Experimental Study on Instability Characteristic and Bearing Capacity of Slope with Bedrock under Rainfall
-
摘要:
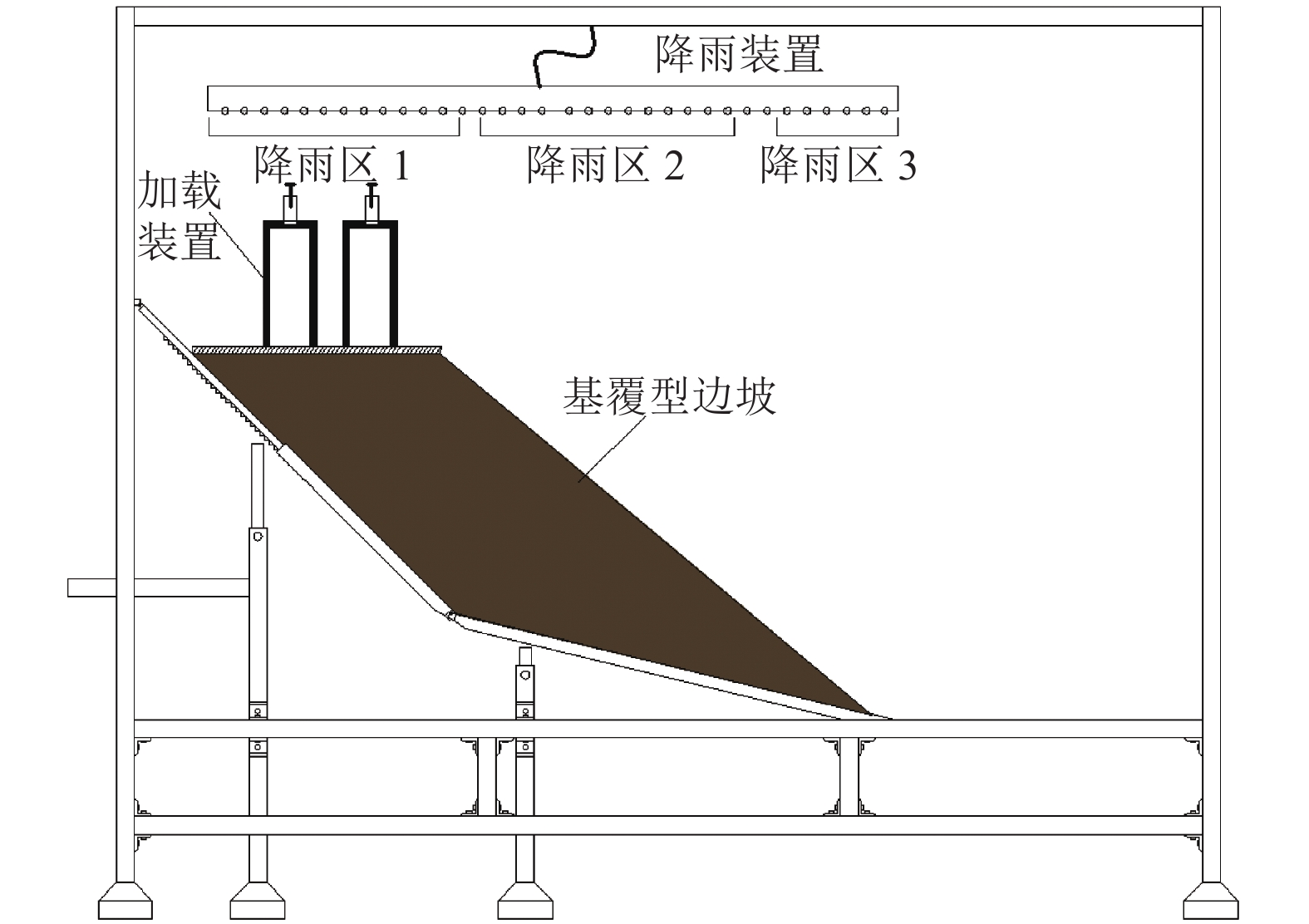
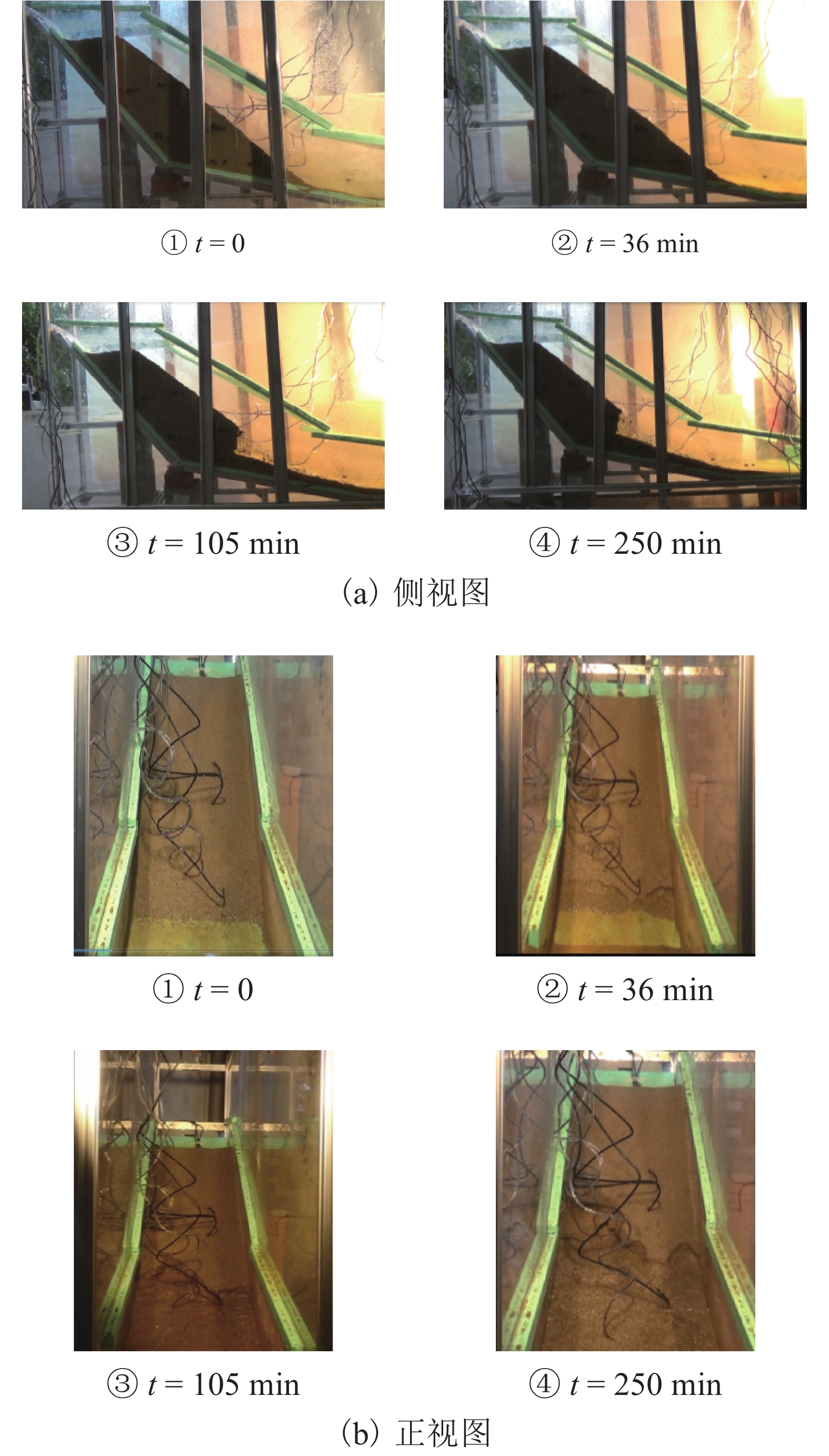
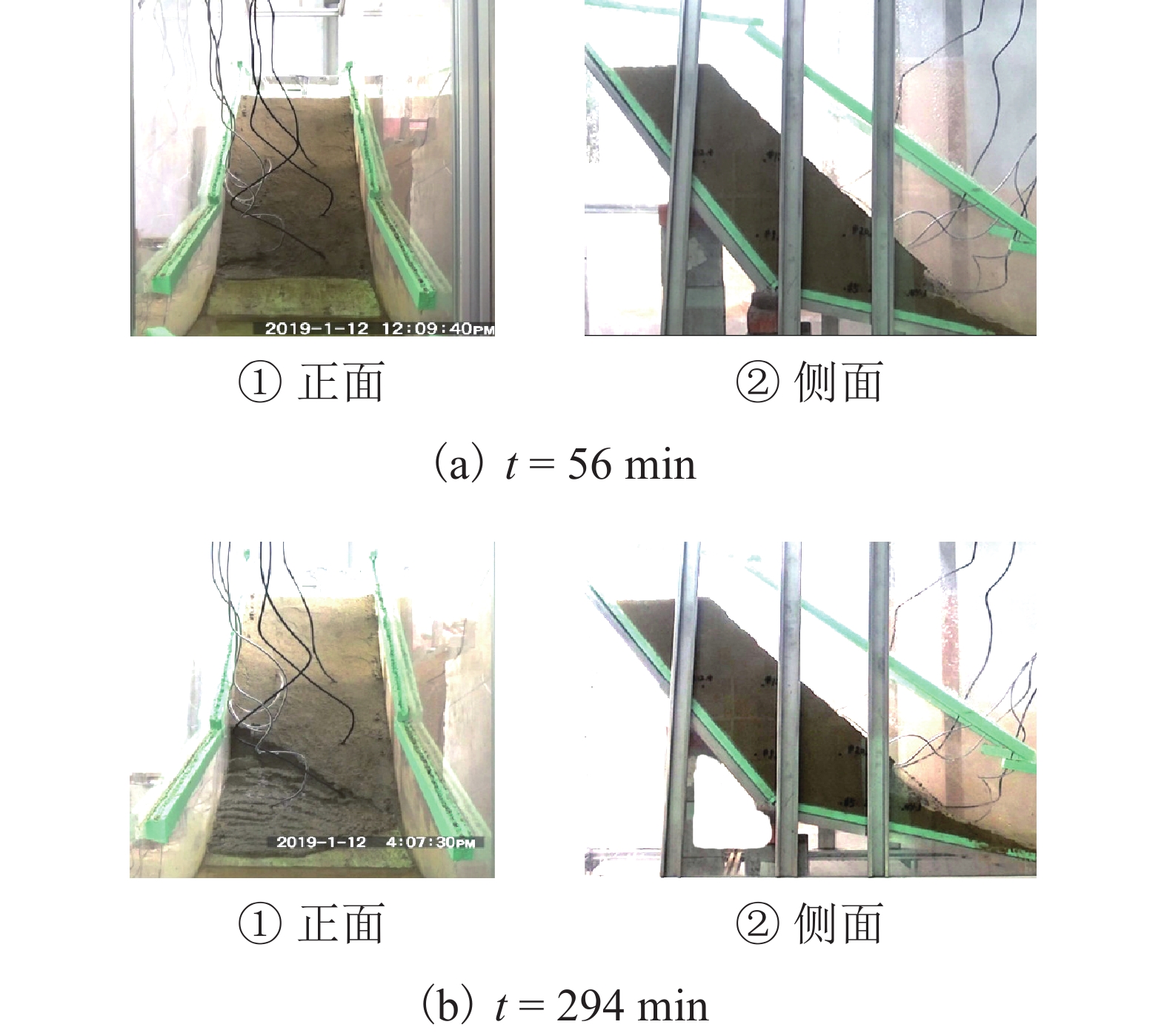
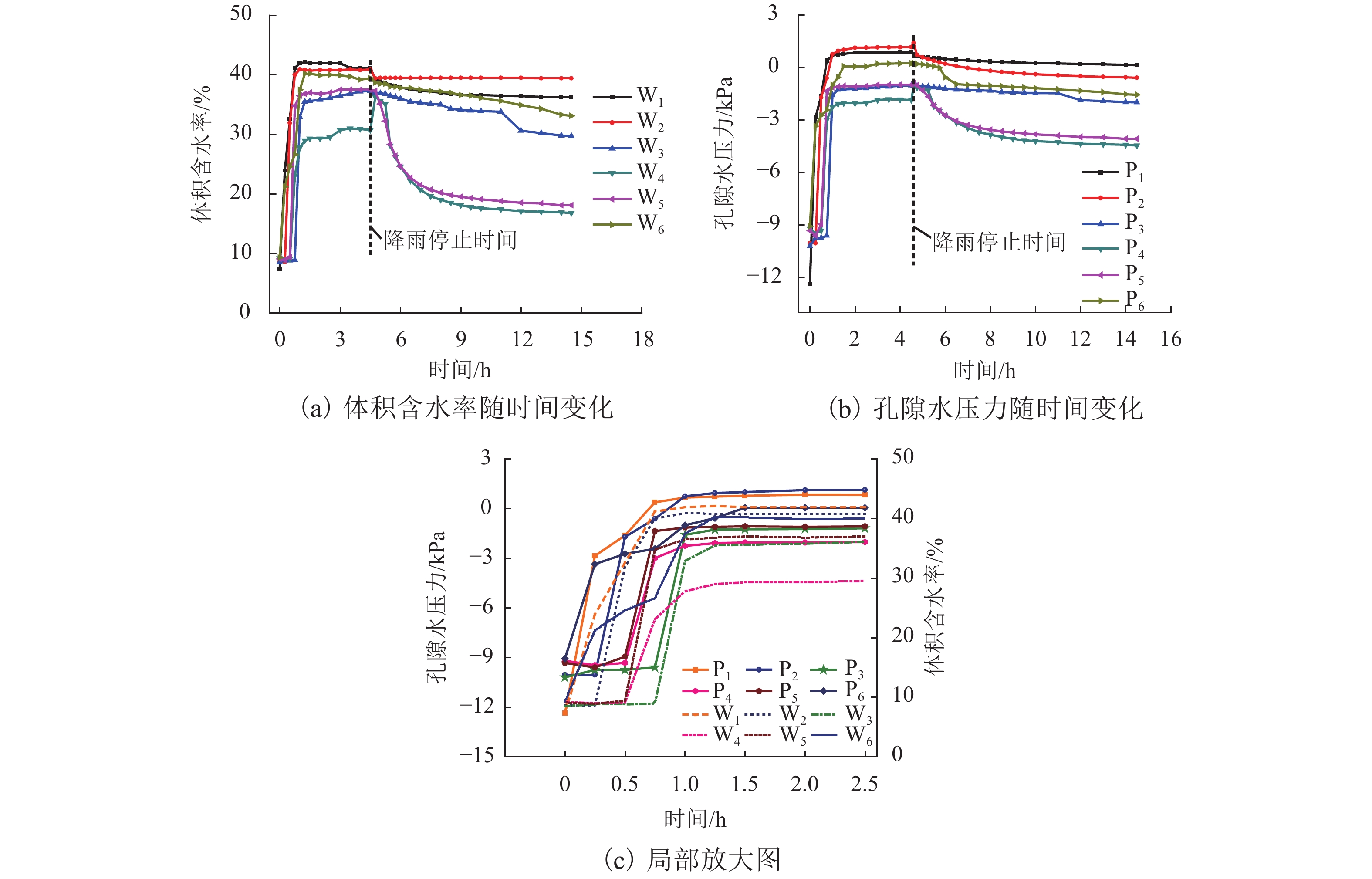
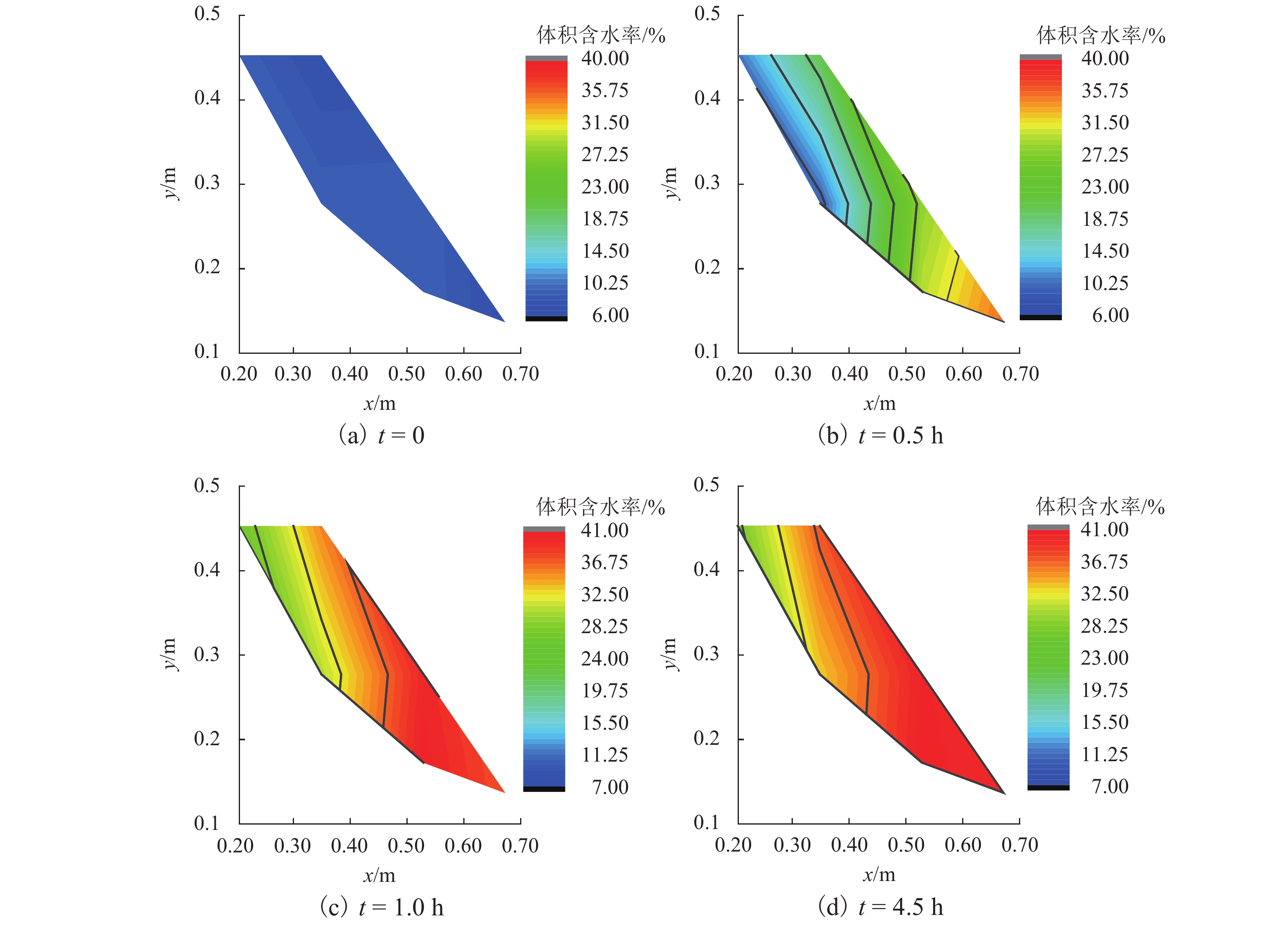
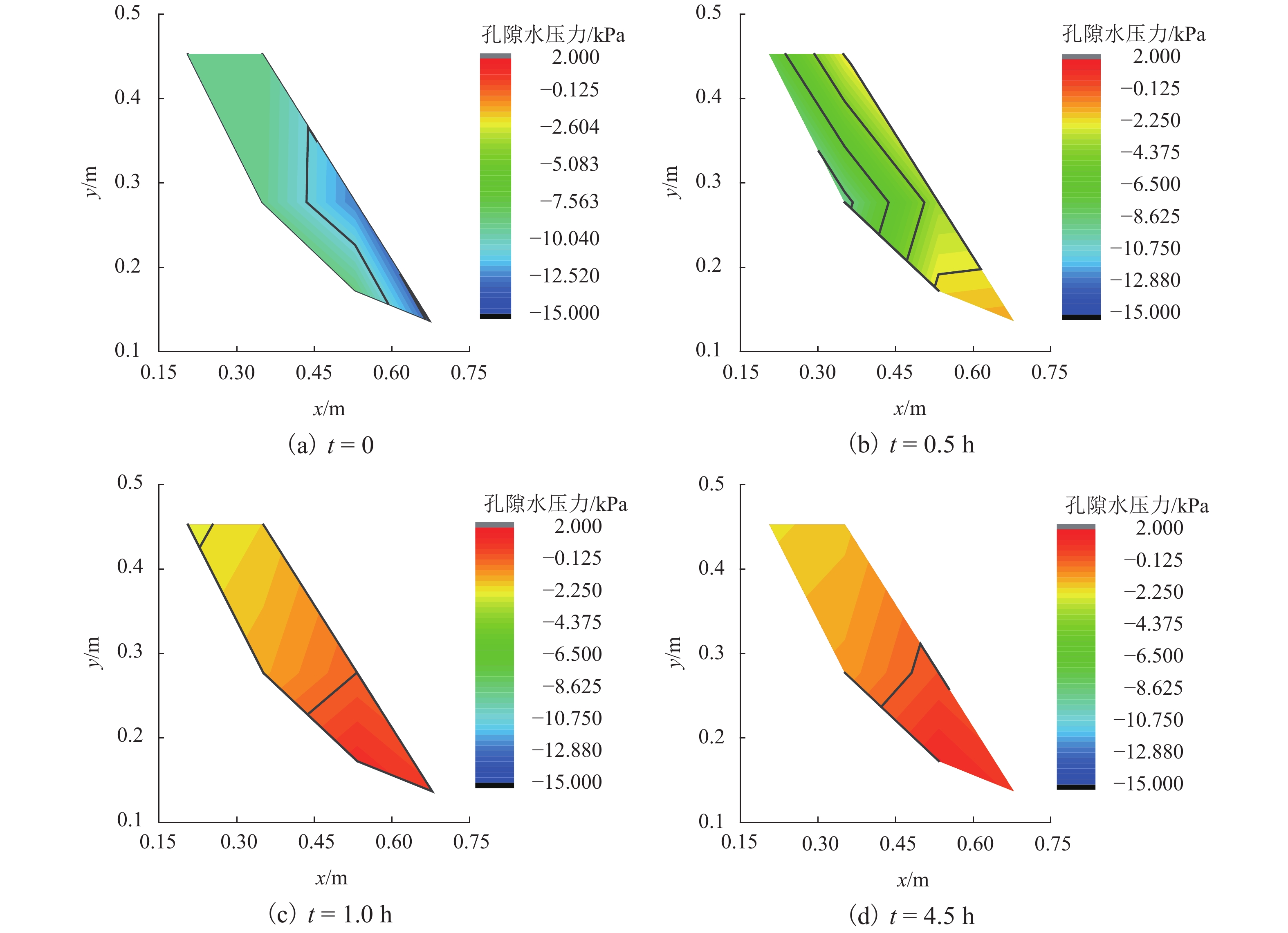
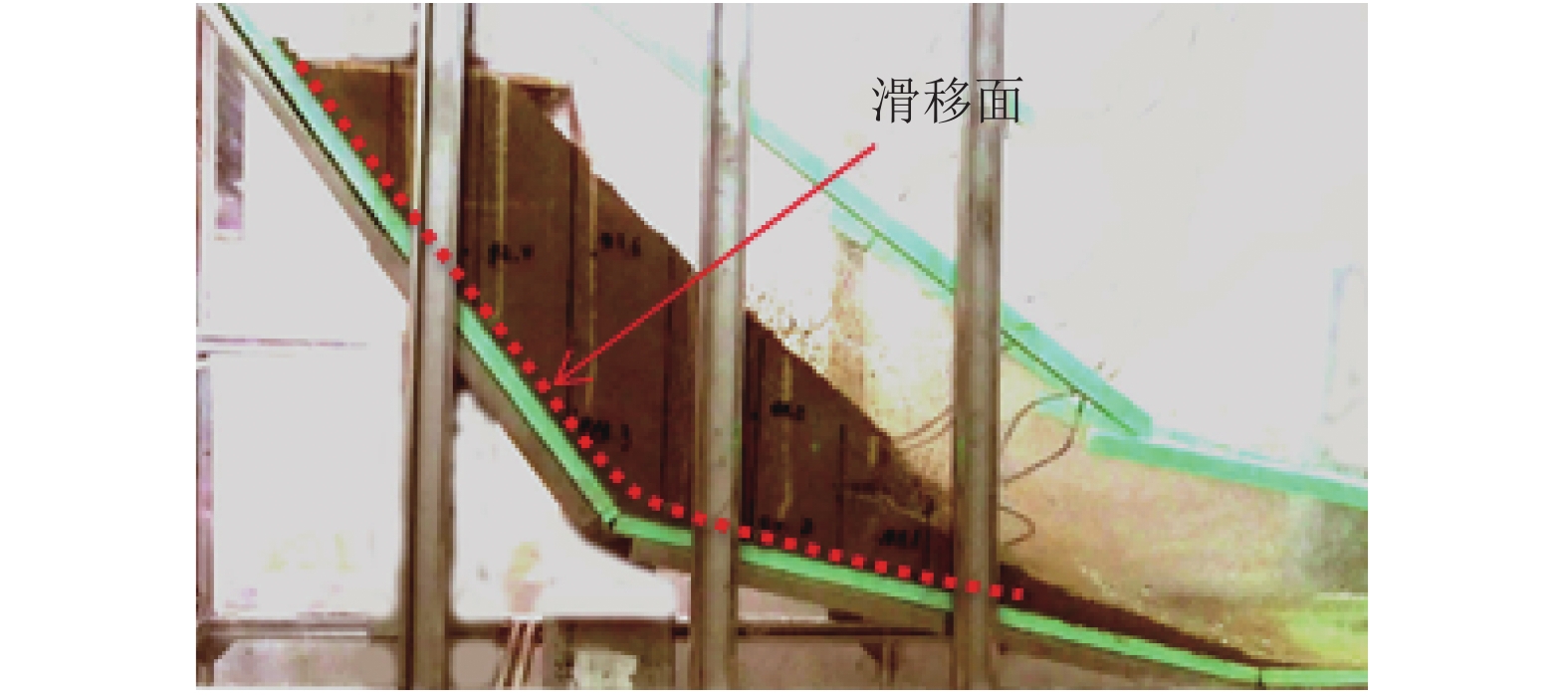
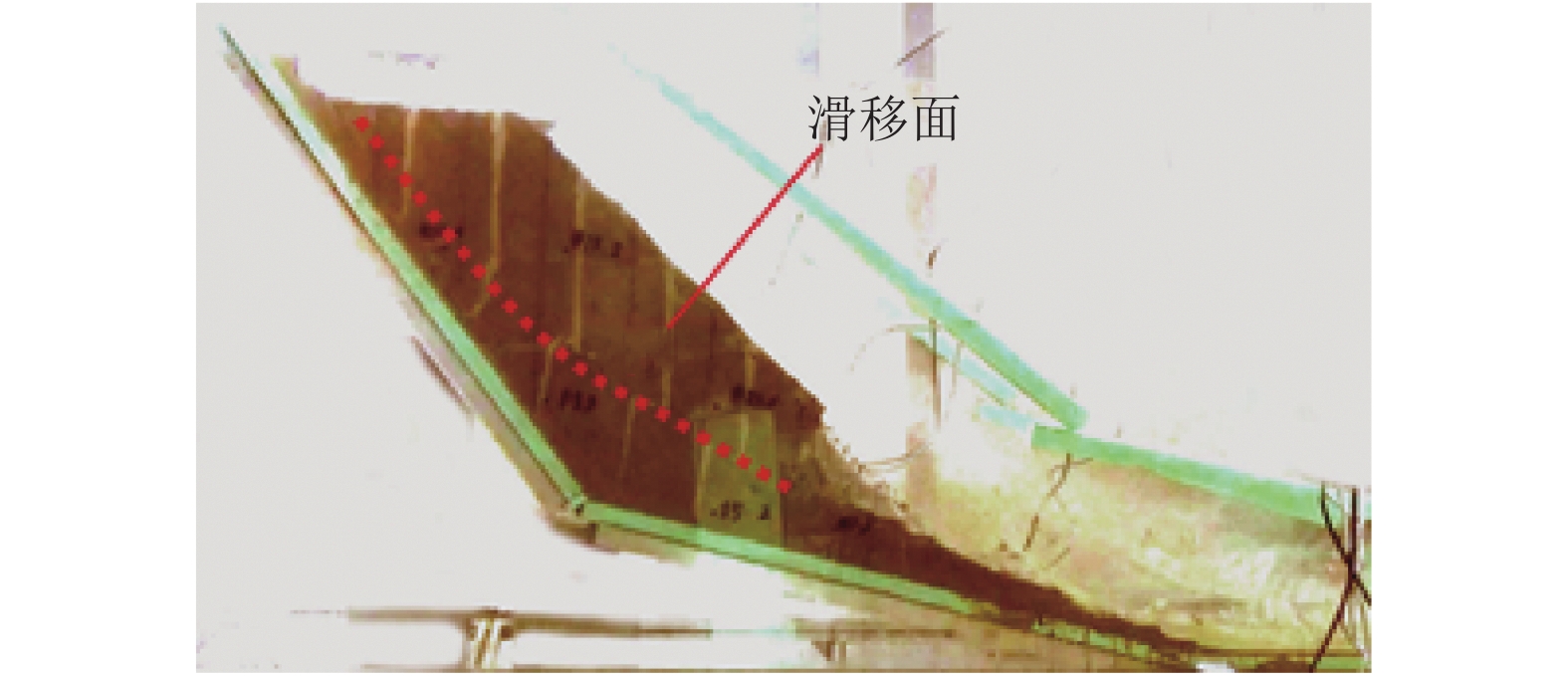
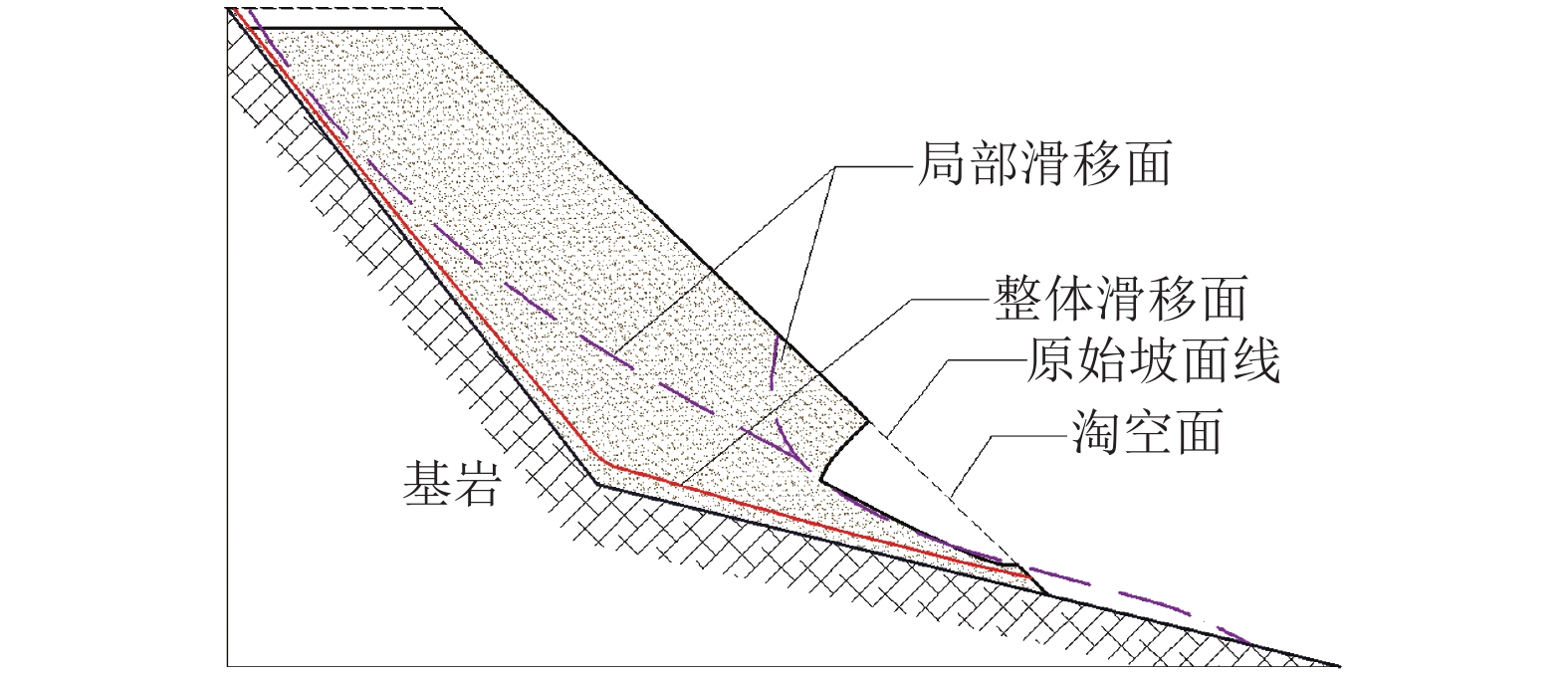
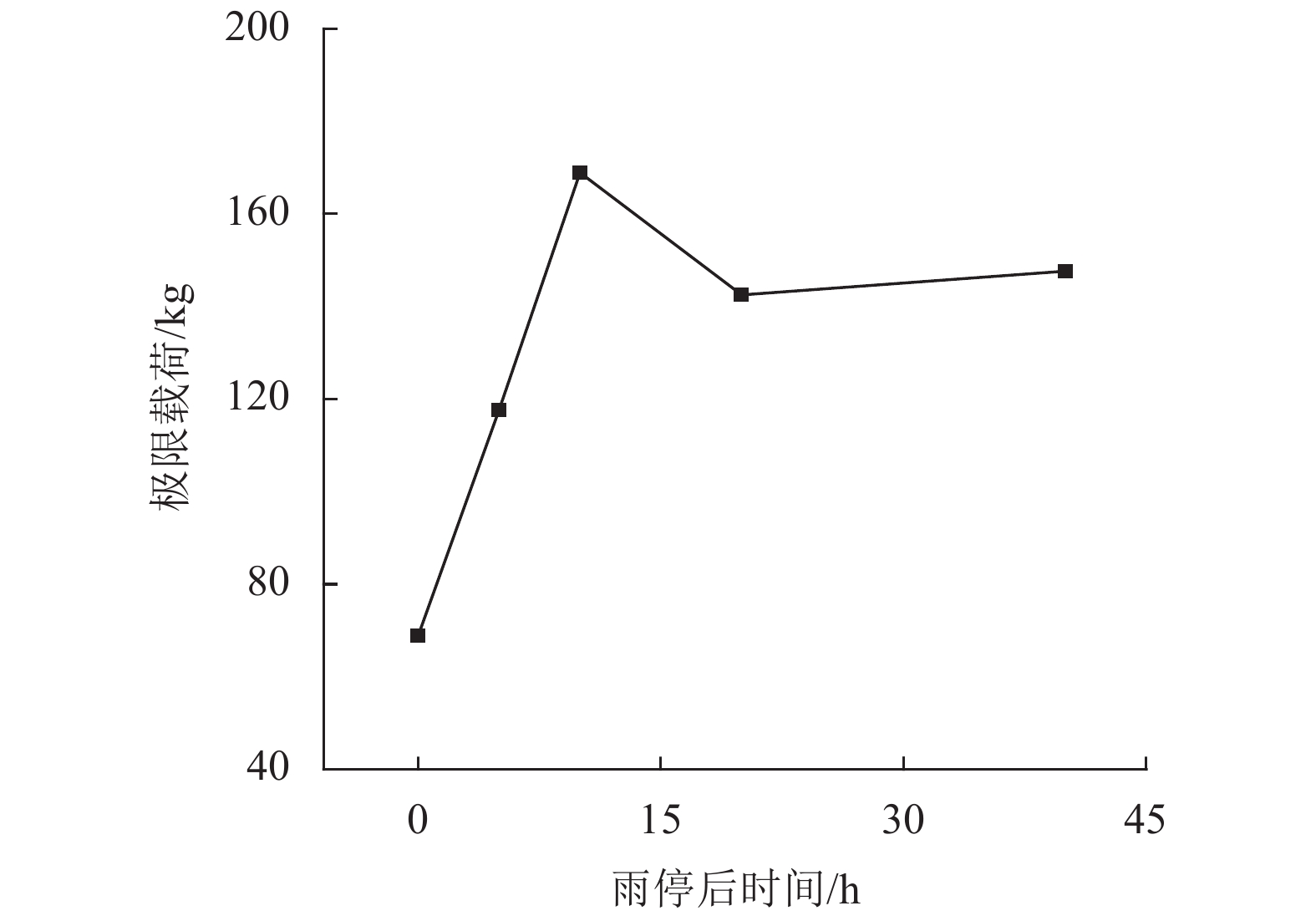
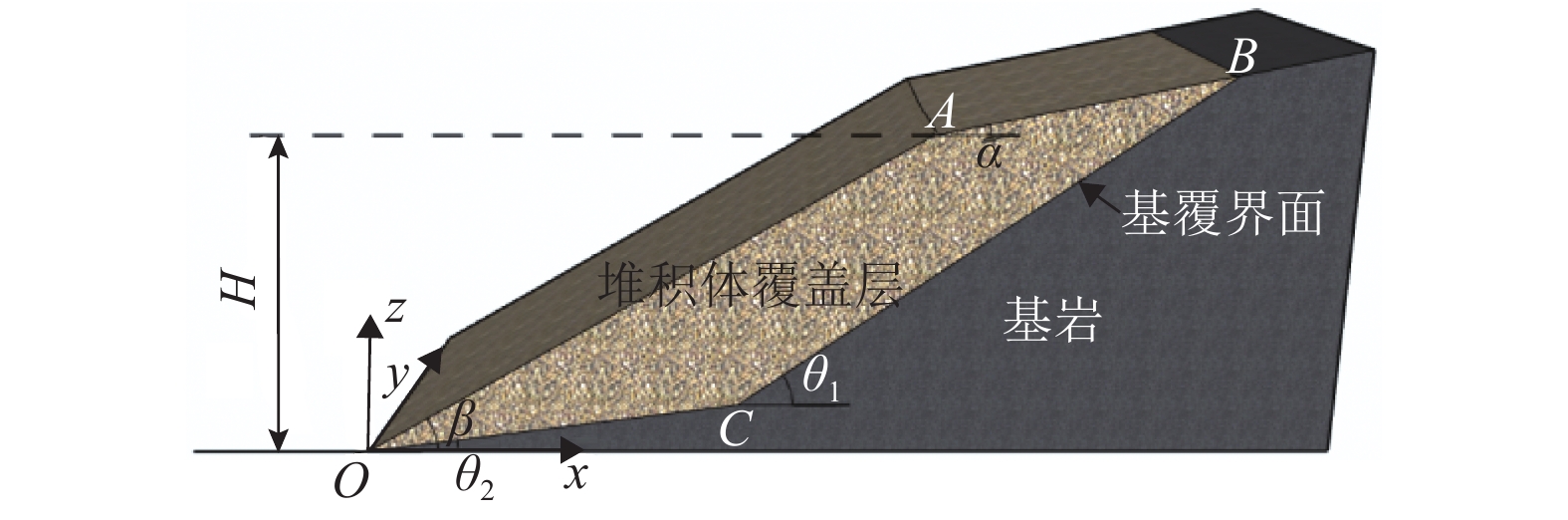
为了研究降雨诱导基覆型边坡失稳特性,采用室内模型试验方法对基覆型边坡在暴雨作用下的失稳过程及机制进行了系统研究. 通过探讨降雨前后边坡内土体含水率和孔隙水压力在时间、空间上的变化特性,揭示降雨诱导的边坡失稳机制. 同时通过坡顶加载方法研究了雨后边坡承载力变化规律. 研究结果表明:随着降雨的发展,在坡脚处首先出现土体液化流动现象,随后出现土体局部脱落;随着降雨的持续进行,土体脱落破坏的范围逐渐增大,进而导致上方土体临空面加大,土体破坏后随即被雨水饱和软化而向下滑动,后方土体进一步被侵蚀,最终造成了一定深度和宽度的边坡破坏现象;边坡内土体含水率升高与孔隙水压力的增大是导致边坡失稳破坏的主要因素;降雨停止后,边坡可以承受的极限荷载先增大后减小,最后趋于稳定,而基覆型边坡在顶部静荷载作用下破坏模式呈现出整体和局部滑移模式.
Abstract:In order to investigate the characteristics of slope with bedrock induced by rainfall, the failure process and mechanism of slope with bedrock under rainstorm were studied systematically by laboratory model test. The variation characteristics of soil moisture content and pore water pressure in time and space before and after rainfall were discussed to reveal the mechanism of slope instability induced by rainfall. Besides, the variation law of slope bearing capacity after rain was studied by loading at the top of slope. The results show that with the development of rainfall, the liquefaction flow of soil appears first at the foot of the slope, and then the local shedding of the soil occurs there. With the continuous rainfall, the scope of soil shedding damage gradually increases, which leads to the increase of the free surface of the upper soil. After the soil is damaged, it is saturated and softened by the rain and slides downward, and the rear soil is further eroded, resulting in the slope failure of a certain depth and width. The increase of soil moisture content and pore water pressure in the slope are the main factors leading to the instability and failure of the slope. After the rainfall stops, the ultimate load that the slope can bear increases at first and then decreases, and finally tends to be stable, while the failure of the slope with bedrock shows either a global slip mode or a local slip mode under the top static load.
-
Key words:
- slope with bedrock /
- rainfall /
- failure characteristic /
- bearing capacity
-
表 1 各物理量的相似关系
Table 1. Similarity law of each physical quantity
物理量 相似常数 物理量 相似常数 H CH c Cc=CγCH γ Cγ ϕ 1 g Cg $ \mathrm{\nu } $ 1 $ \beta $ 1 Ir ${C_{I{\rm{r}}}} = C_H^{0.5}C_g^{0.5} $ $ \alpha $ 1 k ${C_k} = C_H^{0.5}C_g^{0.5} $ z CH t ${C_t} = C_H^{0.5}C_g^{-0.5} $ θ1 1 q ${C_q} = {C_\gamma }{C_H} $ θ2 1 表 2 不同质量含水率条件下的强度指标
Table 2. Strength index under different water moistures
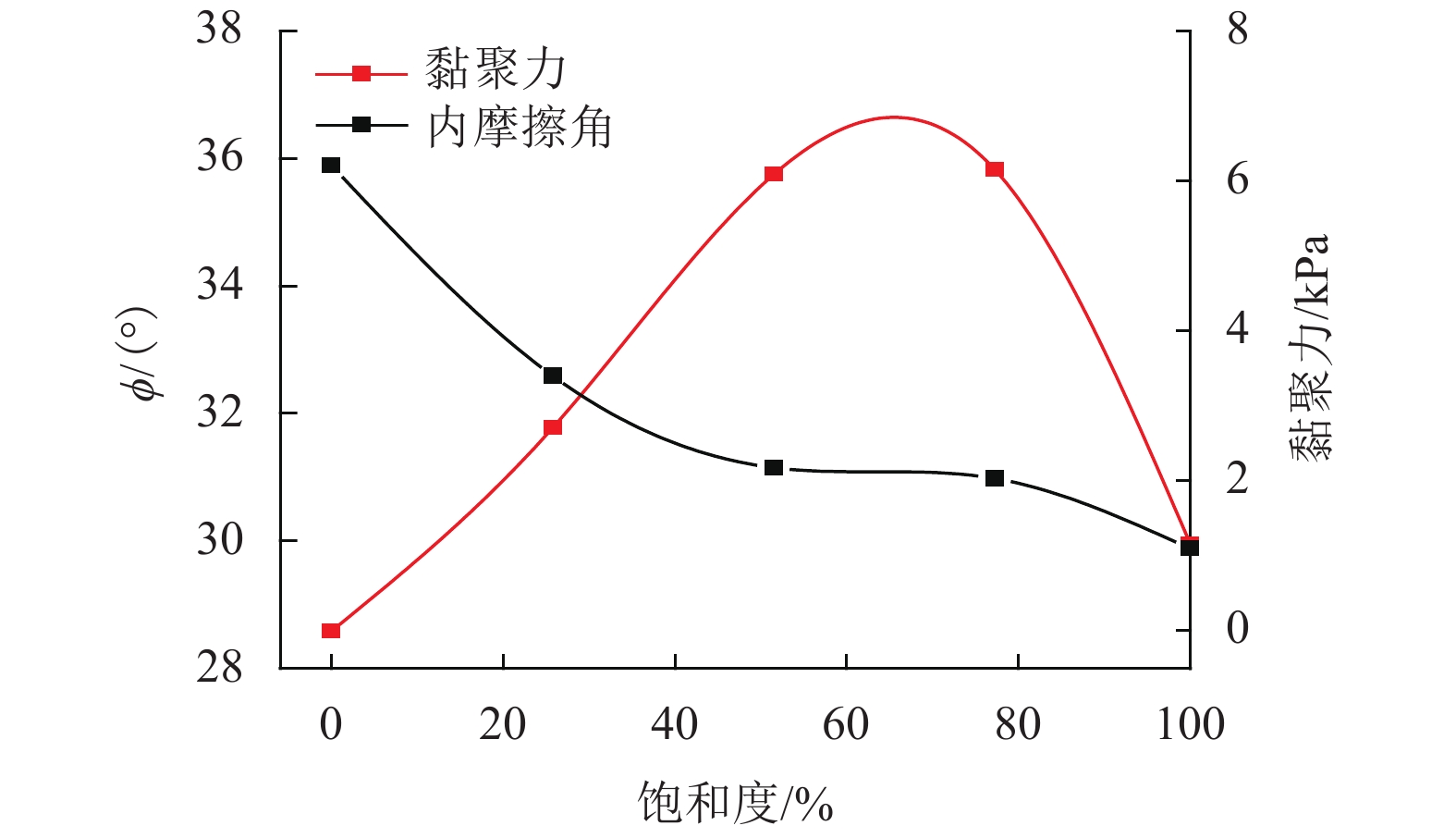
质量含水率/% 饱和度/% c/kPa $\phi $/ (°) 0 0 0 35.89 6 25.75 2.71 32.59 12 51.50 6.09 31.15 18 77.25 6.15 30.98 23 100.00 1.16 29.88 表 3 边坡降雨试验设计
Table 3. Design of slope rain test
工况
编号降雨持续
时间/h降雨强度/
(mm•h–1)降雨
等级雨停后加
载时间/h1 4.5 21.96 暴雨 0 2 4.5 21.96 暴雨 5 3 4.5 21.96 暴雨 10 4 4.5 21.96 暴雨 20 5 4.5 21.96 暴雨 40 6 4.5 21.96 暴雨 无加载 表 4 不同含水率下边坡安全系数理论值
Table 4. Safety factor of slope under different water moistures
质量含水率/% 饱和度/% 安全系数 0 0 < 0.10 6 25.75 1.80 12 51.50 3.70 18 77.25 4.20 23 100.00 0.85 -
[1] 高华喜,殷坤龙. 降雨与滑坡灾害相关性分析及预警预报阀值之探讨[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(5): 1055-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.05.039GAO Huaxi, YIN Kunlong. Discuss on the correlations between landslides and rainfall and threshold for landslide early-warning and prediction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(5): 1055-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.05.039 [2] 李焯芬, 汪 敏. 港渝两地滑坡灾害的对比研究[J. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(4): 493-497.LEE C F, WANG Min. Comparison of landslide hazards between Hong Kong and Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(4): 493-497. [3] 陈丽霞,殷坤龙,刘礼领,等. 江西省滑坡与降雨的关系研究[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(4): 1114-1120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.049CHEN Lixia, YIN Kunlong, LIU Liling, et al. Analysis of relationship between landslide and rainfall in Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(4): 1114-1120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.049 [4] WANG G, SASSA K. Factors affecting rainfall-induced flowslides in laboratory flume tests[J]. Géotechnique, 2001, 51(7): 587-599. doi: 10.1680/geot.2001.51.7.587 [5] WANG G H, SASSA K. Pore-pressure generation and movement of rainfall-induced landslides:effects of grain size and fine-particle content[J]. Engineering geology, 2003, 69(1/2): 109-125. [6] YANG B, ZHOU Z H, HOU J R, et al. Failure characteristics and mechanism of deposit slopes with bedrock for different soil moisture contents under seismic load[J]. Soil dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2022, 154: 107128.1-107128.10. [7] TOHARI A, NISHIGAKI M, KOMATSU M. Laboratory rainfall-induced slope failure with moisture content measurement[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2007, 133(5): 575-587. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:5(575) [8] 林鸿州,于玉贞,李广信,等. 降雨特性对土质边坡失稳的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(1): 198-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.01.026LIN H C, YU Yuzhen, LI Guangxin, et al. Influence of rainfall characteristics on soil slope failure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(1): 198-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.01.026 [9] MORIWAKI H, INOKUCHI T, HATTANJI T, et al. Failure processes in a full-scale landslide experiment using a rainfall simulator[J]. Landslides, 2004, 1(4): 277-288. doi: 10.1007/s10346-004-0034-0 [10] 汤明高,许强,李九乾,等. 降雨诱发震后松散堆积滑坡的启动试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4): 128-134,140.TANG Minggao, XU Qiang, LI Jiuqian, et al. An experimental study of the failure mechanism of shallow landslides after earthquake triggered by rainfall[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(4): 128-134,140. [11] 陈洪凯,周晓涵,谭玲. 降雨特性对滑坡孔隙水压力影响的试验研究[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版),2017,34(1): 2,49-54.CHEN Hongkai, ZHOU Xiaohan, TAN Ling. Experimental study on the influence for rainfall characteristics to pore water pressure in landslide[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 2017, 34(1): 2,49-54. [12] 凌华,殷宗泽. 非饱和土强度随含水量的变化[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(7): 1499-1503. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.07.026LING Hua, YIN Zongze. Variation of unsaturated soil strength with water contents[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(7): 1499-1503. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.07.026 [13] 申春妮,方祥位,王和文,等. 吸力、含水率和干密度对重塑非饱和土抗剪强度影响研究[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(5): 1347-1351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.028SHEN Chunni, FANG Xiangwei, WANG Hewen, et al. Research on effects of suction, water content and dry density on shear strength of remolded unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(5): 1347-1351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.028 [14] 陈东霞,龚晓南,马 亢. 厦门地区非饱和残积土的强度随含水量变化规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(增刊1): 3484-3490.CHEN Dongxia, GONG Xiaonan, MA Kang. Variation of the shear strength of Xiamen unsaturated residual soils with water content[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(S1): 3484-3490. [15] 蔡国庆,车睿杰,孔小昂,等. 非饱和砂土抗拉强度的试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2017,48(5): 623-630.CAI Guoqing, CHE Ruijie, KONG Xiaoang, et al. Experimental investigation on tensile strength of unsaturated fine sands[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2017, 48(5): 623-630. [16] TAYLOR D W. Stability of earth slopes[J]. Journal of the Boston Society of Civil Engineeing, 1937, 24: 197-246. [17] 徐筱,蔡国庆,李 舰,等. 低应力及拉应力条件下非饱和土强度及剪胀特性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(8): 1933-1942.XU Xiao, CAI Guoqing, LI Jian, et al. The strength and dilatancy characteristics of unsaturated soil at low and tensile stresses[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(8): 1933-1942. -




 下载:
下载: