Power Distribution Method of Multi-Stack Fuel Cell System Based on Forgetting Factor Recursive Least Square
-
摘要:
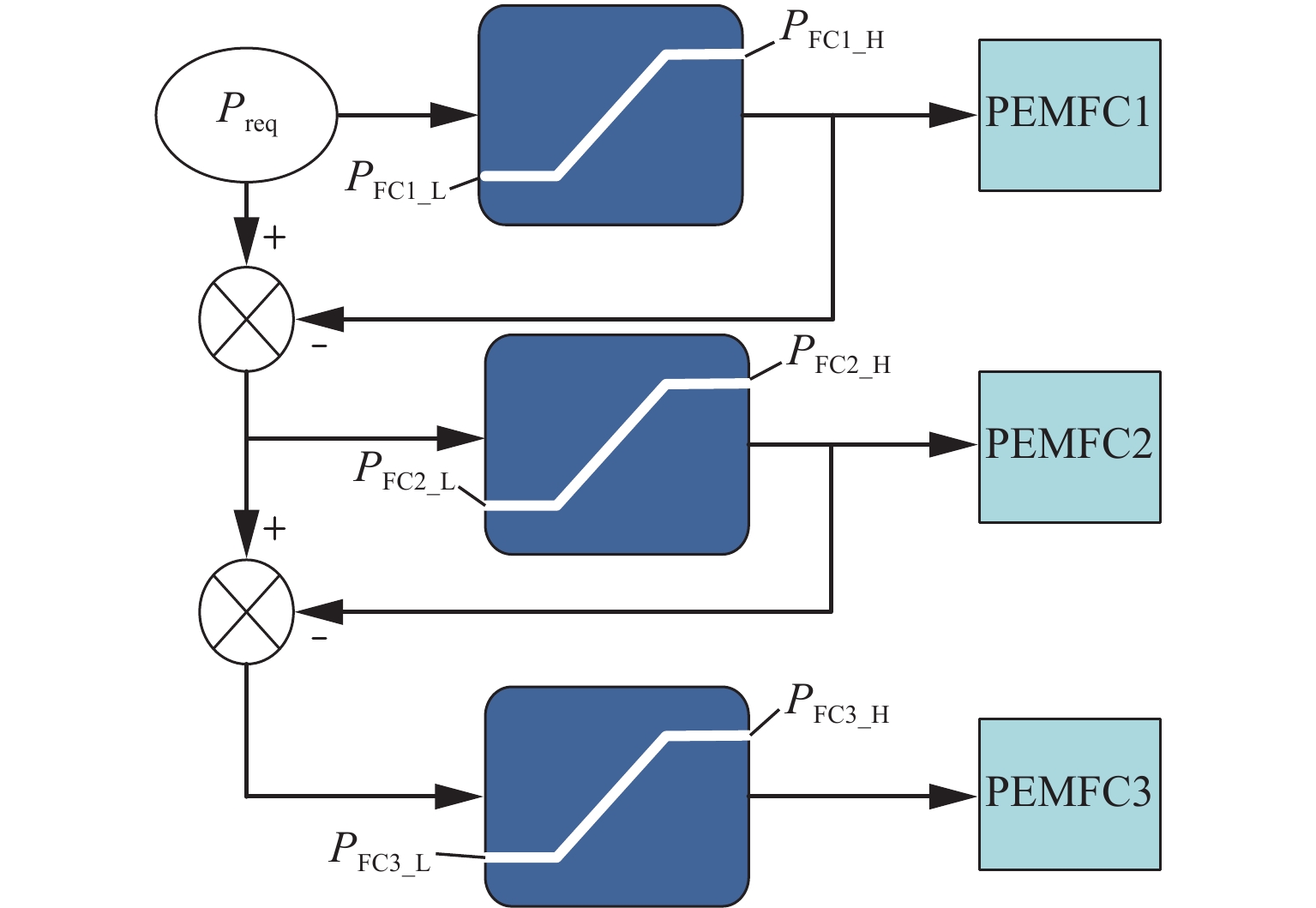
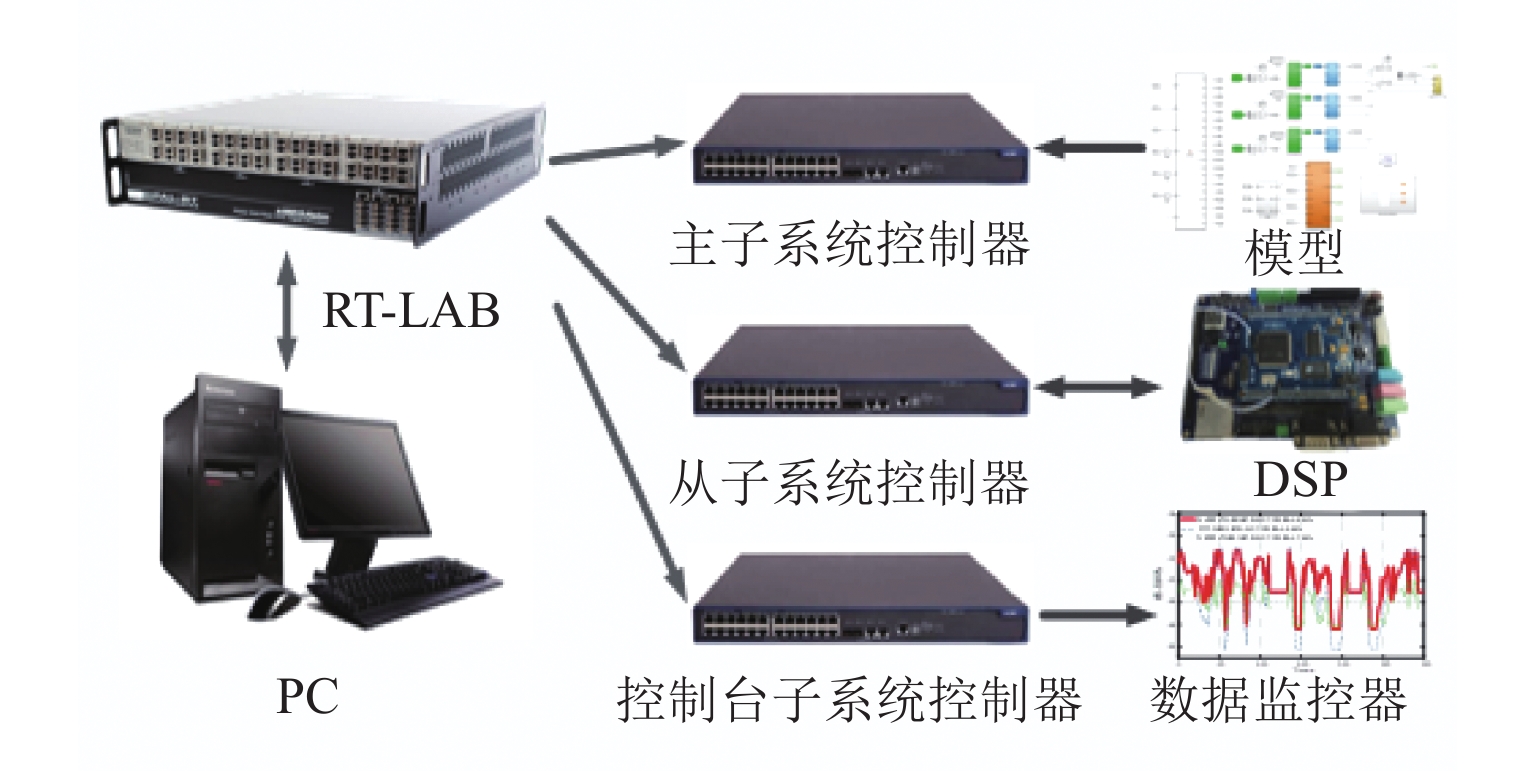
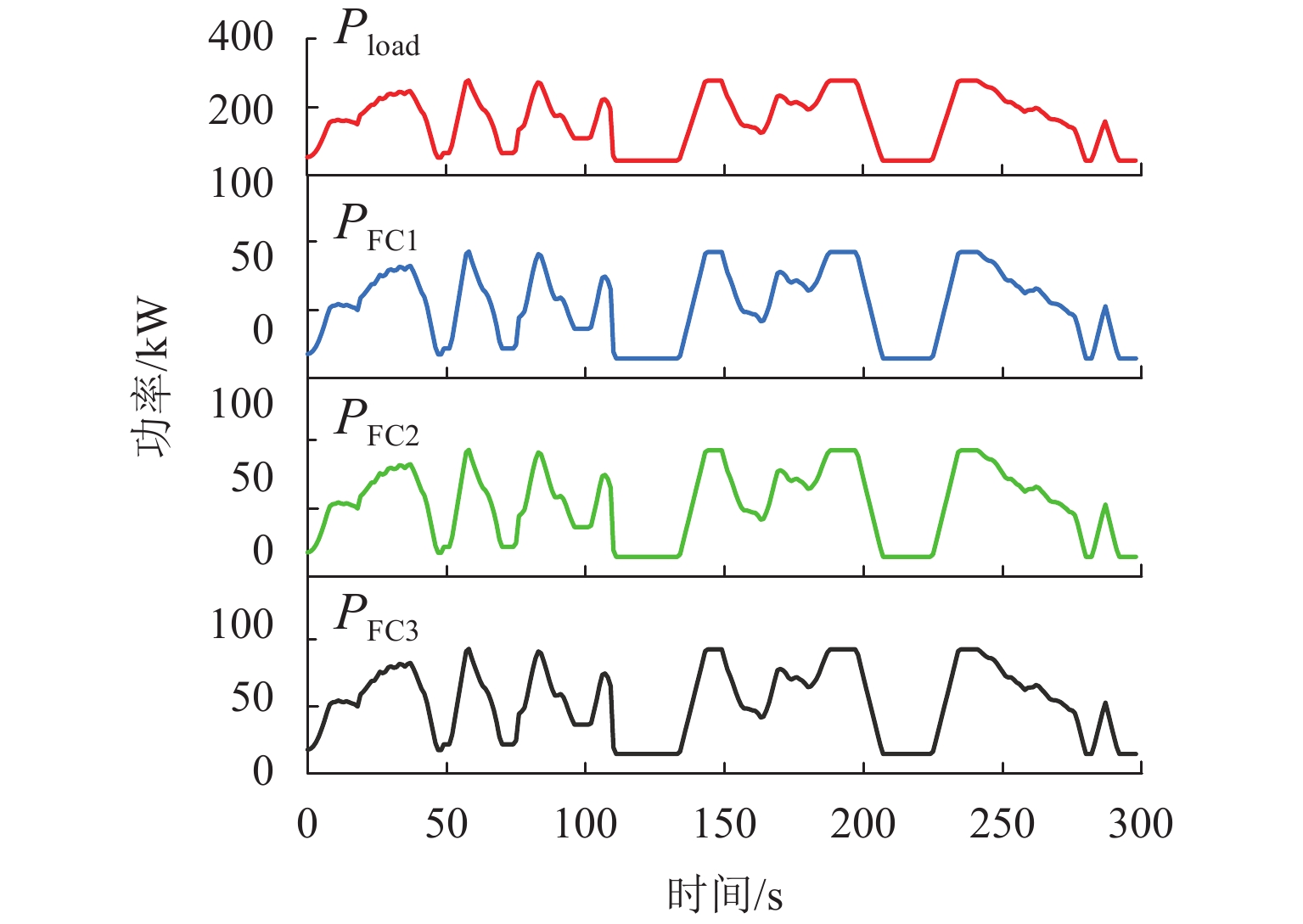
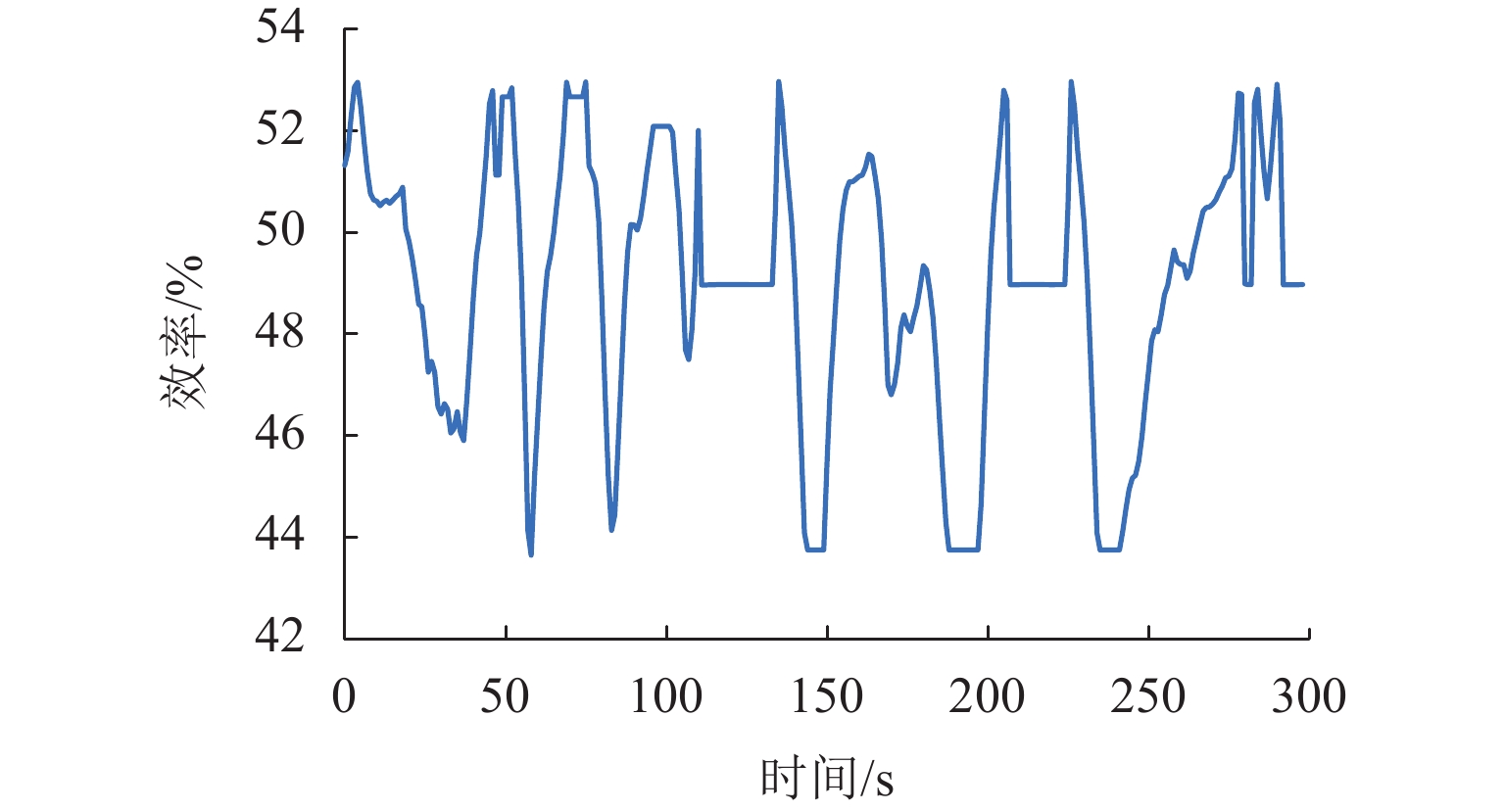
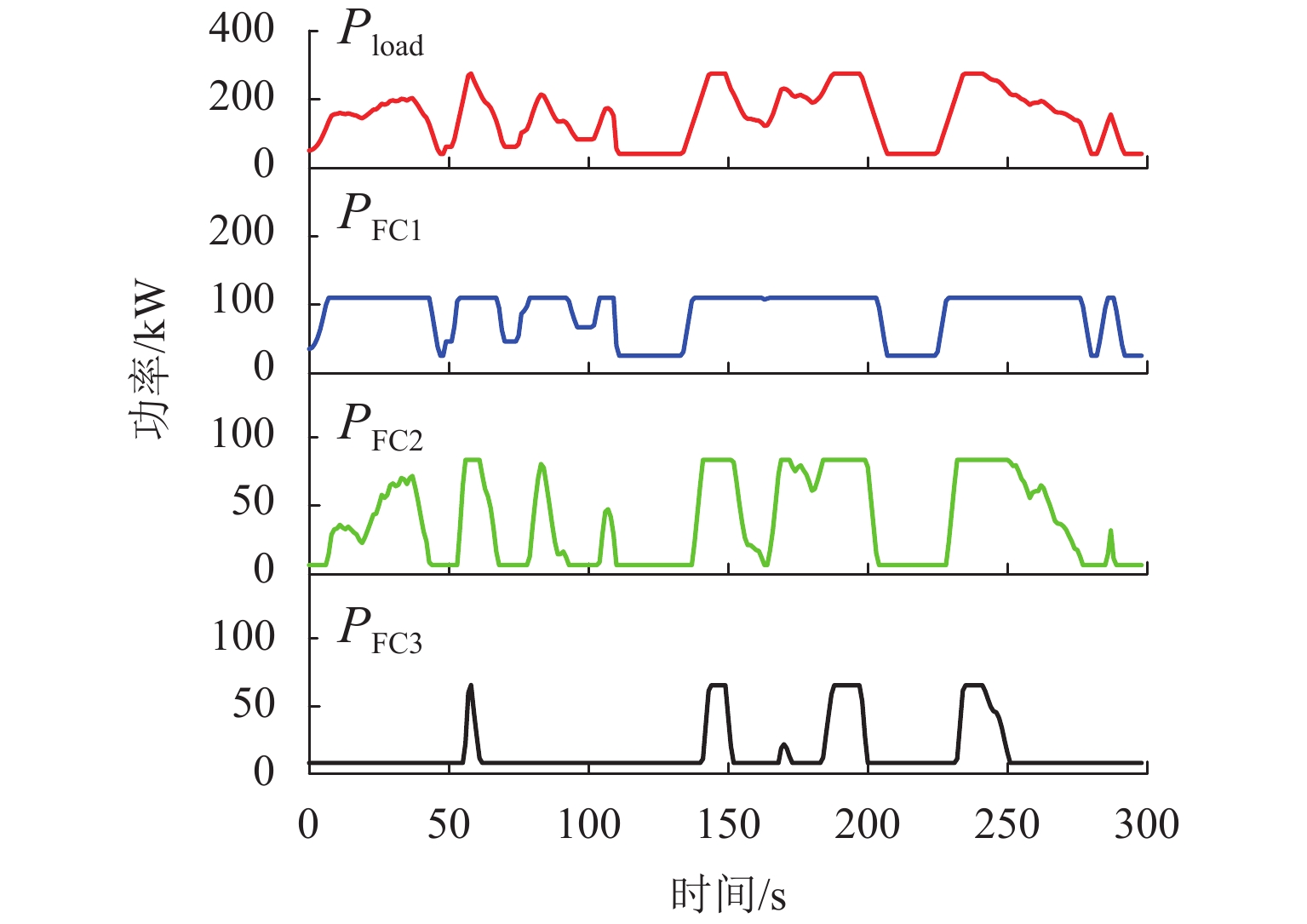
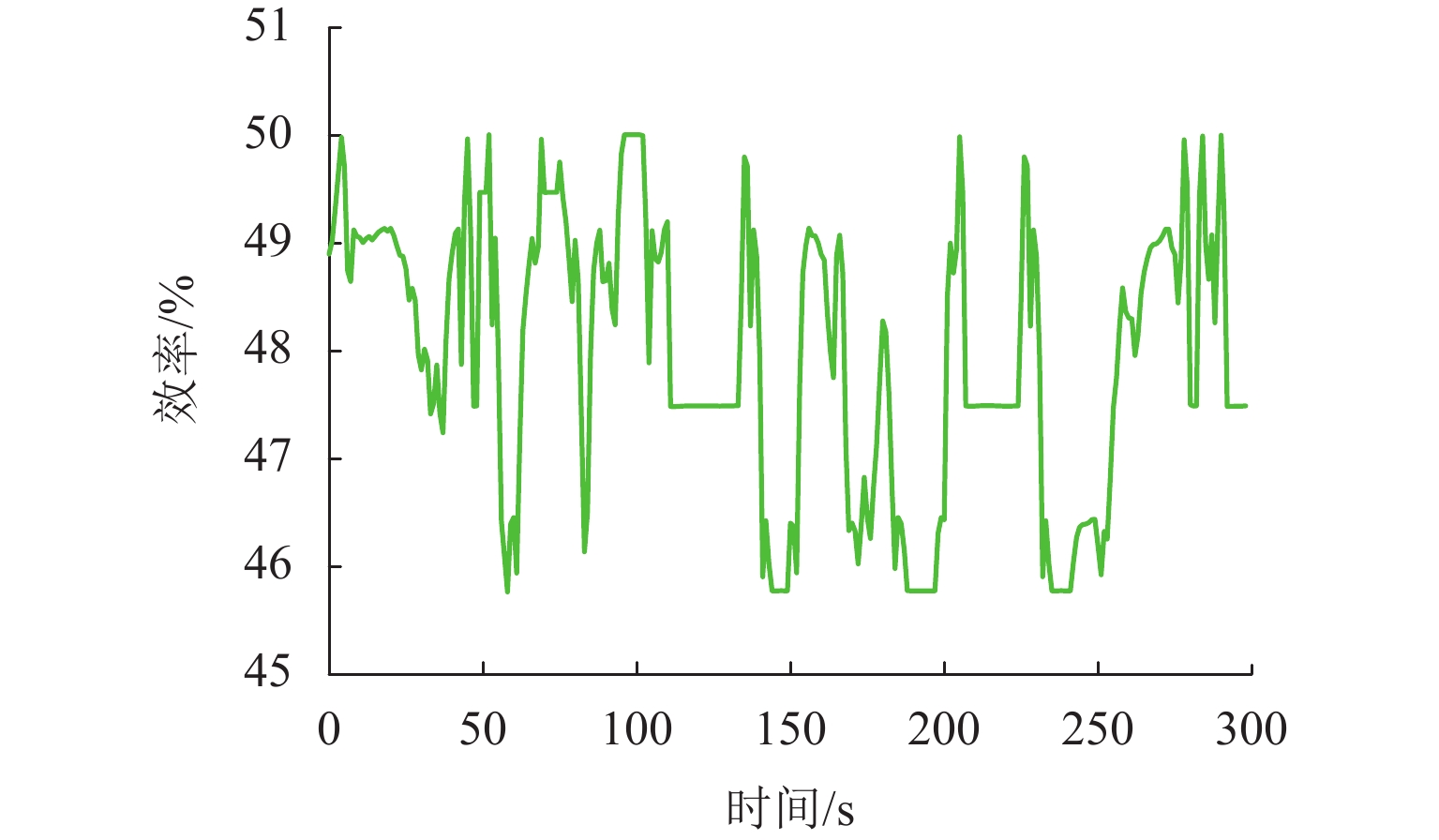
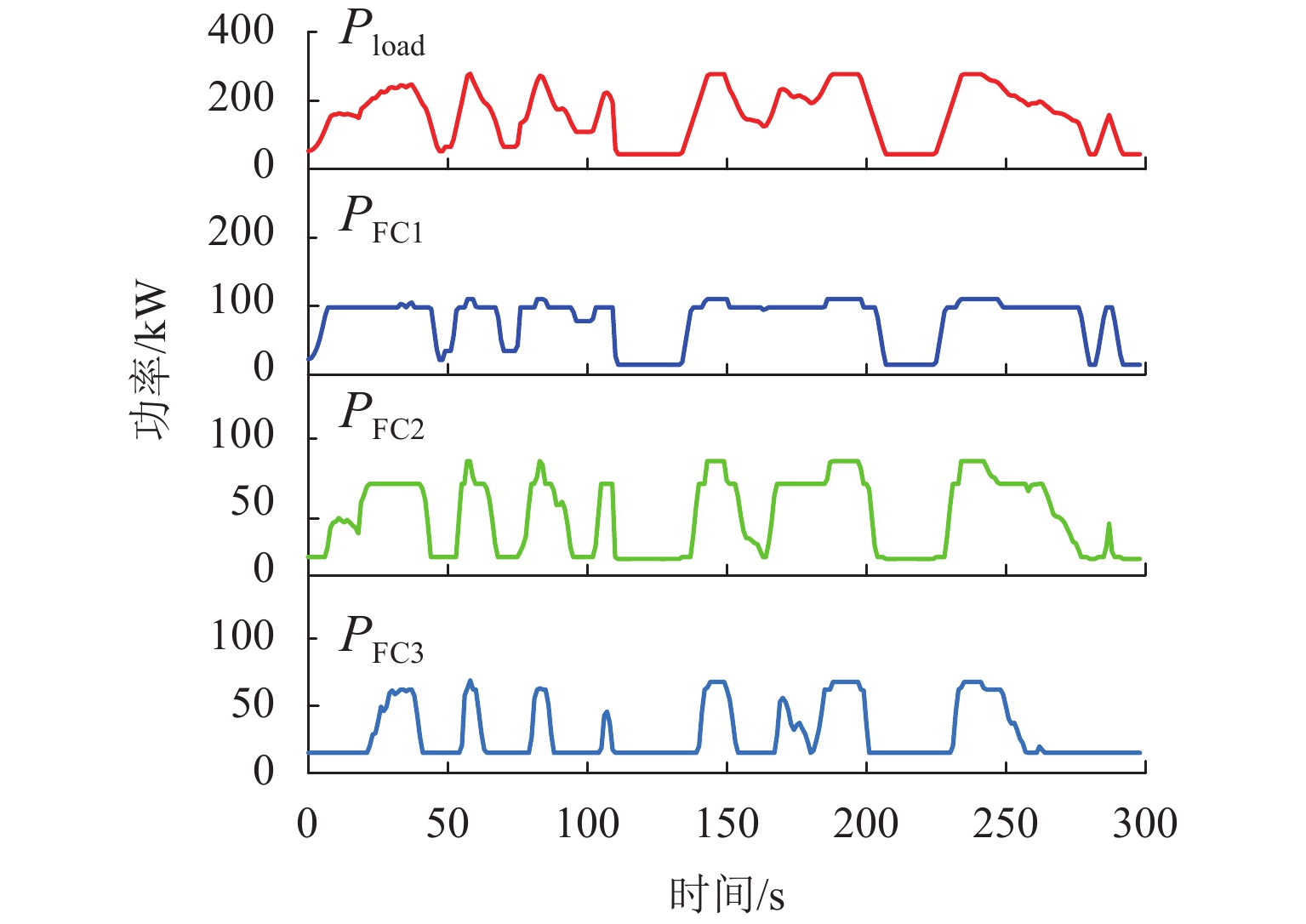
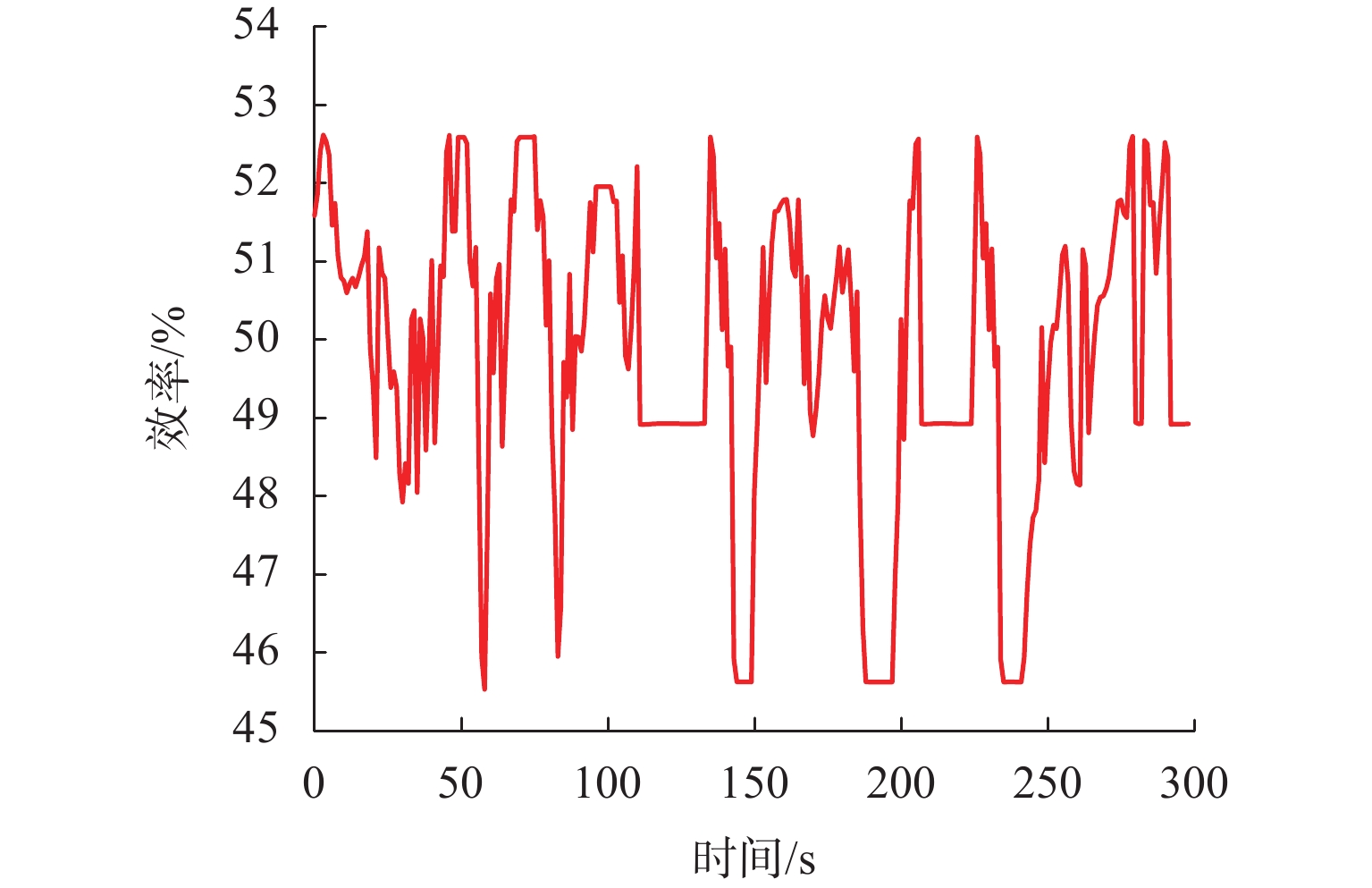
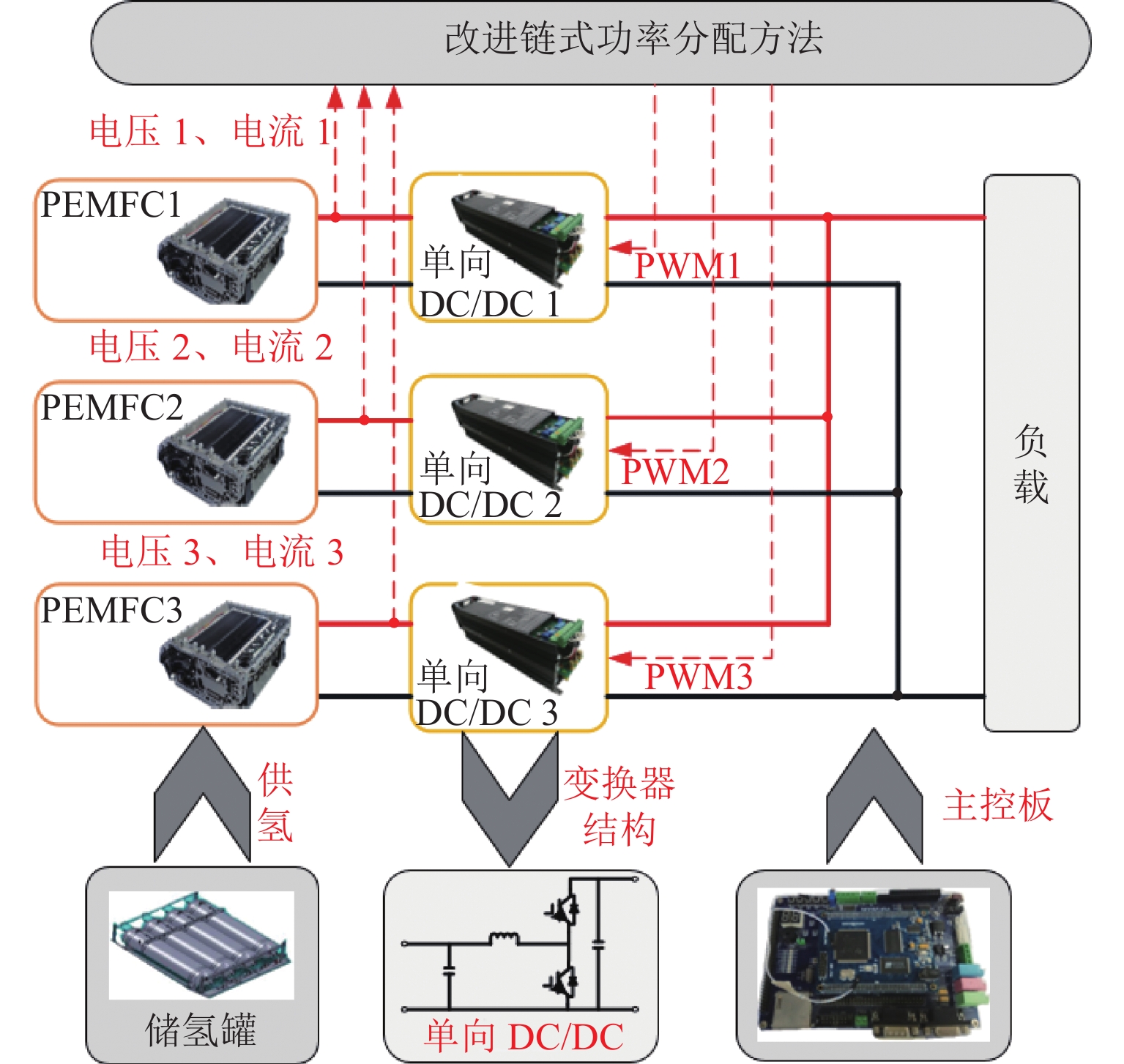
为减小多堆燃料电池系统 (multi-stack fuel cell system, MFCS)中单体燃料电池运行期间输出功率的大范围变化,提高MFCS平均效率,以保证各燃料电池长期稳定运行,针对大功率质子交换膜燃料电池 (proton exchange membrane fuel cell,PEMFC)系统,提出了一种基于遗忘因子递推最小二乘 (forgetting factor recursive least square,FFRLS)在线辨识地改进链式功率分配方法. 该方法利用FFRLS算法的实时在线辨识能力估算运行中的每个燃料电池最大效率范围 (maximum efficiency range,MER),并将其边界值作为约束参考值实时更新链式功率的限定区间;然后,依据负载需求功率变化和各燃料电池效率高低顺序分配各电堆出力;最后,在搭建的RT-LAB半实物平台上进行试验分析. 试验结果表明:与平均功率分配和传统链式功率分配方法相比,本文所提方法对MFCS效率分别提高了0.93%和1.95%.
-
关键词:
- 多堆燃料电池系统 /
- 遗忘因子递推最小二乘 /
- 最大效率范围 /
- 改进链式功率分配 /
- 半实物平台
Abstract:In order to reduce the large-scale variation in the output power of the single fuel cell during the operation of the multi-stack fuel cell system (MFCS), improve the average efficiency of the MFCS and ensure the long-term stable operation of each fuel cell, based on the forgetting factor recursive least squares (FFRLS), an improved chain power distribution method with online identification is proposed for the high-power proton exchange membrane fuel cell system. This method uses the real-time online identification capability of the FFRLS algorithm to estimate the maximum efficiency range (MER) of each fuel cell in operation, and uses its boundary value as the constraint reference value to update the limited range of chain power in real time. Then the output of each stack is distributed according to the load demand power change and the order of fuel cell efficiency. Finally, on the semi-physical platform RT-LAB, compared with the average and traditional chain power distribution methods, the proposed method improves the efficiency of MFCS by 0.93% and 1.95% respectively.
-
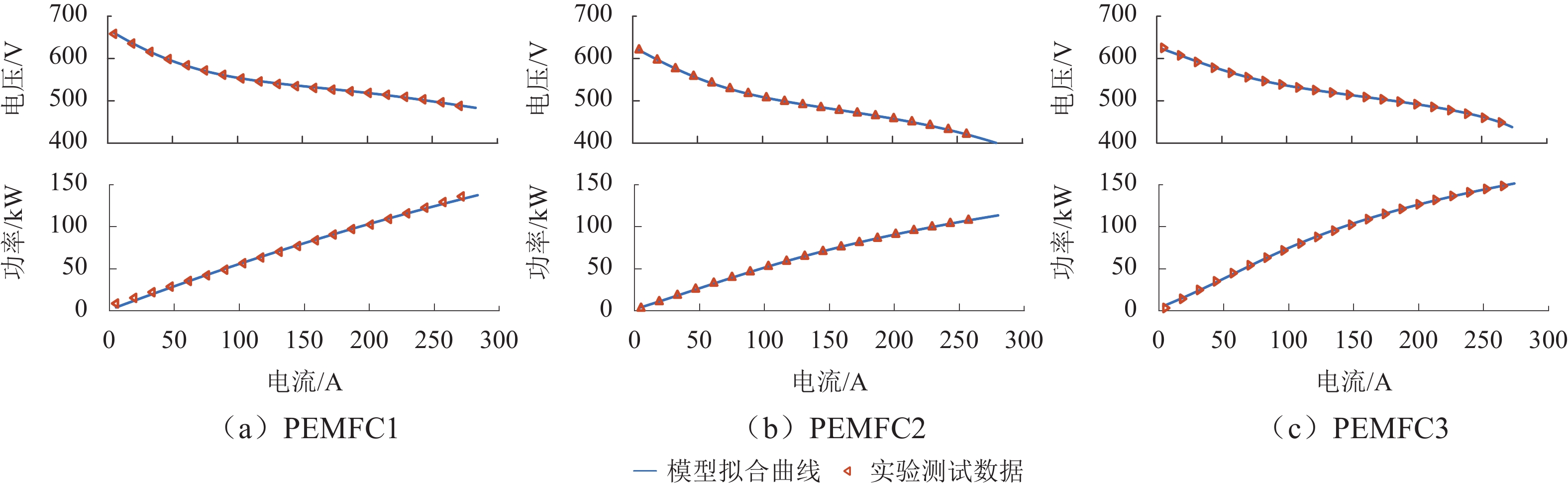
表 1 PEMFC电堆参数
Table 1. PEMFC stack parameters
参数 取值 额定功率/kW 110 额定电流/A 238 电压范围/V 480 ~ 660 氢气压力/MPa 0.8 冷却液温度/℃ 50 ~ 75 表 2 3种功率分配方法下MFCS效率变化
Table 2. Changes in MFCS efficiency under three power distribution methods
% 分配方法 平均效率 最大效率 最小效率 改进链式 49.91 52.43 45.82 平均 48.98 52.56 43.76 传统链式 47.96 50.12 45.91 -
[1] 陈维荣,钱清泉,李奇. 燃料电池混合动力列车的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2009,44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001CHEN Weirong, QIAN Qingquan, LI Qi. Investigation status and development trend of hybrid power train based on fuel cell[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009, 44(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.01.001 [2] 李奇,孟翔,陈维荣,等. 燃料电池混合动力系统参数匹配与多目标优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(5): 1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170117LI Qi, MENG Xiang, CHEN Weirong, et al. Parameter matching and multi-objective optimization of fuel cell hybrid system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170117 [3] JOSHI M C, SAMANTA S. Improved energy management algorithm with time-share-based ultracapacitor charging/discharging for hybrid energy storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(8): 6032-6043. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2871799 [4] LI H, RAVEY A, N’DIAYE A, et al. Equivalent consumption minimization strategy for hybrid electric vehicle powered by fuel cell, battery and super- capacitor[C]//IECON 2016-42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Florence: IEEE, 2016: 4401-4406. [5] ZHAI W M, CAI C B. Train/track/bridge dynamic interactions:simulation and applications[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2002, 37(S1): 653-665. [6] 徐茂峻,肖壮,毛畅海,等. 关于储能式有轨电车节能优化控制研究[J]. 计算机仿真,2019,36(2): 88-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2019.02.020XU Maojun, XIAO Zhuang, MAO Changhai, et al. Energy efficient optimization of multiple intervals for energy storage tram[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36(2): 88-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2019.02.020 [7] ETTIHIR K, BOULON L, AGBOSSOU K. Optimization-based energy management strategy for a fuel cell/battery hybrid power system[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 163: 142-153. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.176 [8] WANG T H, LI Q, YIN L Z, et al. Hydrogen consumption minimization method based on the online identification for multi-stack PEMFCs system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(11): 5074-5081. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.09.181 [9] HAN X, LI F Q, ZHANG T, et al. Economic energy management strategy design and simulation for a dual-stack fuel cell electric vehicle[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(16): 11584-11595. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.01.085 [10] BODDU S, AGARWAL V. Maximum power extraction from series-connected fuel cell stacks by the current compensation technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 30(2): 582-589. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2014.2311323 [11] 黄文强,李奇,陈维荣,等. 基于制动速度优化策略的新型供电方式 有轨电车再生制动能量回收方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(18): 5406-5414.HUANG Wenqiang, LI Qi, CHEN Weirong, et al. Fuel cell tram regenerative braking energy recovery method based on braking speed optimization strategy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(18): 5406-5414. [12] HONG Z H, LI Q, HAN Y, et al. An energy management strategy based on dynamic power factor for fuel cell/battery hybrid locomotive[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(6): 3261-3272. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.117 [13] 陈维荣,刘嘉蔚,李奇,等. 质子交换膜燃料电池故障诊断方法综述及展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2017,37(16): 4712-4721,4896.CHEN Weirong, LIU Jiawei, LI Qi, et al. Review and prospect of fault diagnosis methods for proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(16): 4712-4721,4896. [14] LI Q, CHEN W R, LIU Z X, et al. Development of energy management system based on a power sharing strategy for a fuel cell-battery-supercapacitor hybrid tramway[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 279: 267-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.042 [15] FEROLDI D, SERRA M, RIERA J. Performance improvement of a PEMFC system controlling the cathode outlet air flow[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 169(1): 205-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.01.053 [16] 徐梁飞,华剑锋,包磊,等. 燃料电池混合动力客车等效氢耗优化策略[J]. 中国公路学报,2009,22(1): 104-108. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.01.017XU Liangfei, HUA Jianfeng, BAO Lei, et al. Optimized strategy on equivalent hydrogen consumption for fuel cell hybrid electric bus[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2009, 22(1): 104-108. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2009.01.017 [17] 梁枫,秦斌,王欣,等. 基于粒子群算法的地铁列车节能运行优化[J]. 湖南工业大学学报,2016,30(6): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9833.2016.06.006LIANG Feng, QIN Bin, WANG Xin, et al. Optimization of energy saving operation for metro trains based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Technology, 2016, 30(6): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9833.2016.06.006 [18] SU Shuo, LI Kepeng, SU Shuai, et al. Energy-efficient train driving strategy considering the on-board energy storage[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 392: 062115.1-062115.6. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/392/6/062115 [19] 尹良震,李奇,洪志湖,等. PEMFC发电系统FFRLS在线辨识和实时最优温度广义预测控制方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2017,37(11): 3223-3235,3378.YIN Liangzhen, LI Qi, HONG Zhihu, et al. FFRLS online identification and real-time optimal temperature generalized predictive control method of PEMFC power generation system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(11): 3223-3235,3378. [20] YANG Y P, LIU Z W, WANG F C. An application of indirect model reference adaptive control to a low-power proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 179(2): 618-630. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.01.053 -




 下载:
下载: