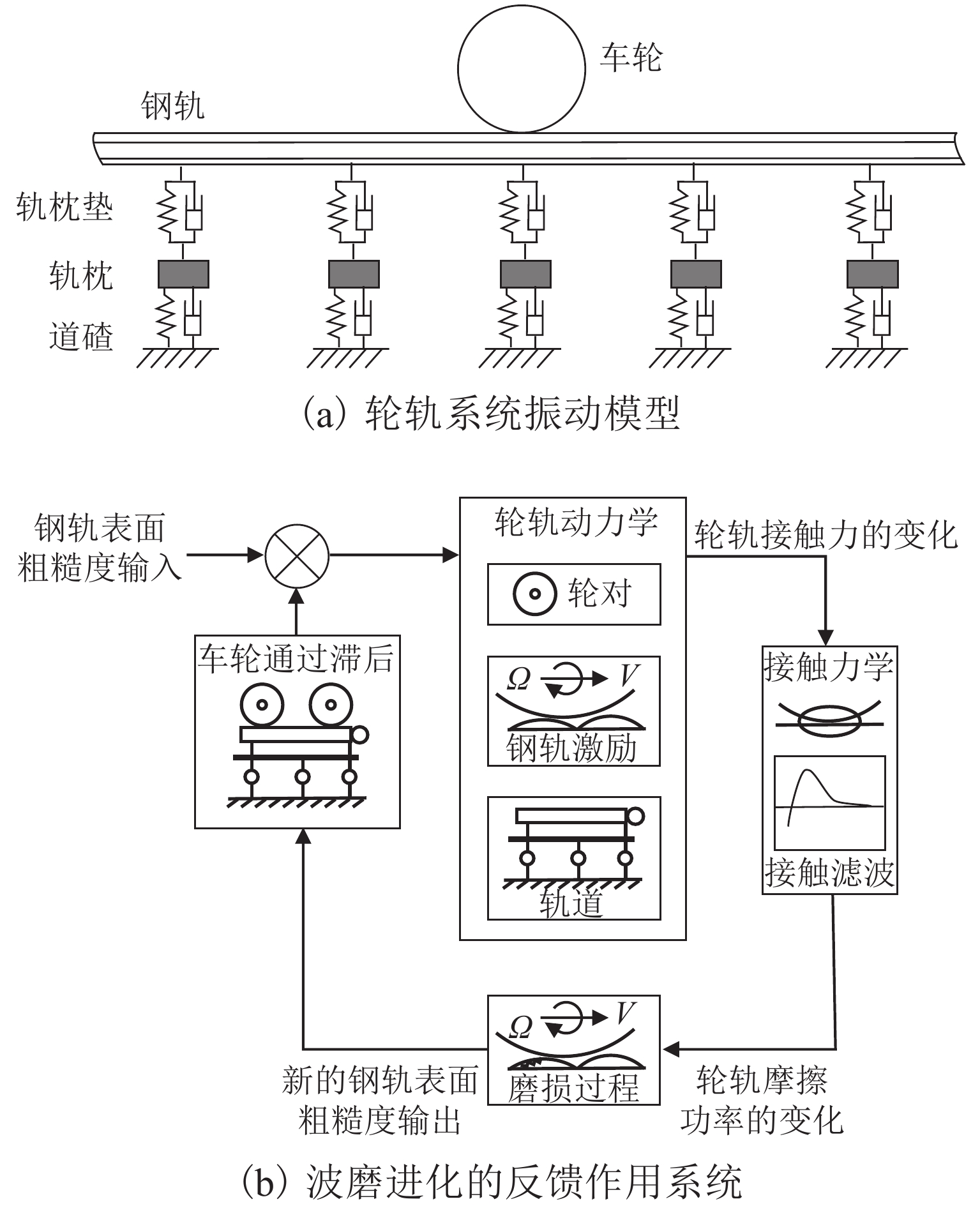
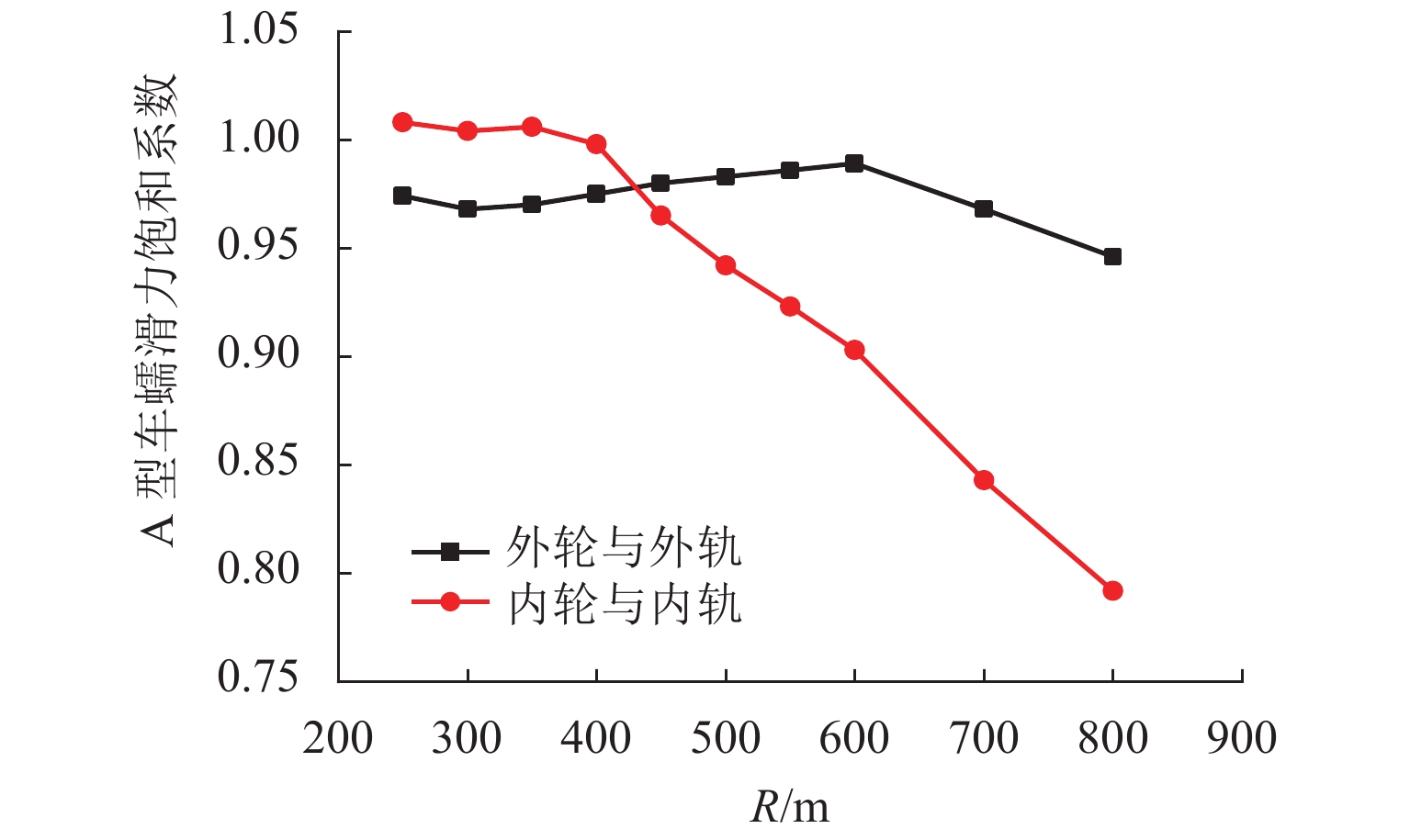
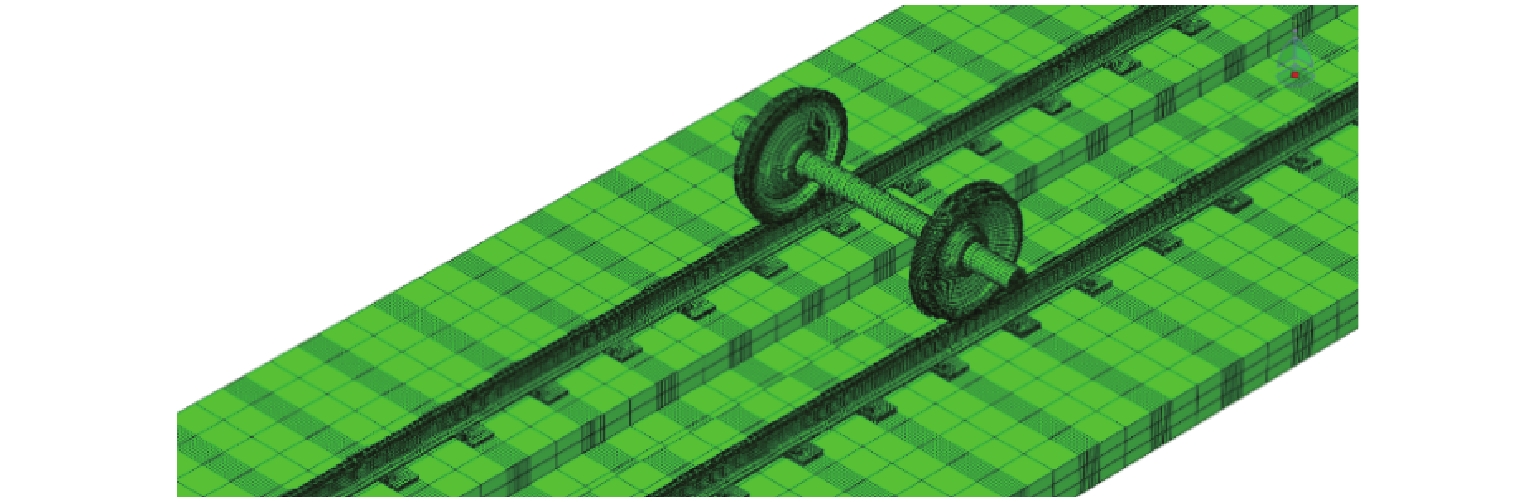
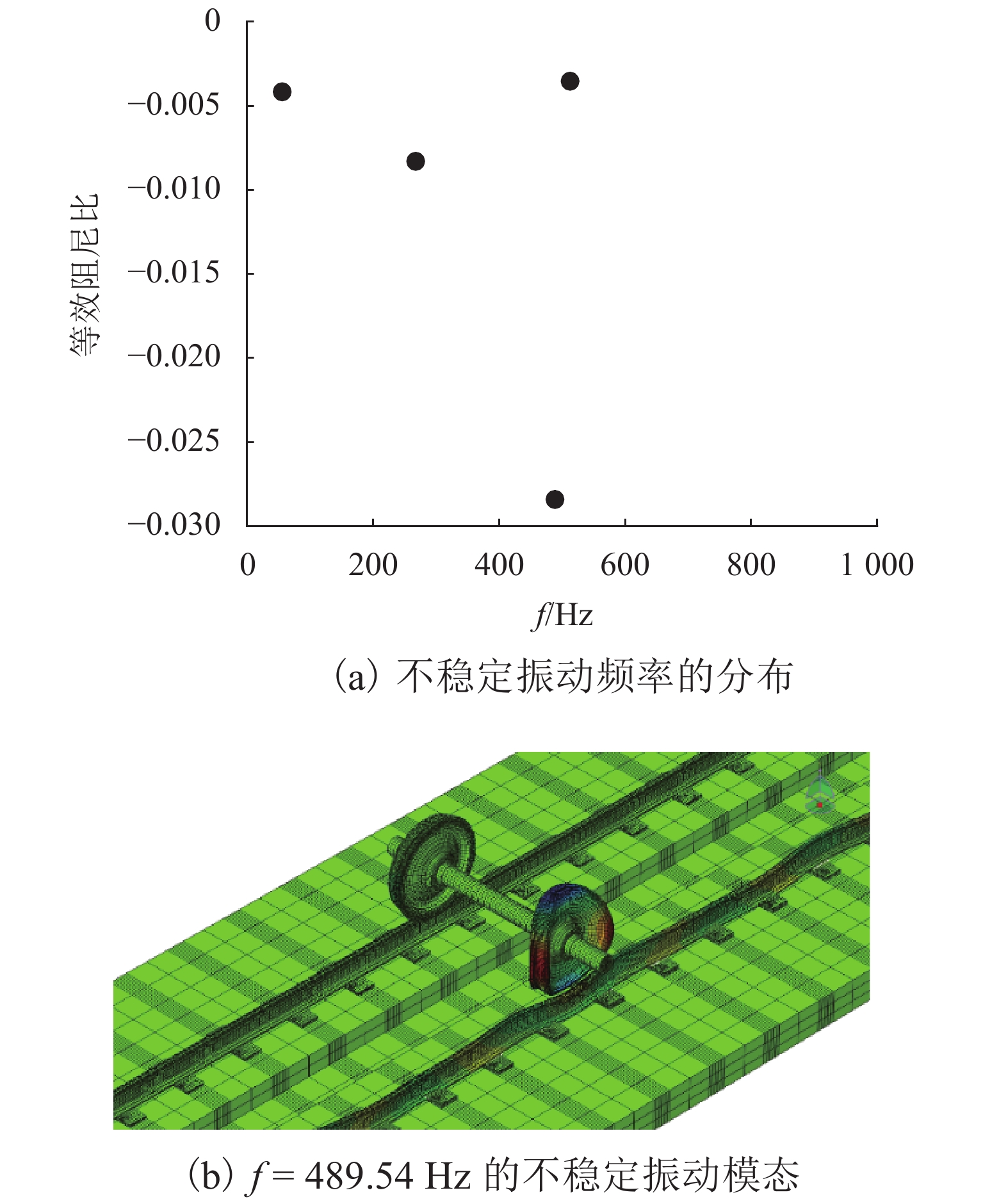
钢轨波磨会降低乘坐舒适性,增大轨道结构伤损,甚至影响列车的安全运行. 为判断钢轨波磨预测模型的准确性,首先,基于钢轨波磨现场调研数据,统计地铁线路和干线铁路的钢轨波磨发生率;其次,针对现有钢轨波磨预测模型验证方法的局限性,同时结合钢轨波磨发生的规律性,提出预测模型验证的3种基本工况:线路曲线半径≤350 m时的内轨波磨和外轨波磨、曲线半径 ≥ 650 m时的非科隆蛋扣件曲线线路或者直线线路钢轨的波磨,并进行实例验证;最后,根据基于轮轨蠕滑力饱和情况,提出了一种快速预测钢轨波磨发生的新方法. 研究结果表明:现有的波磨预测模型验证工况缺乏一般性,大部分没有考虑线路曲线半径的影响,忽视了从新轨到波磨出现阶段的钢轨振动演变规律,造成通过验证的波磨预测模型预测准确率偏低;所提出的波磨快速预测方法准确率可达到85.00%.
Abstract:Rail corrugation not only reduces the ride comfort of passengers, but also increases damages of tracks and vehicles, and even affects the safe operation of trains. In order to verify the correctness of rail corrugation prediction models, firstly the occurrence probability of rail corrugation was calculated based on field investigation data into a metro line and railway main-lines. Secondly, aiming to the shortcomings of the validation method of traditional rail corrugation prediction models, and based on the regularity of rail corrugation occurrence, the benchmark conditions for the verification of the rail corrugation prediction models were proposed, which include the first condition: rail corrugation on the low and high rails at a tight curved tracks whose radii are less than 350 m;the second condition: rail corrugation on the low and high rails at mild curved tracks whose radii are larger than 650 m without Colong-egg fasteners; the third condition: rail corrugation on the two rails of tangential tracks without Colong-egg fasteners. A case study on the prediction of rail corrugation on an actual metro line was performed. Finally, based on whether the creep force is saturated or not, a fast method for predicting rail corrugation was proposed. The research result shows that existing validation conditions for rail corrugation are not universal, that the traditional rail corrugation models neglect the effect of track radii; and that the rail vibration evolution from a new rail without corrugation to the rail with corrugation was ignored in the model validation procedure, which lead to a low model prediction accuracy of rail corrugation. The prediction accuracy of the proposed fast method for predicting rail corrugation reaches 85.00%.
-
Key words:
- rail corrugation /
- wear /
- model validation /
- friction coupling /
- self-excited vibration
-
-
[1] 钟掘, 蔡鹤皋, 郭东明, 等. 10000个科学难题——制造科学卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1194-1197 [2] GRASSIE S L. Rail corrugation: characteristics, causes, and treatments[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2009, 223(6): 581-596. doi: 10.1243/09544097JRRT264 [3] SATO Y, MATSUMOTO A, KNOTHE K. Review on rail corrugation studies[J]. Wear, 2002, 253(1/2): 130-139. [4] OOSTERMEIJER K H. Review on short pitch rail corrugation studies[J]. Wear, 2008, 265(9/10): 1231-1237. [5] JIN X S, WEN Z F, ZHANG W H, et al. Numerical simulation of rail corrugation on a curved track[J]. Computers & Structures, 2005, 83(25/26): 2052-2065. [6] WANG Y R, WU T X. The growth and mitigation of rail corrugation due to vibrational interference between moving wheels and resilient track[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(8): 1257-1284. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2019.1616099 [7] ZHANG H G, LIU W N, LIU W F, et al. Study on the cause and treatment of rail corrugation for Beijing metro[J]. Wear, 2014, 317(1/2): 120-128. [8] 任彤,王安斌,王志强,等. 小半径曲线段钢轨短波波磨的影响因素分析[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2018,38(6): 105-108,112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2018.06.020REN Tong, WANG Anbin, WANG Zhiqiang, et al. Analysis of influencing factors on rail corrugation in small radius curved tracks[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2018, 38(6): 105-108,112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2018.06.020 [9] CHEN G X, ZHOU Z R, OUYANG H, et al. A finite element study on rail corrugation based on saturated creep force-induced self-excited vibration of a wheelset-track system[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2010, 329(22): 4643-4655. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2010.05.011 [10] 肖宏,陈鑫,赵越. 基于摩擦自激理论的单侧钢轨波磨机理分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(1): 83-89,119.XIAO Hong, CHEN Xin, ZHAO Yue. Analysis of unilateral rail corrugation mechanism based on friction self-excited theory[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(1): 83-89,119. [11] BESHBICHI O E, WAN C, BRUNI S, et al. Complex eigenvalue analysis and parameters analysis to investigate the formation of railhead corrugation in sharp curves[J]. Wear, 2020, 450/451: 203150.1-203150.10. [12] FOURIE D, FRÖHLING R, HEYNS S. Railhead corrugation resulting from mode-coupling instability in the presence of veering modes[J]. Tribology International, 2020, 152: 106499.1-106499.12. [13] 陈光雄, 陈若茜, 闫硕, 等. 一种能够明显减少钢轨波磨的铁路车轮: 中国, CN107415575B[P]. 2020-05-15. [14] 刘志伟,刘建新,蔡久凤. 钢轨波磨激励下重载机车振动响应分析[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2020,40(5): 119-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2020.05.020LIU Zhiwei, LIU Jianxin, CAI Jiufeng. Vibration response analysis of heavy haul locomotives excited by rail corrugation[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2020, 40(5): 119-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2020.05.020 [15] 王平,刘奕斌,高原,等. 表面选区强化对钢轨波磨处轮轨滚动接触行为的影响[J]. 铁道学报,2020,42(5): 105-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.05.014WANG Ping, LIU Yibin, GAO Yuan, et al. A study on influence of surface strengthening on wheel-rail rolling contact behavior at rail corrugation[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(5): 105-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2020.05.014 [16] 金锋,肖宏,赵越,等. 重载铁路小半径曲线波磨演化过程实测分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2021,65(5): 49-54.JIN Feng, XIAO Hong, ZHAO Yue, et al. Measurement and analysis of the evolution process of small radius curve corrugation in heavy haul railway[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2021, 65(5): 49-54. [17] 李响,任尊松,徐宁. 地铁小半径曲线段钢弹簧浮置板轨道的钢轨波磨研究[J]. 铁道学报,2017,39(8): 70-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2017.08.010LI Xiang, REN Zunsong, XU Ning. Study on rail corrugation of steel spring floating slab track on subway with small radius curve track[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2017, 39(8): 70-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2017.08.010 [18] 雷震宇,王志强,李莉,等. 地铁普通扣件钢轨波磨特性[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(9): 1334-1340. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2019.09.014LEI Zhenyu, WANG Zhiqiang, LI Li, et al. Rail corrugation characteristics of the common fastener track in metro[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2019, 47(9): 1334-1340. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2019.09.014 [19] 尧辉明,沈钢,高利君. 基于试验验证的磨耗型钢轨波磨形成机理[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(10): 1427-1432. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.10.015YAO Huiming, SHEN Gang, GAO Lijun. Formation mechanism of worn profile rail corrugation based on experimental verification[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(10): 1427-1432. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2018.10.015 [20] 于淼. 高速铁路轨道-车辆系统高频瞬态仿真及波磨机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2019. [21] TASSILLY E, VINCENT N. A linear model for the corrugation of rails[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1991, 150(1): 25-45. doi: 10.1016/0022-460X(91)90400-E [22] HEMPELMANN K, KNOTHE K. An extended linear model for the prediction of short pitch corrugation[J]. Wear, 1996, 191(1/2): 161-169. [23] IGELAND A, ILIAS H. Rail head corrugation growth predictions based on non-linear high frequency vehicle/track interaction[J]. Wear, 1997, 213(1/2): 90-97. [24] SUDA Y, HANAWA M, OKUMURA M, et al. Study on rail corrugation in sharp curves of commuter line[J]. Wear, 2002, 253(1/2): 193-198. [25] TORSTENSSON P T, SCHILKE M. Rail corrugation growth on small radius curves—measurements and validation of a numerical prediction model[J]. Wear, 2013, 303(1/2): 381-396. [26] HIENSCH M, NIELSEN J C O, VERHEIJEN E. Rail corrugation in The Netherlands—measurements and simulations[J]. Wear, 2002, 253(1/2): 140-149. [27] TASSILLY E, VINCENT N. Rail corrugations: analytical model and field tests[J]. Wear, 1991, 144(1/2): 163-178. [28] CORREA N, VADILLO E G, SANTAMARIA J, et al. A versatile method in the space domain to study short-wave rail undulatory wear caused by rail surface defects[J]. Wear, 2016, 352/353: 196-208. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2016.02.012 [29] 陈光雄,崔晓璐,王科. 高速列车车轮踏面非圆磨耗机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 244-250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.004CHEN Guangxiong, CUI Xiaolu, WANG Ke. Generation mechanism for plolygonalization of wheel treads of high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 244-250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.004 -





 下载:
下载: