Main Cable Opening Inspection and Bearing Capacity Evaluation of Suspension Bridge in Service in Myanmar
-
摘要:
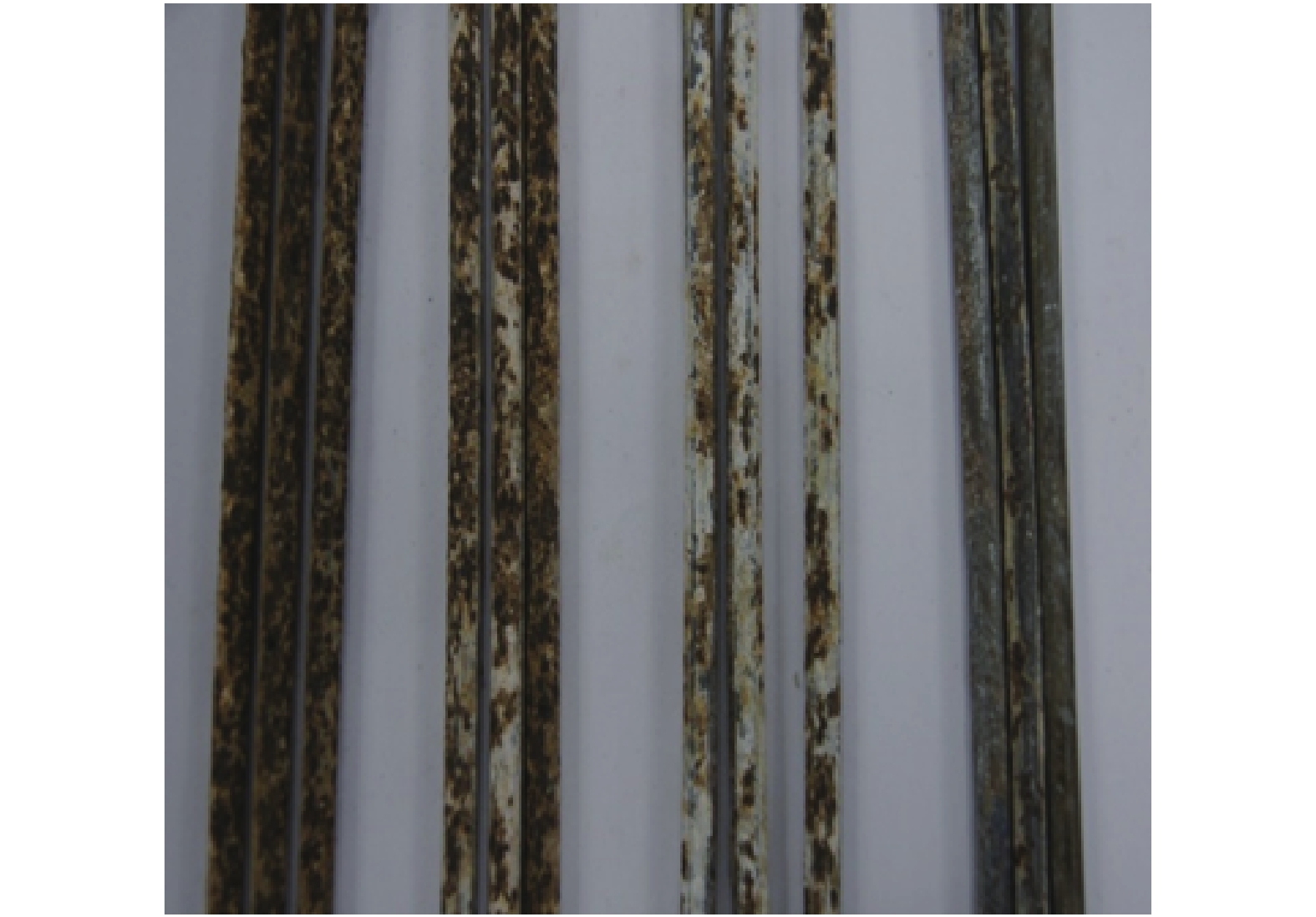
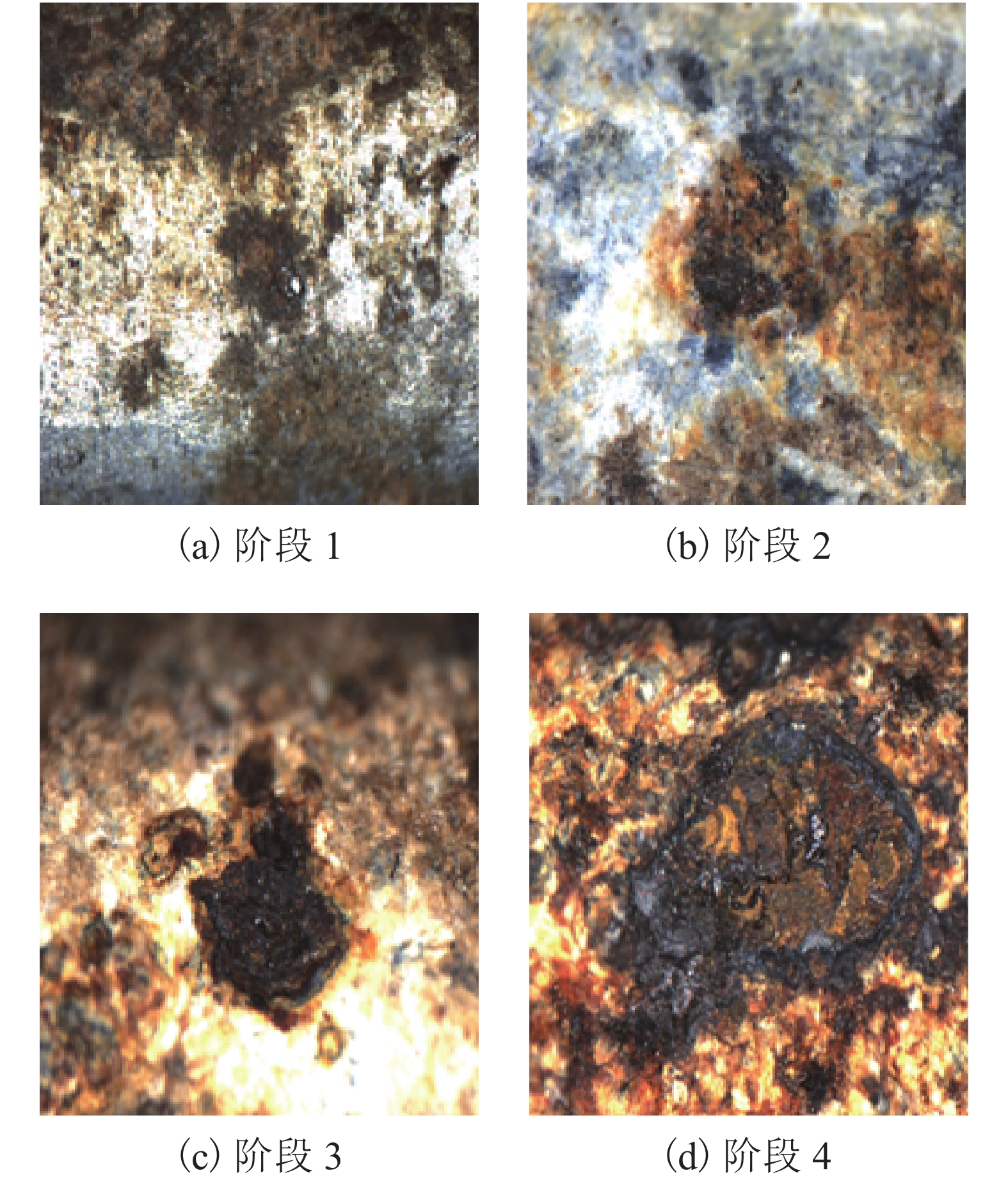
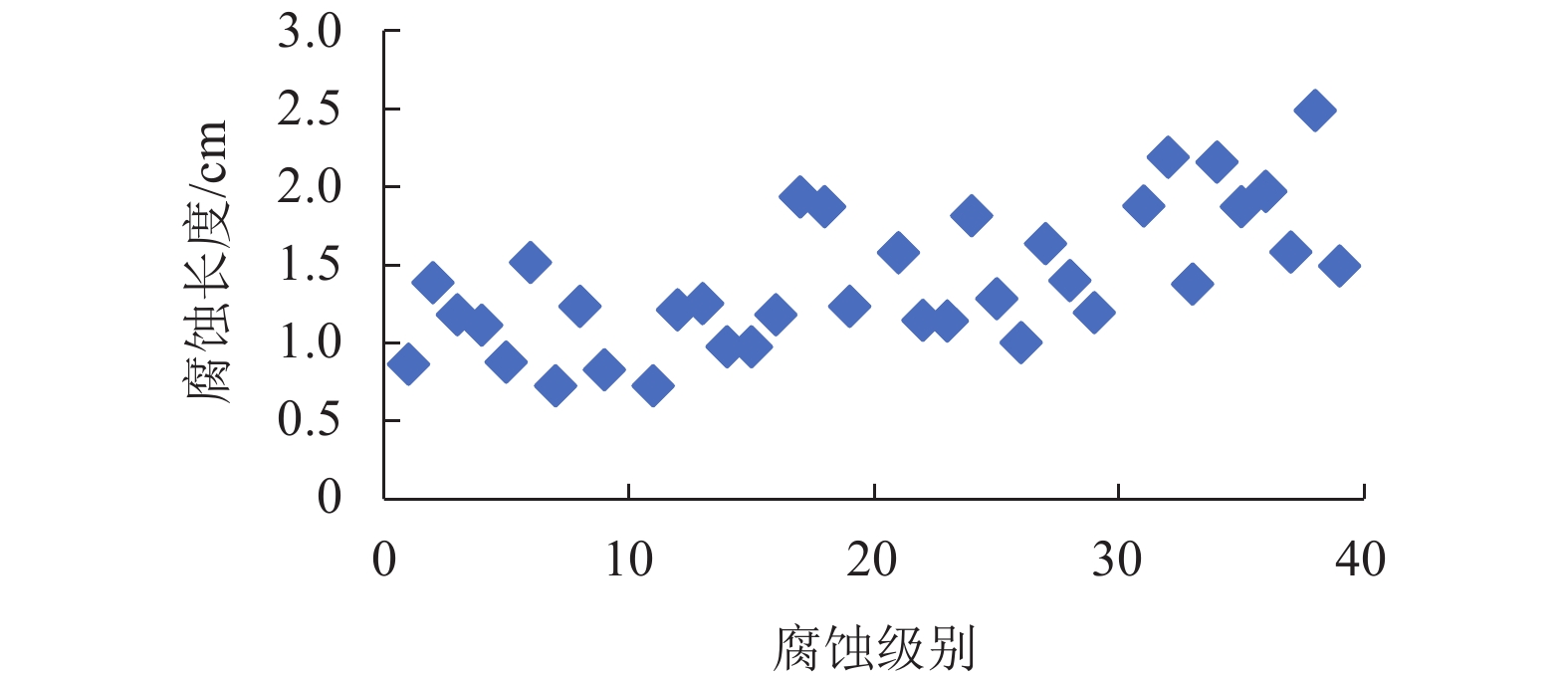
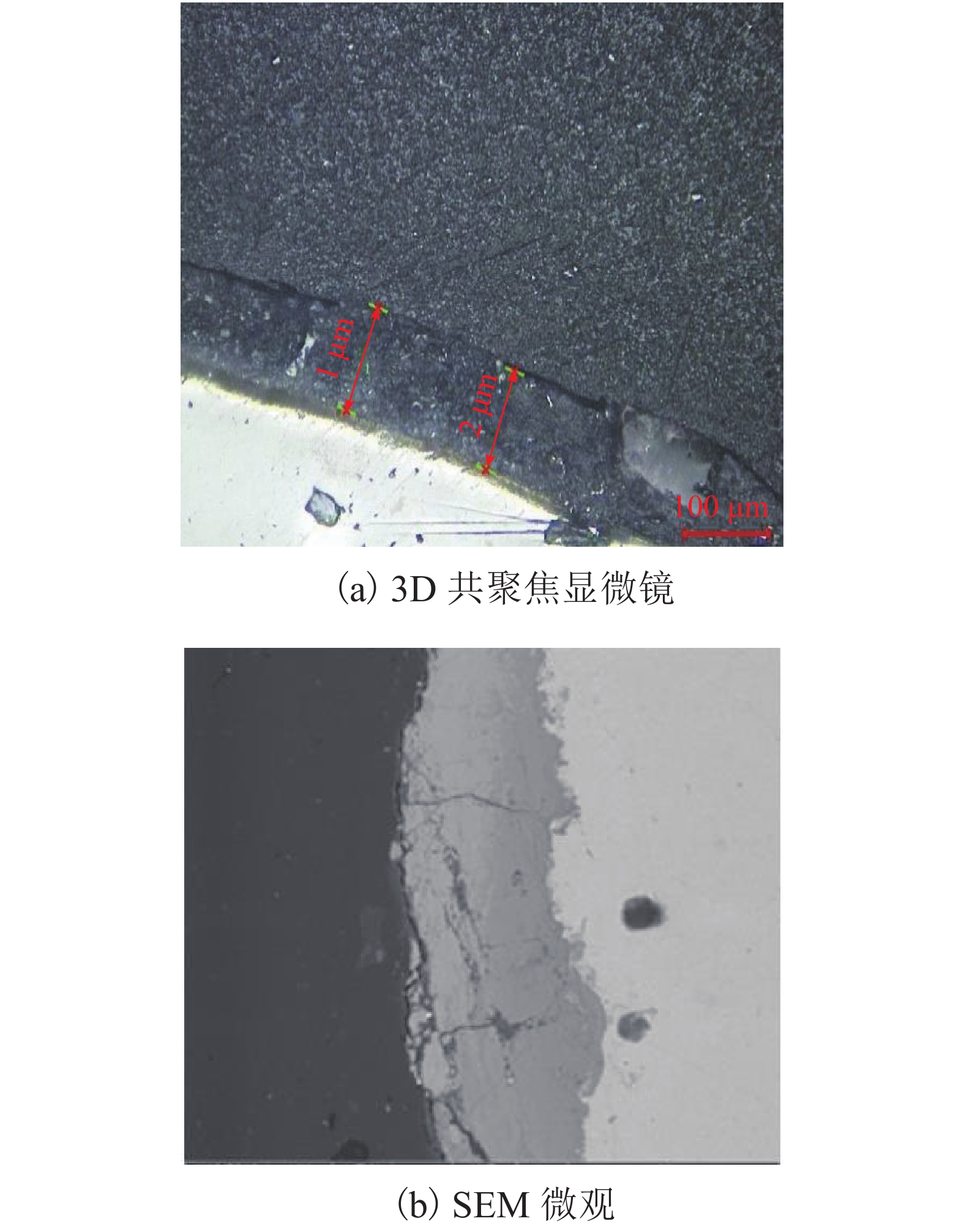
为研究在役悬索桥主缆的腐蚀状况以及剩余承载力,对缅甸某服役25 a的悬索桥主缆进行开缆检测以及承载力评估. 首先,除去主缆外层防护,用楔子将主缆局部楔开,建立主缆开缆截面腐蚀分布图;其次,将实桥主缆钢丝分为4个腐蚀阶段,从缆内截取各阶段的样本钢丝进行实验分析;最后,采用简化模型对主缆剩余承载力进行评估. 研究结果表明:钢丝沿主缆径向由外向内腐蚀程度依次降低,最外层钢丝发生严重的基体腐蚀,样本钢丝腐蚀斑随腐蚀程度加深而尺寸逐渐扩大,钢丝强度和延展性随腐蚀程度加深而降低约3.50%和9.00%,上下游主缆强度降低约5.7%.
Abstract:A cable opening inspection was made on a suspension bridge in service for 25 years in Myanmar to analyze the corrosion status and residual bearing capacity of the main cables. First, the outer protection layer of the main cable was removed; the main cable is partially split with wedge for detection, and the corrosion distribution diagram of the main cable cross-section was established. Then, the main cable steel wire of the bridge was divided into four corrosion stages, and samples of each stage were taken from the cable for laboratory analysis. Finally, a simplified model was used to evaluate the residual bearing capacity of the main cable. The results showed that the corrosion degree of the steel wires decreased from outside to inside along the radial direction of the main cable, and the outermost steel wire had serious matrix corrosion. As the corrosion level increased, the corrosion spot size of the sample steel wires expanded gradually, the strength and ductility of the steel wires decreased by about 3.50% and 9.00%, respectively, and the average tensile strength of the upstream and downstream main cables decreased by about 5.7%.
-
Key words:
- main cable inspection /
- steel wire corrosion /
- bearing capacity evaluation
-
表 1 液体成分测量结果表
Table 1. Results of liquid composition measurements
测量液体 pH 值 (25 ℃) Cl−/(mg•kg−1) ${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - }$/(mg•kg−1) 样本浸泡液 7.26 4.0991 1.2880 雨水样品 8.28 2.0721 26.1308 表 2 样本钢丝拉伸性能测量结果表
Table 2. Test results of tensile properties ofsample steel wires
腐蚀
阶段屈服力/
KN屈服强度/MPa 破断力/
KN抗拉强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 延伸率/% 阶段 1 30.15 1419.15 34.95 1646.22 204 4.41 阶段 2 30.11 1417.37 34.26 1613.93 205 4.36 阶段 3 30.08 1415.54 34.14 1608.25 211 4.16 阶段 4 29.56 1391.47 33.71 1587.87 208 4.01 表 3 断面收缩率
Table 3. Percentage reduction ofcross-section area after fracture
腐蚀
阶段断前直径
(均值)/mm断后直径
(均值)/mm断面收缩率
(均值)/%阶段 1 5.19 4.40 15.2 阶段 2 5.20 4.60 11.5 阶段 3 5.17 4.81 6.9 阶段 4 5.14 4.89 4.8 表 4 上游跨中截面数据统计表
Table 4. Statistics of parameters of upstream midspan section
截面含量 组别 $ {N_k} $/根 ${\mu _{{\rm{s}}k} }$/MPa ${\sigma _{{\rm{s}}k} }$/MPa ${P_{{\rm{u}}k} }$/% 上游 第 1 组 3927 1630.07 28.46 83.6 第 2 组 338 1608.25 25.62 7.2 第 3 组 434 1587.87 47.89 9.2 下游 第 1 组 3796 1630.07 28.46 80.8 第 2 组 442 1608.25 25.62 9.4 第 3 组 461 1587.87 47.89 9.8 -
[1] 陈小雨,沈锐利,唐茂林. 悬索桥主缆检测及承载力评估现状与发展[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2013(增刊1): 760-763.CHEN Xiaoyu, SHEN Ruili, TANG Maolin. Current situation and development for detection and bearing capacity evaluation of main cable of suspension bridge[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science), 2013(S1): 760-763. [2] MAYRBAURL R M. CAMO MICHAEL S T. Guidelines for inspection and strength evaluation of suspension bridge parallel wire cables[R]. New York: Transportation Research Board , 2004. [3] COLFORD B R, CLARK C A. Forth road bridge main cables:replacement/augmentation study[J]. Bridge Engineering, 2010, 163(2): 79-89. [4] 沈平. 英国M48塞文桥主缆检查与修复[J]. 世界桥梁,2011(5): 70-73. [5] COCKSEDGE C, HUDSON T, URBANS B, et al. M48 Severn Bridge—main cable inspection and rehab ilitation[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, 2010, 163(4): 181-195. [6] NAKAMURA S I, SUZUMURA K. Hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion fatigue of corroded bridge wires[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2009, 65(2): 269-277. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2008.03.022 [7] 辛付开, 韩依璇, 张国荣, 等. 某在役悬索桥平行钢丝主缆检查及腐蚀规律研究[J] 水利与建筑工程学报, 2017, 15(3): 118-122.XIN Fukai, HAN Yixuan, ZHANG Guorong, et al. Inspection and corrosion rule of parallel steel wire main cables of suspension bridge in service[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2017, 15(3): 118-122. [8] 陈小雨,唐茂林. 温度和湿度环境下未镀锌高强钢丝的腐蚀速率谱[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(2): 253-259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.02.005CHENG Xiaoyu, TANG Maolin. Corrosion rate of non-galvanized high-strength steel wires under different temperature and humidity conditions[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(2): 253-259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.02.005 [9] 陈小雨,唐茂林. 悬索桥主缆镀锌钢丝腐蚀过程及抗力变化试验研究[J]. 桥梁建设,2018,48(1): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2018.01.011CHENG Xiaoyu, TANG Maolin. Experimental study of corrosion process and resisitance changes of galvanized steel wires for main cable of suspension bridge[J]. Bridge Construction, 2018, 48(1): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4722.2018.01.011 [10] 陈小雨,唐茂林. 悬索桥主缆钢丝腐蚀速率计算方法[J]. 公路交通科技,2019,36(2): 43-49.CHEN Xiaoyu, TANG Maolin. A method for calculating corrosion rate of main cable steel wires of suspension bridge[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(2): 43-49. -





 下载:
下载: