Aeroelastic Instability of Variable-Stiffness Panels with Curvilinear Fibers in Subsonic Flow
-
摘要:
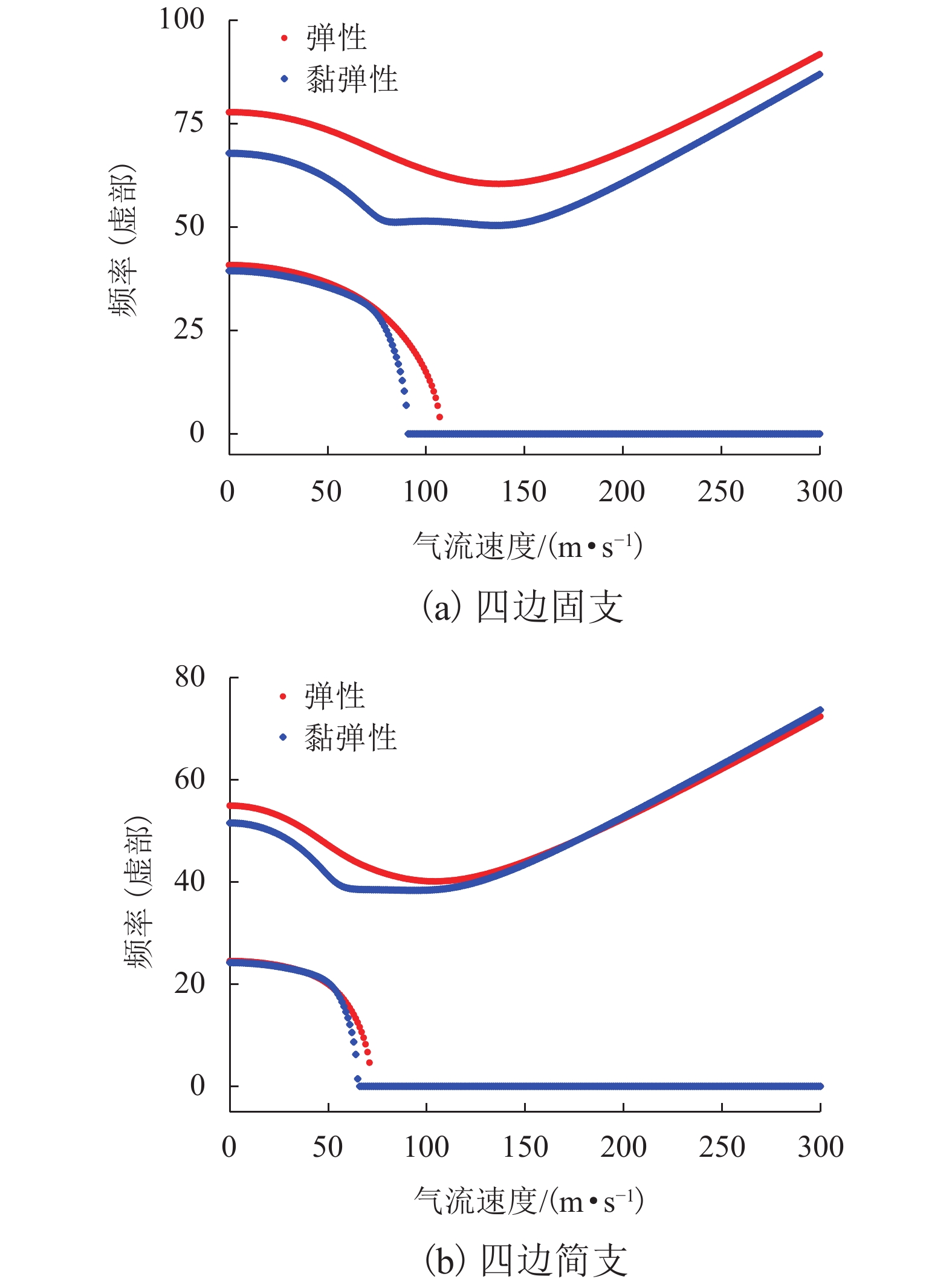
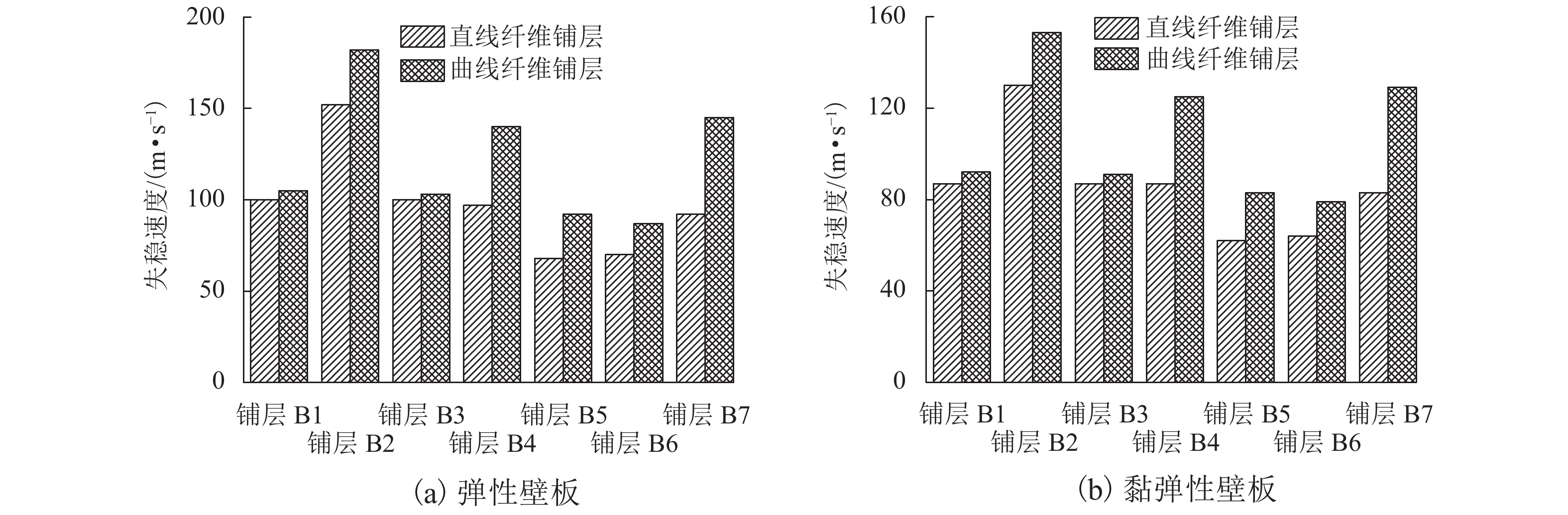
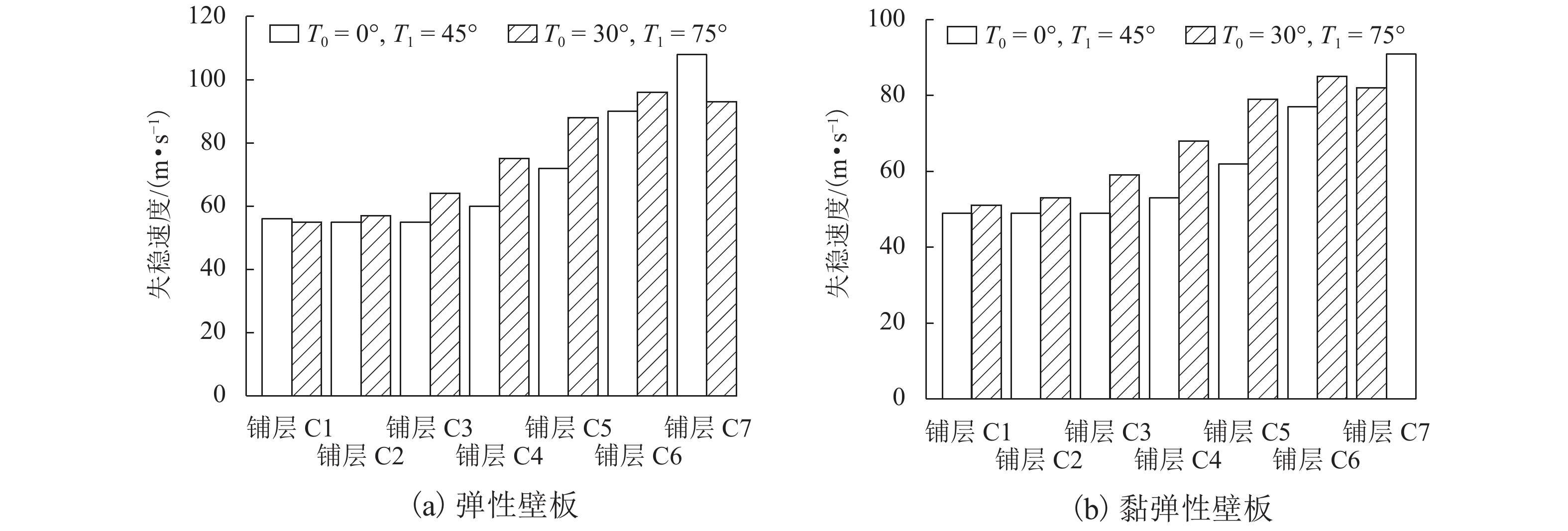
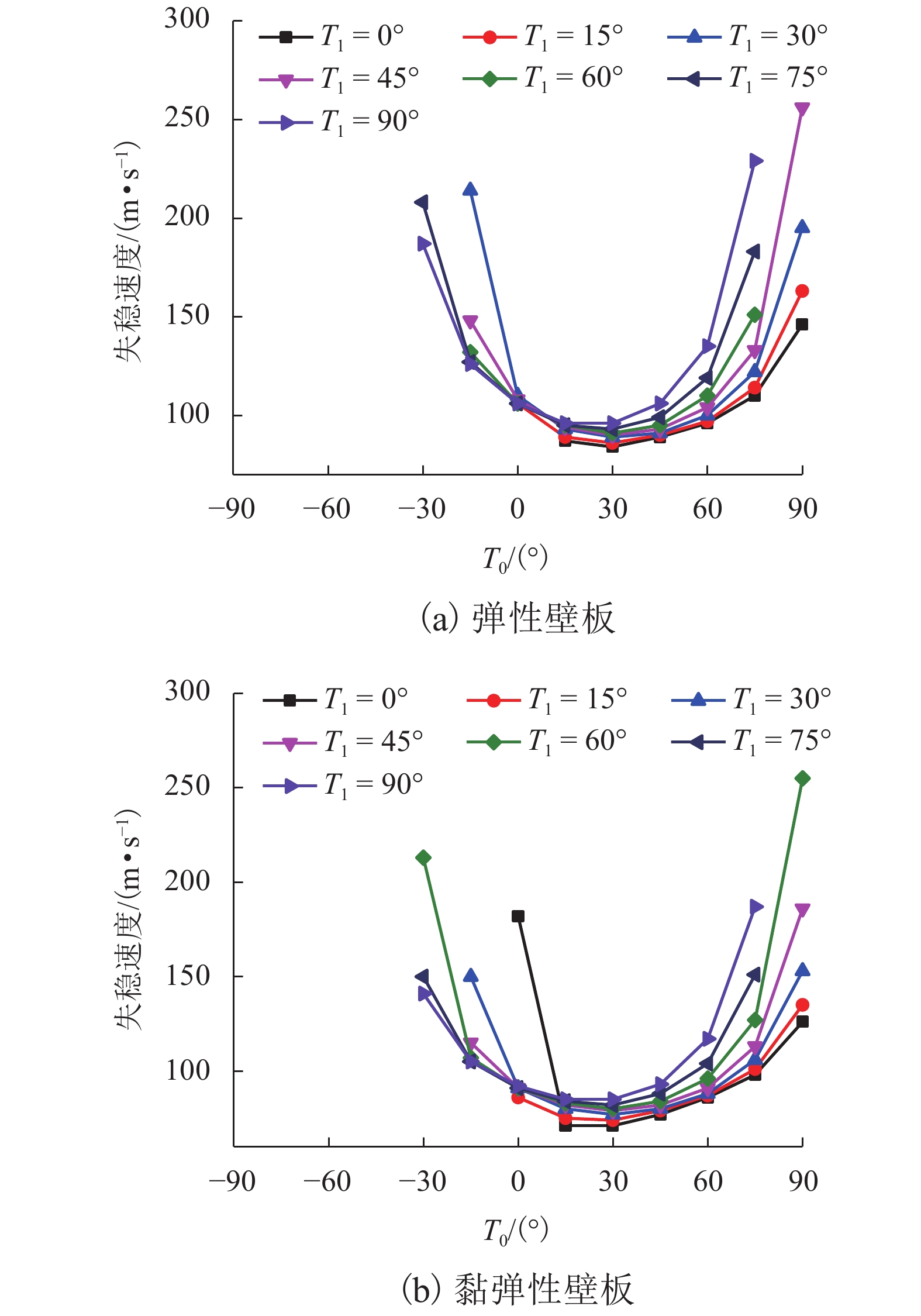
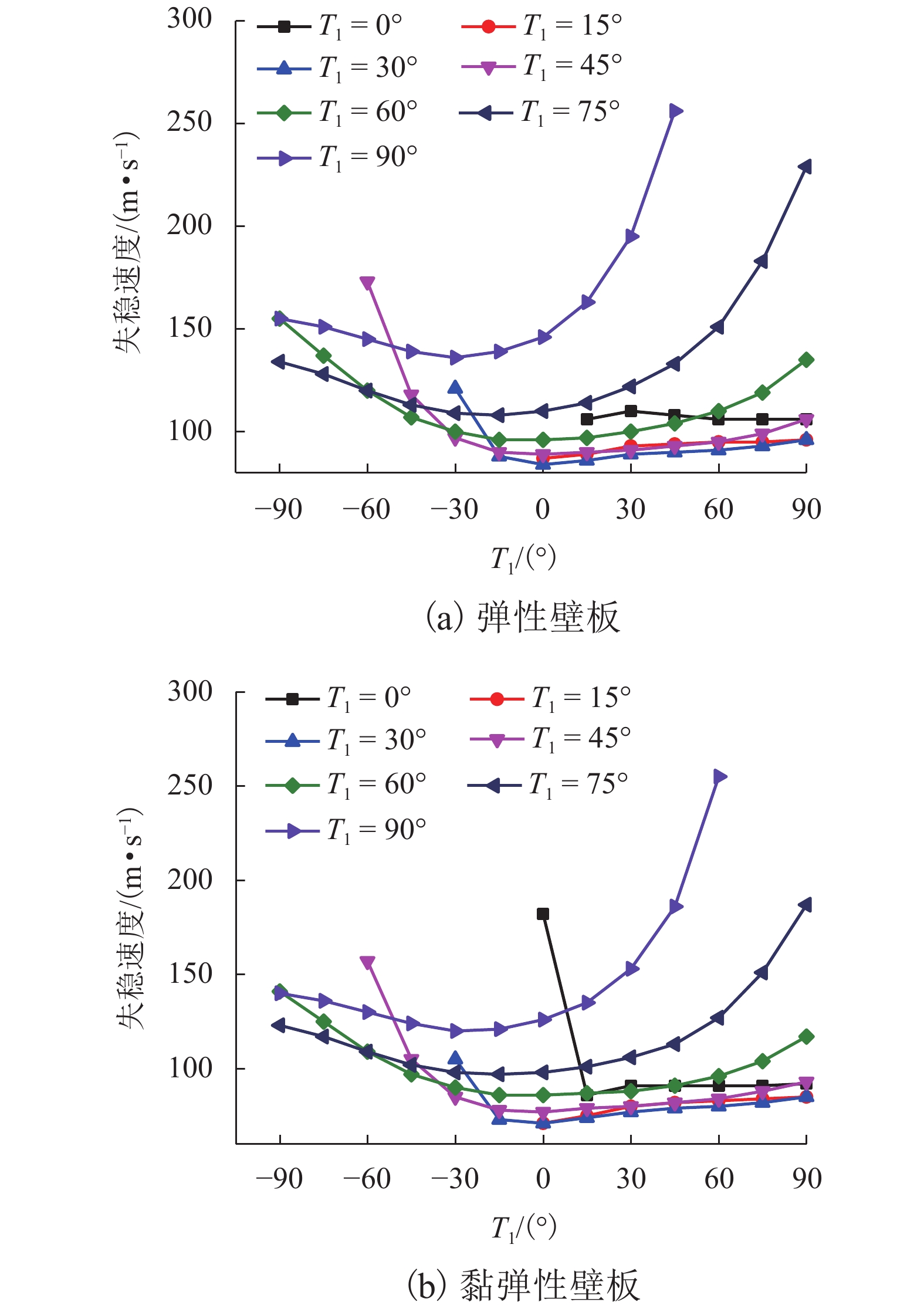
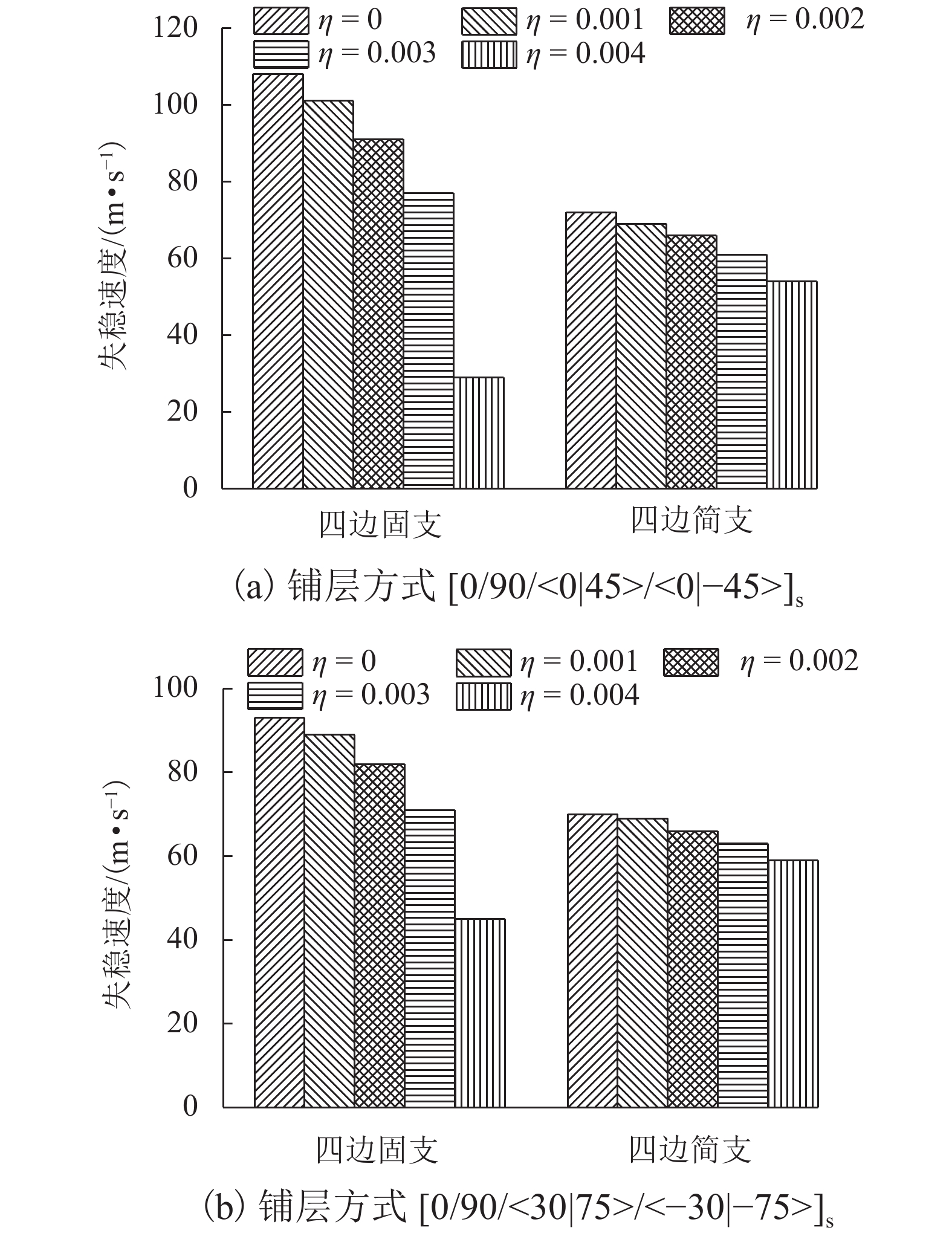
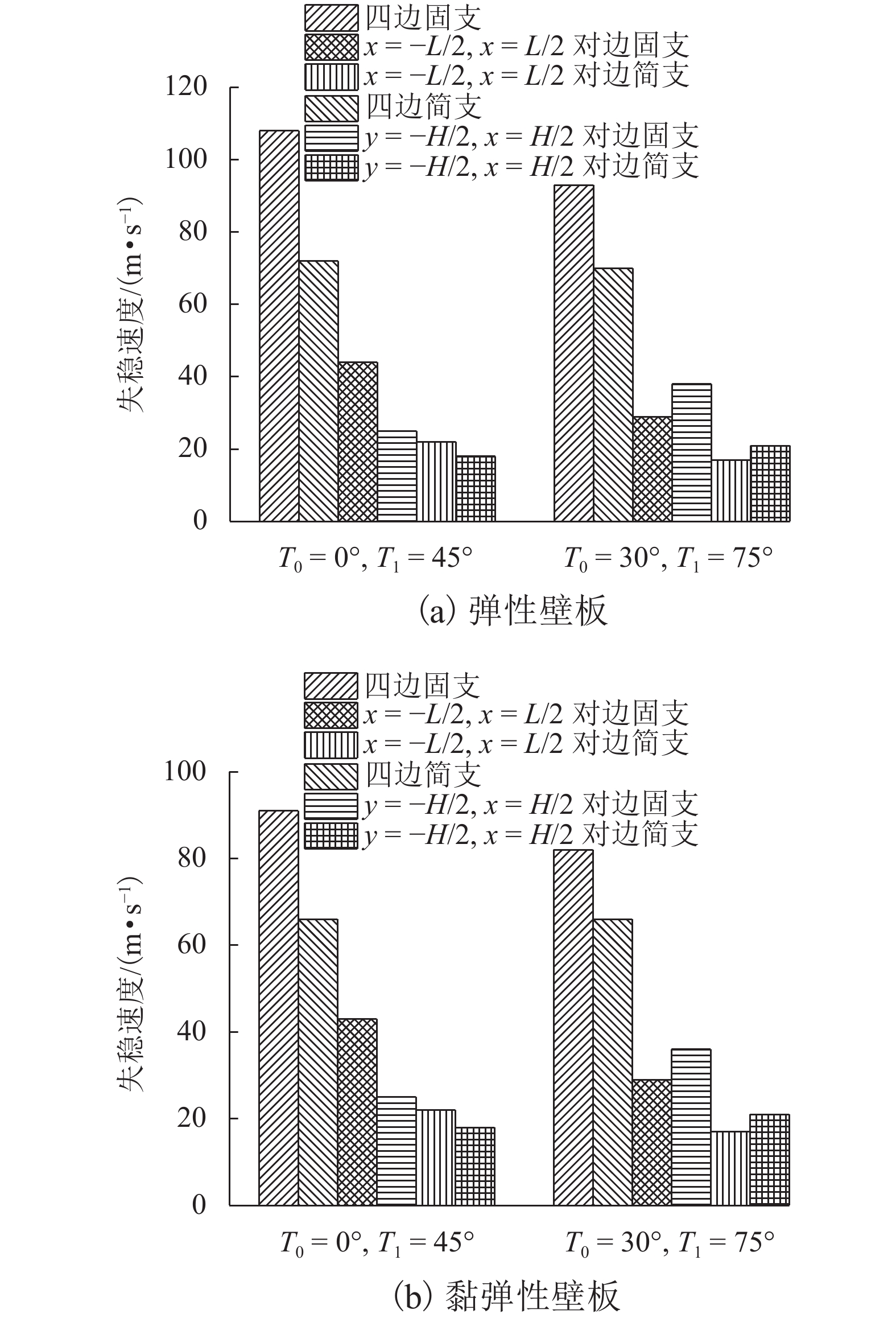
针对曲线纤维变刚度复合材料层合板在高速列车壁板结构轻量化设计中的广阔应用前景,研究了弹性、黏弹性变刚度复合壁板在亚音速流场中的气动弹性稳定性问题. 首先,基于Mindlin厚板理论和势流流动理论分别描述壁板结构变形和亚音速气动力,根据虚功原理和有限元法建立了曲线纤维变刚度复合材料弹性/黏弹性壁板的气动弹性稳定性分析模型,进而采用复模态理论求解复合材料变刚度壁板发散临界速度;在验证方法正确性和收敛性的基础上,研究了壁板关键参数等对复合变刚度壁板发散失稳特性的影响规律. 研究结果表明:与直线纤维壁板相比,通过调整曲线纤维路径可以实现壁板的发散临界速度50%左右的提升,有效增强壁板气动弹性稳定性.
Abstract:In view of the extensive application of curved fiber composite laminates in the lightweight design of high-speed train structures, the aeroelastic stability of elastic and viscoelastic variable-stiffness composite panels in a subsonic flow field was studied. First, classical thick theory along with a Mindlin plate was adopted for structural modeling and potential flow theory for aerodynamic modeling. An aeroelastic model of composite variable-stiffness panels with curvilinear fibers was then established adopting the principle of virtual work and the finite element method, which was solved using complex mode theory in the frequency domain. The divergence characteristics for key parameters were investigated following verification of the validity and convergence of the presented method. Numerical results show that, relative to the straight-fiber panel, the critical divergence speed can be increased by approximately 50% by varying the path orientations of the curvilinear fibers.
-
Key words:
- aeroelastic stability /
- curvilinear fibers /
- variable stiffness /
- composite panels /
- subsonic flow
-
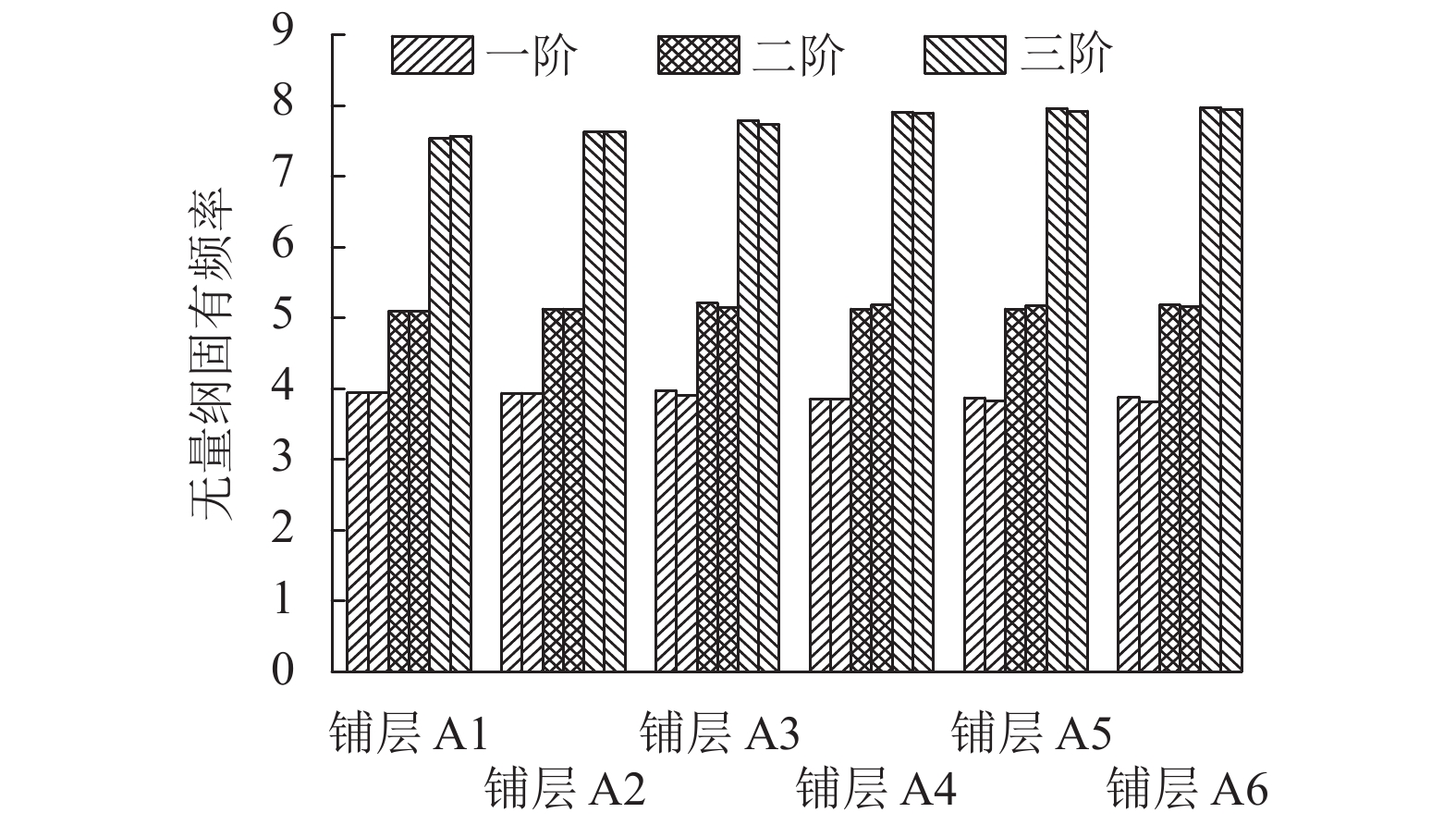
图 2 曲线纤维壁板固有频率结果对比
注:每种图例下第一个柱状条为本文解,第二个柱状条为文献[12]解.
Figure 2. Comparison of natural frequencies of curved fiber composite laminates
表 1 变刚度复合壁板固有频率的网格收敛性
Table 1. Grid convergence of natural frequencies of composite panels with variable stiffness
固有
频率网格规模 文献[12] 误差/% 5 × 5 10 × 10 20 × 20 30 × 30 一阶 3.786 4.060 3.936 3.937 3.941 0.10 二阶 5.853 5.278 5.126 5.090 5.087 0.06 三阶 13.087 7.848 7.582 7.532 7.565 0.43 四阶 16.219 11.012 10.740 10.358 10.385 0.26 五阶 17.409 12.281 10.978 10.658 11.052 3.56 六阶 22.249 12.274 11.939 11.697 11.327 3.27 表 2 两端固支壁板发散稳定性结果对比
Table 2. Divergence stability of the plate with bilateral fixation
厚度/
mm板长 0.8 m 板长 0.9 m 板长 1.0 m 文献 本文 文献 本文 文献 本文 2.40 73.53 71.03 61.62 61.01 52.61 53.01 2.60 82.90 80.25 69.48 68.51 59.23 59.10 2.90 97.66 95.47 81.84 81.06 69.88 70.04 3.30 118.55 116.67 99.35 98.21 84.82 85.12 -
[1] GŰRDAL Z, TATTING B F, WU C K. Variable-stiffness composite panels:effects of stiffness variation on the in-plane and buckling response[J]. Composites:Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2008, 39(5): 911-922. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.11.015 [2] HYPER M W, CHARETTE R F. Use of curvilinear fiber format in composite structure design[J]. AIAA Journal, 1991, 29(6): 1011-1015. doi: 10.2514/3.10697 [3] LOPES C S, GÜRDAL Z, CAMANHO P P. Variable-stiffness composite panels:Buckling and first-ply failure improvements over straight-fibre laminates[J]. Computers & Structures, 2008, 86(9): 897-907. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2007.04.016 [4] HAMED A, PEDRO R, DEMOURA M F S F. Large deflection and stresses in variable stiffness composite laminates with curvilinear fibres[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 73: 14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.03.013 [5] 马洪涛. 变刚度复合材料层合板的力学性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012. [6] 聂国隽,朱佳瑜. 纤维曲线铺放的复合材料层合板的自由振动分析[J]. 力学季刊,2016,37(2): 274-283.NIE Guojun, ZHU Jiayu. Free vibration analysis of composite laminates with curvilinear fibers[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2016, 37(2): 274-283. [7] 马成. 复合材料纤维曲线铺放层合板减振性能分析[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2019. [8] GROH R M J, WEAVER P M. Buckling analysis of variable angle tow,variable thickness panels with transverse shear effects[J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 107: 482-493. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.08.025 [9] HAO P, YUAN X J, LIU C, et al. An integrated framework of exact modeling,isogeometric analysis and optimization for variable-stiffness composite panels[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 339: 205-238. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2018.04.046 [10] 孙士平,张冰,邓同强,等. 复合载荷作用变刚度复合材料回转壳屈曲优化[J]. 复合材料学报,2019,36(4): 1052-1061.SUN Shiping, ZHANG Bing, DENG Tongqiang, et al. Buckling optimization of variable stiffness composite rotary shell under combined loads[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(4): 1052-1061. [11] VAHID K, JAMSHID F. Supersonic panel flutter of variable stiffness composite laminated skew panels subjected to yawed flow by using NURBS-based isogeometric approach[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2018, 82: 198-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2018.07.002 [12] 欧阳小穗,刘毅. 高速流场中变刚度复合材料层合板颤振分析[J]. 航空学报,2018,39(3): 221539.OUYANG Xiaosui, LIU Yi. Panel flutter of variable stiffness composite laminates in supersonic flow[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(3): 221539. [13] TOURAJ F, DAVOOD A, HASAN K. Flutter improvement of a thin walled wing-engine system by applying curvilinear fiber path[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 93(2): 105353.1-105353.14. [14] 许家宝. 亚麻/玻璃纤维混杂复合材料的动态粘弹性及湿热性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2019. [15] KORNECKI A, DOWELL E H, O’BRIEN J. On the aeroelastic instability of two-dimensional panels in uniform incompressible flow[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1976, 47(2): 163-178. [16] GUO Y, LI F M. Chaotic motion of a composite laminated plate with geometric nonlinearity in subsonic flow[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2013, 50: 81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2012.11.010 -





 下载:
下载: