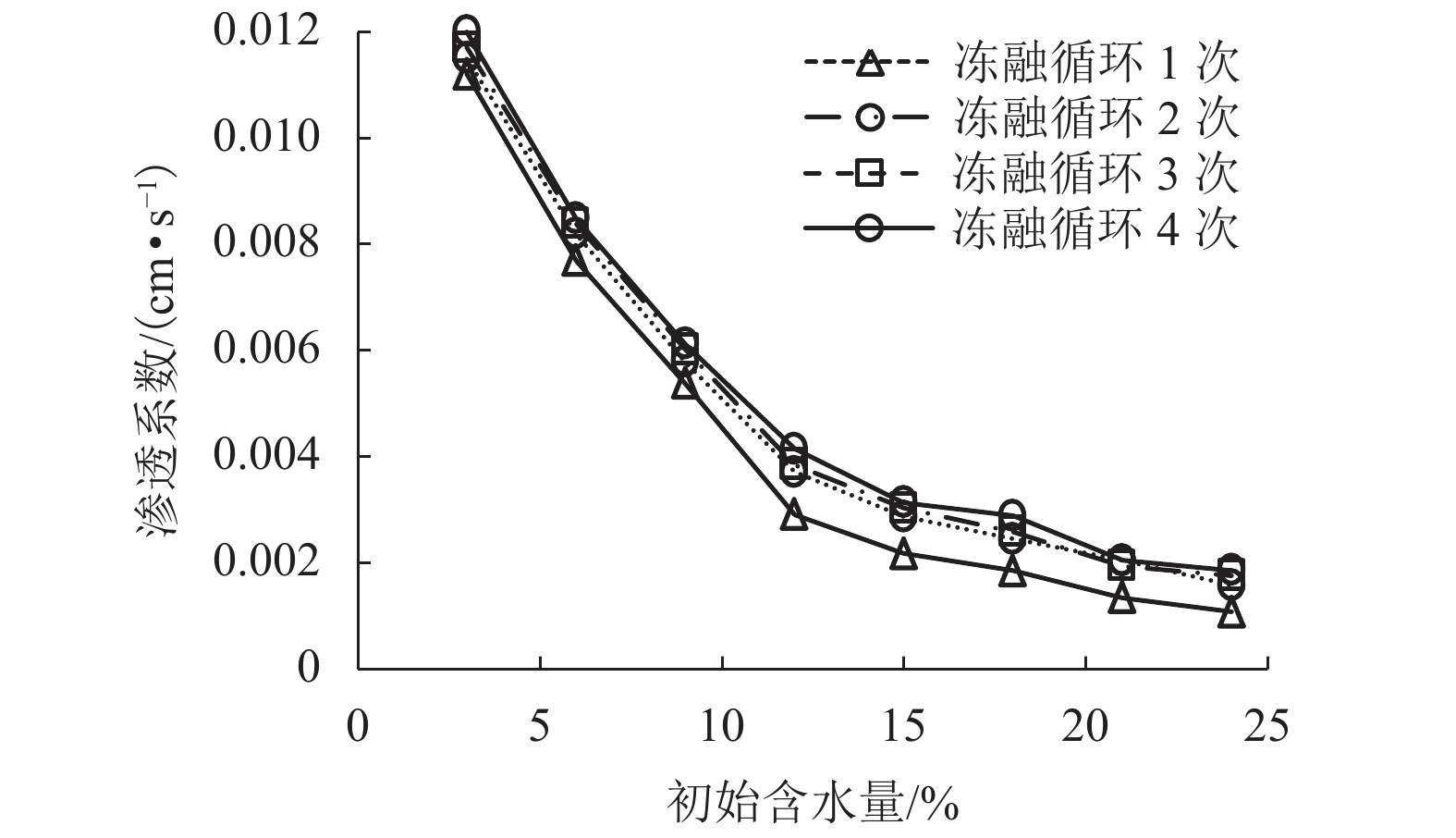
|
SRIKRISHNAN S S, TATSUYA ISHIKAWA, TETSUYA T. Stability assessment approach for soil slopes in seasonal cold regions[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 211: 154-169.
|
|
王丽黎. 冻融循环作用对土体边坡稳定性的影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016
|
|
杨白祥. 川藏铁路季节性粗颗粒冻土边坡破坏模式的模型试验研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017.
|
|
王立娜. 季节冻土区边坡冻融稳定性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008
|
|
NIU Fujun, CHENG Guodong, NI Wankui, et al. Engineering-related slope failure in permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2005, 42(3): 215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2005.02.002
|
|
周志. 冻融循环作用下非饱和路基土水分迁移规律研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.
|
|
曾桂军,张明义,李振萍,等. 饱和正冻土水分迁移及冻胀模型研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(4): 1085-1092.ZENG Guijun, ZHANG Mingyi, LI Zhenping, et al. Study of moisture migration and frost heave model of freezing saturated soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(4): 1085-1092.
|
|
NAKAMURA D, SUZUKI T, GOTO T, et al. Changes in the permeability coefficient and the void ratio of compacted soil by the effect of freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers Ser C, 2011, 67(2): 264-275.
|
|
MCROBERTS E C, MORGENSTERN N R. The stability of thawing slopes[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1974, 11(4): 447-469. doi: 10.1139/t74-052
|
|
KONRAD J M. Physical process during freeze-thaw cycles in clayey silts[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 1989, 16(3): 291-303. doi: 10.1016/0165-232X(89)90029-3
|
|
LI Ning, CHEN Bo, CHEN Feixong, et al. The coupled heat-moisture-mechanic model of the frozen soil[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2000, 31(3): 199-205. doi: 10.1016/S0165-232X(00)00013-6
|
|
刘飞. 渗流条件下多年冻土区斜坡路基稳定性研究[D].北京: 北京交通人学, 2009.
|
|
洪文江. 季节冻土区边坡冻融渗流稳定性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.
|
|
SHOOP S A, BIGL S R. Moisture migration during freeze and thaw of unsaturated soils:Modeling and large scale experiments[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 1997, 25(1): 33-45. doi: 10.1016/S0165-232X(96)00015-8
|
|
KANE D L. Snowmelt infiltration into seasonally frozen soils[J]. Cold Region Science and Technology, 1980, 3(2/3): 153-161.
|
|
OTHMAN M A, BENSON C H. Effect of freeze-thaw on the hydraulic conductivity and morphology of compacted clay[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1993, 30(2): 236-246. doi: 10.1139/t93-020
|
|
VIKLANDER P. Permeability and volume changes in till due to cyclic freeze/thaw[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1998, 35(3): 471-477. doi: 10.1139/t98-015
|
|
CHAMBERLAIN E J, ISKANDER I, HUNSIKER S E. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the permeability and macrostructure of soils[C]//Proceedings of International Symposium on Frozen Soil Impacts on Agricultural. [S.l.]: Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, 1990: 145-155.
|
|
CHAMBERLAIN E J. Physical changes in clays due to frost action and their effect on engineering structures[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Frost in Geotechnical Engineering. Rotterdam: [s.n.], 1989: 863-893.
|
|
梁燕, 邢鲜丽, 李同录, 等. 晚更新世黄土渗透性的各向异性及其机制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(5): 1313-1318.LIANG Yan, XING Xianli, LI Tonglu, et al. Study of the anisotropic permeability and mechanism of Q3 loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(5): 1313-1318.
|
|
肖东辉, 冯文杰, 张泽, 等. 冻融循环对兰州黄土渗透性变化的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2014, 36(5): 1192-1198.XIAO Donghui, FENG Wenjie, ZHANG Ze, et al. Research on the Lanzhou loess’s permeabilities changing with freezing-thawing cycles[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2014, 36(5): 1192-1198
|
|
许健,王掌权,任建威,等. 原状与重塑黄土冻融过程渗透特性对比试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2): 292-299.XU Jian, WANG Zhangquan, REN Jianwei, et al. Comparative experimental study on permeability of undisturbed and remolded loess under freezing-thawing condition[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(2): 292-299.
|
|
杨晴雯, 裴向军, 黄润秋. 改性钠羧甲基纤维素加固土冻融性能及损伤机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(增刊1): 3102-3113.YANG Qingwen, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu. Research on the effect of freeze and thaw cycles on the property and damage mechanism of M-CMC stabilized soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(S1): 3102-3113.
|
|
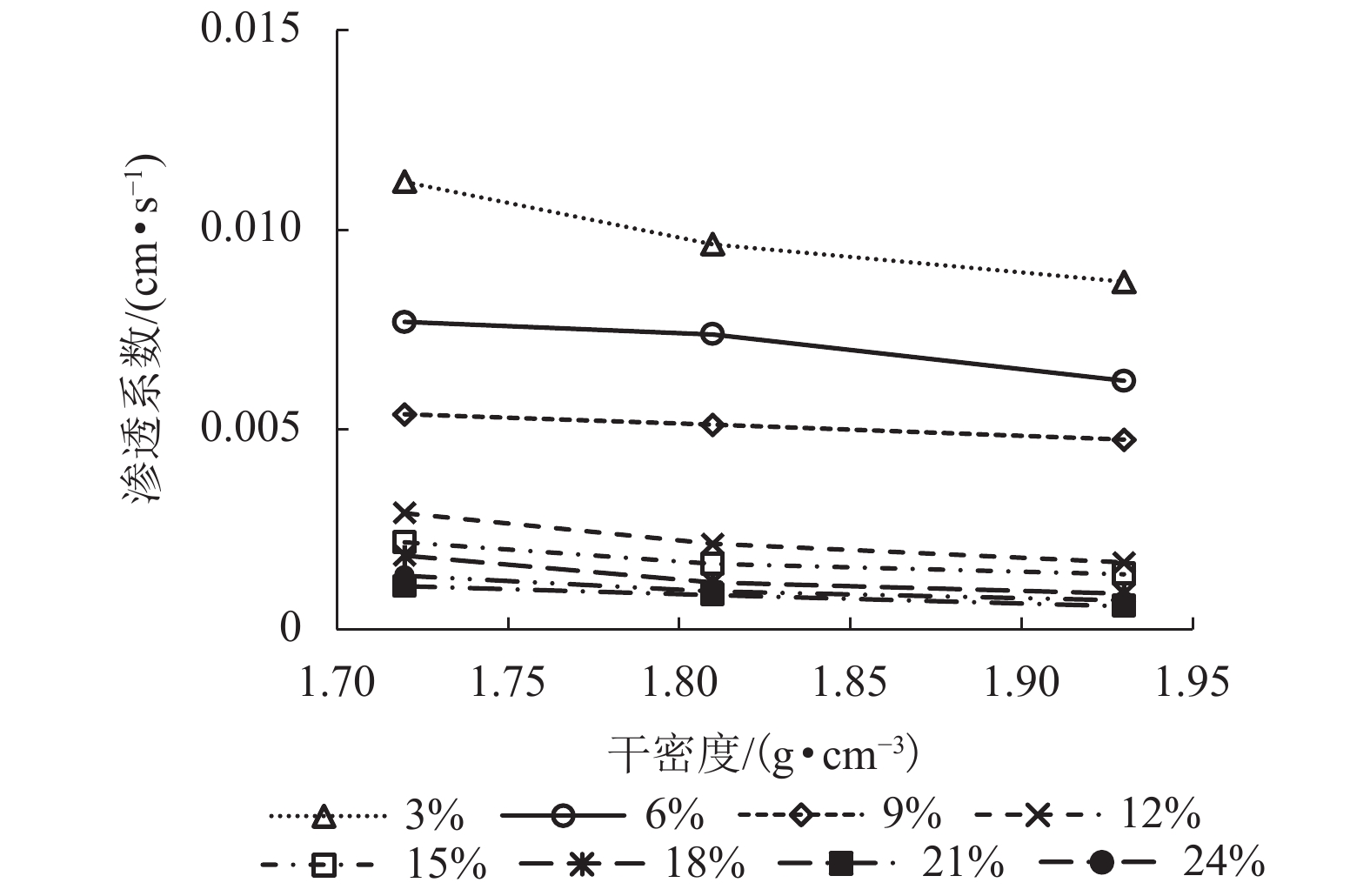
王铁行,卢靖,张建锋. 考虑干密度影响的人工压实非饱和黄土渗透系数的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(11): 2364-2368. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.11.030WANG Tiehang, LU Jing, ZHANG Jianfeng. Experimental study on permeability coefficient of artificially compacted unsaturated loess considering influence of density[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(11): 2364-2368. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.11.030
|
|
张虎,张建明,张致龙,等. 冻结状态青藏粉质黏土的渗透系数测量研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016,38(6): 1030-1035. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201606008ZHANG Hu, ZHANG Jianming, ZHANG Zhilong, et al. Measurement of hydraulic conductivity of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau silty clay under subfreezing temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(6): 1030-1035. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201606008
|
|
胡学涛,梁冰,陈亿军,等. 冻融循环对固化污泥力学及微观结构特性影响[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(5): 1317-1323.HU Xuetao, LIANG Bing, CHEN Yijun, et al. Mechanical and microstructural properties changes of solidified sewage sludge due to cyclic freezing and thawing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(5): 1317-1323.
|
|
CHO S E, LEE S R. Instability of unsaturated soil slopes due to infiltration[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2001, 28(3): 185-208. doi: 10.1016/S0266-352X(00)00027-6
|
|
BENSON C H, DANIEL D E, BOUTWELL G P. Field performance of compacted clay liners[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1999, 125(5): 390-403. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1999)125:5(390)
|
|
DUNCAN J M. Factors of safety and reliability in geotechnical engineering[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2000, 126(4): 307-316. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:4(307)
|
|
CERDA A. Seasonal and spatial variations in infiltration rates in badland surfaces under Mediterranean climatic conditions[J]. Water Resource, 1999, 35(1): 319-328. doi: 10.1029/98WR01659
|
|
OSAWA H, MATSUURA S, MATSUSHI Y, et al. Seasonal change in permeability of surface soils on a slow-moving landslide in a heavy snow region[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 221: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.019
|
|
BORMANN H, KLAASSEN K. Seasonal and land use dependent variability of soil hydraulic and soil hydrological properties of two Northern German soils[J]. Geoderma, 2008, 145(3/4): 295-302.
|
|
NERIS J, JIMENEZ C, FUENTES J, et al. Vegetation and land-use effects on soil properties and water infiltration of Andisols in Tenerife (Canary Islands,Spain)[J]. Catena, 2012, 98: 55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2012.06.006
|
|
HINDS E, LU N, MIRUS B, et al. Effects of infiltration characteristics on spatial-temporal evolution of stability of an interstate highway embankment[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironment Engineering, 2019, 145(9): 1-11.
|
|
LU N, WAYLLACE A, OH S. Infiltration-induced seasonally reactivated instability of a highway embankment near the Eisenhower Tunnel,Colorado,USA[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 162: 22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.05.002
|
|
赵彦旭,张虎元,吕擎峰,等. 压实黄土非饱和渗透系数试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(6): 1809-1812. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.06.022ZHAO Yanxu, ZHANG Huyuan, LÜ Qingfeng, et al. Experimental study of unsaturated permeability coefficient of compacted loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(6): 1809-1812. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.06.022
|
|
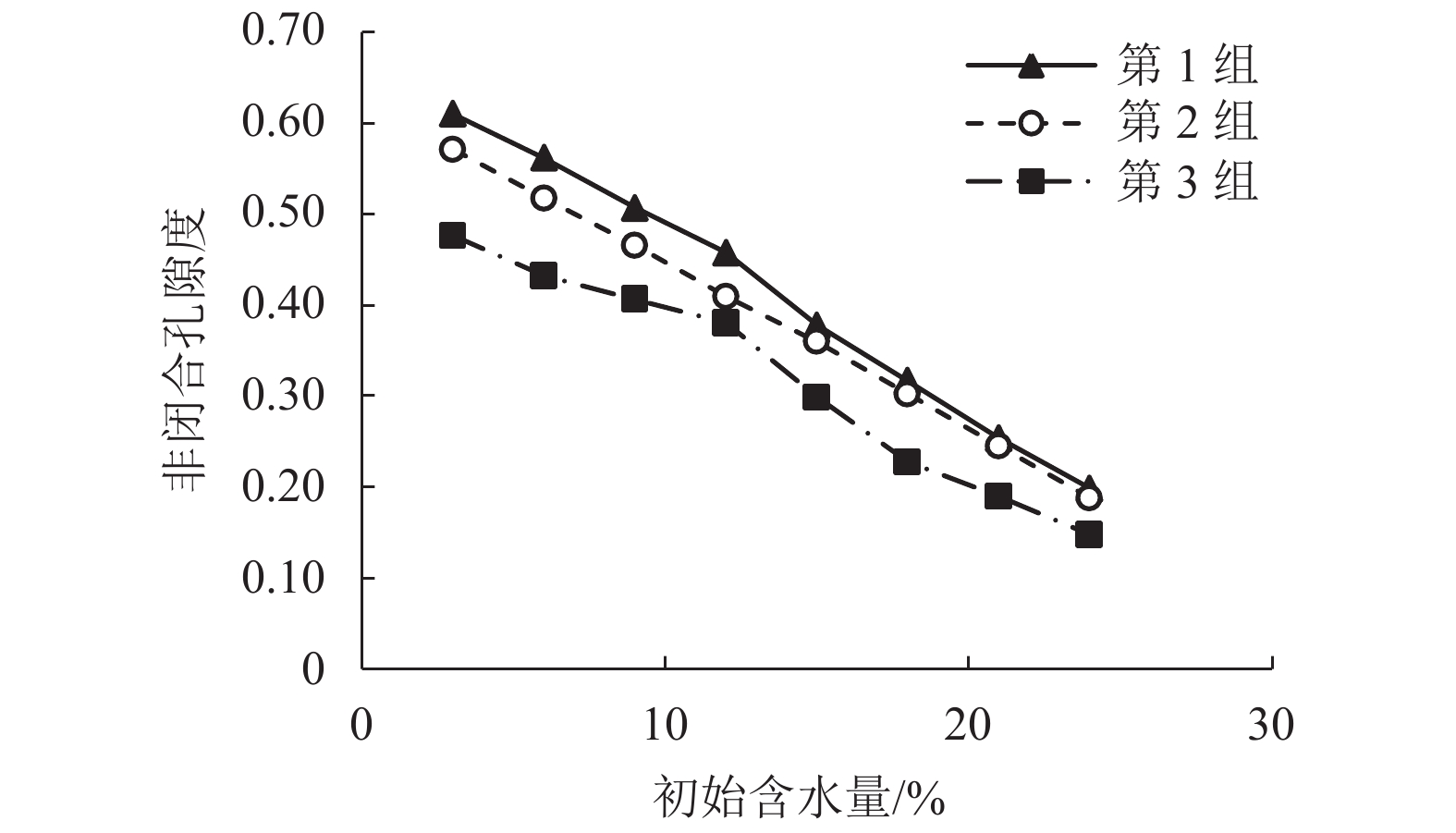
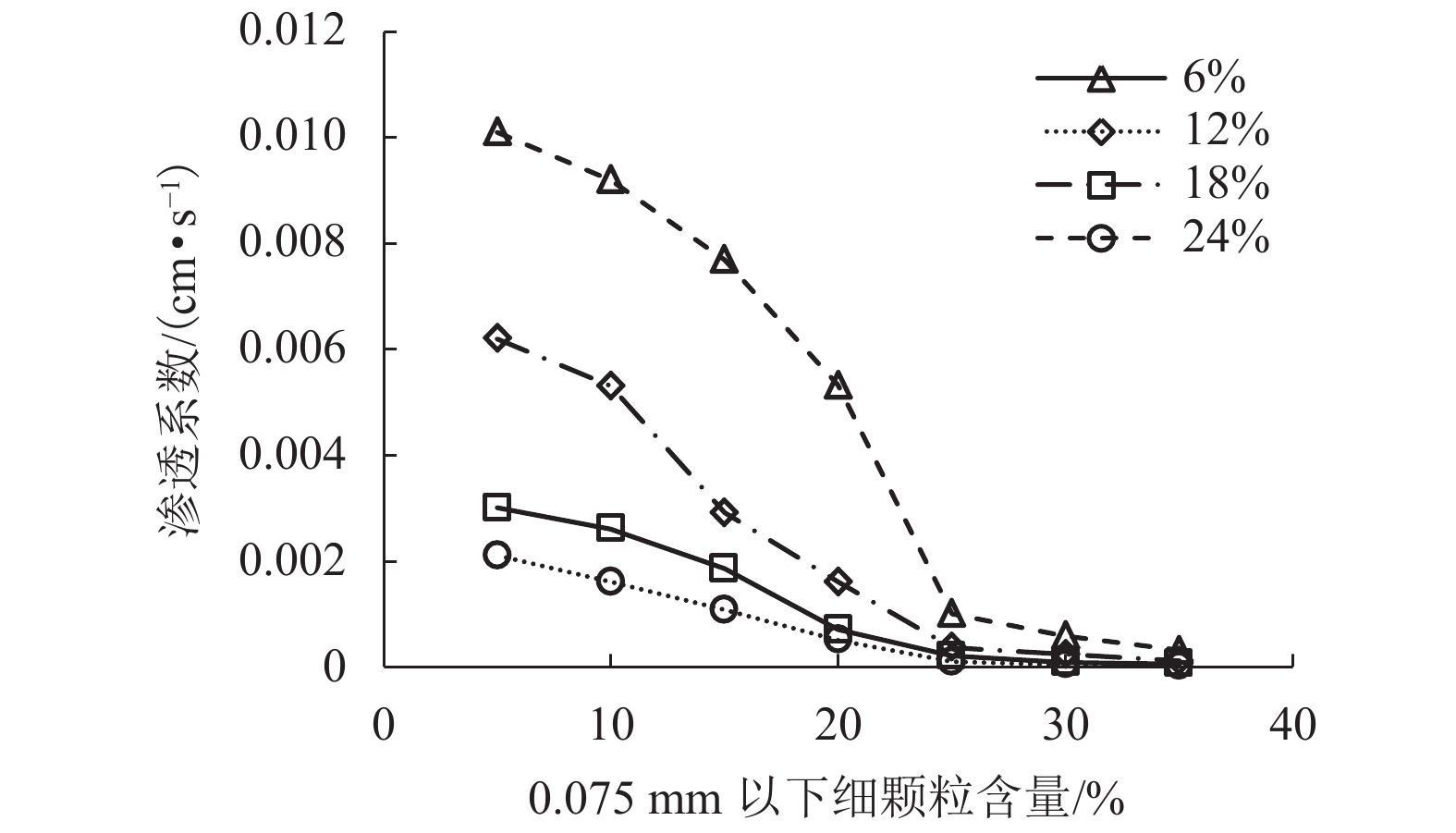
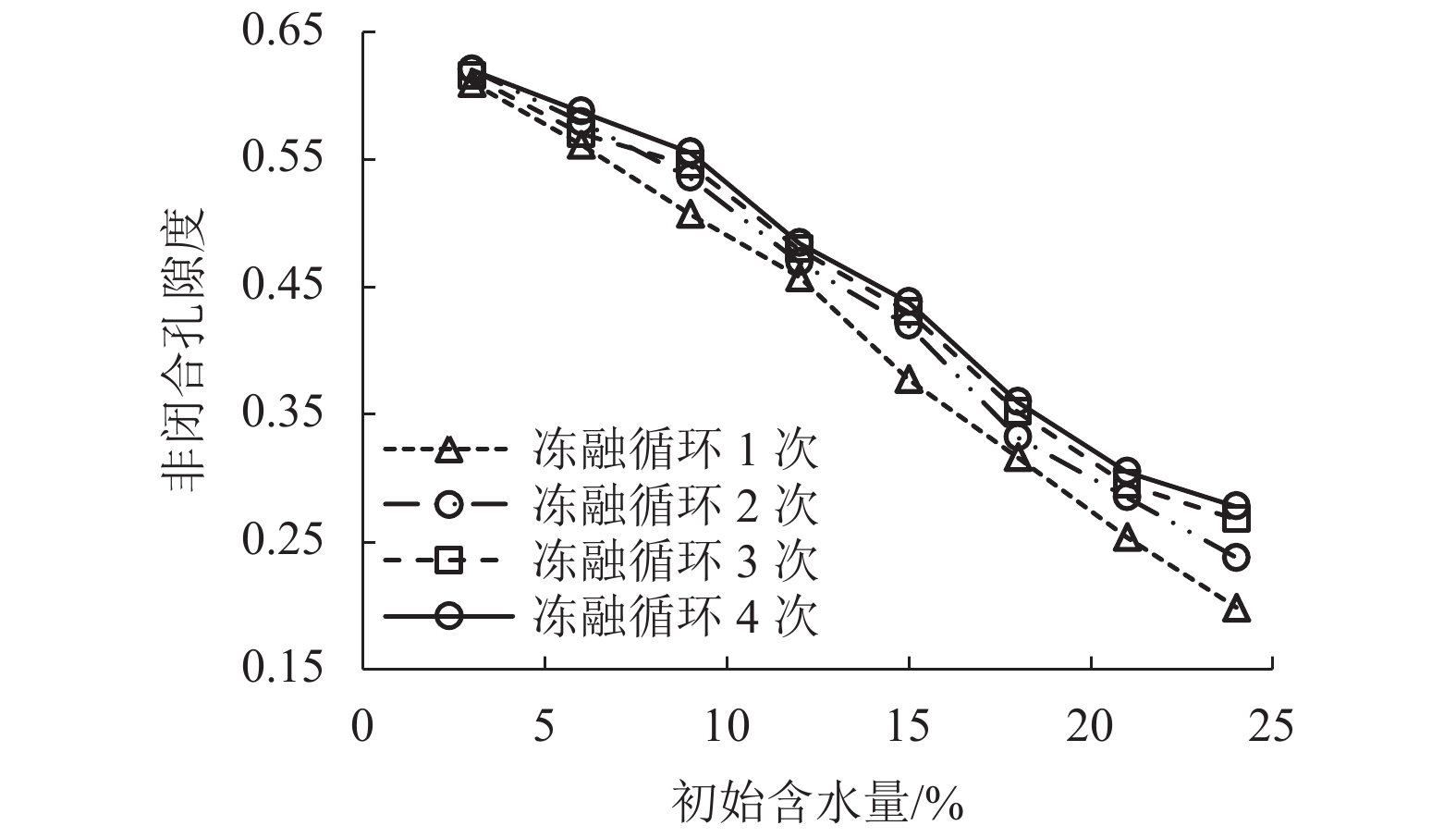
王铁行,杨涛,鲁洁. 干密度及冻融循环对黄土渗透性的各向异性影响[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(增刊1): 72-78.WANG Tiehang, YANG Tao, LU Jie. Influence of dry density and freezing-thawing cycles on anisotropic permeability of loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S1): 72-78.
|
|
陈磊,李东庆,明锋. 分形渗透模型在饱和冻土中的应用[J]. 冰川冻土,2019,41(6): 1414-1421.CHEN Lei, LI Dongqing, MING Feng. Application of the fractal hydraulic conductivity model in the saturated frozen soil[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2019, 41(6): 1414-1421.
|
|
MCCAULEY C A, WHITE D M, LILLEY M R, et al. A comparison of hydraulic conductivities,permeabilities and infiltration rates in frozen and unfrozen soils[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2002, 34(2): 117-125. doi: 10.1016/S0165-232X(01)00064-7
|
|
HORIGUCHI K, MILLER R D. Experimental studies with frozen soil in an ice sandwich permeameter[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 1980, 3(6): 177-183.
|
|
商允虎. 寒区冻土水理性质特征参数综合试验研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学, 2015.
|




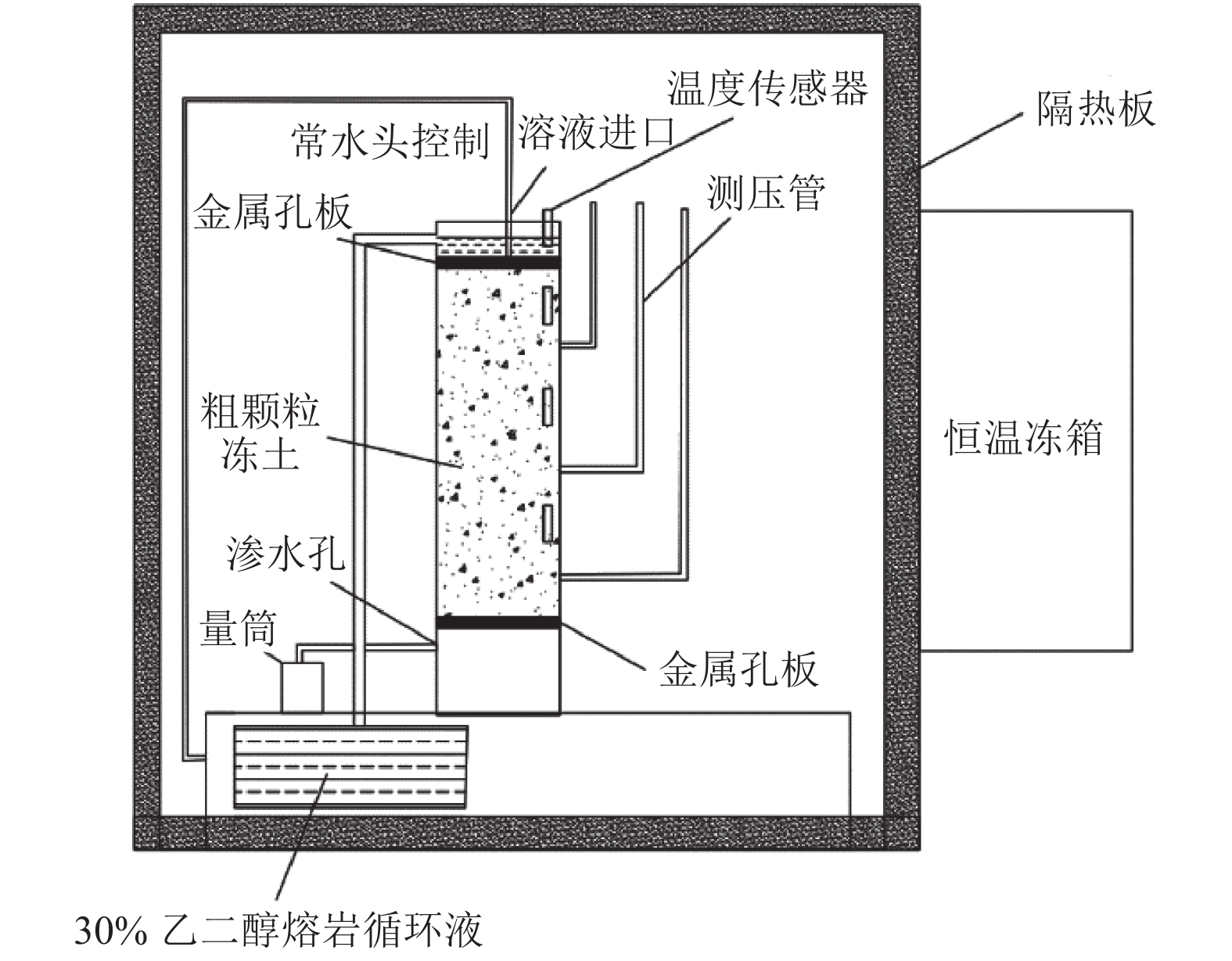
 下载:
下载: