Long-Term Settlements of Composite Stratum of Clay and Silt and Metro Tunnel in It Due to Train Operation
-
摘要:
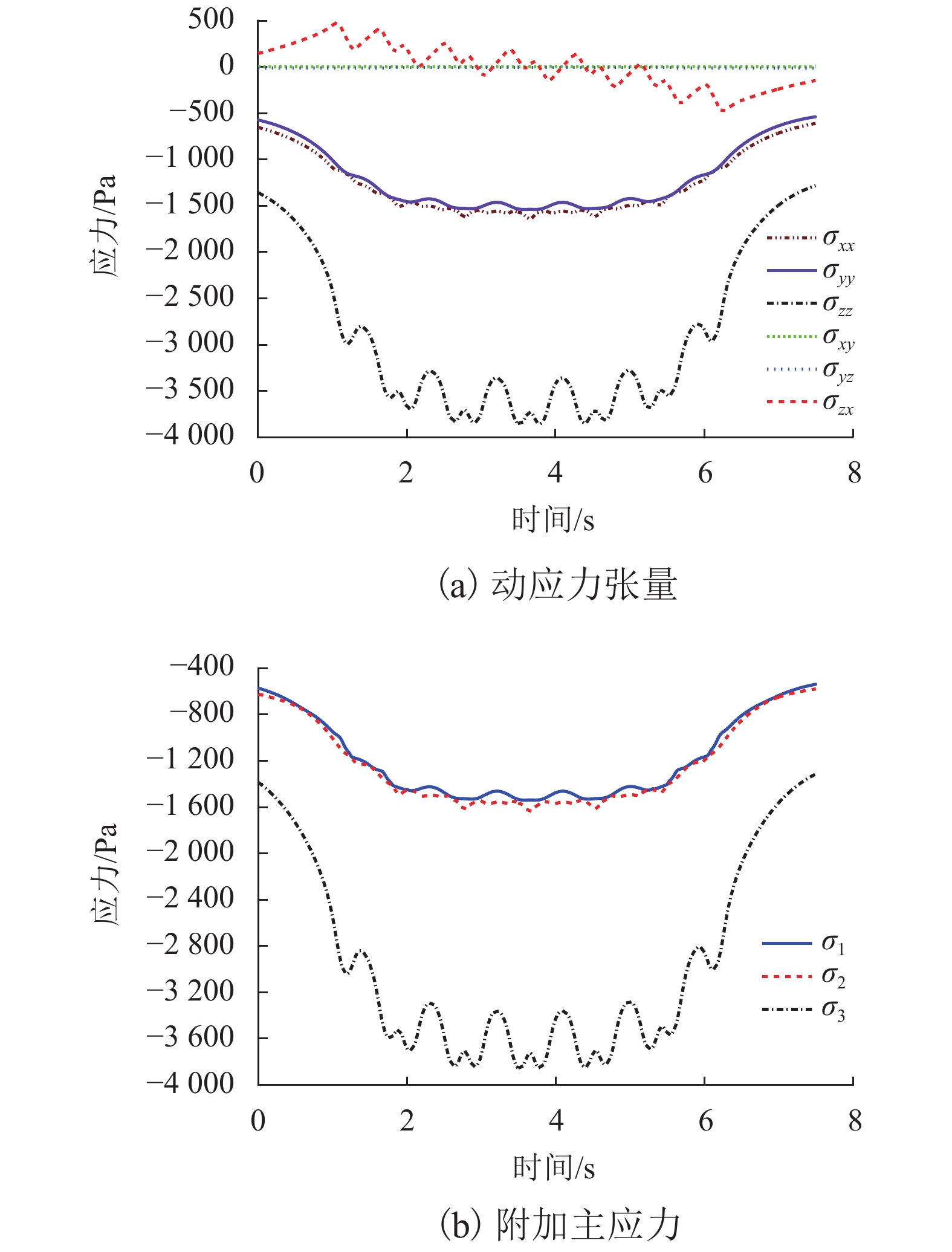
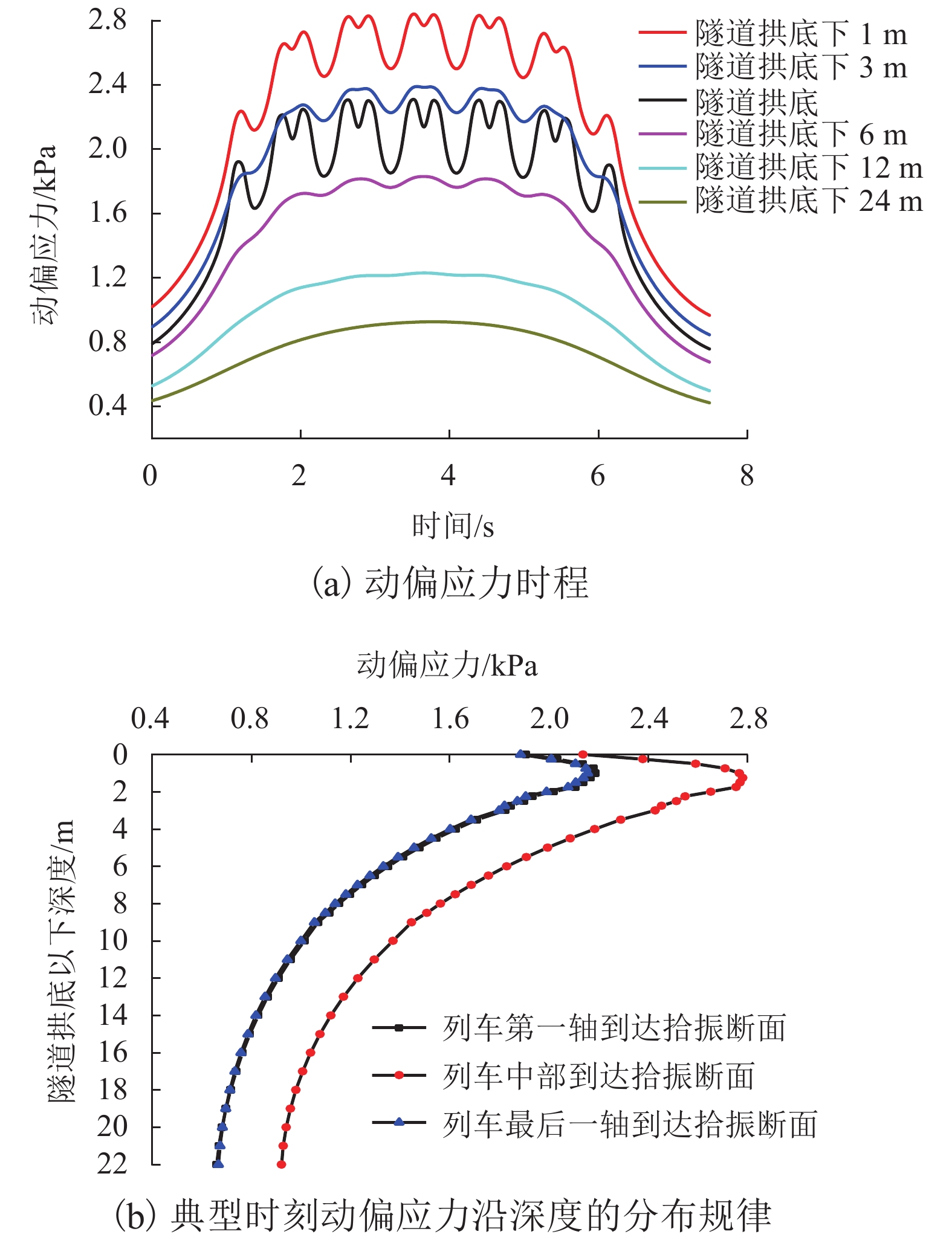
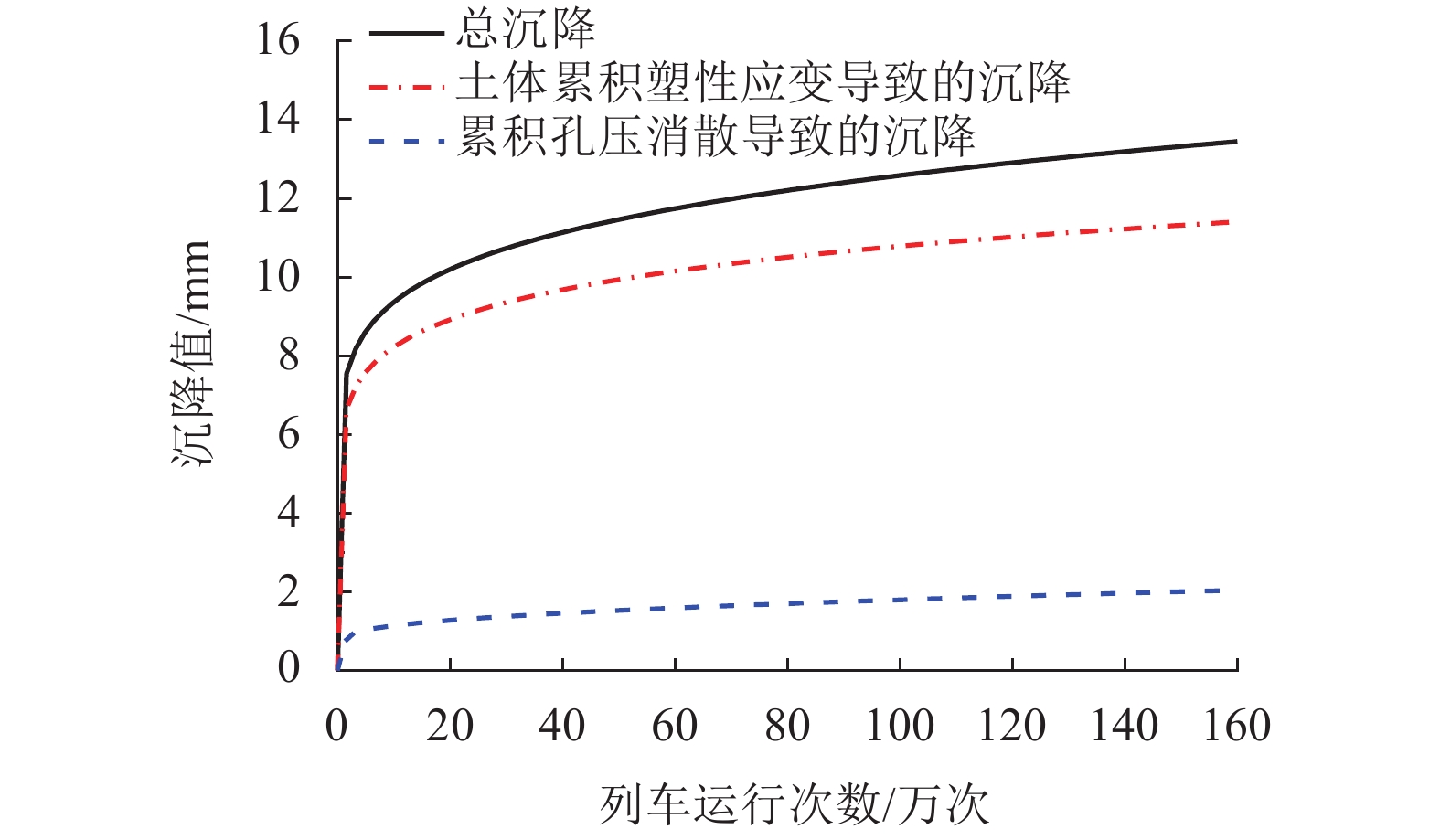
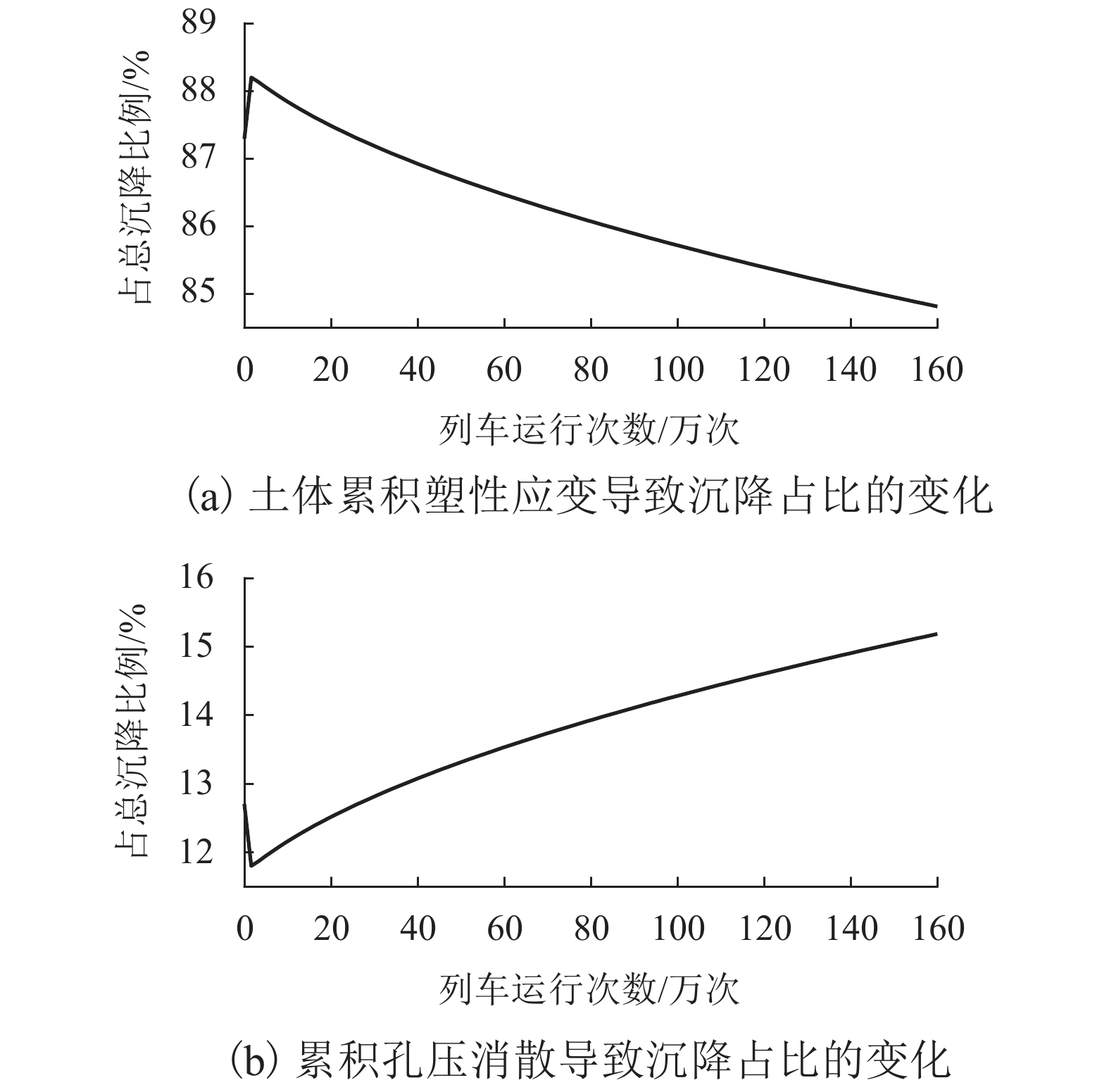
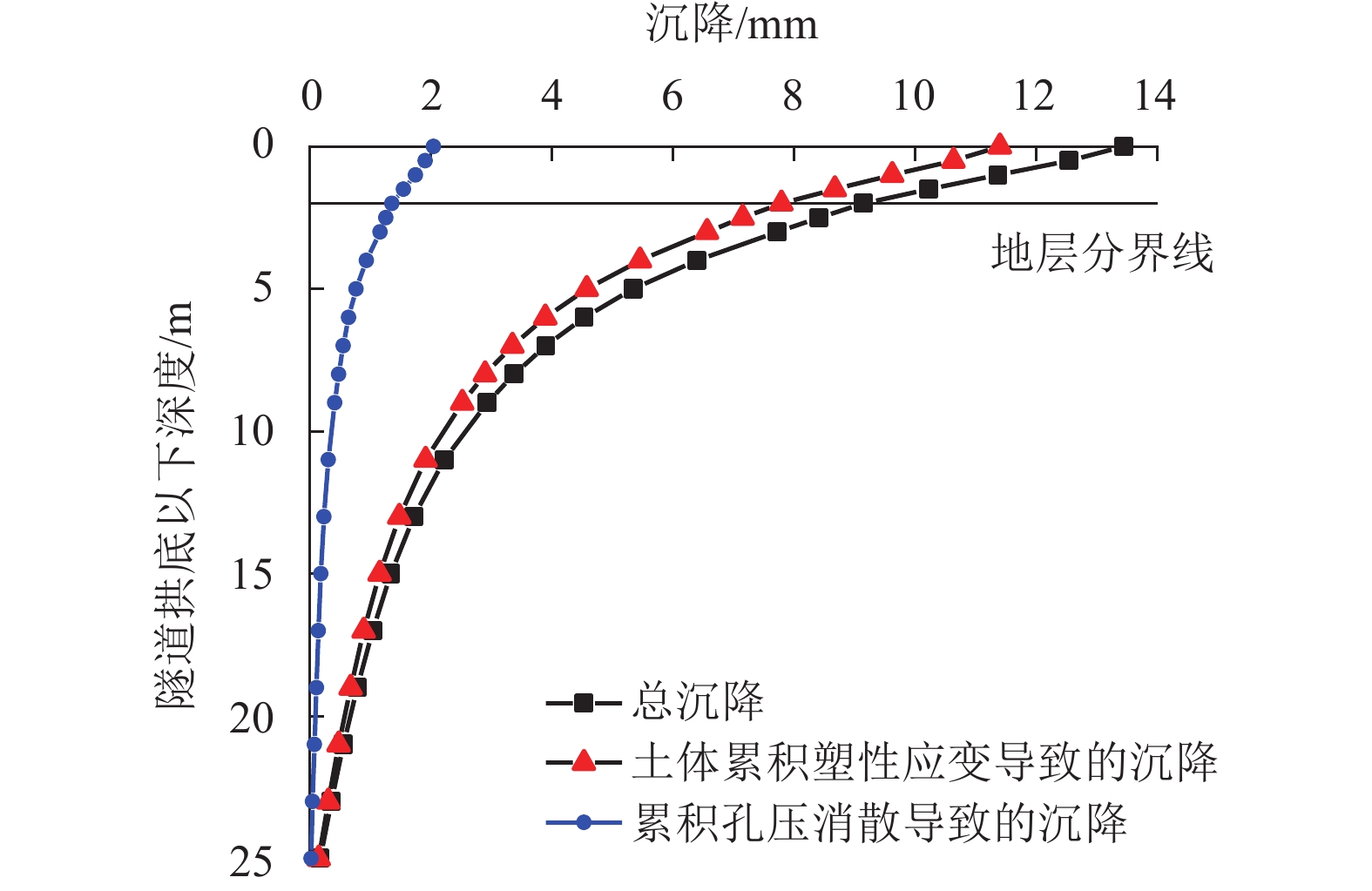
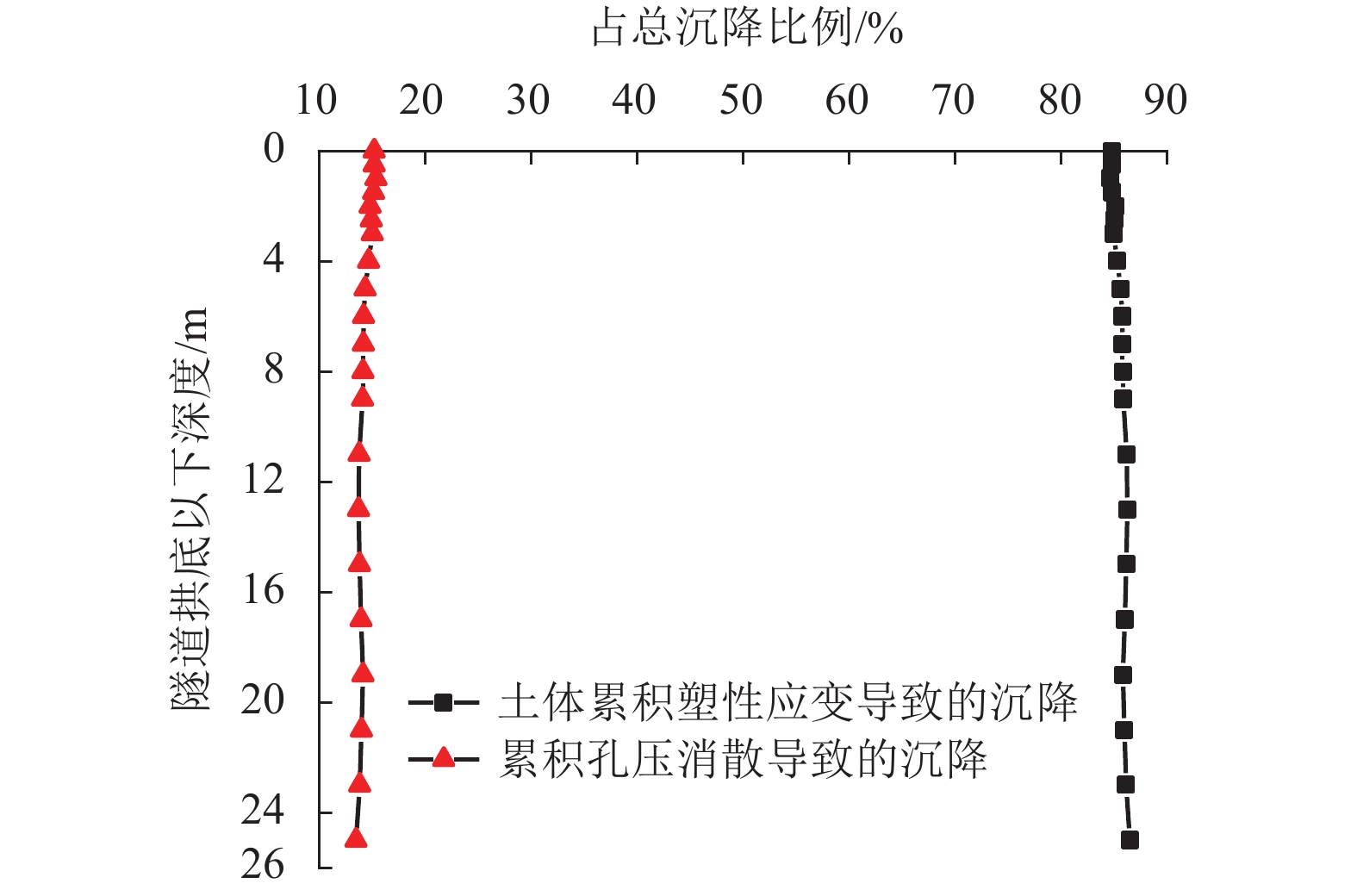
为了探明列车荷载对黏土与粉土复合地层及其中地铁隧道的长期影响,以无锡某地铁区段为研究对象,建立了轨道-隧道-地层系统的耦合2.5维数值模型,分析了运行列车诱发地铁隧道下覆黏土及粉土复合地层的动应力响应规律,进而结合循环荷载作用下黏土及粉土的不排水累积变形特征及孔压累积特征,采用分层总和法研究了列车振动荷载长期作用诱发该复合地层及其中地铁隧道的长期沉降量值及发展规律. 研究结果表明:1) 隧道下覆地基土的动偏应力沿深度方向呈先增大后减小的变化趋势,其最大值出现在隧道下覆约1.3 m深度处,可达2.80 kPa;2) 地铁列车运行导致复合地层中隧道结构的沉降主要发生在地铁列车前20万次运行期内,且隧道结构的沉降在此期间发展得较为迅速;3) 复合地层中隧道结构稳定后的车致沉降量值可达13.44 mm,其中由土体不排水累积塑性应变引起的沉降为11.40 mm,占比85%,由累积孔压消散引起的固结沉降为2.04 mm,占比15%;4) 隧道下覆黏土与粉土复合地层长期变形主要发生在隧道下方15 m范围内,该范围内的土体沉降对隧道结构长期沉降量值的贡献占比达90%.
Abstract:In order to find out the long-term effects of train load on the composite stratum of clay and silt and the metro tunnel in it, the dynamic response characteristics of this kind of composite stratum under a metro tunnel in a typical section of Wuxi Metro lines due to the moving train were firstly studied through a 2.5-dimensional (2.5D) track-tunnel-ground coupling model. Based on this, combined with the undrained deformation accumulated characteristics and the pore water pressure accumulated characteristics of corresponding soils under the cyclic loading, the developments of the long-term settlements of the concerned composite stratum and the tunnel structure due to the train vibration loads were finally obtained and analyzed through the layered summation method. The analysis results show that: 1) the dynamic deviatoric stress of the foundation soil under the tunnel increases first and then decreases with the increase of the depth, and its maximum value can reach 2.8 kPa, which appears at the position with a distance of 1.3 m to the tunnel invert; 2) the train-induced settlement of tunnel structure in the composite stratum mainly occurs within the first 200000 operation periods of metro trains, and it develops rapidly during these periods; 3) the stable train-induced settlement of tunnel structure in the composite stratum has a magnitude of 13.44 mm, in which the part caused by the accumulated undrained plastic strain of soil is 11.40 mm, accounting for 85% of the total value, while the part caused by the dissipation of accumulated pore water pressure and the corresponding consolidation of soil is 2.04 mm, accounting for 15% of the total value; 4) the long-term deformation of the composite stratum of clay and silt mainly occurs within 15 m below the tunnel, and the contribution of soil settlement within this range to the magnitude of the long-term settlement of the tunnel structure can account for 90%.
-
Key words:
- composite stratum /
- metro tunnel /
- long-term settlement /
- 2.5D approach /
- moving train load
-
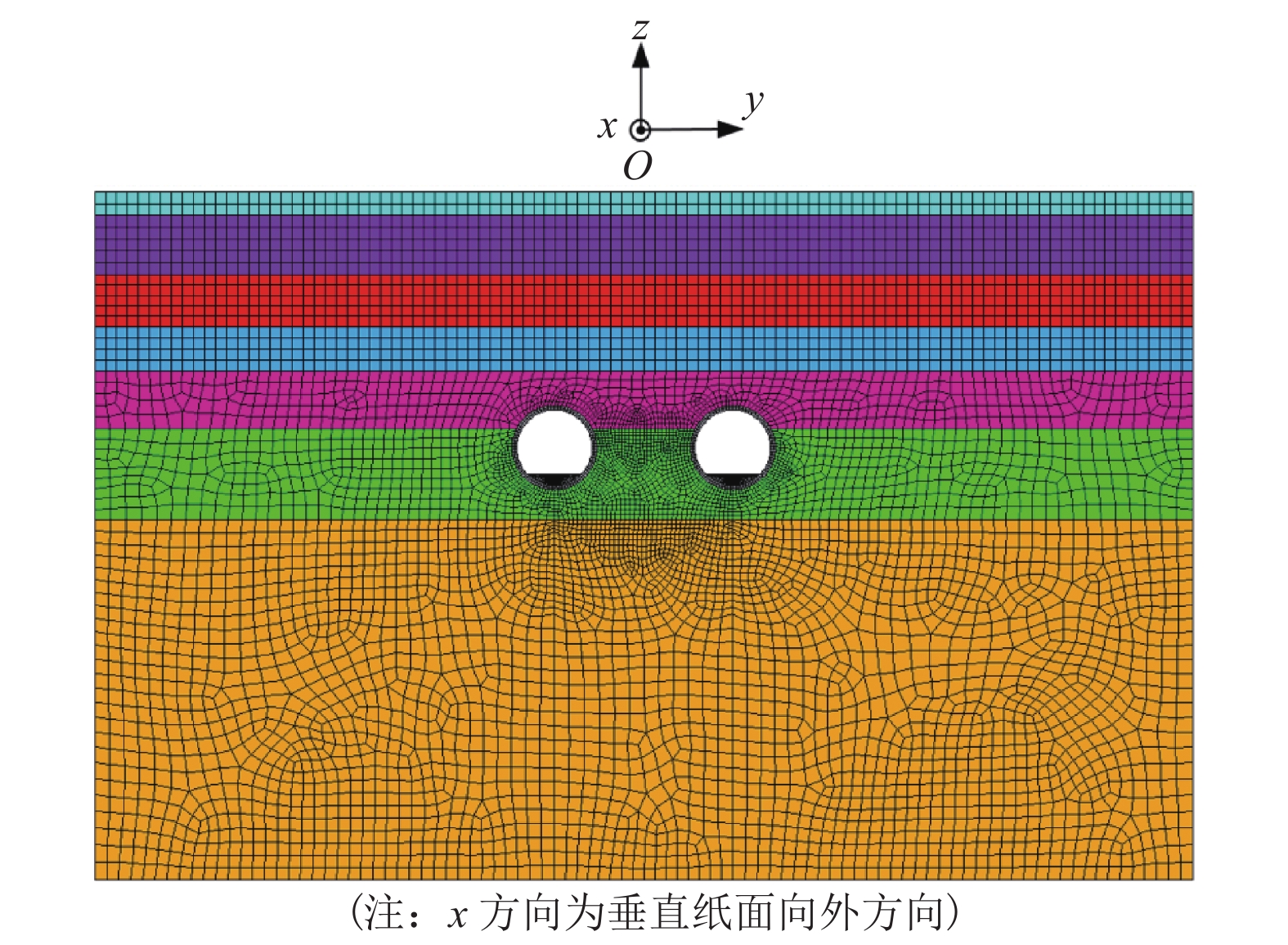
表 1 地层及隧道结构的物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of soils and tunnel structure
地层 层厚/m 弹性
模量/MPa泊松比 阻尼比 密度 /
(kg·m−3)杂填土 1.7 23.5 0.33 0.05 1770 黏土 4.3 34.8 0.32 0.05 1960 粉质黏土
夹粉土3.8 25.2 0.34 0.05 1880 粉土夹
粉质黏土3.2 25.2 0.34 0.05 1830 粉质黏土 4.2 19.2 0.31 0.05 1970 黏土 6.6 38.4 0.31 0.05 1950 粉土 26.2 36.8 0.33 0.05 1940 管片 − 34500.0 0.20 0.02 2600 道床 − 30000.0 0.25 0.02 2500 -
[1] 郑永来,韩文星,童琪华,等. 软土地铁隧道纵向不均匀沉降导致的管片接头环缝开裂研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(24): 4552-4558. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.24.025ZHENG Yonglai, HAN Wenxing, TONG Qihua, et al. Study on longitudinal crack of shield tunnel segment joint due to asymmetric settlement in soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(24): 4552-4558. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.24.025 [2] 郑永来,潘杰,韩文星. 软土地铁隧道沉降分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2005,1(1): 67-74.ZHENG Yonglai, PAN Jie, HAN Wenxing. Analysis on the settlements of metro tunnels in soft soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2005, 1(1): 67-74. [3] SHEN S L, WU H N, CUI Y J, et al. Long-term settlement behaviour of metro tunnels in the soft deposits of Shanghai[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 40: 309-323. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2013.10.013 [4] 王湛. 软土地层中盾构隧道结构沉降与变形机制分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. [5] 刘明,黄茂松,李进军. 地铁荷载作用下饱和软黏土的长期沉降分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,2006,2(5): 813-817.LIU Ming, HUANG Maosong, LI Jinjun. Long-term settlement of saturated soft clay under subway loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2006, 2(5): 813-817. [6] 姚兆明,张明慧,陈军浩. 饱和软黏土循环累积孔压模型及地铁隧道路基长期沉降计算[J]. 铁道学报,2012,34(9): 87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.09.015YAO Zhaoming, ZHANG Minghui, CHEN Junhao. Cyclic accumulative pore pressure explicit model of saturated soft clay and long-term settlement calculation of subway tunnel roadbed[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(9): 87-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.09.015 [7] 高广运,李绍毅,涂美吉,等. 地铁循环荷载作用下交叉隧道沉降分析[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(增刊1): 486-490.GAO Guangyun, LI Shaoyi, TU Meiji, et al. Analysis of settlement of cross tunnels under cyclic metro loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(S1): 486-490. [8] 张冬梅,李钰. 地铁荷载引起的盾构隧道及土层长期沉降研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2015,35(5): 563-567.ZHANG Dongmei, LI Yu. Long-term settlement of shield tunnel in soft clay due to vehicle vibration[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2015, 35(5): 563-567. [9] 曾二贤. 交通动荷载引起的软土地基长期沉降[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. [10] HUANG Q, HUANG H W, YE B, et al. Dynamic response and long-term settlement of a metro tunnel in saturated clay due to moving train load[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2017, 57(6): 1059-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2017.08.031 [11] 边学成,曾二贤,陈云敏. 列车交通荷载作用下软土路基的长期沉降[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(11): 2990-2996. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.11.018BIAN Xuecheng, ZENG Erxian, CHEN Yunmin. Long-term settlements of soft soil ground induced by train traffic loadings[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(11): 2990-2996. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.11.018 [12] 赵春彦,周顺华,袁建议. 地铁荷载作用下叠交隧道长期沉降的半解析法[J]. 铁道学报,2010,32(4): 141-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.04.026ZHAO Chunyan, ZHOU Shunhua, YUAN Jianyi. Semi-analytical solution for long-term settlement of overlapped tunnel under subway loading[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2010, 32(4): 141-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.04.026 [13] LIU J B, DU Y X, DU X L, et al. 3D viscous-spring artificial boundary in time domain[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2006, 5(1): 93-102. doi: 10.1007/s11803-006-0585-2 [14] CHAI J C, MIURA N. Traffic-load-induced permanent deformation of road on soft subsoil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(11): 907-916. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:11(907) [15] LI D Q, SELIG E T. Cumulative plastic deformation for fine-grained subgrade soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1996, 122(12): 1006-1013. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1996)122:12(1006) [16] 黄茂松,李进军,李兴照. 饱和软黏土的不排水循环累积变形特性[J]. 岩土工程学报,2006,28(7): 891-895. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.07.016HUANG Maosong, LI Jinjun, LI Xingzhao. Cumulative deformation behaviour of soft clay in cyclic undrained tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(7): 891-895. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.07.016 [17] 黄凯. 粉土在循环荷载作用下的累积变形研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2009. [18] HUANG X, HUANG H W, ZHANG J. Flattening of jointed shield-driven tunnel induced by longitudinal differential settlements[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2012, 31: 20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2012.04.002 -




 下载:
下载: