Experimental Study on Wear Performance of Rigid Catenary-Pantograph System with Direct Current
-
摘要:
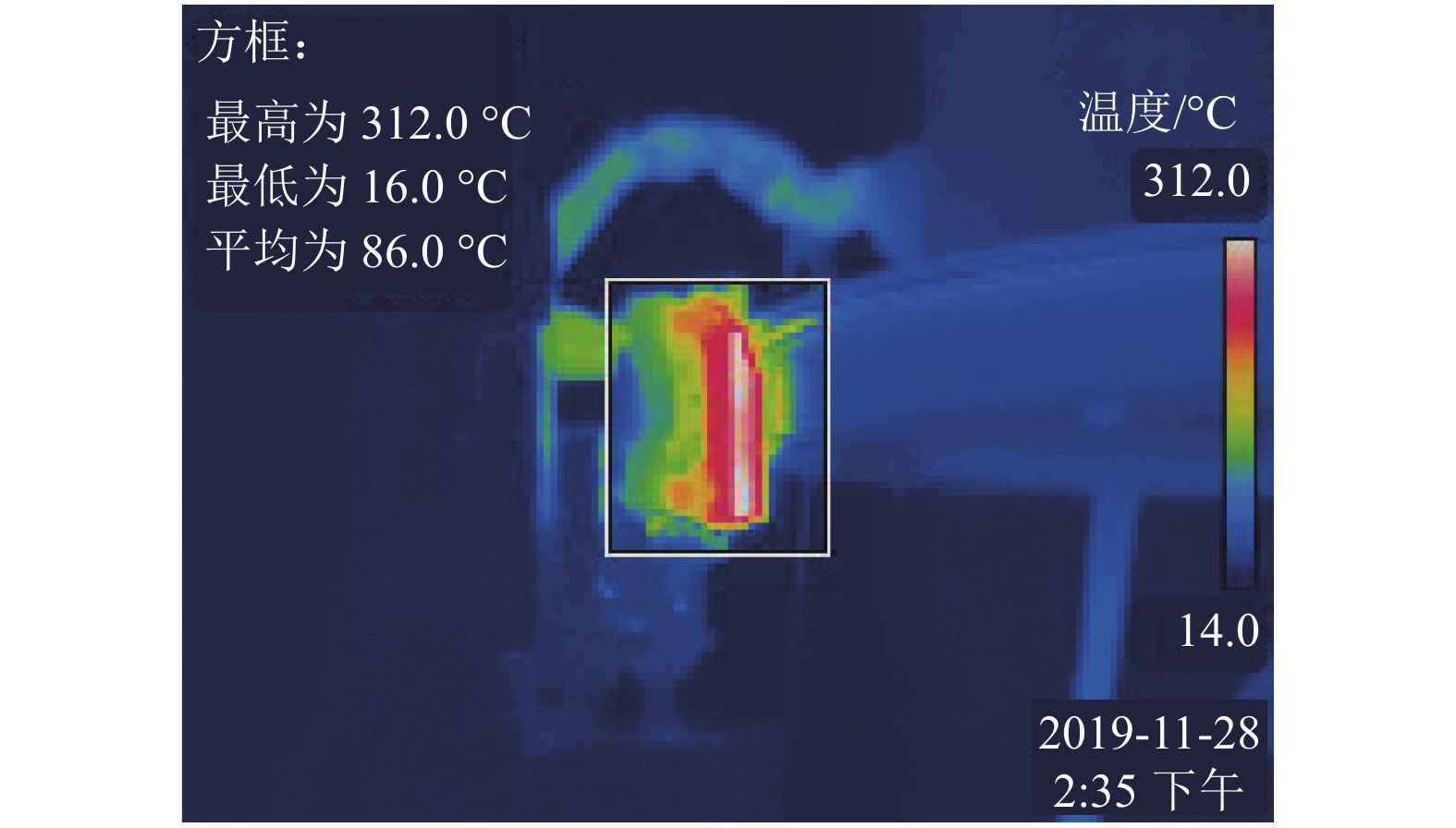
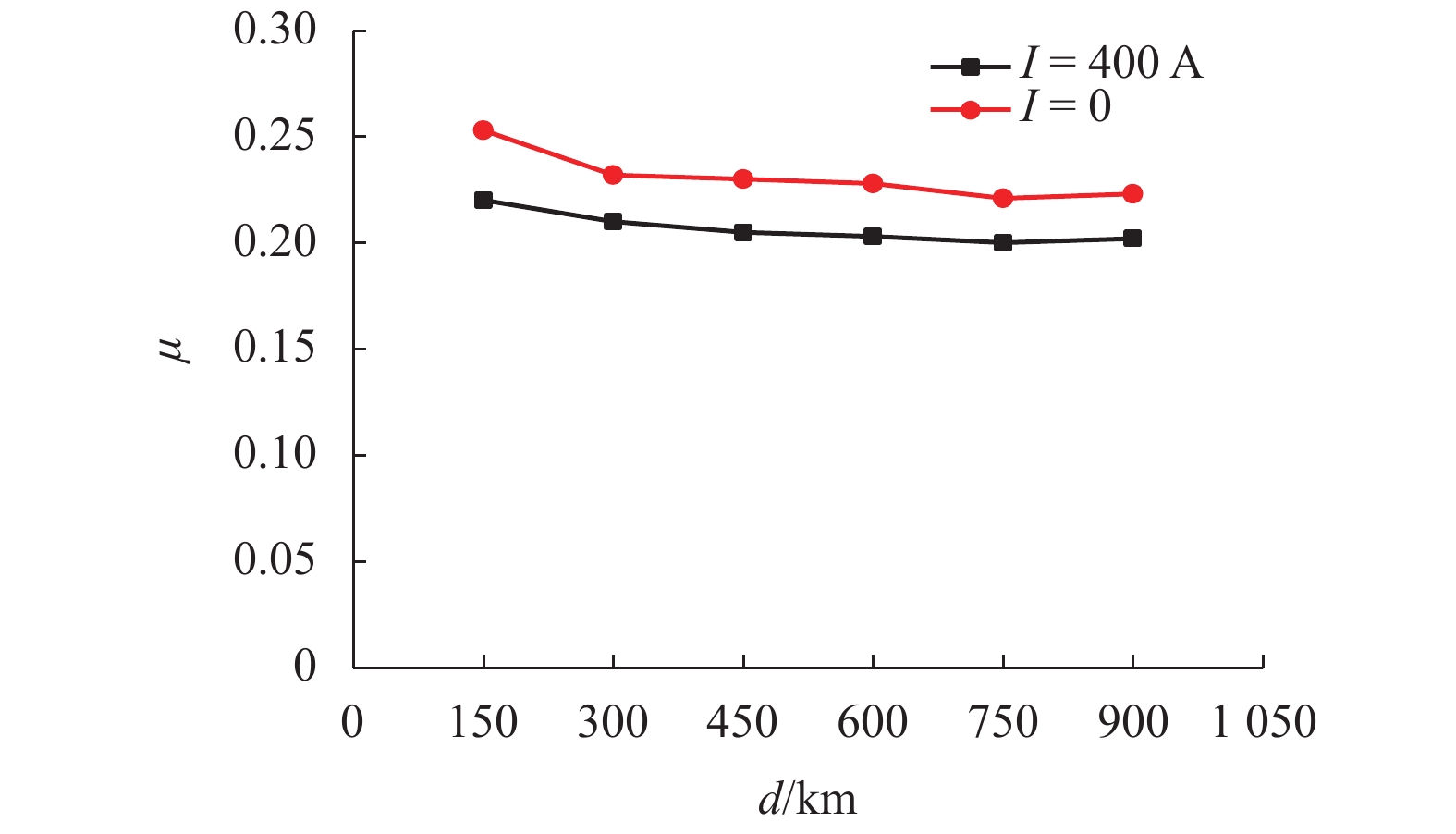
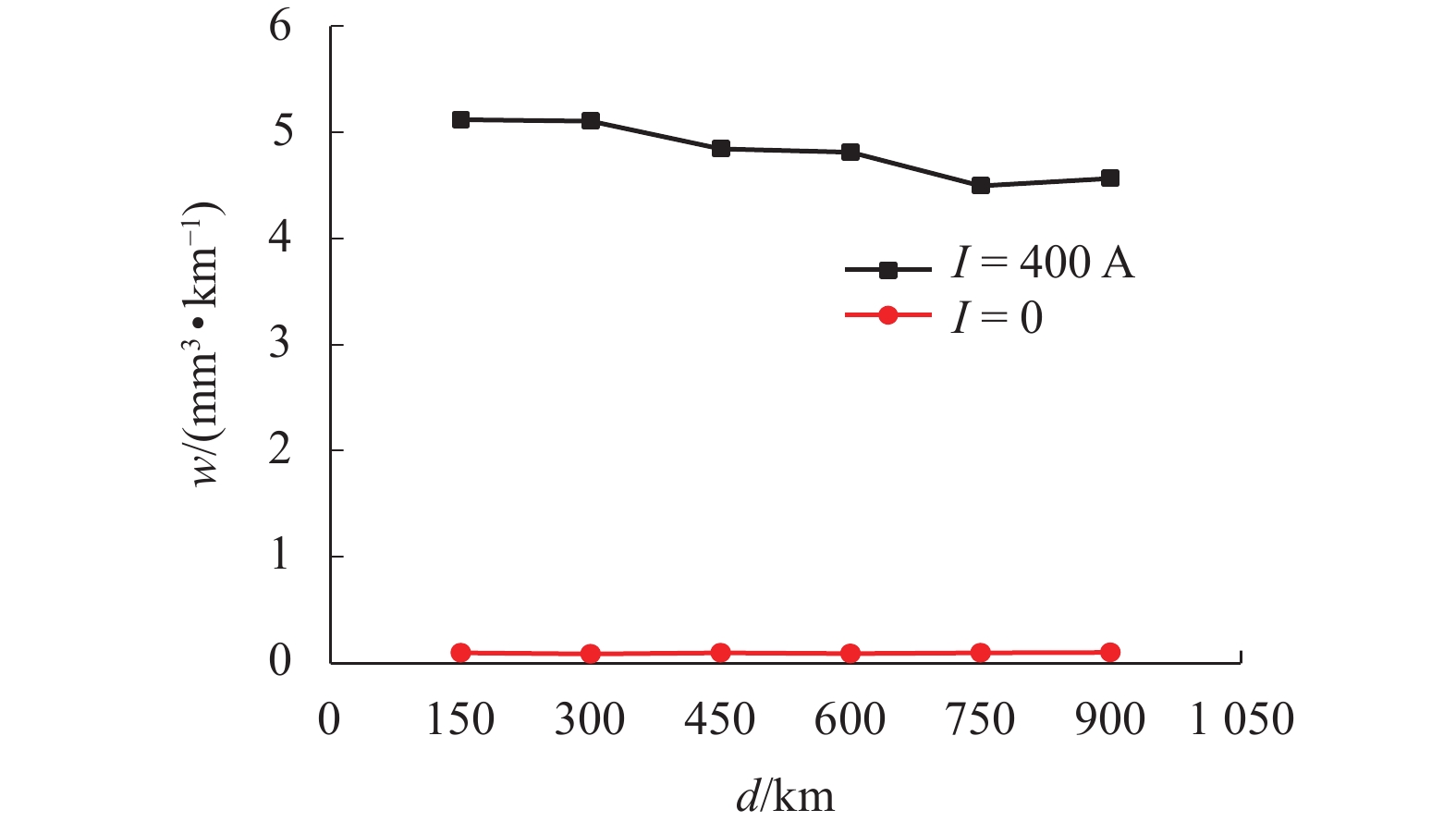
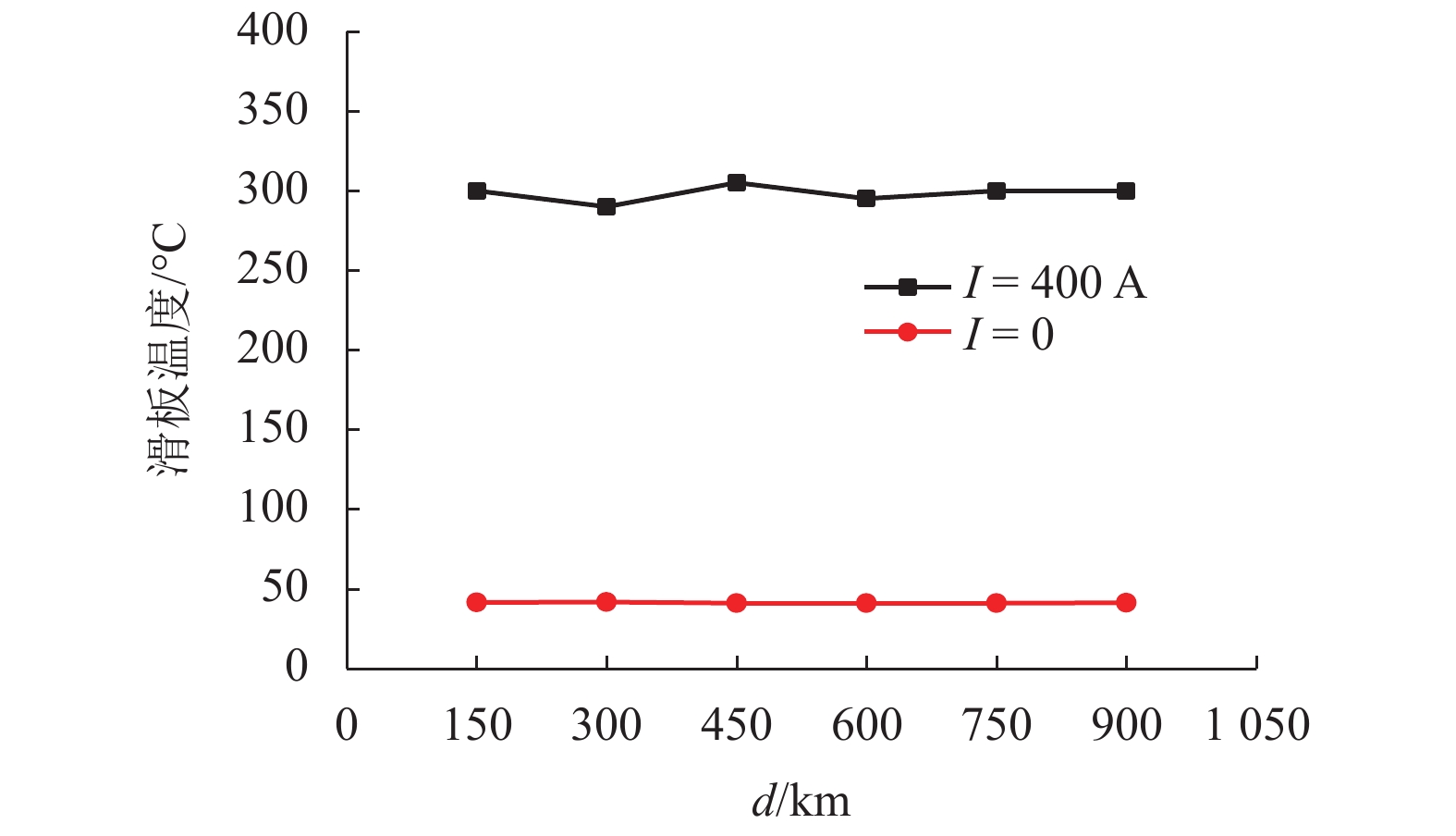
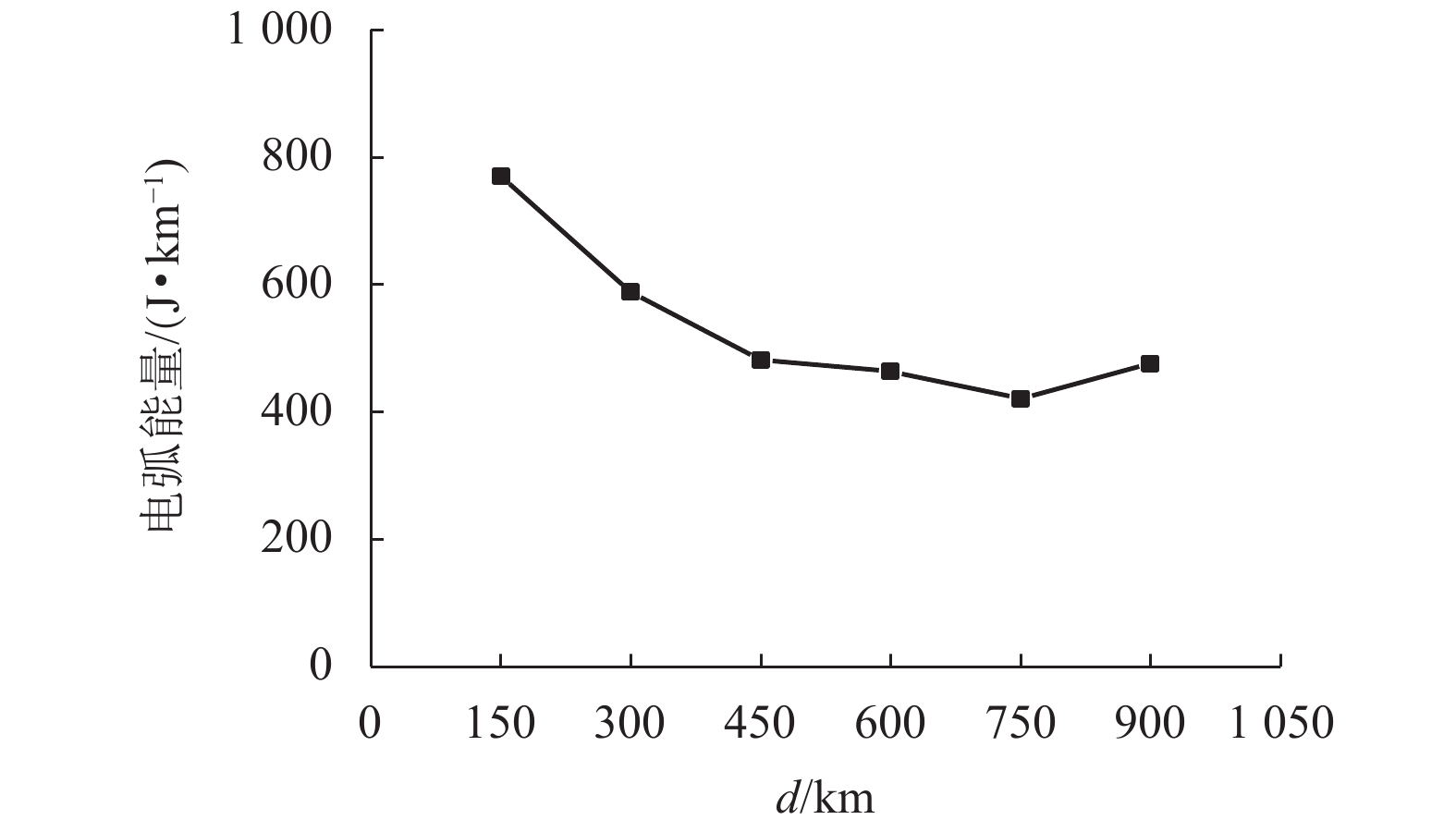
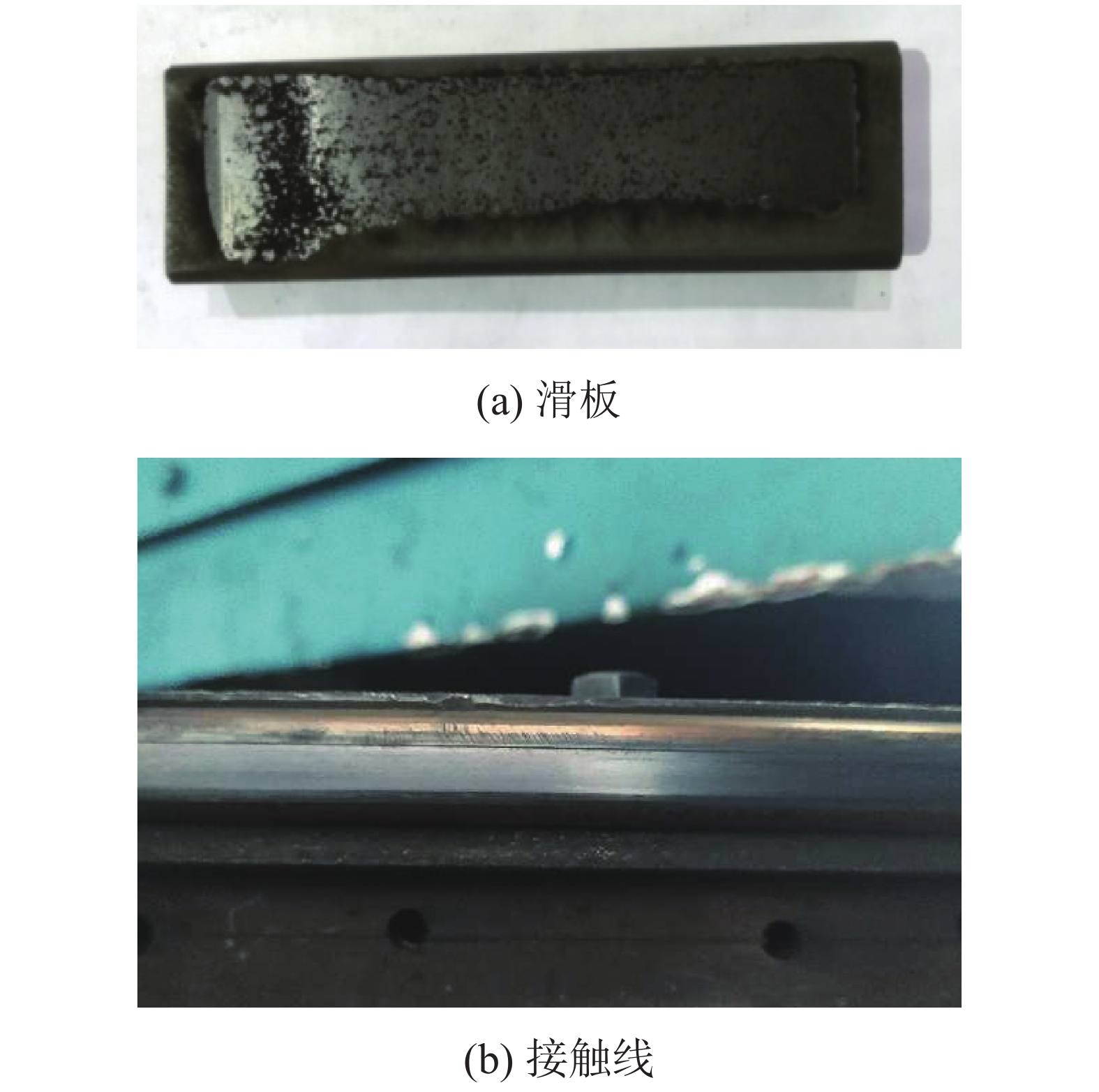
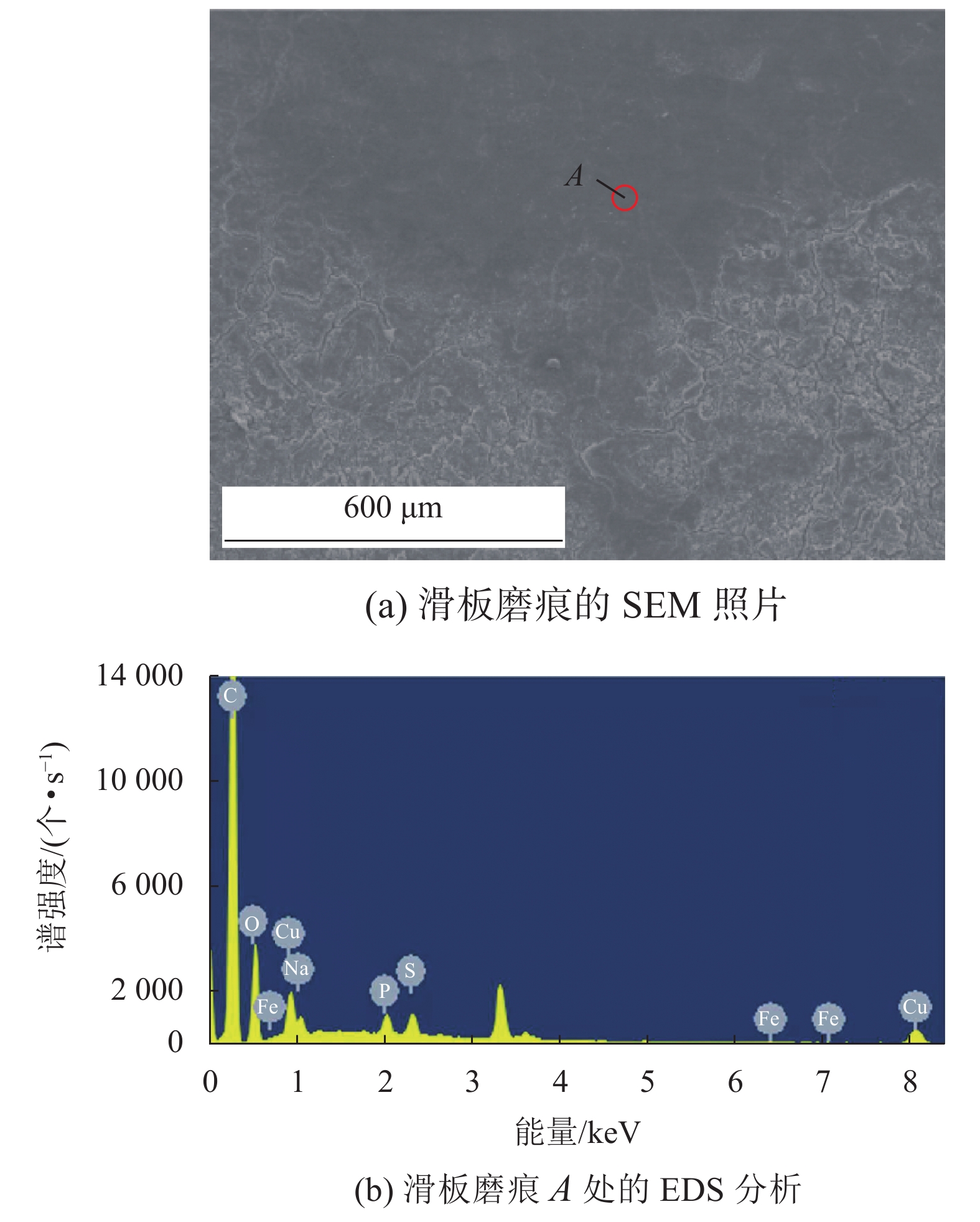
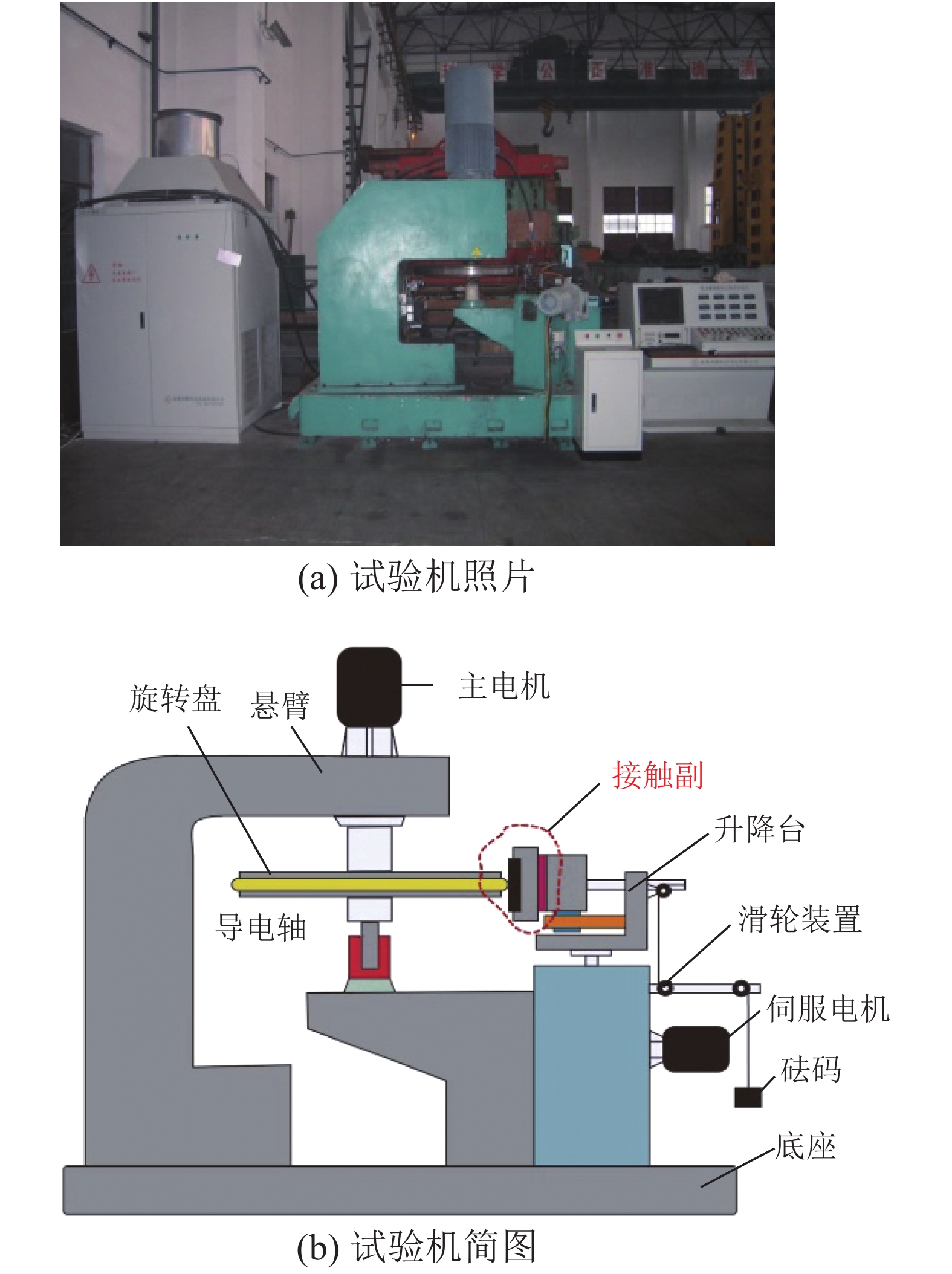
为了认识刚性接触网系统接触线和受电弓滑板异常摩耗的机理、提高刚性接触网系统摩擦元件的使用寿命,根据地铁刚性接触网系统的工作条件,使用环-块式载流摩擦磨损试验机,对刚性接触网系统的载流摩擦磨损性能进行了试验研究. 试验电流为0、400 A (DC),滑动速度为60 km/h,接触法向力为30 N,滑动距离为900 km. 在试验过程中测量了弓网之间的滑动摩擦因数、滑板磨损量、滑板温度、电弧电流和电压等参数,计算了滑板的磨损率和电弧能量. 试验结果表明:试验得到的滑板磨损率与实际地铁线路刚性接触网滑板的磨损率接近;直流电流对滑板的磨耗和温度有严重的影响,有电流时(400 A)滑板磨损率和温度分别是无电流时滑板磨损率和温度的53.0倍和7.4倍;引起滑板严重磨耗的原因主要是电弧烧蚀和黏着磨损.
Abstract:In order to understand the abnormal wear mechanism of the contact wire and the pantograph strip in the rigid catenary system, and to improve the service life of its friction elements, tests were carried out on the current-carrying friction and wear performance of the rigid catenary system with a block-on-ring current-carrying friction and wear tester. The test parameters were set as: the test current of 0, 400 A (DC), sliding speed of 60 km/h, the contact normal force of 30 N, and sliding distance of 900 km. During the tests, the sliding friction coefficient between the pantograph strip and catenary wire, the wear volume and the temperature of the pantograph strip, arc current and voltage were measured, and the wear rate of the pantograph strip and arc energy were calculated. The test results show that the tested wear rate of the pantograph strip is close to the one for actual subway lines. The DC current has a serious impact on the wear and temperature of the pantograph strip. The wear rate and temperature of the pantograph strip with DC 400 A are about 53.0 times and 7.4 times higher than those without electric current, respectively. The serious wear of the pantograph strip is mainly caused by arc ablation and adhesive wear.
-
Key words:
- wear /
- electric contact /
- rigid catenary /
- contact wire /
- pantograph strip
-
表 1 接触线的化学成份和物理性能
Table 1. Physical parameters and chemical compositions of contact wire
成份 质量分数/% 铜 > 99.70 银 0.10 氧 < 0.03 杂质 < 0.03 密度/ (g•cm−3) 8.96 硬度/HB 90 表 2 滑板材料的化学成份和物理性能
Table 2. Chemical compositions and physical parameters of strip
成份 质量分数/% 铜 24.49 碳 71.62 杂质 3.89 密度/(g•cm−3) 2.30 硬度/HS 100 -
[1] 王剑. 地铁刚性接触悬挂弓网磨耗问题研究[J]. 都市快轨交通,2012,25(4): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2012.04.015WANG Jian. Discussion on pantograph-catenary abrasion of metro rigid overhead catenary system[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2012, 25(4): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2012.04.015 [2] 陈显志,陈建君,杨波. 减小架空刚性悬挂接触网弓网磨耗的措施[J]. 现代城市轨道交通,2013,10(1): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7533.2013.01.006CHEN Xianzhi, CHEN Jianjun, YANG Bo. Measures on reducing wear of pantograph and contact wire of overhead rigid suspension catenary[J]. Modern Urban Transit, 2013, 10(1): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7533.2013.01.006 [3] 周成尧,刘畅. 北京地铁6号线受电弓滑板异常磨耗研究[J]. 铁道机车车辆,2019,39(增刊1): 51-54.ZHOU Chengyao, LIU Chang. Research for abnormal wear of pantograph in Beijing subway line 6[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2019, 39(S1): 51-54. [4] 蒋灵君. 刚性接触网线路车辆碳滑板异常磨耗分析[J]. 现代城市轨道交通,2011,8(3): 43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7533.2011.03.014JIANG Lingjun. Analysis of abnormal wear of carbon strips of a rigid catenary-pantograph system[J]. Modern Urban Transit, 2011, 8(3): 43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7533.2011.03.014 [5] WEI X K, MENG H F, HE J H, et al. Wear analysis and prediction of rigid catenary wire and pantograph strip for railway system[J]. Wear, 2020, 442/443: 203118.1-205118.15. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2019.203118 [6] SIMARRO M, POSTIGO S, CABRERA J A, et al. A procedure for validating rigid catenary models using evolutionary techniques[J]. Computers and Structures, 2020, 228: 106145.1-106145.10. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2019.106145 [7] 胡艳,董丙杰,黄海,等. 碳滑板电滑动温升及其对滑板磨损影响的试验研究[J]. 摩擦学学报,2015,35(6): 677-683.HU Yan, DONG Bingjie, HUANG Hai, et al. Experimental study on the temperature rise of a carbon strip and its influence on the wear performances of the carbon strip[J]. Tribology, 2015, 35(6): 677-683. [8] ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG Y Z, DU S M, et al. Tribological properties of pure carbon strip affected by dynamic contact force during current-carrying sliding[J]. Tribology International, 2018, 123: 256-265. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2017.12.032 [9] MEI G M, FU W M, CHEN G X, et al. Effect of high-density current on the wear of carbon sliders against Cu-Ag wires[J]. Wear, 2020, 452/453: 203275.1-203275.7. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2020.203275 [10] HU Y, CHEN G X, ZHANG S D, et al. Comparative investigation into the friction and wear behaviours of a Cu-Ag contact wire/carbon strip and a pure copper contact wire/carbon strip at high speeds[J]. Wear, 2017, 376/377: 1552-1557. [11] 杨红娟,胡艳,陈光雄. 受电弓滑板载流磨损机理演变过程试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(1): 77-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.01.012YANG Hongjuan, HU Yan, CHEN Guangxiong. Experimental study on evolution of wear mechanism of contact strip with electric current[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(1): 77-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.01.012 [12] 吴晓光,张红波,尹健,等. PF/CNTs-Cu复合材料的制备及其载流摩擦磨损机理研究[J]. 摩擦学学报,2018,38(3): 334-341.WU Xiaoguang, ZHANG Hongbo, YIN Jian, et al. Preparation and current carrying wear properties of PF/CNTs-Cu composites[J]. Tribology, 2018, 38(3): 334-341. [13] 丁涛,何宏高,陈光雄,等. 弹性条件下浸金属碳/不锈钢载流摩擦磨损性能[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2009,44(4): 558-563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.04.015DING Tao, HE Honggao, CHEN Guangxiong, et al. Frictionand wear behavior of copper-impregnated metalized carbon strip sliding against stainless steelwith electrical currentunder elastic condition[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009, 44(4): 558-563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.04.015 [14] CHEN G X, YANG H J, ZHANG W H, et al. Experimental study on arc ablation occurring in a contact strip rubbing against a contact wire with electrical current[J]. Tribology International, 2013, 61: 88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2012.11.020 [15] BUCCA G, COLLINA A. A procedure for the wear prediction of collector strip and catenary wire in pantograph-catenary system[J]. Wear, 2009, 266: 46-59. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.05.006 [16] BUCCA G, COLLINA A, MANIGRASSO R, et al. Analysis of electrical interferences related to the current collection quality in pantograph-catenary interaction[J]. Journal of Railand Rapid Transit, 2011, 225: 483-499. doi: 10.1177/0954409710396786 [17] YANG H J, CHEN G X, ZHANG S D, et al. Effect of the vibration on friction and wear behavior between the carbon strip and copper catenary wire pair[J]. Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2012, 226: 722-728. [18] WANG Y A, LI J X, YAN Y, et al. Effect of PV factor on sliding friction and wear of copper-impregnated metallized carbon[J]. Wear, 2012, 289: 119-123. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.04.006 [19] DING T, CHEN G X, BU J, et al. Effect of temperature and arc discharge on friction and wear behaviors of carbon strips/copper catenary wire in pantograph-catenary systems[J]. Wear, 2011, 271: 1629-1636. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2010.12.031 [20] SHANGGUAN B, ZHANG Y Z, XING J D, et al. Comparative study on wear behaviors of metal-impregnated carbon material and C/C composite under electrical sliding[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2010, 53: 933-938. doi: 10.1080/10402004.2010.510622 [21] KUBO S, KATO K. Effect of arc discharge on wear rate of Cu-impregnated carbon strip in unlubricated sliding against Cu trolley under electric current[J]. Wear, 1998, 216: 172-178. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00184-1 [22] KUBO S, KATO K. Effect of arc discharge on the wear rate and wear mode transition of a copper-impregnated metallized carbon strip sliding against a copper disk[J]. Tribology International, 1999, 32: 367-378. -




 下载:
下载: