Effect of Clay Contamination on Stress-Dilatancy Relationships of Ballast Aggregate
-
摘要:
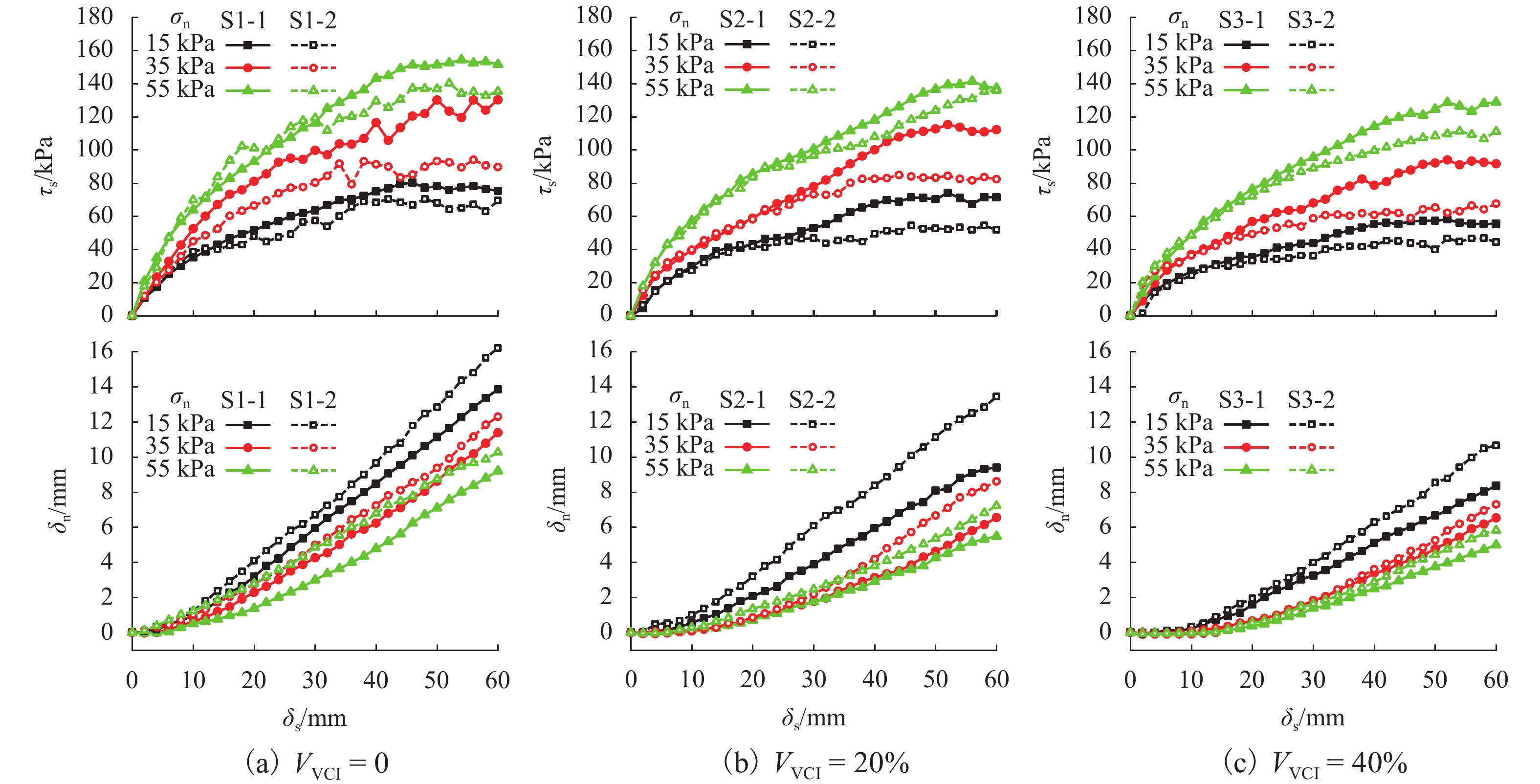
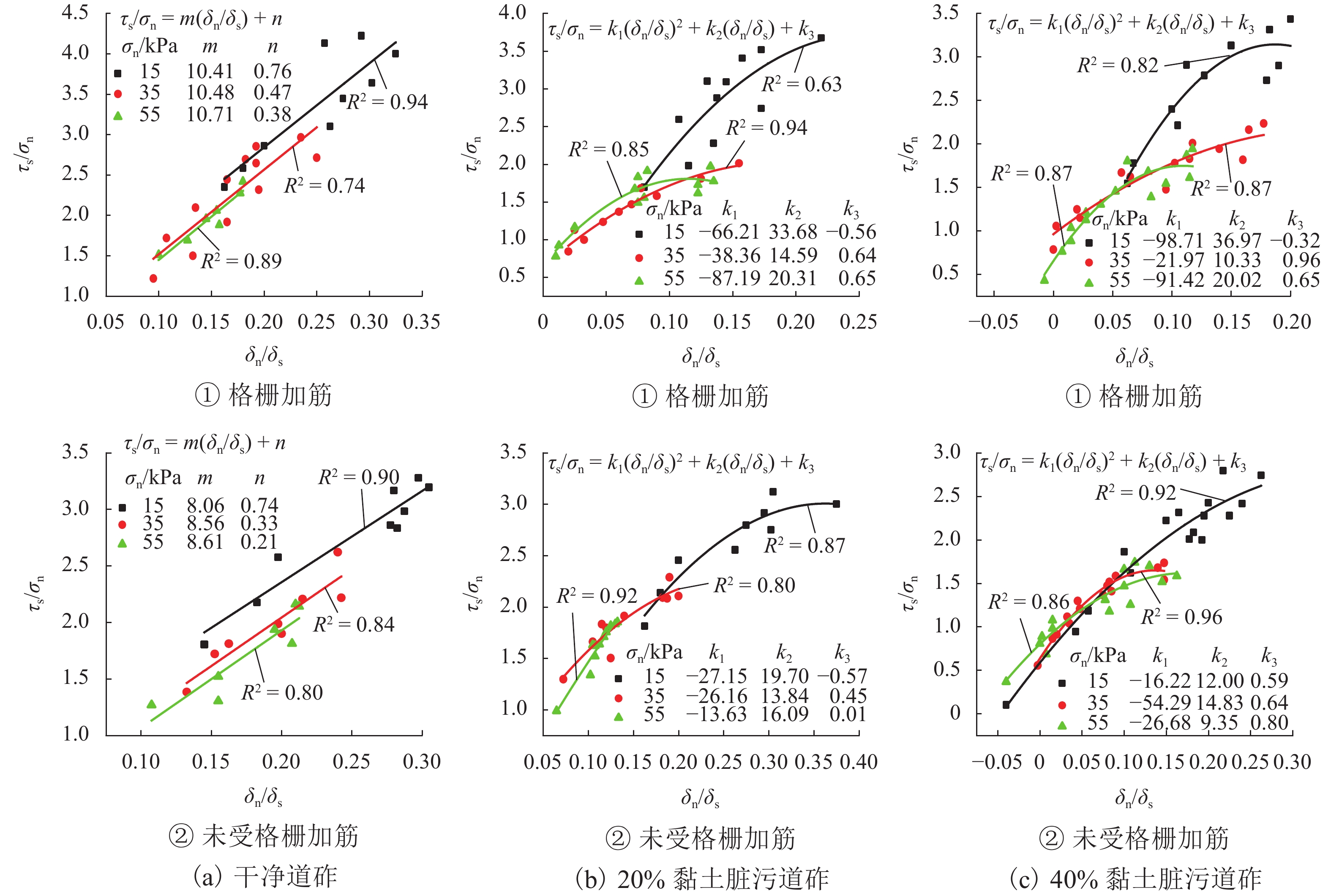
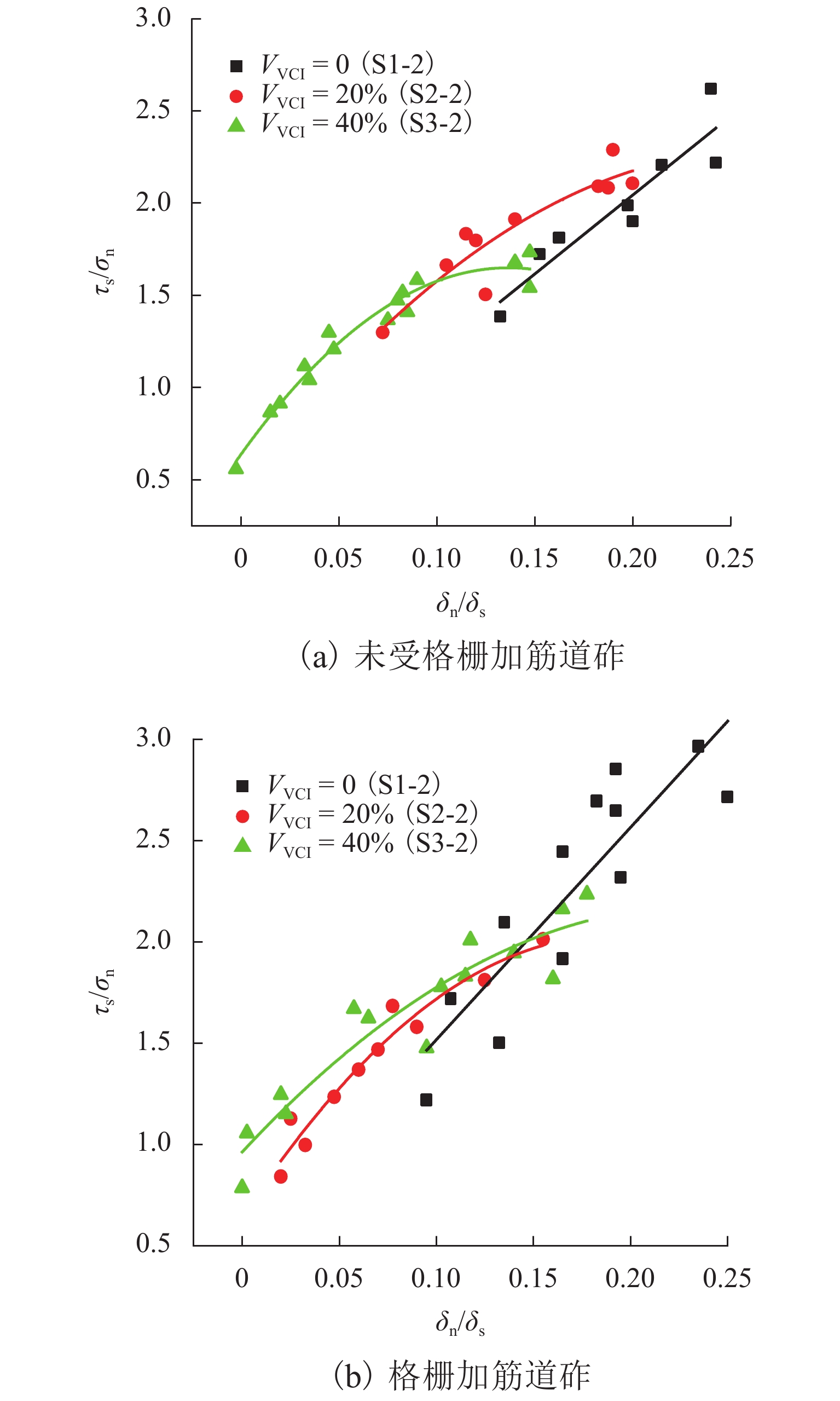
列车循环荷载下,铁路地基层中的黏土颗粒会逐渐侵入道砟层,降低道床承载性能. 通过开展一系列大型直剪试验,对黏土脏污质污染下的受格栅加筋道砟集料和未受格栅加筋道砟集料的强度及变形发展、应力-剪胀关系进行了研究. 试验结果表明:随着脏污程度的增加,道砟集料在剪切过程中强度及法向变形均降低;干净道砟集料的应力比与剪胀比呈一阶线性关系,而黏土污染的道砟集料塑性增强,在剪应力峰值状态下剪胀比更高而抗剪强度发展缓慢,导致应力比与剪胀比呈二阶多项式关系;高法向压力下,道砟集料具有更低的剪胀比;黏土脏污质的存在会减小道砟集料的变形破坏速率,但降低了集料的抗剪强度,而格栅的加筋作用可弥补由于黏土脏污引起的强度降低.
Abstract:Clay fines from subgrade would gradually intrude into the ballast layer under cyclic loadings of passing trains, which would reduce the bearing capacity and impede the free drainage of track beds. A series of large-scale direct shear tests were carried out to investigate the strength and deformation characteristics and stress-dilatancy relationship of the geogrid-reinforced and unreinforced ballast contaminated by clay fines. The results showed that the strength and normal displacement of ballast aggregate decrease with an increase in the contamination level. The stress ratio of clean ballast is linear with the dilatancy ratio, while the addition of clay fines would increase the plasticity of the ballast aggregate. For fouled ballast in the peak state of shear stress, the dilatancy ratio of aggregate increases while the shear strength decreases, and a second-order polynomial relationship between stress ratio and dilatancy ratio is observed. Under a higher normal pressure, the aggregates have a lower dilatancy ratio. The reduction in the dilatancy rate and the shear strength of clay-contaminated ballast can be remedied by the inclusion of geogrid in the aggregate.
-
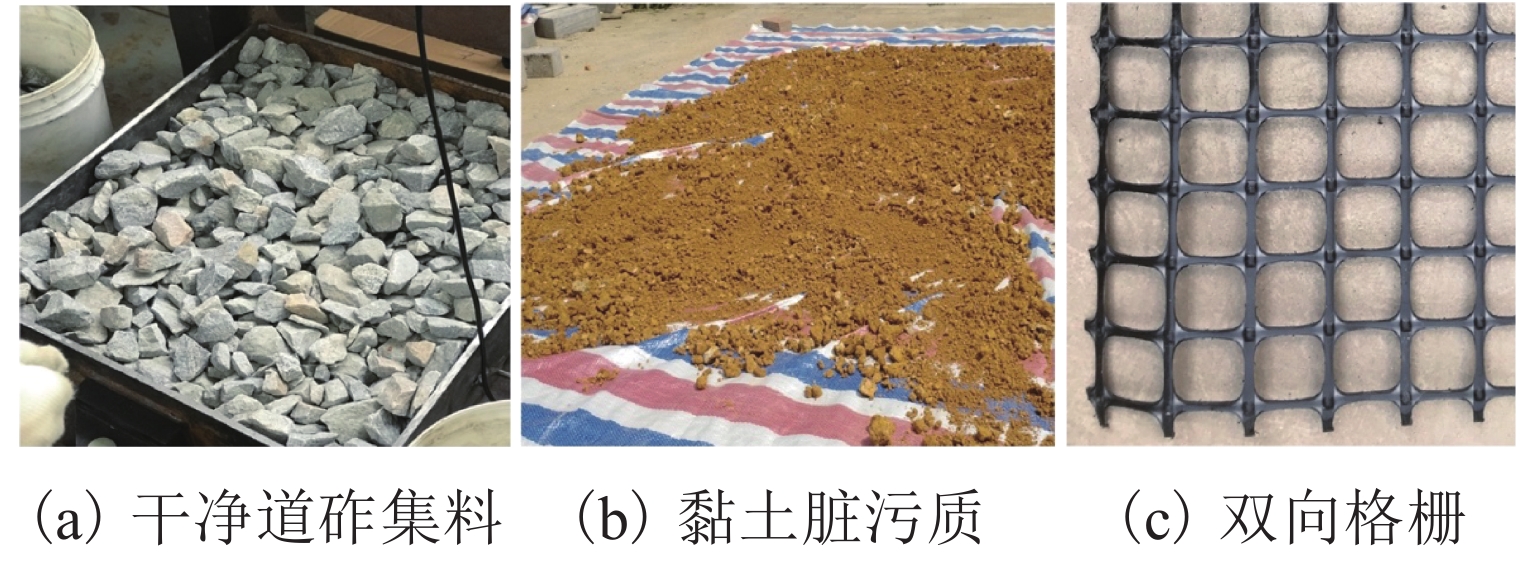
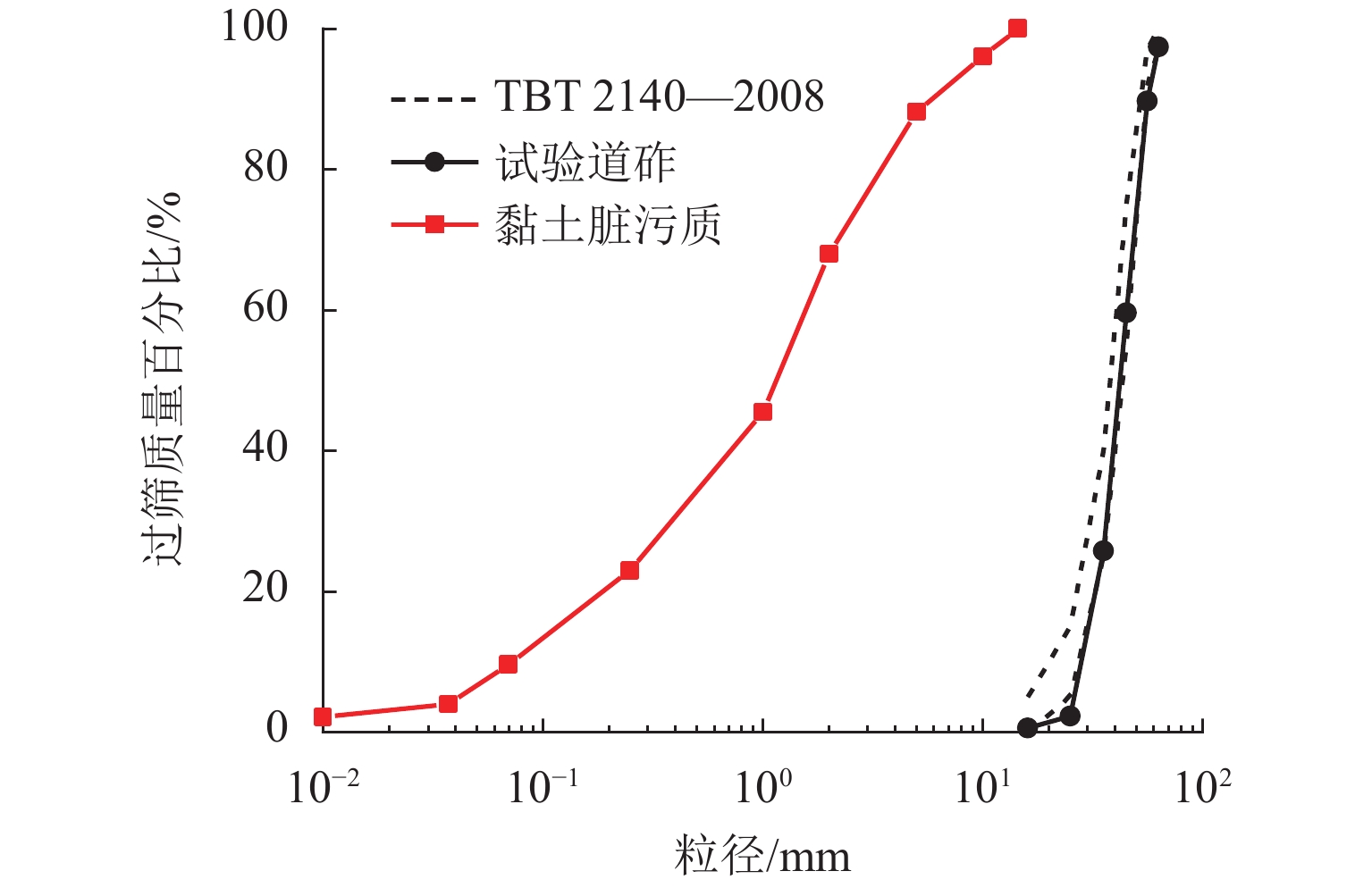
表 1 道砟及黏土脏污质工程性能指标表
Table 1. Engineering properties of clean ballast and clay fines
材料 比重 堆积密度/
(kg·m−3)e ωL/
%ωP/
%D50/
mmCu Cc 道砟 2.66 1432 0.858 39.0 1.15 1.75 黏土 2.70 1178 1.207 42.10 22.40 1.3 24.29 1.34 表 2 格栅参数表
Table 2. Mechanical properties of geogrid
参数 规格 孔径形式 双向孔径 55 mm × 55 mm 材料 聚丙烯 2% 应变时抗拉
强度/(kN·m−1)11 5% 应变时抗拉
强度/(kN·m−1)15 峰值抗拉强度/(kN·m−1) 30 屈服点伸长率/% 13 表 3 试样设置情况表
Table 3. Details of experimental specimens
VCI/% 试样编号 格栅布置 黏土质量/kg 0 S1-1 格栅加筋 S1-2 20 S2-1 格栅加筋 21.70 S2-2 40 S3-1 格栅加筋 43.40 S3-2 -
[1] INDRARATNA B, SINGH M, NGUYEN T T. The mechanism and effects of subgrade fluidisation under ballasted railway tracks[J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2020, 28(2): 113-128. doi: 10.1007/s40534-020-00210-1 [2] TENNAKOON N, INDRARATNA B. Behaviour of clay-fouled ballast under cyclic loading[J]. Géotechnique, 2014, 64(6): 502-506. [3] INDRARATNA B, TENNAKOON N, NIMBALKAR S, et al. Behaviour of clay-fouled ballast under drained triaxial testing[J]. Géotechnique, 2013, 63(5): 410-419. [4] NGO T, INDRARATNA B. Analysis of deformation and degradation of fouled ballast: experimental testing and DEM modeling[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 20(9): 06020020.1-06020020.8. [5] HUANG H, TUTUMLUER E, DOMBROW W. Laboratory characterization of fouled railroad ballast behavior[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2009, 2117(1): 93-101. doi: 10.3141/2117-12 [6] DANESH A, PALASSI M, MIRGHASEMI A A. Effect of sand and clay fouling on the shear strength of railway ballast for different ballast gradations[J]. Granular Matter, 2018, 20(3): 1-14. [7] TRINH V N, TANG A M, CUI Y J, et al. Mechanical characterisation of the fouled ballast in ancient railway track substructure by large-scale triaxial tests[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2012, 52(3): 511-523. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2012.05.009 [8] ROWE P W. The stress-dilatancy relation for static equilibrium of an assembly of particles in contact[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1962, 269(1339): 500-527. [9] MITCHELL J K, SOGA K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior[M]. Manhattan: John Wiley & Sons, 1976. [10] XIAO Y, MENG M Q, CHEN Q S, et al. Friction and dilatancy angles of granular soils incorporating effects of shearing modes[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 18(11): 06018027.1-06018027.9. [11] XIAO Y, LIU H L, LIU H, et al. Strength and dilatancy behaviors of dense modeled rockfill material in general stress space[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 16(5): 04016015.1-04016015.15. [12] DOŁŻYK-SZYPCIO K. Stress-dilatancy relationship for railway ballast[J]. Studia Geotechnica et Mechanica, 2018, 40(2): 79-85. doi: 10.2478/sgem-2018-0018 [13] SZYPCIO Z. Stress-dilatancy of gravel for triaxial compression tests[J]. Annals of Warsaw University of Life Sciences-SGGW. Land Reclamation, 2018, 50(2): 119-128. doi: 10.2478/sggw-2018-0010 [14] DOŁŻYK-SZYPCIO K. Direct shear test for coarse granular soil[J]. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 2019, 17(12): 1871-1878. doi: 10.1007/s40999-019-00417-2 [15] SAROJINIAMMA B K, INDRARATNA B, VINOD J S. A semi-empirical dilatancy model for ballast fouled with plastic fines[J]. Geomechanics and Geoengineering, 2019, 14(1): 12-17. doi: 10.1080/17486025.2018.1476737 [16] 陈静,高睿,刘洋泽鹏,等. 不同脏污质对格栅加筋道砟性能的影响[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(1): 200-206.CHEN Jing, GAO Rui, LIU Yangzepeng, et al. Influence of various fouling materials on geogrid-reinforced ballast performance[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(1): 200-206. [17] 铁道科学研究院. 铁路碎石道砟: TBT 2140—2008. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2008. [18] MCDOWELL G R, HARIRECHE O, KONIETZKY H, et al. Discrete element modelling of geogrid-reinforced aggregates[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers−Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 159(1): 35-48. doi: 10.1680/geng.2006.159.1.35 [19] INDRARATNA B, SU L J, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. A new parameter for classification and evaluation of railway ballast fouling[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2011, 48(2): 322-326. doi: 10.1139/T10-066 [20] SELIG E T, WATERS J M. Track geotechnology and substructure management[M]. London: Homas Telford Publishing, 1994 [21] FELDMAN F, NISSEN D. Alternative testing method for the measurement of ballast fouling: percentage void contamination[C]//CORE 2002, Cost Efficient Railways Through Engineering, Conference on Railway Engineering. Wollongong: [s.n.], 2002: 10-13. [22] BIABANI M M, INDRARATNA B, NIMBALKAR S. Assessment of interface shear behaviour of sub-ballast with geosynthetics by large-scale direct shear test[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 143: 1007-1015. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.094 [23] 高睿,石知政,刘洋泽鹏,等. 土工格栅对受污道砟直剪特性影响的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(6): 1185-1191.GAO Rui, SHI Zhizheng, LIU Yangzepeng, et al. Experimental study on effect of geogrid on direct shear behavior of contaminated ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(6): 1185-1191. [24] INDRARATNA B, NGO N T, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C. Behavior of geogrid-reinforced ballast under various levels of fouling[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2011, 29(3): 313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2011.01.015 [25] SUN Y F, GAO Y F, CHEN C. Critical-state fractional model and its numerical scheme for isotropic granular soil considering state dependence[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 19(3): 04019001.1-04019001.14. [26] BOLTON M D. The strength and dilatancy of sands[J]. Géotechnique, 1986, 36(1): 65-78. [27] INDRARATNA B, NGO N T, RUJIKIATKAMJORN C, et al. Behavior of fresh and fouled railway ballast subjected to direct shear testing: discrete element simulation[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 14(1): 34-44. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000264 -




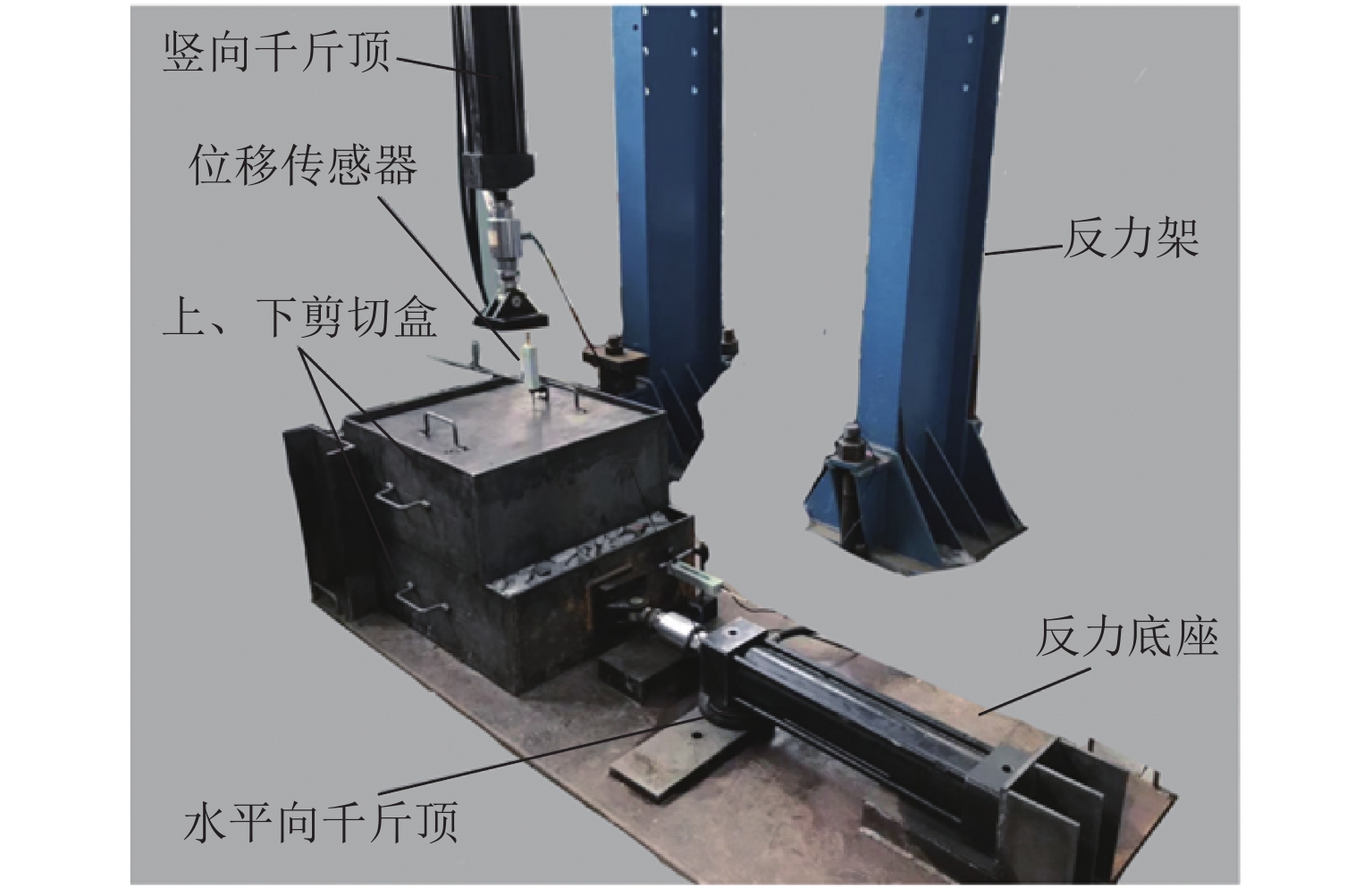
 下载:
下载: