Lateral Resistance of Frictional Sleeper Ballast Bed
-
摘要:
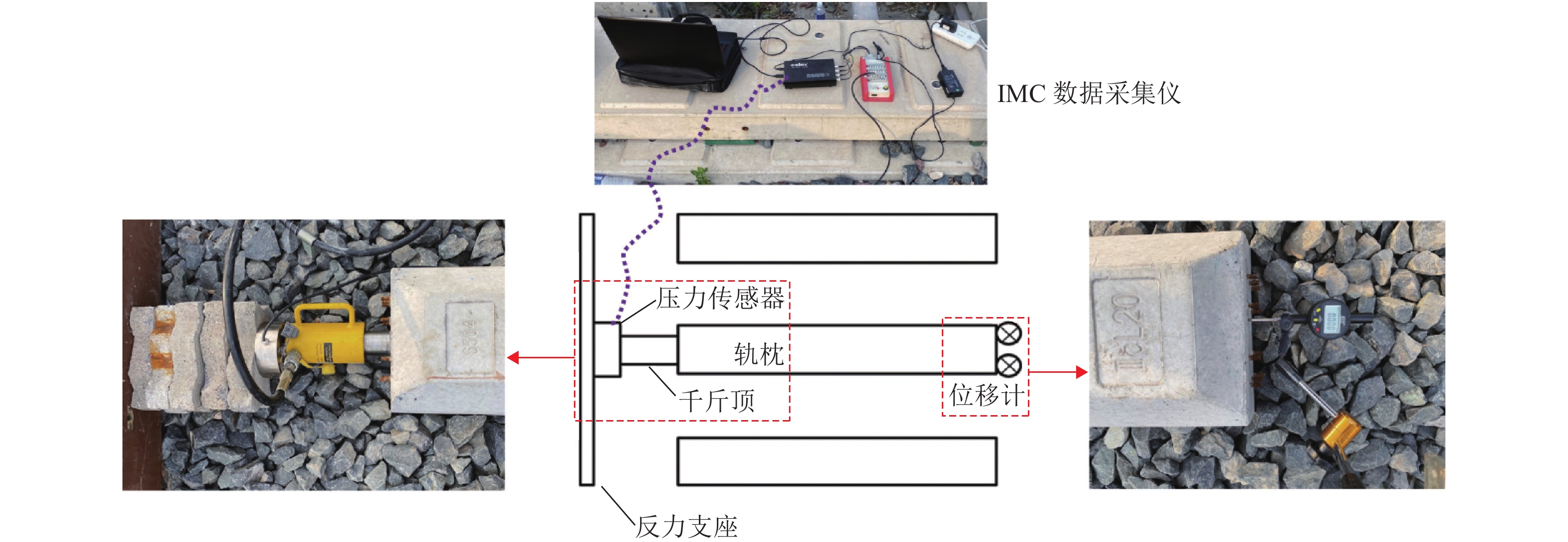
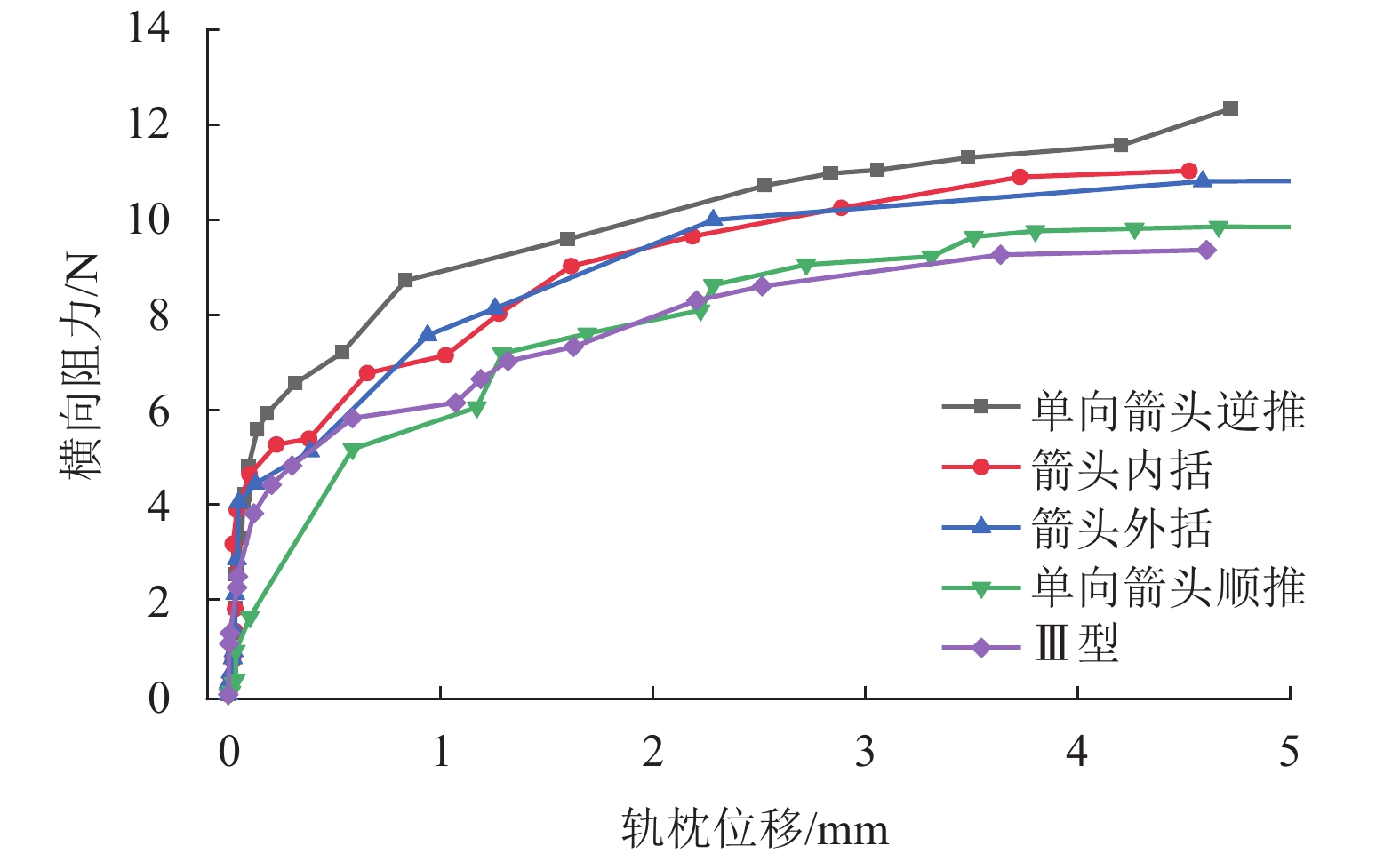
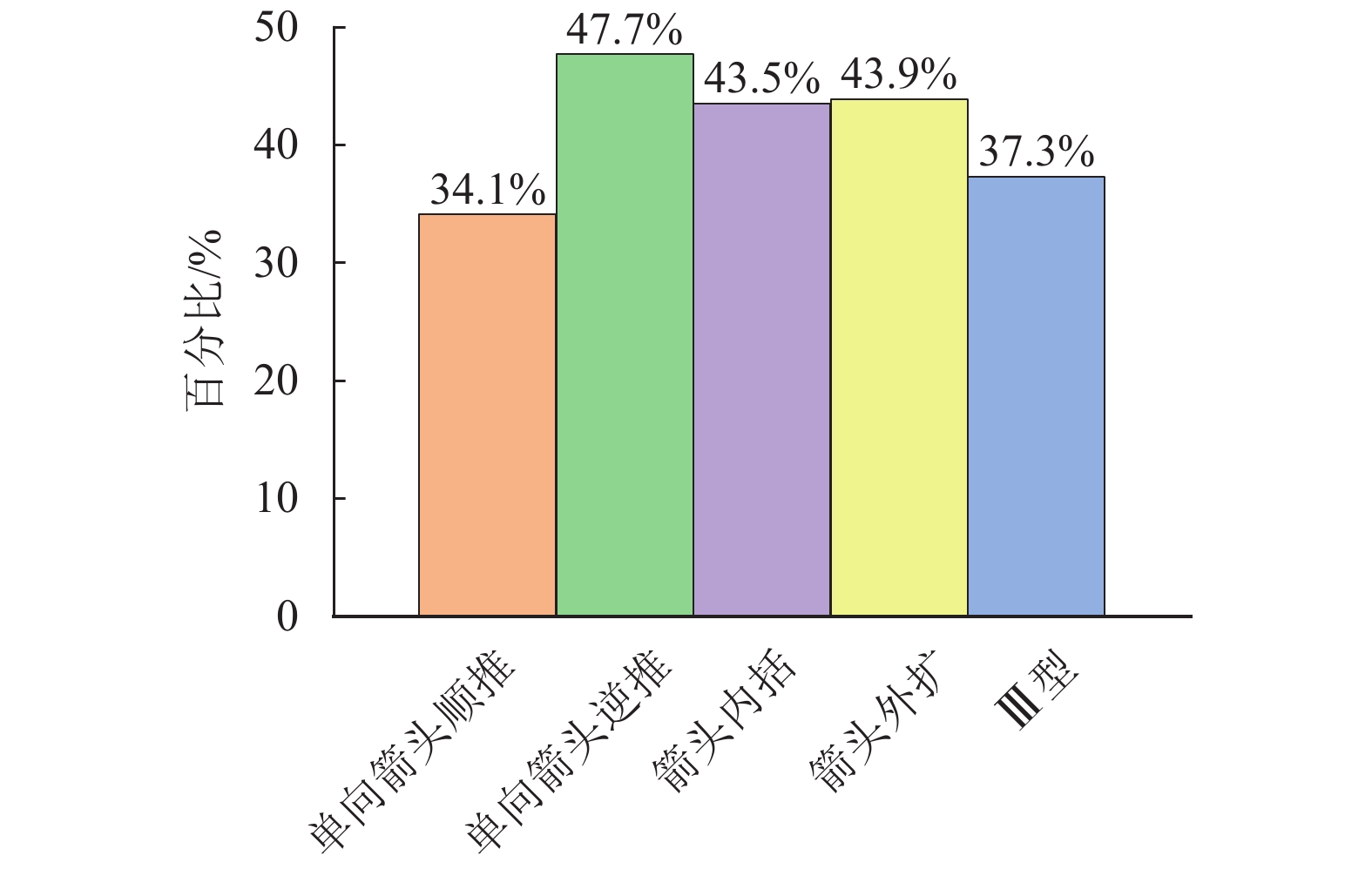
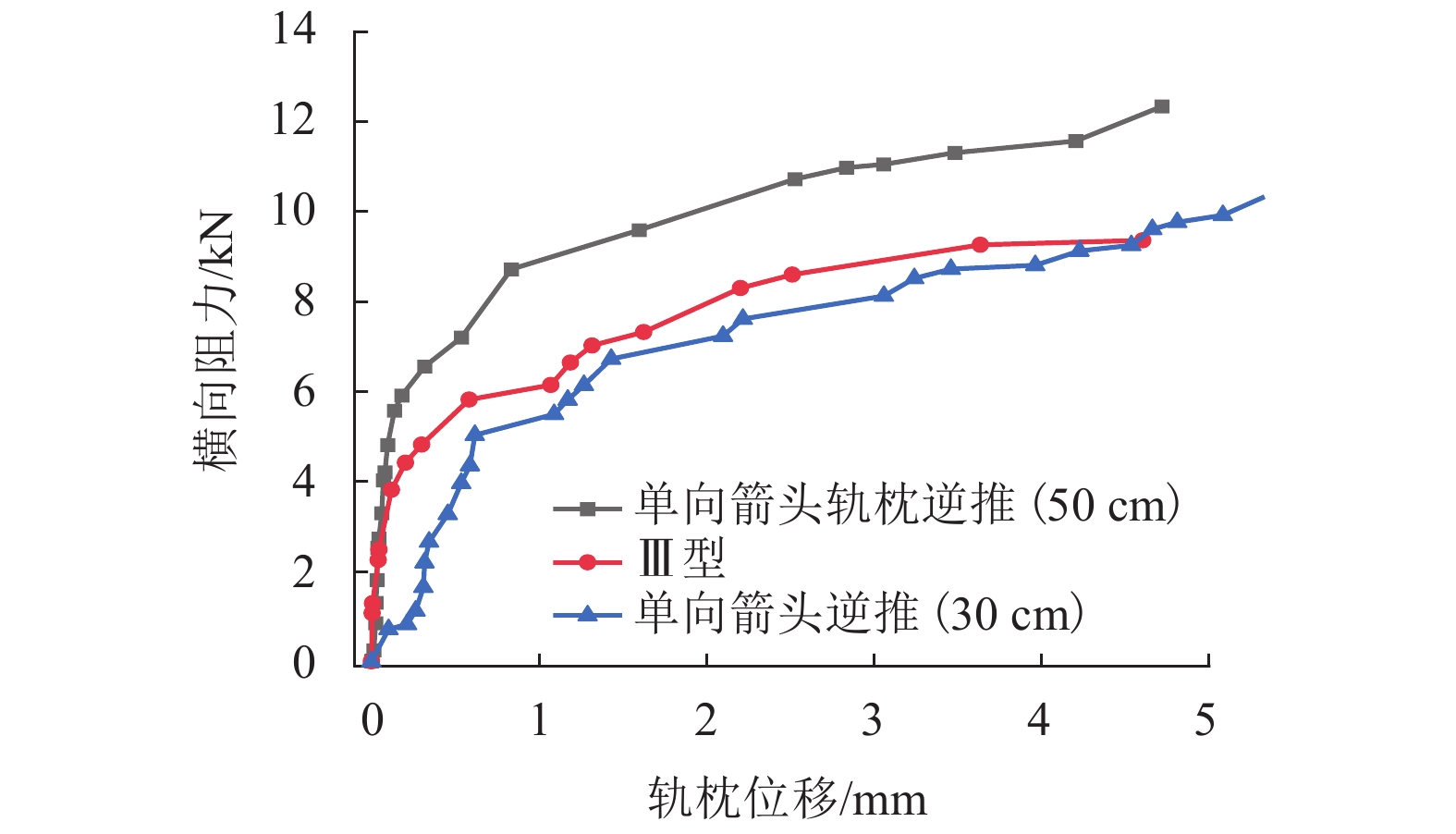
川藏铁路有砟道床断面尺寸受限,所处环境地震多发、日温差大且变化剧烈,这些情况容易导致横向阻力不足,对无缝线路稳定性和震区轨道韧性提出挑战. 为合理设计轨枕底部设有箭头型凹槽的摩擦型轨枕,并量化其提升无缝线路稳定性与韧性,采用道床横向阻力试验,测量摩擦型轨枕对道床横向阻力增幅情况;合理设计并优化了轨枕底部凹槽,制作了3种不同箭头型凹槽,除去凹槽排列方式不同外,箭头型凹槽面积、尺寸完全一致;并且验证砟肩宽度减小情况下摩擦型轨枕提供的横向阻力是否可以满足川藏铁路运维要求. 结果表明:各型摩擦型轨枕均可增大道床横向阻力,可最少提升横向阻力7%,最高提升21%;单向箭头型双向阻力存在较大阻力值差异,相比于普通轨枕顺向可增大7%,逆向可增大24%,因此在曲线地段铺设时候,应严格注意铺设方向;砟肩宽度由50 cm降低到30 cm,采用单向箭头型轨枕逆向仍然可达到Ⅲ型轨枕砟肩宽度50 cm横向阻力值.
Abstract:The Sichuan−Tibet railway is built under some difficult situations, including limited ballast bed profile, frequent earthquakes and large diurnal temperature variation. These difficulties cause insufficient lateral resistance of ballasted track, which is an urgent problem for the stability and resilience of the continuously welded rail (CWR). Aiming to improve and quantify the stability and resilience of CWR, the lateral resistance of frictional sleepers (designed as that normal sleeper with arrowhead shape groove) is evaluated with the single sleeper push test (SSPT). By performing SSPT, the increment of lateral resistance of ballast bed with frictional sleepers is measured. Shapes of sleeper grooves are properly designed and optimized (three groove shapes with the same size and volume but different arrowhead directions). Whether frictional sleeper applied to ballast bed (reduced ballast shoulder width) will provide enough lateral resistance for the ballast bed at Sichuan−Tibet railway line. Results show that frictional sleepers can increase the lateral resistance by minimum 7% and maximum 21%. Arrowhead directions significantly influence the lateral resistance, which is increased by 7% (same pushing direction) and 24% (opposite pushing direction), compared to normal sleepers. Therefore, strict attention should be paid to the laying direction when laying in curved sections of ballasted track. After reducing the ballast shoulder width from 50 cm to 30 cm, using the frictional sleeper (single arrowhead direction pushed in reversed direction) can still provide enough lateral resistance, which is the same value as a mono-block Type Ⅲ sleeper with 50 cm shoulder width.
-
Key words:
- Sichuan−Tibet railway /
- lateral resistance /
- frictional sleeper /
- resilience /
- single sleeper push test
-
表 1 试验工况
Table 1. Test conditions
工况编号 轨枕类型 砟肩宽度/cm 边坡坡度 枕心 A1 Ⅲ型 50 1∶1.75 有 A2 单向箭头(顺、
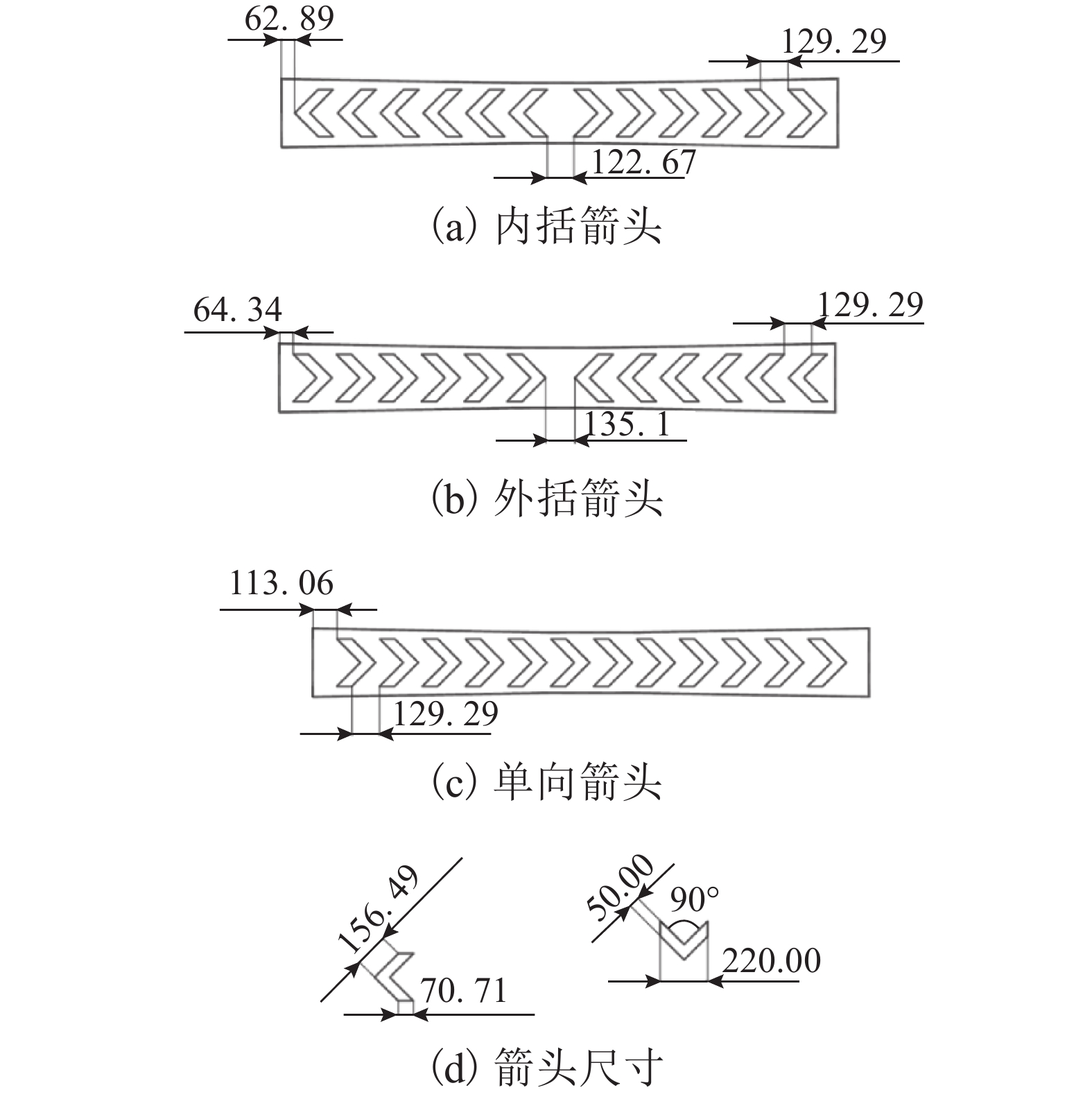
逆向推动轨枕)50 1∶1.75 有 A3 内括箭头 50 1∶1.75 有 A4 外括箭头 50 1∶1.75 有 B1 单向箭头 30 1∶1.75 有 C1 Ⅲ型 0 0 无 C2 内括箭头 0 0 无 C3 外括箭头 0 0 无 C4 单向箭头(顺、
逆向推动轨枕)0 0 无 -
[1] LIU H, XIAO J, WANG P G, et al. Experimental investigation of the characteristics of a granular ballast bed under cyclic longitudinal loading[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 163: 214-224. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.037 [2] JING G, AELA P. Review of the lateral resistance of ballasted tracks[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2019, 234(8): 0954409719866355.1-0954409719866355.14. [3] POWRIE W, LE PEN L M. Contribution of base,crib,and shoulder ballast to the lateral sliding resistance of railway track:a geotechnical perspective[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2011, 225(2): 113-128. doi: 10.1177/0954409710397094 [4] 井国庆. 铁路有砟道床[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2012. [5] 井国庆,贾文利,付豪,等. 高速铁路有砟道床横向阻力特性与固化技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(5): 1087-1092.JING Guoqing, JIA Wenli, FU Hao, et al. High-speed ballasted railway track lateral resistance characteristics and reinforcements[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(5): 1087-1092. [6] 高睿,石知政,刘洋泽鹏,等. 土工格栅对受污道砟直剪特性影响的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(6): 1185-1191.GAO Rui, SHI Zhizheng, LIU Yangzepeng, et al. Experimental study on effect of geogrid on direct shear behavior of contaminated ballast[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(6): 1185-1191. [7] KISH A, SAMAVEDAM G. Track buckling prevention: theory, safety concepts, and applications[R]. [S.l.]: Volpe National Transportation Systems Center, 2013. [8] ESVELD C. Improved knowledge of CWR track[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 1997. [9] ESMAEILI M, ZAKERI J A, BABAEI M. Laboratory and field investigation of the effect of geogrid-reinforced ballast on railway track lateral resistance[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2017, 45(2): 23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2016.11.003 [10] 付豪. 基于模型试验及 DEM 仿真的混凝土轨枕道床横向阻力研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019. [11] 井国庆,王新雨,周强,等. 钢棒加强式轨枕道床的纵横向阻力试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(6): 1192-1196, 1213.JING Guoqing, WANG Xinyu, ZHOU Qiang, et al. Experiments study on longitudinal and lateral resistance of steel rod reinforced sleeper[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(6): 1192-1196, 1213. [12] KASRAEI A, ZAKERI J A, ESMAEILI M, et al. A numerical investigation on the lateral resistance of frictional sleepers in ballasted railway tracks[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2014, 230(2): 440-449. [13] KISH A. On the fundamentals of track lateral resistance[R]. [S.l.]: American Railway Engineering and Maintenance of Way Association, 2011. [14] 中华人民共和国铁道部. 高速铁路有砟轨道线路维修规则(试行)[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2013: 9-10. [15] ZAKERI, J A, MIRFATTAHI B, FAKHARI M. Lateral resistance of railway track with frictional sleepers[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Transport, 2012, 165(2): 151-155. doi: 10.1680/tran.2012.165.2.151 -




 下载:
下载: