Mechanism Investigation on Lateral Displacement Resistance of Diagrid Structures in High-Rise Buildings
-
摘要:
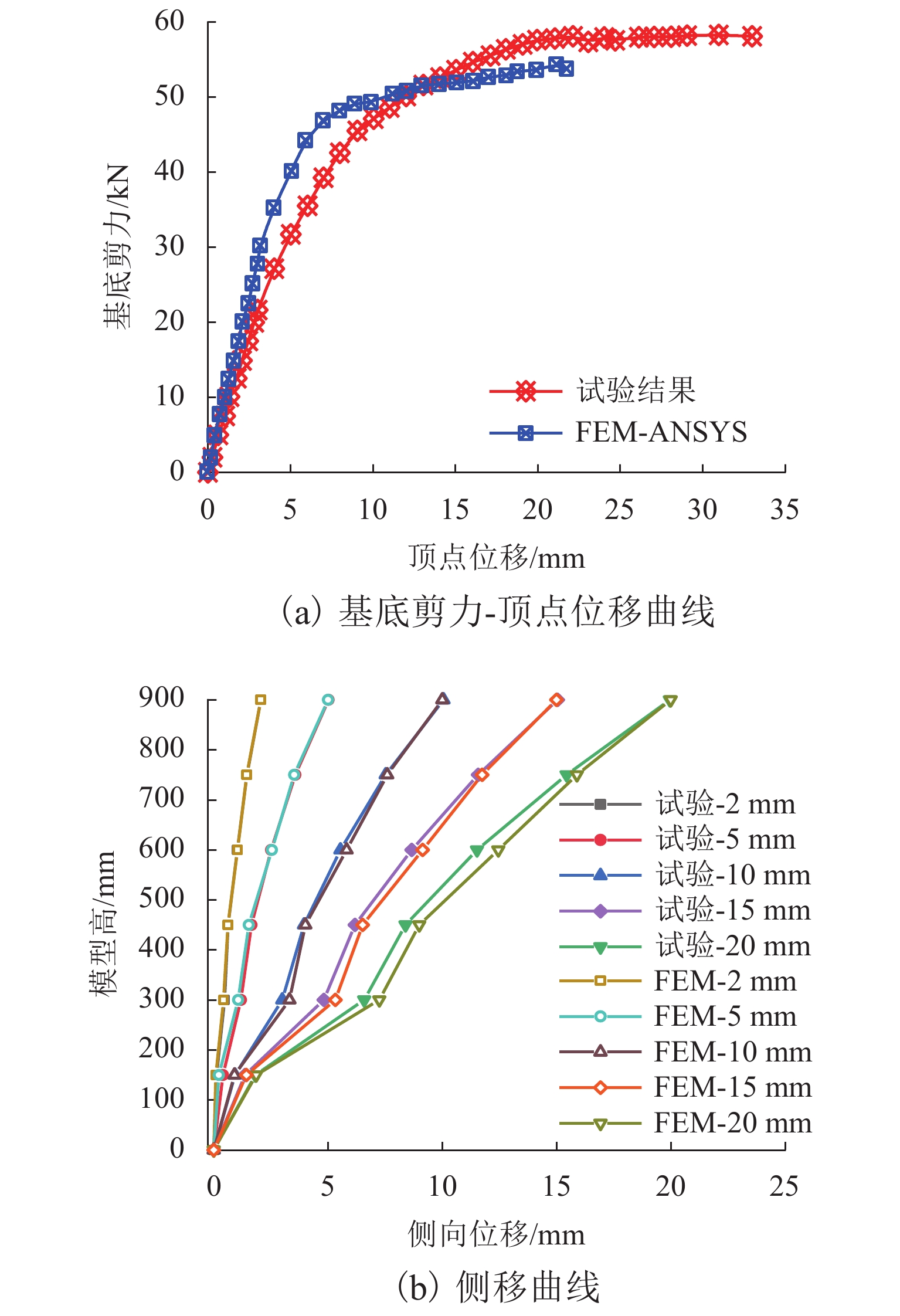
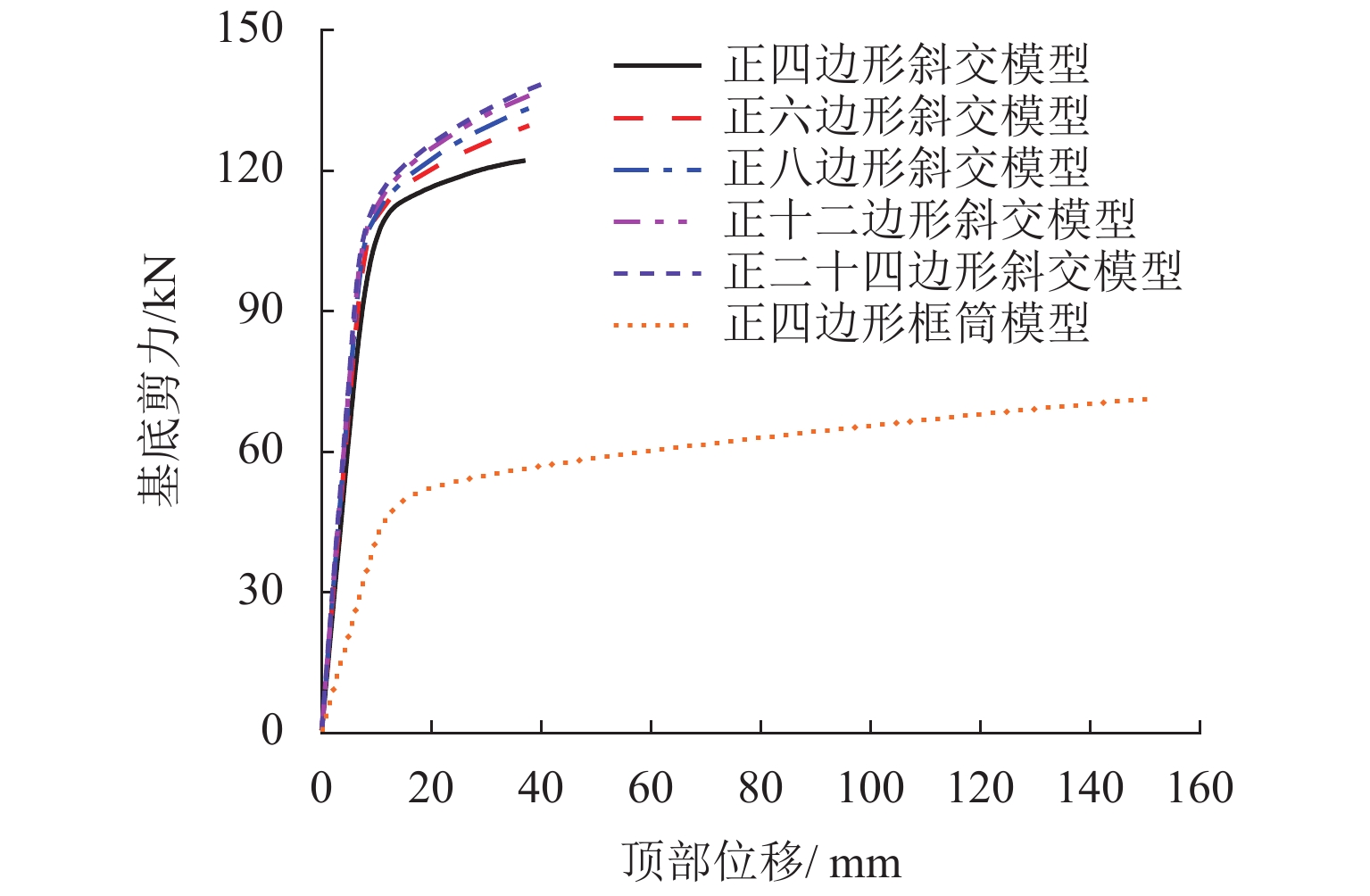
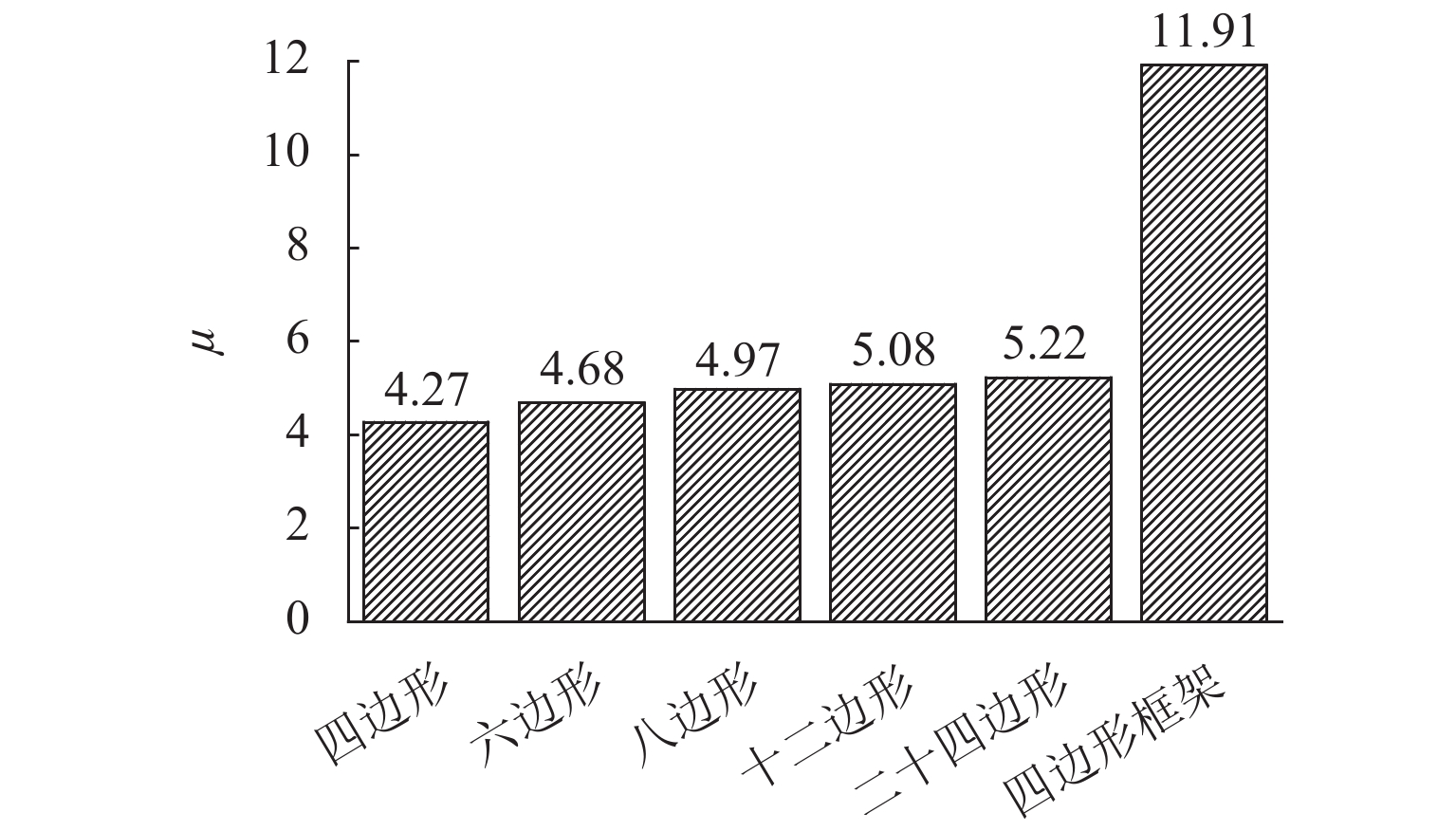
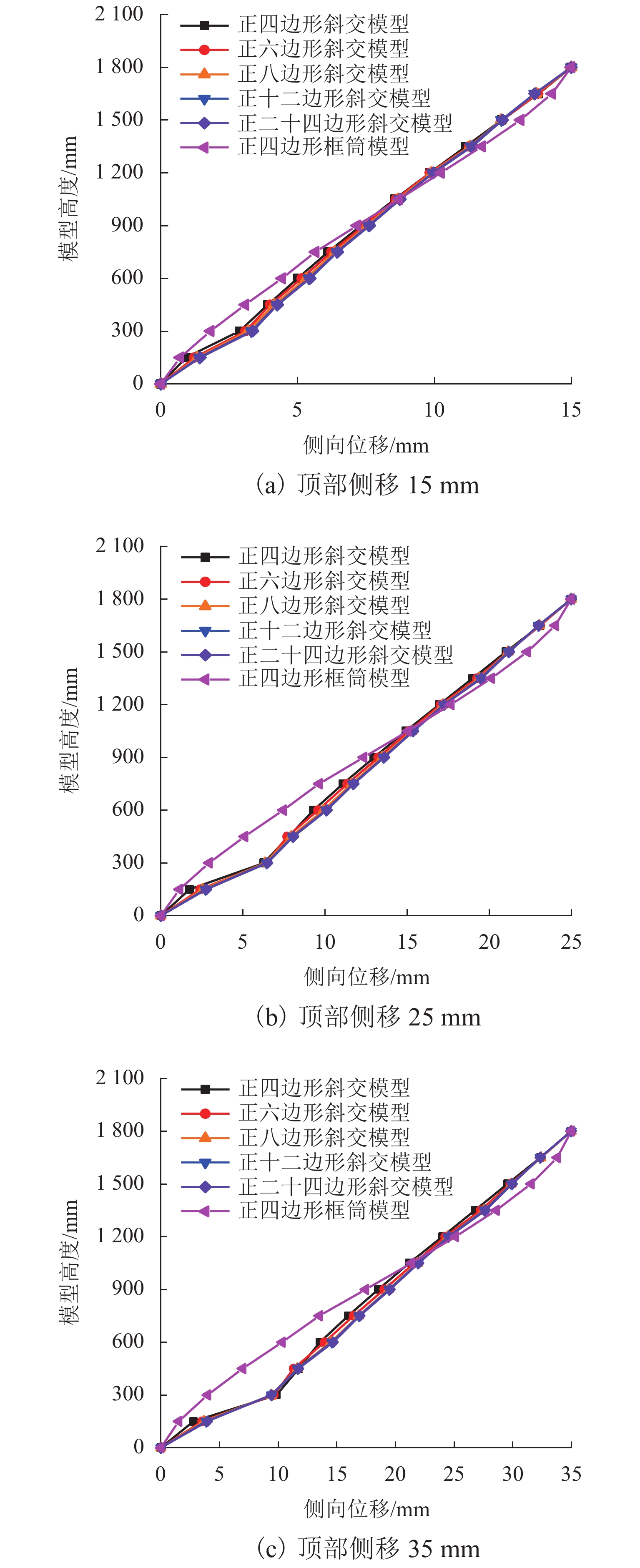
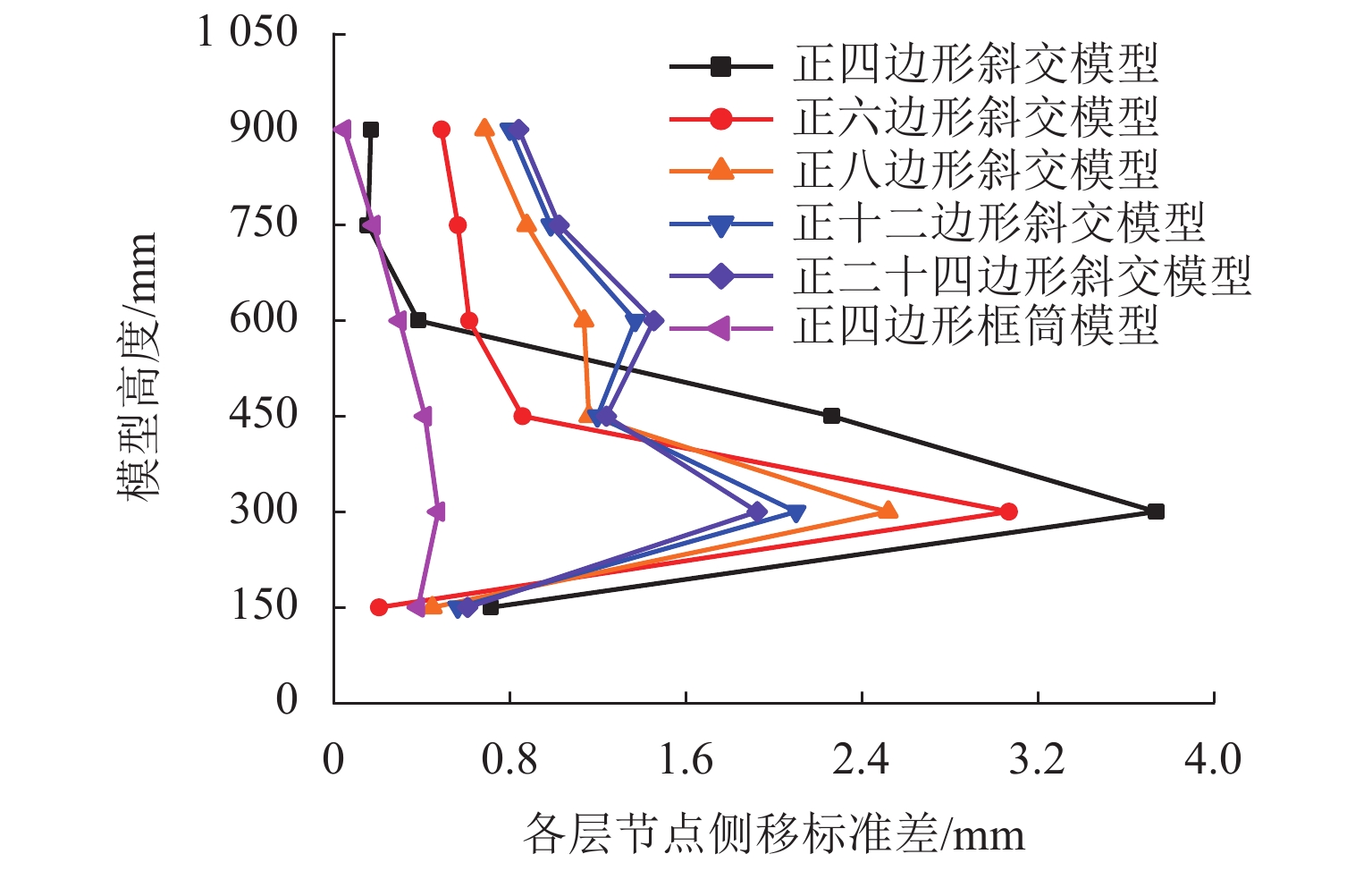
为研究不同平面形式对高层建筑斜交网格结构受力性能及刚度退化的影响,开展了正八边形斜交网格结构模型的水平推覆试验,建立了平面形式为四边形、六边形、八边形、十二边形和二十四边形的斜交网格结构,并与四边形框筒结构模型进行对比,分析了平面形式对斜交网格结构侧向刚度、延性、内力、剪力滞后和屈服顺序等影响. 研究结果表明:不同平面形式斜交网格结构模型的延性系数分布范围为4.27~5.22,随着结构平面边数增加,整体抗侧刚度逐渐增加,且延性越好,受力机理越合理;由于斜交网格结构主要通过斜柱传递轴力,剪力滞后效应明显比框筒结构小,随着平面边数增加,斜交网格结构受压翼缘部的剪力滞比由1.32降为0.82,平面形式为正六边形、正八边形、正十二边形、正二十四边形的斜交网格结构均较平面形式为正四边形时更接近于1.00;在斜交网格结构的水平推覆试验过程中,翼缘部与腹部相交区域的斜柱先屈服,塑性变形增大,再向翼缘部与腹部中部延展,随后沿结构底部向上扩展.
Abstract:In order to study the effects of various plane forms on the mechanical performance and stiffness degradation of diagrid outer tube structures, the numerical model of a regular octagonal diagrid structure is verified by the hor-izontal pushover test. Diagrid structures with plane forms of quadrilateral, hexagon, octagon, dodecagon, and icosikaitera (24-gon) are further established. Compared with the quadrilateral framed tube structure model, the effects of plane forms on the lateral stiffness, ductility, internal force, shear lag and yield order are analyzed. Results show that the distribution range of ductility coefficient of various plane diagrid structure models is 4.27–5.22. With the number of plane edges increasing, the overall lateral stiffness increases gradually, and the better the ductility, the more reasonable the stress mechanism. In addition, since the axial force is mainly transmitted through tilted columns in diagrid structures, the shear lag effect of diagrid structures is obviously smaller than that of the frame tube structure. With the increase of the number of plane edges, the shear lag ratio of the compression flange of the diagrid structures decreases from 1.32 to 0.82. The shear lag ratio of diagrid structures with plane forms of regular hexagon, regular octagon, regular dodecagon and regular 24-gon is closer to 1.00 than that with the plane form of regular quadrilateral. In the horizontal pushover test of diagrid structures, the yield first occurred to the tilted column in the intersection area between the flange and the web with increased plastic deformation, then extended to the flange and the middle of web, and finally extended upward from the structure bottom.
-
Key words:
- high-rise buildings /
- grid structure /
- pushover test /
- ductility /
- shear lag /
- yield sequence /
- seismic performance
-
表 1 翼缘部受压区各阶段剪力滞比
Table 1. Shear lag ratios of each stage incompression zone of flange
模型 斜交
角度/(°)平面
边数水平荷载/ kN 30 50 100 四边形 68 4 1.32 1.35 1.15 六边形 68 6 1.04 1.04 0.80 八边形 68 8 0.82 0.81 0.86 十二边形 68 12 0.83 0.82 0.78 二十四边形 68 24 0.83 0.82 0.76 四边形框筒 90 4 2.87 3.06 -
[1] 吕西林, 施卫星, 刘成清, 等. 广州珠江新城西塔模型振动台试验研究[C]// 第十一届高层建筑抗震技术交流会. 昆明: [出版者不详], 2007: 220-226. [2] SCARAMOZZINO D, LACIDOGNA G, CARPINTERI A. New trends towards enhanced structural efficiency and aesthetic potential in tall buildings: the case of diagrids[J]. Applied Sciences-Basel, 2020, 10(11): 3917. [3] 郭伟亮,滕军. 超高建筑斜交网格筒力学性能研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版),2010,42(2): 174-179. doi: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2010.02.025GUO Weiliang, TENG Jun. Mechanical property research on high-rise diagrid tube[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 42(2): 174-179. doi: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2010.02.025 [4] 韩小雷,唐剑秋,黄艺燕,等. 钢管混凝土巨型斜交网格筒体结构非线性分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2009,29(4): 77-84. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2009.04.025HAN Xiaolei, TANG Jianqiu, HUANG Yiyan, et al. Nonlinear analysis of huge oblique crossing lattice structure with concrete filled steel tube[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2009, 29(4): 77-84. doi: 10.13197/j.eeev.2009.04.025 [5] 刘成清,廖文翔,方登甲,等. 高层建筑斜交网格筒结构抗侧移性能及弹塑性分析[J]. 工业建筑,2020,50(11): 57-64. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzG20010811LIU Chengqing, LIAO Wenxiang, FANG Dengjia, et al. Lateral displacement resistance and elastic-plastic analysis of diagrid core-tube structure in high-rise buildings[J]. Industrial Construction, 2020, 50(11): 57-64. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzG20010811 [6] 张崇厚,赵丰. 高层网筒结构体系的基本概念[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2008,48(9): 1399-1403. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2008.09.007ZHANG Chonghou, ZHAO Feng. Grid tube structures in tall buildings[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2008, 48(9): 1399-1403. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2008.09.007 [7] 周健,汪大绥. 高层斜交网格结构体系的性能研究[J]. 建筑结构,2007,37(5): 87-91. doi: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2007.05.021ZHOU Jian, WANG Dasui. Performance research on high-rise diagonal frame structure[J]. Building Structure, 2007, 37(5): 87-91. doi: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2007.05.021 [8] 江琦. 斜交网格结构伪静力试验及其节点力学性能研究[D]. 深圳: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012. [9] 史庆轩,任浩,戎翀. 高层斜交网格筒结构体系剪力滞后效应研究[J]. 建筑结构,2016,46(4): 1-7. doi: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2016.04.001SHI Qingxuan, REN Hao, RONG Chong. Research of shear lag effect on high-rise diagrid tube structural system[J]. Building Structure, 2016, 46(4): 1-7. doi: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2016.04.001 [10] LEONARD J. Investigation of shear lag effect in high-rise buildings with diagrid system[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2007. [11] 段苏栗. 高层建筑斜交网格筒结构延性影响因素研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019. [12] SHI Q X, ZHANG F. Simplified calculation of shear lag effect for high-rise diagrid tube structures[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2019, 22: 486-495. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2019.01.009 [13] SINGH Y, NAGPAL A K. Negative shear lag in framed-tube buildings[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1994, 120(11): 3105-3121. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1994)120:11(3105) -





 下载:
下载: