Slope Toppling Deformation and Development Characteristics of Bending Belts by Centrifugal Model Test
-
摘要:
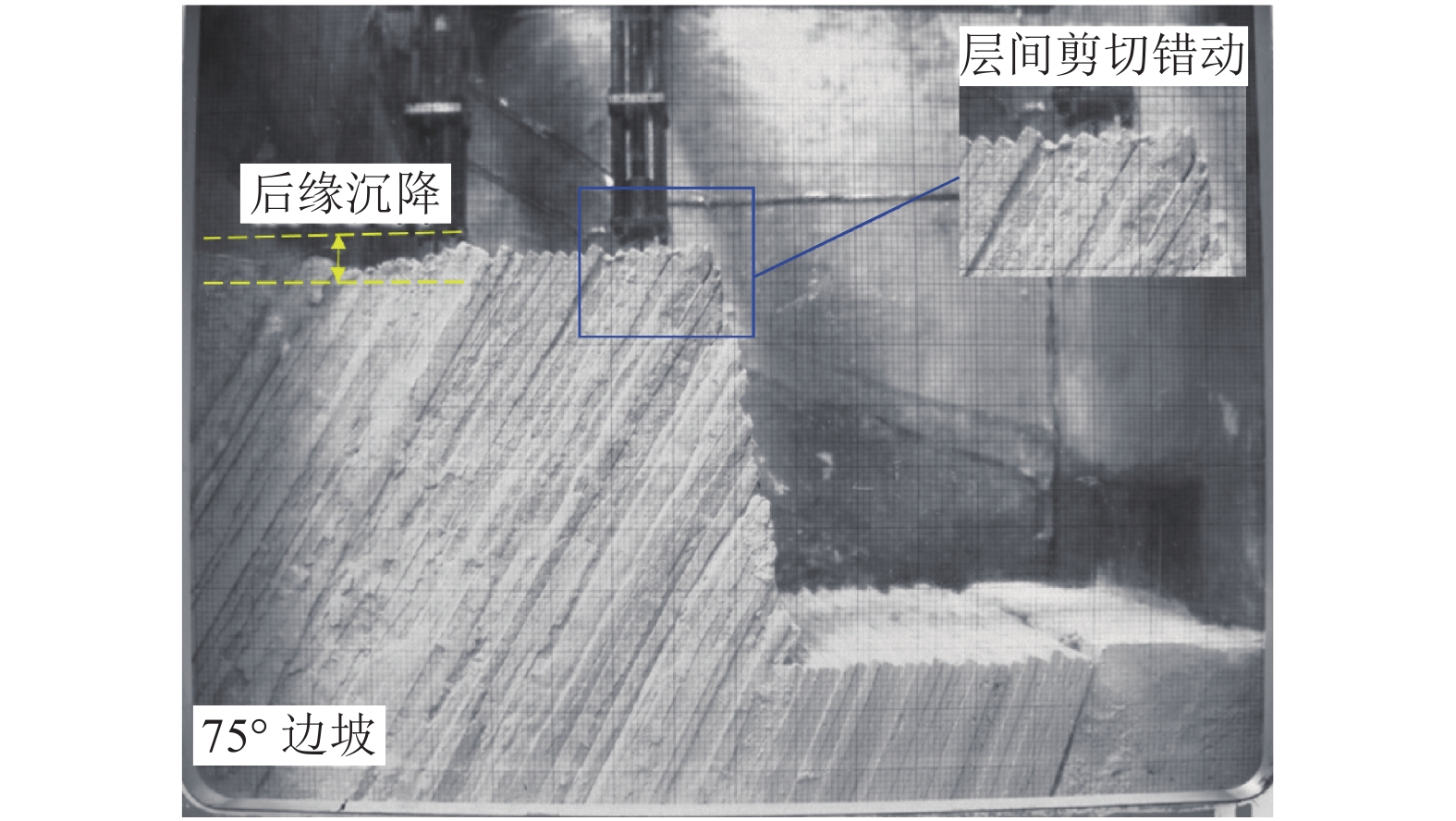
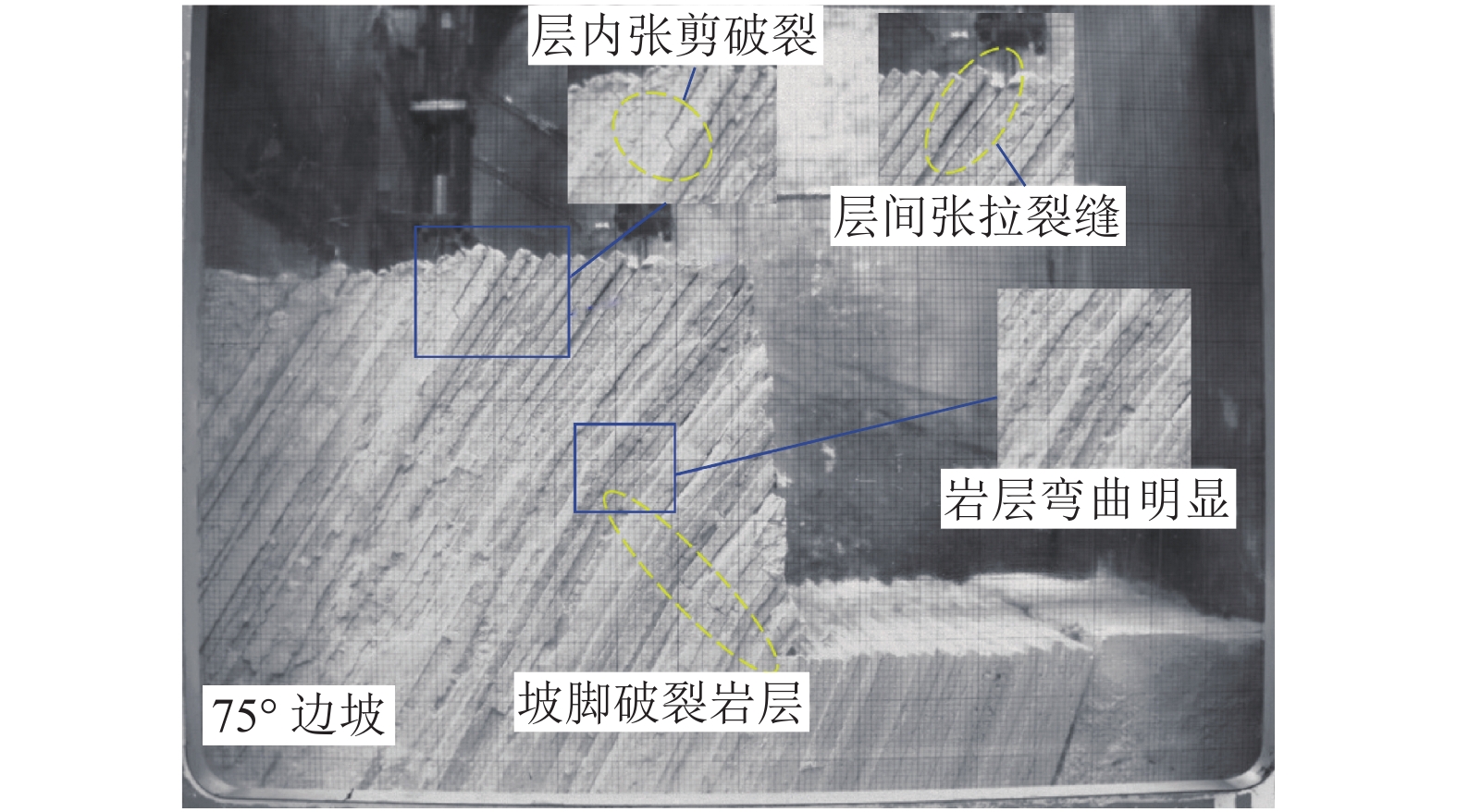
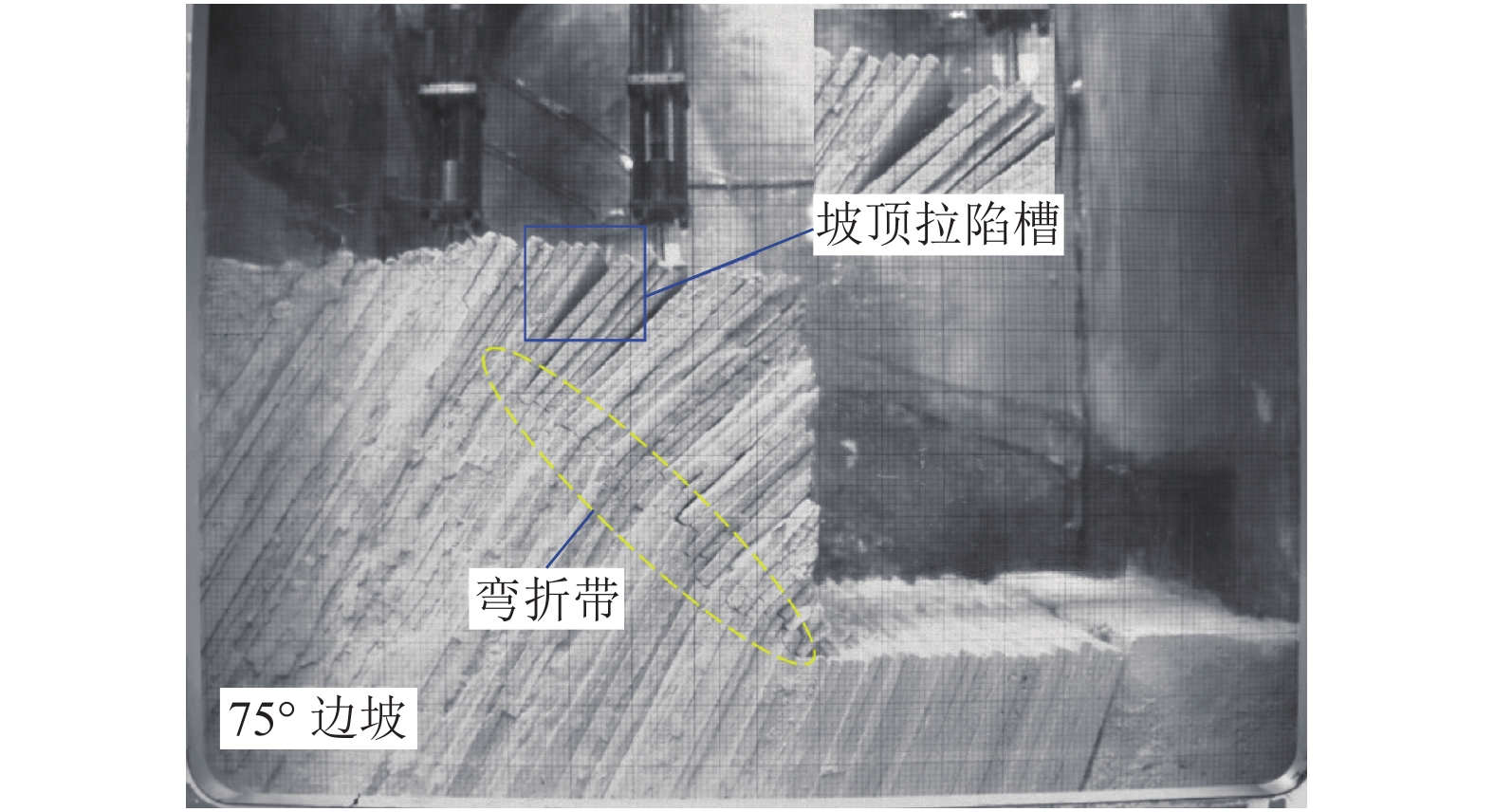
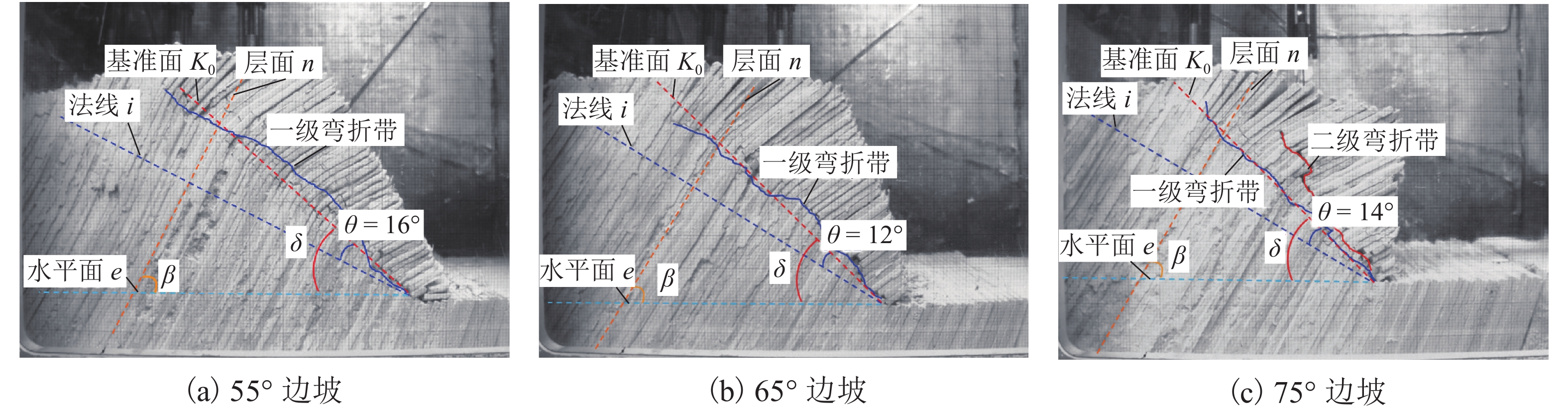
边坡倾倒变形过程中岩层弯折带的发育特征与演化规律是研究该类边坡变形破坏的地质过程与力学行为的关键. 为了揭示坡角变化对弯折带发育规律的影响,以澜沧江古水水电站坝前倾倒变形体为原型边坡,概化设计3组不同坡角的试验模型,通过离心模拟试验,尝试再现反倾层状岩质边坡倾倒变形的演化过程,分析边坡内部岩层弯折带的发育特征. 研究结果表明:边坡倾倒变形主要发生在倾倒折断基准面上方,基准面与层面法线的夹角位于12°~16°,该值不随坡角的改变而发生变化;边坡倾倒变形时,弯折带由坡脚开始以参差阶坎状的形式向坡顶延伸直至贯通,坡度陡的边坡会在一级弯折带上方的已倾倒岩体中产生新的次级弯折带,边坡倾倒折断模式由单级折断逐渐转为多级折断;弯折带孕育过程可概化为3个阶段:岩层弯曲变形、坡脚破裂-弯折带向坡顶延伸、弯折带贯通-坡体临界失稳;坡角变化对边坡倾倒变形发育特征有较大影响,随着坡角的增加,边坡倾倒变形范围扩大,程度加剧.
Abstract:Development characteristics and evolution law of the rock bending belts during the slope toppling deformation process is the key tostudying the geological development and mechanical behaviour of counter-tilt layered rock slopes in the process of deformation and failure. In order to reveal the influence of the slope angle change on the development law of the bending belts, the toppling deformation body in front of the dam of Gushui Hydropower Station of Lancang River is used as a prototype to generalize three sets of slope centrifugal test models with different slope angles. The centrifugal simulation tests were conducted in an effort to reproduce the evolution process of the toppling deformation of the counter-tilt layered rock slope and analyze the development characteristics of the rock bending belts inside the slope. The results indicate that the slope toppling deformation mainly occurs above the dumping and breaking datum plane, the angle between the datum plane and the normal of the rock bedding planes lies between 12° and 16°, and the value does not change with slope angle. In the process of slope deformation, the bending belts extends from the foot of the slope to the top of the slope in a stepped manner until it penetrates. A new secondary bending belts in the dumped rock mass generate above the primary bending belts in steep slope, and the slope failure mode gradually changes from single-level break to multi-level breaks. The evolution process of the bending belts can be generalized into three stages: rock layer toppling deformation, slope foot rupture-bending belts extending to the slope top, bending belts penetration to critical instability of slope. The slope anglechange has great influence on the development characteristics of slope toppling deformation. As the slope angle increases, slope toppling deformation expands and aggravates.
-
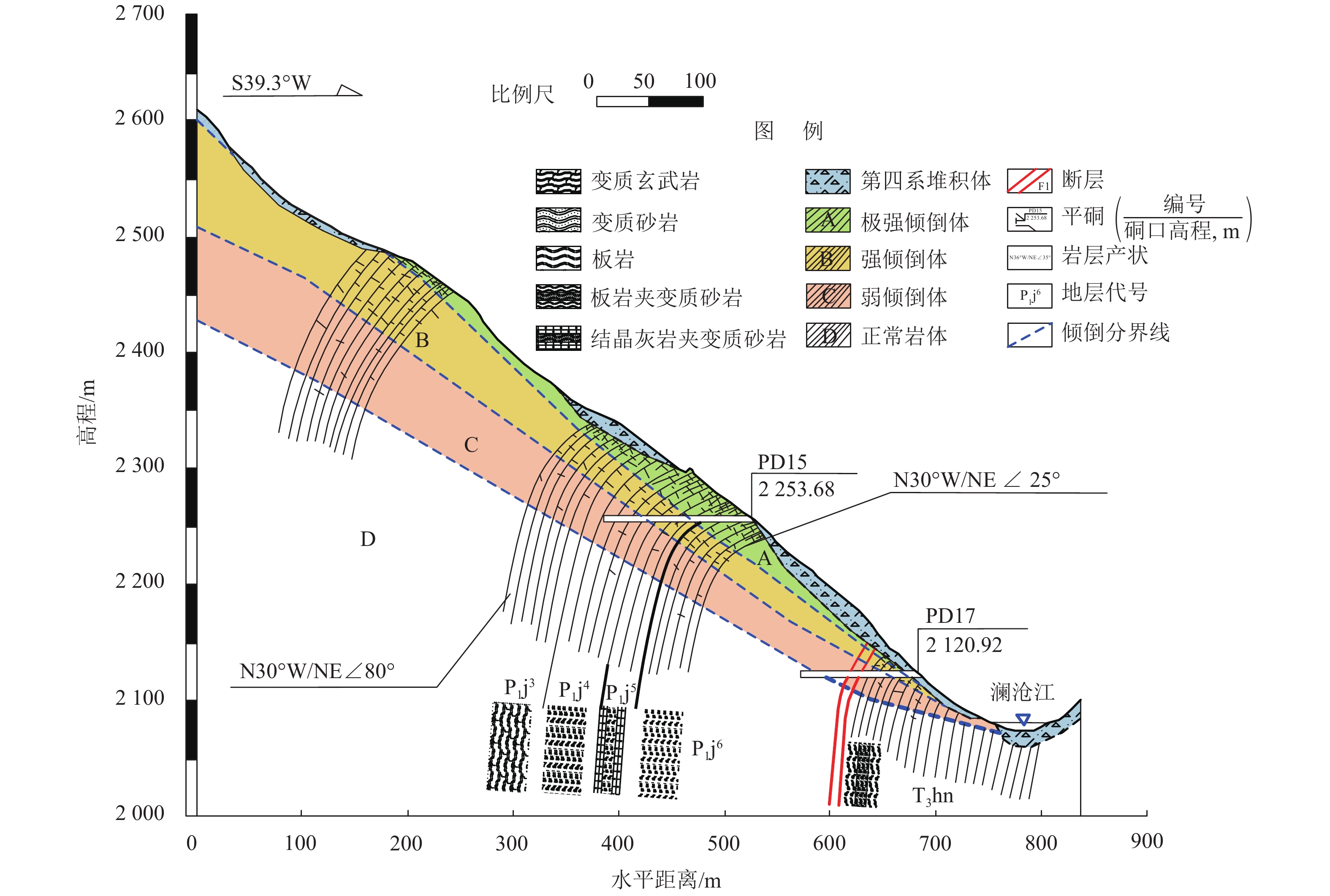
表 1 倾倒变形体的变形破裂类型
Table 1. Deformation and rupture types of toppling deformation body
部位 变形破裂类型 变形破裂特征 前缘 倾倒坠覆 岩层张烈变形显著、架空明显,内部填充大量碎石及岩屑;岩体风化程度高、破碎严重,部分甚至发生坠覆位移. 该类变形主要发生在坡表浅层 内部 倾倒蠕动 受岩层内部片理面的剪切蠕滑错动控制,表现为岩体发生连续倾倒,岩层倾角无突变,其在力学上属于塑性连续变形 后缘 倾倒-弯曲、
倾倒-折断反倾薄层状岩体在自重力矩作用下弯曲变形,当岩层较软时其发育深度较深,可以在岩层倾角发生较大变化时仍不出现破裂现象;当弯矩较大或岩层为硬质岩时,其在弯矩强烈部位较易发生脆性折断破裂 内部、底界 倾倒-折断 在重力力矩作用下,变形体底部弯折强烈处发生折断变形,形成 25°~40° 的倾向坡外的折断面,该面并非连续的平面,受原有软弱结构面控制,往往呈参差阶坎状,岩层倾角发生突变,该变形在力学上属于不连续脆性破裂 表 2 各分区倾倒变形发育概况
Table 2. General situation of toppling deformation development in each district
变形分区 变形特征 岩层倾角/(°) 层内拉张量/mm 卸荷变形 风化特征 A 岩体强烈倾倒,破碎现象严重,部分甚至发生坠覆位移,松弛现象严重,局部架空 < 40 ≥ 20 强卸荷 强风化 B 岩层倾倒较为强烈,层内张拉变形明显,局部发生切层剪切位移 40~60 2~24 总体强卸荷,
下部弱卸荷总体为弱风化,
上部为强风化C 岩体倾倒变形较弱,主要发生层间的剪切错动,层内张拉变形较小 55~72 2~8 弱卸荷 弱风化 D 岩体未倾倒,岩层无张拉、错动 70~80 ≤ 2 弱卸荷 弱风化 表 3 离心模型试验主要相似参数关系
Table 3. Relationship of major similar parameters for centrifugal model tests
物理量 符号 相似比符号 比例系数(模型/原型) 长度 $ L $ $ {C}_{L} $ 1/120 密度 $ \rho $ $ {C}_{\rho } $ 1/1 弹性模量 $ E $ $ {C}_{E} $ 1/1 加速度 $ a $ $ {C}_{a} $ 120/1 位移 $ u $ $ {C}_{u} $ 1/120 黏聚力 $ c $ $ {C}_{c} $ 1/1 内摩擦角 $ \phi $ $ {C}_{\phi } $ 1/1 应力 $ \sigma $ $ {C}_{\sigma } $ 1/1 应变 $ \varepsilon $ $ {C}_{\varepsilon } $ 1/1 泊松比 $ \mu $ $ {C}_{\mu } $ 1/1 表 4 原型及相似材料物理力学参数
Table 4. Physical and mechanical parameters of prototypes and similar materials
材料
种类密度/
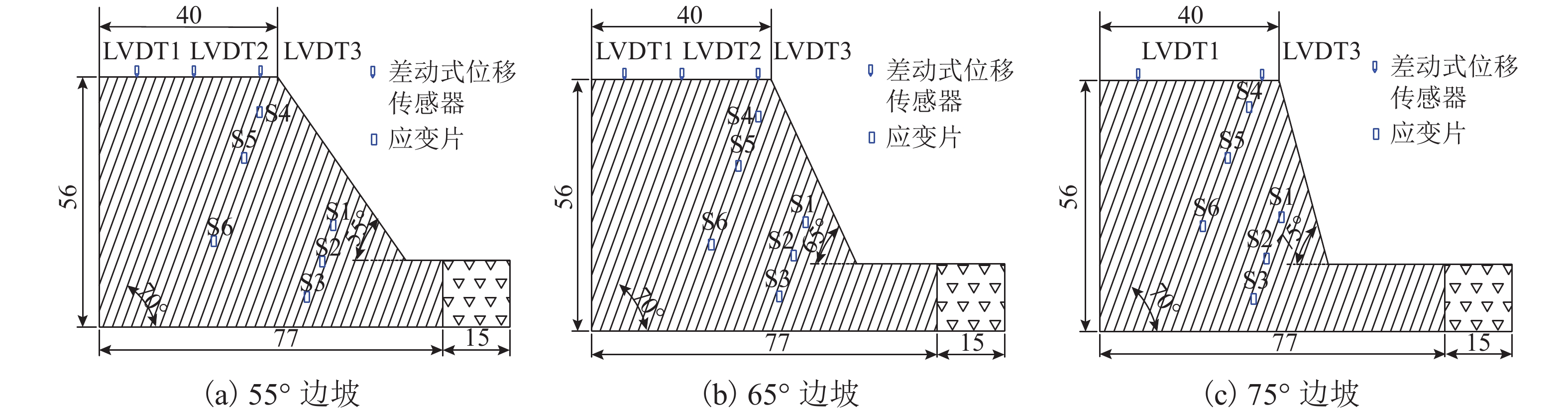
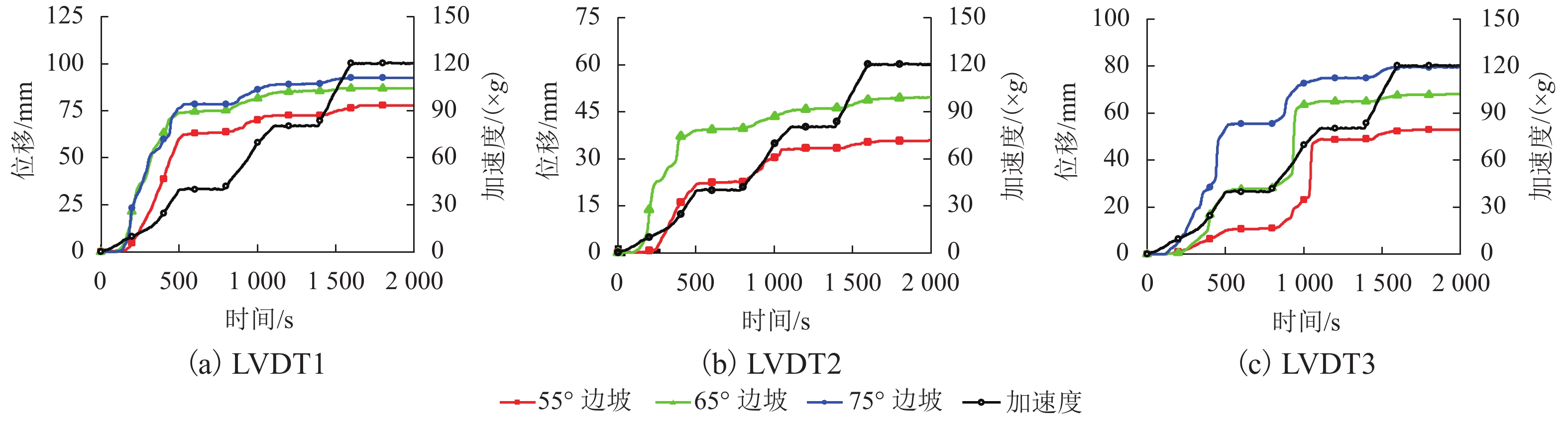
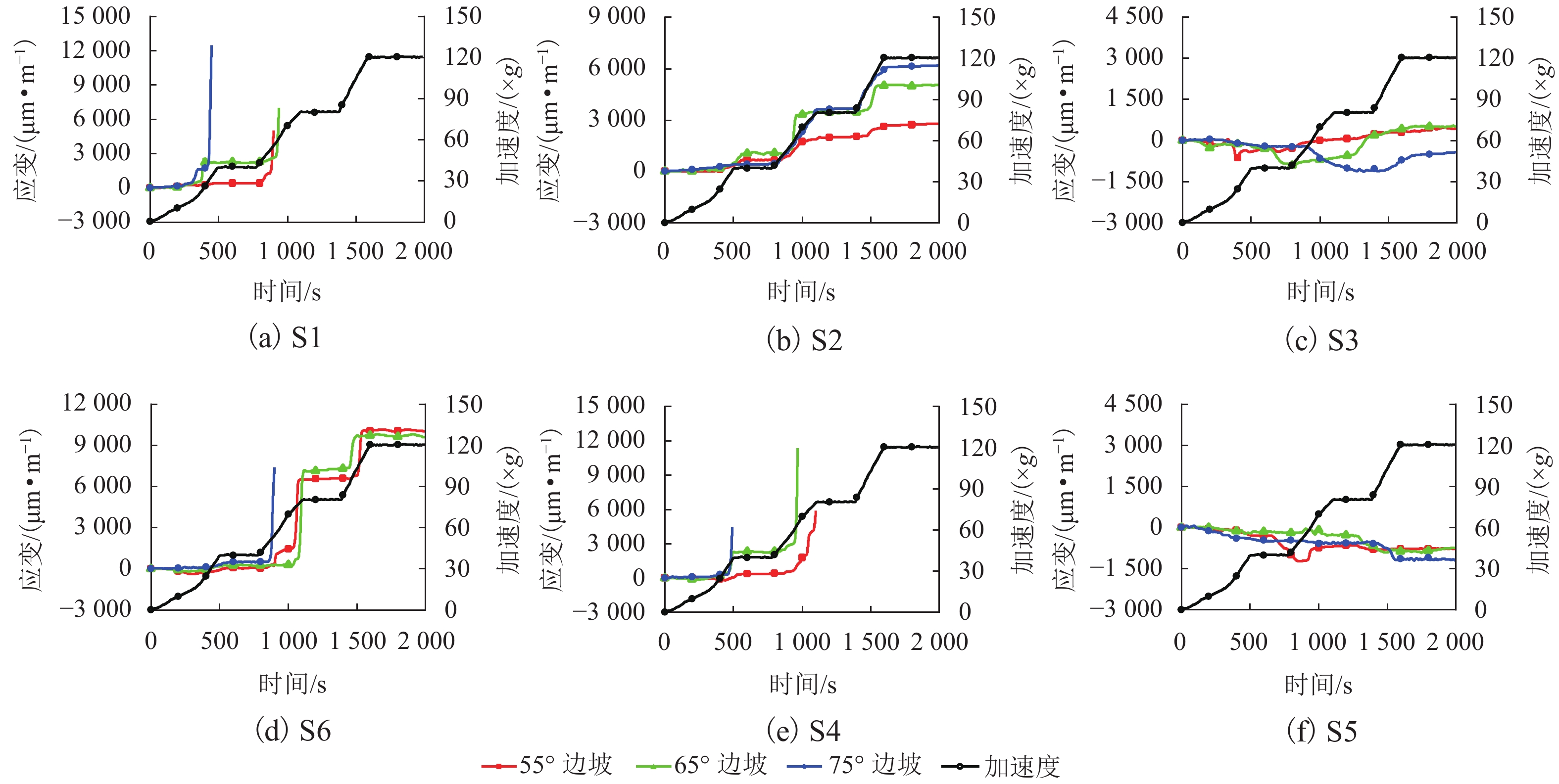
(g•cm−3)弹性模量/MPa 抗压强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 内聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 原型 变质砂岩 2.42 3000 15 1.75 层间粘结 35 16 模型 变质砂岩 2.38 2800 14.8 1.84 层间粘结 34.5 15.8 表 5 三组边坡LVDT3位移突变值及其对应加速度值
Table 5. Three sets of slope LVDT3 mutation displacement values and corresponding acceleration values
边坡坡度/(°) LVDT3 位移
突变值/mm对应重力加
速度值/(×g)对应边坡
变形阶段55 22 74.8 一级弯折带贯通 65 23 58.2 一级弯折带贯通 75 16 33.1 一级弯折带贯通 7 49.8 二级弯折带贯通 -
[1] GOODMAN R E, BRAY J W. Toppling of rock slopes[C]//Rock Engineering: American Society of Civil Engineers, Geotechnical Engineering Division Conference. Boulder: [s.n.], 1976: 201-234. [2] 黄润秋,李渝生,严明. 斜坡倾倒变形的工程地质分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(5): 1165-1181.HUANG Runqiu, LI Yusheng, YAN Ming. The implication and evaluation of toppling failure in engineering geology practice[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(5): 1165-1181. [3] ALEJANO L R, GÓMEZ-MÁRQUEZ I, MARTÍNEZ-ALEGRÍA R. Analysis of a complex toppling-circular slope failure[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114(1/2): 93-104. [4] 张丙先. 西藏玉曲河下游岸坡倾倒变形机制及稳定性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2018,48(5): 1539-1545.ZHANG Bingxian. Deformation mechanism and stability analysis of bank slope in downstream of Yuqu river in Tibet[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1539-1545. [5] 王俊杰,郭建军. 反倾岩质边坡次生倾倒机理及稳定性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(9): 1619-1627.WANG Junjie, GUO Jianjun. Mechanism and stability of secondary toppling of counter-tilt rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(9): 1619-1627. [6] 蔡国军,黄润秋,严明等. 反倾向边坡开挖变形破裂响应的物理模拟研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(4): 811-817. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.04.022CAI Guojun, HUANG Runqiu, YAN Ming, et al. Physical simulation study on deformation and failure response of an anti-inclined slope during excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(4): 811-817. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.04.022 [7] 郑达,毛峰,王沁沅,等. 上硬下软反倾边坡开挖变形响应的物理模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5): 89-95,112.ZHENG Da, MAO Feng, WANG Qinyuan, et al. Physical simulation of the excavation deformation response of counter-tilt slope with rigid layers on the soft[J]. Hydrogeologiy & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(5): 89-95,112. [8] ADHIKARY D P, DYSKIN A V, JEWELL R J, et al. A study of the mechanism of flexural toppling failure of rock slopes[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1997, 30(2): 75-93. doi: 10.1007/BF01020126 [9] GORICKI A, GOODMAN R E. Failure modes of rock slope demonstrated with base friction and simple numerical models[J]. Felsbau, 2003, 21(2): 25-30. [10] 吴昊,赵维,年廷凯,等. 反倾层状岩质边坡倾倒破坏的离心模型试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2018,49(2): 223-231.WU Hao, ZHAO Wei, NIAN Tingkai, et al. Study on the anti-dip layered rock slope toppling failure based on centrifuge model test[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(2): 223-231. [11] 李祥龙,唐辉明. 逆层岩质边坡地震动力破坏离心机试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(4): 687-694. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201404013LI Xianglong, TANG Huiming. Dynamic centrifugal modelling tests on toppling rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(4): 687-694. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201404013 [12] 郑达,王沁沅,毛峰,等. 反倾层状岩质边坡深层倾倒变形关键致灾因子及成灾模式的离心试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(10): 1954-1963.ZHENG Da, WANG Qinyuan, MAO Feng, et al. Centrifuge model test study on key hazard-inducing factors of deep toppling deformation and disaster patterns of counter-tilt layered rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(10): 1954-1963. [13] FUGLSANG L D, OVESEN N K. The application of the theory of modelling to centrifuge studies[M]// Centrifuge in Soil Mechanics. Rotterdam: Balkema, 1989: 119-138. [14] 侯伟龙. 陡倾层状岩质边坡的大型振动台物理模拟试验研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011. -




 下载:
下载: