Analysis of Electrosurgical Unit Parameters on Sealing Effect of Porcine Pancreatic Duct
-
摘要:
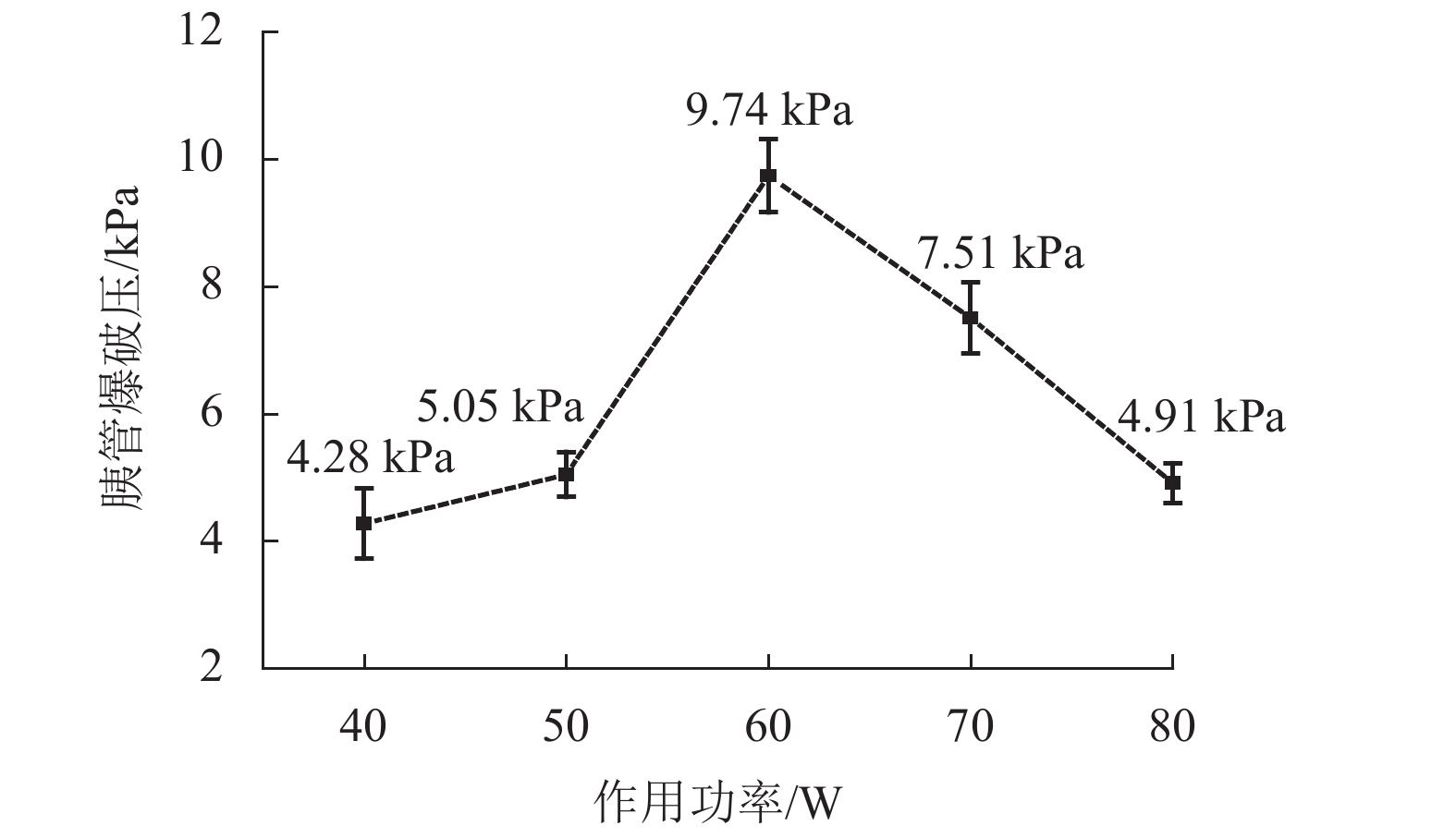
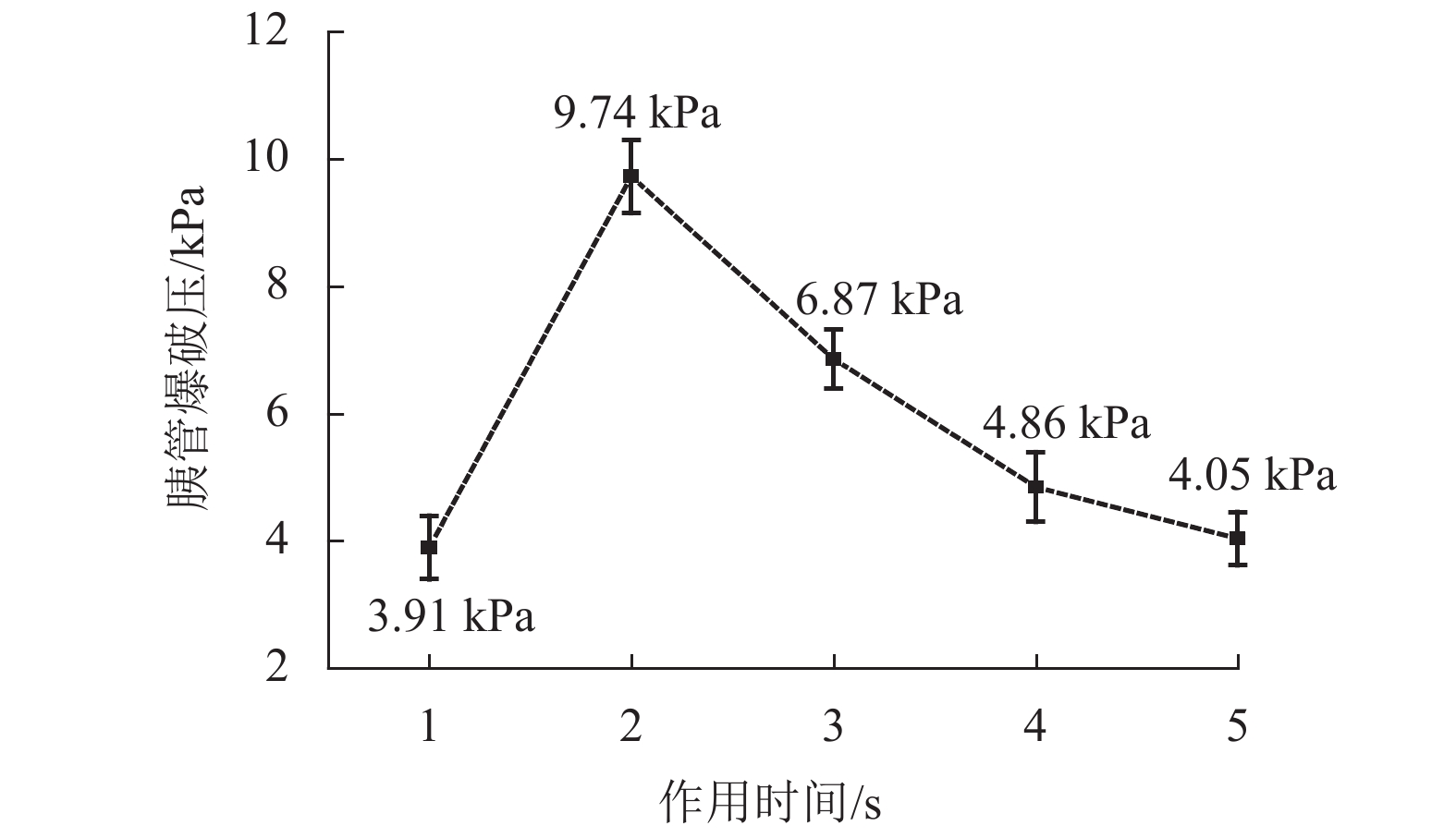
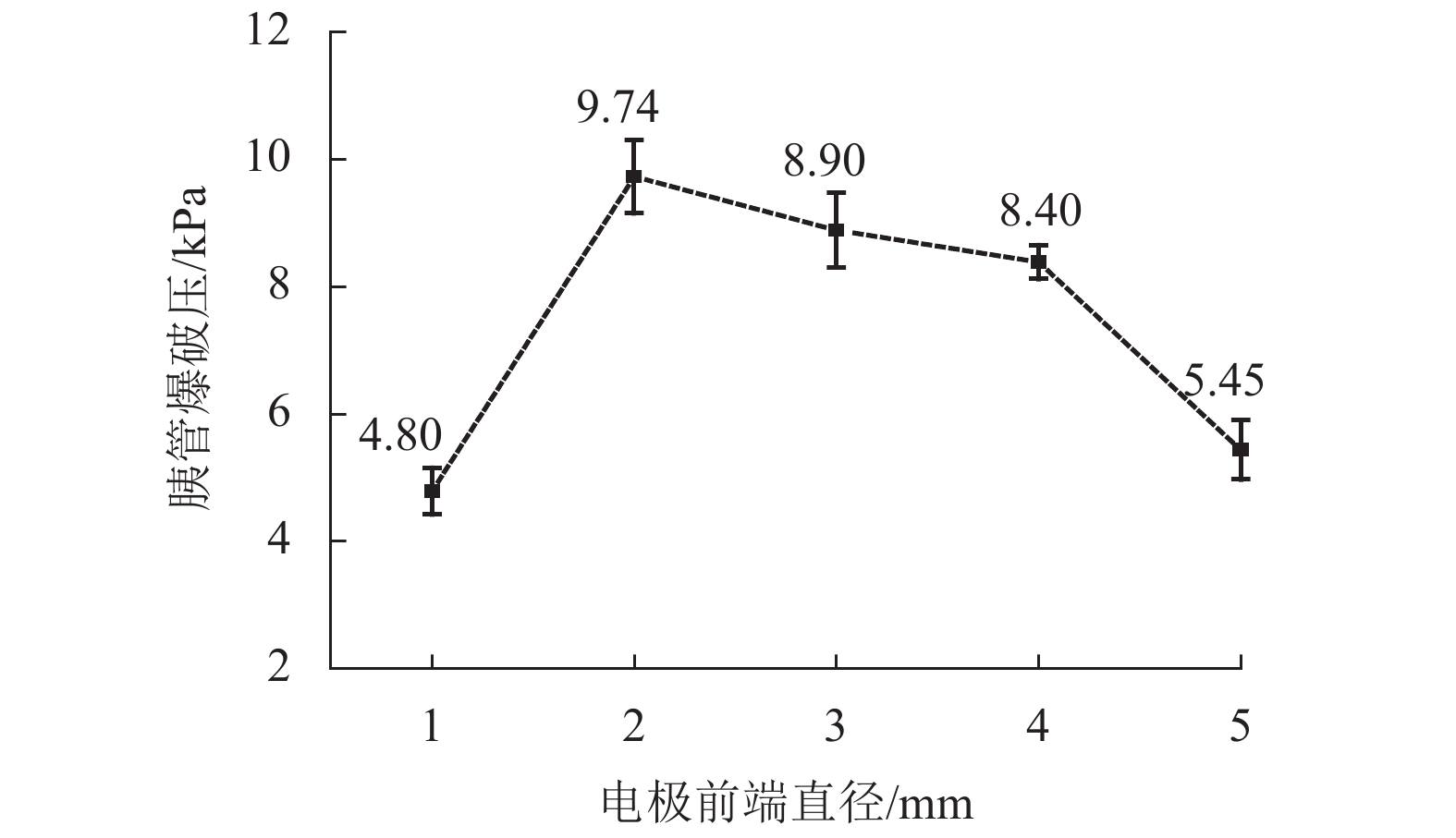
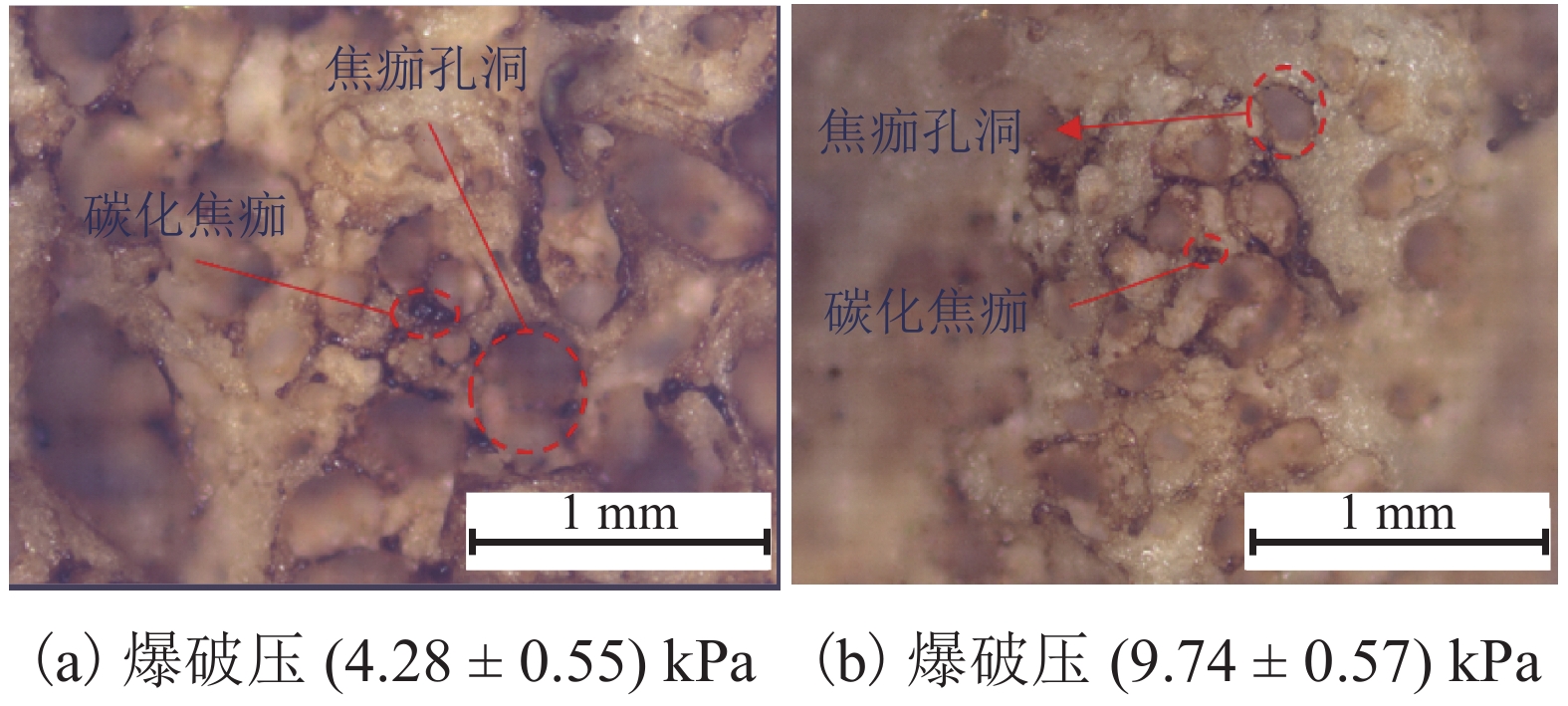
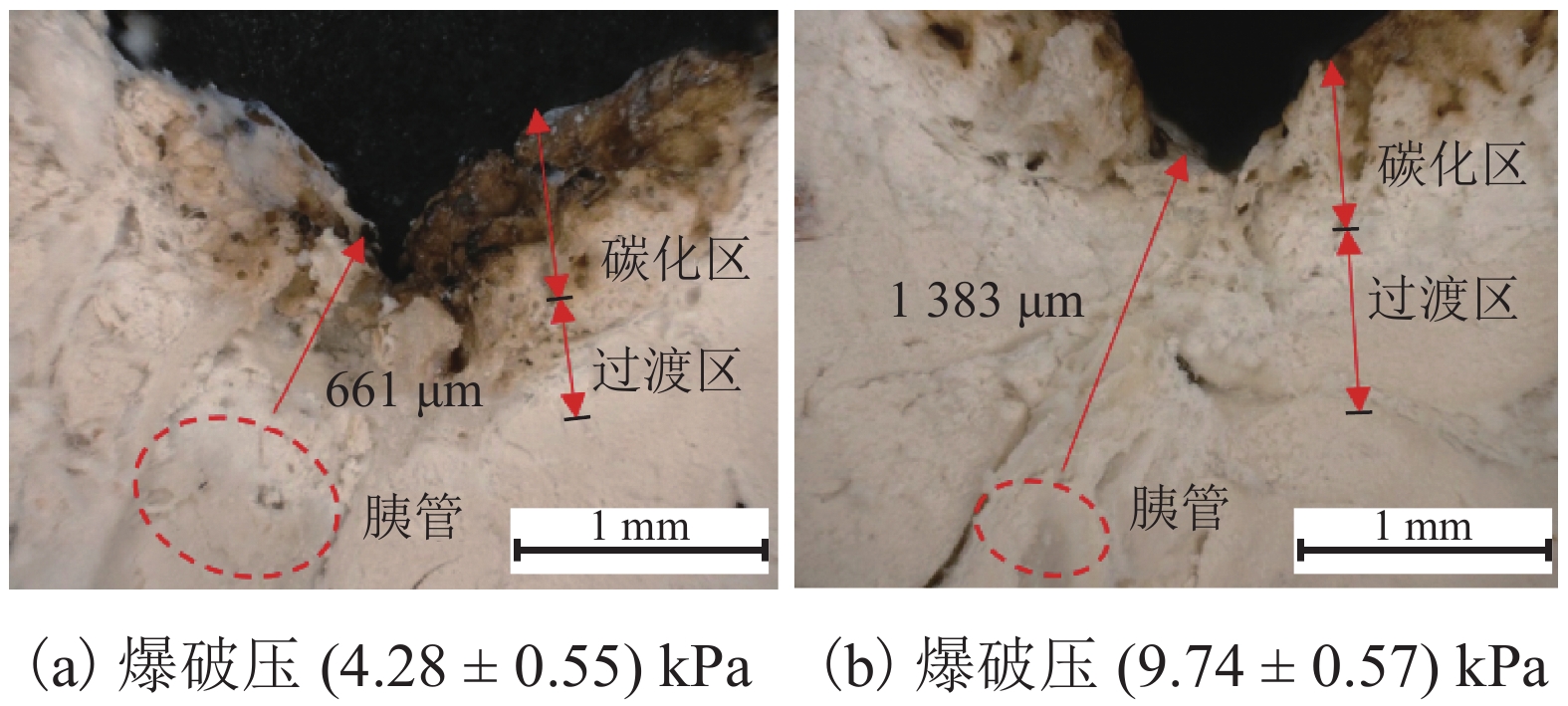
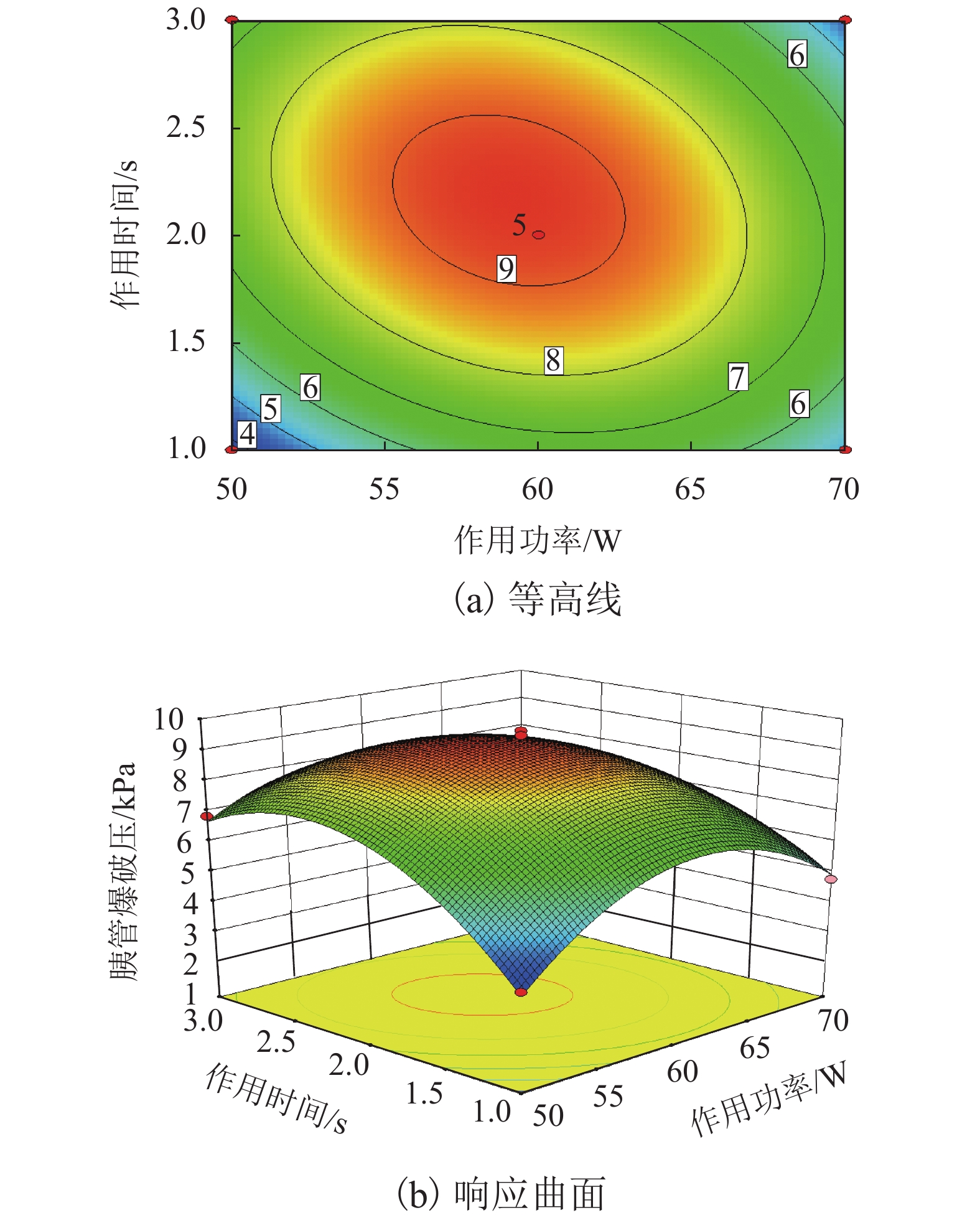
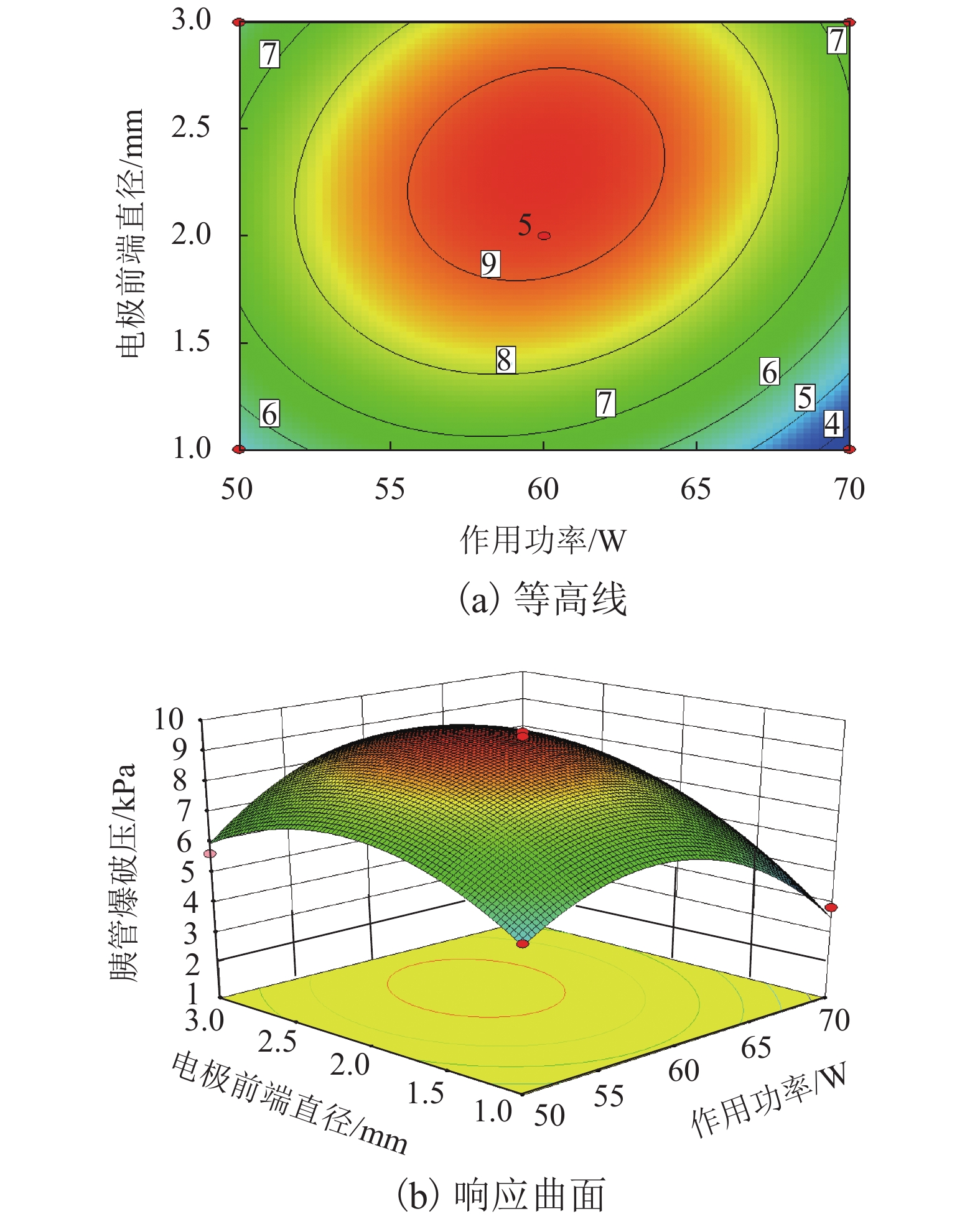
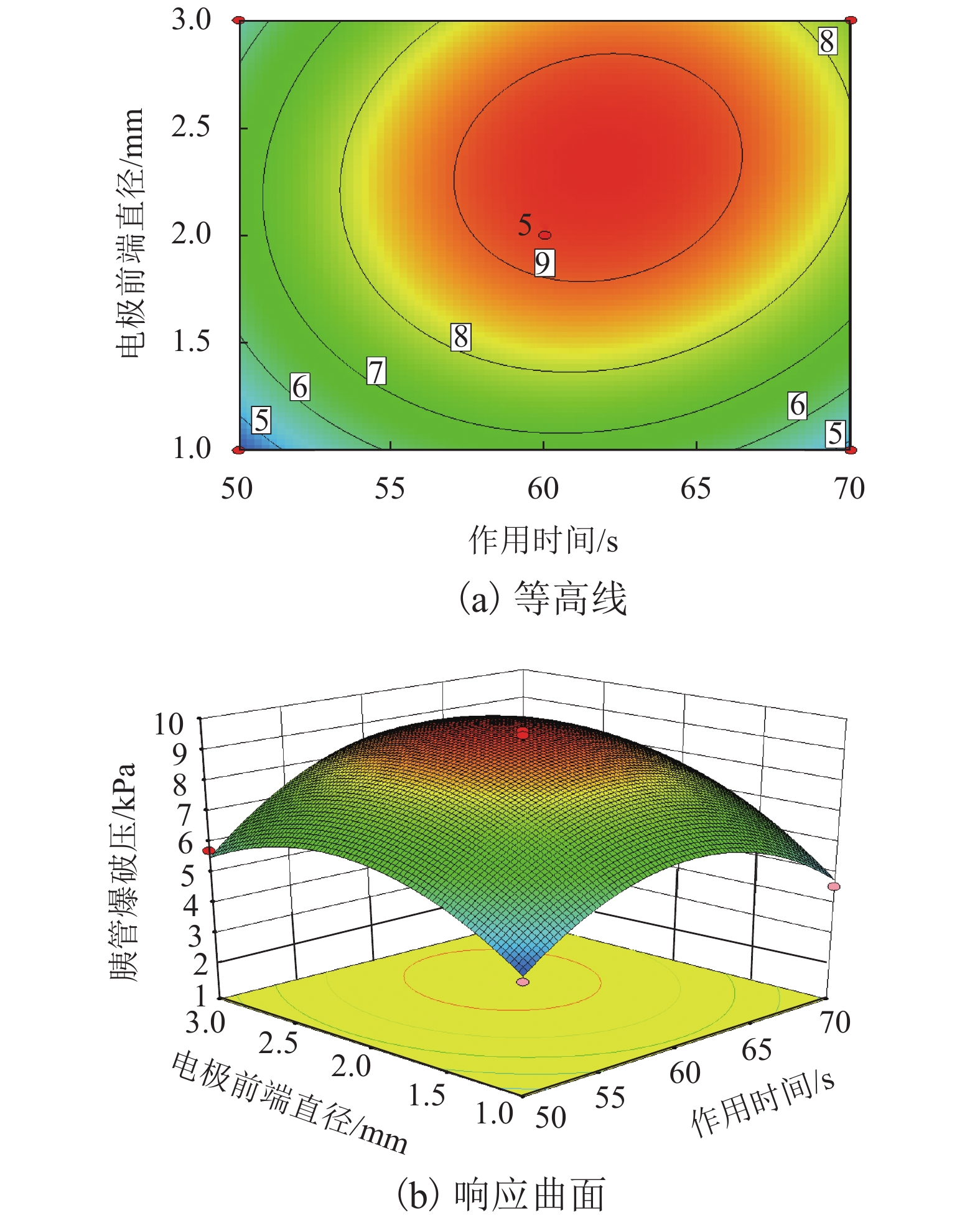
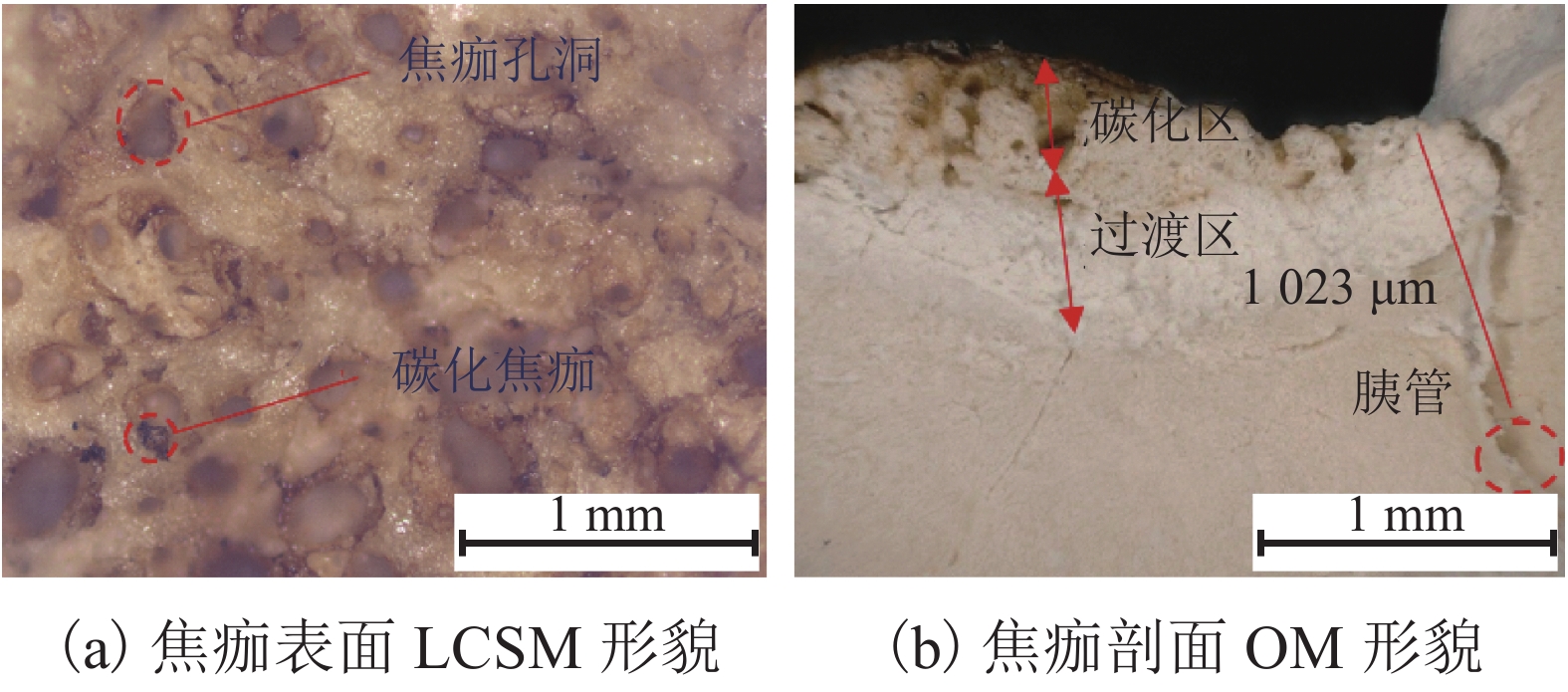
高频电刀的组织热效应可以使胰腺组织表面生成焦痂,具有止血防胰瘘的效果. 高频电刀机电参数对焦痂止血防胰瘘功能具有显著影响,但尚缺乏对其作用规律的深入研究. 采用体外模拟试验方法,结合胰管爆破压测试和焦痂形貌研究了干燥模式下3种关键机电参数(电刀功率、作用时间和电极前端直径)对胰管封闭效果的影响规律;基于此,采用响应面分析法获取电刀功率、作用时间和电极前端直径之间的交互作用关系以及具有最佳胰管封闭效果的机电参数. 研究结果表明:单一变量下,电刀功率为60 W时胰管爆破压处于峰值,作用时间为2.00 s时胰管爆破压处于峰值,电极前端直径为2.00 mm时胰管爆破压处于峰值;干燥模式下的最佳机电参数为电刀功率59.39 W、作用时间2.18 s、电极前端直径2.31 mm;此外,电极前端直径是影响胰管封闭效果的独立因素,电刀功率和作用时间有显著性的交互作用,共同影响胰管封闭效果.
Abstract:The tissue thermal effect of electrosurgical unit (ESU) can cause eschar on the surface of pancreatic tissue, which has the effect of hemostasis and preventing pancreatic fistula. The electro-mechanical parameters of ESU have a significant effect on the function of eschar hemostasis and preventing pancreatic fistula, but there is still a lack of in-depth study on the law of its action. In this study, three key electro-mechanical parameters, i.e. power, acting time and diameter of electrode front end, were studied in the DESICCATE mode by using in vitro simulation test method, combined with burst pressure test of pancreatic duct and eschar morphology analysis. Based on the above, the interaction between power, acting time and diameter of electrode front end was obtained by response surface analysis and the electro-mechanical parameters with the best effect of pancreatic duct sealing. The results show that the burst pressure of the pancreatic duct is at the peak value when the power is 60 W, the burst pressure of the pancreatic duct is at the peak value when the acting time is 2.00 s, and the burst pressure of the pancreatic duct is at the peak value when the diameter of the front end of the electrode is 2.00 mm. The best electro-mechanical parameters in the DESICCATE mode are: the power of electric knife is 59.39 W, the action time is 2.18 s, and the diameter of electrode front end is 2.31 mm. In addition, the diameter of the electrode front end is an independent factor affecting the pancreatic duct sealing effect, the power and acting time of the ESU have significant synergistic effect on the pancreatic duct sealing.
-
表 1 响应面试验设计因素水平表
Table 1. Levels of independent variables for BBD
因素 水平 −1 0 1 高频电刀功率/W 50 60 70 作用时间/s 1.00 2.00 3.00 电极前端直径/mm 1.00 2.00 3.00 表 2 响应面试验点与试验结果
Table 2. Test points and results of BBD
试验号 作用
功率/W作用
时间/s电极
直径/mm胰管爆
破压/kPa1 50 2.00 3.00 5.65 2 50 3.00 2.00 6.85 3 60 2.00 2.00 8.95 4 70 2.00 1.00 3.83 5 60 2.00 2.00 9.04 6 70 2.00 3.00 6.56 7 70 1.00 2.00 4.75 8 50 2.00 1.00 5.36 9 60 3.00 1.00 4.55 10 60 1.00 3.00 5.75 11 50 1.00 2.00 3.85 12 60 1.00 1.00 4.23 13 60 2.00 2.00 9.47 14 60 3.00 3.00 7.69 15 60 2.00 2.00 9.62 16 70 3.00 2.00 4.17 17 60 2.00 2.00 9.18 表 3 爆破压响应面回归模型方差分析
Table 3. ANOVA test results for burst pressure model
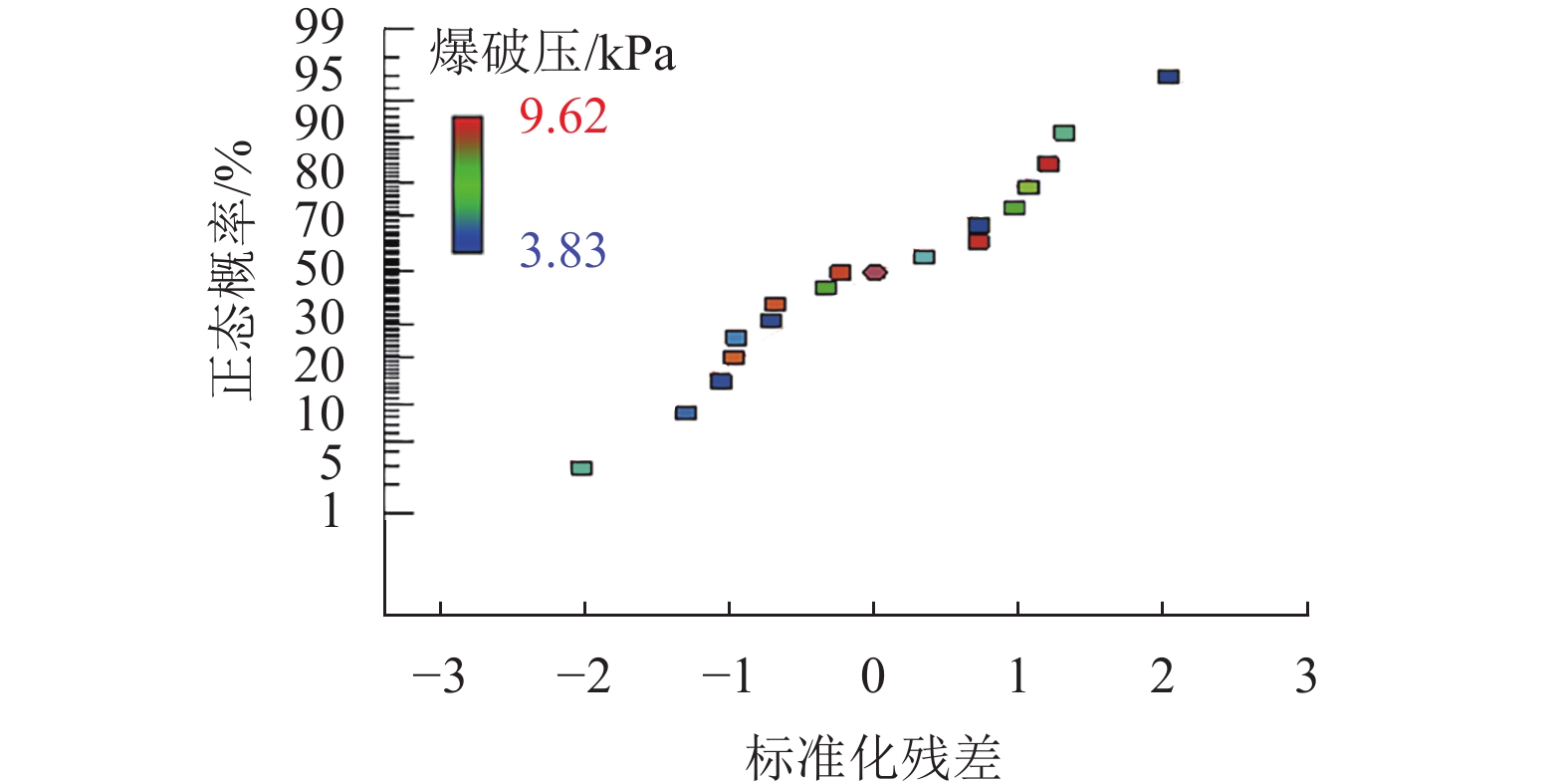
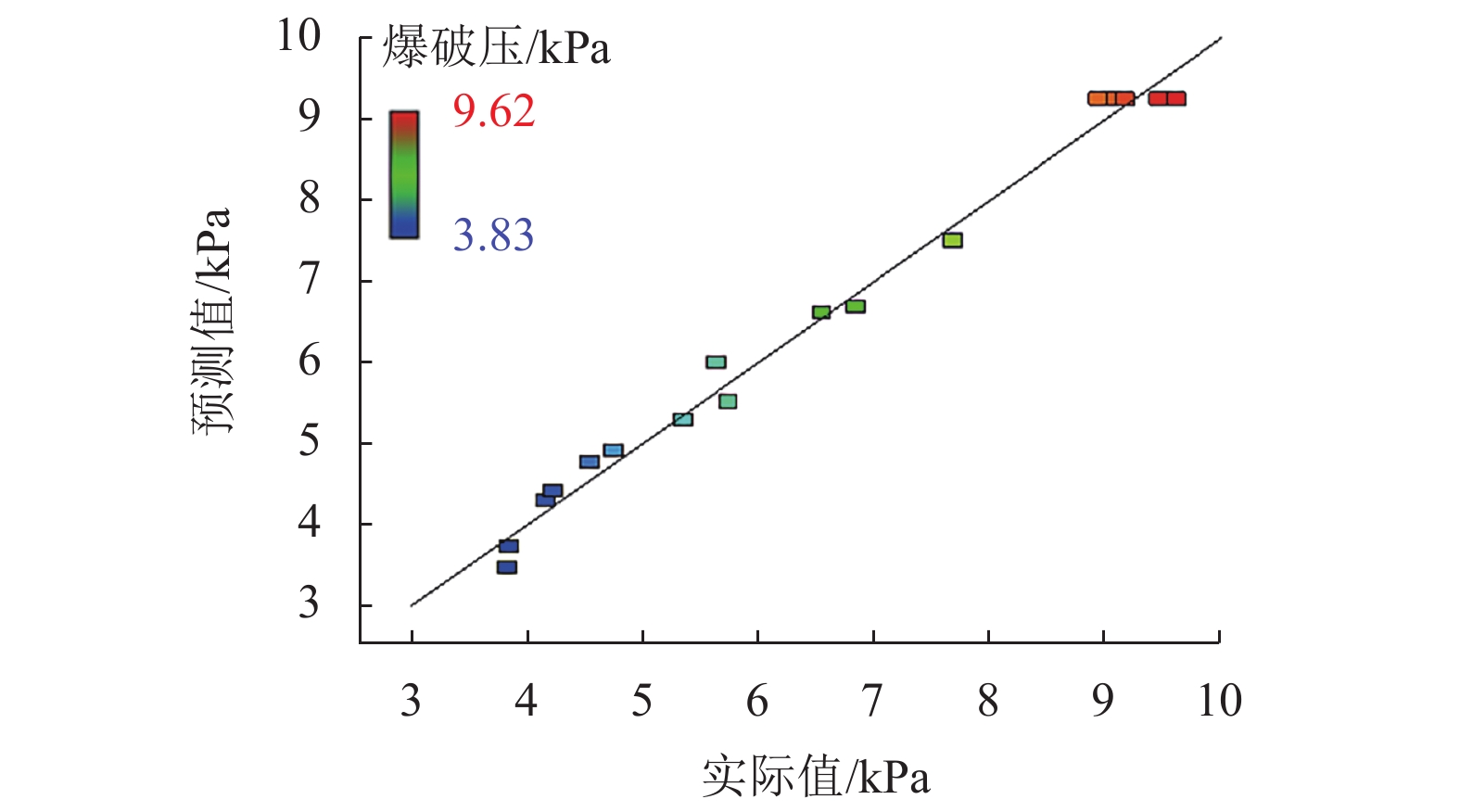
方差来源 离差平方和 自由度 均方差 F 检验值 P 值 显著性 模型 73.006 9 8.112 67.95 < 0.001 ** A 0.723 1 0.723 6.06 0.043 * B 2.735 1 2.735 22.92 0.002 * C 7.367 1 7.367 61.71 < 0.001 ** AB 3.188 1 3.188 26.71 0.001 * AC 1.484 1 1.484 12.43 0.010 * BC 0.663 1 0.663 5.56 0.051 − A2 21.797 1 21.797 182.59 < 0.001 ** B2 18.033 1 18.033 151.06 < 0.001 ** C2 11.170 1 11.170 93.57 < 0.001 ** 残差 0.836 7 0.119 − − − 失拟性 0.508 3 0.169 2.070 0.247 不显著 标准差 0.346 复相关系数 0.988 平均数 6.440 校正复相关系数 0.974 变异系数/% 5.365 预测复相关系数 0.883 预测残差平方和 8.642 信噪比 21.786 注:**为极显著,*为显著. -
[1] MIYASAKA Y, MORI Y, NAKATA K, et al. Attempts to prevent postoperative pancreatic fistula after distal pancreatectomy[J]. Surgery Today, 2017, 47(4): 416-424. doi: 10.1007/s00595-016-1367-8 [2] HÜTTNER F J, KOESSLER-EBS J, HACKERT T, et al. Meta-analysis of surgical outcome after enucleation versus standard resection for pancreatic neoplasms[J]. The British Journal of Surgery, 2015, 102(9): 1026-1036. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9819 [3] SHRIKHANDE S, D’SOUZA M A. Pancreatic fistula after pancreatectomy:evolving definitions,preventive strategies and modern management[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2008, 14(38): 5789-5796. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5789 [4] RICCI C, CASADEI R, BUSCEMI S, et al. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy:what factors are related to the learning curve[J]. Surgery Today, 2015, 45(1): 50-56. doi: 10.1007/s00595-014-0872-x [5] RAMACCIATO G, MERCANTINI P, PETRUCCIANI N, et al. Risk factors of pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy:a collective review[J]. The American Surgeon, 2011, 77(3): 257-269. doi: 10.1177/000313481107700310 [6] BASSI C, MARCHEGIANI G, DERVENIS C, et al. The 2016 update of the international study group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula:11 years after[J]. Surgery, 2017, 161(3): 584-591. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.014 [7] BURDÍO F, DORCARATTO D, HERNANDEZ L, et al. Radiofrequency-induced heating versus mechanical stapler for pancreatic stump closure:in vivo comparative study[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2016, 32(3): 272-180. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2015.1136845 [8] IKEDA T, AKAHOSHI T, KAWANAKA H, et al. Evaluation of a transection method for distal pancreatectomy:a comparative study on the use of electrosurgical and stapling devices in swine[J]. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi, 2013, 104(9): 515-522. [9] CHAMBERLAIN R S, KORVICK D, MOOTOO M, et al. Can harmonic focus curved shear effectively seal the pancreatic ducts and prevent pancreatic leak?feasibility evaluation and testing in ex vivo and in vivo porcine models[J]. Journal of Surgical Research, 2009, 157(11): 279-283. [10] NAGAKAWA Y, TSUCHIDA A, SAITO H, et al. The VIO soft-coagulation system can prevent pancreatic fistula following pancreatectomy[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surgery, 2008, 15(4): 359-365. doi: 10.1007/s00534-008-1329-7 [11] 李宵宇. 高频电刀操作参数对猪胰管闭合效果的影响研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2018. [12] 崔海坡,黄嘉平,宋成利,等. 不同尺寸参数对双极高频电刀热应力场的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2019,34(2): 179-185.CUI Haipo, HUANG Jiaping, SONG Chengli, et al. Influence of different sizes on thermal stress field of bipolar high-frequency electric knife[J]. Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 2019, 34(2): 179-185. [13] SPANIKOVA G, MURGAS D, SPANIK P, et al. Analysis of critical current field distribution in tissues during electrosurgical procedures[C]//2016 ELEKTRO. Slovakia: IEEE, 2016: 589-592. [14] 张峰,张长宝,田建明,等. 猪正常胰腺的影像学表现[J]. 放射学实践,2010,25(2): 129-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0313.2010.02.004ZHANG Feng, ZHANG Changbao, TIAN Jianming, et al. Imaging features of normal porcine pancreas[J]. Radiol Practice, 2010, 25(2): 129-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0313.2010.02.004 [15] OKHUNOV Z, YOON R, LUSCH A, et al. Evaluation and comparison of contemporary energy-based surgical vessel sealing devices[J]. Journal of Endourology, 2018, 32(4): 329-337. doi: 10.1089/end.2017.0596 [16] 徐向宏, 何明珠. 试验设计与Design-Expert、SPSS应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 146-157. [17] MILLER I, FREUND J E, HALL P. Probability and statistics for engineers[M]. 9th Edition. [S.l.]: Pearson, 2016: 314-323. [18] HALLE-SMITH J M, VINUELA E, BROWN R M, et al. A comparative study of risk factors for pancreatic fistula after pancreatoduodenectomy or distal pancreatectomy[J]. HPB, 2017, 19(8): 727-734. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.04.013 [19] LIU Q Y, ZHANG W Z, XIA H T. Analysis of risk factors for postoperative pancreatic fistula following pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. World Journal Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(46): 17491-17497. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17491 -





 下载:
下载: