Image Encryption Based on 2D Coupled Map Lattices
-
摘要:
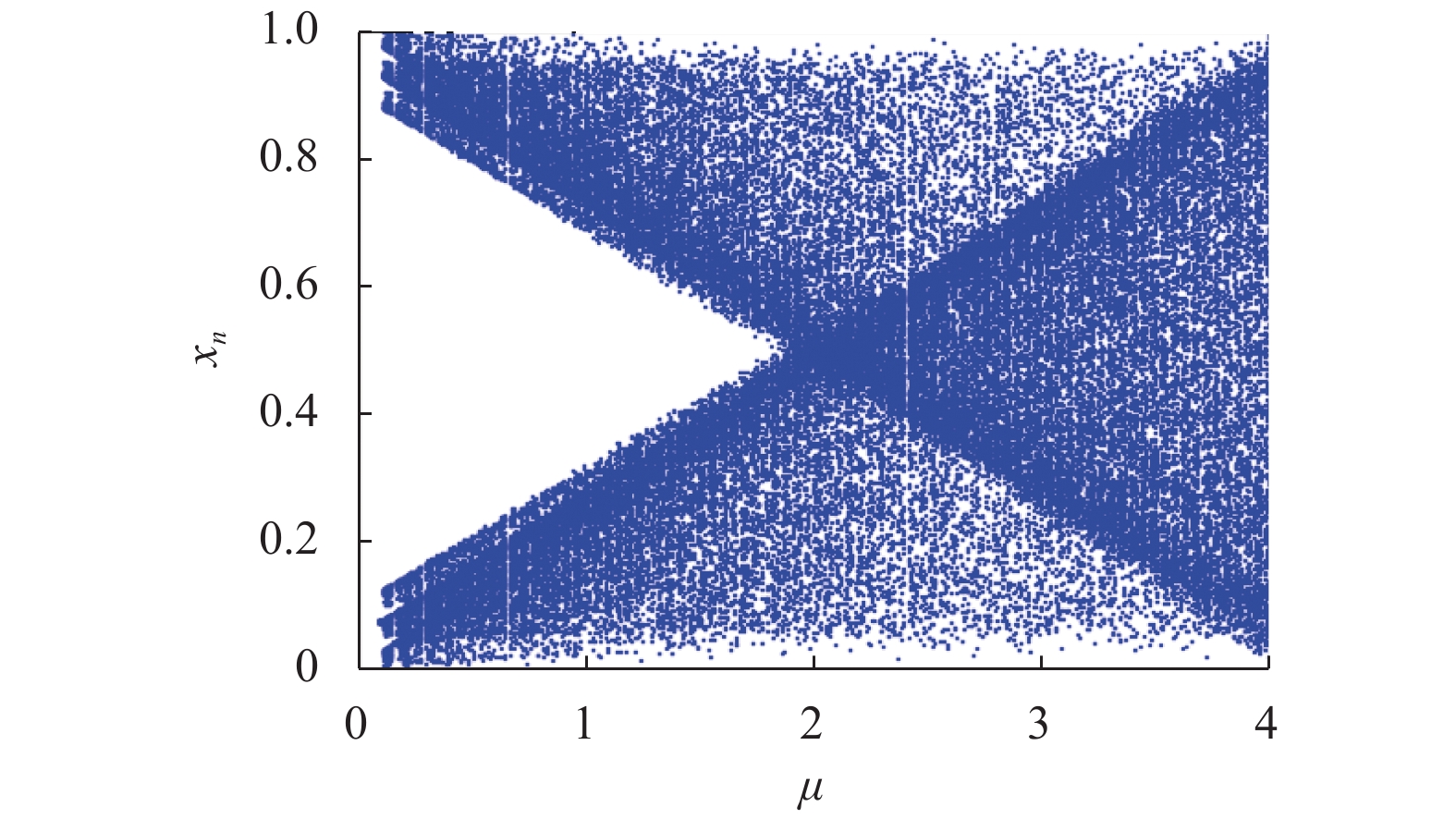
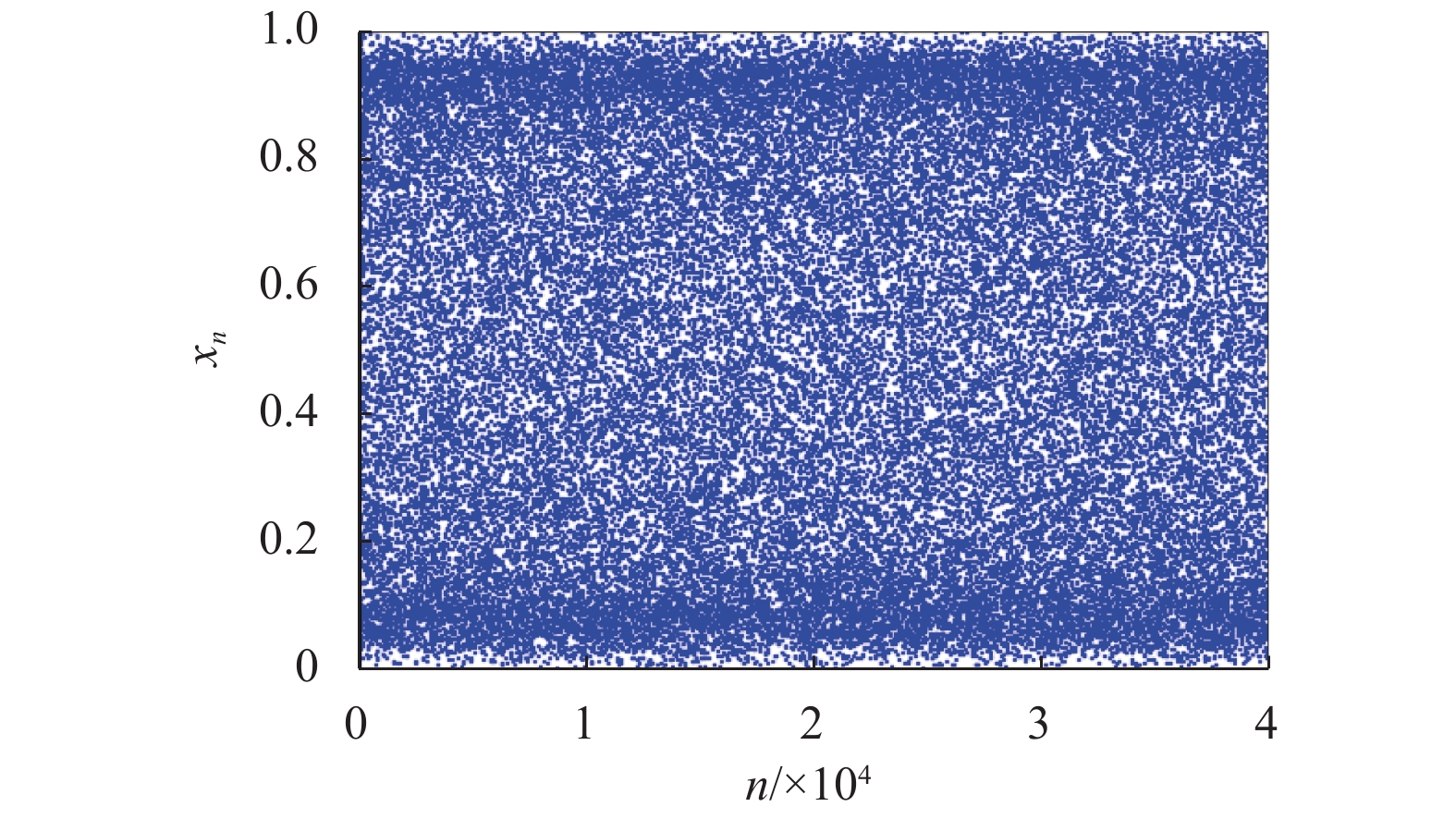
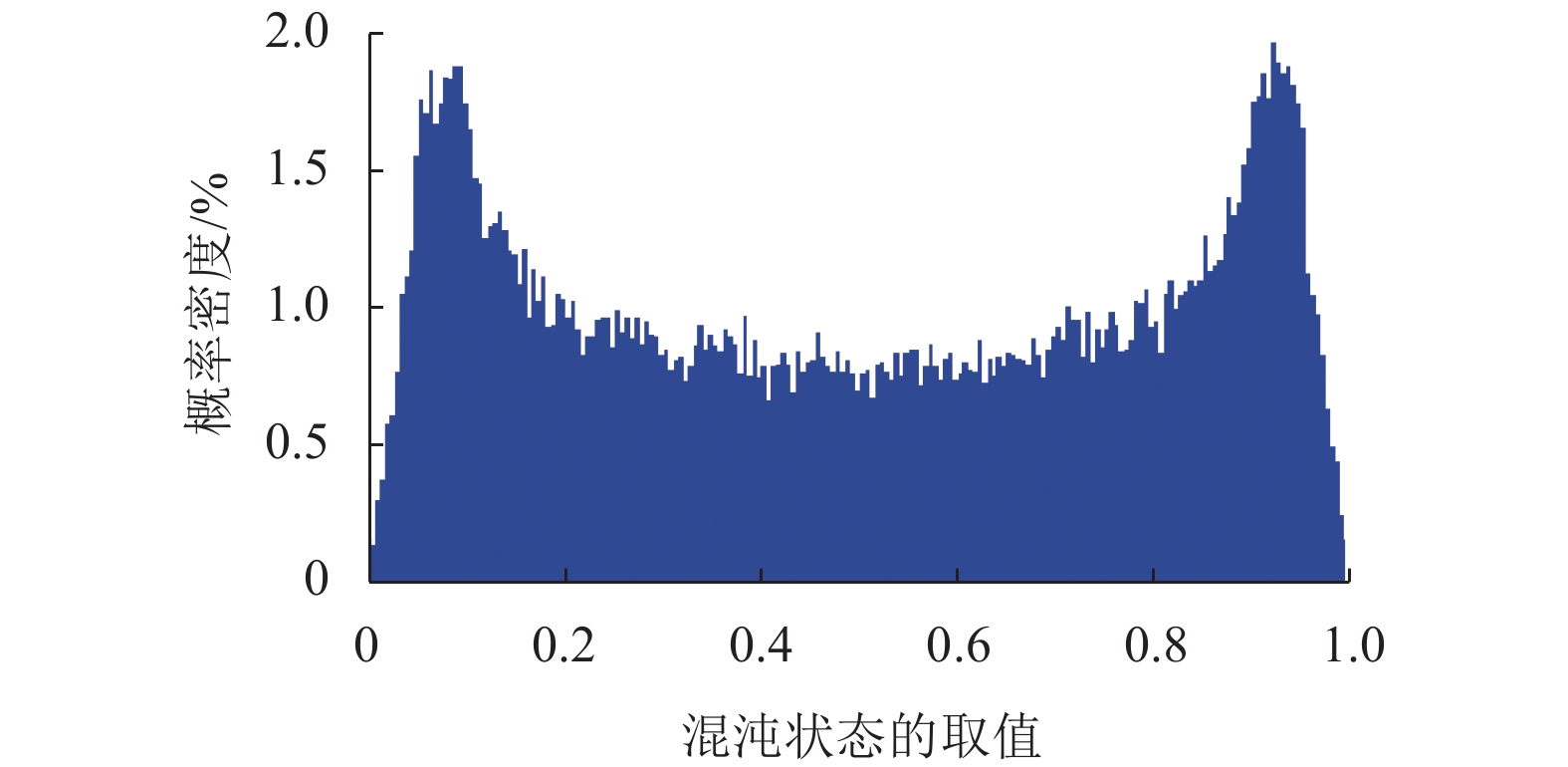
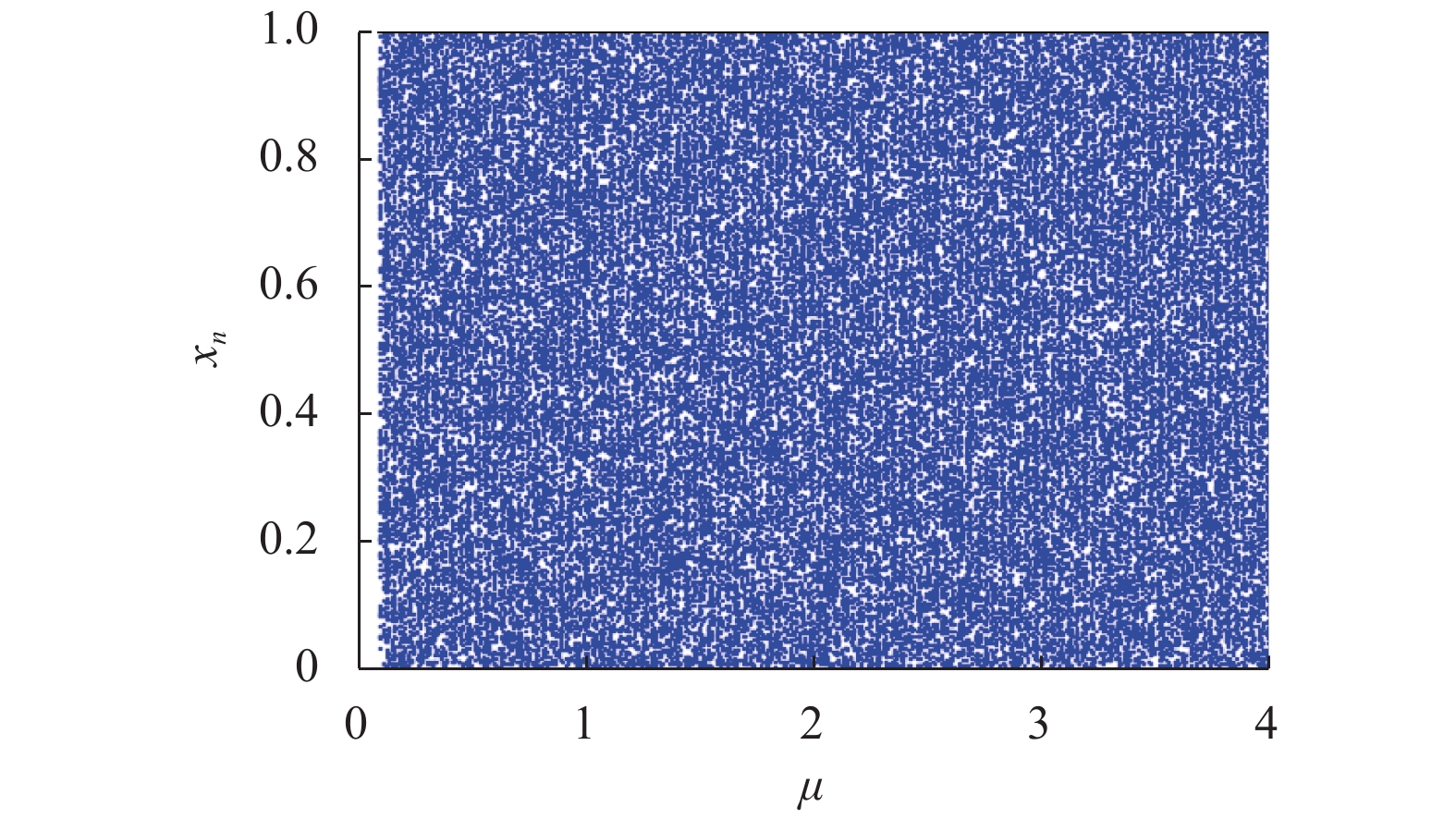
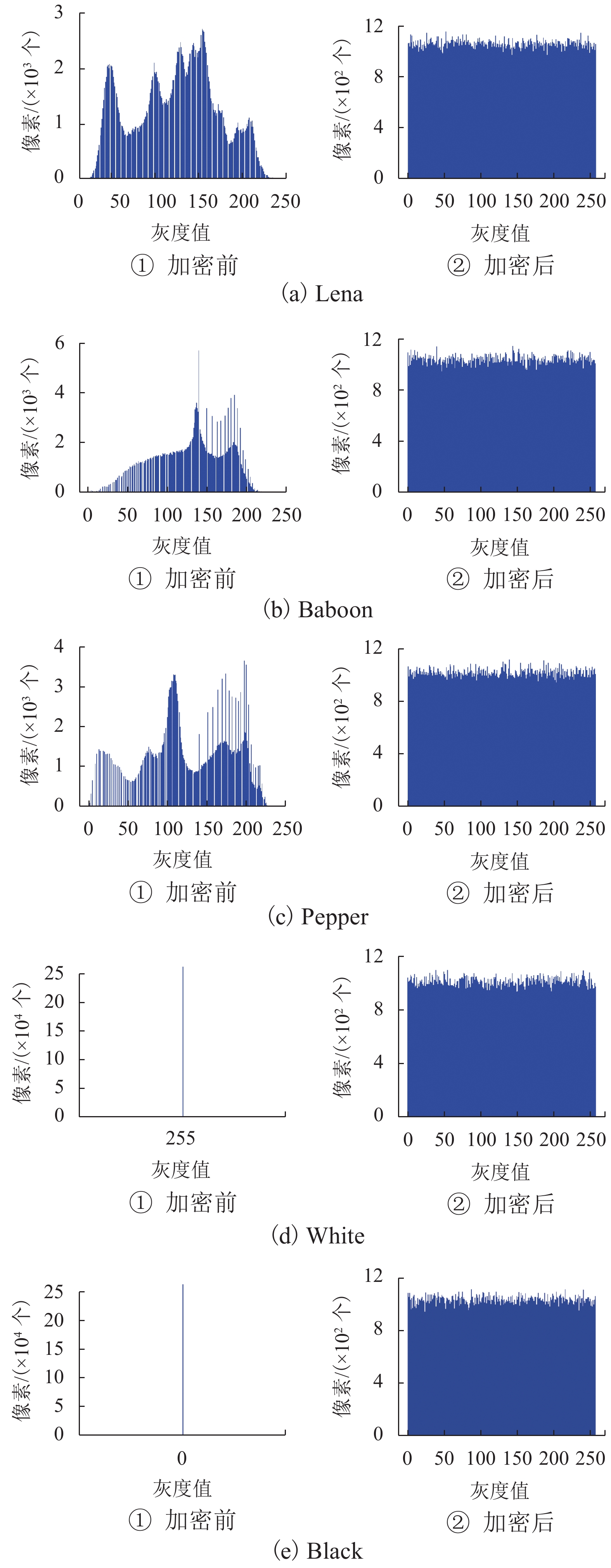
为了平衡混沌系统的复杂性和效率之间的关系,将分段Logistic映射(piecewise Logistic map,PLM)引入到二维耦合映像格子(2D coupled map lattices,2DCML)模型中. 采用暂态转换以使模型的输出序列服从均匀分布,进而得到T2DCML模型,基于此模型提出了一类图像加密算法. 在加密算法中,利用模型输出的伪随机序列构造两个初等变换矩阵,对图像进行置乱操作;然后再从模型中提取状态值的比特构造整数序列,对置乱后的图像进行扩散操作;经过若干轮的置乱与扩散操作,产生最后的加密图像. 仿真实验及性能分析表明:该算法的相关系数的绝对平均值为0.001 3,信息熵为7.999 3,像素变化率(number of pixel change rate,NPCR)和统一平均变化强度(unified average change intensity,UACI)分别为99.63%和33.60%,能够有效满足图像在网络中安全传输的需求.
-
关键词:
- 分段Logistic映射 /
- 二维耦合映像格子模型 /
- 混沌序列 /
- 图像加密
Abstract:Piecewise Logistic map (PLM) is introduced into 2D coupled map lattices (2DCML) model to face a tradeoff between complexity and efficiency of chaotic systems, and a transformation method based on transient status values is used to make the output sequence of the model obey a uniform distribution. Then, the T2DCML model is built. According to the T2DCML model, an image encryption algorithm is proposed, in which encryption algorithm, the pseudo-random sequence output by the model is used to construct two elementary transformation matrices and the image is scrambled by the matrices. Then, the bits of the state value are extracted from the model to construct an integer sequence and the scrambled image is diffused by the integer sequence. Finally, the encrypted image is produced by multi-rounds of confusion and diffusion. Simulation experiments and performance analysis show that the absolute average correlation coefficient of the algorithm is 0.001 3, the information entropy is 7.999 3, and the number of pixel change rate (NPCR) and the unified average change intensity (UACI) is 99.63% and 33.60%, respectively, revealing that the algorithm can effectively meet the needs of the safe transmission of images in the network.
-
Key words:
- piecewise Logistic map /
- 2D coupled map lattices /
- chaotic sequences /
- image encryption
-
表 1 NIST套件的测试结果
Table 1. Test results of NIST suites
测试指标 P 值 通过率 结果 Frequency 0.719 747 0.993 通过 BlockFrequency 0.996 335 0.988 通过 CumulativeSums* 0.817 162 0.995 通过 Runs 0.765 632 0.988 通过 LongestRun 0.071 620 0.987 通过 Rank 0.179 584 0.990 通过 FFT 0.492 436 0.992 通过 NonOverlappingTemplate* 0.496 164 0.990 通过 OverlappingTemplate 0.209 948 0.983 通过 Universal 0.755 819 0.989 通过 ApproximateEntropy 0.075 719 0.986 通过 RandomExcursions* 0.627 887 0.989 通过 RandomExcursionsVariant* 0.540 402 0.992 通过 Serial* 0.676 598 0.986 通过 LinearComplexity 0.096 000 0.997 通过 表 2 加密前后相邻像素间的相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficients between adjacent pixels
图像 水平方向 垂直方向 对角方向 Lena 明文 0.975 1 0.983 1 0.958 2 Lena 密文 0.001 2 0.000 6 0.001 6 Baboon 明文 0.888 0 0.746 8 0.716 0 Baboon 密文 0.001 1 0.000 4 0.003 3 Pepper 明文 0.977 4 0.975 8 0.962 7 Pepper 密文 0.000 8 0.002 6 0.001 2 White 明文 1.000 0 1.000 0 1.000 0 White 密文 −0.001 4 −0.000 1 0.002 9 Black 明文 1.000 0 1.000 0 1.000 0 Black 密文 0.003 0 −0.000 5 −0.002 2 表 3 加密前后图像的信息熵
Table 3. Information entropies of images
图像 明文信息熵 密文信息熵 Lena 7.445 5 7.999 3 Baboon 7.222 2 7.999 2 Pepper 7.364 4 7.999 3 White 0 7.999 3 Black 0 7.999 2 表 4 密文图像的差异
Table 4. Differences between ciphertext images
% 图像 测试 1 测试 2 测试 3 测试 4 Lena 99.592 99.614 99.598 99.602 Baboon 99.619 99.599 99.592 99.598 Pepper 99.621 99.622 99.615 99.619 White 99.623 99.618 99.613 99.617 Black 99.607 99.611 99.617 99.579 表 5 密文图像的NPCR和UACI
Table 5. NPCR and UACI of ciphertext images
% 图像 NPCR UACI Lena 99.59 33.44 Baboon 99.64 33.50 Pepper 99.60 33.50 White 99.59 33.53 Black 99.60 33.49 表 6 算法性能对比
Table 6. Comparison of algorithm performance
加密算法 相关系数 信息熵 NPCR/% UACI/% 水平 垂直 对角 绝对平均值 本文算法 −0.002 5 −0.000 2 0.001 1 0.001 3 7.999 3 99.63 33.60 文献[4] −0.022 3 −0.008 4 −0.008 6 0.013 1 7.997 4 99.61 33.46 文献[5] −0.038 1 −0.029 1 0.002 7 0.023 3 7.999 2 99.61 33.45 文献[6] 0.069 3 0.061 0 −0.024 2 0.051 5 7.999 1 99.57 33.41 文献[7] 0.001 4 0.003 8 0.001 1 0.002 1 7.999 3 99.59 文献[8] −0.023 0 0.001 9 −0.003 4 0.009 4 7.969 6 99.62 33.51 文献[9] −0.014 4 −0.003 4 0.010 7 0.009 5 7.997 0 99.60 32.91 文献[10] 0.016 3 −0.002 9 0.030 9 0.016 7 7.999 3 99.60 33.45 -
[1] GARCIA-BOSQUE M, DÍEZ-SEÑORANS G, PÉREZ-RESA A, et al. A 1 gbps chaos-based stream cipher implemented in 0.18 μm CMOS technology[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(6): 623. doi: 10.3390/electronics8060623 [2] TEH J S, TAN K J, ALAWIDA M. A chaos-based keyed hash function based on fixed point representation[J]. Cluster Computing, 2019, 22(2): 649-660. doi: 10.1007/s10586-018-2870-z [3] ÖZKAYNAK F. Construction of robust substitution boxes based on chaotic systems[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2019, 31(8): 3317-3326. doi: 10.1007/s00521-017-3287-y [4] ZHANG Y. The fast image encryption algorithm based on lifting scheme and chaos[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 520: 177-194. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.02.012 [5] ZHOU Minjun, WANG Chunhua. A novel image encryption scheme based on conservative hyperchaotic system and closed-loop diffusion between blocks[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 171: 107484.1-107484.14. [6] FARAH M A B, GUESMI R, KACHOURI A, et al. A novel chaos based optical image encryption using fractional Fourier transform and DNA sequence operation[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2020, 121: 105777.1-105777.9. [7] 张健,霍达. 基于混沌系统和DNA编码的量子图像加密算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(6): 1142-1149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.06.008ZHANG Jian, HUO Da. Quantum image encryption algorithm based on chaotic system and DNA coding[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(6): 1142-1149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.06.008 [8] XU Lu, ZHI Li, JIAN Li, et al. A novel bit-level image encryption algorithm based on chaotic maps[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2016, 78: 17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2015.09.007 [9] YE Guodong. A block image encryption algorithm based on wave transmission and chaotic systems[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2014, 75(3): 417-427. doi: 10.1007/s11071-013-1074-6 [10] HUANG Xiaoling, YE Guodong. An image encryption algorithm based on hyper-chaos and DNA sequence[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2014, 72(1): 57-70. doi: 10.1007/s11042-012-1331-6 [11] NEPOMUCENO E G, NARDO L G, ARIAS-GARCIA J, et al. Image encryption based on the pseudo-orbits from 1D chaotic map[J]. Chaos:an Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2019, 29(6): 061101.1-061101.8. doi: 10.1063/1.5099261 [12] ALAWIDA M, TEH J S, SAMSUDIN A, et al. An image encryption scheme based on hybridizing digital chaos and finite state machine[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 164: 249-266. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.06.013 [13] GOPALAKRISHNAN T, RAMAKRISHNAN S. Image encryption using hyper-chaotic map for permutation and diffusion by multiple hyper-chaotic maps[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2019, 109(1): 437-454. doi: 10.1007/s11277-019-06573-x [14] 张健,霍达. 基于混沌系统的量子彩色图像加密算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(2): 421-427.ZHANG Jian, HUO Da. Quantum colour image encryption algorithm based on chaotic systems[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(2): 421-427. [15] WANG Xingyuan, ZHAO Hongyu, HOU Yutao, et al. Chaotic image encryption algorithm based on pseudo-random bit sequence and DNA plane[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2019, 33(22): 1950263.1-1950263.24. doi: 10.1142/S0217984919502634 [16] GAYATHRI J, SUBASHINI S. A spatiotemporal chaotic image encryption scheme based on self adaptive model and dynamic keystream fetching technique[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(19): 24751-24787. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-5675-4 [17] WEN Heping, YU Simin, LÜ Jinhu. Breaking an image encryption algorithm based on DAN encoding and spatiotemporal chaos[J]. Entropy, 2019, 21(3): 246. doi: 10.3390/e21030246 [18] WANG Yong, LIU Zhaolong, MA Jianbin, et al. A pseudorandom number generator based on piecewise logistic map[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 83(4): 2373-2391. doi: 10.1007/s11071-015-2488-0 [19] 王永,赵毅,GAO J,等. 基于分段Logistic映射的二维耦合映像格子模型的密码学相关特性分析[J]. 电子学报,2019,47(3): 657-663.WANG Yong, ZHAO Yi, GAO J, et al. Cryptographic feature analysis on 2D coupled map lattices based on piecewise logistic map[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(3): 657-663. [20] 李佩玥,石俊霞,郭嘉亮,等. 一种混沌伪随机序列均匀化普适算法的改进[J]. 电子学报,2015,43(4): 753-759. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.04.018LI Peiyue, SHI Junxia, GUO Jialiang, et al. Improvement of a universal algorithm for uniformization of chaotic pseudo-random sequences[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(4): 753-759. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2015.04.018 [21] WANG Xiaomin, ZHANG Jiashu. An image scrambling encryption using chaos-controlled Poker shuffle operation[C]//2008 International Symposium on Biometrics and Security Technologies. Isalambad: IEEE, 2008: 1-6. -




 下载:
下载: