Day-Ahead Optimal Scheduling of Co-phase Traction Power Supply System with Photovoltaic and Hybrid Energy Storage
-
摘要:
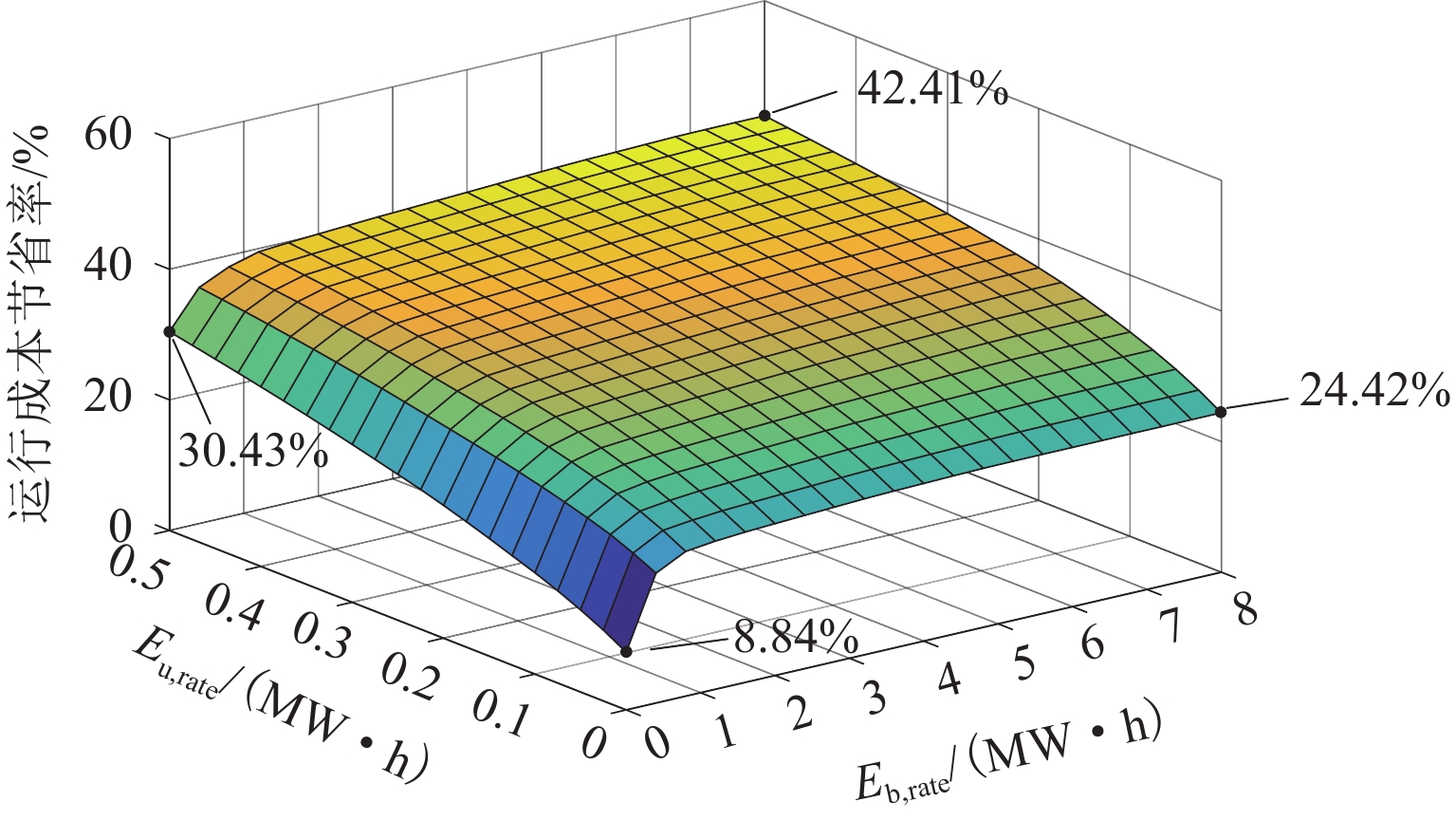
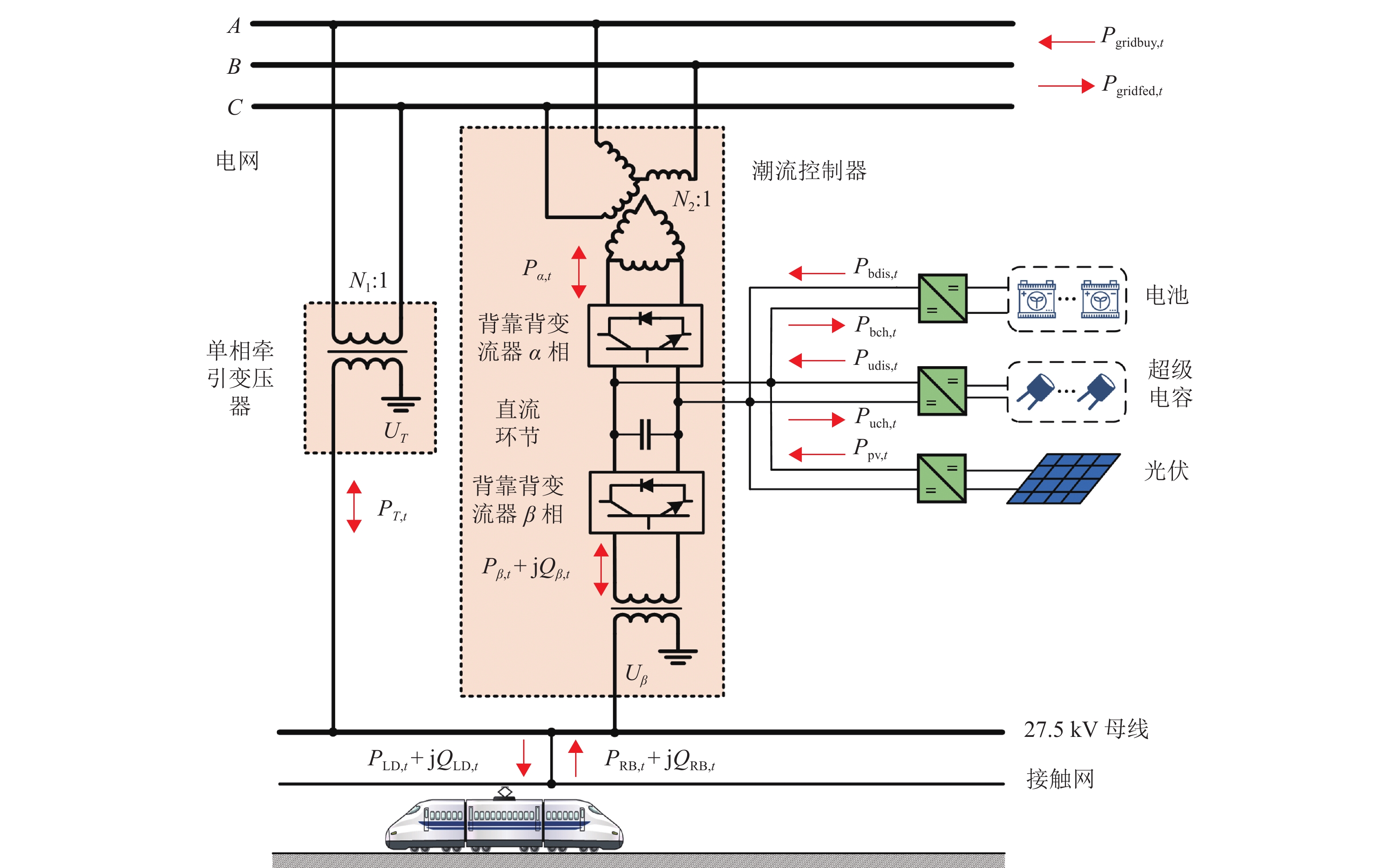
既有牵引供电系统中以负序为主的电能质量问题以及电分相环节严重制约了其安全、高效运行,目前理想的解决方案是基于对称补偿理论的同相供电技术. 通过同相补偿装置中的直流母线接入光伏发电系统以及混合储能装置,进一步实现再生回馈能量利用和牵引负荷削峰填谷,提高光伏渗透率. 因此,建立了一种同相牵引供电系统优化运行模型,该模型以同相牵引变电所日运行成本最低为目标,以混合储能装置充放电策略、光伏出力以及潮流控制器功率为决策变量,尤其考虑了电网侧三相电压不平衡度约束;进一步将原始优化模型中非线性约束进行线性化处理,得到混合整数线性规划模型,并利用商业规划求解器CPLEX进行求解. 算例分析结果表明:接入光伏与混合储能装置后日运行成本可节省36.45%,且三相电压不平衡度满足国标上限2%的要求.
Abstract:Power quality issues represented by voltage unbalance and the electrical sectioning issues have severely restricted the safe and efficient operation of the traction power supply system. At present, the ideal solution is the co-phase power supply technology based on symmetrical compensation theory. By integrating the photovoltaic power generation system and the hybrid energy storage system with the DC bus of power flow controller, the utilization of regenerative braking energy, and peak-shaving and valley-filling of traction load can be further achieved to improve photovoltaic penetration rate. For this purpose, the optimal operation model of co-phase traction power supply system is established, which sets the minimum daily operation cost of traction substation as the objective, and takes the charging and discharging strategy of hybrid energy storage, photovoltaic output and power flow controller power as decision variables, and also takes into account the three-phase voltage unbalance constraint. The nonlinear constraints are linearized to formulate the mixed-integer linear programming model, which can be solved by programming solver CPLEX. The case study results show that the integration of photovoltaic and hybrid energy storage can effectively reduce 36.45% of daily operating cost, while the three-phase voltage unbalance meets the upper limit of 2% in the national standard.
-
表 1 模型输入参数
Table 1. Input parameters of model
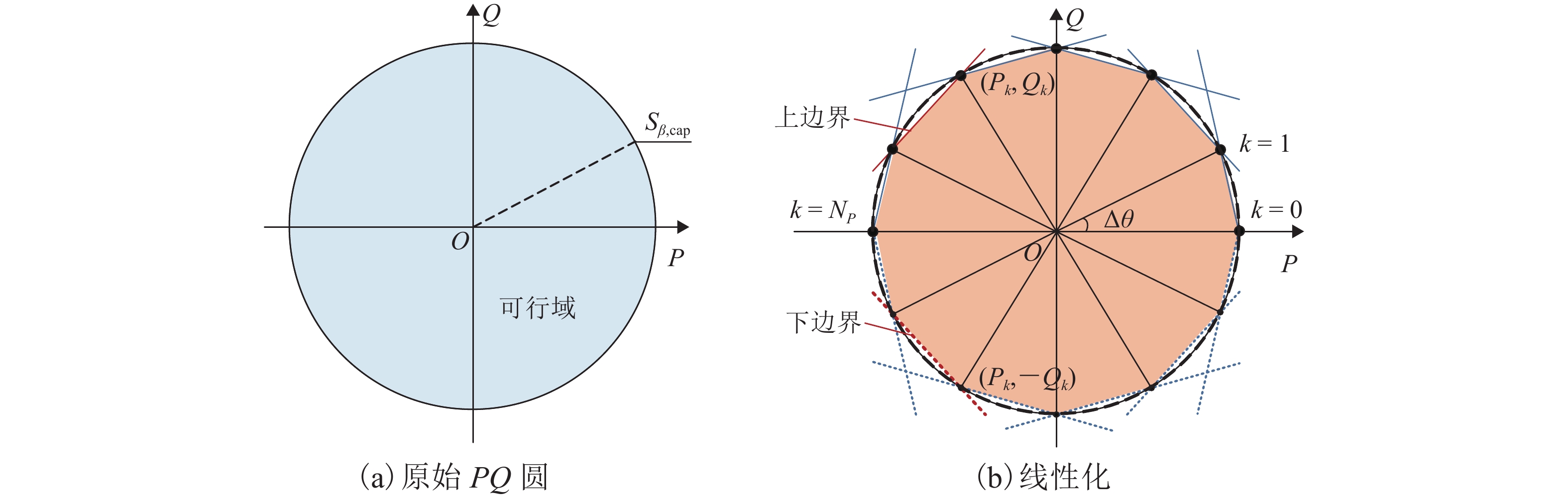
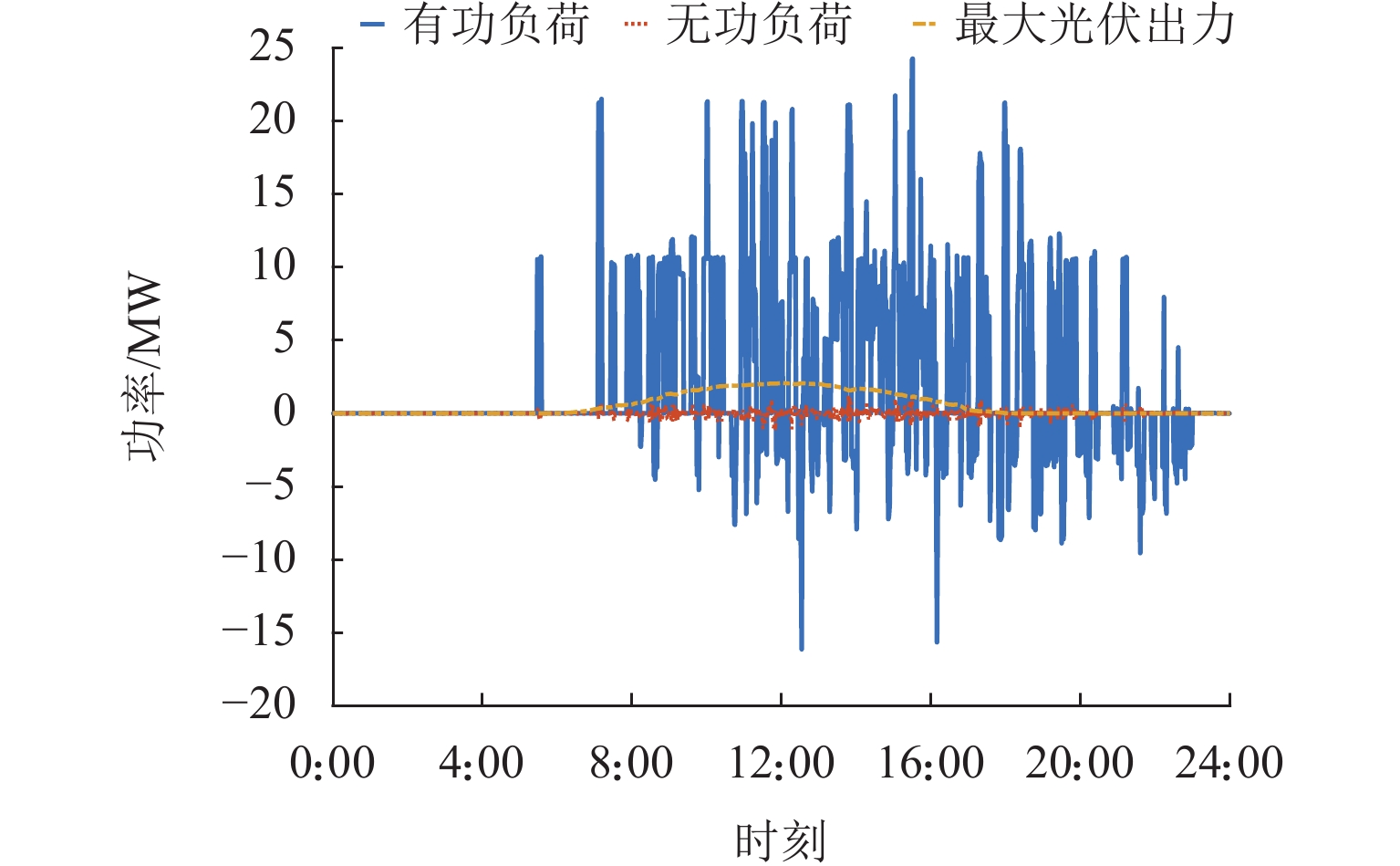
项目 参数 参数取值 电网 US/kV 220.0 Scap/(MV·A) 750 $ {{\overline \varepsilon _{\text{U}}}} $/% 2 牵引变压器 N1 4 N2 4$/ {\sqrt 3 }$ UT/kV 27.5 潮流控制器 Uα/kV 27.5 Uβ/kV 27.5 Sα,cap/(MV·A) 10 Sβ,cap/ (MV·A) 10 混合储能装置 电池 超级电容 SOC 范围 [0.20, 0.80] [0.05, 0.95] 初始 SOC 0.5 0.5 效率(充/放电) 0.80/0.80 0.95/0.95 额定容量/(MW·h) 5.00 0.25 额定功率/MW 2 10 日最大循环数/次 15 不限 电价 峰时 平时 谷时 电度/ (元·(kW·h)−1) 1.252 0.782 0.370 需量/
(元·(kW·月−1)−1)42.000 42.000 42.000 时间段 8:00—11:00,
18:00—21:007:00—8:00,
12:00—17:000:00—6:00,
22:00—0:00反馈电能
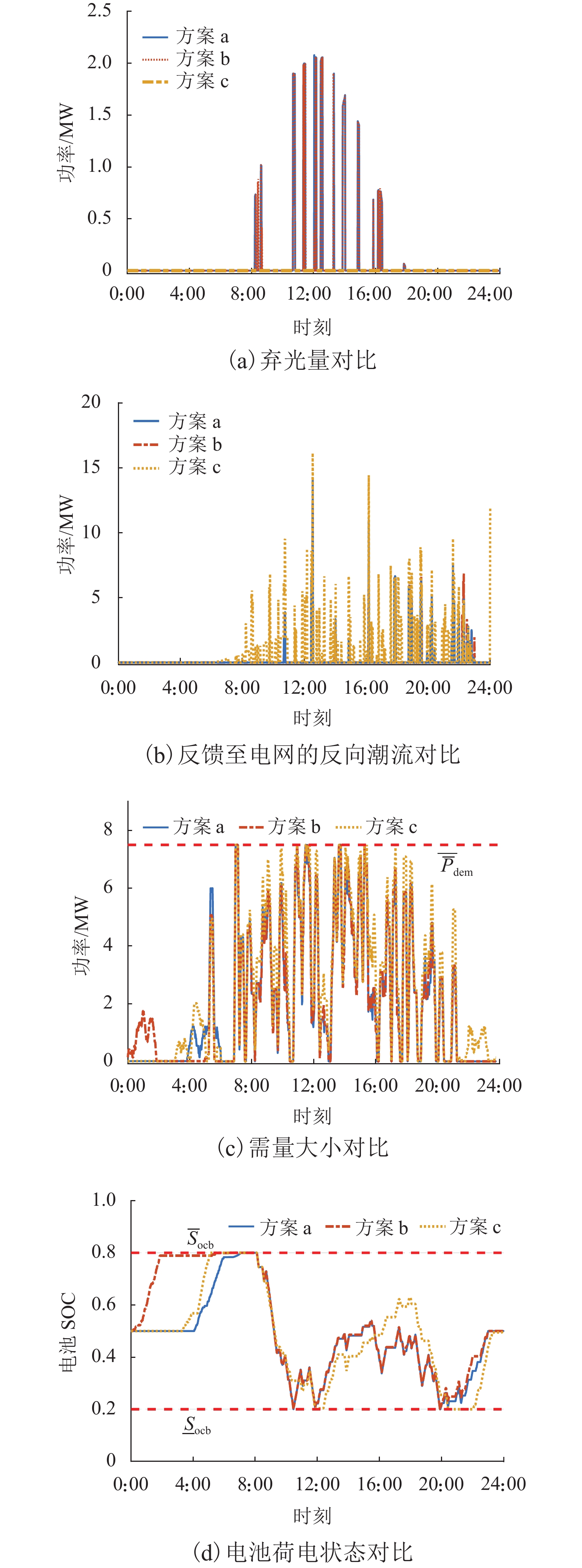
计费方案方案 a cfed = 0 方案 b cfed = cbuy 方案 c cfed = −0.8cbuy 表 2 方案Ⅰ与方案Ⅱ优化结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of scheme Ⅰ and scheme Ⅱ
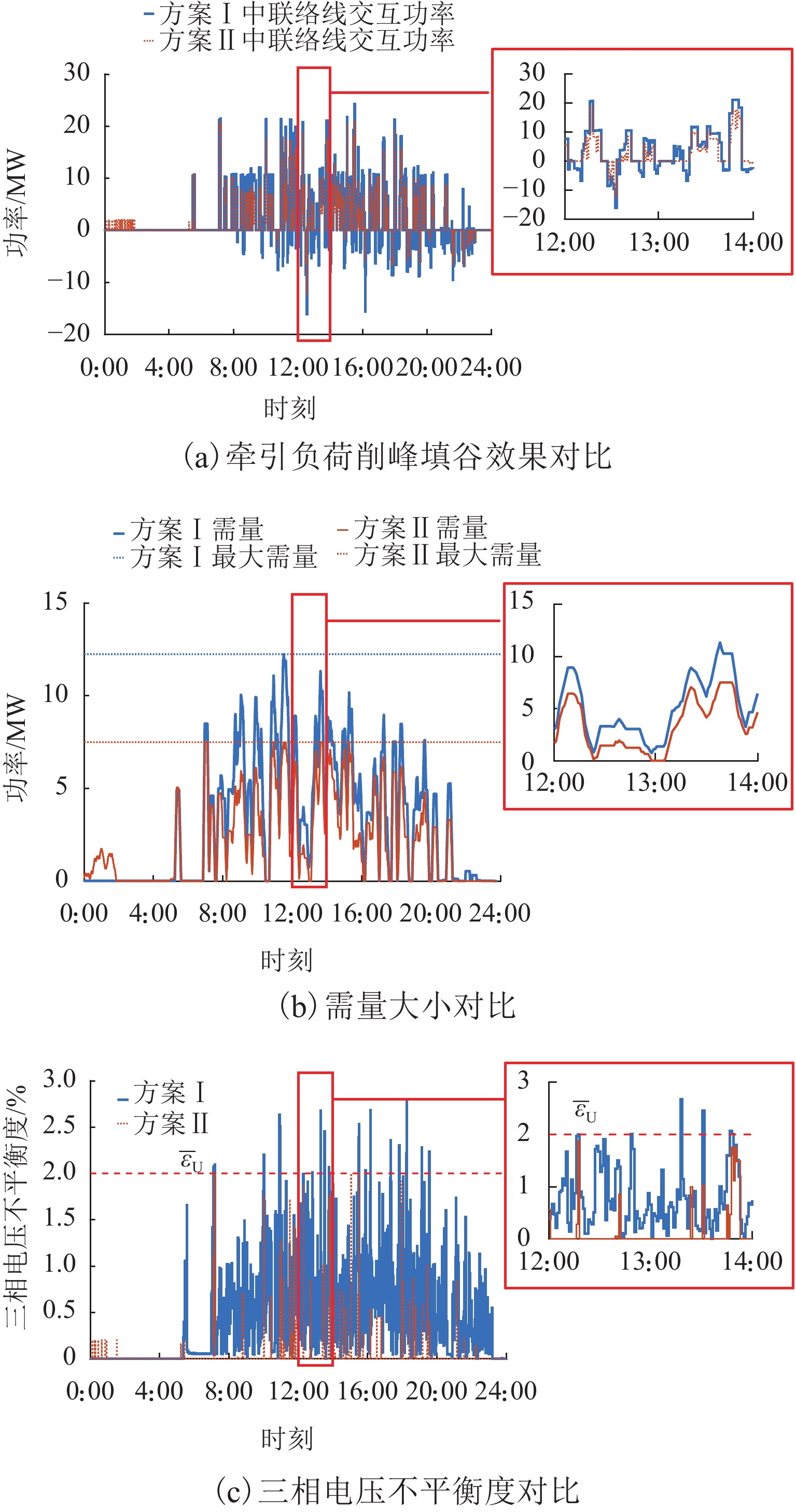
指标 方案Ⅰ 方案Ⅱ 优化率/% 经济 电度电费/元 67 077.81 44 674.85 33.40 需量电费/元 17 129.90 10 489.85 38.76 回馈电能计费/元 14 759.58 26 36.13 82.14 光伏运维费用/元 0 12 56.80 储能运维费用/元 0 3 833.72 总成本/元 98 967.29 62 891.35 36.45 技术 制动能量
利用率/%0 80.27 80.27 最大电压
不平衡度/%2.79 2.00 28.32 表 3 反馈电能计费方案a、b和c优化结果对比
Table 3. Optimal result comparison of feedback power billing schemes a, b and c
项目 方案 a 方案 b 方案 c 总弃光量/(MW·h) 1.43 1.47 0 电池日循环数 15 15 6 电度电费/元 44 674.85 44 674.85 53 149.54 需量电费/元 10 489.85 10 489.85 10 489.85 回馈电能收费/元 0 2 636.13 −12 704.86 光伏运维费用/元 1 261.25 1 256.80 1 409.51 储能运维费用/元 3 770.44 3 833.72 1 713.61 总成本/元 60 196.39 62 891.35 5 4057.66 总成本节省率
(相较方案Ⅰ) /%28.51 36.45 25.33 -
[1] 李群湛. 我国高速铁路牵引供电发展的若干关键技术问题[J]. 铁道学报,2010,32(4): 119-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.04.022LI Qunzhan. On some technical key problems in the development of traction power supply system for high-speed railway in China[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2010, 32(4): 119-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2010.04.022 [2] 李群湛. 论新一代牵引供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2014,49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001LI Qunzhan. On new generation traction power supply system and its key technologies for electrification railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(4): 559-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2014.04.001 [3] 邓文丽,戴朝华,陈维荣. 轨道交通能源互联网背景下光伏在交/直流牵引供电系统中的应用及关键问题分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(19): 5692-5702,5897. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.181848DENG Wenli, DAI Chaohua, CHEN Weirong. Application of PV generation in AC/DC traction power supply system and the key problem analysis under the background of rail transit energy Internet[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(19): 5692-5702,5897. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.181848 [4] 李群湛,王喜军,黄小红,等. 电气化铁路飞轮储能技术研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(7): 2025-2033. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.180919LI Qunzhan, WANG Xijun, HUANG Xiaohong, et al. Research on flywheel energy storage technology for electrified railway[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(7): 2025-2033. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.180919 [5] 黄小红,赵艺,李群湛,等. 电气化铁路同相储能供电技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(4): 856-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20181083HUANG Xiaohong, ZHAO Yi, LI Qunzhan, et al. Co-phase traction power supply and energy storage technology for electrified railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(4): 856-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20181083 [6] MERLIN Project. Sustainable and intelligent management of energy for smarter railway systems in europe[EB/OL]. (2015-12-10)[2020-3-25]. http://www.merlin-rail.eu. [7] KHAYYAM S, PONCI F, GOIKOETXEA J, et al. Railway energy management system: centralized-decentralized automation architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(2): 1164-1175. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2015.2421644 [8] RAZIK L, BERR N, KHAYYAM S, et al. REM-S–railway energy management in real rail operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(2): 1266-1277. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2885007 [9] AGUADO J A, SÁNCHEZ RACERO A J, DE LA TORRE S. Optimal operation of electric railways with renewable energy and electric storage systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(2): 993-1001. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2016.2574200 [10] ŞENGÖR İ, KILIÇKIRAN H C, AKDEMIR H, et al. Energy management of a smart railway station considering regenerative braking and stochastic behaviour of ESS and PV generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9(3): 1041-1050. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2017.2759105 [11] CHEN M W, CHENG Z, LIU Y L, et al. Multitime-scale optimal dispatch of railway FTPSS based on model predictive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2020, 6(2): 808-820. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2020.2992693 [12] 葛乐,陆文涛,袁晓冬,等. 基于多维动态规划的柔性光储参与主动配电网优化运行[J]. 电网技术,2017,41(10): 3300-3306. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2016.2523GE Le, LU Wentao, YUAN Xiaodong, et al. Optimal operation of active distribution network based on photovoltaic and energy-storage system of multi-dimensional dynamic programming[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41(10): 3300-3306. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2016.2523 [13] 周丹,孙可,张全明,等. 含多个综合能源联供型微网的配电网日前鲁棒优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(14): 4473-4485,4727. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.190390ZHOU Dan, SUN Ke, ZHANG Quanming, et al. Day-ahead robust dispatch of distribution network with multiple integrated energy System-based Micro-grids[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(14): 4473-4485,4727. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.190390 [14] ZHANG C, XU Y, DONG Z Y, et al. Robust operation of microgrids via two-stage coordinated energy storage and direct load control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 32(4): 2858-2868. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2016.2627583 [15] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 电能质量 三相电压不平衡: GB/T 15543—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009 [16] CHEN M W, LI Q Z, ROBERTS C, et al. Modelling and performance analysis of advanced combined co-phase traction power supply system in electrified railway[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2016, 10(4): 906-916. [17] HAMIDI A, GOLSHANNAVAZ S, NAZARPOUR D. D-FACTS cooperation in renewable integrated microgrids: a linear multiobjective approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, 10(1): 355-363. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2017.2723163 -




 下载:
下载: