Evaluation Method of Railway Schemes Along Rivers in Risk Areas of Moraine-Dammed Lake Outburst
-
摘要:
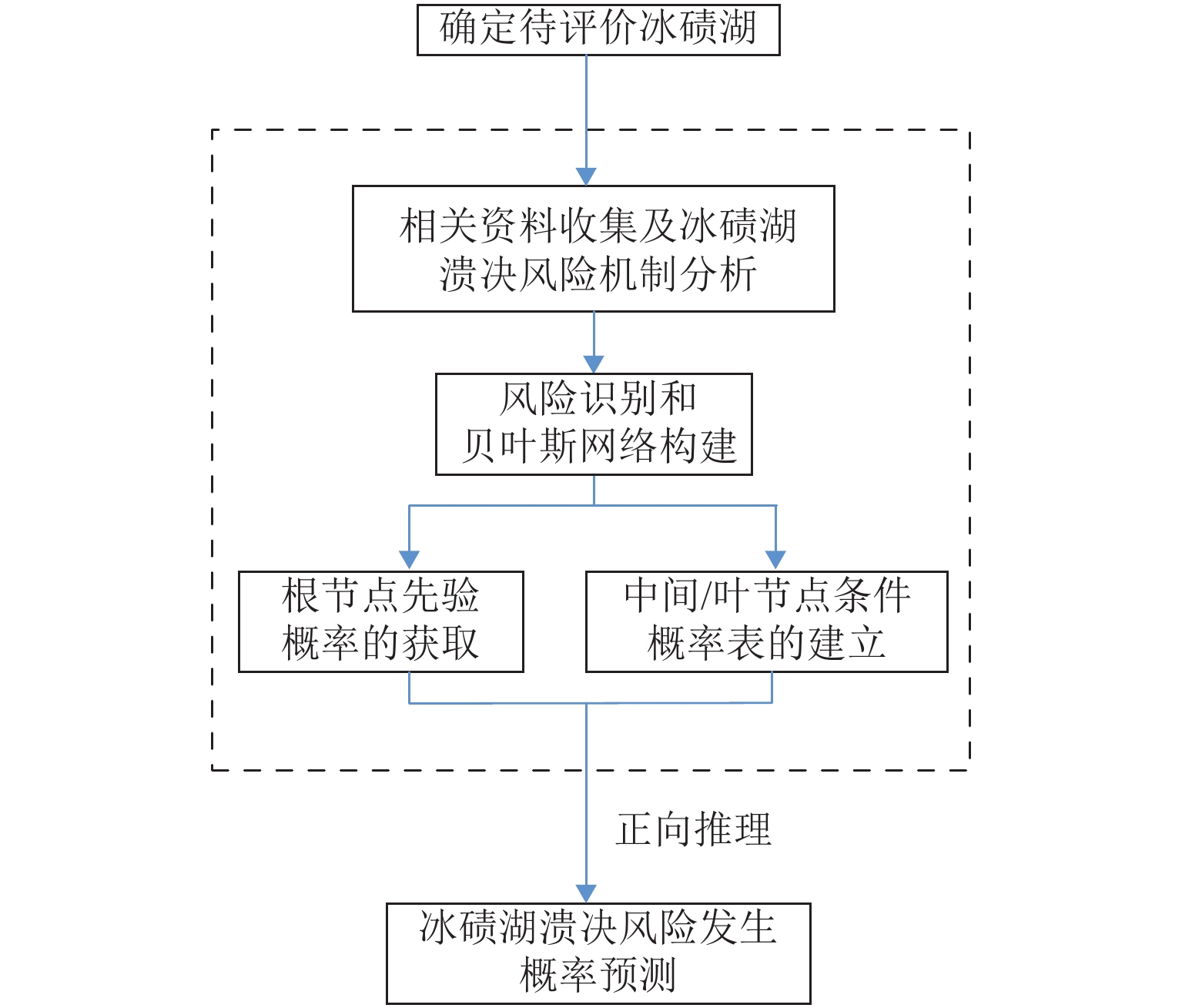
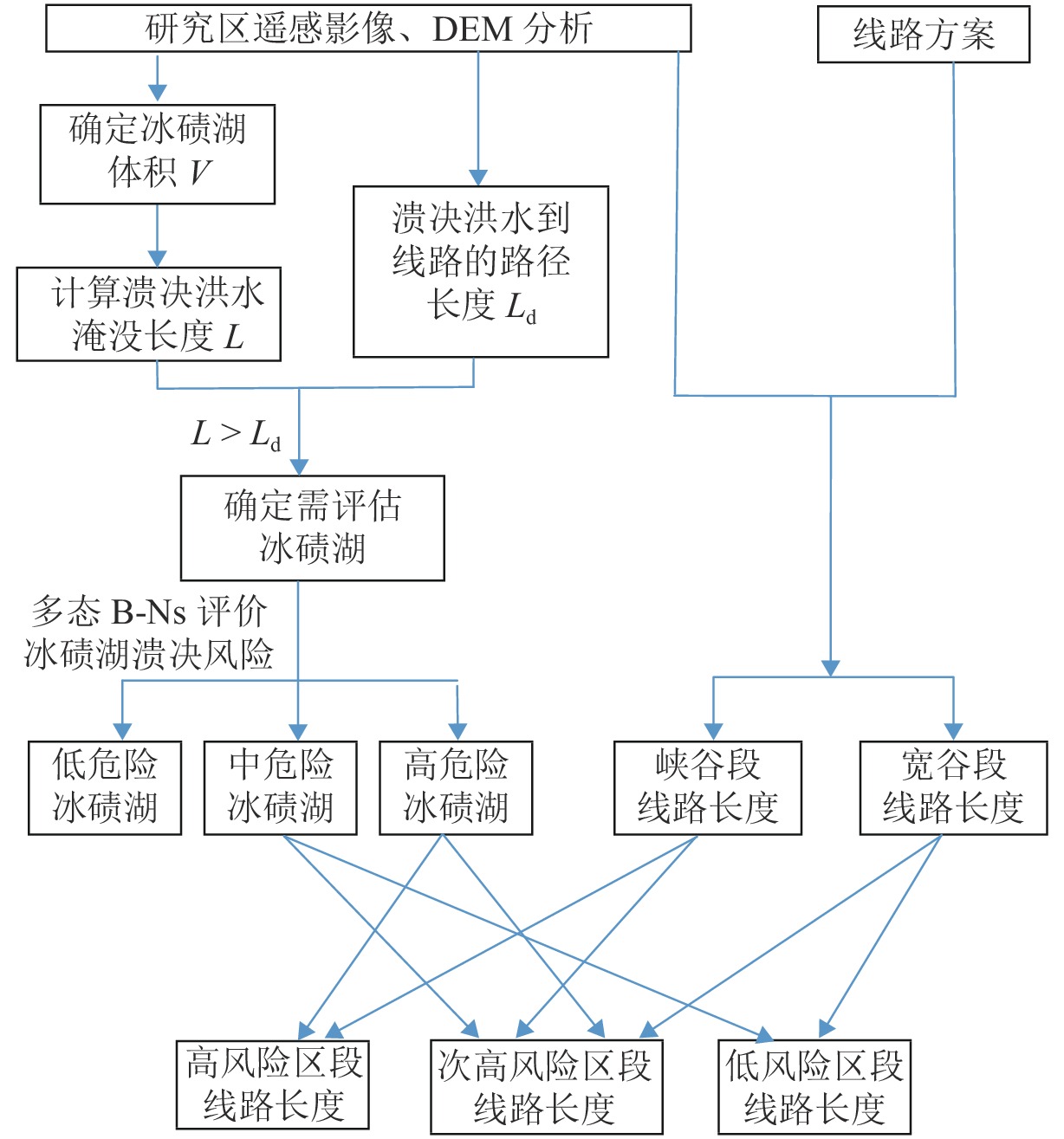
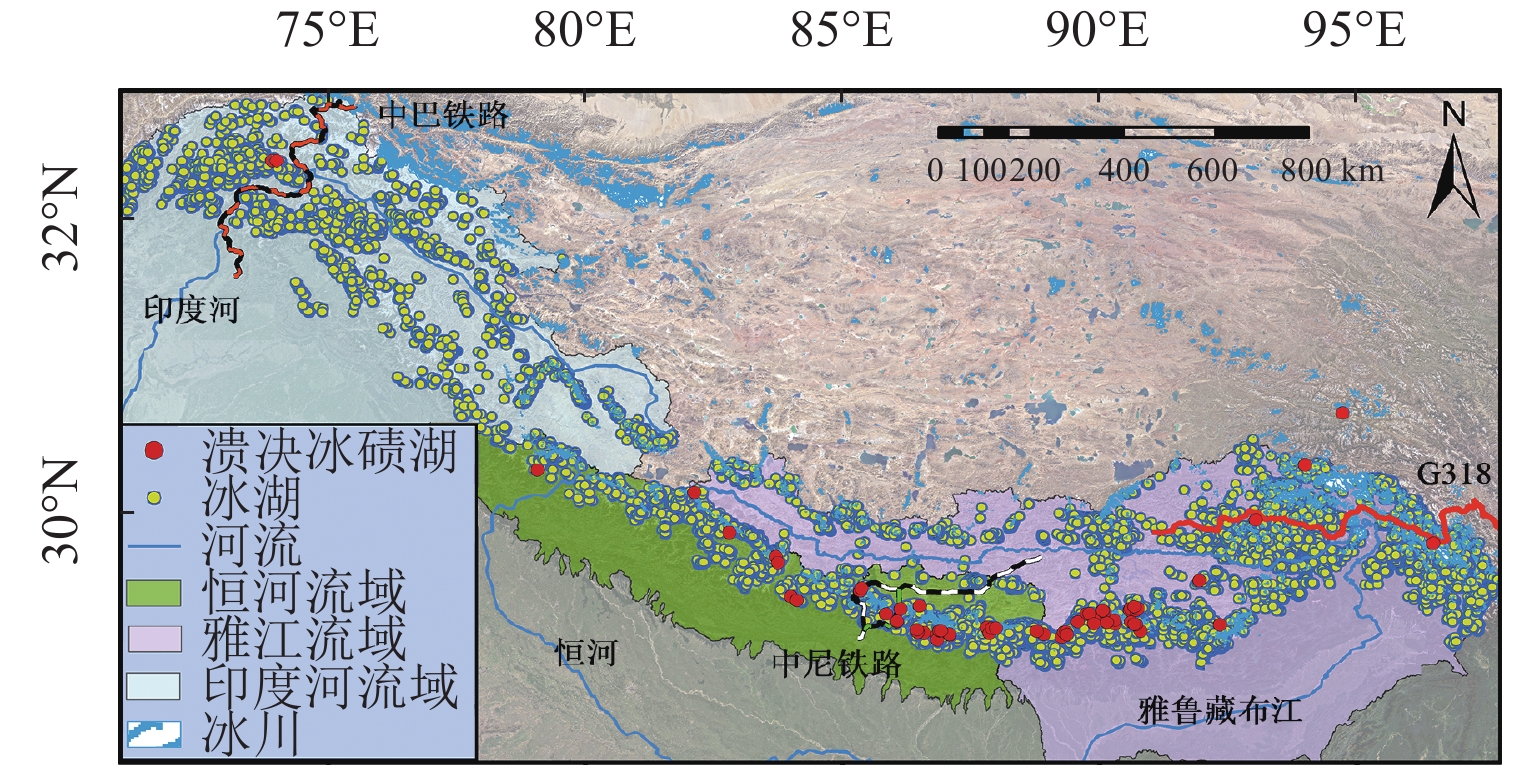
为建立青藏高原南缘冰碛湖溃决危险区铁路方案风险评价方法,首先,对青藏高原南缘74例冰碛湖溃决灾害实例溃决机制进行统计分析;在此基础上,针对冰碛湖溃决影响因素众多、关系复杂且具有高度不确定性的特点,利用多态贝叶斯网络建立了冰碛湖溃决概率预测模型;然后,以冰碛湖溃决危险区沿河线路工程为承灾体,综合冰碛湖溃决危险性评估与沿河线河谷地貌特征提出了各类风险区线路长度计算程式,建立了针对冰碛湖溃决危险性的铁路选线方案评价方法;最后,以中尼铁路跨喜马拉雅段的樟木、吉隆局部走向方案为例,说明评价方法的作业程式. 研究结果表明:樟木方案在冰碛湖分布区的线路长度小于吉隆方案,从选线角度属于线路短直方案,但樟木方案各风险区段线路总长超出吉隆方案约45%;从冰碛湖溃决风险角度,吉隆方案优于樟木方案.
Abstract:This study is aimed at risk assessments of railway schemes in moraine-dammed lake outburst risk areas in the southern Tibet Plateau. Based on the mechanism analysis of 74 outburst events in the study area, a multi-state Bayesian-Network prediction model is established considering the complex relationships among the influencing factors and high uncertainties of the outburst events. Taking the railway line engineering along rivers in moraine-dammed lake outburst risk areas as the hazard bearing body and combining the risk assessment of moraine-dammed lakes with geomorphological characteristics of the river valley, a calculation program of the railway scheme length in various risk areas and an evaluation system for railway schemes considering moraine-dammed lake outburst risk are proposed. In addition, the operation procedure of the proposed method is demonstrated taking the Zhangmu and Gyirong schemes of the China-Nepal railway as examples The results show that the Zhangmu scheme has a smaller route length in the moraine lake distribution area than the Gyirong scheme, and belongs to the short straight scheme from the perspective of route selection; however, the total length of the Zhangmu scheme in each risk area exceeds that of the Gyirong scheme by about 45%. Therefore, the Gyirong scheme is the better selection when considering the moraine lake outburst risk.
-
Key words:
- moraine-dammedlake outburst /
- B-Ns /
- China–Nepal railway /
- risk assessment
-
表 1 青藏高原南缘冰碛湖主要溃决机制统计
Table 1. Main outburst mechanisms of the moraine-dammed lakes in the southern Tibet Plateau
冰碛湖主要溃决机制 案例数 占比/% (冰崩/冰滑坡)涌浪漫顶 46 74.2 (降雨/冰川融水)洪水漫顶 12 19.4 管涌 5 8.1 冰碛物坍塌 5 8.1 外界动力激发 1 1.6 表 2 根节点因素多区间状态划分标准
Table 2. Division of risk factors in multi-interval safety states for root nodes
二级指标变量 二级指标状态值 0 1 x1/(°) < 8 > 8 x2 < 0.11 > 0.11 x3/km > 1 < 1 x4 相对不发育 相对较发育 x5 < 0.23 > 0.23 x6/m > 60 < 60 x7 固结 松散 x8 未满水 满水 x9 < 0.20 > 0.20 x10/(°) < 20 > 20 x11 无/少量 丰富 x12 < 0.25g > 0.25g 表 3 冰碛湖溃决根节点的先验概率
Table 3. Prior probabilities of root nodes of moraine-dammed lake outburst
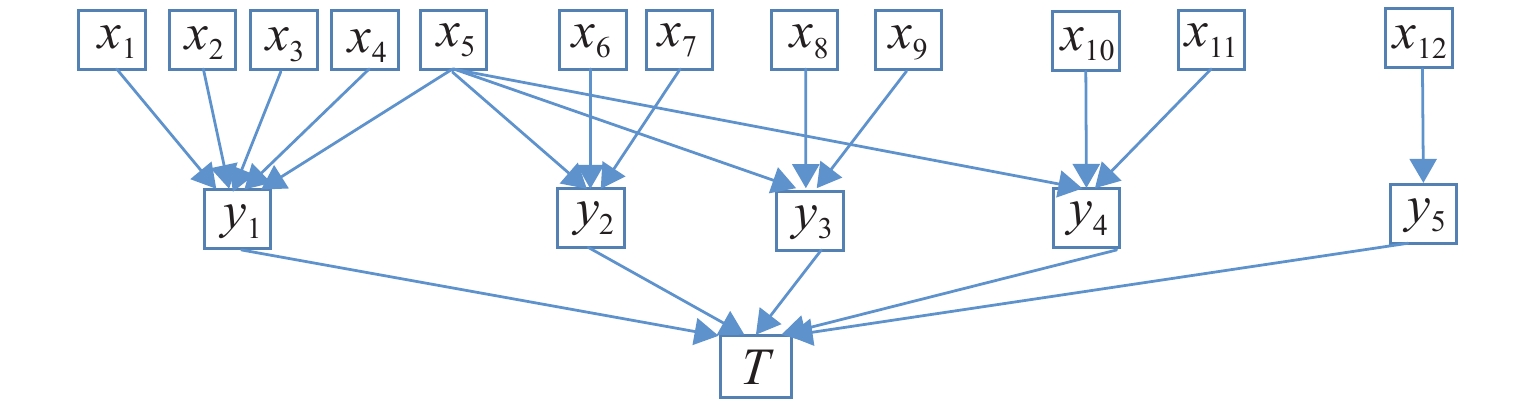
节点 状态数量 先验概率 状态 1 状态 2 x1 2 0.524 0.476 x2 0.286 0.714 x3 0.625 0.375 x4 0.192 0.808 x5 0.632 0.368 x6 0.240 0.760 x7 0.823 0.177 x8 0.423 0.577 x9 0.577 0.423 x10 0.712 0.288 x11 0.481 0.519 x12 0.900 0.100 表 4 中间节点y1的条件概率
Table 4. Conditional probabilities of node y1
x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 y1 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 1.0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1.0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1.0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0.2 0.8 0 0 0 1 0 0 1.0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0.2 0.8 0 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ 1 1 1 0 1 0 0.2 0.8 1 1 1 1 0 0 0.2 0.8 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1.0 表 5 铁路方案冰碛湖溃决危险性评价指标
Table 5. Evaluation indexes of railway schemes considering moraine-dammed lake outburst risk
指标名称 比选因素 流域指标 冰碛湖总数量/个 冰碛湖总面积/km2 历史冰碛湖溃决案例数/次 线路指标 冰碛湖分布区线路总长度/km 溃决高风险区段线路长度/km 溃决次高风险区段线路长度/km 溃决中风险区段线路长度/km 表 6 吉隆、樟木线路方案比选表
Table 6. Comparison of the railway schemes in the Gyirong and Poiqu river basins
指标类型 比选因素 吉隆 樟木 流域指标 冰碛湖总数量/个 130 121 冰碛湖总面积/ km2 5.8 17.3 历史冰碛湖溃决次数/次 2 6 线路指标 冰碛湖分布区
线路长度/ km107.9 93.5 冰碛湖溃决高危险区段
线路长度/ km21.2 38.3 冰碛湖溃决次高危险区
段线路长度/ km54.1 132.0 冰碛湖溃决中危险区段
线路长度/ km10.5 54.1 -
[1] 王欣, 刘时银, 丁永建. 中国喜马拉雅山冰碛湖溃决灾害评价方法与应用研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. [2] ZHANG C, HUANG Y D, YAO L K, et al. Prediction of the maximum wave elevation in moraine-dammed lakes during resonant earthquake excitation[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 146(2): 04019118.1-04019118.13. [3] 徐道明,冯清华. 西藏喜马拉雅山区危险冰湖及其溃决特征[J]. 地理学报,1989,44(3): 343-351,385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.03.011XU Daoming, FENG Qinghua. Dangerous glacial lake and outburst features in Xizang Himalayas[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1989, 44(3): 343-351,385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.03.011 [4] 吕儒仁, 唐邦兴, 朱平一, 等. 西藏泥石流与环境[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1999. [5] HUGGEL C, KÄÄB A, HAEBERLI W, et al. Remote sensing based assessment of hazards from glacier lake outbursts: a case study in the Swiss Alps[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2002, 39(2): 316-330. doi: 10.1139/t01-099 [6] 陈晓清,崔鹏,杨忠,等. 喜马拉雅山中段波曲流域近期冰湖溃决危险性分析与评估[J]. 冰川冻土,2007,29(4): 509-516.CHEN Xiaoqing, CUI Peng, YANG Zhong, et al. Risk assessment of glacial lake outburst in the poiqu river basin of Tibet Autonomous Region[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2007, 29(4): 509-516. [7] 舒有锋,王钢城,庄树裕,等. 基于粗糙集的权重确定方法在我国喜马拉雅山地区典型冰碛湖溃决危险性评价中的应用[J]. 水土保持通报,2010,30(5): 109-114. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2010.05.008SHU Youfeng, WANG Gangcheng, ZHUANG Shuyu, et al. A weight determination method based on rough set for hazard assessment of typical moraine-dammed lake outburst in Himalayan region[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 30(5): 109-114. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2010.05.008 [8] 王欣,刘时银,郭万钦,等. 我国喜马拉雅山区冰碛湖溃决危险性评价[J]. 地理学报,2009,64(7): 782-790. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.07.002WANG Xin, LIU Shiyin, GUO Wanqin, et al. Hazard assessment of moraine-dammed lake outburst floods in the Himalayas, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2009, 64(7): 782-790. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.07.002 [9] 马德仲,周真,于晓洋,等. 基于模糊概率的多状态贝叶斯网络可靠性分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2012,34(12): 2607-2611. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2012.12.35MA Dezhong, ZHOU Zhen, YU Xiaoyang, et al. Reliability analysis of multi-state Bayesian networks based on fuzzy probability[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(12): 2607-2611. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2012.12.35 [10] 林鹏智,陈宇. 基于贝叶斯网络的梯级水库群漫坝风险分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,2018,50(3): 46-53.LIN Pengzhi, CHEN Yu. Risk analysis of dam overtopping for cascade reservoirs based on Bayesian network[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2018, 50(3): 46-53. [11] 程尊兰,田金昌,张正波,等. 藏东南冰湖溃决泥石流形成的气候因素与发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2009,16(6): 207-214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.06.023CHENG Zunlan, TIAN Jinchang, ZHANG Zhengbo, et al. Debris flow induced by glacial-lake break in Southeast Tibet[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(6): 207-214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.06.023 [12] 姚晓军,刘时银,孙美平,等. 20世纪以来西藏冰湖溃决灾害事件梳理[J]. 自然资源学报,2014,29(8): 1377-1390. [13] NIE Y, LIU Q, WANG J, et al. An inventory of historical glacial lake outburst floods in the Himalayas based on remote sensing observations and geomorphological analysis[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 308: 91-106. [14] ICIMOD. Glacial lakes and glacial lake outburst floods in Nepal[R]. Kathmandu: ICIMOD, 2011. [15] KOMORI J, KOIKE T, YAMANOKUCHI T, et al. Glacial lake outburst events in the Bhutan Himalayas[J]. Global Environmental Research, 2012, 16(1): 59-70. [16] BHAMBRI R, HEWITT K, KAWISHWAR P, et al. Ice-dams, outburst floods, and movement heterogeneity of glaciers, Karakoram[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 180: 100-116. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.05.004 [17] GURUNG D R, KHANAL N R, BAJRACHARYA S R, et al. Lemthang Tsho glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) in Bhutan: cause and impact[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 2017, 4(17): 1-13. doi: 10.1186/s40677-017-0080-2 [18] AI H Z, YAO L K, ZHOU Y L. Laboratory investigations of earthquake-and landslide-induced composite surges[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2017, 14(8): 1537-1549. doi: 10.1007/s11629-016-4339-y [19] 刘宁, 程尊兰, 崔鹏. 堰塞湖及其风险控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. [20] WASHAKH R, CHEN N, WANG T, et al. GLOF risk assessment model in the Himalayas: a case study of a Hydropower project in the upper Arun river[J]. Water, 2019, 11(9): 1-23. doi: 10.3390/w11091839 -




 下载:
下载: