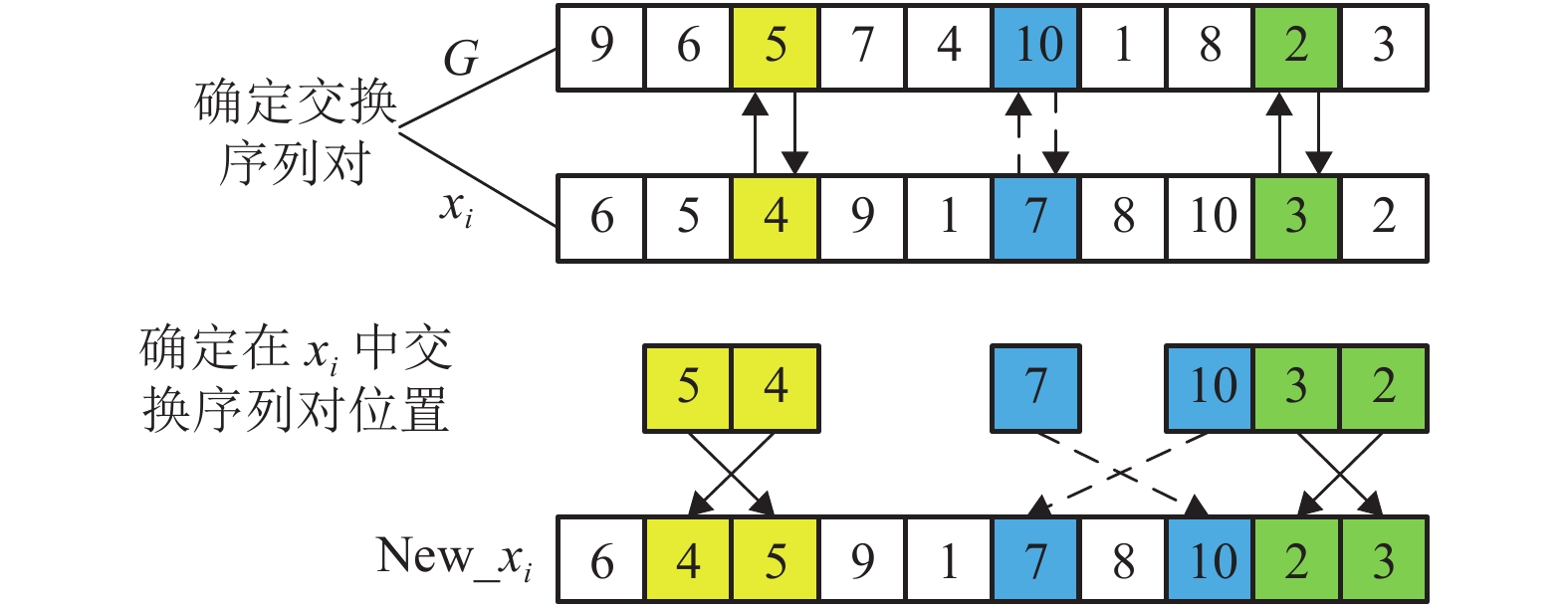
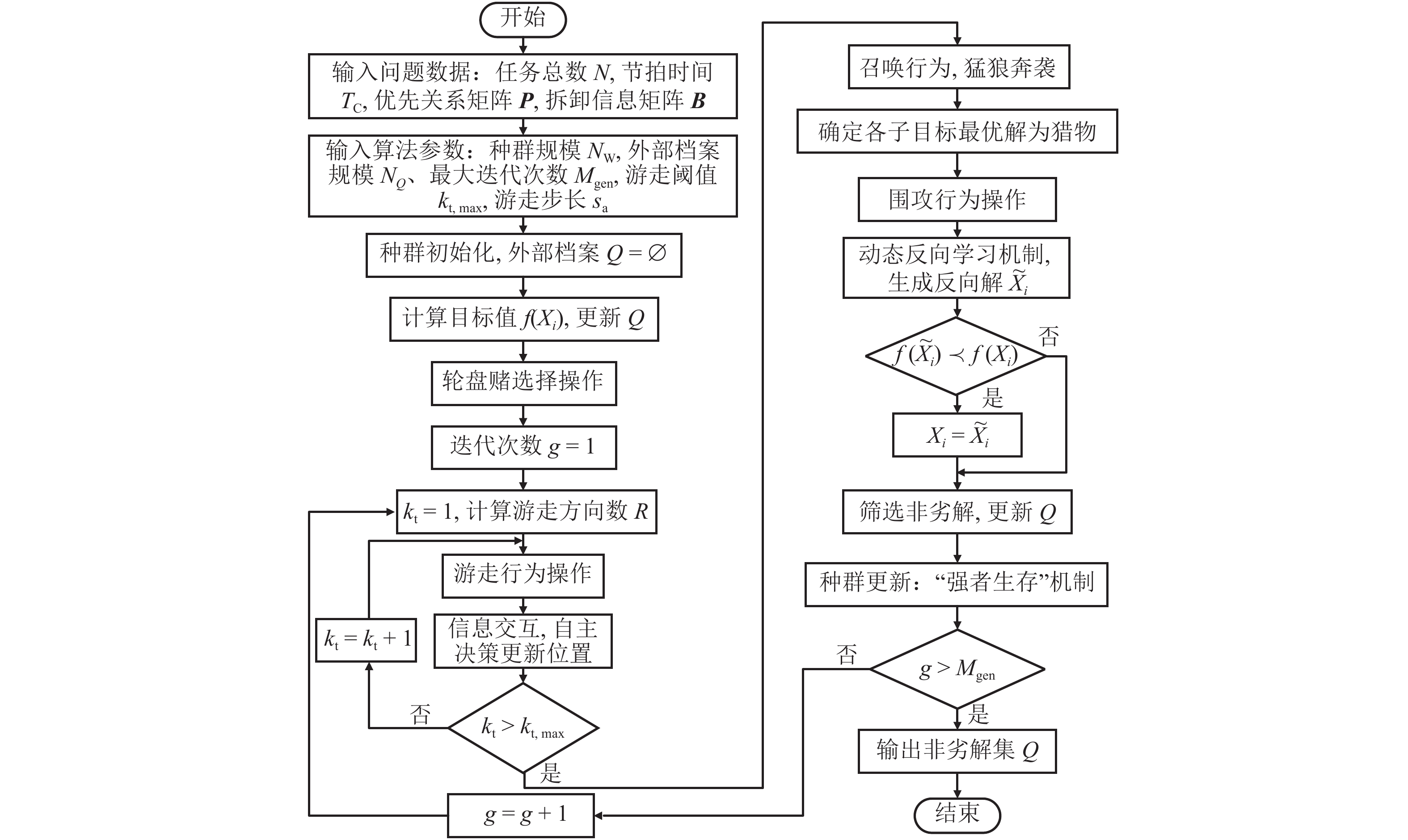
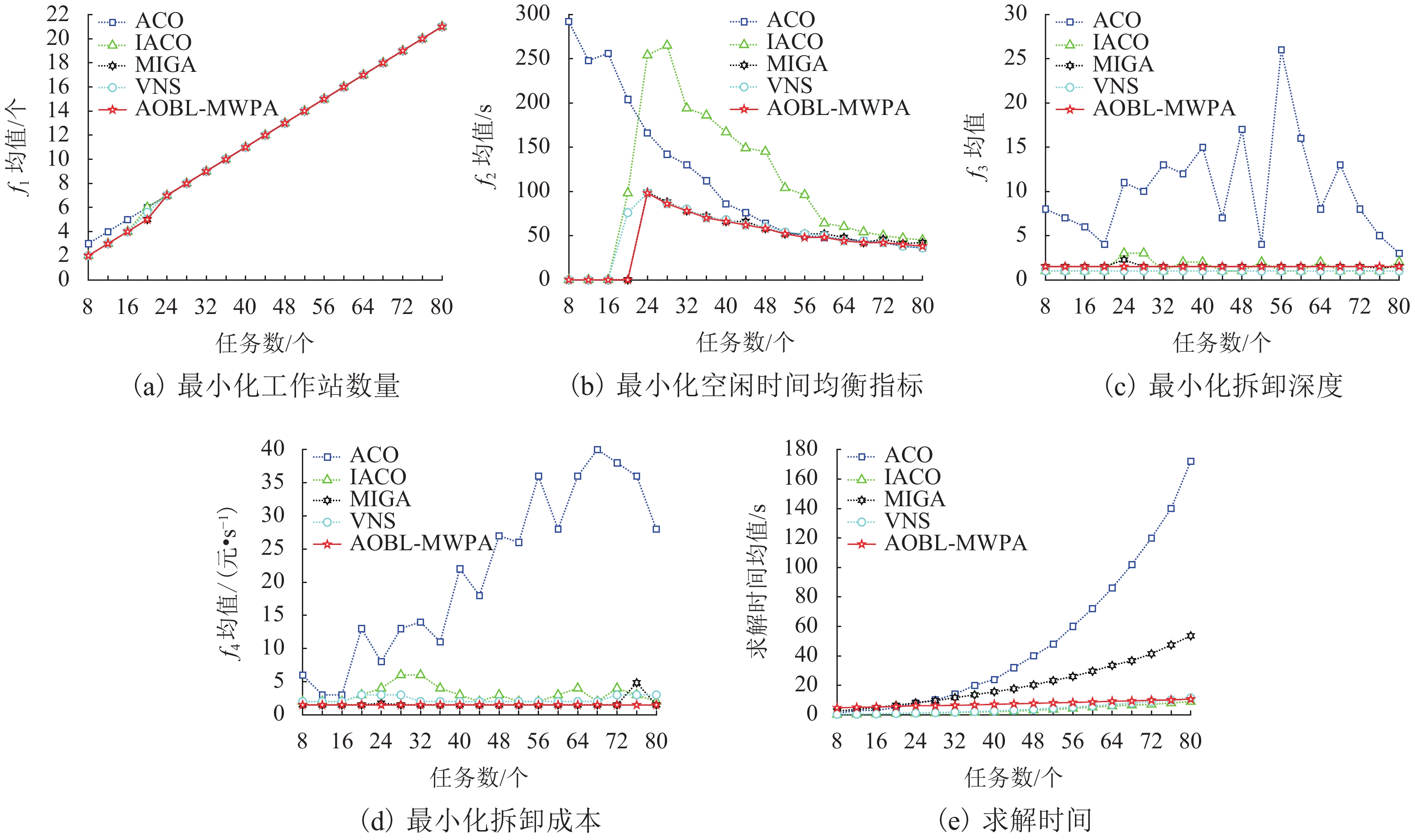
Modeling and Optimization for U-shaped Partial Multi-Objective Disassembly Line Balancing Problem
-
摘要:
针对U型布局所具有的生产柔性强、效率高等优点,结合仅需考虑需求零部件和危害性零部件的实际拆卸过程,提出U型不完全拆卸线平衡问题(U-shaped partial disassembly line balance problem,UPDLBP) ,以最小化工作站数量、空闲时间均衡指标、拆卸深度和拆卸成本为优化目标建立数学模型. 在此基础上,提出一种自适应反向学习多目标狼群算法(adaptive opposition-based learning multi-objective wolfpack algorithm,AOBL-MWPA)进行求解计算. 该算法采用自适应游走行为,兼顾算法迭代前期的全局寻优性能和后期的稳定性;在满足优先关系约束前提下对召唤行为和围攻行为进行离散化;引入反向学习策略(opposition-based learning,OBL)以避免算法陷入局部最优;利用Pareto解集思想和非支配排序遗传算法Ⅱ(NSGA-Ⅱ)拥挤距离机制筛选获得多个非劣解;将所提算法应用于19个基准算例中,并与现有文献算法对比;最后,将所提模型和算法应用于某汽车U型不完全拆卸线的实例设计中. 结果表明:针对工作站开启数量和空闲时间均衡指标而言所提算法能求解获得小规模问题的最优值,且在中大规模问题中所得结果优于其他算法,危害指标和需求指标均能获得最优值,寻优率为100%;实例设计获得10组可选方案,验证了所提算法的实用性和有效性.
Abstract:Aiming at the advantages of U-shaped layout such as high production efficiency and strong flexibility, combined with the actual disassembly process that only needs to consider the required parts and hazardous parts, the U-shaped partial disassembly line balancing problem (UPDLBP) is proposed, and multi-objective mathematics model is established with the optimization objectives of minimizing the number of workstations, idle time balance indicators, disassembly depth and disassembly costs. On this basis, adaptive opposition-based learning multi-objective wolfpack algorithm (AOBL-MWPA) is proposed for solution calculation. The algorithm adopts adaptive scouting behavior and takes into account the global optimization performance in the early stage of the algorithm iteration and the stability in the later stage; The calling behavior and besieging behavior are discretized under the premise of satisfying the constraints of the priority relationship; Opposition-based learning strategy (OBLS) is used to avoid the algorithm from falling into the local optimum; Pareto solution set idea and crowding distance mechanism of non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm Ⅱ (NSGA-Ⅱ) are given to screen to obtain multiple non-inferior solutions. The proposed algorithm is applied to 19 benchmark examples and compared with existing literature algorithms. Finally, the proposed model and algorithm are applied to the example design of a U-shaped partial disassembly line of a certain automobile. The results show that, the proposed algorithm can solve the optimal value of small-scale problems in terms of the number of workstations on and the idle time balance index. The results obtained in medium and large-scale problems are better than other algorithms; the optimal value can be obtained for both the hazard index and the demand index, and the optimization rate is 100%. Ten sets of optional design schemes are obtained from the case study, which verifies the practicability and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 某汽车拆卸信息
Table 1. Disassembly information of a car
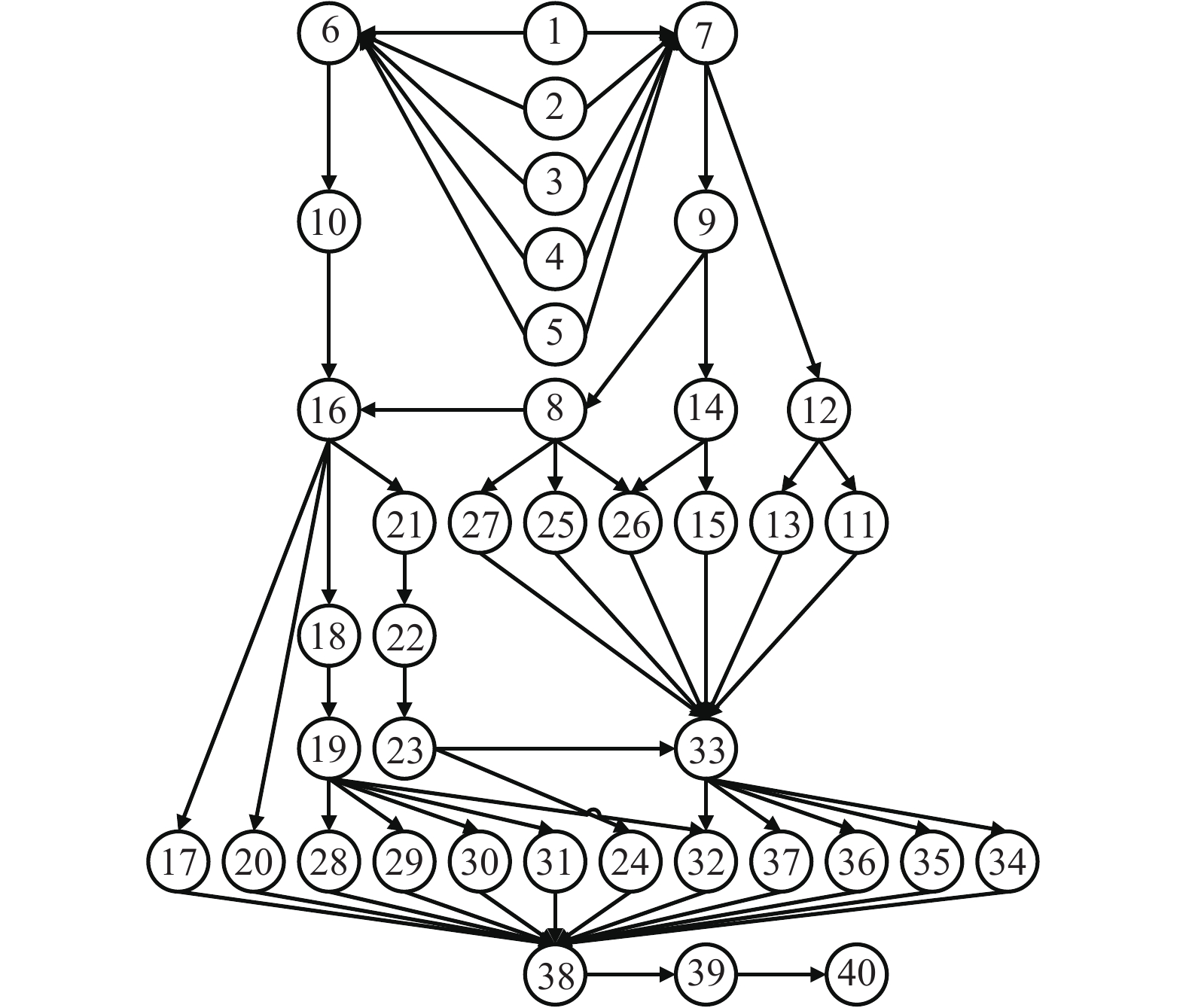
序号 任务名称 t/s h d C/(元•s–1) 序号 任务名称 t/s h d C/(元•s–1) 1 安全气囊 62 1 0 0.0096 21 底部护板 60 0 0 0.0083 2 蓄电池 162 1 1 0.0083 22 排气管 114 1 1 0.0090 3 废电液 405 1 0 0.0084 23 邮箱 118 1 1 0.0081 4 冷媒 120 1 1 0.0081 24 碳罐 28 0 1 0.0154 5 车轮 130 0 1 0.0110 25 散热器 112 0 0 0.0160 6 车门 353 0 1 0.0131 26 油液存储装置 344 1 1 0.0090 7 引擎盖 80 0 1 0.0119 27 空气滤清器 50 0 0 0.0109 8 保险杠 120 0 1 0.0112 28 制动组件 170 0 1 0.0152 9 车灯 115 0 0 0.0136 29 离合器踏板 52 0 0 0.0113 10 后备箱盖 112 0 1 0.0151 30 加速踏板 58 0 0 0.0171 11 挡风玻璃 80 1 0 0.0106 31 空调组件 132 0 0 0.0107 12 刮雨器 53 0 0 0.0089 32 转向系统 240 0 1 0.0095 13 刮雨电机 58 0 1 0.0128 33 发动机舱管路 172 0 0 0.0123 14 翼子板 60 0 1 0.0097 34 前悬架 231 0 1 0.0095 15 挡泥板 55 0 1 0.0161 35 后悬架 234 0 1 0.0140 16 座椅 238 0 1 0.0094 36 变速器 210 0 1 0.0074 17 安全带总成 115 0 0 0.0116 37 发动机 270 0 1 0.0149 18 方向盘 105 0 0 0.0152 38 内饰组件 240 1 0 0.0140 19 仪表板 302 0 0 0.0117 39 车身附件 98 0 0 0.0140 20 换挡手柄 116 0 0 0.0085 40 线速 115 0 0 0.0158 表 2 U型汽车拆卸线任务分配方案
Table 2. Task allocation plan for U-shaped car disassembly line
编号 拆卸任务分配方案 f1/个 f2/s f3 f4/(元 • s–1) 1 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,9,−24,
−28]→[6,−34,12]→[−33,−25,−30,13,10,14,15]→[8,16,17,20,−27]→[−23,−26,−22,21]→[18,19,31,11]9 33.0151 38 381.9464 2 [−38,−37,4]→[3,1,2]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,12,9,8,
−24]→[−28,−34,−33,13]→[−25,14,6,15,−27]→[10,16,20,
18,21]→[17,26,22,−30]→[−31,−19,−23,−11]9 28.1425 38 387.9549 3 [−38,−37,4]→[3,1,2]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,12,9,8,
−24]→[−28,−34,−33,13]→[−25,14,6,15,−27]→[10,16,20,
18,−30]→[19,−31,−23,−11]→[−26,−17,−22,−21]9 28.2843 38 385.6883 4 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,9,8,12,
−24]→[−28,−34,−33,−30]→[−31,−19,−11,−23]→[−26,−20,−22,13]→[−18,−21,−17,−16,−10]→[−6,14,25,−15,−27]9 28.1780 38 386.4461 5 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,9,−24,
−28]→[6,−34,12]→[−20,−33,−25,14,−30,15,−27]→[8,10,16,18,−13]→[17,19,31,−11]→[−26,−23,−22,−21]9 30.6268 38 382.1177 6 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,9,−24,
−28]→[6,−34,12]→[−33,−25,14,−30,15,10,−27]→[8,16,
17,18,−13]→[20,19,31,−11]→[−23,−26,−22,−21]9 32.1870 38 382.1146 7 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,12,13,9,
14,−24]→[−34,−33,−25,−30,15]→[6,10,8,−27]→[16,−28,20,18]→[17,19,31,−11]→[26,−23,−22,−21]9 29.2575 38 383.4016 8 [−38,−37,4]→[3,1,2]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,12,9,8,
−24]→[−28,−34,−33,13]→[−25,14,6,15,−27]→[10,16,
17,18,−30]→[19,31,−11,−23]→[26,20,−22,−21]9 28.4605 38 384.0424 9 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,9,−24,
−28]→[6,−34,12]→[−33,−30,−25,13,14,15,10]→[8,16,18,17,−27]→[19,31,−11,−23]→[−20,−26,−22,−21]9 29.5973 38 382.1352 10 [−38,−37,4]→[3,2,1]→[−32,−36,5,−29]→[−35,7,9,−24,
−28]→[6,−34,12]→[−33,−30,−25,13,14,15,10]→[8,16,18,20,−27]→[17,19,31,−11]→[26,−23,−22,−21]9 29.8329 38 382.1253 -
[1] GÜNGÖR A, GUPTA S M. Disassembly line in product recovery[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2002, 40(11): 2569-2589. doi: 10.1080/00207540210135622 [2] KALAYCI C B, HANCILAR A, GUNGOR A, et al. Multi-objective fuzzy disassembly line balancing using a hybrid discrete artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2015, 37: 672-682. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2014.11.015 [3] REN Y P, YU D Y, ZHANG C Y, et al. An improved gravitational search algorithm for profit-oriented partial disassembly line balancing problem[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2017, 55(24): 7302-7316. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2017.1341066 [4] BENTAHA M L, BATTAÏA O, DOLGUI A. Lagrangian relaxation for stochastic disassembly line balancing problem[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2014, 17: 56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2014.02.049 [5] AVIKAL S, JAIN R, MISHRA P K, et al. A heuristic approach for U-shaped assembly line balancing to improve labor productivity[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2013, 64(4): 895-901. [6] 肖钦心,郭秀萍,谷新军. 多类约束下的随机混流U型拆卸线平衡排序问题优化[J]. 工业工程与管理,2019,24(5): 87-96.XIAO Qinxin, GUO Xiuping, GU Xinjun. The stochastic mixed-model U-shaped disassembly line balancing and sequencing optimization problem with multiple constraints[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2019, 24(5): 87-96. [7] 张则强,汪开普,朱立夏,等. 多目标U型拆卸线平衡问题的Pareto蚁群遗传算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(3): 628-637,660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.03.026ZHANG Zeqiang, WANG Kaipu, ZHU Lixia, et al. Pareto hybrid ant colony and genetic algorithm for multi-objective U-shaped disassembly line balancing problem[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(3): 628-637,660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.03.026 [8] GÜNGÖR A, GUPTA S M. Disassembly sequence plan generation using a branch-and-bound algorithm[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2001, 39(3): 481-509. doi: 10.1080/00207540010002838 [9] MCGOVERN S M, GUPTA S M. A balancing method and genetic algorithm for disassembly line balancing[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 179(3): 692-708. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2005.03.055 [10] KOC A, SABUNCUOGLU I, EREL E. Two exact formulations for disassembly line balancing problems with task precedence diagram construction using an AND/OR graph[J]. IIE Transactions, 2009, 41(10): 866-881. doi: 10.1080/07408170802510390 [11] AVIKAL S, MISHRA P K, JAIN R. A Fuzzy AHP and PROMETHEE method-based heuristic for disassembly line balancing problems[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2014, 52(5): 1306-1317. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2013.831999 [12] KALAYCI C B, POLAT O, GUPTA S M. A hybrid genetic algorithm for sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2016, 242(2): 321-354. doi: 10.1007/s10479-014-1641-3 [13] 张则强,胡扬,陈冲. 求解拆卸线平衡问题的改进人工蜂群算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5): 910-917. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.013ZHANG Zeqiang, HU Yang, CHEN Chong. Improved artificial bee colony algorithm for disassembly line balancing problem[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 910-917. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.013 [14] 苏亚军,张则强,胡扬. 求解拆卸线平衡问题的一种变邻域搜索算法[J]. 现代制造工程,2016(10): 19-25.SU Yajun, ZHANG Zeqiang, HU Yang. A variable neighborhood search algorithm for disassembly line balancing problem[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2016(10): 19-25. [15] 朱兴涛,张则强,朱勋梦,等. 求解多目标拆卸线平衡问题的一种蚁群算法[J]. 中国机械工程,2014,25(8): 1075-1079. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2014.08.016ZHU Xingtao, ZHANG Zeqiang, ZHU Xunmeng, et al. An ant colony optimization algorithm for multi-objective disassembly line balancing problem[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 25(8): 1075-1079. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2014.08.016 [16] WU H S, ZHANG F M. Wolf pack algorithm for unconstrained global optimization[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering., 2014, 2014: 465082.1-465082.17. [17] TIZHOOSH H R. Opposition-based learning: a new scheme for machine intelligence[C]//International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation. Vienna: IEEE, 2005: 695-701. [18] 丁力平,谭建荣,冯毅雄,等. 基于Pareto蚁群算法的拆卸线平衡多目标优化[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2009,15(7): 1406-1413,1429.DING Liping, TAN Jianrong, FENG Yixiong, et al. Multiobjective optimization for disassembly line balancing based on Pareto ant colony algorithm[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2009, 15(7): 1406-1413,1429. [19] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [20] MCGOVERN S M, GUPTA S M. Ant colony optimization for disassembly sequencing with multiple objectives[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2006, 30(5/6): 481-496. [21] 李六柯,张则强,邹宾森,等. 免疫机制协作遗传算法的多目标拆卸线平衡优化[J]. 信息与控制,2018,47(6): 671-679.LI Liuke, ZHANG Zeqiang, ZOU Binsen, et al. Optimization of multi-objective disassembly line balancing problem using immune mechanism cooperative genetic algorithm[J]. Information and Control, 2018, 47(6): 671-679. -





 下载:
下载: